Acoustic Emission Source Location Using Finite Element Generated Delta-T Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method for Simulating H-N Sources and Its Validation
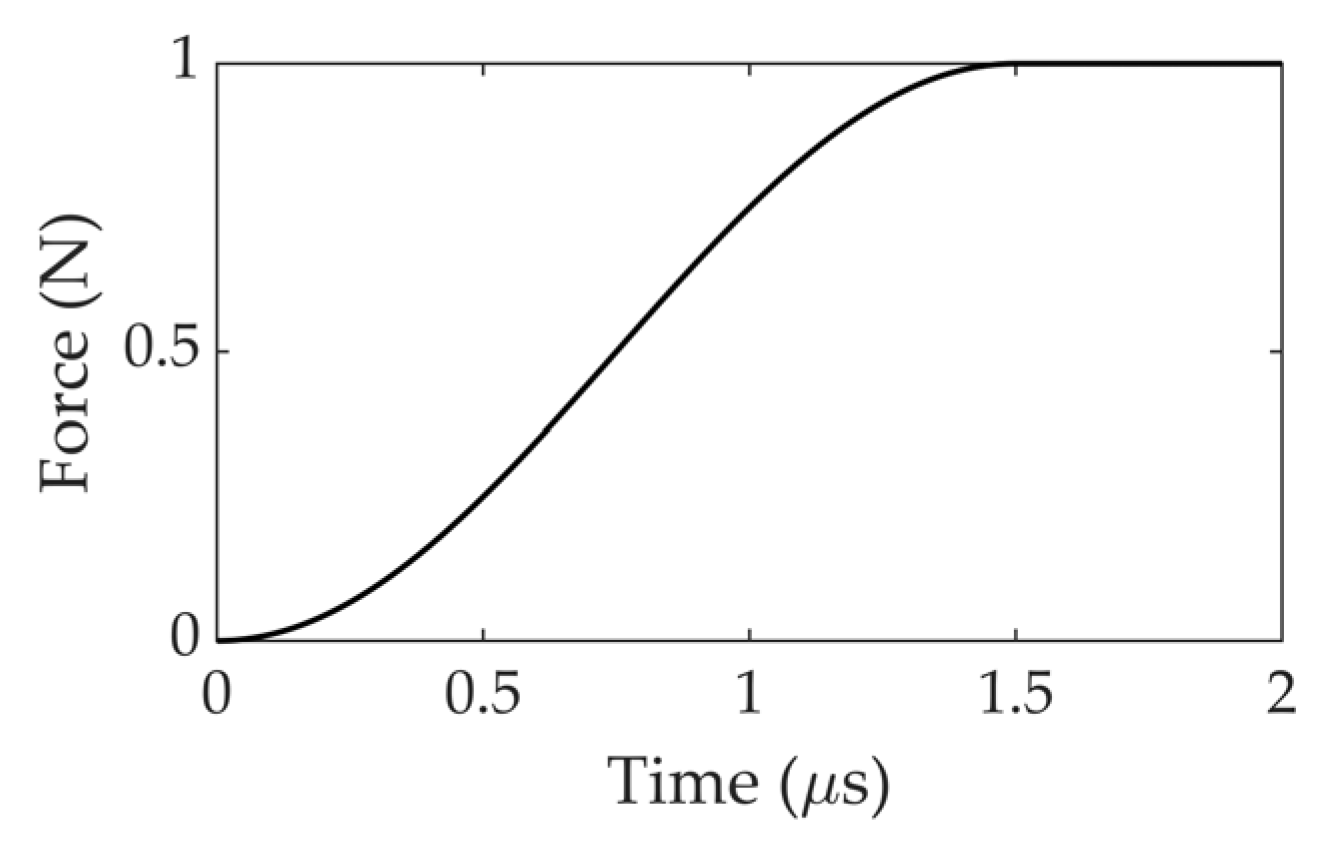
2.1. Numerical Method for Simulating H-N Sources
2.2. FE Model for Simulating an H-N Source on a Simple Plate
2.3. Experimental Verification of FE Model for Simulating an H-N Source on a Simple Plate
2.3.1. Modal Analysis
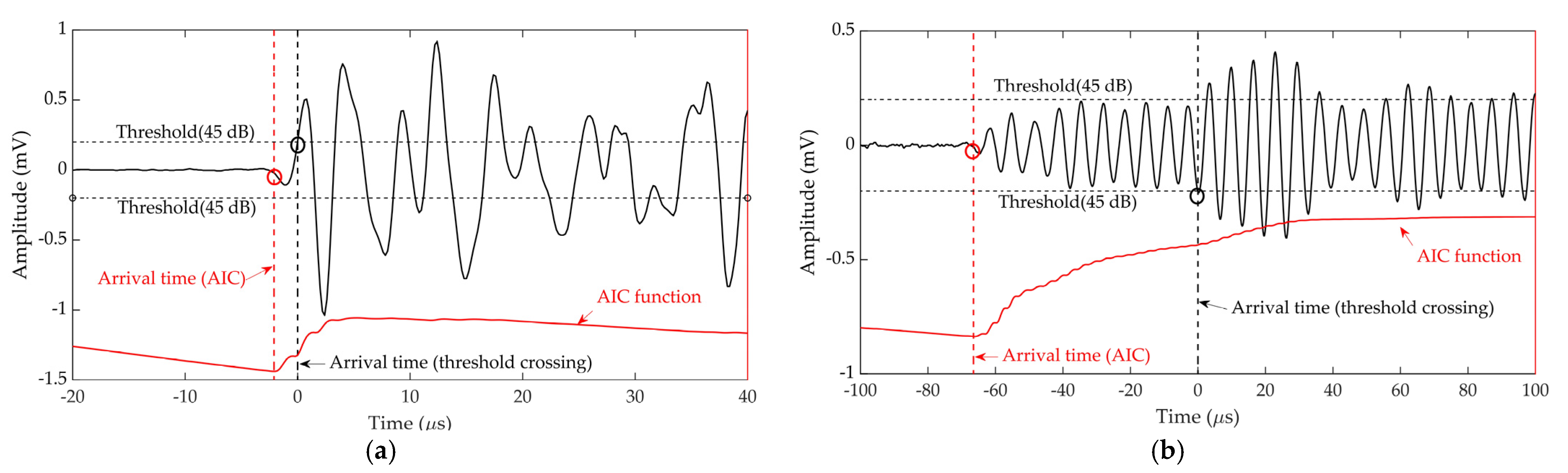
2.3.2. Arrival Time Estimation
3. Experimental and Numerical Delta-T Mapping Training on Complex Plate
3.1. Experimental Delta-T Mapping Training on Complex Plate
3.2. FE Generated Delta-T Mapping Training on Complex Plate
3.3. Experimental Test Data on Complex Plate
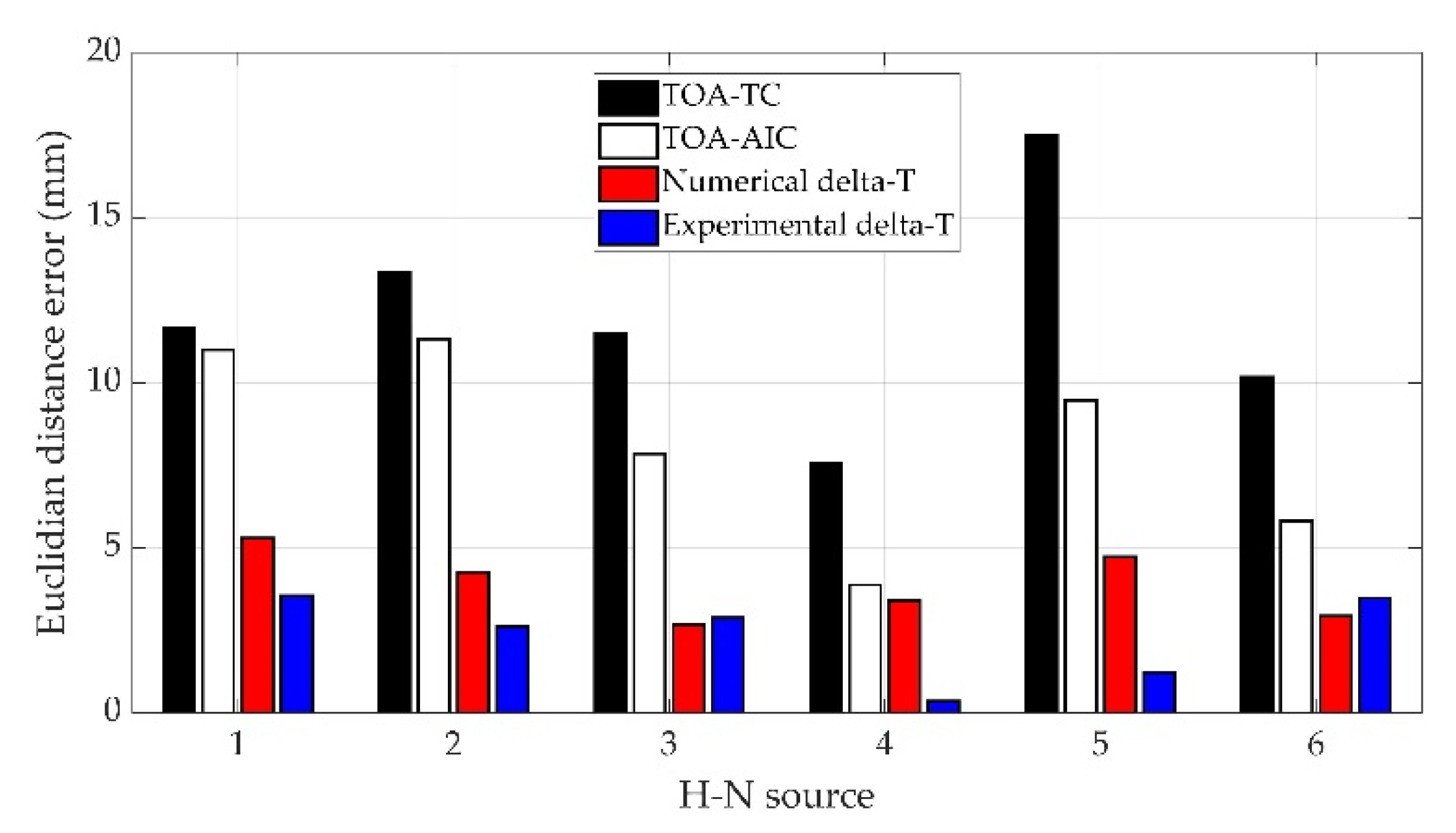
3.4. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biondini, F.; Frangopol, D.M. Life-cycle performance of deteriorating structural systems under uncertainty. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, F4016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinachandran, S.; Rajan, G. Fibre Bragg Grating Based Acoustic Emission Measurement System for Structural Health Monitoring Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, B.; Jayakumar, T.; Rao, B.P.C. Non-destructive testing and evaluation for structural integrity. Sadhana 1995, 20, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.K.; Hill, E.V.K.; Moore, P.O. Nondestructive Testing Handbook, Acoustic Emission Testing; The American Society For Nondestructive Testing Inc.: Columbus, OH, USA, 2005; Volume 5, p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, M.G.; Pullin, R.; Holford, K.M.; Evans, S.L. Delta T source location for acoustic emission. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.R.; Eaton, M.; Featherston, C.; Pullin, R.; Holford, K. Improved acoustic emission source location during fatigue and impact events in metallic and composite structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 16, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E650; Standard Guide for Mounting Piezoelectric Acoustic Emission Sensors. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017; Volume 97, pp. pp. 1–4.
- Eaton, M.J.; Pullin, R.; Holford, K.M. Acoustic emission source location in composite materials using Delta T Mapping. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, S.; Featherston, C.A.; Pearson, M.; Pullin, R. Advanced Acoustic Emission Source Location in Aircraft Structural Testing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1024, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, Q.; He, C.; Wu, B. Time difference mapping method for locating the acoustic emission source in a composite plate. Chin. J. Acoust. 2019, 38, 490–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; He, C.; Wu, B. Acoustic emission source localization with generalized regression neural network based on time difference mapping method. Exp. Mech. 2020, 60, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, R. Methodology Platform for Prediction of Damage Events for Self-Sensing Aerospace Panels Subjected to Real Loading Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gary, J.; Hamstad, M.A. On the far-field structure of waves generated by a pencil lead break on a thin plate. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1994, 12, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Hamstad, M.A.; Gary, J.; O’Gallagher, A. Far-field acoustic emission waves by three-dimensional finite element modeling of pencil-lead breaks on a thick plate. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1996, 14, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sause, M. Investigation of pencil-lead breaks as acoustic emission sources. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2011, 29, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hamstad, M.A. Acoustic emission signals generated by monopole (pencil lead break) versus dipole sources: Finite element modeling and experiments. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2007, 25, 92–106. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gall, T.; Monnier, T.; Fusco, C.; Godin, N.; Hebaz, S.-E. Towards quantitative acoustic emission by finite element modelling: Contribution of modal analysis and identification of pertinent descriptors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Xin, H.; Groves, R.M.; Veljkovic, M. Acoustic emission source location using Lamb wave propagation simulation and artificial neural network for I-shaped steel girder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A. Acoustic Emission Source Based on Pencil Lead Breaking; The Danish Welding Institute Publication: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1980; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, N.N.; Breckenridge, F.R. Characterization and calibration of acoustic emission sensors. Mater. Eval. 1981, 39, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E976-15; Standard Guide for Determining the Reproducibility of Acoustic Emission Sensor Response. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–7.
- Grosse, C.U.; Ohtsu, M. Acoustic Emission Testing; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3540699724. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E1106-12; Standard Test Method for Primary Calibration of Acoustic Emission Sensors. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–13.
- Prosser, W.H.; Hamstad, M.A.; Gary, J.; O’Gallagher, A. Finite Element and Plate Theory Modeling of Acoustic Emission Waveforms. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 1999, 18, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaings, M.; Bacon, C.; Hosten, B.; Predoi, M.V. Finite element predictions for the dynamic response of thermo-viscoelastic material structures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, D.W.; Neumann, J.J.; Nieuwenhuis, J.H.; Oppenheim, I.J.; Tyson, N.L. Use of Lamb waves to monitor plates: Experiments and simulations. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2005: Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–10 March 2005; Volume 5765, pp. 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Nienwenhui, J.H.; Neumann, J.J.; Greve, D.W.; Oppenheim, I.J. Generation and detection of guided waves using PZT wafer transducers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engineering ToolBox. Solids and Metals—Speed of Sound. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/sound-speed-solids-d_713.html (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Moser, F.; Jacobs, L.J.; Qu, J. Modeling elastic wave propagation in waveguides with the finite element method. NDT E Int. 1999, 32, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, M.R. Plate wave acoustic emission. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullin, R.; Holford, K.M.; Baxter, M.G. Modal analysis of acoustic emission signals from artificial and fatigue crack sources in aerospace grade steel. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 293–294, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, S.; Holford, K.M.; Pullin, R. Continuous wavelet transform analysis and modal location analysis acoustic emission source location for nuclear piping crack growth monitoring. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1584, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, J.H.; Grosse, C.U.; Reinhardt, H.W. Strategies for reliable automatic onset time picking of acoustic emissions and of ultrasound signals in concrete. Ultrasonics 2005, 43, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Mizutani, Y.; Nishino, H.; Takemoto, M.; Ono, K. Lamb wave source location of impact on anisotropic plates. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2000, 18, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Hamstad, M.A.; Gary, J. A wavelet transform applied to acoustic emission signals: Part 2: Source location. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2002, 20, 62–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Jang, Y.-S. Wavelet analysis of plate wave propagation in composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2000, 49, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullin, R.; Baxter, M.; Eaton, M.; Holford, K.M.; Evans, S.L. Novel acoustic emission source location. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2007, 25, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jumaili, S.K.; Pearson, M.R.; Holford, K.M.; Eaton, M.J.; Pullin, R. Acoustic emission source location in complex structures using full automatic delta T mapping technique. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 72, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadra, J.; Vanniamparambil, P.A.; Servansky, D.; Bartoli, I.; Kontsos, A. Acoustic emission source modeling using a data-driven approach. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 341, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamam, Z.; Godin, N.; Fusco, C.; Doitrand, A.; Monnier, T. Acoustic Emission Signal Due to Fiber Break and Fiber Matrix Debonding in Model Composite: A Computational Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangouri, E.; Aggelis, D.G. The influence of sensor size on acoustic emission waveforms—A numerical study. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

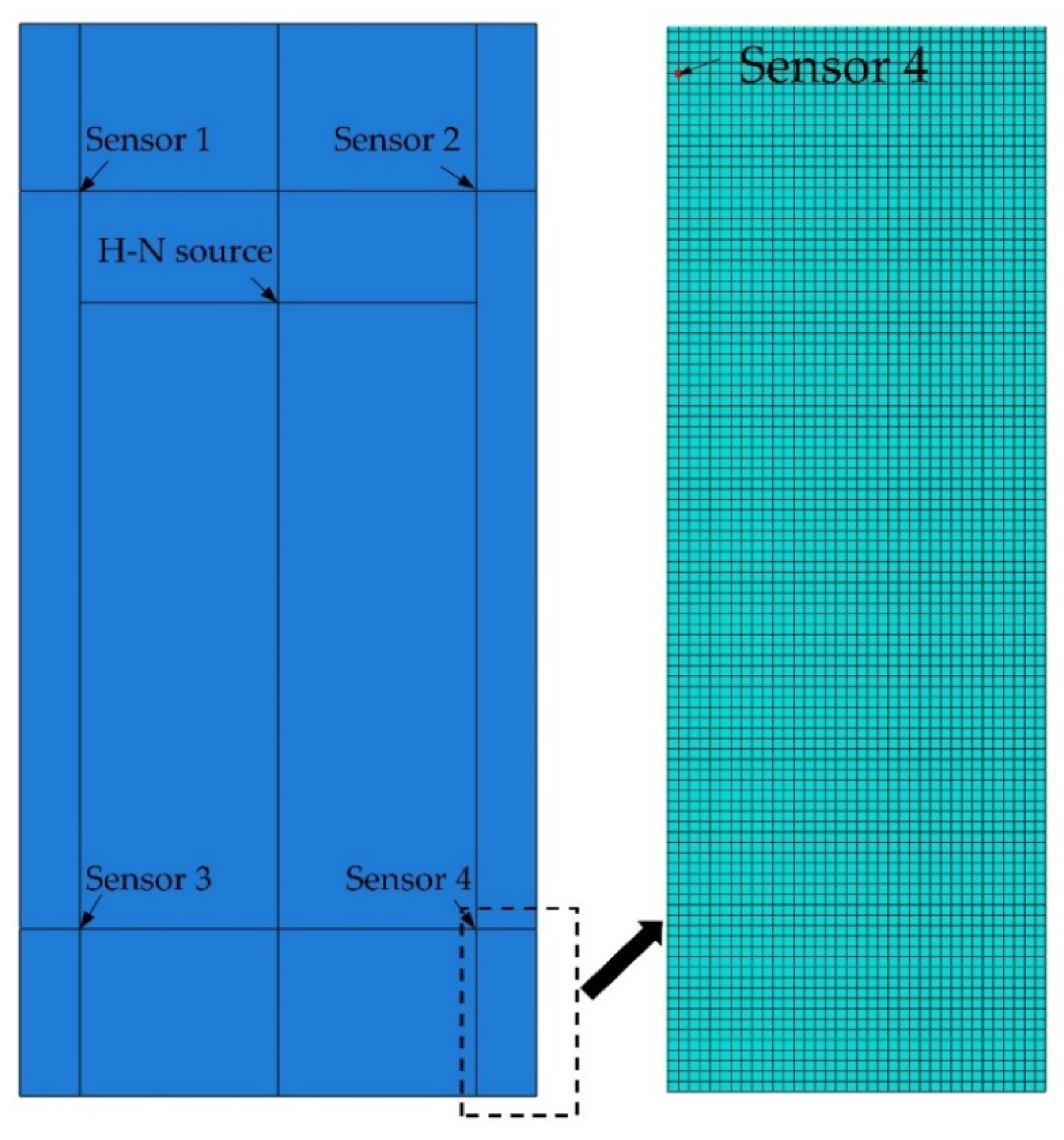







| X Coordinate | Y Coordinate | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor 1 | 35 | 465 |
| Sensor 2 | 265 | 465 |
| Sensor 3 | 35 | 35 |
| Sensor 4 | 265 | 35 |
| H-N source | 150 | 400 |
| Threshold (dB) | Sample Length (ms) | Sample Rate (MHz) | Pre-Trigger (ms) | Rearm Time (ms) | Duration Discrimination Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 1.6 | 5 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Threshold Crossing | AIC | WT Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | 48.4 | 46.8 | 47.2 |
| FE modelling | - | 46.74 | 46.57 |
| Difference | - | 0.06 | 0.63 |
| H-N Source 1 | H-N Source 2 | H-N Source 3 | H-N Source 4 | H-N Source 5 | H-N Source 6 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Error | X | Y | Error | X | Y | Error | X | Y | Error | X | Y | Error | X | Y | Error | |
| Actual | 70 | 70 | - | 70 | 210 | - | 130 | 90 | - | 170 | 390 | - | 230 | 230 | - | 250 | 430 | - |
| TOA-TC | 74.42 | 59.19 | 11.68 | 83.04 | 207.21 | 13.34 | 134.54 | 79.42 | 11.51 | 168.99 | 397.51 | 7.58 | 213.60 | 223.92 | 17.49 | 244.54 | 438.59 | 10.18 |
| TOA-AIC | 77.13 | 61.63 | 11.00 | 81.29 | 210.88 | 11.32 | 133.89 | 83.19 | 7.84 | 167.79 | 393.18 | 3.87 | 222.44 | 224.29 | 9.47 | 246.58 | 434.70 | 5.81 |
| Numerical delta-T | 74.82 | 67.80 | 5.30 | 73.99 | 211.46 | 4.25 | 132.26 | 91.41 | 2.66 | 169.33 | 386.67 | 3.40 | 225.27 | 229.86 | 4.73 | 251.17 | 432.7 | 2.94 |
| Experimental delta-T | 71.54 | 66.80 | 3.55 | 67.39 | 210.13 | 2.61 | 132.89 | 90.03 | 2.89 | 169.93 | 390.35 | 0.36 | 231.13 | 230.45 | 1.22 | 248.96 | 433.33 | 3.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Grigg, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, D.; Marks, R. Acoustic Emission Source Location Using Finite Element Generated Delta-T Mapping. Sensors 2022, 22, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072493
Yang H, Wang B, Grigg S, Zhu L, Liu D, Marks R. Acoustic Emission Source Location Using Finite Element Generated Delta-T Mapping. Sensors. 2022; 22(7):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072493
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Han, Bin Wang, Stephen Grigg, Ling Zhu, Dandan Liu, and Ryan Marks. 2022. "Acoustic Emission Source Location Using Finite Element Generated Delta-T Mapping" Sensors 22, no. 7: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072493
APA StyleYang, H., Wang, B., Grigg, S., Zhu, L., Liu, D., & Marks, R. (2022). Acoustic Emission Source Location Using Finite Element Generated Delta-T Mapping. Sensors, 22(7), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072493







