Permanent Magnet Tracking Method Resistant to Background Magnetic Field for Assessing Jaw Movement in Wearable Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Linear Position Calculation
2.2. Background Magnetic Field Calculation
2.3. Predicting Jaw Rotation from Sensor-Based Translation Estimate
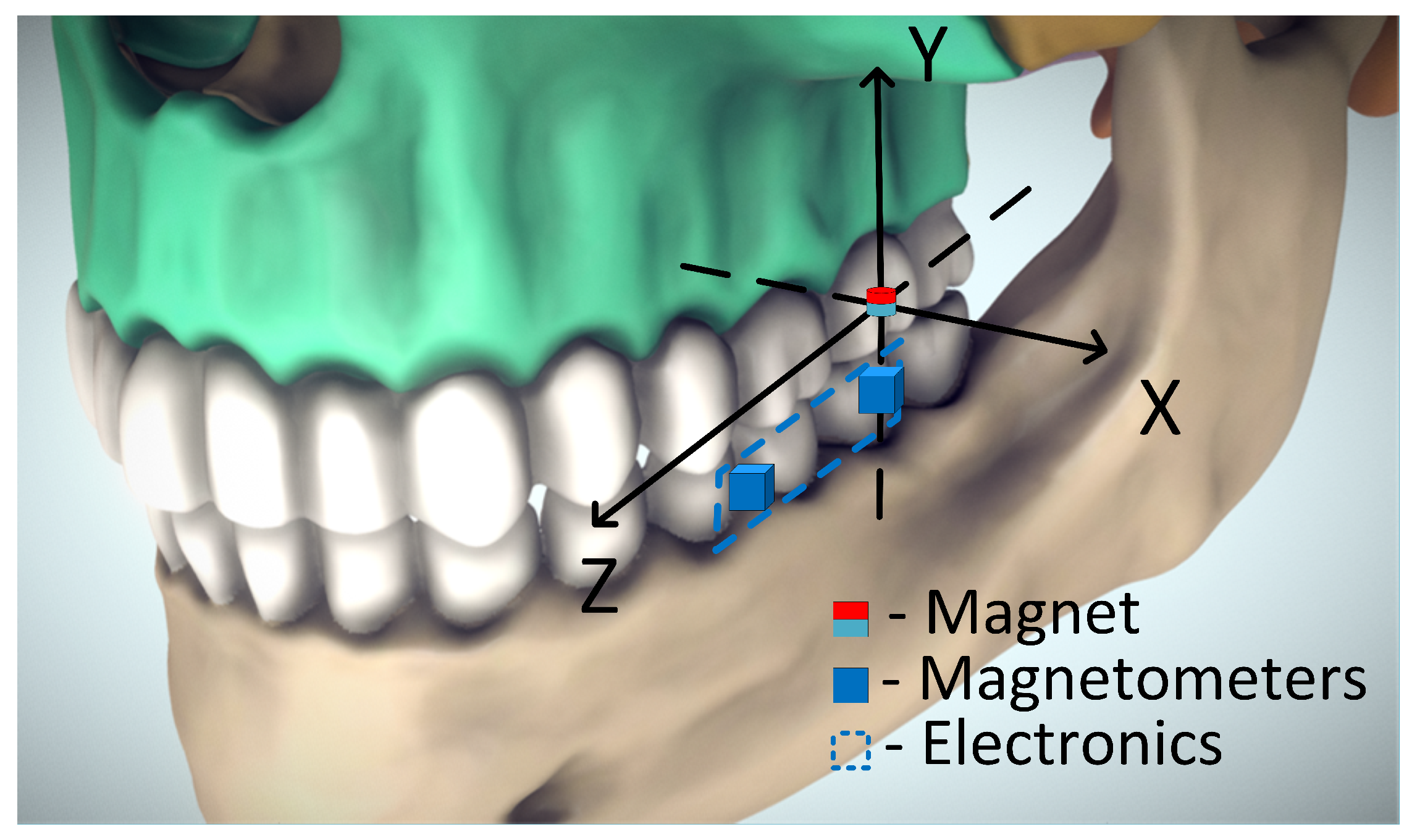
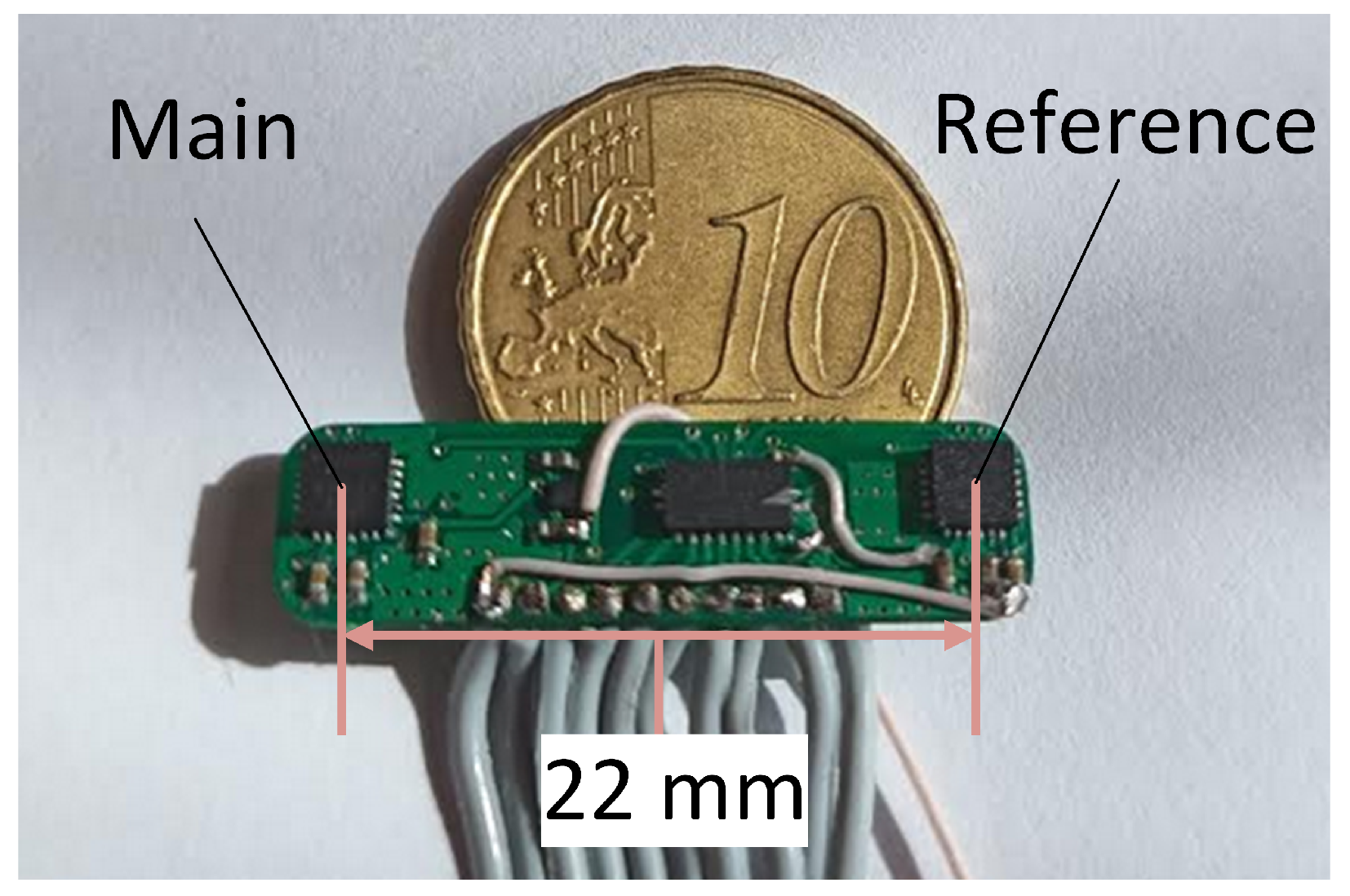
2.4. Sensor Prototype
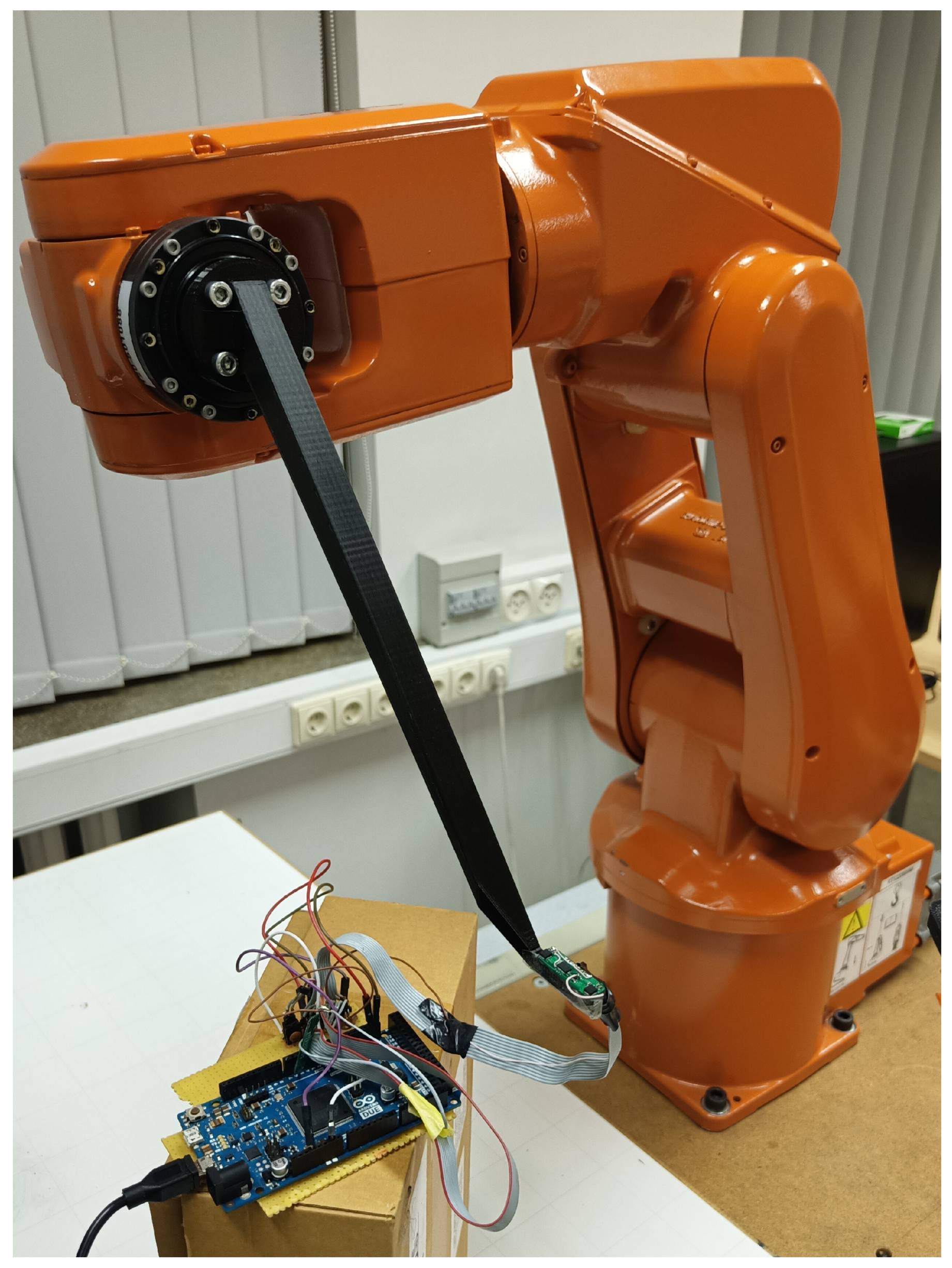
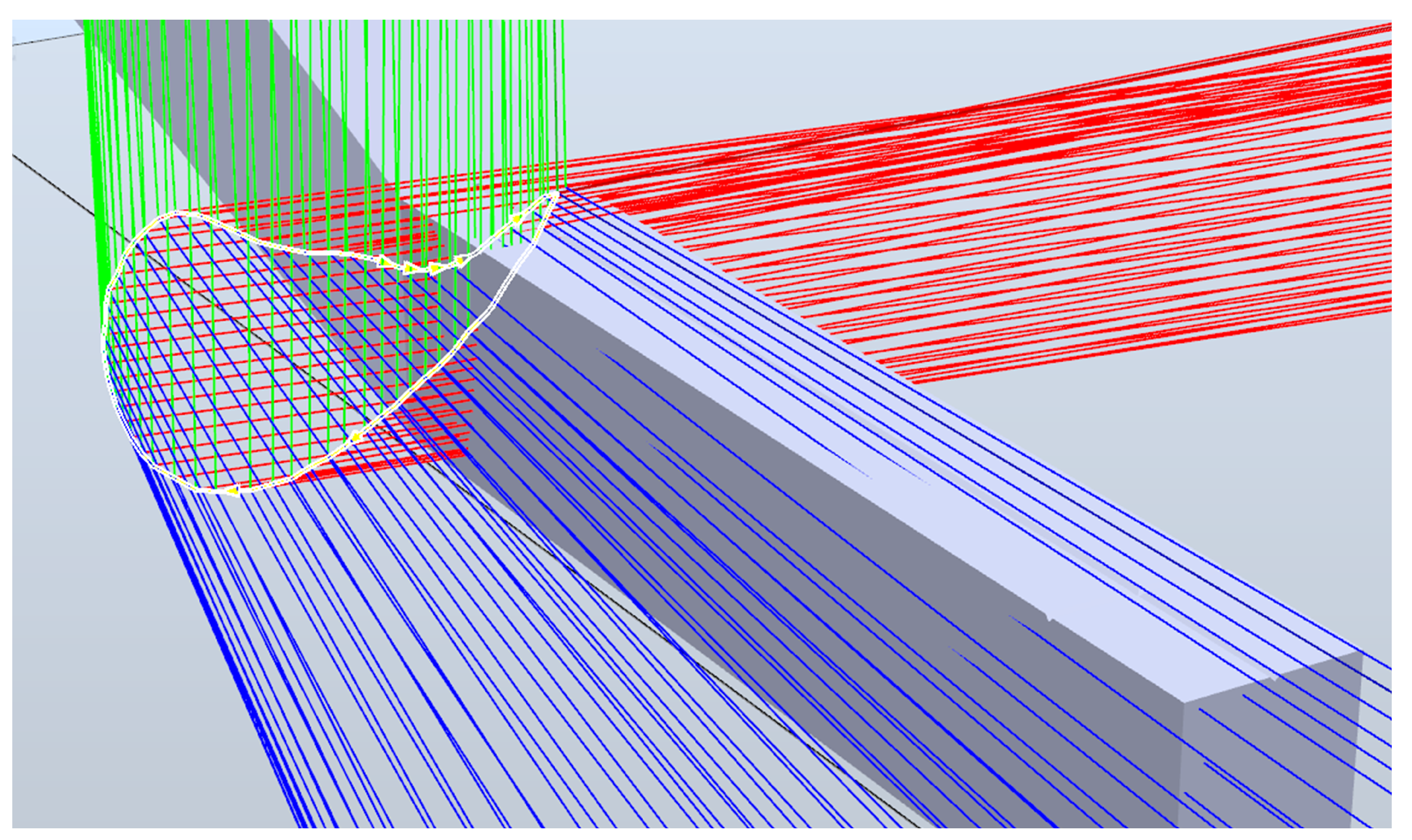
2.5. 5-DOF Method Experiments
3. Results
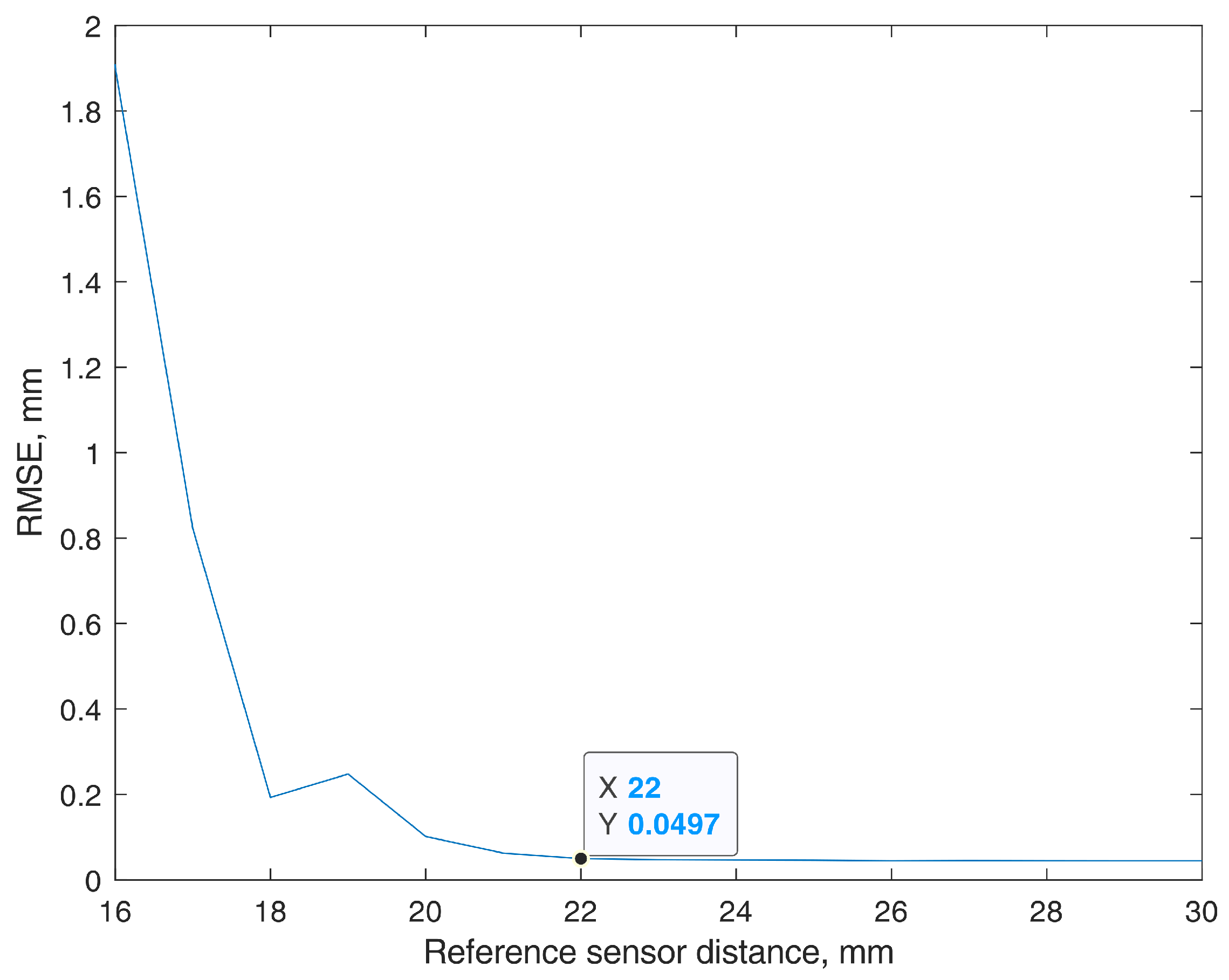
3.1. Background Magnetic Field Calculation
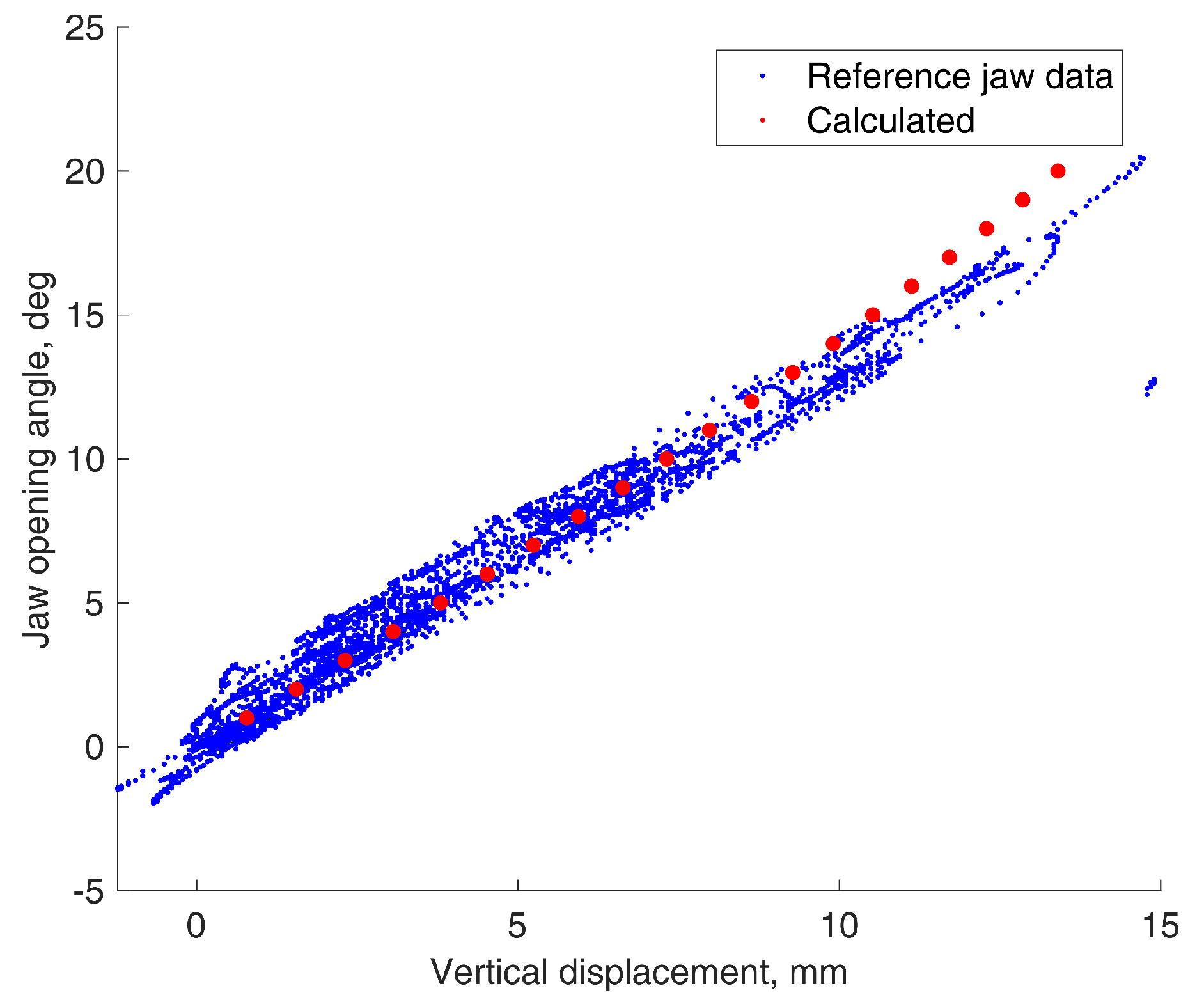
3.2. Jaw Angle Calculation
3.3. 5-DOF Prototype Experiments
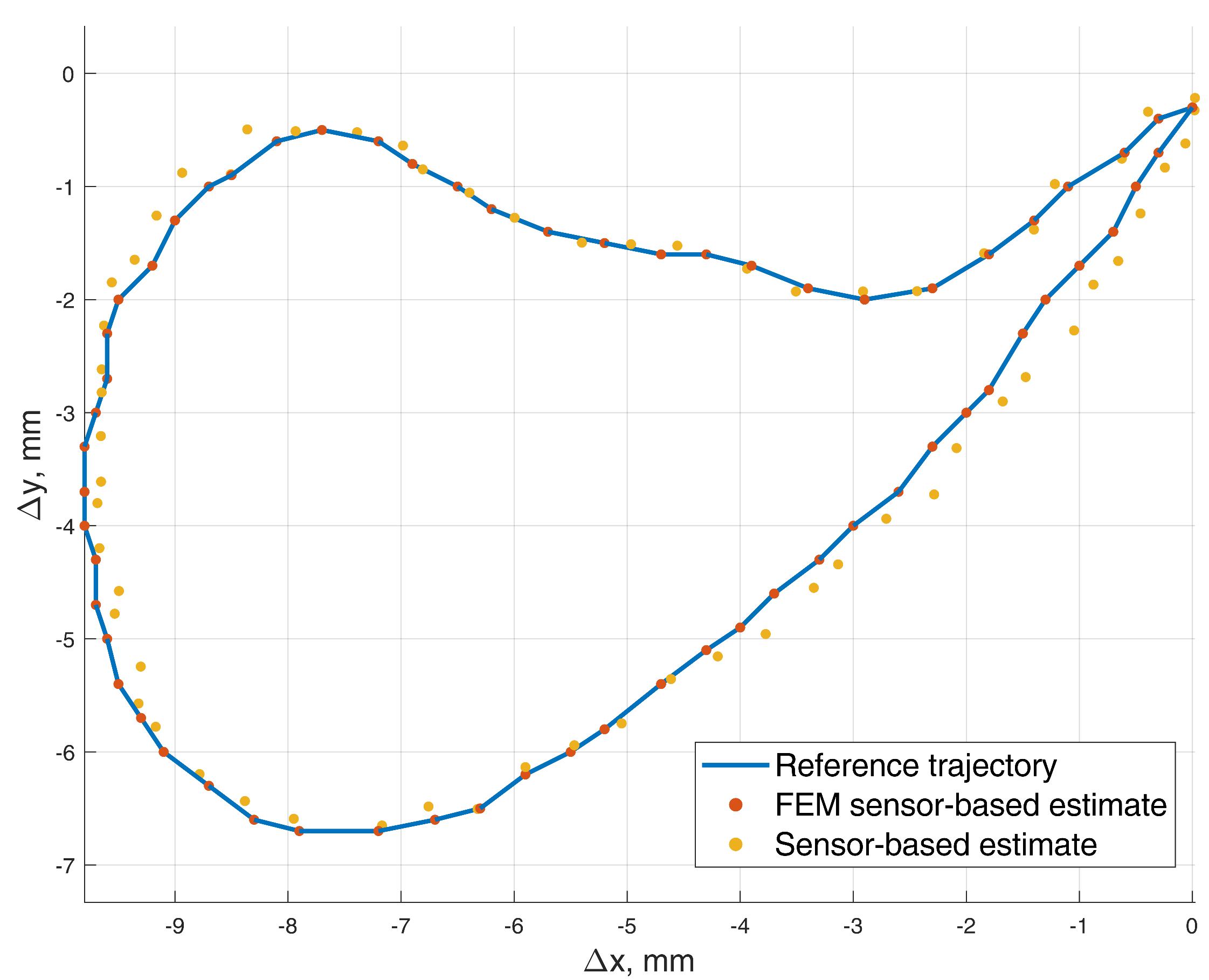
3.3.1. Static Positioning Test
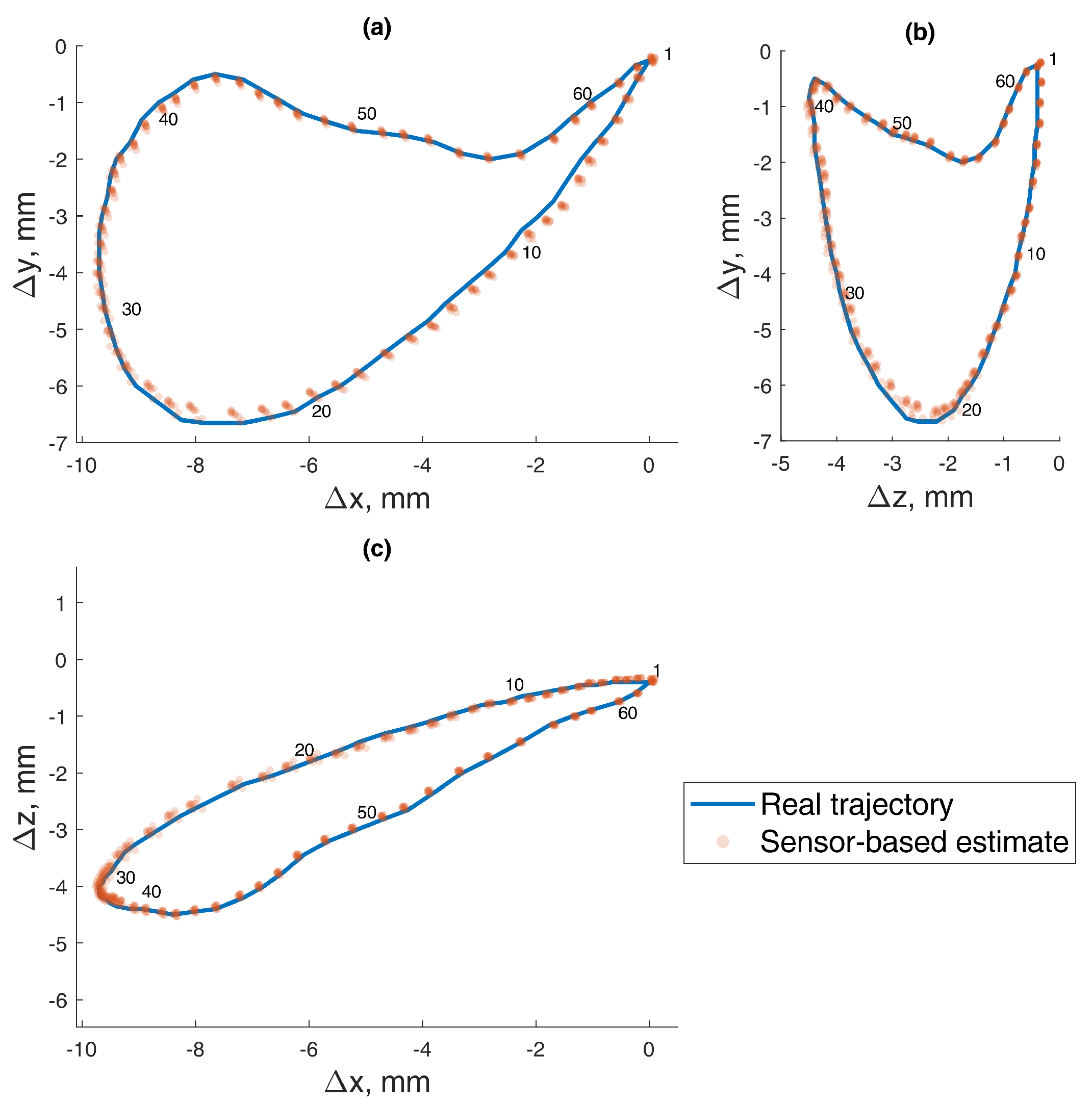
3.3.2. Dynamic Test
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMF | Background magnetic field |
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| ED | Euclidean distance |
| FEM | Finite element model |
| RMSE | Root-mean-squared error |
| STD | Standard deviation |
References
- KaVo Arcus Digma. Available online: https://www.kavo.com/dental-lab-equipment/arcus-arcusevo-articulation (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- ModJaw. Available online: https://www.modjaw.com/en (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Planmeca 4D™ Jaw Motion. Available online: https://www.planmeca.com/imaging/3d-imaging/planmeca-4d-jaw-motion/ (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Manfredini, D.; Winocur, E.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Paesani, D.; Lobbezoo, F. Epidemiology of Bruxism in Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Orofac. Pain 2013, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Kisch, J.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Bruxism and dental implant treatment complications: A retrospective comparative study of 98 bruxer patients and a matched group. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BruxOff Diagnosis Device. Available online: http://www.bruxoff.com/en/ (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Bruxane. Available online: https://www.bruxane.de/home.html (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Jucevičius, M.; Ožiūnas, R.; Mažeika, M.; Marozas, V.; Jegelevičius, D. Accelerometry-enhanced magnetic sensor for intra-oral continuous jaw motion tracking. Sensors 2021, 21, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, Y.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Kim, E.S.; Moon, C.J.; Lim, Y.C.; Yang, S.H. Cancellation of Background Field Using Magnetic Compass Sensor for Magnetometer Based Autonomous Vehicle. Proc. IEEE Sens. 2003, 2, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; Burrows, P.N.; Buzio, M.; Gohil, C.; Pentella, M.; Schulte, D. Magnetic characterization of Mumetal® for passive shielding of stray fields down to the nano-Tesla level. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2021, 988, 164904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, H. Skull For Reference—3D Model. Available online: https://skfb.ly/Lqtz (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Biancalana, V.; Cecchi, R.; Chessa, P.; Mandalà, M.; Bevilacqua, G.; Dancheva, Y.; Vigilante, A. Validation of a fast and accurate magnetic tracker operating in the environmental field. Instruments 2021, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K. Wearable magnetic field sensing for finger tracking. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Wearable Computers, ISWC, Cancun, Mexico, 12–17 September 2020; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, M.; Nichols, E.D.; Fenoglietto, F.L.; Stubbs, J. Real-Time, Non-Contact Position Tracking of Medical Devices and Surgical Tools through the Analysis of Magnetic Field Vectors. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MI, USA, 9–12 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Song, S.; Hu, C.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Meng, M.Q. A new calibration method for magnetic sensor array for tracking capsule endoscope. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, ROBIO 2009, Guilin, China, 19–23 December 2009; pp. 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, T.D.; Alici, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, W. A review of localization systems for robotic endoscopic capsules. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Meng, M.Q.; Mandal, M. A linear algorithm for tracing magnet position and orientation by using three-axis magnetic sensors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 4096–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruska, A.J.; Abbott, J.J. Optimal permanent-magnet geometries for dipole field approximation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, M.M. Anatomy and Function of the Temporomandibular Joint. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 1980, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Dundee, School of Dentistry. 3D Skull Model. Available online: https://skfb.ly/KQsq (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Raabe, D.; Harrison, A.; Alemzadeh, K.; Ireland, A.; Sandy, J. Capturing motions and forces of the human masticatory system to replicate chewing and to perform dental wear experiments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Bristol, UK, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mapelli, A.; Galante, D.; Lovecchio, N.; Sforza, C.; Ferrario, V.F. Translation and rotation movements of the mandible during mouth opening and closing. Clin. Anat. 2009, 22, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, W.D.; Rohan, E.J. A Linear Position Transducer Using a Magnet and Hall Effect Devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1977, 26, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




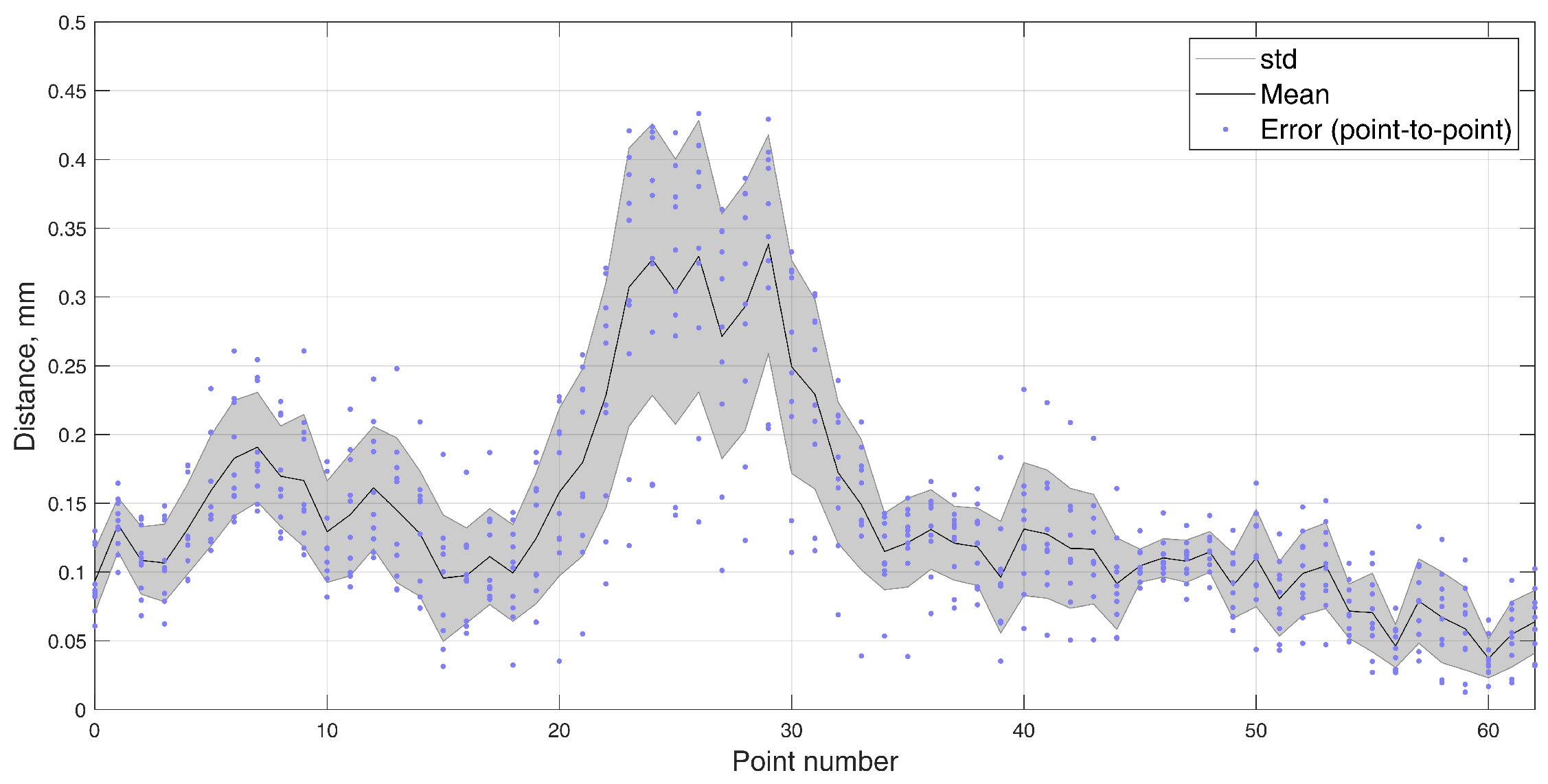
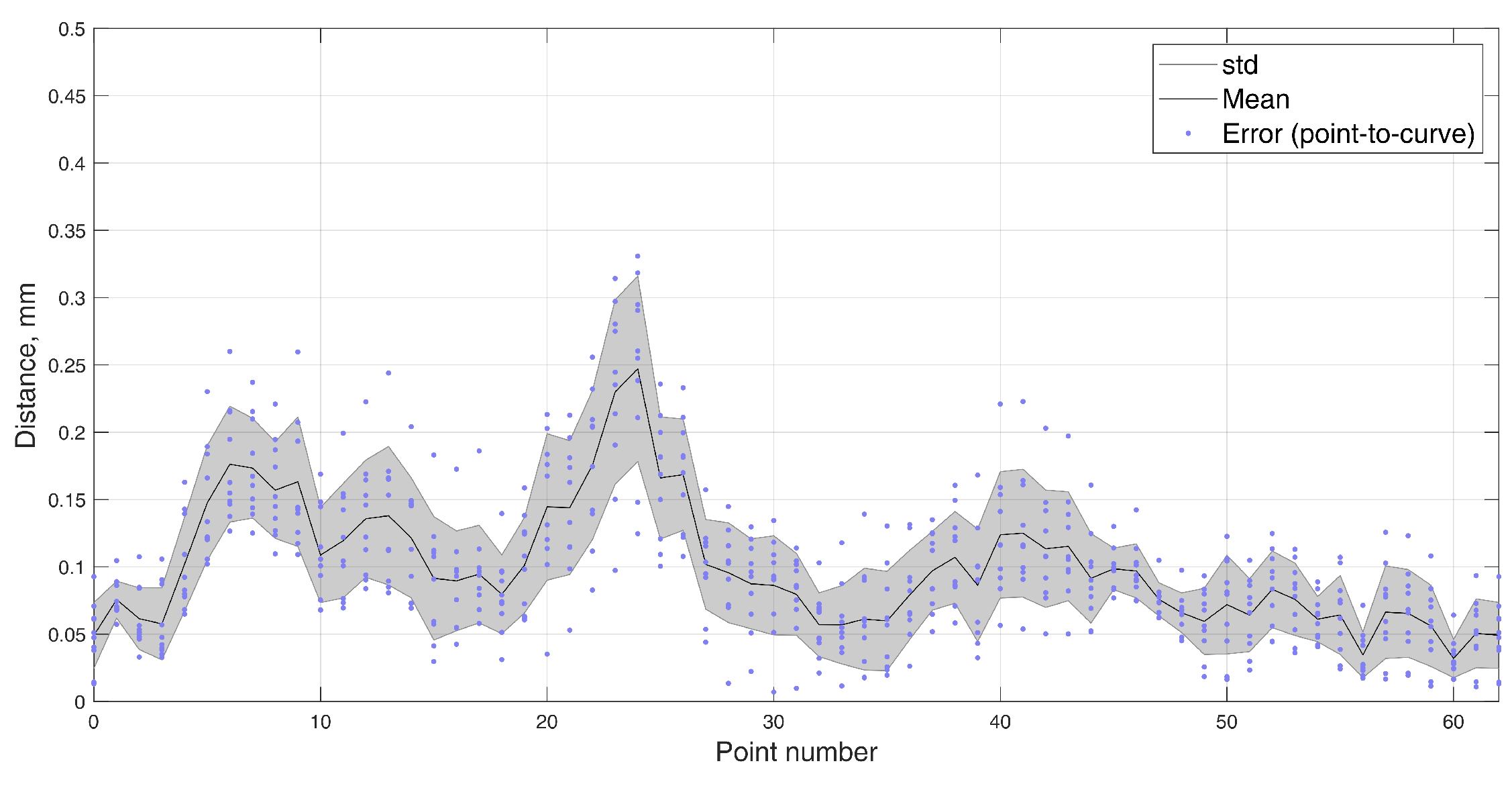



| Approach, Test | RMSE | RMSE, x proj. | RMSE, y proj. | RMSE, z proj. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 magnetometer, static | ||||
| 2 magnetometers, static |
| Approach, Test | ED | ED, x proj. | ED, y proj. | ED, z proj. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 magnetometer, static | ||||
| 2 magnetometers, static | ||||
| 2 magnetometers, dynamic |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jucevičius, M.; Ožiūnas, R.; Narvydas, G.; Jegelevičius, D. Permanent Magnet Tracking Method Resistant to Background Magnetic Field for Assessing Jaw Movement in Wearable Devices. Sensors 2022, 22, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030971
Jucevičius M, Ožiūnas R, Narvydas G, Jegelevičius D. Permanent Magnet Tracking Method Resistant to Background Magnetic Field for Assessing Jaw Movement in Wearable Devices. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030971
Chicago/Turabian StyleJucevičius, Mantas, Rimantas Ožiūnas, Gintautas Narvydas, and Darius Jegelevičius. 2022. "Permanent Magnet Tracking Method Resistant to Background Magnetic Field for Assessing Jaw Movement in Wearable Devices" Sensors 22, no. 3: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030971
APA StyleJucevičius, M., Ožiūnas, R., Narvydas, G., & Jegelevičius, D. (2022). Permanent Magnet Tracking Method Resistant to Background Magnetic Field for Assessing Jaw Movement in Wearable Devices. Sensors, 22(3), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030971








