A Machine Learning Approach for an Improved Inertial Navigation System Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The development of an ML-based ANFIS algorithm as an ML technique to leverage a low-grade IMU;
- Comparing the low-grade IMU measurements before and after applying the proposed algorithm to the reference IMU;
- The validation of the proposed algorithm by applying the tested IMU data to the INS mechanization.
2. Background
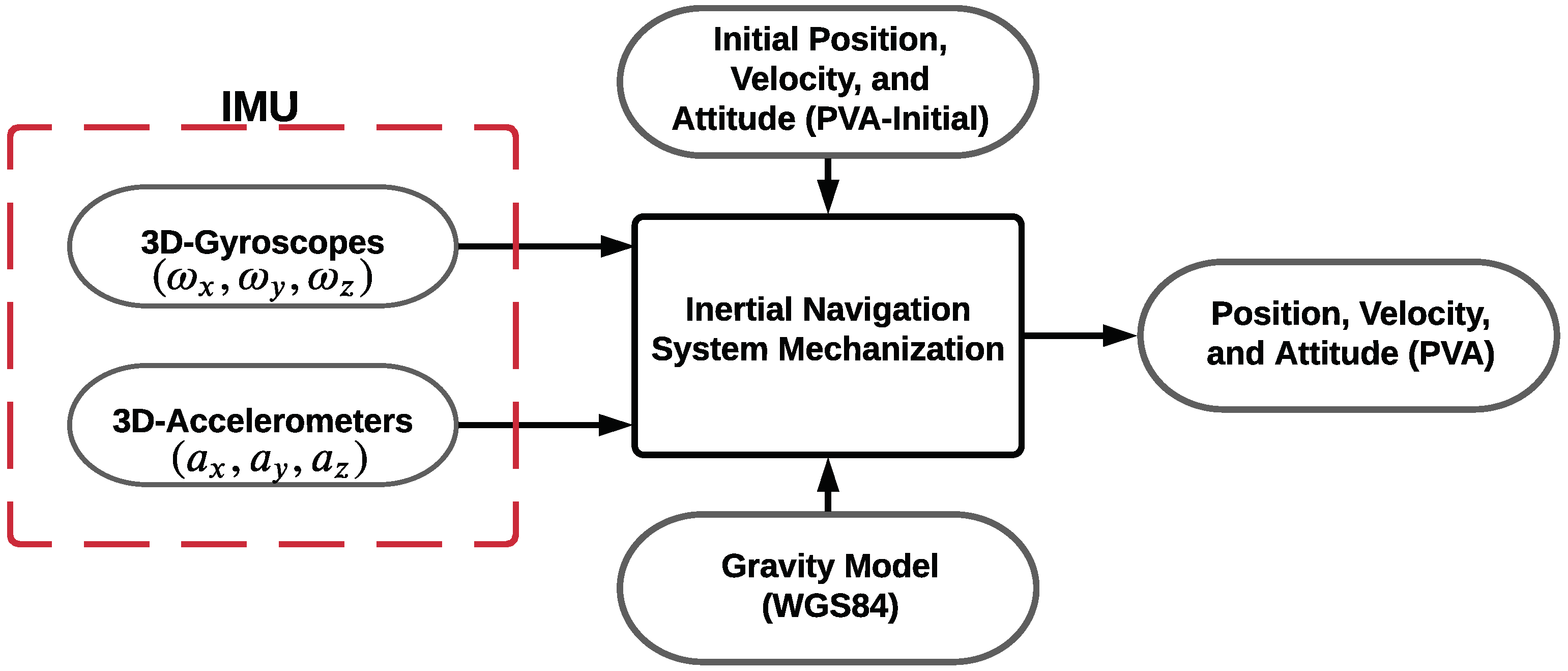
2.1. Inertial Navigation Systems
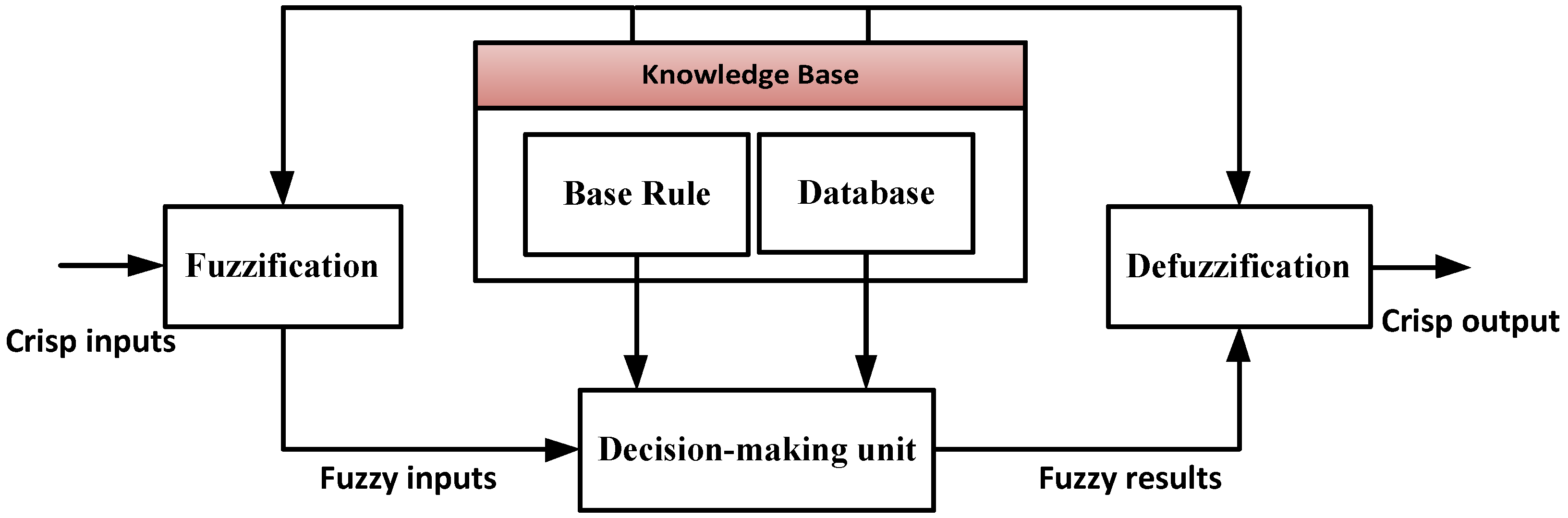
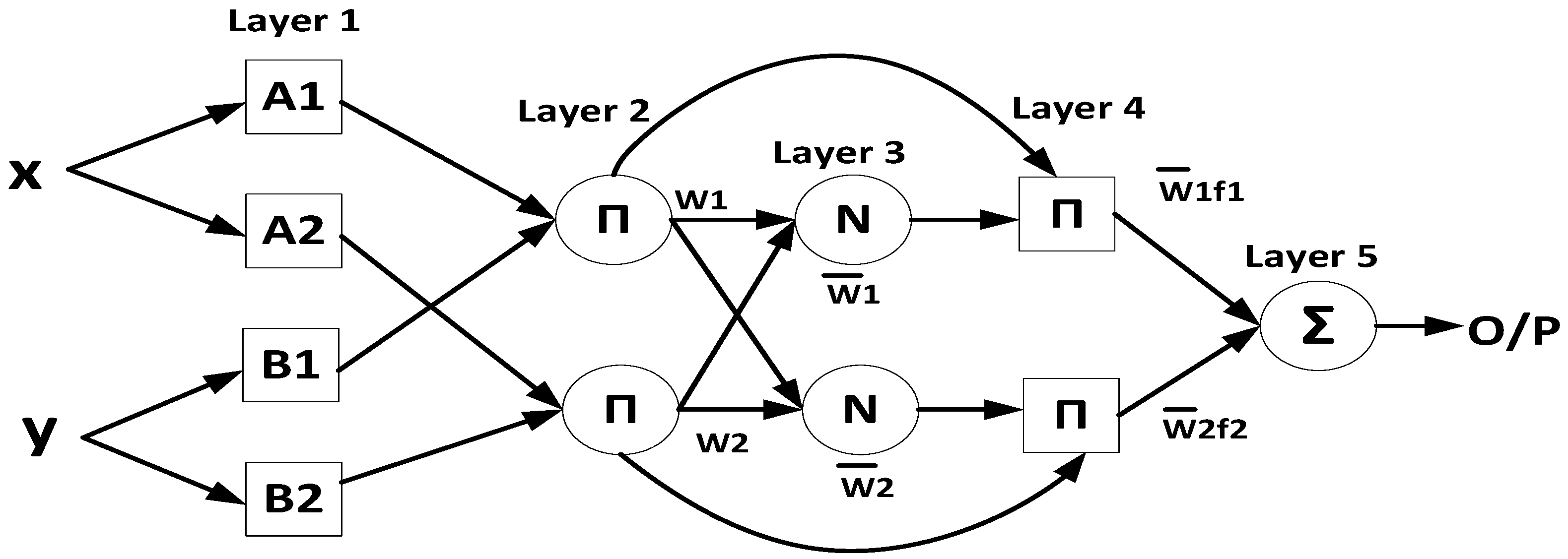
2.2. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
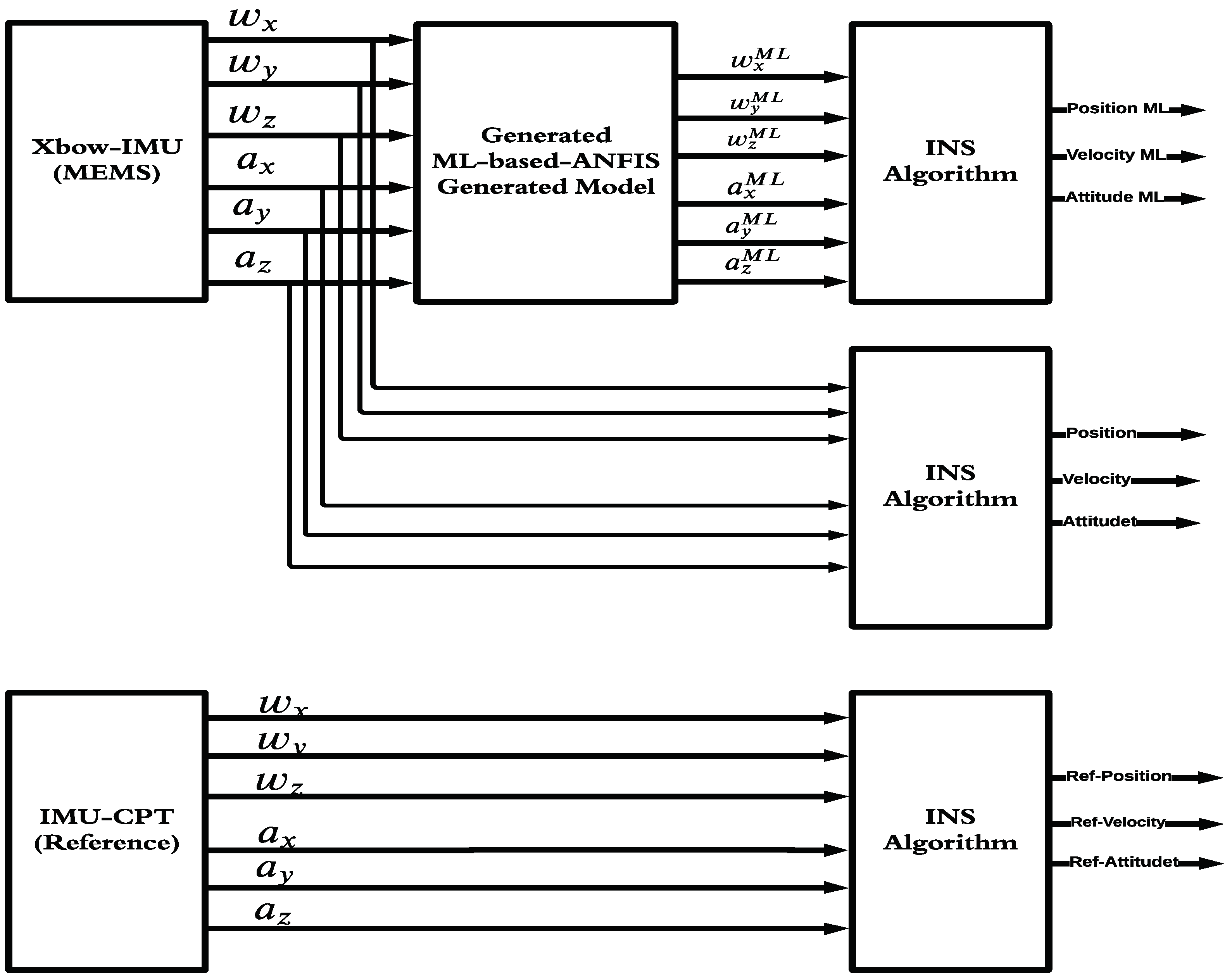
3. Methodology
| Algorithm 1 INS Solution Improvement Using ML | |
| Input | IMU’s sensor measurements of three gyroscopes and three accelerometers for the MEMS-IMU and the reference IMU, initial PVA states , and the navigation solution of the reference IMU (). |
| Step 1 | Prepare and tune the ML-ANFIS options (input data, output data, type of clustering, MF type, number of Ms, F and epochs/iterations). |
| Step 2 | Apply the ML-ANFIS on of the input data (training phase). |
| Step 3 | Generate the ML-ANFIS. |
| Step 4 | Evaluate and apply the ML-ANFIS on the remaining data (testing phase). |
| Step 5 | Evaluate the ML-ANFIS’s output (improved IMU sensor measurements . |
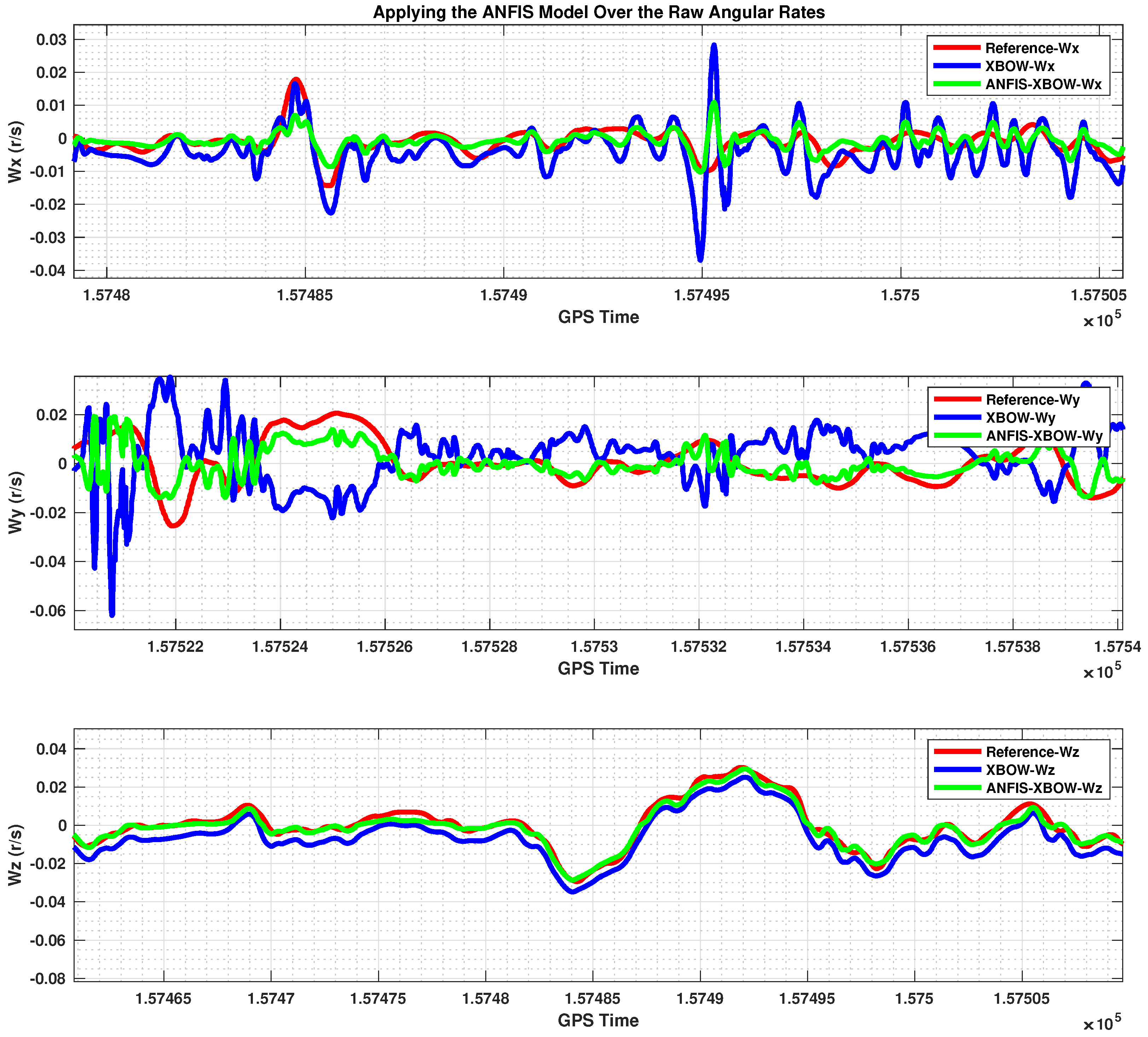
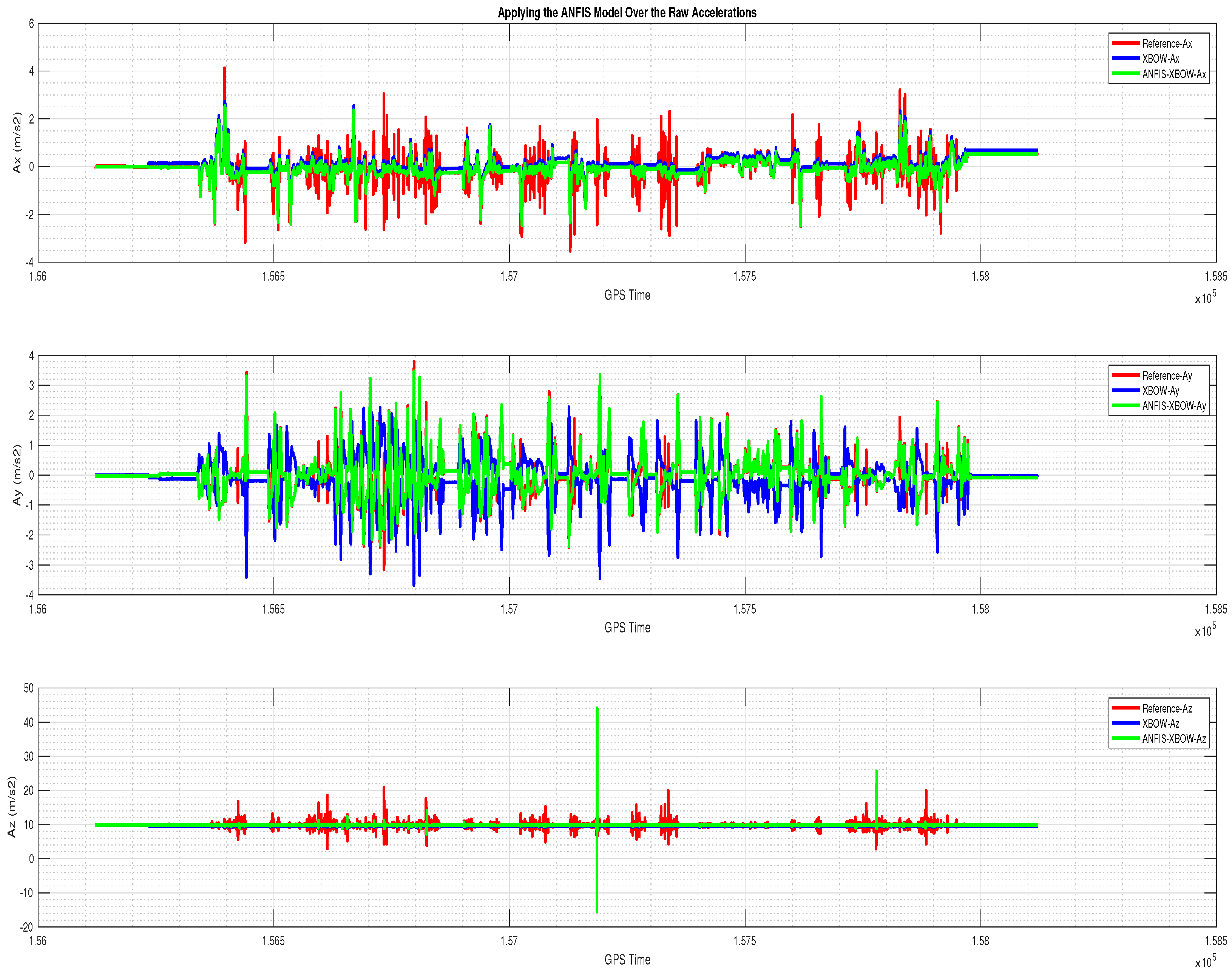
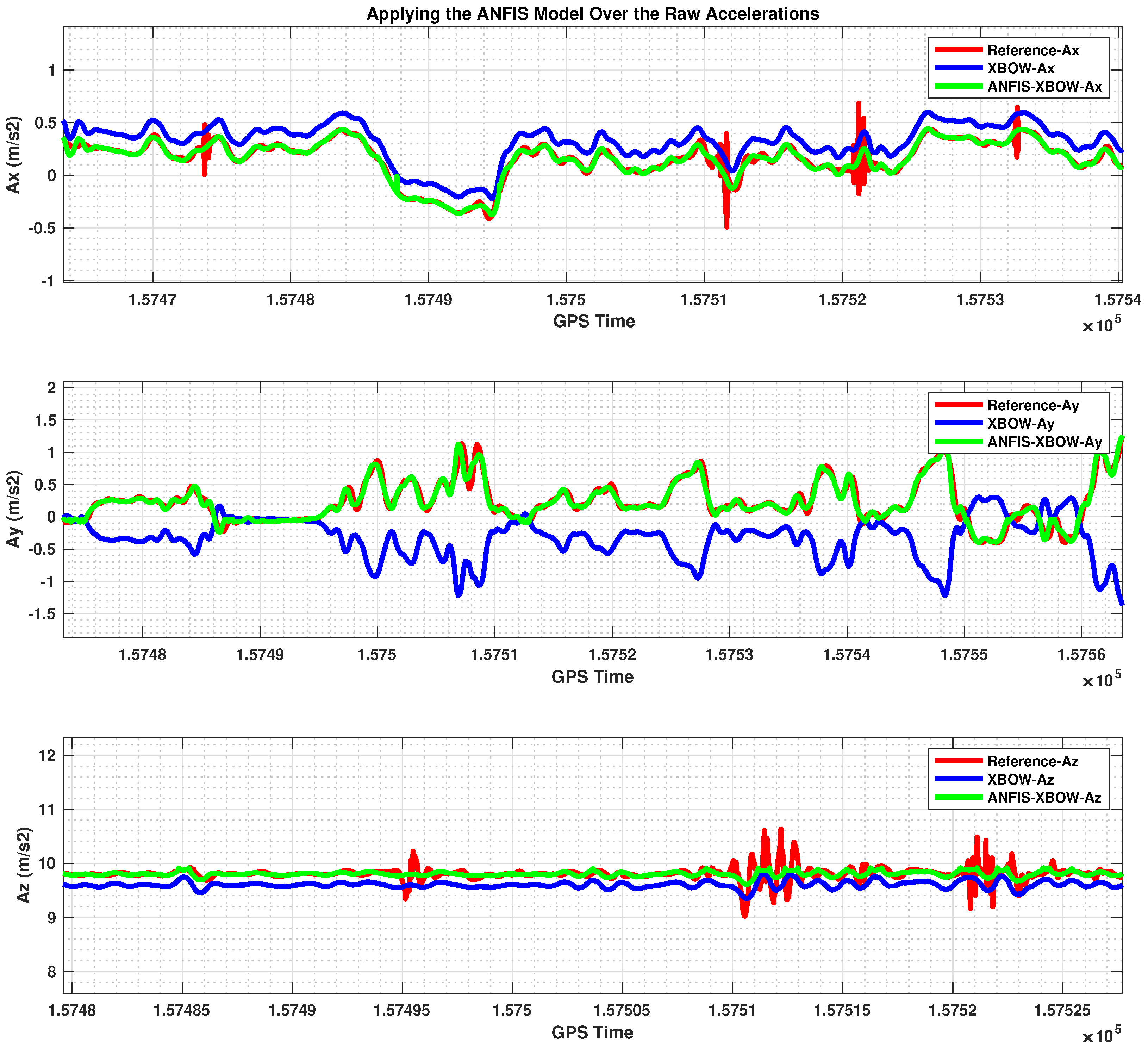
| Step 6 | Compare the MEMS IMU’s sensor measurements and the ML-ANFIS IMU’s sensor measurements to the reference IMU’s sensor measurements to compute the percentage of improvement caused by the ML-ANFIS (RMSE). where and are the reference IMU and trained IMU measurements, respectively. |
| Step 7 | Compute the ML-ANFIS’s navigation solution (PVA) by using the output of the ML-ANFIS as the input to the INS. |
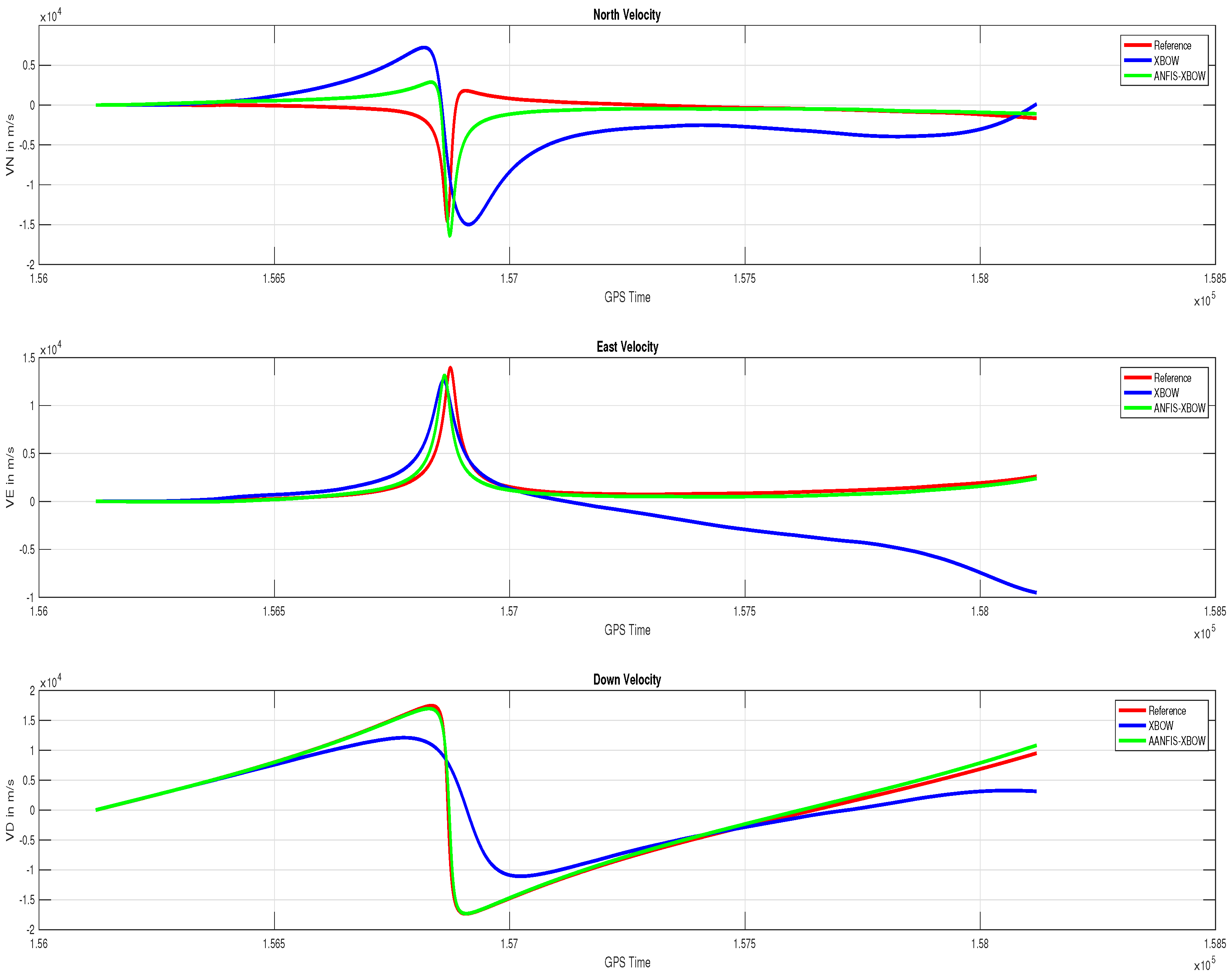
| Step 8 | Compare the MEMS IMU (PVA) and the ML-ANFIS (PVA) to the reference IMU (PVA) to compute the percentage of improvement of the ML-ANFIS (PVA) using the RMSE metric. |
| Output | The INS solution (PVA) of the MEMS-IMU and the ML model compared to the output using the reference IMU. |
4. Experimental Setup
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.B.; Georgy, J. Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation, Satellite-Based Positioning and their Integration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, p. 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterton, D.; Weston, J. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosekeen, A.; Iqbal, U.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M.J. A Novel Multi-Level Integrated Navigation System for Challenging GNSS Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 4838–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Niu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hu, X.; El-Sheimy, N. Inertial Sensing Meets Artificial Intelligence: Opportunity or Challenge? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.06727. [Google Scholar]
- Abosekeen, A.; Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.; Korenberg, M.J. Comparative Analysis of Magnetic-Based RISS using Different MEMS-Based Sensors. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 2944–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosekeen, A.; Iqbal, U.; Noureldin, A. Improved Navigation Through GNSS Outages: Fusing Automotive Radar and OBD-II Speed Measurements with Fuzzy Logic. GPS World 2021, 32, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, D.V.; Gon-Woo, K. Robust Stereo Visual Inertial Navigation System Based on Multi-Stage Outlier Removal in Dynamic Environments. Sensors 2020, 20, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abosekeen, A.; Iqbal, U.; Noureldin, A. Enhanced Land Vehicles Navigation by Fusing Automotive Radar and Speedometer Data. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2020), St. Louise, MO, USA, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 2206–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosekeen, A.; Abdalla, A. Fusion of Low-Cost MEMS IMU/GPS Integrated Navigation System. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Cairo, Egypt, 29–31 May 2012; Volume 8, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.A.; Abosekeen, A.; Ragab, H.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M.J. Leveraging FMCW-radar for autonomous positioning systems: Methodology and application in downtown Toronto. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS+ 2019, Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 2659–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T. What are the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in GNSS positioning? Inside GNSS 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, R.; Noureldin, A.; Osman, A.; El-Sheimy, N. Online INS/GPS Integration with a Radial Basis Function Neural Network. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2005, 20, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, L.; Noureldin, A. Bridging GPS outages using neural network estimates of INS position and velocity errors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 2783–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, R.; Noureldin, A. Sensor Integration for Satellite-Based Vehicular Navigation Using Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2007, 18, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.M.; Ragab, H.; Givigi, S.; Noureldin, A. Performance evaluation of neural-network-based integration of vision and motion sensors for vehicular navigation. In Autonomous Systems: Sensors, Processing, and Security for Vehicles and Infrastructure 2019; Dudzik, M.C., Ricklin, J.C., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019; Volume 11009, pp. 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, M.A.; Abdel-Hafez, M.F.; Saadeddin, K.; Jarrah, M.A. Intelligent fault detection and fusion for INS/GPS navigation system. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Symposium on Mechatronics and its Applications (ISMA), Amman, Jordan, 9–11 April 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Gan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Z. The Integration of Rotary MEMS INS and GNSS with Artificial Neural Networks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bitar, N.; Gavrilov, A. A new method for compensating the errors of integrated navigation systems using artificial neural networks. Measurement 2021, 168, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamazin, M.; Korenberg, M.J.; Elghamrawy, H.; Noureldin, A. GPS Swept Anti-Jamming Technique Based on Fast Orthogonal Search (FOS). Sensors 2021, 21, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, U.; Abosekeen, A.; Georgy, J.; Umar, A.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M.J. Implementation of Parallel Cascade Identification at Various Phases for Integrated Navigation System. Future Internet 2021, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Morales, E.; Dauth, J.; Huber, B.; García Higuera, A.; Botsch, M. High Precision Outdoor and Indoor Reference State Estimation for Testing Autonomous Vehicles. Sensors 2021, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semanjski, S.; Semanjski, I.; De Wilde, W.; Muls, A. Use of Supervised Machine Learning for GNSS Signal Spoofing Detection with Validation on Real-World Meaconing and Spoofing Data—Part I. Sensors 2020, 20, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabzevari, D.; Chatraei, A. INS/GPS Sensor Fusion based on Adaptive Fuzzy EKF with Sensitivity to Disturbances. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosekeen, A.; Abdalla, A. Improving the Navigation System of a UAV Using Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Based on Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Int. Conf. Aerosp. Sci. Aviat. Technol. 2011, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Shen, C.; Duan, X. A Temperature Compensation Approach for Dual-Mass MEMS Gyroscope Based on PE-LCD and ANFIS. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 95180–95193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Zhang, K. INS Error Estimation Based on an ANFIS and Its Application in Complex and Covert Surroundings. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouf, A.; Boussaid, L.; Sakly, A. TLBO-Based Adaptive Neurofuzzy Controller for Mobile Robot Navigation in a Strange Environment. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. A Fusion Methodology to Bridge GPS Outages for INS/GPS Integrated Navigation System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 61296–61306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Cong, L.; Qin, H.; Li, B.; Yao, J. A Robust Fusion Methodology for MEMS-Based Land Vehicle Navigation in GNSS-Challenged Environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 44087–44099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.V.; Kim, G.W. Online Self-Calibration of Multiple 2D LiDARs Using Line Features with Fuzzy Adaptive Covariance. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13714–13726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Niu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hu, X.; El-Sheimy, N. Inertial Sensing Meets Machine Learning: Opportunity or Challenge? IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2008; p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, P.G. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Integration Algorithm Design Part 2: Velocity and Position Algorithms. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1998, 21, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosekeen, A. Multi-Sensor Integration and Fusion in Navigation Systems. Master’s Thesis, Military Technical College, Cairo, Egypt, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corke, P.; Lobo, J.; Dias, J. An Introduction to Inertial and Visual Sensing. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2007, 26, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Visual-Inertial Navigation: A Concise Review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 9572–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abosekeen, A.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M.J. Improving the RISS/GNSS Land-Vehicles Integrated Navigation System Using Magnetic Azimuth Updates. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebel, J. Representing attitude: Euler angles, unit quaternions, and rotation vectors. Matrix 2006, 58, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Lai, J.; Xiong, Z. Performance analysis of adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system control for mems navigation system. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hmouz, A.; Shen, J.; Al-Hmouz, R.; Yan, J. Modeling and Simulation of an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) for Mobile Learning. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2012, 5, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Dutta, P. Fuzzy Logic: Concepts, System Design, and Applications to Industrial Informatics. In Handbook of Research on Industrial Informatics and Manufacturing Intelligence: Innovations and Solutions; Khan, M.A., Ansari, A.Q., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012; Chapter 3; pp. 33–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, R.; Sahana, C.; Savitha, P. Design of ANFIS based Estimation and Control for MIMO Systems. Int. J. Eng. 2012, 2, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, H. Application of Neuro-Fuzzy Controller for Sumo Robot control. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 9752–9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Bose, B. Evaluation of membership functions for fuzzy logic controlled induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society. IECON 02, Seville, Spain, 5–8 November 2002; Volume 1, pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.; Fernandez, E. Performance Evaluation of Membership Function on Fuzzy Logic Model for Solar PV array. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), Greater Noida, India, 2–4 October 2020; pp. 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
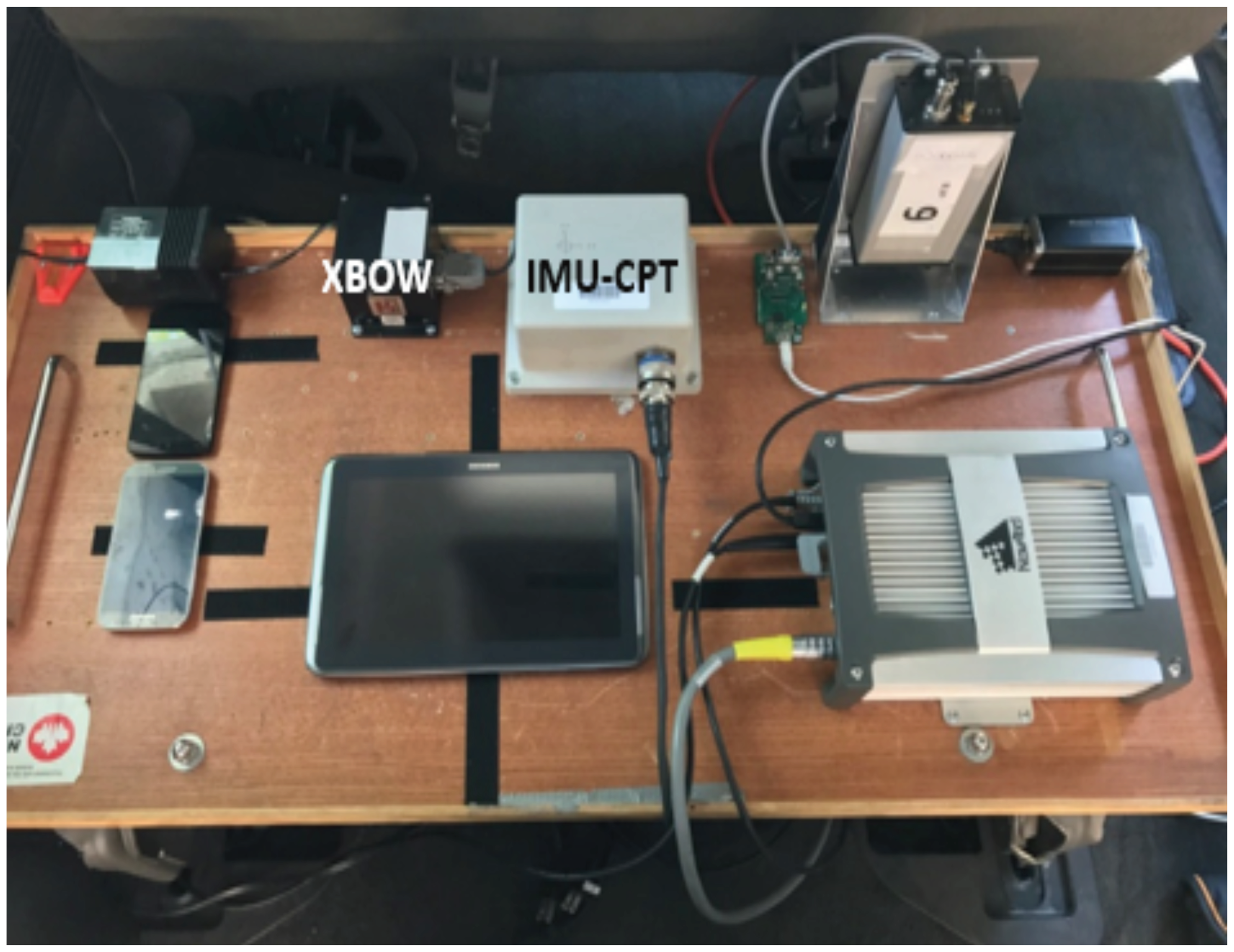








| IMUs | IMU300CC(XBOW) | IMU-CPT |
|---|---|---|
| (100 HZ) | (100 Hz) | |
| Size (cm) | 7.62 × 9.53 × 3.2 | 15.2 × 16.8 × 8.9 |
| Weight | 0.59 Kg | 2.28 Kg |
| Max data rate | 200 Hz | 100 Hz |
| Start-up time | <1 s | <5 s |
| Accelerometer | ||
| Range | ±2 g | ±10 g |
| Bias instability | ±30 mg | ±0.75 mg |
| Scale factor | <1%, 1 | 300 ppm, 1 |
| Gyroscope | ||
| Range | ±100/s | ±375/s |
| Bias instability | <±2.0/s | ±1.0/h |
| Scale factor | <1%, 1 | 1500 ppm, 1 |
| RMSE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XBOW | 0.0158 | 0.0213 | 0.0064 | 0.1902 | 1.2629 | 0.3542 |
| ML-XBOW | 0.0084 | 0.0069 | 0.0026 | 0.1084 | 0.0757 | 0.2873 |
| Units | XBOW | ML-XBOW | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position RMSE (m) | North | 311,899.4 | 222,857.2 |
| East | 732,549.2 | 83,613.3 | |
| Down | 967,706.2 | 291,313.6 | |
| 2D Pos | 796,184.3 | 238,026.2 | |
| 3D Pos | 1,253,141.9 | 376,191.6 | |
| Velocity RMSE (m/s) | VN | 2730.5 | 360.5 |
| VE | 5879.4 | 338.9 | |
| VD | 2242.8 | 655.2 | |
| 2D Vel | 6482.5 | 494.8 | |
| 3D Vel | 6859.5 | 821 | |
| Attitude RMSE (Deg) | Roll | 55.6 | 6.09 |
| Pitch | 42.6 | 6.5 | |
| Yaw | 86.3 | 79.3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdi, A.E.; Azouz, A.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosekeen, A. A Machine Learning Approach for an Improved Inertial Navigation System Solution. Sensors 2022, 22, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041687
Mahdi AE, Azouz A, Abdalla AE, Abosekeen A. A Machine Learning Approach for an Improved Inertial Navigation System Solution. Sensors. 2022; 22(4):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041687
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdi, Ahmed E., Ahmed Azouz, Ahmed E. Abdalla, and Ashraf Abosekeen. 2022. "A Machine Learning Approach for an Improved Inertial Navigation System Solution" Sensors 22, no. 4: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041687
APA StyleMahdi, A. E., Azouz, A., Abdalla, A. E., & Abosekeen, A. (2022). A Machine Learning Approach for an Improved Inertial Navigation System Solution. Sensors, 22(4), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041687








