sSfS: Segmented Shape from Silhouette Reconstruction of the Human Body
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. 3D Reconstruction Methods Used for Human Body Scanning
2.2. SfS Visual Hull Estimation
2.3. Parametric Body Models
2.4. Deep Neural Network Architectures
2.5. Local Shape Approximation and Meshing
2.6. Summary
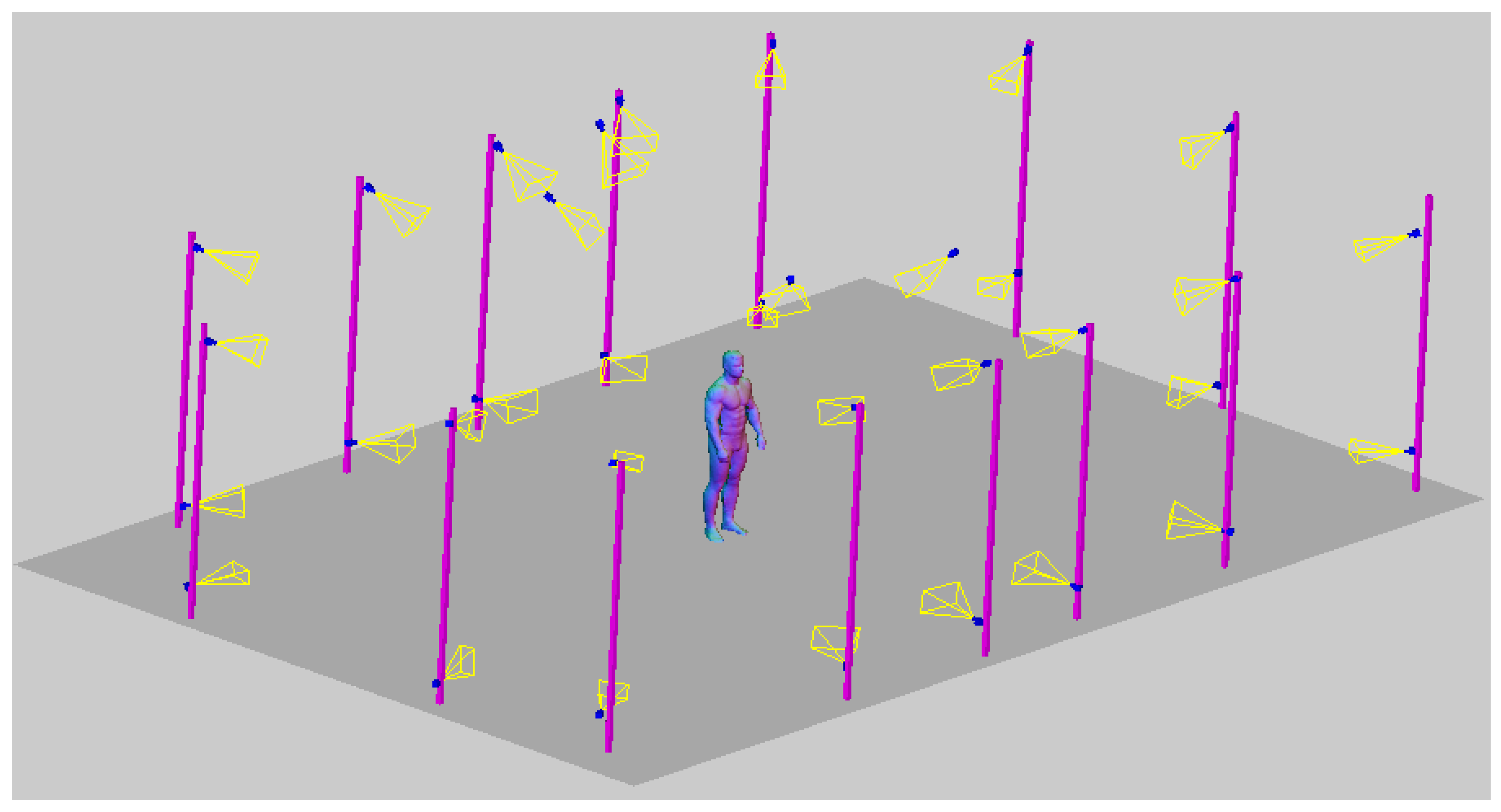
3. Materials
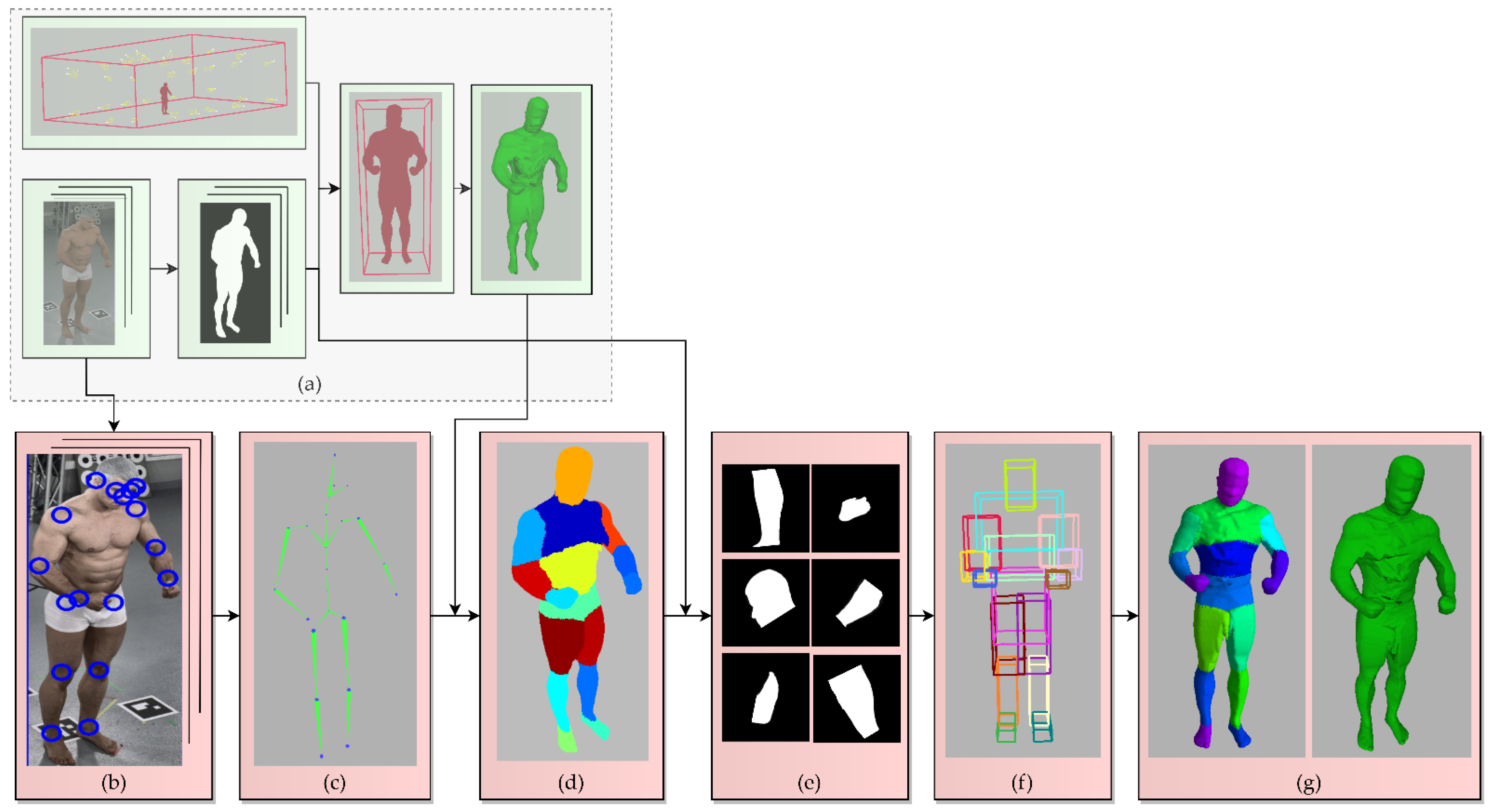
4. Methods
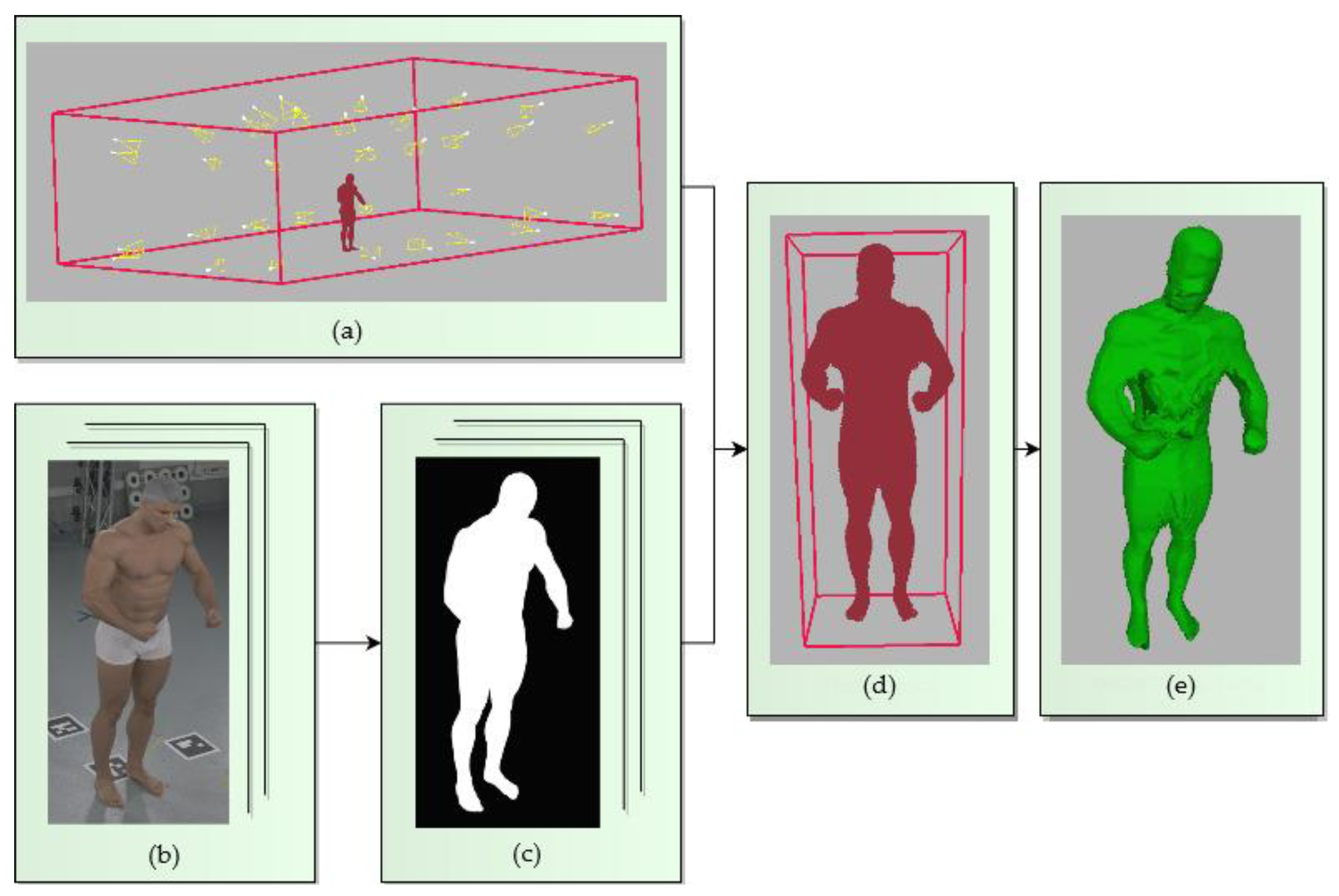
4.1. The Conventional SfS VISUAL Hull Reconstruction of the Entire Human Body
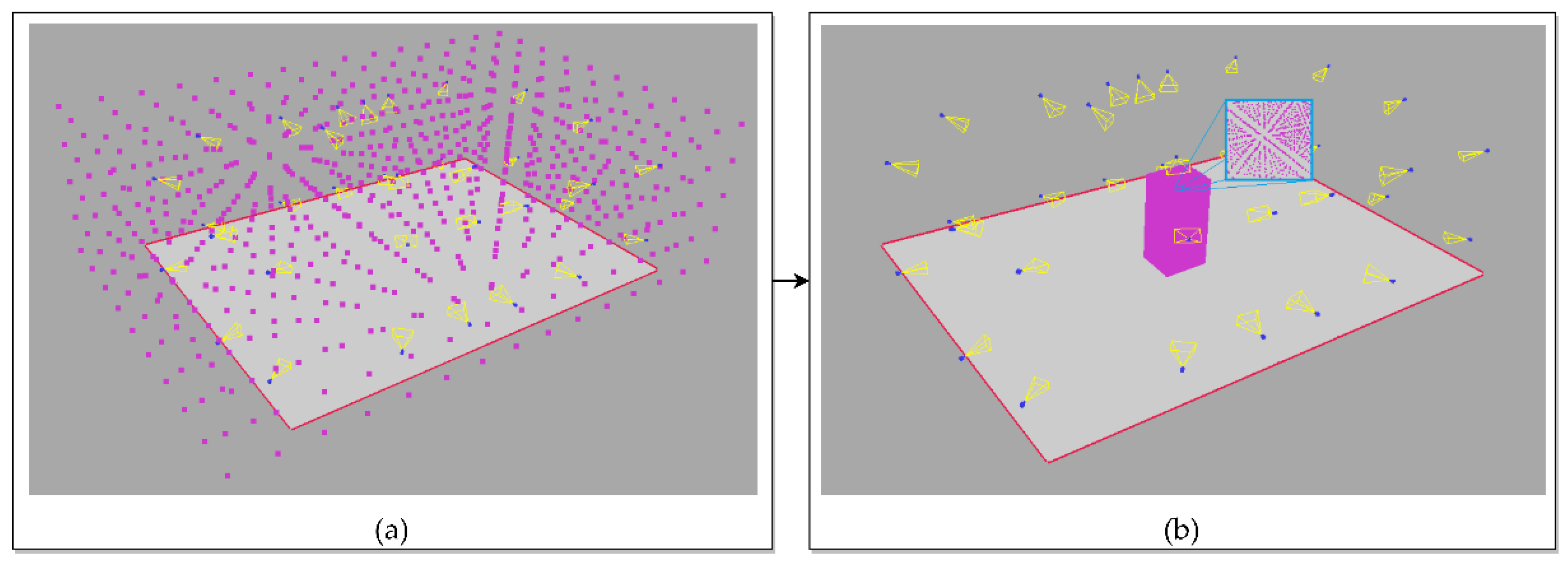
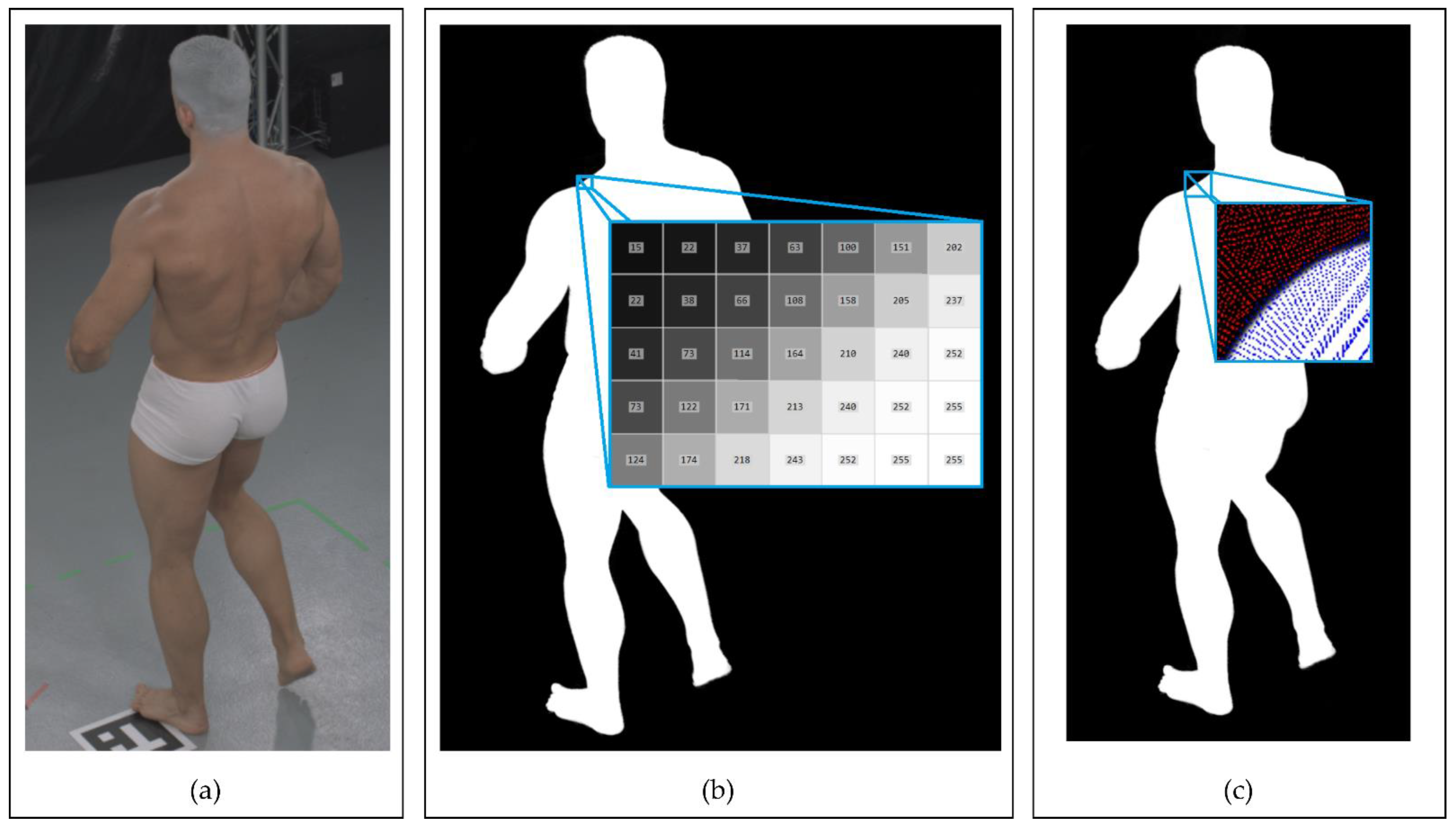
4.1.1. Calculation of the Subject’s Volume
4.1.2. Visual Hull Estimation with the Voxel Projections
4.2. sSfS Body Segment Reconstruction
- F uncertain pixels ratio,
- M number of pixels in the silhouette segment image in range <1, 254>,
- N number of pixels in the segment projection image with intensity 255.
4.3. Hardware and Software Environment
5. Results
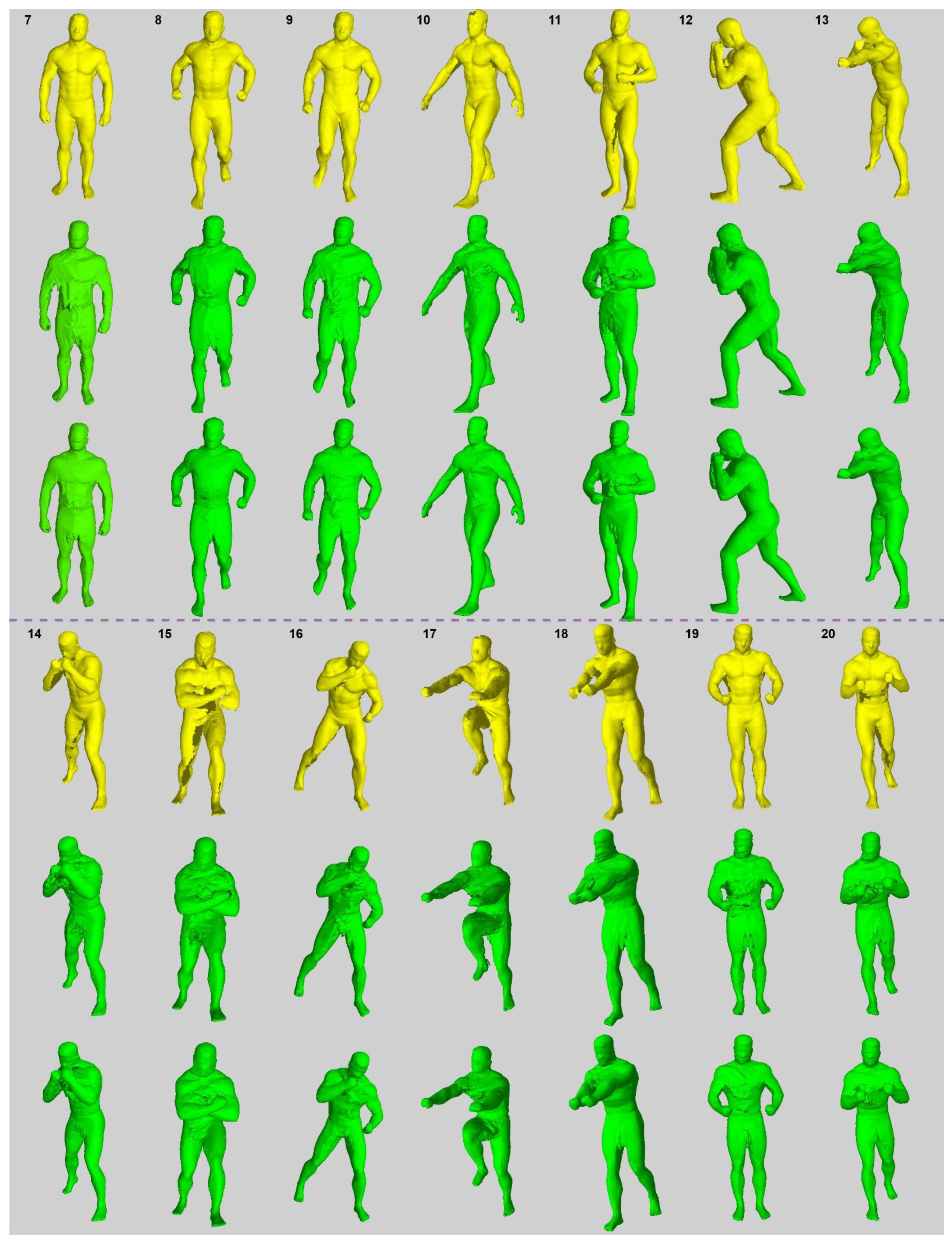
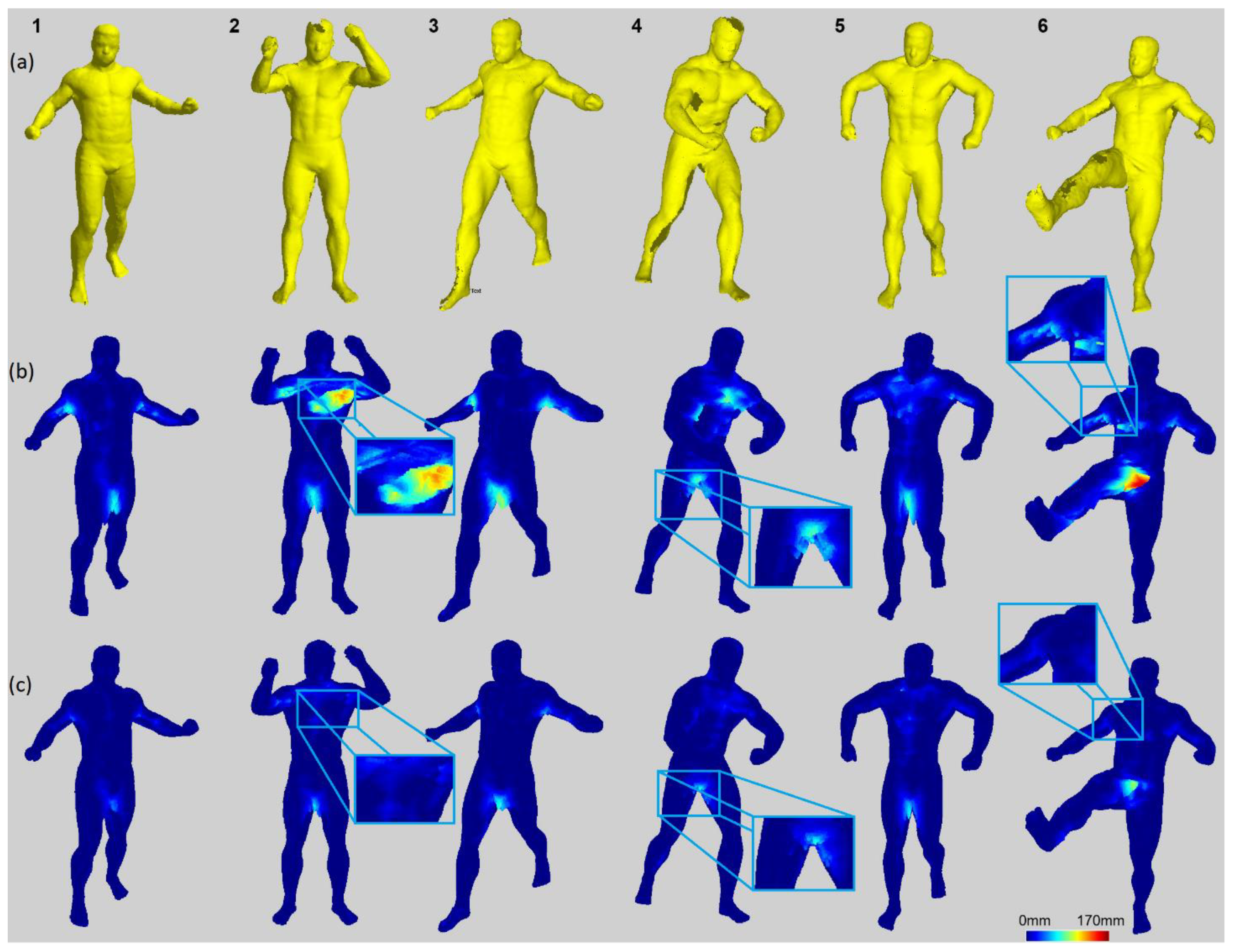
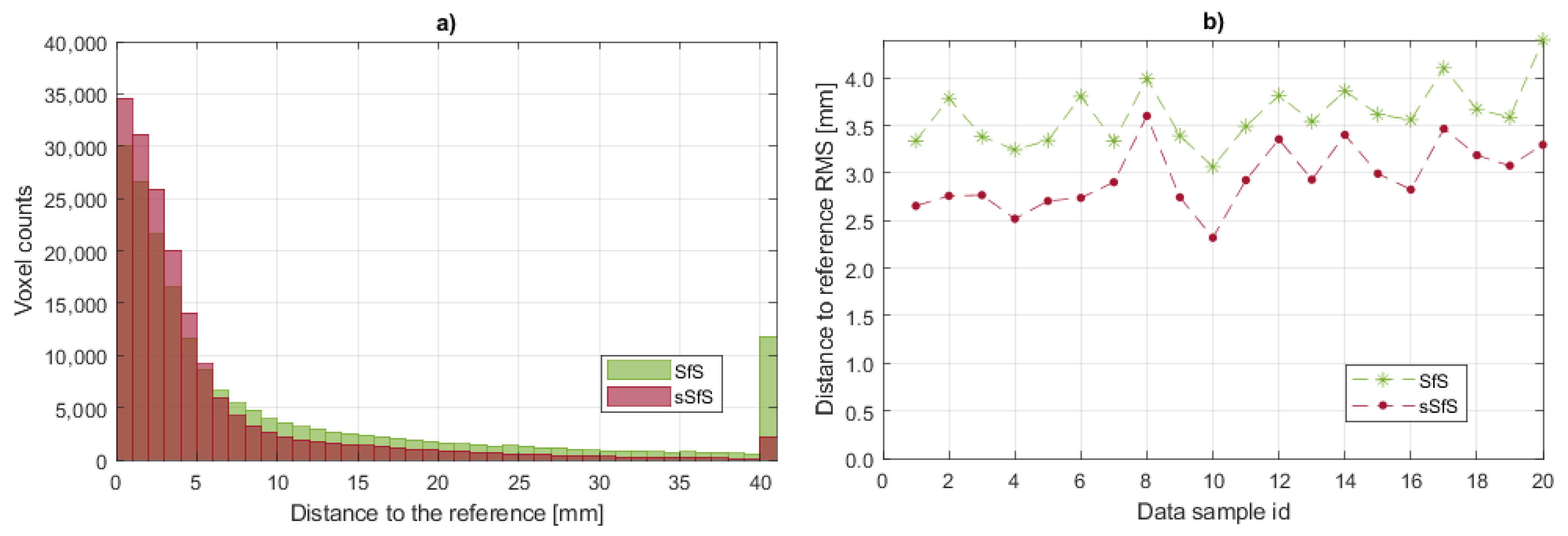
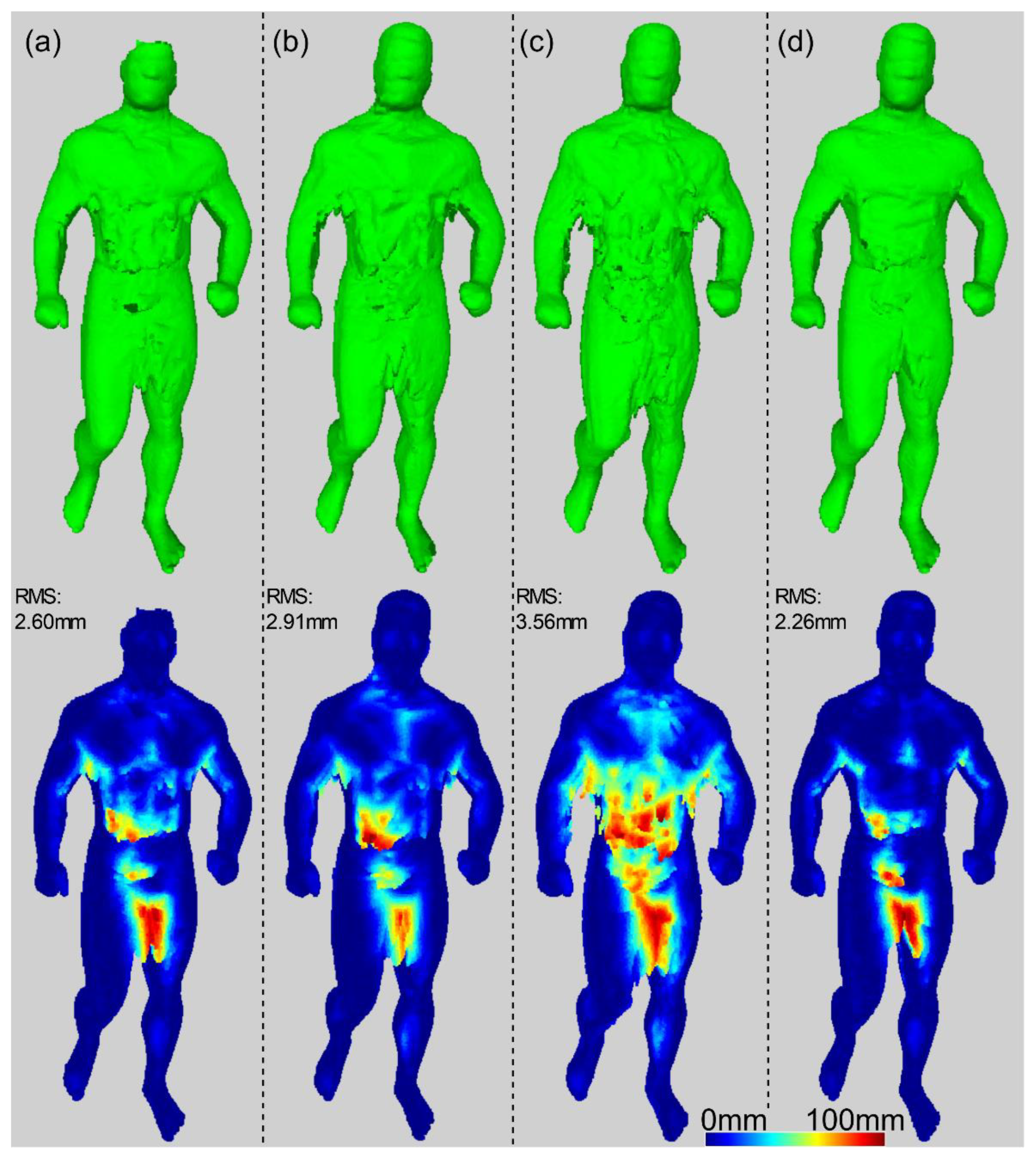
5.1. Surface Shape Comparison
5.2. Metric Description and Results
- The number of erroneous visual hull voxels outside of the reference surface—For each voxel center, the closest point of the SfM reconstruction was found. Then, the dot product A between the vector from the voxel center to the SfM point and the SfM point’s normal vector was estimated. The voxel was considered erroneous when the value of the dot product A was less than 0. Additionally, when the distance between the voxel center and SfM point was less than the voxel size (4 mm), the voxel was not counted as erroneous.
- The distance between the SfS/sSfS reconstruction voxel and the reference cloud’s surface (point to surface, P2S)—The Euclidean 3D distance between the voxel center on the surface of the SfS/sSfS reconstruction and the closest SfM point.
5.2.1. The Number of Erroneous Voxels
5.2.2. Surface Voxels’ Distance to the Reference
5.3. Computation Time Comparison
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Id. | Sample RGB Images | Sample Silhouettes | SfM Ground-Truth Reconstruction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| 3 |  |  |  |
| 4 |  |  |  |
| 5 |  |  |  |
| 6 |  |  |  |
| 7 |  |  |  |
| 8 |  |  |  |
| 9 |  |  |  |
| 10 |  |  |  |
| 11 |  |  |  |
| 12 |  |  |  |
| 13 |  |  |  |
| 14 |  |  |  |
| 15 |  |  |  |
| 16 |  |  |  |
| 17 |  |  |  |
| 18 |  |  |  |
| 19 |  |  |  |
| 20 |  |  |  |


References
- Gipsman, A.; Rauschert, L.; Daneshvar, M.; Knott, P. Evaluating the Reproducibility of Motion Analysis Scanning of the Spine during Walking. Adv. Med. 2014, 2014, 721829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betsch, M.; Wild, M.; Johnstone, B.; Jungbluth, P.; Hakimi, M.; Kühlmann, B.; Rapp, W. Evaluation of a Novel Spine and Surface Topography System for Dynamic Spinal Curvature Analysis during Gait. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Moll, G.; Romero, J.; Mahmood, N.; Black, M.J. Dyna: A model of dynamic human shape in motion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2015, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pujades, S.; Black, M.; Pons-Moll, G. Detailed, Accurate, Human Shape Estimation from Clothed 3D Scan Sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/mixed-reality/capture-studios (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Available online: https://scanable.com/mobile-photogrammetry/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Michoński, J.; Glinkowski, W.; Witkowski, M.; Sitnik, R. Automatic recognition of surface landmarks of anatomical structures of back and posture. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 056015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberadzki, P.; Markiewicz, L.; Witkowski, M.; Sitnik, R. Novel 4D Whole Body Scanning Solution and its Medical Application. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference and Exhibition on 3D Body Scanning and Processing Technologies, Lugano, Switzerland, 16–17 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Treleaven, P.; Wells, J. 3D Body Scanning and Healthcare Applications. Computer 2007, 40, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markiewicz, Ł.; Witkowski, M.; Sitnik, R.; Mielicka, E. 3D anthropometric algorithms for the estimation of measurements required for specialized garment design. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 85, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.-M.; Baker, S.; Kanade, T. Shape-From-Silhouette across Time Part I: Theory and Algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 62, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daanen, H.A.M.; Haar, F.B.T. 3D whole body scanners revisited. Displays 2013, 34, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, M. 3D Laser Scanners: History, Applications and Future. 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mostafa-Ebrahim-3/publication/267037683_3D_LASER_SCANNERS_HISTORY_APPLICATIONS_AND_FUTURE/links/5442bdf10cf2e6f0c0f93727/3D-LASER-SCANNERS-HISTORY-APPLICATIONS-AND-FUTURE.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Foix, S.; Alenya, G.; Torras, C. Lock-in Time-of-Flight (ToF) Cameras: A Survey. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvi, J.; Fernandez, S.; Pribanic, T.; Llado, X. A state of the art in structured light patterns for surface profilometry. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2666–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.R.; Robson, S. Straightforward reconstruction of 3D surfaces and topography with a camera: Accuracy and geoscience application. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.vitronic.com/en-us/3d-bodyscan/scanner-for-performance-diagnostics (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- D’Apuzzo, N. 3D body scanning technology for fashion and apparel industry. In Proceedings of the IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging 2007, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 January–1 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pribanic, T.; Petkovic, T.; Bojanic, D.; Bartol, K. Smart Time-Multiplexing of Quads Solves the Multicamera Interference Problem. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Fukuoka, Japan, 25–28 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jeught, S.V.; Dirckx, J.J.J. Real-time structured light profilometry: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 87, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberadzki, P.; Adamczyk, M.; Witkowski, M.; Sitnik, R. Structured-Light-Based System for Shape Measurement of the Human Body in Motion. Sensors 2018, 18, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartol, K.; Bojanic, D.; Petkovic, T.; Pribanic, T. A Review of Body Measurement Using 3D Scanning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 67281–67301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, E.; Stathopoulou, E.K.; Rigon, S.; Remondino, F. Surface Reconstruction Assessment in Photogrammetric Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://ccwu.me/vsfm/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Available online: https://www.agisoft.com (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Joo, H.; Simon, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; Gui, L.; Banerjee, S.; Godisart, T.; Nabbe, B.; Matthews, I.; et al. Panoptic Studio: A Massively Multiview System for Social Interaction Capture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 41, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matusik, W.; Buehler, C.; Raskar, R.; Gortler, S.J.; McMillan, L. Image-based visual hulls. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, J.-S.; Boyer, E. Efficient Polyhedral Modeling from Silhouettes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.-S.; Lapierre, M.; Boyer, E.; Boyer, J.-S.F.M.L.E. Visual Shapes of Silhouette Sets. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and Transmission (3DPVT′06), Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, Y.; Ponce, J. LNCS 3951—Carved Visual Hulls for Image-Based Modeling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mulayim, A.Y.; Yilmaz, U.; Atalay, V. Silhouette-based 3-D model reconstruction from multiple images. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2003, 33, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.-J.; Cho, H.; Won, Y.-Y.; Yoon, S.M. Three-Dimensional Density Estimation of Flame Captured From Multiple Cameras. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 8876–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabb, A. Shape from Silhouette Probability Maps: Reconstruction of Thin Objects in the Presence of Silhouette Extraction and Calibration Error. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boros, E.; Hammer, P.L. Pseudo-Boolean optimization. Discret. Appl. Math. 2002, 123, 155–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loop, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. Real-time high-resolution sparse voxelization with application to image-based modeling. In Proceedings of the 5th High-Performance Graphics Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 19–21 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.M.; Aledo, P.G.; Sanchez, P.P. Real-time voxel-based visual hull reconstruction. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2012, 36, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, S.; Mündermann, L.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Demattio, T.; Cobelli, C.; Andriacchi, T.P. A Markerless Motion Capture System to Study Musculoskeletal Biomechanics: Visual Hull and Simulated Annealing Approach. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaujia, A.; Kittens, N.; Ramanathan, N. Part Segmentation of Visual Hull for 3D Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roeck, S.D.; Cornelis, N.; Gool, L.V. Augmenting fast stereo with silhouette constraints for dynamic 3D capture. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR′06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Wu, J.-R. 3D reconstruction by combining shape from silhouette with stereo. In Proceedings of the 2008 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–11 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. 2015, 34, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelov, D.; Srinivasan, P.; Koller, D.; Thrun, S.; Rodgers, J.; Davis, J. SCAPE: Shape completion and animation of people. ACM Trans. Graph. 2005, 24, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, A.O.; Sigal, L.; Black, M.J.; Davis, J.E.; Haussecker, H.W. Detailed Human Shape and Pose from Images. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, P.; Weiss, A.; Balan, A.O.; Black, M.J. Estimating human shape and pose from a single image. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dibra, E.; Jain, H.; Oztireli, C.; Ziegler, R.; Gross, M. HS-Nets: Estimating Human Body Shape from Silhouettes with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Heyden, A.; Oskarsson, M. Parametric Model-Based 3D Human Shape and Pose Estimation from Multiple Views. In Proceedings of the Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Norrköping, Sweden, 11–13 June 2019; pp. 336–347. [Google Scholar]
- Bogo, F.; Kanazawa, A.; Lassner, C.; Gehler, P.; Romero, J.; Black, M.J. Keep It SMPL: Automatic Estimation of 3D Human Pose and Shape from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 561–578. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, V.; Budvytis, I.; Cipolla, R. Indirect deep structured learning for 3D human body shape and pose prediction. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2017, London, UK, 4–7 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dibra, E.; Jain, H.; Oztireli, C.; Ziegler, R.; Gross, M. Human Shape from Silhouettes Using Generative HKS Descriptors and Cross-Modal Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xing, J.; LeGendre, C.; Luo, L.; Ma, C.; Li, H. Deep Volumetric Video From Very Sparse Multi-view Performance Capture. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, A.; Volino, M.; Collomosse, J.; Hilton, A. Volumetric performance capture from minimal camera viewpoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Natsume, R.; Saito, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, W.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Morishima, S. SiCloPe: Silhouette-Based Clothed People. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Chatterjee, A.; Zollhöfer, M.; Rhodin, H.; Mehta, D.; Seidel, H.-P.; Theobalt, C. MonoPerfCap. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Oskarsson, M.; Heyden, A. Detailed 3D Human Body Reconstruction from Multi-view Images Combining Voxel Super-Resolution and Learned Implicit Representation. Appl. Intell. 2020. Available online: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10489-021-02783-8.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Saito, S.; Huang, Z.; Natsume, R.; Morishima, S.; Li, H.; Kanazawa, A. PIFu: Pixel-Aligned Implicit Function for High-Resolution Clothed Human Digitization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M.; Hoppe, H. Screened poisson surface reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekumalla, L.; Cohen, E. A Hole-Filling Algorithm for Triangular Meshes. 2004. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.142.3960&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Davis, J.; Marschner, S.R.; Garr, M.; Levoy, M. Filling holes in complex surfaces using volumetric diffusion. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on 3D Data Processing Visualization and Transmission, Padua, Italy, 19–21 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmovianský, P.; Jüttler, B. Filling Holes in Point Clouds. In Mathematics of Surfaces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.; Michoński, J.; Sitnik, R. Filling cavities in point clouds representing human body surface using Bezier patches. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 15093–15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Cole, F.; Dekel, T.; Zisserman, A.; Freeman, W.T.; Rubinstein, M. Omnimatte: Associating Objects and Their Effects in Video. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.06993. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://pytorch.org/hub/pytorch_vision_deeplabv3_resnet101/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Lin, K.; Wang, L.; Luo, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M.-T. Cross-Domain Complementary Learning Using Pose for Multi-Person Part Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y. Self-Correction for Human Parsing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple Baselines for Human Pose Estimation and Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jertec, A.; Bojanic, D.; Bartol, K.; Pribanic, T.; Petkovic, T.; Petrak, S. On using PointNet Architecture for Human Body Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 23–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ueshima, T.; Hotta, K.; Tokai, S.; Zhang, C. Training PointNet for human point cloud segmentation with 3D meshes. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision, Tokushima, Japan, 12–14 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jonker, P.P. Morphological Operations on 3D and 4D Images: From Shape Primitive Detection to Skeletonization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Discrete Geometry for Computer Imagery, Uppsala, Sweden, 13–15 December 2000; pp. 371–391. [Google Scholar]





| Method Name | Measurement Technique | Type of Illumination |
|---|---|---|
| Laser triangulation (LT) [13] | Detection of laser stripes projected onto the object’s surface | Laser |
| Time-of-Flight (ToF) [14] | Measurement of the depth data of the subject surface from return time of light impulse or phase shift | Infrared laser |
| Structured Light (SL) [15] | Analysis of a light pattern (e.g., fringes) projected onto the measured object’s surface | Structured two-dimensional (2D) pattern projected by laser or digital projectors |
| Photogrammetry [16] | Detection and analysis of the key point correspondences between images of the object taken from different angles simultaneously | Natural sunlight or shadowless illumination |
| Sample RGB Images | Sample Silhouettes | Ground-Truth SfM Reconstruction |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krajnik, W.; Markiewicz, Ł.; Sitnik, R. sSfS: Segmented Shape from Silhouette Reconstruction of the Human Body. Sensors 2022, 22, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030925
Krajnik W, Markiewicz Ł, Sitnik R. sSfS: Segmented Shape from Silhouette Reconstruction of the Human Body. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030925
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrajnik, Wiktor, Łukasz Markiewicz, and Robert Sitnik. 2022. "sSfS: Segmented Shape from Silhouette Reconstruction of the Human Body" Sensors 22, no. 3: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030925
APA StyleKrajnik, W., Markiewicz, Ł., & Sitnik, R. (2022). sSfS: Segmented Shape from Silhouette Reconstruction of the Human Body. Sensors, 22(3), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030925







