3DMesh-GAR: 3D Human Body Mesh-Based Method for Group Activity Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Group Activity Recognition Approaches
2.2. 3D Human Body Mesh Reconstruction Methods
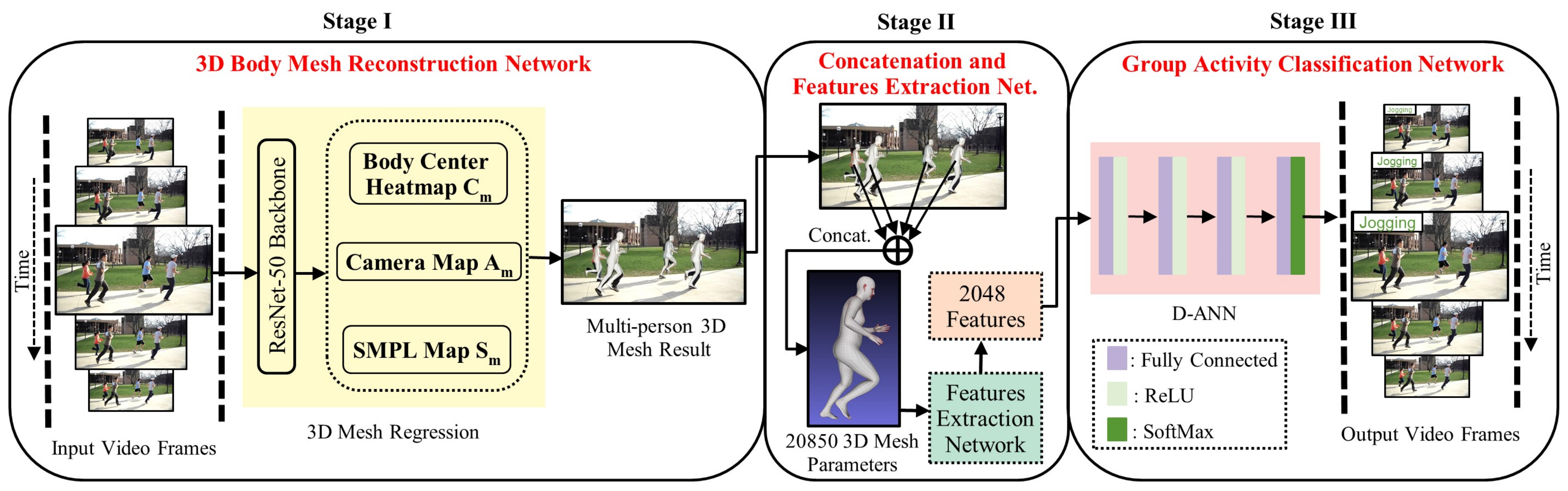
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. 3D Body Mesh Reconstruction: Stage I
3.1.1. Body Center Heatmap: C
3.1.2. Camera Map: A
3.1.3. SMPL Map: S
3.1.4. Mesh Parameter Map: P
3.1.5. Collision-Aware Representation (CAR)
3.2. Concatenation and Features Extraction: Stage II
3.3. Activity Classification Network: Stage III
4. Experiments and Result Analysis
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art
4.4. Results Analysis
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAR | Group Activity Recognition |
| 3DMesh-GAR | 3D Mesh-based Group Activity Recognition |
| GCNs | Graph Convolutional Networks |
| RNNs | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| DNNs | Deep Neural Networks |
| D-ANN | Deep Artificial Neural Network |
| GNNs | Graph Neural Networks |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| SVMs | Support Vectors Machines |
| ARG | Actor Relation Graph |
| SMPL | Skinned Multi-Person Linear model |
| R-CNN | Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks |
| 3DMPPE | 3D Multi-Person Pose Estimation |
| LCR-Net++ | Localization Classification Regression Network |
| LoCO | Learning on Compressed Output |
| GPUs | Graphics Processing Units |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Units |
References
- Demrozi, F.; Pravadelli, G.; Bihorac, A.; Rashidi, P. Human activity recognition using inertial, physiological and environmental sensors: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 210816–210836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, S.M.; Atigh, M.G.; Nickabadi, A. A multi-stream convolutional neural network framework for group activity recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.10328. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Liu, M.; Ding, R.; Liu, H. A survey on 3d skeleton-based action recognition using learning method. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05907. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cang, S.; Yu, H. A survey on wearable sensor modality centred human activity recognition in health care. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 137, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2199. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Gan, C.; Han, S. Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In Proceedings of the CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 7082–7092. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.07455. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Govindarajan, L.N.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L. Lie-x: Depth image based articulated object pose estimation, tracking, and action recognition on lie groups. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 123, 454–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J.; Grauman, K.; Malik, J.; Feichtenhofer, C. Audiovisual slowfast networks for video recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08740. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Savarese, S. A unified framework for multi-target tracking and collective activity recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Vahdat, A.; Hu, H.; Mori, G. Structure inference machines: Recurrent neural networks for analyzing relations in group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Muralidharan, S.; Deng, Z.; Vahdat, A.; Mori, G. A hierarchical deep temporal model for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, V.; Huang, J.; Abu-El-Haija, S.; Gorban, A.; Murphy, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Detecting events and key actors in multi-person videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Ni, B.; Yang, X. Recurrent modeling of interaction context for collective activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Choo Chuah, M. Sbgar: Semantics based group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Bogo, F.; Lassner, C.; Kanazawa, A.; Gehler, P.V.; Romero, J.; Akhter, I.; Black, M.J. Towards accurate marker-less human shape and pose estimation over time. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.C. Learning pose grammar to encode human body configuration for 3d pose estimation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.06513. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakos, G.; Choutas, V.; Ghorbani, N.; Bolkart, T.; Osman, A.A.; Tzionas, D.; Black, M.J. Expressive body capture: 3d hands, face, and body from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Bao, Q.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Black, M.J.; Mei, T. Monocular, One-stage, Regression of Multiple 3D People. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.12272. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Joo, H.; Sheikh, Y. Monocular Total Capture: Posing Face, Body, and Hands in the Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, K.; Shao, D.; Lin, D.; Dai, B. Revisiting Skeleton-based Action Recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.13586. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Sotnychenko, O.; Mueller, F.; Xu, W.; Elgharib, M.; Fua, P.; Seidel, H.P.; Rhodin, H.; Pons-Moll, G.; Theobalt, C. XNect: Real-time multi-person 3D motion capture with a single RGB camera. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2020, 39, 82:1–82:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Bian, S.; Yang, L.; Lu, C. HybrIK: A Hybrid Analytical-Neural Inverse Kinematics Solution for 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 3383–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, D.; Liew, J.H.; Nie, X.; Feng, J. Body meshes as points. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Piao, Z.; Min, J.; Luo, W.; Ma, L.; Gao, S. Liquid warping gan: A unified framework for human motion imitation, appearance transfer and novel view synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, G.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C.; Zisserman, A. Synthetic humans for action recognition from unseen viewpoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2264–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.; Alldieck, T.; Pons-Moll, G. Learning to transfer texture from clothing images to 3d humans. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Shahid, K.; Savarese, S. What are they doing?: Collective activity classification using spatio-temporal relationship among people. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1282–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Savarese, S. Understanding collective activitiesof people from videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimirsadeghi, H.; Yan, W.; Vahdat, A.; Mori, G. Visual recognition by counting instances: A multi-instance cardinality potential kernel. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Robinovitch, S.N.; Mori, G. Discriminative latent models for recognizing contextual group activities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amer, M.R.; Lei, P.; Todorovic, S. Hirf: Hierarchical random field for collective activity recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 572–585. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, T.; Todorovic, S.; Zhu, S.C. Cern: Confidence-energy recurrent network for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bagautdinov, T.; Alahi, A.; Fleuret, F.; Fua, P.; Savarese, S. Social scene understanding: End-to-end multi-person action localization and collective activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4315–4324. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Mori, G. Hierarchical relational networks for group activity recognition and retrieval. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 721–736. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07261. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, S.M.; Atigh, M.G.; Nickabadi, A.; Alahi, A. Convolutional relational machine for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wu, G. Learning actor relation graphs for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F. Multi-modality cross attention network for image and sentence matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sendo, K.; Ukita, N. Heatmapping of people involved in group activities. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Shahid, K.; Savarese, S. Learning context for collective activity recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 3273–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international Conference on Image Processing (ICIP); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave, K.; Belongie, S.; Lim, S.N. A metric learning reality check. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 681–699. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Cui, B.; He, Y.; Yu, S. Progressive relation learning for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Ai, H.; Lao, S. Localizing activity groups in videos. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 144, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhai, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Muralidharan, S.; Roshtkhari, M.J.; Mori, G. Deep structured models for group activity recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Hua, G.; Zheng, N. Action recognition by an attention-aware temporal weighted convolutional neural network. Sensors 2018, 18, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Chang, M.C.; Lyu, S. Who did what at where and when: Simultaneous multi-person tracking and activity recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01253. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Van Gool, L. stagnet: An attentive semantic rnn for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Gan, C.; De Melo, G.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Wen, S. Attention clusters: Purely attention based local feature integration for video classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gupta, A. Videos as space-time region graphs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01810. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gavrilyuk, K.; Gavves, E.; Jain, M.; Snoek, C.G. Videolstm convolves, attends and flows for action recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 166, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Hu, J.F.; Zheng, W.S. Latent embeddings for collective activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Di, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Spatio-temporal attention mechanisms based model for collective activity recognition. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 74, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradel, F.; Wolf, C.; Mille, J. Human activity recognition with pose-driven attention to rgb. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2018-29th British Machine Vision Conference, Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, B.; Gavves, E.; Oramas, J.; Ghodrati, A.; Tuytelaars, T. Rank pooling for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; Carreira, J.; Doersch, C.; Zisserman, A. Video action transformer network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilyuk, K.; Sanford, R.; Javan, M.; Snoek, C.G. Actor-transformers for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, G.; Ceylan, D.; Russell, B.; Yang, J.; Yumer, E.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Bodynet: Volumetric inference of 3d human body shapes. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04875. [Google Scholar]
- Gabeur, V.; Franco, J.S.; Martin, X.; Schmid, C.; Rogez, G. Moulding humans: Non-parametric 3d human shape estimation from single images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.; Hossain, R.; Romero, J.; Little, J.J. A simple yet effective baseline for 3d human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tome, D.; Russell, C.; Agapito, L. Lifting from the deep: Convolutional 3d pose estimation from a single image. In Proceedings of the EEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakos, G.; Zhou, X.; Daniilidis, K. Ordinal depth supervision for 3d human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, X.; Feng, J. Inference stage optimization for cross-scenario 3d human pose estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.02054. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, K.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. PoseAug: A Differentiable Pose Augmentation Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2015, 34, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Bao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Mei, T. Recent Advances in Monocular 2D and 3D Human Pose Estimation: A Deep Learning Perspective. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.11536. [Google Scholar]
- Bogo, F.; Kanazawa, A.; Lassner, C.; Gehler, P.; Romero, J.; Black, M.J. Keep it SMPL: Automatic estimation of 3D human pose and shape from a single image. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 561–578. [Google Scholar]
- Kolotouros, N.; Pavlakos, G.; Daniilidis, K. Convolutional mesh regression for single-image human shape reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, M.; Lassner, C.; Pons-Moll, G.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. Neural body fitting: Unifying deep learning and model based human pose and shape estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 484–494. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, H.Y.F.; Tung, H.W.; Yumer, E.; Fragkiadaki, K. Self-supervised learning of motion capture. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.01337. [Google Scholar]
- Arnab, A.; Doersch, C.; Zisserman, A. Exploiting temporal context for 3D human pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kocabas, M.; Athanasiou, N.; Black, M.J. Vibe: Video inference for human body pose and shape estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guler, R.A.; Kokkinos, I. Holopose: Holistic 3d human reconstruction in-the-wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, A.; Black, M.J.; Jacobs, D.W.; Malik, J. End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, B.; Katircioglu, I.; Salzmann, M.; Lepetit, V.; Fua, P. Structured prediction of 3d human pose with deep neural networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.05180. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakos, G.; Zhou, X.; Derpanis, K.G.; Daniilidis, K. Coarse-to-fine volumetric prediction for single-image 3D human pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Shang, J.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Compositional human pose regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, X.; Xue, X.; Wei, Y. Towards 3d human pose estimation in the wild: A weakly-supervised approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, B.; Márquez-Neila, P.; Salzmann, M.; Fua, P. Learning to fuse 2d and 3d image cues for monocular body pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Rhodin, H.; Casas, D.; Fua, P.; Sotnychenko, O.; Xu, W.; Theobalt, C. Monocular 3d human pose estimation in the wild using improved cnn supervision. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.; Saqlain, M.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Park, W.-H.; Baek, S. Towards single 2D image-level self-supervision for 3D human pose and shape estimation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfir, A.; Marinoiu, E.; Sminchisescu, C. Monocular 3d pose and shape estimation of multiple people in natural scenes-the importance of multiple scene constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Kolotouros, N.; Pavlakos, G.; Zhou, X.; Daniilidis, K. Coherent reconstruction of multiple humans from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dabral, R.; Mundhada, A.; Kusupati, U.; Afaque, S.; Sharma, A.; Jain, A. Learning 3d human pose from structure and motion. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.09250. [Google Scholar]
- Rogez, G.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Schmid, C. Lcr-net: Localization-classification-regression for human pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, A.; Zhang, J.Y.; Felsen, P.; Malik, J. Learning 3d human dynamics from video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, G.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, K.M. Camera distance-aware top-down approach for 3d multi-person pose estimation from a single rgb image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Yan, W.; Tan, R.T. Occlusion-aware networks for 3d human pose estimation in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pavllo, D.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Grangier, D.; Auli, M. 3d human pose estimation in video with temporal convolutions and semi-supervised training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 7753–7762. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Qian, C.; Lu, C. Hmor: Hierarchical multi-person ordinal relations for monocular multi-person 3d pose estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00206. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Lee, G.H. Hdnet: Human depth estimation for multi-person camera-space localization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 633–648. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri, M.; Lanzi, F.; Calderara, S.; Alletto, S.; Cucchiara, R. Compressed volumetric heatmaps for multi-person 3d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imtiaz, S.I.; ur Rehman, S.; Javed, A.R.; Jalil, Z.; Liu, X.; Alnumay, W.S. DeepAMD: Detection and identification of Android malware using high-efficient Deep Artificial Neural Network. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 115, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.E.; Sainath, T.N.; Hinton, G.E. Improving deep neural networks for LVCSR using rectified linear units and dropout. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsanpour, M.; Abedin, A.; Saleh, F.; Shi, J.; Reid, I.; Rezatofighi, H. Joint learning of social groups, individuals action and sub-group activities in videos. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part IX 16; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, L. Part-level graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
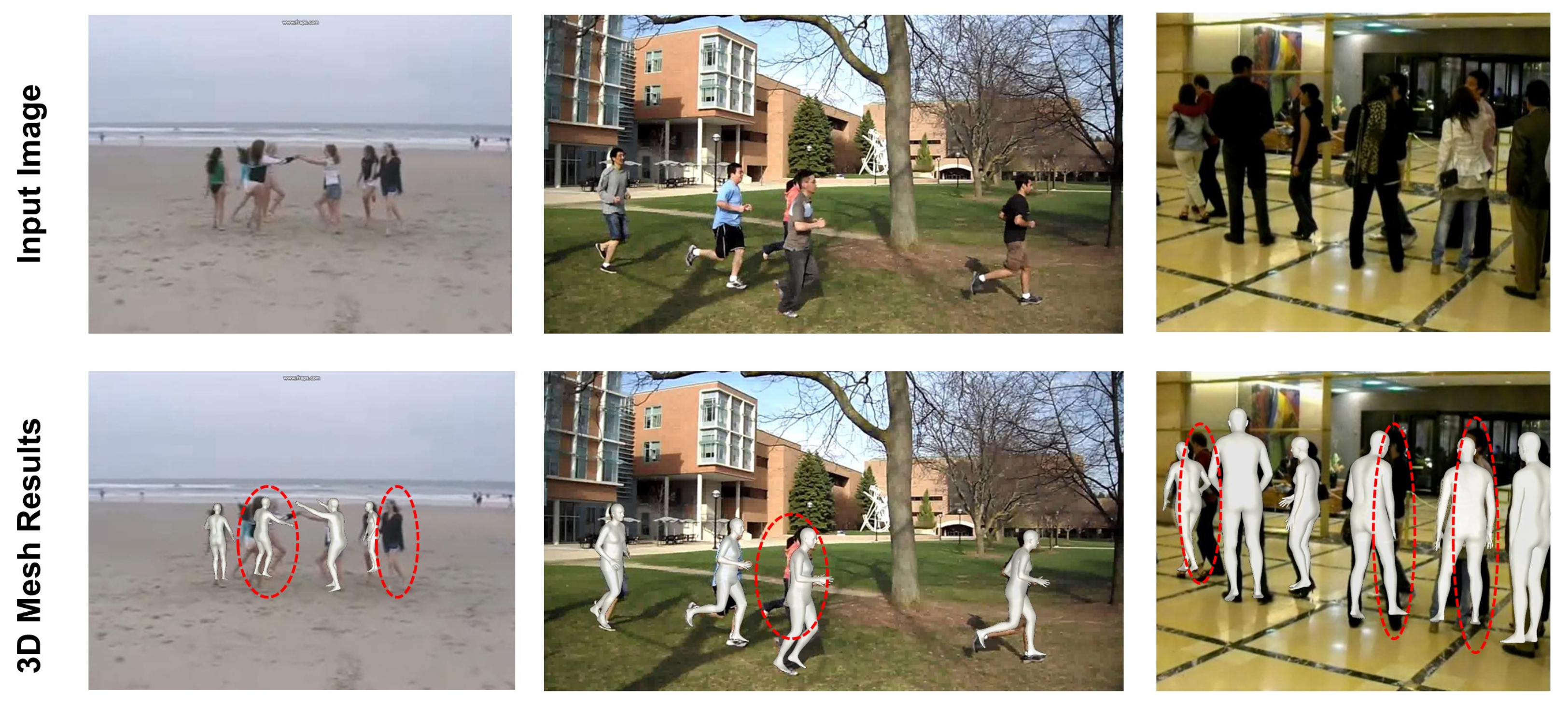





| Methods | Backbone | Group Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Lan et al. [33] | None | 79.7% |
| Choi and Savarese [11] | None | 80.4% |
| Deng et al. [12] | AlexNet | 81.2% |
| Ibrahim et al. [13] | AlexNet | 81.5% |
| Hajimirsadeghi et al. [32] | None | 83.4% |
| Azar et al. [41] | I3D | 85.8% |
| Li and Chuah [16] | Inception-v3 | 86.1% |
| Shu et al. [35] | VGG16 | 87.2% |
| Qi et al. [55] | VGG16 | 89.1% |
| Ehsanpour et al. [107] | I3D | 89.4% |
| Wu et al. [42] | Inception-v3 | 91.0% |
| Gavrilyuk et al. [65] | I3D | 92.8% |
| Ours (3DMesh-GAR) | ResNet-50 | 93.6% |
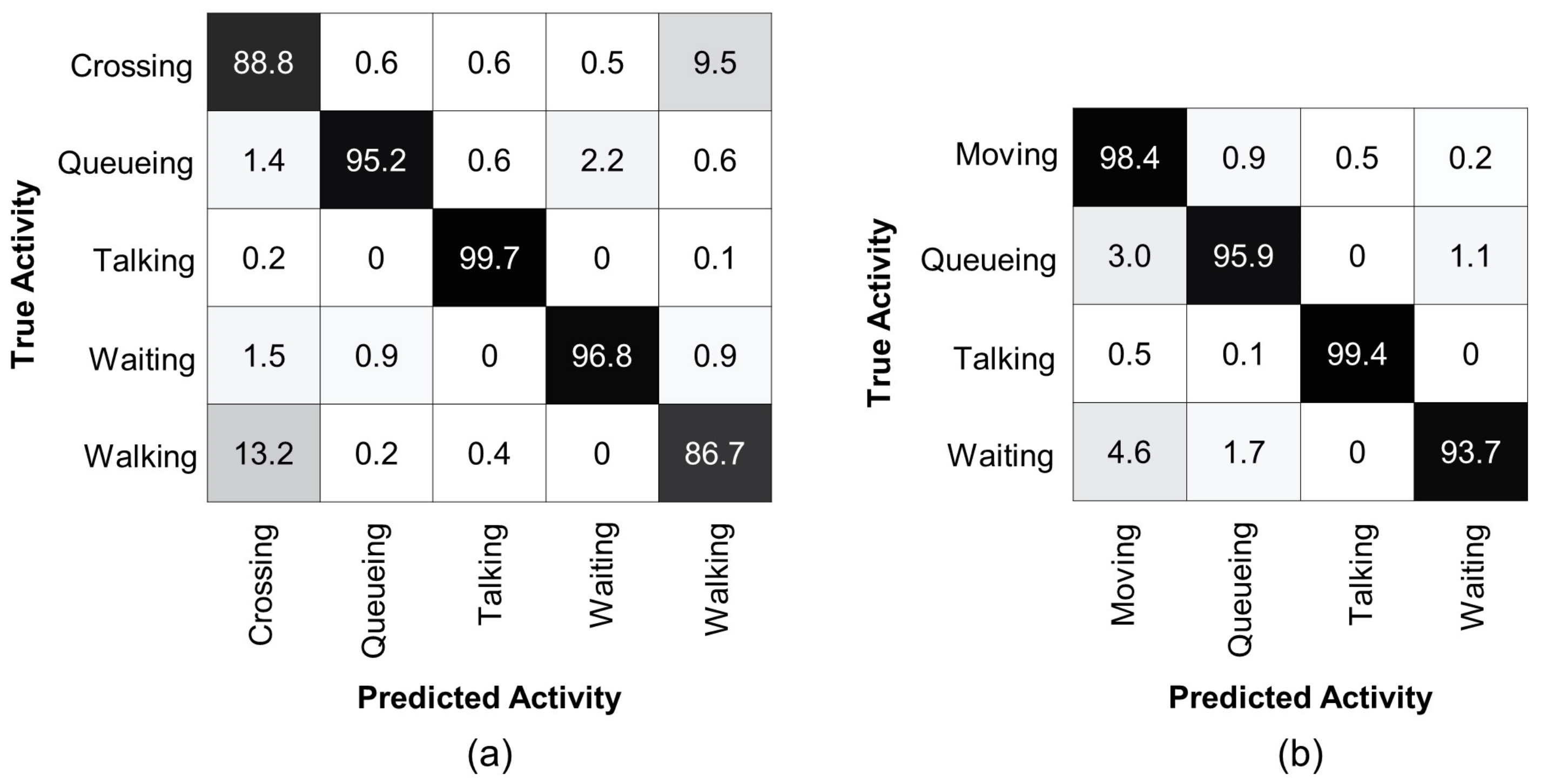
| Methods | Crossing | Queueing | Talking | Waiting | Walking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gavrilyuk et al. [65] | 83.3 | 100 | 100 | 96.1 | 88.1 |
| Ours | 88.8 | 95.2 | 99.7 | 96.8 | 86.7 |
| Methods | Back-Pain | Bow | Brush-Teeth | Cheer-Up | Shaking-Hands | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al. [108] | 88.7 | 90.9 | 85.9 | 87.7 | 93.8 | 89.4 |
| Ours | 90.2 | 93.7 | 88.1 | 95.0 | 91.9 | 92.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saqlain, M.; Kim, D.; Cha, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Baek, S. 3DMesh-GAR: 3D Human Body Mesh-Based Method for Group Activity Recognition. Sensors 2022, 22, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041464
Saqlain M, Kim D, Cha J, Lee C, Lee S, Baek S. 3DMesh-GAR: 3D Human Body Mesh-Based Method for Group Activity Recognition. Sensors. 2022; 22(4):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041464
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaqlain, Muhammad, Donguk Kim, Junuk Cha, Changhwa Lee, Seongyeong Lee, and Seungryul Baek. 2022. "3DMesh-GAR: 3D Human Body Mesh-Based Method for Group Activity Recognition" Sensors 22, no. 4: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041464
APA StyleSaqlain, M., Kim, D., Cha, J., Lee, C., Lee, S., & Baek, S. (2022). 3DMesh-GAR: 3D Human Body Mesh-Based Method for Group Activity Recognition. Sensors, 22(4), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041464







