Antenna/Propagation Domain Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC) for In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Communication Systems
Abstract
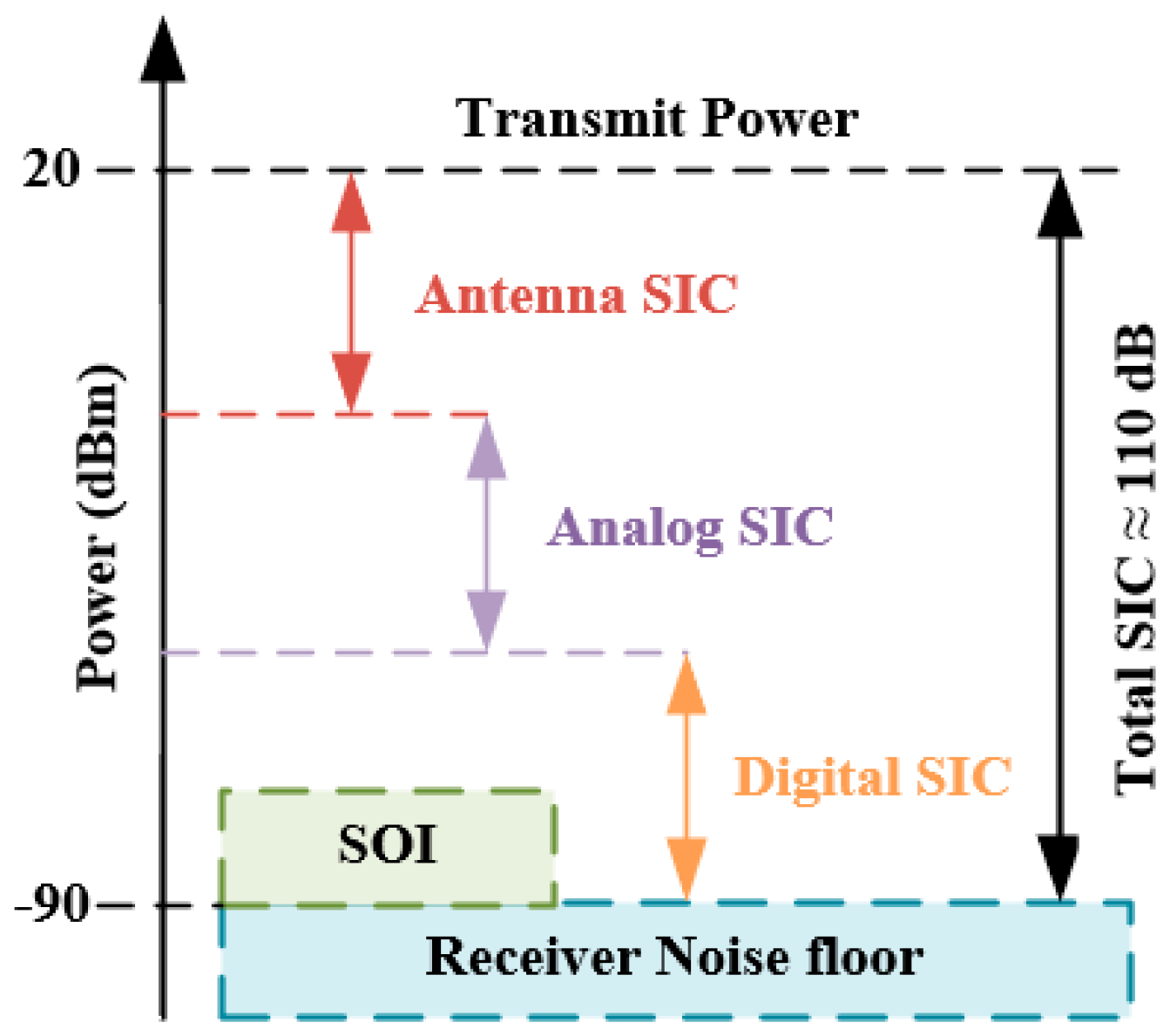
:1. Introduction
2. Passive Self-Interference Cancellation
2.1. Antenna Separation
2.2. Polarization Orthogonality
2.3. Near-Field Cancellation
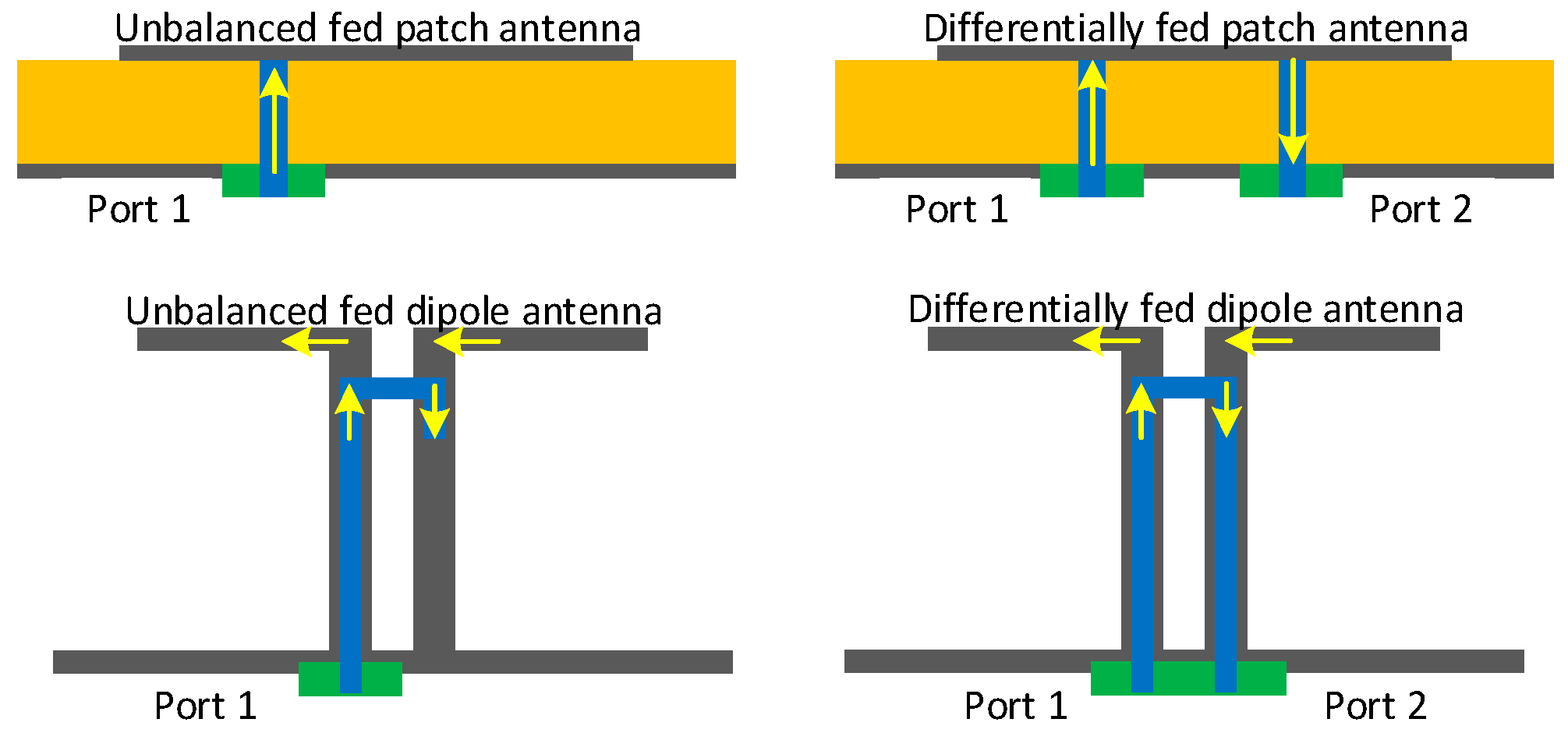
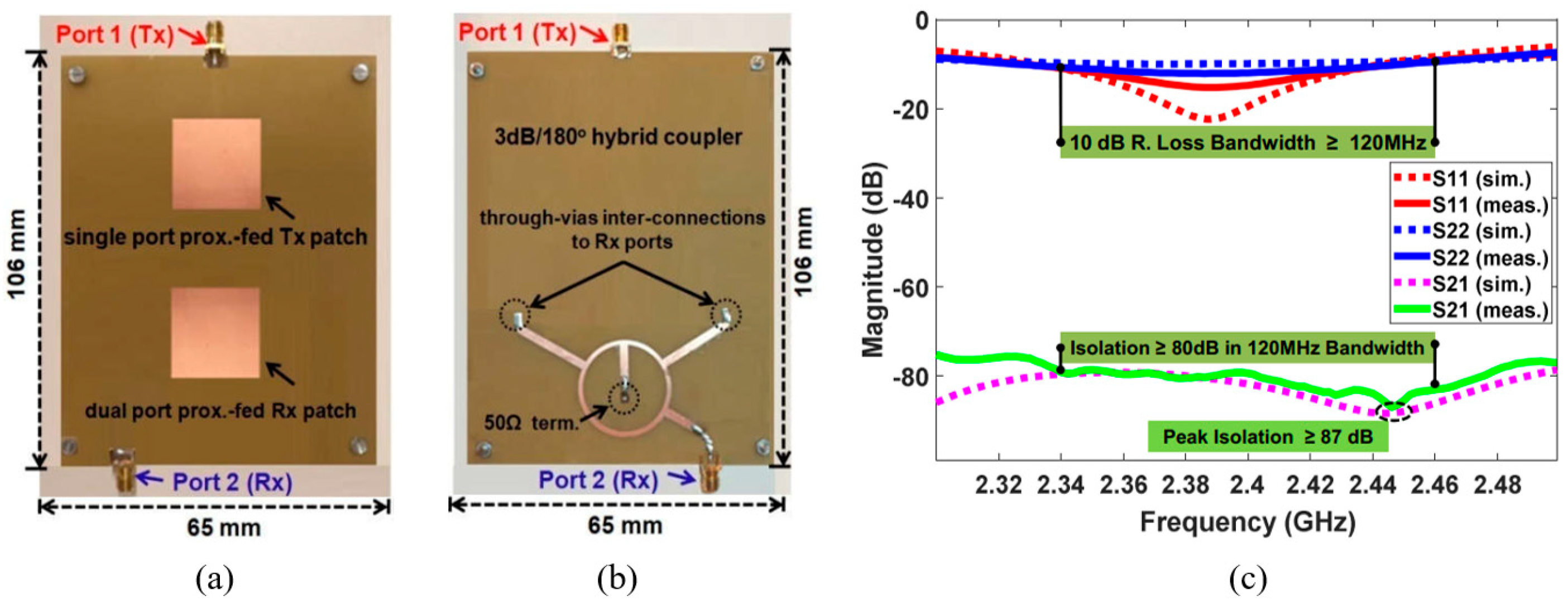
2.4. Isolation Feed Network
2.5. Decoupling Structure
2.6. Orthogonal Antenna Modes
3. Opportunity and Challenges
3.1. Combination of Multiple SIC Techniques in the AP Domain
3.2. Adaptive/Tunable SIC Techniques in the AP Domain
3.3. SIC for MIMO Antenna Systems
3.4. IBFD Antenna with Two Polarizations in Both TX and RX Modes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group. 5G Vision and Requirements. White Paper. 2015. Available online: http://www.imt2020.org.cn/zh/documents/download/11.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2022).
- Gohil, A.; Modi, H.; Patel, S.K. 5G technology of mobile communication: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Signal Processing (ISSP), Vallabh Vidyanagar, India, 1–2 March 2013; pp. 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal, A.; Schniter, P.; Guo, D.; Bliss, D.W.; Rangarajan, S.; Wichman, R. In-band full-duplex wireless: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1637–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J. Integrated full duplex radios. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.I.; Jain, M.; Srinivasan, K.; Levis, P.; Katti, S. Achieving single channel, full duplex wireless communication. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Chicago, IL, USA, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadia, D.; Katti, S. Full duplex MIMO radios. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Symposium (NSDI), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–4 April 2014; pp. 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Debaillie, B. Analog/RF solutions enabling compact full-duplex radios. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. Applications of self-interference cancellation in 5G and beyond. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadia, D.; McMilin, E.; Katti, S. Full duplex radios. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM, Hong Kong, China, 12–16 August 2013; pp. 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, E.; Sahai, A.; Sabharwal, A. Passive self-interference suppression for full-duplex infrastructure nodes. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2014, 13, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Long, K.; Vasilakos, V.A.; Hanzo, L. Full-duplex wireless communications: Challenges, solutions and future research directions. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1369–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z. Compact co-horizontally polarized full-duplex antenna with omnidirectional patterns. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.Z.; Xie, Z.M.; Xie, Q.Q.; Cen, X.L. A dual circularly polarized RFID reader antenna with wideband isolation. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, K.; Perry, B. Vehicle-mounted STAR antenna isolation performance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Hobart, TAS, Australia, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1602–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chai, X.; Long, K.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Hanzo, L. Full duplex techniques for 5G networks: Self-interference cancellation, protocol design, and relay selection. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J. A dual-polarized antenna array with enhanced interport isolation for far-field wireless data and power transfer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10258–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yu, F.R.; Ji, H.; Leung, V.C.M.; Li, X. In-band full-duplex relaying: A survey, research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 500–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. A 5G-enabling technology: Benefits, feasibility, and limitations of in-band full-duplex mMIMO. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2018, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, S.; Choudhury, D.; Dimou, K.; Aryafar, E.; Bangerter, B.; Stewart, K. Enabling technologies and architectures for 5G wireless. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 1–6 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihonen, T.; Korpi, D.; Rantula, O.; Valkama, M. On the prospects of full-duplex military radios. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Military Communications and Information Systems, Oulu, Finland, 15–16 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, K.E.; Perry, B.T.; Herd, J.S. In-Band Full-Duplex Technology: Techniques and Systems Survey. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 2019, 67, 3025–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, H.; Hong, D. A survey of in-band full-duplex transmission: From the perspective of PHY and MAC layers. IEEE Commun. Surveys Tuts. 2015, 17, 2017–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman, W.; Thiele, G. Antenna Theory and Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 60. ISBN 0-471-04458-X. [Google Scholar]
- Prasannakumar, P.V.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Filipovic, D.S. Wideband dual-polarized bi-static simultaneous transmit and receive antenna system. In Proceedings of the Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Okinawa, Japan, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 1855–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansouri, M.A.; Prasannakumar, V.P.; Tianang, E.; Etellisi, E.; Filipovic, D.S. Single and dual-polarized wideband simultaneous transmit and receive antenna system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 1105–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, D.W.; Parker, P.A.; Margetts, A.R. Simultaneous transmission and reception for improved wireless network performance. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, Madison, WI, USA, 26–29 August 2007; pp. 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Sabharwal, A. Full-duplex wireless communications using off-the-shelf radios: Feasibility and first results. In Proceedings of the Asilomar Conference on Signals Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 7–10 November 2010; pp. 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yetisir, E.; Chen, C.-C.; Volakis, J.L. Wideband low profile multiport antenna with omnidirectional pattern and high isolation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 3777–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Tekin, I. Three dual polarized 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antennas for active antenna and in-band full duplex applications. In Proceedings of the 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–16 November 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Broadband and high-isolation dual-polarized microstrip antenna with low radar cross section. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Karmakar, N.C. A 4×4 dual polarized mm-wave ACMPA array for a universal mm-wave chipless RFID tag reader. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, A.; Tian, Y. A novel broadband and highisolation dual-polarized microstrip antenna array based on quasi-substrate integrated waveguide technology. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, T.; Krishnaswamy, H. A T/R antenna pair with polarizationbased reconfigurable wideband self-interference cancellation for simultaneous transmit and receive. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 May 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Che, W.; Yang, W.; Feng, W.; Gu, L. Self-interference cancellation antenna using auxiliary port reflection for full-duplex application. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2873–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Morawski, R.; Le-Ngoc, T. Self-interference channel characterization for wideband 2 × 2 MIMO full-duplex transceivers using dual-polarized antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, P.; Mirshekar-Syahkal, D.; Zheng, G.; Pal, A.; Mehta, A. Broadband antenna for passive self-interference suppression in fullduplex communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–18 January 2018; pp. 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.S.; Cheng, Y.J.; Wu, Y.F.; Fan, Y. A W-Band Low-Profile Dual-Polarized Reflectarray With Integrated Feed for In-Band Full-Duplex Application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7222–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.-C.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Li, J.-L.; Pedersen, G.F.; Zhang, S. High-Isolation Dual-Polarized Leaky-Wave Antenna With Fixed Beam for Full-Duplex Millimeter-Wave Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7202–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Sun, H.H.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y.J. Achieving wider bandwidth with full-wavelength dipoles for 5G base stations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-H.; Zhu, H.; Ding, C.; Guo, Y.J. Wideband planarized duallinearly-polarized dipole antenna and its integration for dual-circularlypolarized radiation. IEEE Antenna Wireless Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2289–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, Z.; Yin, Y. Differentially-fed, wideband dual polarized filtering antenna with novel feeding structure for 5G sub-6 GHz base station applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 184718–184725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Sun, H.; Ziolkowski, R.W.; Guo, Y.J. A dual layered loop array antenna for base stations with enhanced cross-polarization discrimination. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 6975–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Tekin, I. Dual-polarized, differential fed microstrip patch antennas with very high interport isolation for full-duplex communication. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 7355–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Tekin, I. Compact dual-polarised microstrip patch antenna with high interport isolation for 2.5 GHz in-band full-duplex wireless applications. IET Microw., Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Tekin, I. Double-differential-fed, dual-polarized patch antenna with 90 dB interport RF isolation for a 2.4 GHz in-band fullduplex transceiver. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.L. Simultaneous transmit and receive system architecture with four stages of cancellation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 520–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetcov, M.V.; Podilchak, S.K.; McDermott, A.J.; Sellathurai, M. Dual-Polarized Antenna With Dual-Differential Integrated Feeding for Wideband Full-Duplex Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7192–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, G.; Jeong, J.; Jeong, Y. Differential fed antenna with high self-interference cancellation for in-band full-duplex communication system. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 45340–45348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Pedersen, G.F. A dual-polarized linear antenna array with improved isolation using a slotline-based 180° hybrid for full-duplex applications. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Li, J.-L. A Differential-Series-Fed dual-polarized traveling-wave array for full-duplex applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4097–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, D.; Surma, M.; Noga, A.; Magnuski, M. High Port-to-Port Isolation Dual-Polarized Antenna Array Dedicated for Full-Duplex Base Stations. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.B.; Roshani, S.; Talla, J. Size reduction and performance improvement of a microstrip Wilkinson power divider using a hybrid design technique. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, H.; Ahmad, N.; Aslam, J. A unidirectional, printed antenna with high interport isolation over wider bandwidth for 2.4 GHz full duplex applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7183–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Niazi, A.U.; Basit, M.A.; Usman, M. Single layer, differentially driven, LHCP antenna with improved isolation for full fuplex wireless applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 169796–169806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojastepour, M.A.; Sundaresan, K.; Rangarajan, S.; Zhang, X.; Barghi, S. The case for antenna cancellation for scalable full-duplex wireless communications. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks (HotNets-X), Cambridge, MA, USA, 14–15 November 2011; p. 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Zang, Y.; Luyen, H.; Li, M.; Behdad, N. A compact, low-profile simultaneous transmit and receive antenna with monopole-like radiation characteristics. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, T.; Fulton, C.; Chappell, W.J. Multi-antenna near field cancellation duplexing for concurrent transmit and receive. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–10 June 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, K.E.; Hurst, P.T.; Fenn, A.J.; Parad, L.I. Ring array antenna with optimized beam former for simultaneous transmit and receive. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Chicago, IL, USA, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, W.F.; Perry, B.T.; Herd, J.S. Wideband antenna array for simultaneous transmit and receive (STAR) applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), Memphis, TN, USA, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Yin, T.Y.; Yin, Y.; Behdad, N. A high-isolation, ultrawideband simultaneous transmit and receive antenna with monopole-like radiation characteristics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Behdad, N. A wideband, unidirectional circularly polarized antenna for full-duplex applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, M.E. Single antenna full duplex communications using a common carrier. In Proceedings of the IEEE Annual Conference on Wireless and Microwave Technology, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 15–17 April 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, D.S.; Elmansouri, M.; Etellisi, E.A. On wideband simultaneous transmit and receive (STAR) with a single aperture. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Okinawa, Japan, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etellisi, E.A.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Filipovic, D.S. Wideband monostatic simultaneous transmit and receive (STAR) antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, P.V.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Filipovic, D.S. Broadband reflector antenna with high isolation feed for full-duplex applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, P.V.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Boskovic, L.B.; Ignatenko, M.; Filipovic, D.S. Wideband quasi-monostatic simultaneous transmit and receive reflector antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Prasannakumar, P.V.; Filipovic, D.S. Monostatic co-polarized full-duplex antenna with left- or right-hand circular polarization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 5103–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.H.; Filipovic, D.S. Antenna system for full-duplex operation of handheld radios. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansouri, M.A.; Boskovic, L.B.; Filipovic, D.S. Compact Wideband Dual-Polarized In-Band Full-Duplex Antenna Subsystem. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7166–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etellisi, E.A.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Filipović, D.S. Wideband multimode Monostatic Spiral Antenna STAR Subsystem. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.H.; Abdullah, H.H.; Attia, M.A.; Abada, A.M. S-band compact microstrip full-duplex Tx/Rx patch antenna with high isolation. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, M.; Venkatasubramanian, S.N.; Icheln, C.; Haneda, K. Design of wavetraps for isolation improvement in compact in-band full-duplex relay antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korpi, D.; Heino, M.; Icheln, C.; Haneda, K.; Valkama, M. Compact in-band full-duplex relays with beyond 100 dB self-interference suppression: Enabling techniques and field measurements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, P.V.; Elmansouri, M.A.; Filipovic, D.S. Wideband decoupling techniques for dual-polarized bi-static simultaneous transmit and receive antenna subsystem. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 4991–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lim, S. High isolation transmitter and receiver antennas using high-impedance surfaces for repeater applications. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2013, 27, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Decoupling and low-profile design of dual-band dual-polarized base station antennas using frequency-selective surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5272–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Ghalyon, H.A.; Farahani, M.; Sebak, A.; Denidni, T.A. Spatially decoupling of CP antennas based on FSS for 30 GHz MIMO systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gong, S. Isolation enhancement in patch antenna array with fractal UC-EBG structure and cross slot. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kishk, A.A. Enhancing isolation in dual-band meander-line multiple antenna by employing split EBG structure. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, A.T.; Chappell, W.J. Simultaneous transmit and receive with a small planar array. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–22 June 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, A.T. Broadband near-field filters for simultaneous transmit and receive in a small two-dimensional array. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 1–6 June 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.; Wei, C.; Mei, X.; Zhang, Z. Array-antenna decoupling surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6728–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Lee, C.; Chang, F. Printed MIMO-antenna system using neutralization-line technique for wireless USB-dongle applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pedersen, G.F. Mutual coupling reduction for UWB MIMO antennas with a wideband neutralization line. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, R.; Holzman, E.; Carpenter, L.; Gagnon, S. Impact of transmit interference on receive sensitivity in a bi-static active array system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology(PAST), Waltham, MA, USA, 18–21 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shih, T.Y. Characteristic-mode-based design of planar in-band full-duplex antennas. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 1, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, K.K.; Hum, S.V. A two-port chassis-mode MIMO antenna. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.A. Dual-Polarized Slot Antenna for Full-Duplex Systems with High Isolation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7119–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, T.; Dong, Y. Compact In-Band Full Duplexing Antenna for Sub-6 GHz 5G Applications. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Y. Compact Co-Linearly Polarized Microstrip Antenna With Fence-Strip Resonator Loading for In-Band Full-Duplex Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7125–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Compact Co-polarized PIFAs for Full-Duplex Application Based on CM/DM Cancellation Theory. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 7103–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, M.R.; Wu, J.; Luyen, H.; Behdad, N. A concurrently dual-polarized, simultaneous transmit and receive (STAR) antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashanianfard, M.; Sarabandi, K. directional full-duplex RF booster for 2450 MHz ISM band. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, C.G.; Tawk, Y.; Lane, S.A.; Erwin, S.R. Reconfigurable antennas for wireless and space applications. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Guo, Y.J.; Qin, P.; Yang, Y. A Compact Microstrip Phase Shifter Employing Reconfigurable Defected Microstrip Structure (RDMS) for Phased Array Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qin, P.; Ding, C.; Guo, Y.J. Cavity-Backed Proximity-Coupled Reconfigurable Microstrip Antenna With Agile Polarizations and Steerable Beams. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 5553–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.G.; Buzzi, S.; Choi, W.; Hanly, S.V.; Lozano, A.; Soong, A.C.K.; Zhang, J.C. What will 5G be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




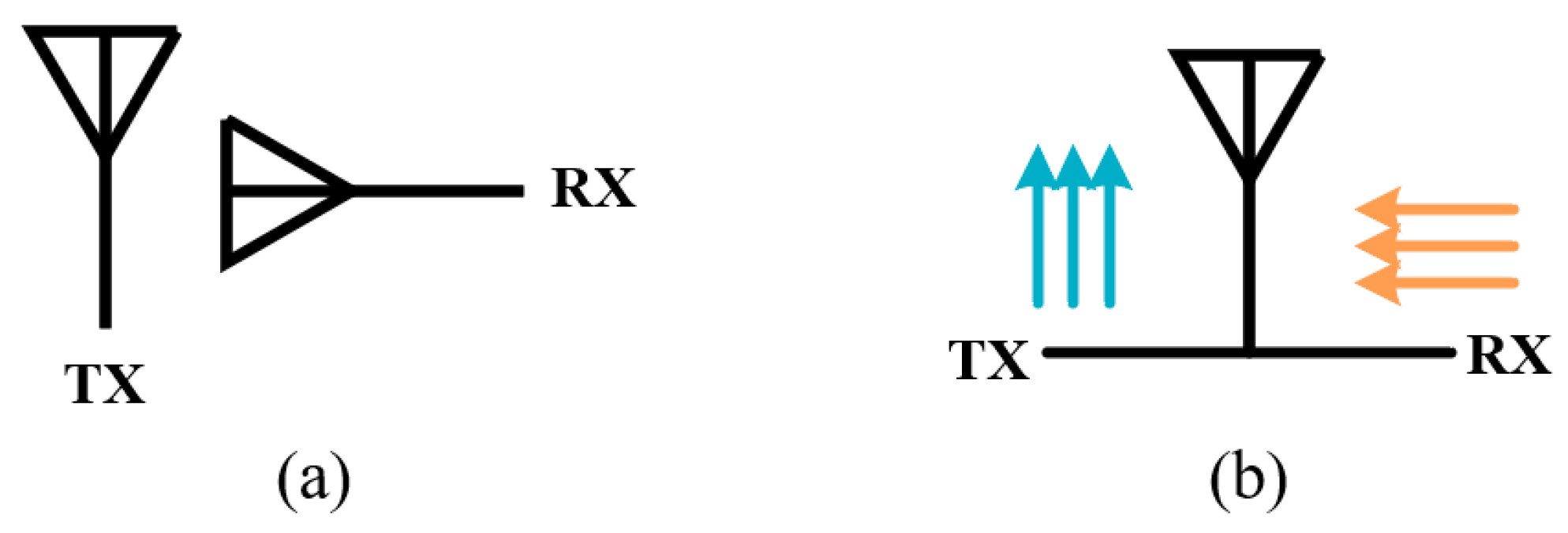
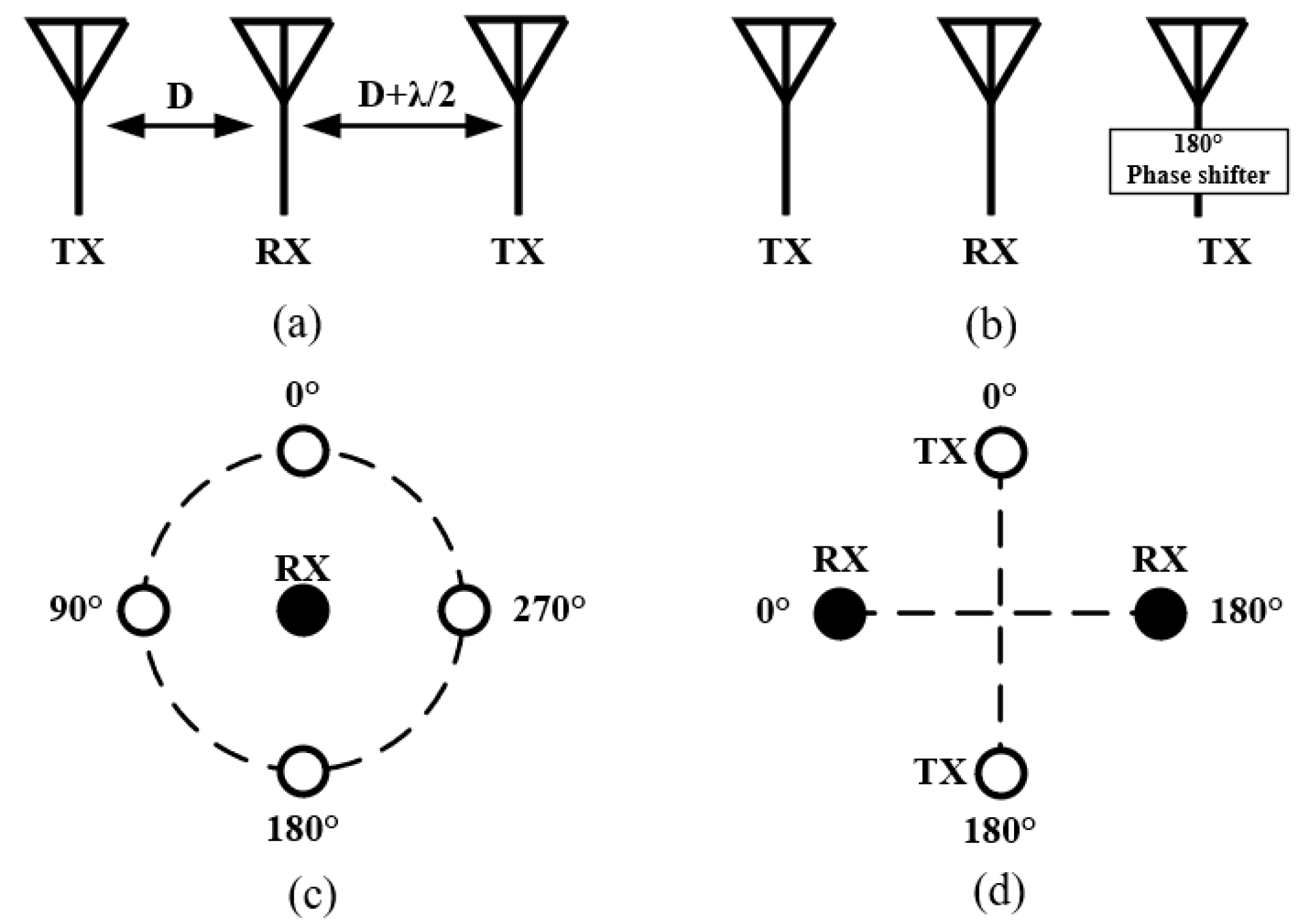
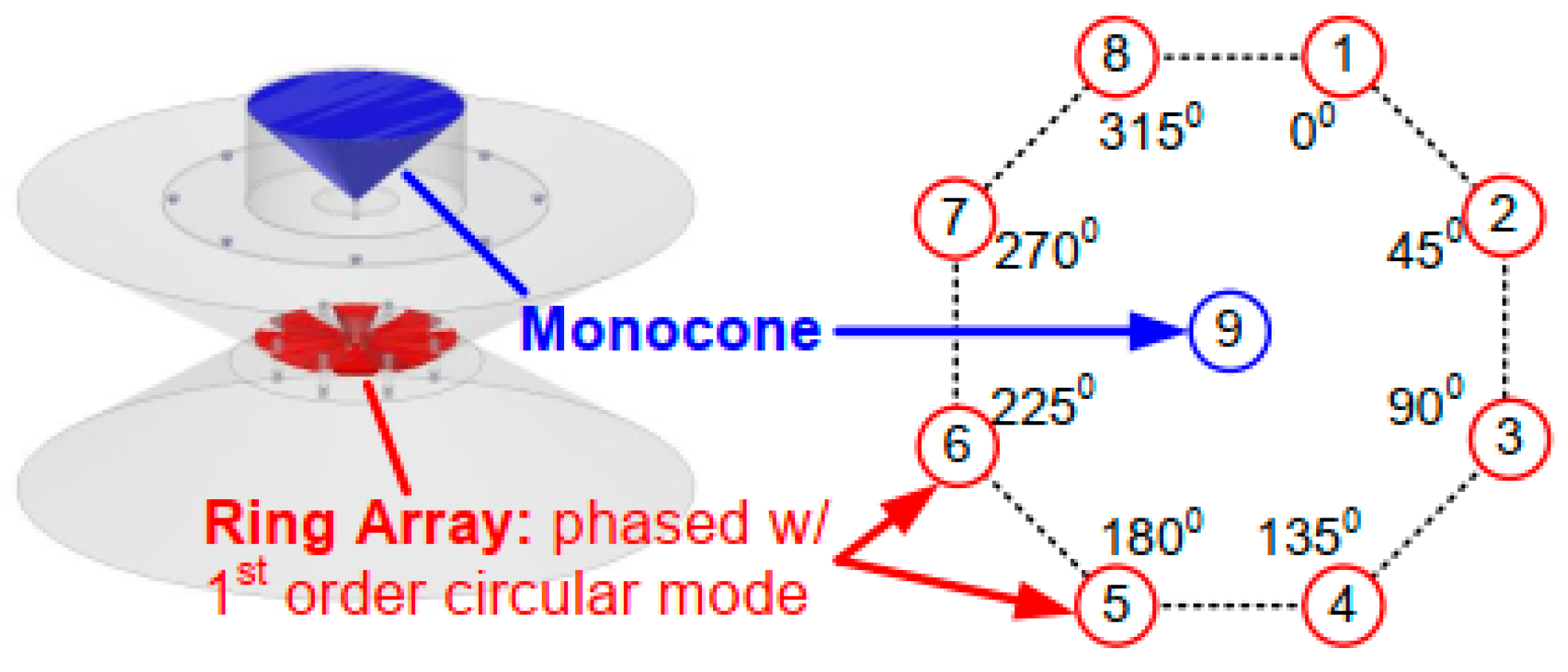

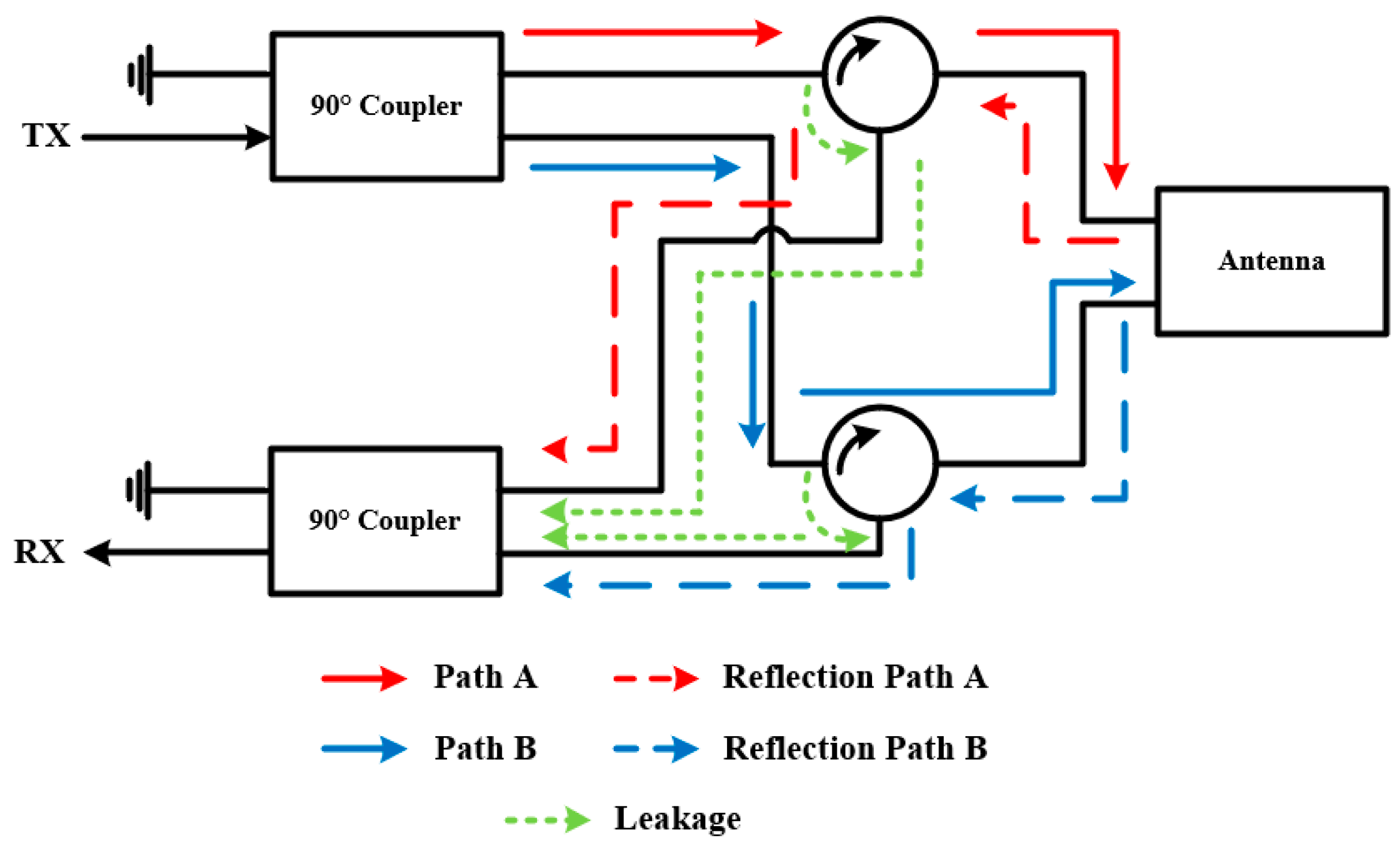
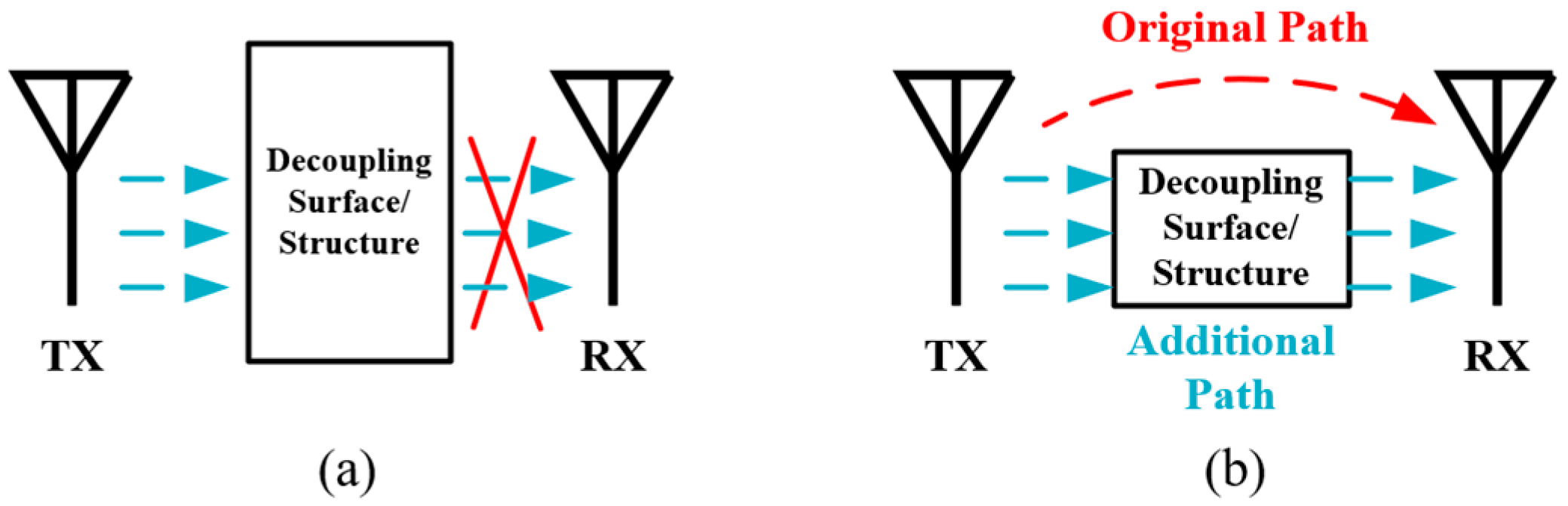
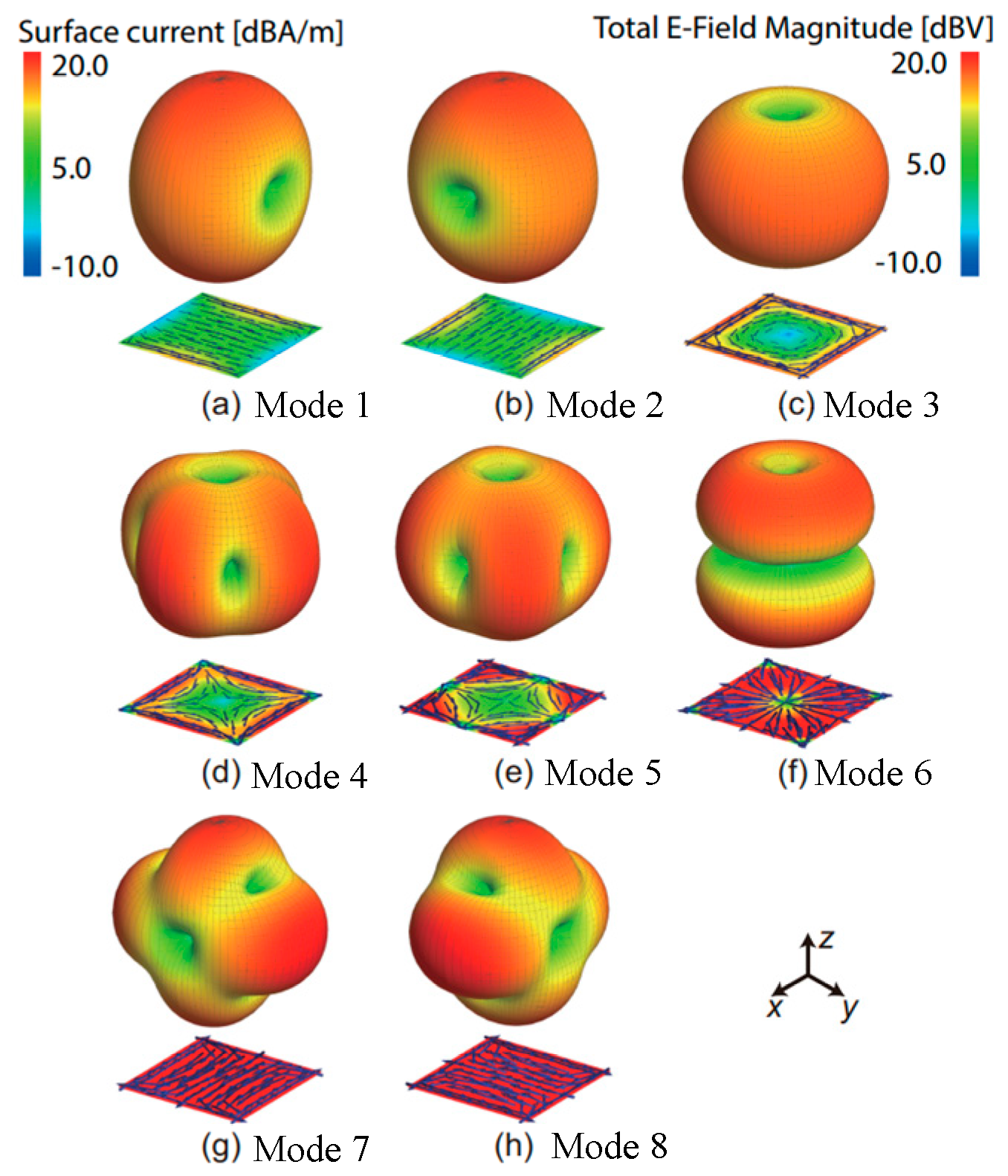
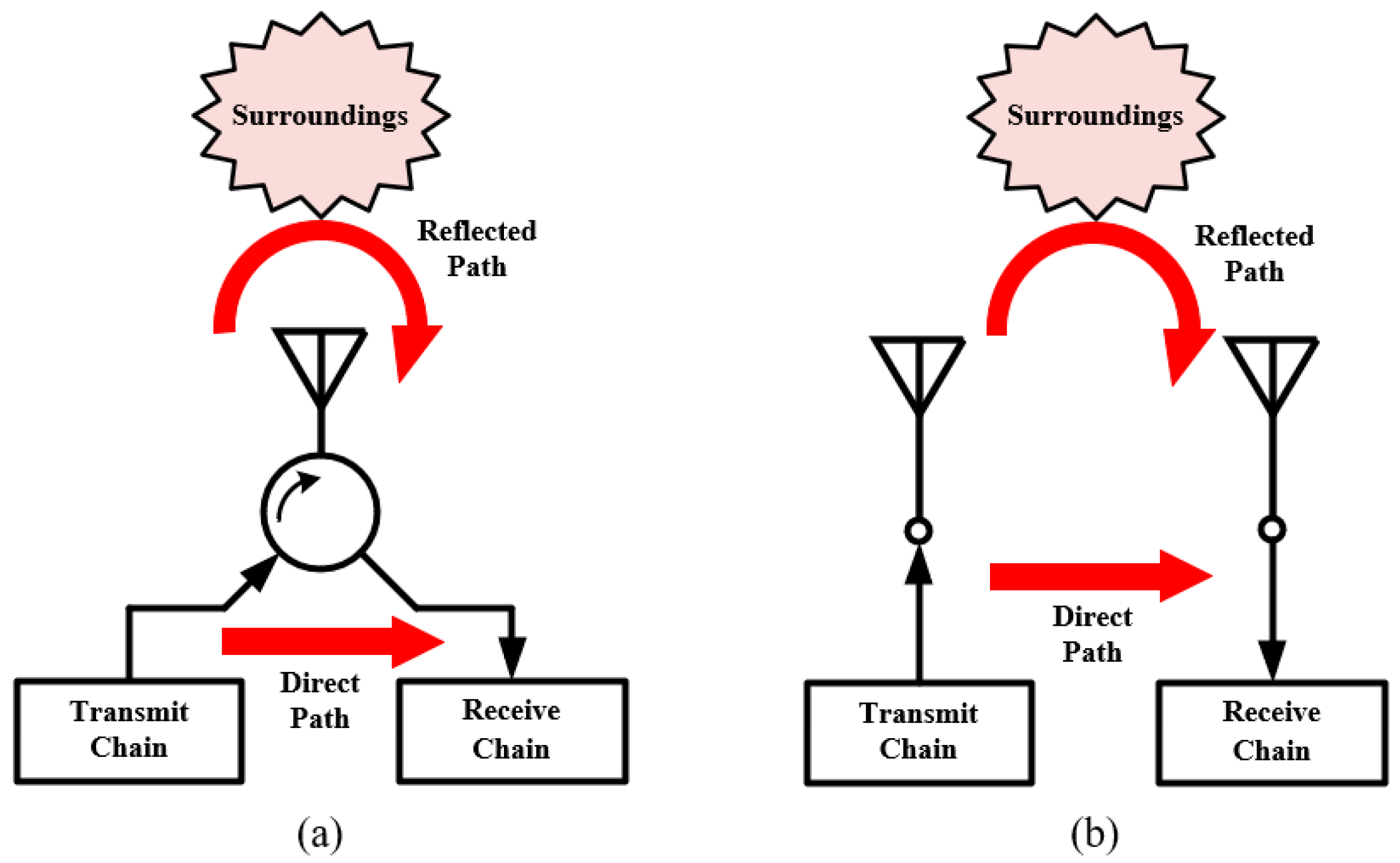
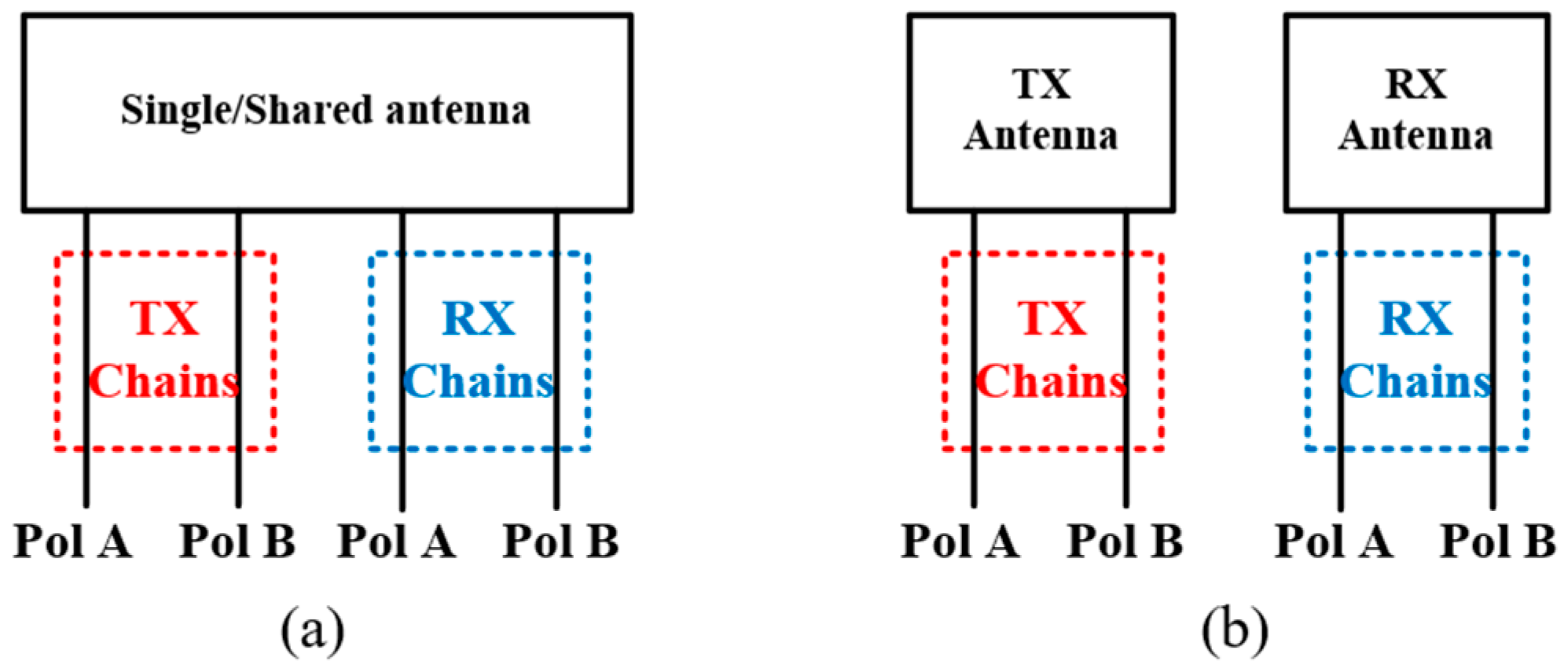
| Ref. | Antenna Type | FD Antenna Type | Feed Type | Polarization | Bandwidth (−10 dB) (FBW) | Isolation (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | Patch | Shared antenna | UF | Two LPs | 50 MHz @ 2.4 GHz (2%) | >55 |
| [36] | Horn | Shared antenna | UF | Two LPs | 1.7–2.7 GHz (45.5%) | >45 |
| [29] | 1 Cone + 4 Dipoles | Multiple antennas | UF | Two LPs | 0.8–2.7 GHz (−8.5 dB) (108.6%) | >37 |
| [40] | Dipole | Shared antenna | UF | Two LPs | 1.63–3.71 GHz (77.9%) | >28 |
| [34] | 2 Patches | Multiple antennas | UF | Two LPs | 400 MHz @ 4.6GHz (8.7%) | >50 |
| [14] | Patch | Shared antenna | Two CPs | 860–940 MHz (−18 dB) (8.9%) | >25 | |
| [37] | 2 Spirals | Multiple antennas | UF | Two CPs | 2.5–4.7 GHz (61.1%) | >21.5 |
| [44] | Patch | Shared antenna | UF; DF | Two LPs | 50 MHz @ 2.4 GHz (2%) | >70 |
| [54] | 2 Patches | Multiple antennas | UF; DF | Two LPs | 120 MHz @ 2.4 GHz (5%) | >80 |
| [49] | 2 Patches | Multiple antennas | UF; DF | Two LPs | 110 MHz @ 2.5 GHz (4.4%) | >64 |
| [46] | Patch | Shared antenna | DF | Two LPs | 50 MHz @ 2.4 GHz (2%) | >72 |
| [38] | Slot | Shared antenna | DF | Two LPs | 93.4–95.6 GHz (2.3%) | >55 |
| [48] | Patch | Shared antenna | DF | Two LPs | 2.2–2.5 GHz (12.8%) | >40 |
| Ref. | NFC Type | Number of Antennas | Antenna Spacing | Bandwidth (−10 dB) (FBW) | Gain (dBi) | Isolation (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | λ/2 distance difference | TX-2; RX-1 | D; D+λ/2 | 5 MHz @ 2.48 GHz (0.2%) | - | ~30 dB |
| [55] | 180° phase difference | TX-1; RX-2 | λ0/4 | 2.435–2.51 GHz (3%) | <3.4 (TX); <6.4 (RX) | >47 |
| [57] | Circular array | TX-1; RX-4 | 0.44 λ0 | 2.4–2.7 GHz (11.8%) | <3.2 | >38 |
| [13] | Circular array | TX-4; RX-1 | 0.38 λ0 | 2.33–2.85 GHz (20.1%) | <3.6 (TX); <0.6 (RX) | >40 |
| [58] | Circular array | TX-4; RX-1 | - | 3.1–3.6 GHz (14.9%) | - | >50 |
| [59] | Circular array | TX-8; RX-1 | - | 2.4–2.5 GHz (4.1%) | -2 | >50 |
| [60] | Circular array | TX-1; RX-8 | - | 0.96–8.2 GHz (158.1%) | - | >50 |
| [61] | Circular array | TX-1; RX-4 | 0.77 λ0 | 0.6–1.75 GHz (97.9%) | - | >50 |
| [15] | Circular array | TX-8; RX-1 | - | 60 MHz @ 2.45 GHz (2.4%) | - | >53 |
| [62] | TX and RX pairs | TX-2; RX-2 | ~ λ0 | 6–7.2 GHz (18.2%) | >8.7 | >40 |
| Ref. | IFN Configuration | Polarizations | Insertion Loss (dB) | Bandwidth (−10 dB) (FBW) | Gain (dBi) | Isolation (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [63] | 2 90° hybrids; 2 circulators | Same CP of TX and RX | 0.75 | 902–928 MHz (2.9%) | - | >40 |
| [65] | 2 180° hybrids | Same CP of TX and RX | - | 0.5–3.5 GHz (150%) | >3 | >37 |
| [66] | 2 90° hybrids; 2 180° hybrids; 2 circulators | Same CP of TX and RX | 0.35 (circulator) | 4–8 GHz (66.7%) | >1 | >30 |
| [67] | 2 90° hybrids; 4 180° hybrids | TX: RHCP; RX: LHCP | - | 4–8 GHz (66.7%) | >7 | 61 (average) |
| [64] | 2 90° hybrids; 4 180° hybrids; 4 circulators | Same CP of TX and RX | - | 0.5–2.5 GHz (133.3%) | - | >40 |
| [68] | 2 90° hybrids; 4 180° hybrids | TX: RHCP; RX: LHCP | - | 2.4–2.5 GHz (−22 dB) (4.1%) | ~7 | >47 |
| [69] | 1 90° hybrids; 1 power divider; 2 180° hybrids | - | - | 1.75–1.85 GHz (5.6%) | - | >30 |
| [71] | 2 90° hybrids; 5 180° hybrids; 4 circulators | TX: RHCP/LHCP; RX: RHCP/LHCP | - | 2–8 GHz (120%) | >3 | >27 |
| [70] | 2 90° hybrids; 4 180° hybrids | TX: RHCP/LHCP; RX: RHCP/LHCP | - | 0.8–3 GHz (115.8%) | TX: >10 RX: >5 | >40 |
| Ref. | Decoupling Structure | Spacing | Bandwidth (−10 dB) (FBW) | Gain (dBi) | Isolation (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [72] | DGS | - | 770 MHz @ 3.2 GHz (24.1%) | <4 | >36 |
| [73,74] | WTS | ~0.9λ | 222 MHz @ 2.6 GHz (−6 dB) (8.5%) | >9 | >60 |
| [75] | HIS | 4λ | 6–19 GHz (104%) | >7 | >60 |
| [76] | HIS | - | 2.04–2.06 GHz (1%) | - | >45 |
| [78] | FSS | 0.5λ | 28–34 GHz (19.4%) | - | >20 |
| [79] | EBG | 0.5λ | 125 MHz @ 5 GHz (2.5%) | - | >30 |
| [81] | Baffles | - | 3.3 GHz | - | >60 |
| [83] | ADS | ~0.6λ | 3.3–3.8 GHz (14.1%) | ~9 | ~25 |
| [84] | NL | ~0.06λ | 3.1–5 GHz (46.9%) | ~3 | >22 |
| SIC Techniques | Antenna Number | Antenna Size | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antenna separation | Multiple antennas | Large | (1) Easy to implement (2) Easy to integrate with other techniques | Restrictions on antenna radiation pattern (for directional separation only) |
| Polarization orthogonality | Single/shared antenna; Multiple antennas | Small | (1) Easy to implement (2) High performance of SIC (3) Good radiation performance | (1) Sensitive to the symmetry of the antenna structure and the imperfection of feed network |
| Near-field cancellation | Multiple antennas | Large | (1) Wide bandwidth (2) High performance of SIC | (1) High complexity of feed network (2) Sensitive to the imperfection of feed network 3) Additional insertion loss. |
| Isolation feed network | Single/shared antenna; Multiple antennas | Small antenna, large feed network | (1) Simple antenna configuration (2) It transmit and receive signals using the same polarization, so it can be combined with polarization orthogonality to generate more isolated signal paths | (1) Extra components in the feed network (2) Sensitive to the performance of circulators and hybrids |
| Decoupling surface/structure | Multiple antennas | Medium | (1) Various designs available for different application scenarios (2) Reconfigurability | (1) Complex antenna configuration (2) Narrow bandwidth (3) Probable negative effects on radiation pattern |
| Orthogonal antenna modes | Single/shared antenna; Multiple antennas | Small | Flexible choice of radiation patterns and polarizations of antennas | (1) High complexity of antenna design and configuration (2) Narrow bandwidth |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ding, C.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y. Antenna/Propagation Domain Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC) for In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051699
Chen Y, Ding C, Jia Y, Liu Y. Antenna/Propagation Domain Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC) for In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors. 2022; 22(5):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051699
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuenian, Can Ding, Yongtao Jia, and Ying Liu. 2022. "Antenna/Propagation Domain Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC) for In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Communication Systems" Sensors 22, no. 5: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051699
APA StyleChen, Y., Ding, C., Jia, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). Antenna/Propagation Domain Self-Interference Cancellation (SIC) for In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors, 22(5), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051699






