Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description and Proposed Solution
2.1. Emotional Speech Recognition Method
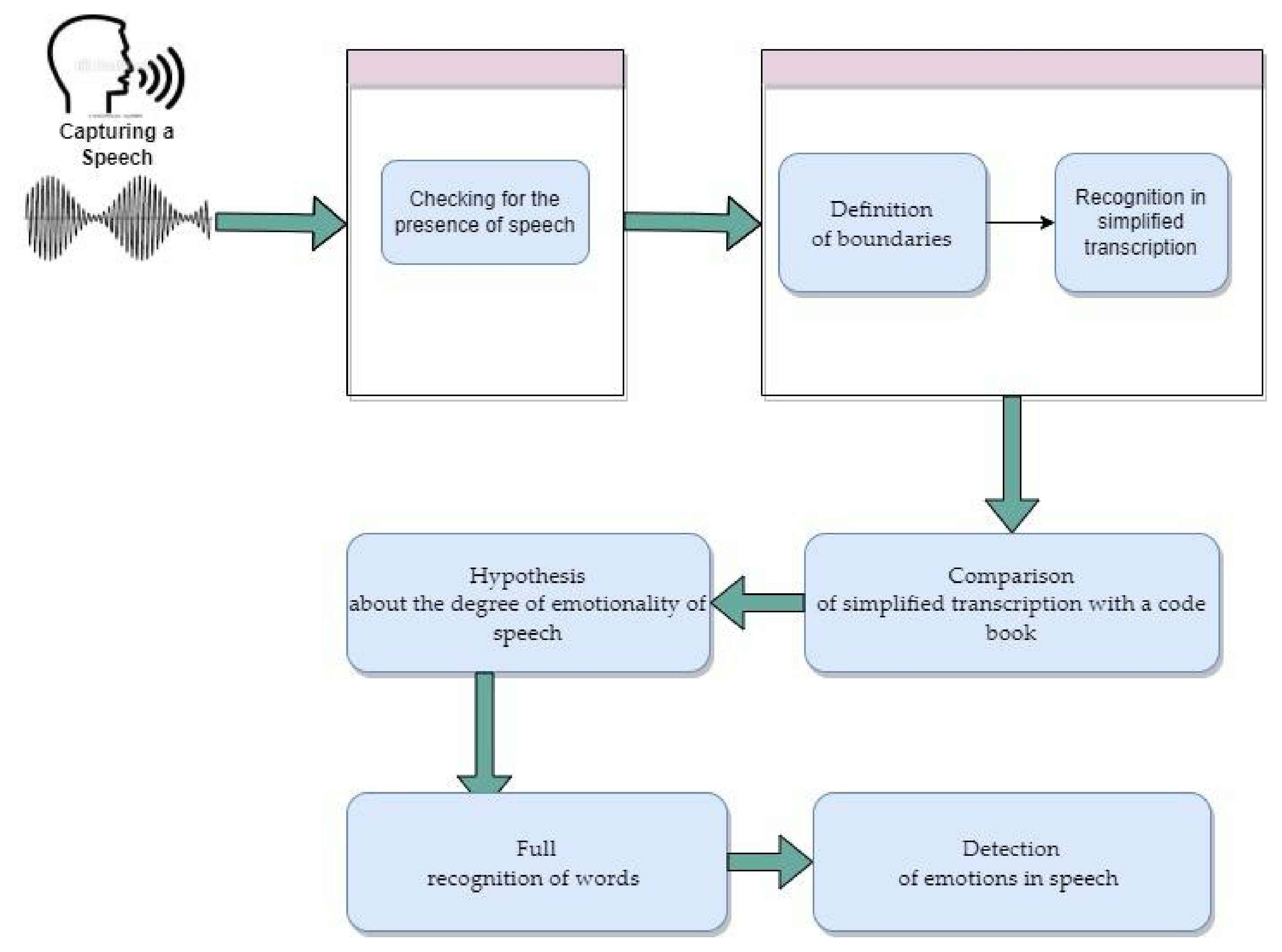
2.1.1. Stages of Speech Signal Recognition
Capturing an Audio Signal
Checking a Signal for Speech
2.1.2. Development of an Automatic Transcriptor
2.1.3. Formalization of Phonological Rules of Sound Combinations in the Kazakh Language
2.1.4. Structural Classification of Kazakh Words and Use of Generalized Transcriptions
Construction of Averaged Standards
2.1.5. Codebook and Its Construction Technique
2.1.6. Recognizer Using a Codebook
2.1.7. Step Recognition Algorithm
2.2. Defining Emotions
2.2.1. Construction of Emotion Vocabulary Generalized Transcriptions
2.2.2. Emotion Recognition Model
- 1.
- If a lexical unit contains a noun with the emotional color of happiness and the next word after it is a verb (of a positive form) with a neutral tone, then the emotional description of this phrase is happiness.
- 2.
- If a lexical unit contains an adjective describing the emotion anger and the next word after it is a verb (positive form) with a neutral tonality, then the emotional description of this phrase is anger.
- 3.
- If a lexical unit contains an interjection with an emotional connotation sadness, then the emotional description of this phrase is sadness.
3. Experiment
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franzoni, V.; Milani, A.; Nardi, D.; Vallverdú, J. Emotional machines: The next revolution. Web Intell. 2019, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Hazarika, D.; Mihalcea, R.; Gelbukh, A.; Cambria, E. DialogueRNN: An attentive RNN for emotion detection in conversations. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, G.; Franzoni, V.; Poggioni, V. A deep learning semantic approach to emotion recognition using the IBM watson bluemix alchemy language. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; Volume 10406, pp. 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappen, L.; Baird, A.; Cambria, E.; Schuller, B.W.; Cambria, E. Sentiment Analysis and Topic Recognition in Video Transcriptions. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Alsadoon, A.; Prasad, P.W.C.; Singh, A.K.; Elchouemi, A. An Emotion Recognition Model Based on Facial Recognition in Virtual Learning Environment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 125, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, O.; Raviv, D.; Raskar, R. Deep video gesture recognition using illumination invariants. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.06531. [Google Scholar]
- Kahou, S.E.; Pal, C.; Bouthillier, X.; Froumenty, P.; Gülçehre, Ç.; Memisevic, R.; Vincent, P.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Ferrari, R.C.; et al. Combining modality specific deep neural networks for emotion recognition in video. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Sydney, Australia, 9–13 December 2013; pp. 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, M.; Elagöz, B.; Alaybeyoglu, A.; Akan, A. Deep Learning Based Facial Emotion Recognition System (Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Yüz Duyguları Tanıma Sistemi). In Proceedings of the 2020 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Antalya, Turkey, 19–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahou, S.E.; Michalski, V.; Konda, K.; Memisevic, R.; Pal, C. Recurrent neural networks for emotion recognition in video. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, ICMI 2015, Seattle, DC, USA, 9–13 November 2015; pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G. Emotion recognition using deep learning approach from audio–visual emotional big data. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Koolagudi, S.G. Recognition of emotions from video using acoustic and facial features. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.; Bhanu, B.; Thakoor, N. Facial emotion recognition in continuous video. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2012, Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 1880–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Tamil Selvi, P.; Vyshnavi, P.; Jagadish, R.; Srikumar, S.; Veni, S. Emotion recognition from videos using facial expressions. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2017, 517, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Siddiqui, M.F.H.; Javaid, A.Y. Recognition of emotion intensities using machine learning algorithms: A comparative study. Sensors 2019, 19, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzoni, V.; Biondi, G.; Milani, A. Emotional sounds of crowds: Spectrogram-based analysis using deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 36063–36075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salekin, A.; Chen, Z.; Ahmed, M.Y.; Lach, J.; Metz, D.; De La Haye, K.; Bell, B.; Stankovic, J.A. Distant Emotion Recognition. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2017, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayek, H.M.; Lech, M.; Cavedon, L. Towards real-time speech emotion recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems, ICSPCS 2015, Cairns, Australia, 14–16 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsamadi, S.; Barsoum, E.; Zhang, C. Automatic speech emotion recognition using recurrent neural networks with local attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, V.; Biondi, G.; Milani, A. A web-based system for emotion vector extraction. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; Volume 10406, pp. 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, V.; Li, Y.; Mengoni, P. A path-based model for emotion abstraction on facebook using sentiment analysis and taxonomy knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence, WI 2017, Leipzig, Germany, 23–26 August 2017; pp. 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, L.; Martinez-Barco, P. Emotion detection from text: A survey. In Proceedings of the Processing in the 5th Information Systems Research Working Days, JISIC 2014, Hague, The Netherlands, 24–26 September 2014; pp. 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulsalam, W.H.; Alhamdani, R.S.; Abdullah, M.N. Facial emotion recognition from videos using deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2014, 9, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gervasi, O.; Franzoni, V.; Riganelli, M.; Tasso, S. Automating facial emotion recognition. Web Intell. 2019, 17, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavian, D.; Bejani, M.; Sheikhan, M. Audio-visual emotion recognition using FCBF feature selection method and particle swarm optimization for fuzzy ARTMAP neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 2331–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinith, M.S.; Aswathi, E.; Deepa, T.M.; Shameema, C.P.; Rajan, S. Emotion recognition from audio signals using Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems, RAICS 2015, Trivandrum, Kerala, India, 10–12 December 2015; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S. A CNN-assisted enhanced audio signal processing for speech emotion recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannadaguli, P.; Bhat, V. Comparison of hidden markov model and artificial neural network based machine learning techniques using DDMFCC vectors for emotion recognition in Kannada. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, WIECON-ECE 2019, Bangalore, India, 15–16 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tursunov, A.; Choeh, J.Y.; Kwon, S. Age and gender recognition using a convolutional neural network with a specially designed multi-attention module through speech spectrograms. Sensors 2021, 21, 5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, I. Emotion recognition based on third-order circular suprasegmental hidden markov model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Jordan International Joint Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, JEEIT 2019, Amman, Jordan, 9–11 April 2019; pp. 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abo Absa, A.H.; Deriche, M. A two-stage hierarchical multilingual emotion recognition system using hidden markov models and neural networks. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE-GCC Conference and Exhibition, GCCCE 2017, Manama, Bahrain, 8–11 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Ren, F. Weighted high-order hidden Markov models for compound emotions recognition in text. Inf. Sci. 2016, 329, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, M.; Minker, W.; Semenkin, E.S. Speech-based emotion recognition and speaker identification: Static vs. dynamic mode of speech representation. J. Sib. Fed. Univ.-Math. Phys. 2016, 9, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Damasio, A. We feel, therefore we learn: The relevance of affective and social neuroscience to education. Mind Brain Educ. 2007, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, D.; Toala, R.; Novais, P. Emotion Analysis in Distance Learning. In Educating Engineers for Future Industrial Revolutions; Auer, M.E., Rüütmann, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1328, pp. 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Andriessen, J.; Järvelä, S. Affective Learning Together. Social and Emotional Dimension of Collaborative Learning; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; 312p. [Google Scholar]
- van der Haar, D.T. Student Emotion Recognition in Computer Science Education: A Blessing or Curse? In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2019; Volume 11590, pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Krithika, L.B.; Lakshmi, G.G. Student Emotion Recognition System (SERS) for e-learning Improvement Based on Learner Concentration Metric. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 85, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzoni, V.; Biondi, G.; Perri, D.; Gervasi, O. Enhancing Mouth-Based Emotion Recognition Using Transfer Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Jiménez, C.; Griol, D.; Callejas, Z.; Kleinlein, R.; Montero, J.M.; Fernández-Martínez, F. Multimodal emotion recognition on RAVDESS dataset using transfer learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergesh, B.; Bekmanova, G.; Sharipbay, A.; Yergesh, M. Ontology-based sentiment analysis of kazakh sentences. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; Volume 10406, pp. 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergesh, B.; Bekmanova, G.; Sharipbay, A. Sentiment analysis of Kazakh text and their polarity. Web Intell. 2019, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhetkenbay, L.; Bekmanova, G.; Yergesh, B.; Sharipbay, A. Method of Sentiment Preservation in the Kazakh-Turkish Machine Translation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2020; Volume 12250, pp. 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergesh, B.; Bekmanova, G.; Sharipbay, A. Sentiment analysis on the hotel reviews in the Kazakh language. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, UBMK 2017, Antalya, Turkey, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmanova, G.; Yelibayeva, G.; Aubakirova, S.; Dyussupova, N.; Sharipbay, A.; Nyazova, R. Methods for Analyzing Polarity of the Kazakh Texts Related to the Terrorist Threats. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2019; Volume 11619, pp. 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelepov, V.J.; Nicenko, A.V. Recognition of the continuous-speech russian phrases using their voiceless fragments. Eurasian J. Math. Comput. Appl. 2016, 4, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelepov, V.Y.; Nitsenko, A.V. On the recognition of Russian words using generalized transcription. Probl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 1, 50–56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nitsenko, A.V.; Shelepov, V.Y. Algorithms for phonemic recognition of words for a given dictionary. Artif. Intell. [Iskusstv. Intell.] 2004, 4, 633–639. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shelepov, V.Y. The concept of phonemic recognition of separately pronounced Russian words. Recognition of syn-tactically related phrases. Materials of international scientific-technical conference. Artif. Intell. 2007, 162–170. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shelepov, V.Y.; Nitsenko, A.V. To the problem of phonemic recognition. Artif. Intell. [Iskusstv. Intell.] 2005, 4, 662–668. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sharipbayev, A.A.; Bekmanova, G.T.; Shelepov, V.U. Formalization of Phonologic Rules of the Kazakh Language for System Automatic Speech Recognition. Available online: http://dspace.enu.kz/handle/data/1013 (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Bekmanova, G.T.; Nitsenko, A.V.; Sharipbaev, A.A.; Shelepov, V.Y. Algorithms for recognition of the Kazakh word as a whole. In Structural Classification of Kazakh Language Words; Bulletin of the L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2010; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shelepov, V.J.; Nitsenko, A.V. The refined identification of beginning-end of speech; the recognition of the voiceless sounds at the beginning-end of speech. On the recognition of the extra-large vocabularies. Eurasian J. Math. Comput. Appl. 2017, 5, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakh Grammar. Phonetics, Word Formation, Morphology, Syntax; Astana-Poligraphy: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2002; p. 784. (In Kazakh) [Google Scholar]
- Bekmanova, G.; Yergesh, B.; Sharipbay, A. Sentiment Analysis Model Based on the Word Structural Representation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2021; Volume 12960, pp. 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharipbaev, A.A.; Bekmanova, G.T.; Buribayeva, A.K.; Yergesh, B.Z.; Mukanova, A.S.; Kaliyev, A.K. Semantic neural network model of morphological rules of the agglutinative languages. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems, and 13th International Symposium on Advanced Intelligence Systems, SCIS/ISIS 2012, Kobe, Japan, 20–24 November 2012; pp. 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergesh, B.; Mukanova, A.; Sharipbay, A.; Bekmanova, G.; Razakhova, B. Semantic hyper-graph based representation of nouns in the Kazakh language. Comput. Sist. 2014, 18, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharipbay, A.; Yergesh, B.; Razakhova, B.; Yelibayeva, G.; Mukanova, A. Syntax parsing model of Kazakh simple sentences. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Science, E-Learning and Information Systems, DATA 2019, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2–5 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakhova, B.S.; Sharipbaev, A.А. Formalization of Syntactic Rules of the Kazakh Language; Bulletin of the L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2012; pp. 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yelibayeva, G.; Sharipbay, A.; Mukanova, A.; Razakhova, B. Applied ontology for the automatic classification of simple sentences of the kazakh language. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, UBMK 2020, Diyarbakir, Turkey, 9–10 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhakhmet, K.; Zhumaliyeva, R.; Shoinbek, A.; Sultanova, N. Speech emotion recognition for Kazakh and Russian languages. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2020, 14, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Current Alphabet | Intermediate Alphabet | Transcription | Current Alphabet | Intermediate Alphabet | Transcription |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| А | А | (ɑ) | Б | Б | (b) |
| Ә | Ә | (æ) | В | В | (v) |
| Е | Е | (е) | Г | Г | (g) |
| О | О | (ɔ) | Ғ | Ғ | (ɣ) |
| Ө | Ө | (ɵ) | Д | Д | (d) |
| Ұ | Ұ | (ʊ, u) | Ж | Ж | (Ʒ) |
| Ү | Ү | (ү) | З | З | (z) |
| Ы | Ы | (ɯ) | Й | Й | (y) |
| І | І | (ɪ, i) | К | К | (k) |
| Э | Е | (jɪ) | Қ | Қ | (q) |
| Я | ЙА | (yɑ) | Л | Л | (l) |
| Ю | ЙУ | (yw) | М | М | (m) |
| Ё | ЙО | (yɔ) | Н | Н | (n) |
| И | ІЙ | (iy) | Ң | Ң | (ŋ) |
| И | ЫЙ | (ɯj) | П | П | (p) |
| Ч | Ш | (tʃ) | Р | Р | (r) |
| Щ | Ш | (ʃ) | С | С | (s) |
| Ц | С | (tc) | Т | Т | (t) |
| Һ | Х | (h) | У | У | (w) |
| Ъ | - | Ш | Ш | (ʃ) | |
| Ь | - | Ф | Ф | (f) | |
| Х | Х | (h) |
| Classes | Symbols | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| W | аұыoеәүіөу | vowels and consonant «У» |
| C | бвгғджзйлмнңр | voiced consonants |
| F | сш | voiceless hush consonants |
| P | кқптфх | voiceless consonants |
| Kazakh Word | Transcription | Generalized Transcription |
|---|---|---|
| бұлдану | bʊldɑnw | CWCCWCW |
| бұлдыра | bʊldɯrɑ | CWCCWCW |
| бүлдіру | bүldɪrw | CWCCWCW |
| Word | Transcription | Translation | POS | Emotion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| діріл | dɪrɪl | trembling | N | fear |
| қoрқақтық | qɔrqɑqtɯq | cowardice | N | fear |
| ақылсыз | ɑqɯlswz | stupid | N | anger |
| қызғаныш | qɯzɣɑnɯʃ | jealousy | N | anger |
| құрмет | qʊrmеt | honor | N | happiness |
| нәзіктік | næzɪktɪk | tenderness | N | happiness |
| шапшаң | ʃɑpʃɑŋ | quick | Adv | happiness |
| шарасыздан | ʃɑrɑsɯzdɑn | involuntarily | Adv | sadness |
| сөзқұмар | sɵzqʊmɑr | garrulous, chatty | Adj | disgust |
| Word | Transcription | Translation | POS | Emotion | Generalized Transcriptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| қoрқақтық | qɔrqɑqtɯq | cowardice | N | fear | PWCPWPPWP |
| ақылсыз | ɑqɯlswz | stupid | N | anger | WPWCFWC |
| көз жасы | kɵz Ʒɑsɯ | tear | N | sadness | PWC CWFW |
| құрмет | qʊrmеt | honor | N | happiness | PWCCWP |
| шапшаң | ʃɑpʃɑŋ | quick | Adv | happiness | FWPFWC |
| шарасыздан | ʃɑrɑsɯzdɑn | involuntarily | Adv | sadness | FWCWFWCCWC |
| сөзқұмар | sɵzqʊmɑr | garrulous, chatty | Adj | disgust | FWCPWCWC |
| тату | tɑtw | amicably | Adj | happiness | PWPW |
| тиянақсыз | tiyyɑnɑqsɯz | fragile | Adj | anger | PWCCWCWPFWC |
| пішту! | pɪʃtw! | my gosh | Intj | disgust | PWFPW! |
| туу | tww | Holy | Intj | sadness | PWW |
| уай | wɑy | Wow | Intj | happiness | WWC |
| бұзықтық істеу | bʊzɯqtɯq ɪstеw | roughhouse | V | anger | CWCWPPWP WFPWW |
| бәрекелді | bærеkеldɪ | Bravo | Intj | happiness | CWCWPWCCW |
| әй | æy | hey | Intj | anger | WC |
| әттеген-ай | ættеgеn-ɑy | What a pity | Intj | sadness | WPPWCWC-WC |
| қап | qɑp | it’s a shame | Intj | sadness | PWP |
| масқарай | mɑsqɑrɑy | What a mess | Intj | sadness | CWFPWCWC |
| мәссаған | mæssɑɣɑn | Gee | Intj | fear | CWFFWCWC |
| Designation | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Many words in the language—Variables | |
| —Lexical units (non-empty word or phrase) | |
| Set of sentences in the language | |
| Set of nouns | |
| Set of adjectives | |
| Set of pronouns | |
| Set of positive verb forms | |
| Set of negative verb forms | |
| Set of interjections | |
| Set of adverbs or enhancing | |
| emo | Emotion Establishment—Predicate |
| @ | Negation words “емес/жoқ”(no)—Constants |
| Transformation to negative form—Operation | |
| Concatenation—Operation |
| Emotion Classes | Polarity | Example |
|---|---|---|
| happiness | positive | Алақай! Мен сәтті аяқтадым (Hooray! I finished successfully) |
| fear | negative | Жауаптарды ұмытып қалдым (I forgot the answers) |
| disgust | negative | Туу, oйдағыдай баға алмадым (Tuu, didn’t get the expected grade) |
| sadness | negative | Қап! кейбір жауапты білмей қалдым. (Qap, I didn’t know the answer.) |
| anger | negative | Кедергі жасама! Уақыт тығыз (do not bother, time is running out) |
| neutral | neutral | Бүгін барлығы емтихан тапсырады (everyone is taking exams today) |
| Method | Dataset Language | Number of Classes | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Speech Recognition Method | Kazakh | 6 | 79.7% |
| DNN model [59] | Kazakh, Russian | 3 | 82.07% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekmanova, G.; Yergesh, B.; Sharipbay, A.; Mukanova, A. Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription. Sensors 2022, 22, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051937
Bekmanova G, Yergesh B, Sharipbay A, Mukanova A. Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription. Sensors. 2022; 22(5):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051937
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekmanova, Gulmira, Banu Yergesh, Altynbek Sharipbay, and Assel Mukanova. 2022. "Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription" Sensors 22, no. 5: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051937
APA StyleBekmanova, G., Yergesh, B., Sharipbay, A., & Mukanova, A. (2022). Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription. Sensors, 22(5), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051937






