Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hydrogen Using Pd-Coated SnO2 Nanorod Arrays for Breath-Analyzer Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization
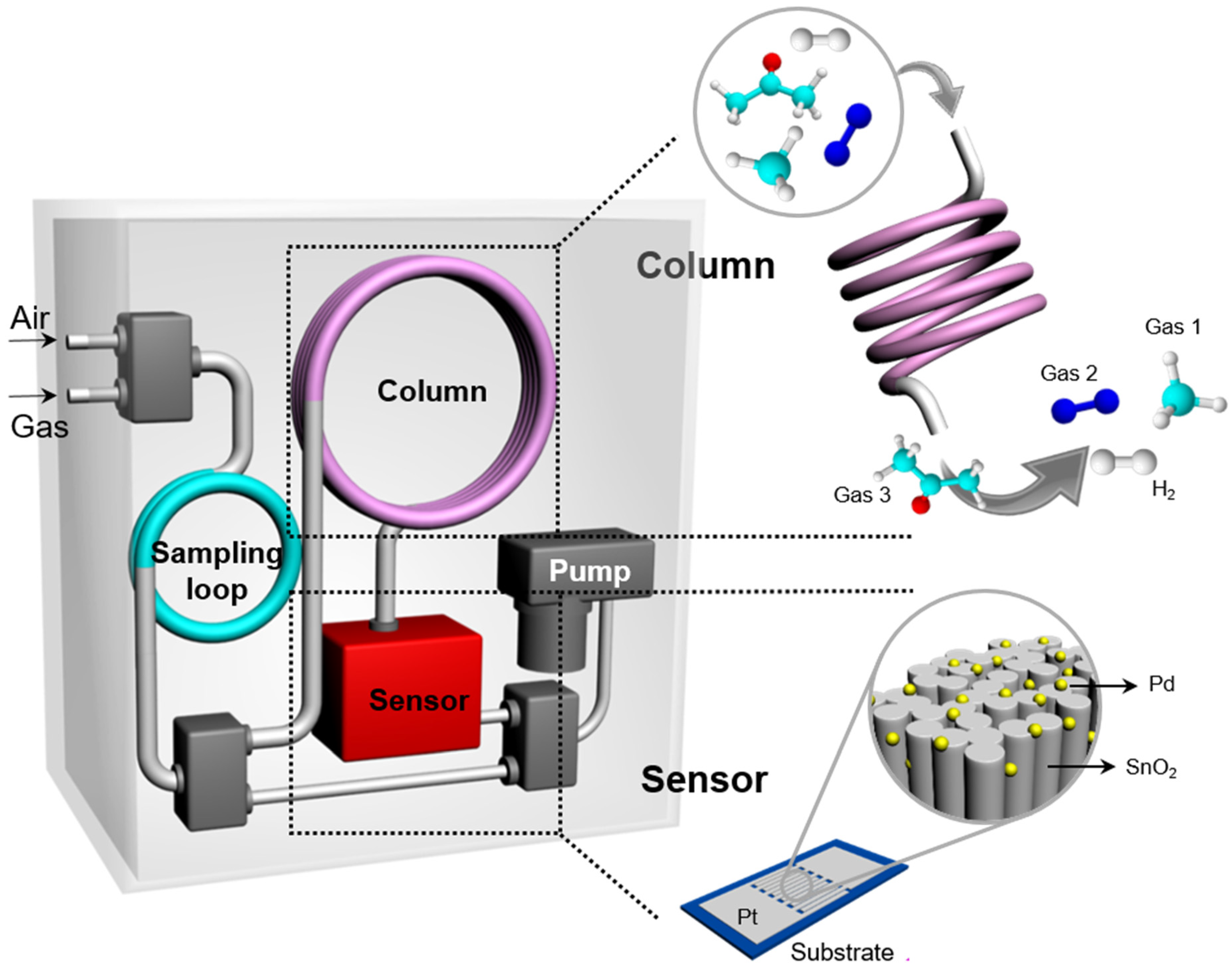
2.2. Gas Sensing Test
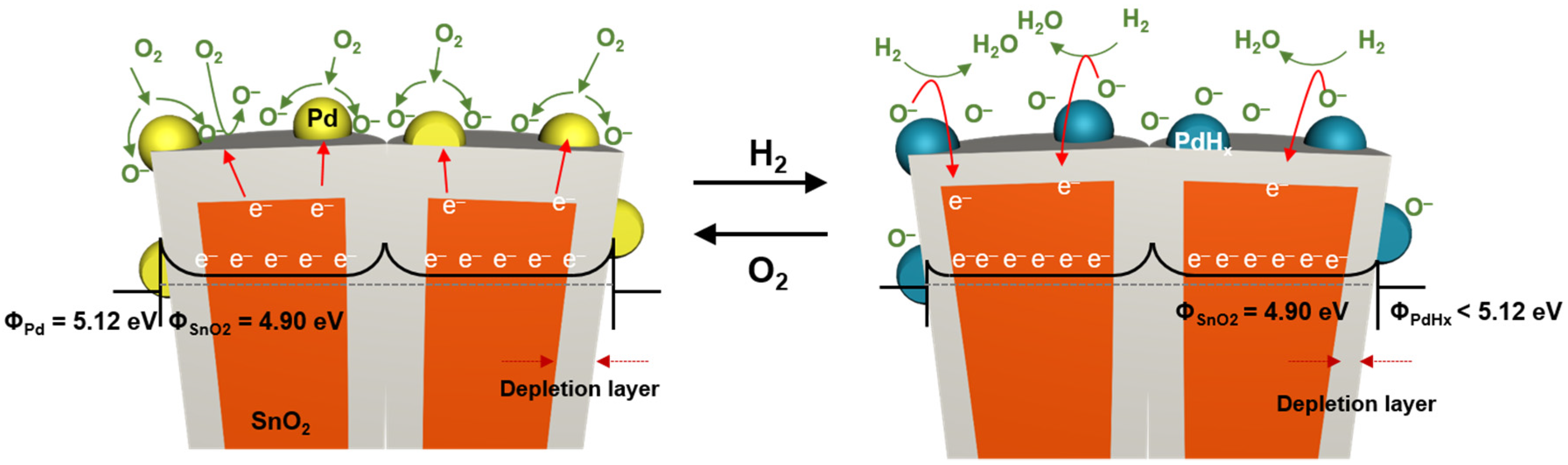
2.3. Gas Sensing Mechanism
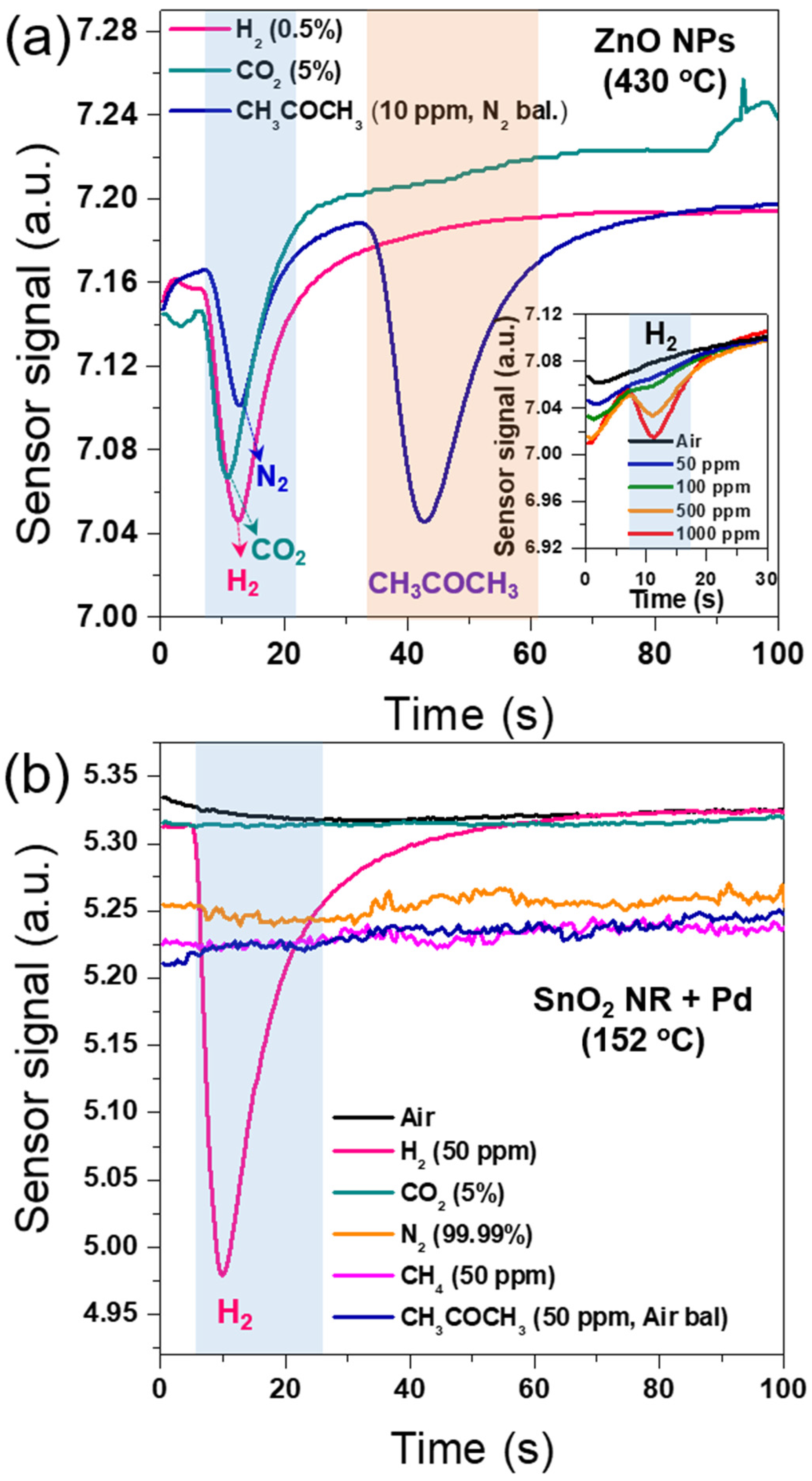
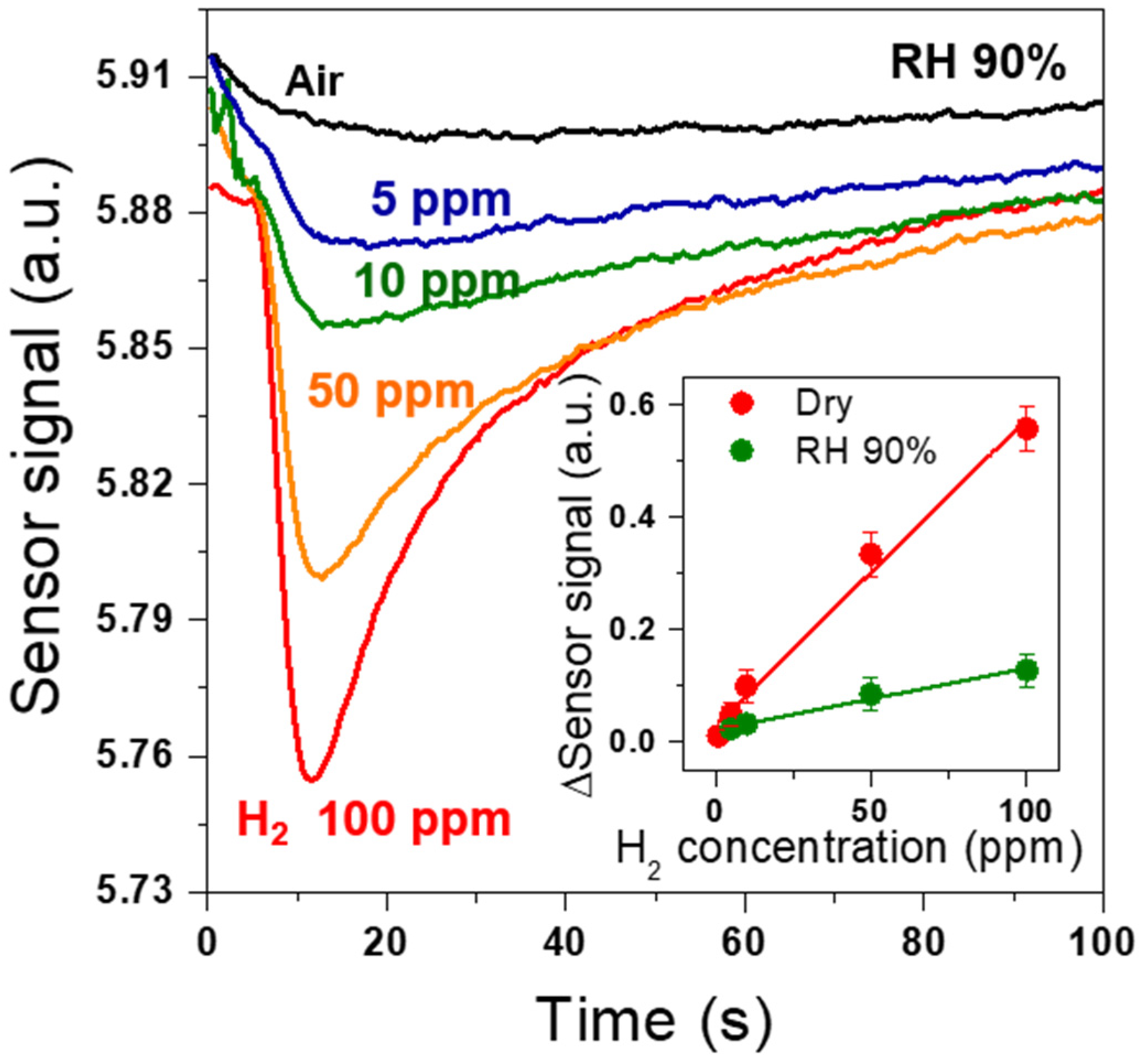
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dukowicz, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Levine, G.M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A comprehensive review. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 3, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10011–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Wagnet, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Interactions between gut microbiota and host metabolism predisposing to obesity and diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhoffs, A.P.M.; Samsom, M.; Rest, M.E.; Vogel, J.; Knol, J.; Amor, K.B.; Akkermans, L.M.A. Lower Bifidobacteria counts in both duodenal mucosa-associated and fecal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, S.M.; Bharucha, A.E.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Comperison of breath testing with fructose and high fructose corn syrups in health and IBS. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.J.; Shen, B. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, G.R.; Strocchi, A.; Gasbarrini, G. Fasting breath hydrogen in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellas, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Applicability of short hydrogen breath test for screening of lactose malabsorption. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Mathur, R.; Chang, C. Gas and the microbiome. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Malik, A. Hydrogen breath test in gastrointestinal diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C. How to interpret hydrogen breath tests. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pimentel, M.; Mayer, A.G.; Park, S.; Chow, E.J.; Hasan, A.; Kong, Y. Methane Production During Lactulose Breath Test Is Associated with Gastrointestinal Disease Presentation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai-Satta, P.; Oppia, F.; Lai, M.; Cabras, F. Hydrogen Breath Tests: Are They Really Useful in the Nutritional Management of Digestive Disease? Nutrients 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.P. Final Report, Contract No. 12-14-100-2628 (74); Western Regional Research Laboratory, U.S.D.A.: Albany, CA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Stefano, M.D.; Missanelli, A.; Miceli, E.; Strocchi, A.; Corazza, G.R. Hydrogen breath test in the diagnosis of lactose malabsorption: Accuracy of new versus conventional criteria. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2004, 144, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basseri, R.J.; Basseri, B.; Pimentel, M.; Chong, K.; Youdim, A.; Low, K.; Hwang, L.; Soffer, E.; Chang, C.; Mathur, R. Intestinal Methane Production in Obese Individuals Is Associated with a Higher Body Mass Index. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, R.; Amichai, M.; Chua, K.S.; Mirocha, J.; Barlow, G.M.; Pimentel, M. Methane and Hydrogen Positivity on Breath Test Is Associated With Greater Body Mass Index and Body Fat. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E698–E702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lacy Costello, B.P.J.; Ledochowski, M.; Ratcliffe, N.M. The importance of methane breath testing: A review. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, A.K.Y.; Persijn, S.T.; von Busum, G.; Harren, F.J.M. Automatically tunable continuous-wave optical parametric oscillator for high-resolution spectroscopy and sensitive trace-gas detection. Appl. Phys. B 2006, 85, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberge, M.T.; Finley, J.W.; Lukaski, H.C.; Borgerding, A.L. Evaluation of the pulsed discharge helium ionization detector for the analysis of hydrogen and methane in breath. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1027, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogozi, T.; Popp, J.; Frosch, T. Fiber-enhanced Raman multi-gas spectroscopy: What is the potential of its application to breath analysis. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanf, S.; Bogozi, T.; Keiner, R.; Frosch, T.; Popp, J. Fast and Highly Sensitive Fiber-Enahced Raman Spectroscopic Monitoring of Molecular H2 and CH4 for Point-of Care Diagnosis of Malabsorption Disorders in Exhaled Human Breath. Anal. Chem. 2015, 77, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kien, N.; Hung, C.M.; Ngoc, T.M.; Le, D.T.T.; Hoa, N.D.; Duy, N.V.; Hieu, N.V. Low-temperature prototype hydrogen sensors using Pd-decorated SnO2 nanowires for exhaled breath applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Hydrogen Gas Sensors Based on Semiconductor Oxide Nanostructures. Sensors 2012, 12, 5517–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hübert, T.; Boon-Brett, L.; Black, G.; Banach, U. Hydrogen sensors—A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Improving the hydrogen sensing properties of SnO2 nanowire-based conductometric sensors by Pd-decoration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Xue, Q.; Han, Z.; Lu, H.; Xia, F.; Yan, Z.; Deng, L. Room temperature hydrogen sensor with ultrahigh-responsive characteristics based on Pd/SnO2/SiO2/Si heterojunctions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.-S.; Jang, B.; Suh, J.M.; Noh, M.S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.D.; Song, Y.G.; Kang, C.-Y.; Jang, H.W.; Lee, W. Nanogap-controlled Pd coating for hydrogen sensitive switches and hydrogen sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Han, S.D.; Stetter, J.R. Review of electrochemical hydrogen sensors. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1402–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Vandermaar, A.J.; Srivastava, K.D. Review of condition assessment of power transformers in service. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2002, 18, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perman, J.A.; Modler, S.; Barr, R.G.; Rosenthal, P. Fasting breath hydrogen concentration: Normal values and clinical application. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Däbritz, J.; Mühlbauer, M.; Domagk, D.; Voos, N.; Henneböhl, G.; Siemer, M.L.; Foell, D. Significance of hydrogen breath tests in children with suspected carbohydrate malabsorption. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.; Yoo, R.; Park, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive and selective isoprene sensing performance of ZnO quantum dots for a breath analyzer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNair, H.M.; Miller, J.M. Basic Gas Chromatography, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.; Cho, W.; Yoo, R.; Lee, H.; Choe, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, W. Highly Selective Real-time Detection of Breath Acetone by Using ZnO Quantum Dots with a Miniaturized Gas Chromatographic Column. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C. Oxygen chemisorption on tin oxide: Correlation between electrical conductivity and EPR measurements. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1980, 17, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Schweizer-Berberrich, M.; Gopel, W. Fundamental and practical aspects in the design of nanoscaled SnO2 gas sensors: A status report. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 365, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.R. Selectivity in semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 1987, 12, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaraman, M.S.; Svensson, C.; Hammarsten, H.; Lundstrom, I. Hydrogen Sensitivity of Palladium-Thin-Oxide-Silicon Schottky Barriers. Electron. Lett. 1976, 12, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, W. Low-Dimensional Palladium Nanostructures for Fast and Reliable Hydrogen Gas Detection. Sensors 2011, 11, 825–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cloarec, D.; Bornet, F.; Gouilloud, S.; Barry, J.L.; Salim, B.; Galmiche, J.P. Breath hydrogen response to lactulose in healthy subjects: Relationship to methane producing status. Gut 1990, 31, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rumessen, J.J.; Hamberg, O.; Gudmand-Høyer, E. Influence of orocaecal transit time on hydrogen excretion after carbohydrate malabsorption. Gut 1989, 30, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, W. Medical applications of breath hydrogen measurements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3931–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Hwang, J.; Choe, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hydrogen Using Pd-Coated SnO2 Nanorod Arrays for Breath-Analyzer Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052056
Jung H, Hwang J, Choe Y-S, Lee H-S, Lee W. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hydrogen Using Pd-Coated SnO2 Nanorod Arrays for Breath-Analyzer Applications. Sensors. 2022; 22(5):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052056
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Hwaebong, Junho Hwang, Yong-Sahm Choe, Hyun-Sook Lee, and Wooyoung Lee. 2022. "Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hydrogen Using Pd-Coated SnO2 Nanorod Arrays for Breath-Analyzer Applications" Sensors 22, no. 5: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052056
APA StyleJung, H., Hwang, J., Choe, Y.-S., Lee, H.-S., & Lee, W. (2022). Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Hydrogen Using Pd-Coated SnO2 Nanorod Arrays for Breath-Analyzer Applications. Sensors, 22(5), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052056






