The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment and Program Development
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Outcome Measure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
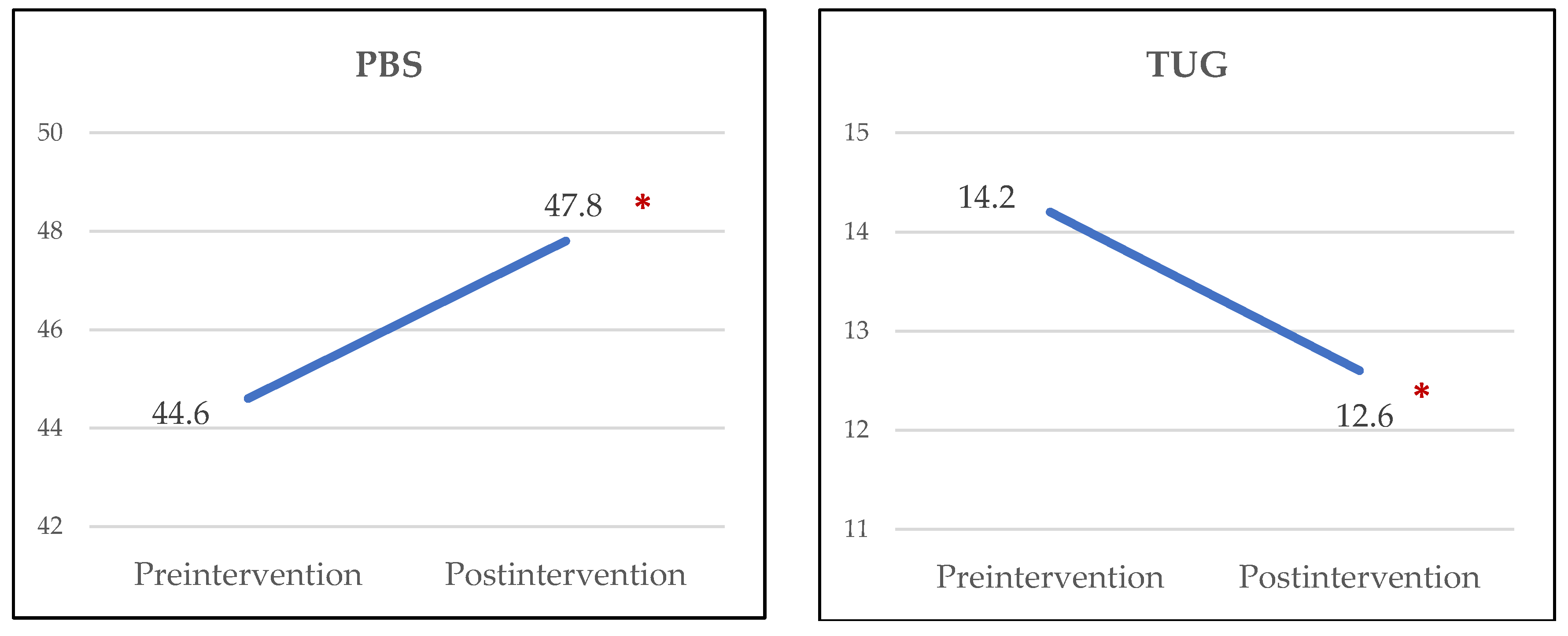
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guindos-Sanchez, L.; Lucena-Anton, D.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Salazar, A.; Carmona-Barrientos, I. The effectiveness of hippotherapy to recover gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Children 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Namara, M.M.; Paton, M.C.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the evidence traffic lights 2019: Systematic review of interventions for preventing and treating children with cerebral palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominguez-Romero, J.G.; Molina-Aroca, A.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Luque-Moreno, C.; Lucena-Anton, D. Effectiveness of mechanical horse-riding simulators on postural balance in neurological rehabilitation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Temcharoensuk, P.; Lekskulchai, R.; Akamanon, C.; Ritruechai, P.; Sutcharitpongsa, S. Effect of horseback riding versus a dynamic and static horse riding simulator on sitting ability of children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svraka, E. Cerebral Palsy-Challenges for the Future; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Ren, Z. The rehabilitative effects of virtual reality games on balance performance among children with cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, J. The effect of virtual reality games on the gross motor skills of children with cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, J.J.; Chruscikowski, E.; Fry, N.R.D.; Lewis, A.P.; Gough, M.; Shortland, A.P. The relationship between lower limb muscle volume and body mass in ambulant individuals with bilateral cerebral palsy. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.H.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, M.G.; Jin, J.J.; Hong, J.; Choi, Y.T.; Kim, M.H.; Jee, Y.S. The effect of horse simulator riding on visual analogue scale, body composition and trunk strength in the patients with chronic low back pain. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeong, J. The efficacy of indoor horseback-riding exercise on health-related fitness, serum lipids, and defecation satisfaction of female collegiate students. Korea Sport Res. 2005, 16, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, D.J.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Cadman, D.T.; Gowland, C.; Hardy, S.; Jarvis, S. The Gross Motor Function Measure: A means to evaluate the effects of physical therapy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1989, 31, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M.; Long, T.; Kennedy, E.; Bavishi, S. The efficacy of GMFM-88 and GMFM-66 to detect changes in gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy (CP): A literature review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.J.; Avery, L.M.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Raina, P.S.; Walter, S.D.; Palisano, R.J. Improved scaling of the Gross Motor Function Measure for children with cerebral palsy: Evidence of reliability and validity. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.M.; Park, E.; Ahn, Y.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kang, H.G.; Cheong, H.I.; Ha, I.S. Measurement of fluid status using bioimpedance methods in Korean pediatric patients on hemodialysis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayanama, K.; Putadechakun, S.; Srisuwarn, P.; Vallibhakara, S.A.; Chattranukulchai Shantavasinkul, P.; Sritara, C.; Kantachuvesiri, S.; Komindr, S. Evaluation of body composition in hemodialysis Thai patients: Comparison between two models of bioelectrical impedance analyzer and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. J. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 2018, 4537623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyle, U.G.; Earthman, C.P.; Pichard, C.; Coss-Bu, J.A. Body Composition during growth in children: Limitations and perspectives of bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franjoine, M.R.; Gunther, J.S.; Taylor, M.J. Pediatric Balance Scale: A modified version of the Berg Balance Scale for the school-age child with mild to moderate motor impairment. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2003, 15, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, E.N.; Carroll, S.G.; Reddihough, D.S.; Phillips, B.A.; Galea, M.P. Investigation of the Timed ‘Up & Go’ test in children. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2005, 47, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.L.; Walter, S.D.; Hanna, S.E.; Palisano, R.J.; Russell, D.J.; Raina, P.; Wood, E.; Bartlett, D.J.; Galuppi, B.E. Prognosis for gross motor function in cerebral palsy: Creation of motor development curves. JAMA 2002, 288, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, S.E.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Bartlett, D.J.; Palisano, R.J.; Walter, S.D.; Avery, L.; Russell, D.J. Stability and decline in gross motor function among children and youth with cerebral palsy aged 2 to 21 years. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2009, 51, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, D.L. Activity, activity, activity: Rethinking our physical therapy approach to cerebral palsy. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Fogarty, M.J.; Sieck, G.C. Why individuals with cerebral palsy are at higher risk for respiratory complications from COVID-19. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 13, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cankurtaran, D.; Tezel, N.; Yildiz, S.Y.; Celik, G.; Unlu Akyuz, E. Evaluation of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on children with cerebral palsy, caregivers’ quality of life, and caregivers’ fear of COVID-19 with telemedicine. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 190, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bıyık, K.S.; Özal, C.; Tunçdemir, M.; Üneş, S.; Delioğlu, K.; Günel, M.K. The functional health status of children with cerebral palsy during the COVID-19 pandemic stay-at-home period: A parental perspective. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2021, 63, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, P.; Gómez-Trullén, E.M.; Asensio, A.; García, E.; Casas, R.; Monserrat, E.; Pandyan, A. Study of the therapeutic effects of a hippotherapy simulator in children with cerebral palsy: A stratified single-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyns, P.; Roman de Mettelinge, T.; van der Spank, J.; Coussens, M.; Van Waelvelde, H. Motivation in pediatric motor rehabilitation: A systematic search of the literature using the self-determination theory as a conceptual framework. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2018, 21, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva e Borges, M.B.; Werneck, M.J.; da Silva Mde, L.; Gandolfi, L.; Pratesi, R. Therapeutic effects of a horse riding simulator in children with cerebral palsy. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2011, 69, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.L.; Bell, K.L.; Stevenson, R.D.; Weir, K.A.; Boyd, R.N.; Davies, P.S. Differences in body composition according to functional ability in preschool-aged children with cerebral palsy. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.G.; Singh, H.; Miller, F.; Barbe, M.F.; Slade, J.M.; Pohlig, R.T.; Modlesky, C.M. Cortical bone deficit and fat infiltration of bone marrow and skeletal muscle in ambulatory children with mild spastic cerebral palsy. Bone 2017, 94, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arruda, R.C.B.F.; Tassitano, R.M.; da Silva Brito, A.L.; de Sousa Martins, O.S.; Cabral, P.C.; de Castro Antunes, M.M. Physical activity, sedentary time and nutritional status in Brazilian children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | HRS Group (n = 10) | Control Group (n = 7) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Months) | 112.1 ± 25.3 | 109.0 ± 29.0 | 0.82 | |
| Gender | Male | 7 | 4 | 0.64 |
| Female | 3 | 3 | ||
| GMFCS level | I | 6 | 4 | 0.83 |
| II | 1 | 1 | ||
| III | 1 | |||
| IV | 2 | 2 | ||
| Topography | Unilateral | 6 | 4 | 0.91 |
| Bilateral | 4 | 3 | ||
| HRS Group (n = 10) | Control Group (n = 7) | p-Value for Difference between Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMFM | Preintervention | Postintervention | p-Value | Preintervention | Postintervention | p-Value | |
| A | 95.1 ± 9.7 | 96.9 ± 5.4 | 0.32 | 97.5 ± 4.6 | 97.5 ± 4.6 | 0.99 | 0.74 |
| B | 90.2 ± 20.0 | 91.2 ± 17.6 | 0.18 | 89.8 ± 20.2 | 89.8 ± 20.2 | 0.99 | 0.54 |
| C | 84.5 ± 29.2 | 86.7 ± 26.0 | 0.32 | 84.0 ± 29.7 | 83.0 ± 29.6 | 0.18 | 0.23 |
| D | 72.6 ± 35.8 | 74.4 ± 35.6 | 0.03 | 68.1 ± 38.1 | 67.8 ± 37.6 | 0.71 | 0.06 |
| E | 68.6 ± 39.6 | 69.3 ± 39.7 | 0.03 | 66.8 ± 43.2 | 66.5 ± 42.6 | 0.68 | 0.19 |
| GMFM-88 total | 82.2 ± 26.1 | 83.5 ± 24.3 | <0.01 | 81.2 ± 26.7 | 80.9 ± 26.5 | 0.25 | <0.01 |
| GMFM-66 | 73.4 ± 20.1 | 75.3 ± 21.7 | <0.01 | 71.4 ± 20.8 | 70.6 ± 20.1 | 0.14 | <0.01 |
| HRS Group (n = 10) | Control Group (n = 7) | p-Value for Difference between Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preintervention | Postintervention | p-Value | Preintervention | Postintervention | p-Value | ||
| Height | 1.28 ± 0.19 | 1.30 ± 0.20 | 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.13 | 1.28 ± 0.13 | 0.99 | 0.42 |
| Weight | 34.9 ± 18.1 | 35.4 ± 17.4 | 0.07 | 31.3 ± 9.4 | 31.4 ± 9.4 | 0.99 | 0.03 |
| BMI | 19.9 ± 4.8 | 19.5 ± 4.2 | 0.48 | 18.9 ± 3.2 | 18.7 ± 3.2 | 0.99 | 0.74 |
| FM | 9.5 ± 7.1 | 8.1 ± 6.4 | 0.10 | 7.6 ± 4.7 | 7.5 ± 4.8 | >0.99 | 0.19 |
| FFM | 25.4 ± 11.5 | 27.3 ± 11.5 | <0.01 | 23.7 ± 5.6 | 23.9 ± 5.6 | 0.74 | 0.07 |
| SMM | 13.0 ± 6.8 | 14.2 ± 6.8 | <0.01 | 12.0 ± 3.3 | 12.1 ± 3.3 | 0.80 | 0.04 |
| BF | 24.5 ± 11.1 | 19.8 ± 9.8 | 0.04 | 22.3 ± 9.9 | 22.1 ± 10.0 | >0.99 | 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, Y.G.; Chang, H.J.; Jo, E.S.; Kim, D.H. The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082903
Jung YG, Chang HJ, Jo ES, Kim DH. The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study. Sensors. 2022; 22(8):2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082903
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Yong Gi, Hyun Jung Chang, Eun Sol Jo, and Da Hye Kim. 2022. "The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study" Sensors 22, no. 8: 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082903
APA StyleJung, Y. G., Chang, H. J., Jo, E. S., & Kim, D. H. (2022). The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study. Sensors, 22(8), 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082903






