A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting: Applications and Performance Determinants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We overview a range of application domains benefiting from RF energy harvesting to achieve an optimum performance level, where we outline a number of performance requirements with respect to each of the application domains, in order to familiarize the readers with the baseline performance requirements that are expected to be met by RF energy harvesting systems.
- We investigate different RF power harvesting techniques along with their average and peak power densities in order to assess their suitability and limitations for a number of use cases in different application domains.
- We thoroughly study the performance determinants for RF power harvesting systems that critically influence the performance of these systems. This includes the evaluation metrics for RF energy harvesting and energy propagation models that affect the performance of RF-based systems. In addition, there is an analysis of rectenna architectures and the power conversion efficiency associated with different rectenna design approaches, and medium access protocols to support energy exhaustive operation in RF powered networks.
- We highlight the open issues, challenges, and lessons learned from recent implementations, and future research directions by synthesizing the research efforts that have been put in place in the field of RF energy harvesting in recent years.
2. Applications of RF Energy Harvesting
2.1. Ubiquitous Internet of Things
2.2. Industrial Automation
2.3. Healthcare Informatics
2.4. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
2.5. Smart Buildings and Structural Health Monitoring
3. Dedicated vs. Ambient RF Energy Harvesting
3.1. Dedicated RF Energy Harvesting Sources
3.2. Ambient RF Energy Harvesting Sources
4. RF Energy Harvesting Evaluation Metrics
4.1. Range and Frequency
4.2. Conversion Efficiency
4.3. Resonance Factor
4.4. Sensitivity
4.5. Output Power
5. Energy Propagation Models
5.1. Deterministic Models
5.1.1. Free-Space Model
5.1.2. Two-Ray Ground Model
5.2. Probabilistic Models
6. Rectenna Architecture for RF Energy Harvesters
6.1. Antenna Design Considerations
6.1.1. Antenna Characteristics
6.1.2. Polarization
6.1.3. Harmonic Rejection
6.1.4. Reconfigurability
6.2. Single and Multi-Antenna RF Harvesters
6.2.1. Single Antenna RF Harvesters
Dual-Band Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting
Broadband Antenna for RF Energy Harvesting
Multi-Band Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting
6.2.2. Multi-Antenna RF Harvesters
6.3. Matching Networks
6.4. Rectifiers/Voltage Multipliers
7. Medium Access Control Protocols for RF Power Harvesting
8. Limitations, Open Issues, and Future Research Directions
8.1. Limitations
8.2. Open Issues and Mitigation Actions
8.3. Other Research Directions
9. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VXCHNGE. Comprehensive Guide to IoT Statistics. Available online: https://www.vxchnge.com/blog/iot-statistics (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- Palattella, M.R.; Accettura, N.; Vilajosana, X.; Watteyne, T.; Grieco, L.A.; Boggia, G.; Dohler, M. Standardized protocol stack for the internet of (important) things. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 15, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, D.O.M. Sustainable Development Challenges and Risks of Industry 4.0: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2019 Global IoT Summit (GIoTS), Aarhus, Denmark, 17–21 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luthra, S.; Mangla, S.K. Evaluating challenges to Industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elijah, O.; Rahman, T.A.; Orikumhi, I.; Leow, C.Y.; Hindia, M.N. An overview of Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics in agriculture: Benefits and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 3758–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkoska, B.L.R.; Trivodaliev, K.V. A review of Internet of Things for smart home: Challenges and solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.N.; Khan, M.; Han, K. Towards sustainable smart cities: A review of trends, architectures, components, and open challenges in smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherazi, H.H.R.; Grieco, L.A.; Boggia, G.; Imran, M.A. Cost Efficiency Optimization for Industrial Automation. In Wireless Automation as an Enabler for the Next Industrial Revolution; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 141–171. ISBN 9781119552635. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Mechanical Engineers. Engineering News. 2021. Available online: https://www.vox.com/energy-and-environment/2018/4/27/17283830/batteries-energy-storage-carbon-emissions (accessed on 27 March 2021).
- Benedek, J.; Sebestyén, T.T.; Bartók, B. Evaluation of renewable energy sources in peripheral areas and renewable energy-based rural development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasz, J.; Canales, F.; Kies, A.; Guezgouz, M.; Beluco, A. A review on the complementarity of renewable energy sources: Concept, metrics, application and future research directions. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 703–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mil, P.; Jooris, B.; Tytgat, L.; Catteeuw, R.; Moerman, I.; Demeester, P.; Kamerman, A. Design and implementation of a generic energy-harvesting framework applied to the evaluation of a large-scale electronic shelf-labeling wireless sensor network. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2010, 2010, 343690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Code, S. Limits of Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in the Frequency Range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz; Environmental Health Directorate, Health Protection Branch, Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Powercast Corporation. TX91501b POWERCASTER® TRANSMITTER. Available online: https://www.powercastco.com/products/powercaster-transmitter (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Powercast Corporation. POWERCASTER® POWERSPOT. Available online: https://www.powercastco.com/products/powerspot (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Ossia. Ossia’s Cota: Real Wireless Power. Available online: https://www.ossia.com/cota (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Ren, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X. RF energy harvesting and transfer in cognitive radio sensor networks: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Sharma, V. A survey on hardware design issues in RF energy harvesting for wireless sensor networks (WSN). In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Embedded Systems (WECON), Rajpura, India, 14–16 October 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mukminin, M.K.; Nurhayati, N.; Rakhmawati, L.; Baskoro, F. Literature Study of Harvesting Energy with Resources Radio Frequency. INAJEEE (Indones. J. Electr. Electron. Eng.) 2020, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, P.; Niyato, D.; Kim, D.I.; Han, Z. Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 17, 757–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nintanavongsa, P. A survey on RF energy harvesting: Circuits and protocols. Energy Procedia 2014, 56, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidhu, R.K.; Ubhi, J.S.; Aggarwal, A. A survey study of different RF energy sources for RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Automation, Computational and Technology Management (ICACTM), London, UK, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 530–533. [Google Scholar]
- Soyata, T.; Copeland, L.; Heinzelman, W. RF energy harvesting for embedded systems: A survey of tradeoffs and methodology. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2016, 16, 22–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.G.; Cha, H.K.; Park, W.T. RF power harvesting: A review on designing methodologies and applications. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasu, G.; Sharma, V.; Anveshkumar, N. A Survey on Conceptualization of RF Energy Harvesting. J. Appl. Sci. Comput. (JASC) 2019, 6, 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Stoopman, M.; Keyrouz, S.; Visser, H.; Philips, K.; Serdijn, W. A self-calibrating RF energy harvester generating 1V at −26.3 dBm. In Proceedings of the 2013 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 12–14 June 2013; pp. C226–C227. [Google Scholar]
- Stoopman, M.; Keyrouz, S.; Visser, H.J.; Philips, K.; Serdijn, W.A. Co-design of a CMOS rectifier and small loop antenna for highly sensitive RF energy harvesters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, A.P.; Parks, A.N.; Southwood, S.; Smith, J.R. Wireless ambient radio power. In Wirelessly Powered Sensor Networks and Computational RFID; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Papotto, G.; Carrara, F.; Finocchiaro, A.; Palmisano, G. A 90-nm CMOS 5-Mbps crystal-less RF-powered transceiver for wireless sensor network nodes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 49, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerckx, B.; Popović, Z.; Murch, R. Future Networks With Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerckx, B.; Kim, J.; Choi, K.W.; Kim, D.I. Foundations of Wireless Information and Power Transfer: Theory, Prototypes, and Experiments. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K. Far-Field Wireless Power Harvesting: Nonlinear Modeling, Rectenna Design, and Emerging Applications. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, E.; Estrada, J.A.; López-Yela, A.; Popović, Z. Broadband RF Energy-Harvesting Arrays. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, P.; Han, J.; Li, L.; Huang, Y. Metamaterials and Metasurfaces for Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Guan, X.; Zhang, R. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Energy and Information Transmission: An Overview. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.E.; Rosenthal, J.D.; Smith, J.R.; Reynolds, M.S. Adaptive Wireless Power Transfer and Backscatter Communication for Perpetual Operation of Wireless Brain–Computer Interfaces. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ding, Y.; Eid, A.; Hester, J.G.D.; He, X.; Bahr, R.; Georgiadis, A.; Goussetis, G.; Tentzeris, M.M. Advances in Wirelessly Powered Backscatter Communications: From Antenna/RF Circuitry Design to Printed Flexible Electronics. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, X.; Ng, D.W.K.; Schober, R. Resource Allocation for Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer Systems: A Tutorial Overview. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomas, C.; You, M.; Liang, K.; Zheng, G.; Krikidis, I. Design and Analysis of SWIPT With Safety Constraints. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Cong Luong, N.; Hoang, D.T.; Niyato, D.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, P. Secure Wirelessly Powered Networks at the Physical Layer: Challenges, Countermeasures, and Road Ahead. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost & Sullivan. What’s Hot in the Industrial Automation and Process Control Industry. 2012. Available online: https://pdfslide.net/business/frost-sullivan-whats-hot-in-the-industrial-automation-and-process-control-industry.html (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Asghari, P.; Rahmani, A.M.; Javadi, H.H.S. Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Comput. Netw. 2019, 148, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Bhargava, L.; Singh, V.; Choudhary, M.; Kumar Suhag, A. A survey–Energy harvesting sources and techniques for internet of things devices. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Kim, S.; Kuruoğlu, N. Energy Harvesting Techniques for Wireless Sensor Networks/Radio-Frequency Identification: A Review. Symmetry 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adila, A.S.; Husam, A.; Husi, G. Towards the self-powered Internet of Things (IoT) by energy harvesting: Trends and technologies for green IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Symposium on Small-Scale Intelligent Manufacturing Systems (SIMS), Cavan, Ireland, 16–18 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupitzer, C.; Müller, S.; Lesch, V.; Züfle, M.; Edinger, J.; Lemken, A.; Schäfer, D.; Kounev, S.; Becker, C. A Survey on Human Machine Interaction in Industry 4.0. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.01025. [Google Scholar]
- Sherazi, H.H.R.; Grieco, L.A.; Imran, M.A.; Boggia, G. Energy-efficient LoRaWAN for Industry 4.0 Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahir, M.A.; Ferrer, B.R.; Luis, J.; Lastra, M. An Approach for Managing Manufacturing Assets through Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting. Sensors 2019, 19, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Wang, X.; Cattley, R.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Energy harvesting technologies for achieving self-powered wireless sensor networks in machine condition monitoring: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuhaiber, A.; Mashal, I. Understanding users’ acceptance of smart homes. Technol. Soc. 2019, 58, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.B.; Xiang, W.; Atkinson, I. Internet of things for smart healthcare: Technologies, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26521–26544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalee, A.; Ho, H.W. Smarter and more connected: Future intelligent transportation system. IATSS Res. 2018, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikhrouhou, O.; Koubâa, A.; Zarrad, A. A Cloud Based Disaster Management System. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prati, A.; Shan, C.; Wang, K.I.K. Sensors, vision and networks: From video surveillance to activity recognition and health monitoring. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2019, 11, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zungeru, A.M.; Ang, L.M.; Prabaharan, S.; Seng, K.P. Radio frequency energy harvesting and management for wireless sensor networks. In Green Mobile Devices and Networks: Energy Optimization and Scavenging Techniques; Number 13 in 0; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 341–368. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, H.J.; Vullers, R.J.M. RF Energy Harvesting and Transport for Wireless Sensor Network Applications: Principles and Requirements. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, S.; Despesse, G. Energy harvesting, wireless sensor networks & opportunities for industrial applications. EE Times, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nintanavongsa, P.; Muncuk, U.; Lewis, D.R.; Chowdhury, K.R. Design optimization and implementation for RF energy harvesting circuits. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2012, 2, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, A.; Smith, J.R. Experimental results with two wireless power transfer systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 January 2009; pp. 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar, A.; Kundu, A.; Pallis, G. Healthcare Informatics and Privacy. IEEE Internet Comput. 2018, 22, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.M.; Yang, X.X.; Tan, C. Compact multiband wireless energy harvesting based battery-free body area networks sensor for mobile healthcare. IEEE J. Electromagn. Microwaves Med. Biol. 2018, 2, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Abdullah, A.H.; Qureshi, K.N.; Majid, A.H. Wireless body area networks for healthcare applications: An overview. Telkomnika 2017, 15, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Pu, L.; Zhao, Y. RF Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks for Healthcare of Animals: Opportunities and Challenges. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.00106. [Google Scholar]
- Saraereh, O.A.; Alsaraira, A.; Khan, I.; Choi, B.J. A hybrid energy harvesting design for on-body Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghi, M.; Thurow, K.; Stoll, R. Wearable devices in medical internet of things: Scientific research and commercially available devices. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2017, 23, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, L.M.; Chávez-Santiago, R.; Barroca, N.; Velez, F.J.; Balasingham, I. Radio-frequency energy harvesting for wearable sensors. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Chiu, C.; Gong, J. A Wearable Rectenna to Harvest Low-Power RF Energy for Wireless Healthcare Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Beijing, China, 13–15 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Meng, M.H.; Chen, X. Physiological information acquisition through wireless biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Information Acquisition, Hong Kong, China, 27 June–3 July 2005; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Feng, Q.; Fan, T.; Lei, Q. RFID technology and its applications in Internet of Things (IoT). In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Communications and Networks (CECNet), Yichang, China, 21–23 April 2012; pp. 1282–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Mhatre, P.; Duche, R.; Nawale, S.; Patil, P. RF power harvesting system for RFID applications in multiband systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Denton, TX, USA, 13–15 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, A.; Bridgelall, R.; Bhatia, D. Energy harvesting for active RF sensors and ID tags. In Energy Harvesting Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 459–492. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, M.P.; Bakkali, A.; Pelegri-Sebastia, J.; Sogorb, T.; Bou, V. Radio frequency energy harvesting-sources and techniques. In Renewable Energy: Utilisation and System Integration; Intechopen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, N.; Meng, Z.; Li, Z. Radio frequency identification and sensing techniques and their applications—A review of the state-of-the-art. Sensors 2019, 19, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olgun, U.; Chen, C.; Volakis, J.L. Wireless power harvesting with planar rectennas for 2.45 GHz RFIDs. In Proceedings of the 2010 URSI International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory, Berlin, Germany, 16–19 August 2010; pp. 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Pellerano, S.; Alvarado, J.; Palaskas, Y. A mm-Wave Power-Harvesting RFID Tag in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiar, A.S.; Jalali, M.S.; Mirabbasi, S. An RF power harvesting system with input-tuning for long-range RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, France, 30 May–2 June 2010; pp. 4085–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesinski, R.J. Power Harvesting for Actively Powered RFID Tags and Other Electronic Sensors. U.S. Patent App. 12/039,691, 3 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sony, S.; Laventure, S.; Sadhu, A. A literature review of next-generation smart sensing technology in structural health monitoring. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Ali, U.H.H. Energy harvesting wireless sensor for achieving self-powered structural health monitoring system. Circuit World 2020, 46, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubet, G.; Takacs, A.; Gardner, E.; De Luca, A.; Udrea, F.; Dragomirescu, D. LoRaWAN Battery-Free Wireless Sensors Network Designed for Structural Health Monitoring in the Construction Domain. Sensors 2019, 19, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loubet, G.; Takacs, A.; Dragomirescu, D. Implementation of a battery-free wireless sensor for cyber-physical systems dedicated to structural health monitoring applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24679–24690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidibe, A.; Takacs, A.; Okba, A.; Aubert, H. Design and Characterization of a Compact Rectenna for Structural Health Monitoring Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–12 July 2019; pp. 1803–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, J. A survey on ambient energy sources and harvesting methods for structural health monitoring applications. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017696210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Available online: https://www.fcc.gov (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Zorbas, D.; Raveneau, P.; Ghamri-Doudane, Y. Assessing the cost of RF-power harvesting nodes in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM 2016—Proceedings, Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, N.; Tandon, P.; Prabhakar, T.V.; Vinoy, K.J. RF Energy Harvesting For Self Powered Sensor Platform. In Proceedings of the 2018 16th IEEE International New Circuits and Systems Conference (NEWCAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 24–27 June 2018; pp. 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Cheng, R.S. Optimal Charge Scheduling for Energy-Constrained Wireless-Powered Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, P.S.; Jibukumar, M.G.; Neenu, V.S. Network lifetime enhancement of multi-hop wireless sensor network by RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Networking, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 10–12 January 2018; pp. 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Liang, H.; Zhao, L.; Tang, X. Optimal power allocation for wireless sensor powered by dedicated RF energy source. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2791–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Suresense: Sustainable wireless rechargeable sensor networks for the smart grid. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2012, 19, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Mission-aware placement of RF-based power transmitters in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Cappadocia, Turkey, 1–4 July 2012; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. DRIFT: Differentiated RF power transmission for wireless sensor network deployment in the smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; pp. 1491–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Grauwin, L.; Dousset, D.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K. Dynamic ambient RF energy density measurements of Montreal for battery-free IoT sensor network planning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13209–13221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñuela, M.; Mitcheson, P.D.; Lucyszyn, S. Ambient RF energy harvesting in urban and semi-urban environments. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, S.; Ban, H.; Kobayashi, K. Energy harvesting from ambient RF sources. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Innovative Wireless Power Transmission: Technologies, Systems, and Applications, Kyoto, Japan, 10–11 May 2012; pp. 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchouicha, D.; Dupont, F.; Latrach, M.; Ventura, L. Ambient RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality, Granada, Spain, 23–25 March 2010; Volume 13, pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Vyas, R.; Bito, J.; Niotaki, K.; Collado, A.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. Ambient RF Energy-Harvesting Technologies for Self-Sustainable Standalone Wireless Sensor Platforms. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.H.P.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K. Physical Mechanism and Theoretical Foundation of Ambient RF Power Harvesting Using Zero-Bias Diodes. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2146–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungan, T.; Reindl, L.M. Harvesting Low Ambient RF-Sources for Autonomous Measurement Systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Victoria, BC, Canada, 12–15 May 2008; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, I.; Lu, X.; Privault, N.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P. Performance analysis of ambient RF energy harvesting: A stochastic geometry approach. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Zhang, R.; Huang, K. Opportunistic wireless energy harvesting in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 4788–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, W.; Shoaib, N.; Cheema, H.M.; Khan, M.U. RF energy harvesting for ubiquitous, zero power wireless sensors. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2018, 2018, 8903139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, H.; Åkerberg, J.; Björkman, M.; Tran, H.V. RF energy harvesting: An analysis of wireless sensor networks for reliable communication. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.H. The design of cmos radio-frequency integrated circuits. Commun. Eng. 2004, 2, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, T.K.; Ji, Z.; Kim, K.; Medouri, A.; Salazar-Palma, M. A survey of various propagation models for mobile communication. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2003, 45, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H.; Ai, B. Wireless powered UAV relay communications over fluctuating two-ray fading channels. Phys. Commun. 2019, 35, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S. Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice; Prentice Hall PTR New Jersey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, R. Modeling energy availability in RF Energy Harvesting Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), Poznan, Poland, 20–23 September 2016; pp. 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.T.; Landesa, L.; Serna, A. Modeling the energy harvested by an RF energy harvesting system using gamma processes. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8763580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, R. Characterization of energy availability in RF energy harvesting networks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7849175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, Z.; Andrenko, A.S.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, H.Z. A compact dual-band rectenna for GSM900 and GSM1800 energy harvesting. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2018, 2018, 4781465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, M.A.; Keshavarz, R.; Abolhasan, M.; Lipman, J.; Esselle, K.P.; Shariati, N. A Review on Antenna Technologies for Ambient RF Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer: Designs, Challenges and Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 17231–17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.R. Bandwidth and the lower bound on Q for small wideband antennas. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–14 July 2006; pp. 647–650. [Google Scholar]
- Microstrip. Microstrip Patch Antenna. Available online: https://www.antenna-theory.com/antennas/patches/antenna.php (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Divakaran, S.K.; Krishna, D.D. RF energy harvesting systems: An overview and design issues. Int. J. Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Noh, S.K.; Choi, D.Y. Comparative study of antenna designs for RF energy harvesting. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013, 2013, 385260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahal, M.; Tiwari, V. Review of circular polarization techniques for design of microstrip patch antenna. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Cognizance in Wireless Communication & Image Processing; Springer: New Delhi, India, 29 April 2016; pp. 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Heikkinen, J.; Kivikoski, M. Low-profile circularly polarized rectifying antenna for wireless power transmission at 5.8 GHz. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2004, 14, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allane, D.; Vera, G.A.; Duroc, Y.; Touhami, R.; Tedjini, S. Harmonic power harvesting system for passive RFID sensor tags. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.R.; Kochuthundil Lalitha, S. Filtennas for wireless application: A review. Int. J. Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. Design of Compact Filtennas with Enhanced Bandwidth. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Qingdao, China, 14–16 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.A.; da Silva, L.G.; Vilas Boas, E.C.; Spadoti, D.H.; Arismar Cerqueira, S. Continuously frequency-tunable horn filtennas based on dual-post resonators. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2019, 2019, 6529343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, L.; Alves, A.; Cerqueira Sodré, A. Optically controlled reconfigurable filtenna. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2016, 2016, 7161070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi, B. The harmonic-rejection mixer [a circuit for all seasons]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2018, 10, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, T.; Ho, W.; Gharpurey, R. Design and Analysis of Harmonic Rejection Mixers With Programmable LO Frequency. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, A.A. Harmonic Rejection Mixers for Wideband Receivers. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, J.; Kim, D. Harmonic suppression characteristic of a CPW-FED circular slot antenna using single slot on a ground conductor. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 11, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.; Gudan, K.; Hull, J.J. A mechanically beam-steered phased array antenna for power-harvesting applications [antenna applications corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2016, 58, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaroudi Parchin, N.; Jahanbakhsh Basherlou, H.; Al-Yasir, Y.I.; M Abdulkhaleq, A.; A Abd-Alhameed, R. Reconfigurable Antennas: Switching Techniques—A Survey. Electronics 2020, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojaroudi Parchin, N.; Jahanbakhsh Basherlou, H.; Al-Yasir, Y.I.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Abdulkhaleq, A.M.; Noras, J.M. Recent developments of reconfigurable antennas for current and future wireless communication systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. A reconfigurable patch antenna using switchable slots for circular polarization diversity. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2002, 12, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Mathur, D.; Tanwar, M. A novel CPW-fed ultra wide band T-shaped slot antenna design. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2011, 1, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesan, A.; Alphones, A.; Karim, M.; Ong, L. Metamaterial based reconfigurable multiband antenna. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 2389–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Budimir, D. Switchable filtennas with sharp dual bandnotch using looped resonators. In Proceedings of the 2016 46th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Switchable Filtennas with Sharp Dual Bandnotch Using Looped Resonators, London, UK, 4–6 October 2016; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Carter, P. Recent advances in broadband rectennas for wireless power transfer and ambient RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Guo, Y.x.; He, M.; Zhong, Z. Design of a high-efficiency 2.45-GHz rectenna for low-input-power energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 929–932. [Google Scholar]
- Harouni, Z.; Cirio, L.; Osman, L.; Gharsallah, A.; Picon, O. A dual circularly polarized 2.45-GHz rectenna for wireless power transmission. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, Y.x.; He, M.; Zhong, Z. A dual-band rectenna using broadband Yagi antenna array for ambient RF power harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali, A.; Pelegrí-Sebastiá, J.; Sogorb, T.; Llario, V.; Bou-Escriva, A. A dual-band antenna for RF energy harvesting systems in wireless sensor networks. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 5725836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakkali, A.; Pelegri-Sebastia, J.; Sogorb, T.; Bou-Escriva, A.; Lyhyaoui, A. Design and simulation of dual-band RF energy harvesting antenna for WSNs. Energy Procedia 2017, 139, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebelka, V.; Velim, J.; Raida, Z. Dual band Koch antenna for RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 10–15 April 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Beg, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Khandelwal, M.K. A dual band rectifying antenna for RF energy harvesting. J. Comput. Electron. 2018, 17, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, A.M.; Nasimuddin, N.; Karim, M.F.; Chandrasekaran, K.T. A dual-band efficient circularly polarized rectenna for RF energy harvesting systems. Int. J. Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrawatia, M.; Baghini, M.S.; Kumar, G. Broadband bent triangular omnidirectional antenna for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 15, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; Carter, P. A high-efficiency broadband rectenna for ambient wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 3486–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, G.; He, F. RF energy harvesting with broadband antenna. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, S.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Beg, M.T.; Kumar, S. A compact broadband GFET based rectenna for RF energy harvesting applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jing, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. A novel compact broadband rectenna for ambient RF energy harvesting. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 95, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, N.; Kesavamurthy, T. Design and performance analysis of broadband rectenna for an efficient RF energy harvesting application. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Carter, P.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, S.; Xu, Q.; Kod, M. A novel six-band dual CP rectenna using improved impedance matching technique for ambient RF energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 3160–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Beg, M.T.; Khan, T.; Kumar, S. A dual polarized multiband rectenna for RF energy harvesting. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 93, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandravanshi, S.; Sarma, S.S.; Akhtar, M.J. Design of triple band differential rectenna for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 2716–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. On the Performance of Multi-antenna Wireless-Powered Communications with Energy Beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, M.; Shahid, A.; Jang, J.W.; Lee, K. Energy Harvesting Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access System with Multi-Antenna Relay and Base Station. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 17660–17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Q. Performance Analysis of Energy Harvesting Multi-Antenna Relay Networks with Different Antenna Selection Schemes. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 5654–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhong, M.; Mickle, M.H.; Capelli, C.; Swift, H. RF energy harvesting with multiple antennas in the same space. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2005, 47, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrnka, M.; Vasina, P.; Kufa, M.; Hebelka, V.; Raida, Z. The RF energy harvesting antennas operating in commercially deployed frequency bands: A comparative study. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2016, 2016, 7379624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Glesner, M. RF energy harvester design with autonomously adaptive impedance matching network based on auxiliary charge-pump rectifier. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 2477–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, Z.; Moez, K. Design of impedance matching circuits for RF energy harvesting systems. Microelectron. J. 2017, 62, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felini, C.; Merenda, M.; Della Corte, F.G. Dynamic impedance matching network for RF energy harvesting systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE RFID Technology and Applications Conference (RFID-TA), Tampere, Finland, 8–9 September 2014; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Pandey, S.K.; Singh, J.; Parihar, M.S. Realization of efficient RF energy harvesting circuits employing different matching technique. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 3–5 March 2014; pp. 754–761. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Cheng, J.; Glover, N.E.; Chiang, P. 0.56 V,–20 dBm RF-powered, multi-node wireless body area network system-on-a-chip with harvesting-efficiency tracking loop. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Moez, K. Fully-integrated passive threshold-compensated PMOS rectifier for RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 56th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Columbus, OH, USA, 4–7 August 2013; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Wentzloff, D.D. A- 32dBm sensitivity RF power harvester in 130nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–19 June 2012; pp. 483–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Ki, W.H. A 13.56 MHz CMOS active rectifier with switched-offset and compensated biasing for biomedical wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 8, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raben, H.; Borg, J.; Johansson, J. A Model for MOS Diodes With Cancellation in RFID Rectifiers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2012, 59, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansalee, E.; Zhao, Y.; Leelarasmee, E.; Nuanyai, K. A dual-band rectifier for RF energy harvesting systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand, 14–17 May 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- ur Rehman, M.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, W.T. Highly efficient dual band 2.45/5.85 GHz rectifier for RF energy harvesting applications in ISM band. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–16 November 2017; pp. 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Khansalee, E.; Nuanyai, K.; Zhao, Y. A dual-band rectifier for RF energy harvesting. Eng. J. 2015, 19, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafekirt, H.; Pelegri-Sebastia, J.; Bouajaj, A.; Reda, B.M. A sensitive triple-band rectifier for energy harvesting applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 73659–73664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.Y. Compact triple-band rectifier for ambient RF energy harvesting application. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 19018–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.S.; Chandravanshi, S.; Akhtar, M.J. Triple band differential rectifier for RF energy harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), New Delhi, India, 5–9 December 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sherazi, H.H.R.; Grieco, L.A.; Boggia, G. A comprehensive review on energy harvesting MAC protocols in WSNs: Challenges and tradeoffs. Ad Hoc Netw. 2018, 71, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, Z.A.; Tan, H.P.; Seah, W.K. Design and performance analysis of MAC schemes for wireless sensor networks powered by ambient energy harvesting. Ad Hoc Netw. 2011, 9, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafoutis, X.; Dragoni, N. ODMAC: An on-demand MAC protocol for energy harvesting-wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM Symposium on Performance Evaluation of Wireless ad Hoc, Sensor, and Ubiquitous Networks, Miami, FL, USA, 3–4 November 2011; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lin, G.Y.; Wei, H.Y. Markov chain performance model for IEEE 802.11 devices with energy harvesting source. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; pp. 5212–5217. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.W. Energy adaptive MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks with RF energy transfer. In Proceedings of the 2011 Third International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Dalian, China, 15–17 June 2011; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.W. Energy adaptive MAC for wireless sensor networks with RF energy transfer: Algorithm, analysis, and implementation. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 64, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.Y.; Nintanavongsa, P.; Chowdhury, K.R. RF-MAC: A medium access control protocol for re-chargeable sensor networks powered by wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 3926–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Khan, J.Y.; Ngo, D.T. An adaptive MAC protocol for RF energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, T.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.M. HE-MAC: Harvest-then-transmit based modified EDCF MAC protocol for wireless powered sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 17, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, R. Throughput Maximization in Wireless Powered Communication Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, P.; Cui, S.; Zhang, J. Distributed opportunistic scheduling for energy harvesting based wireless networks: A two-stage probing approach. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2015, 24, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.; Cho, S. REACH: An efficient MAC protocol for RF energy harvesting in wireless sensor network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 6438726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.; Mayaram, K.; Fiez, T. Efficient far-field radio frequency energy harvesting for passively powered sensor networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, V.; Hemadeh, I.; Mourad, A.; Shojaeifard, A.; Juntti, M. Survey on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces below 10 GHz. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Chen, M.; Chi, K.; Zhu, Y.h. RF-based charger placement for duty cycle guarantee in battery-free sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 1802–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ejaz, W.; Kandeepan, S.; Anpalagan, A. Optimal placement and number of energy transmitters in wireless sensor networks for RF energy transfer. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 26th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Hong Kong, China, 30 August–2 September 2015; pp. 1238–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Zorbas, D.; Raveneau, P.; Ghamri-Doudane, Y.; Douligeris, C. The charger positioning problem in clustered RF-power harvesting wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2018, 78, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnickel, V.; Manolakis, K.; Zirwas, W.; Panzner, B.; Braun, V.; Lossow, M.; Sternad, M.; Apelfröjd, R.; Svensson, T. The role of small cells, coordinated multipoint, and massive MIMO in 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Code, S. Limits of Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Energy in the Frequency Range from 3 khz to 300 ghz; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.W. How dangerous are mobile phones, transmission masts, and electricity pylons? Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlbom, A.; Bridges, J.; De Seze, R.; Hillert, L.; Juutilainen, J.; Mattsson, M.O.; Neubauer, G.; Schüz, J.; Simko, M.; Bromen, K. Possible effects of electromagnetic fields (EMF) on human health–opinion of the scientific committee on emerging and newly identified health risks (SCENIHR). Toxicology 2008, 246, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Hardell, L.; Sage, C. Biological effects from electromagnetic field exposure and public exposure standards. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breckenkamp, J.; Berg-Beckhoff, G.; Münster, E.; Schüz, J.; Schlehofer, B.; Wahrendorf, J.; Blettner, M. Feasibility of a cohort study on health risks caused by occupational exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habash, R.W.; Elwood, J.M.; Krewski, D.; Lotz, W.G.; McNamee, J.P.; Prato, F.S. Recent advances in research on radiofrequency fields and health: 2004–2007. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2009, 12, 250–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
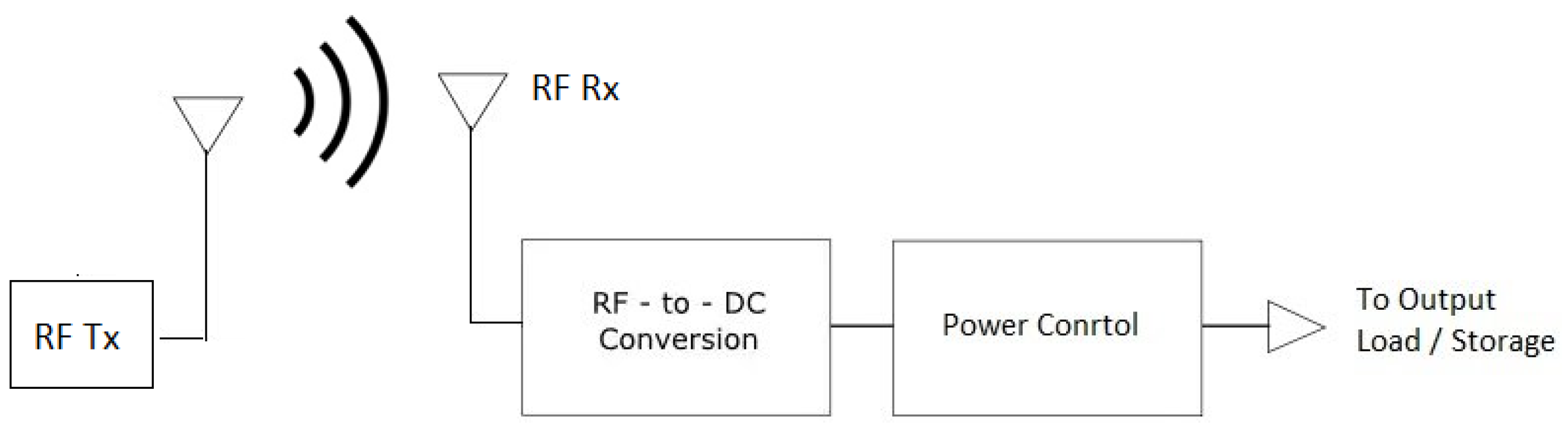

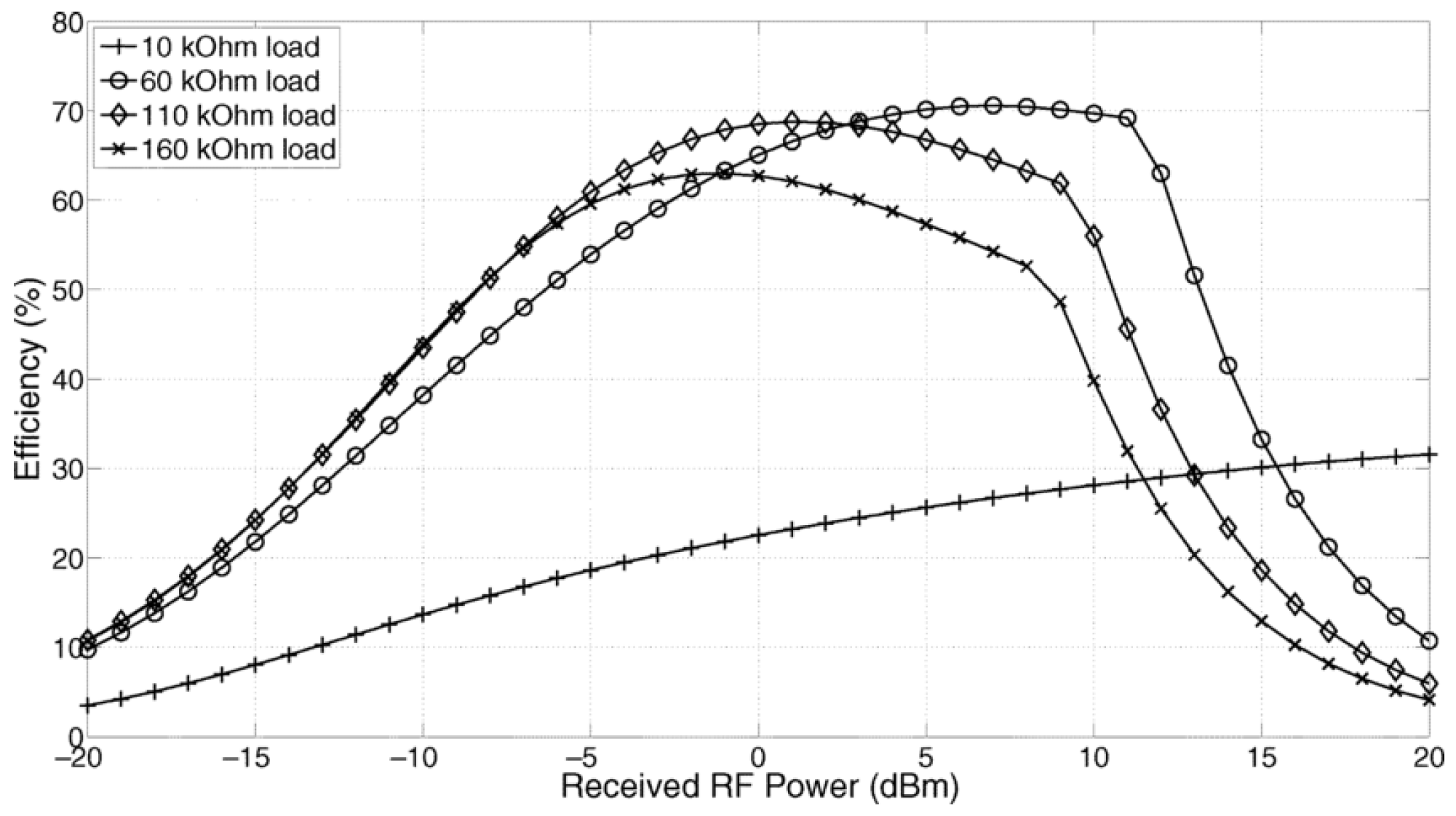
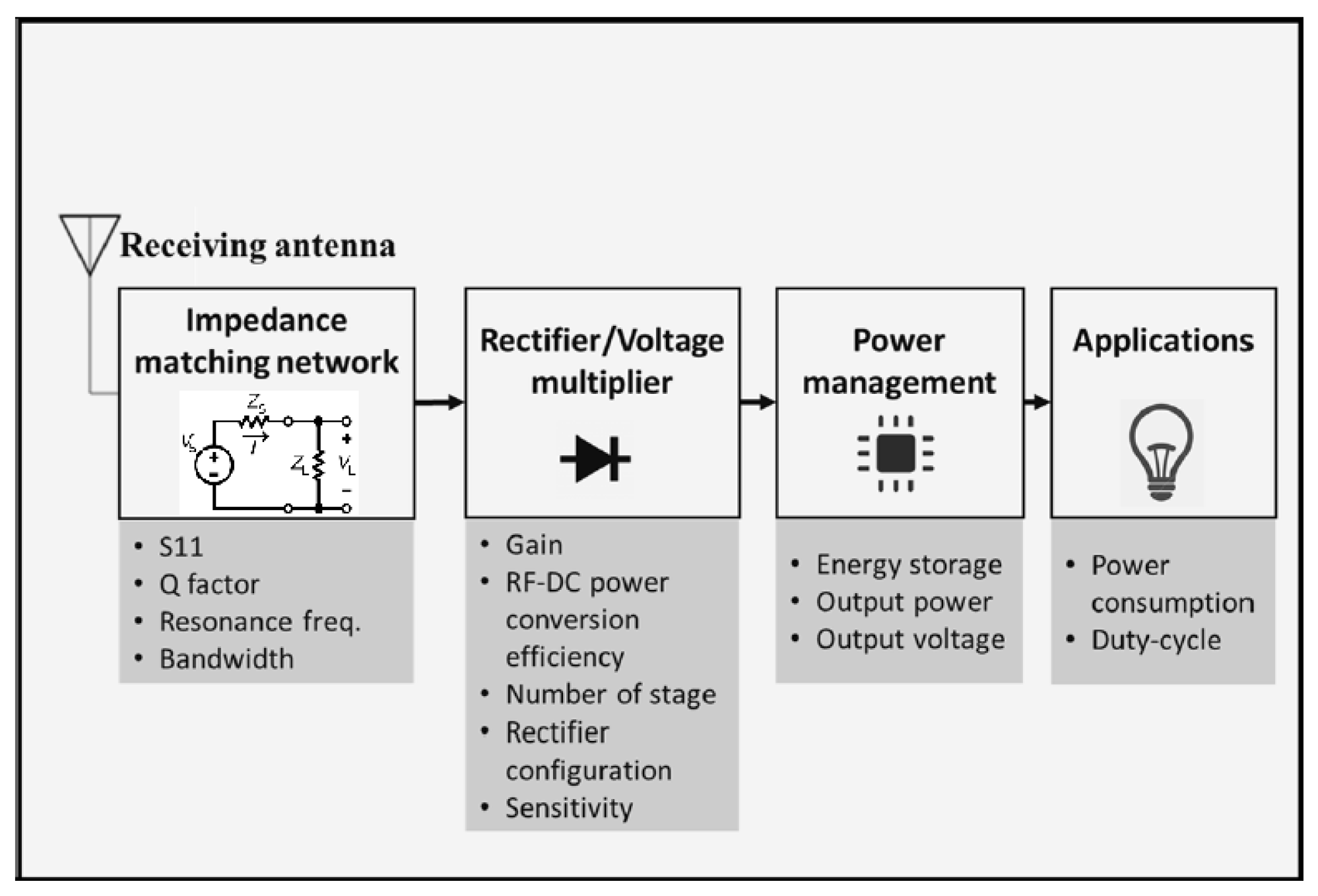
| Harvesting Method | Power Density | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Solar energy—outdoors | 15 mW/cm-bright sunny day | 10–25% |
| 0.15 mW/cm-cloudy day | ||
| Solar energy—indoors | 100 µW/cm | |
| Vibrations (piezoelectric—shoe inserts) | 330 µW/cm-105 Hz | 25–50% |
| Vibrations (electrostatic conversion) | 184 µW/cm-10 Hz | |
| Vibrations (electromagnetic conversion) | 0.21 mW/cm-12 Hz | |
| Thermoelectric (5–20 °C gradient) | 40 µW-10 mW/cm | 0.1–3% |
| Magnetic field energy | 130 µW/cm-200 µT, 60 Hz | 30–74.4% |
| Wind energy | 65.2 µW/cm-5 m/s | 20–40% |
| RF energy | 0.08 nW-1 µW/cm | 30–88% |
| Transmitter | Transmit Power | Frequency | Distance | Harvesting Power (at a Reference Distance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isotropic RF transmitter [27] | 4 W | 902–928 MHz | 15 m | 5.5 W |
| Isotropic RF transmitter [28] | 1.78 W | 868 MHz | 25 m | 2.3 W |
| Isotropic RF transmitter [15] | 1.78 W | 868 MHz | 27 m | 2 W |
| TX91501 powercaster transmitter [29] | 3 W | 915 MHz | 5 m | 189 W |
| TX91501 powercaster transmitter [29] | 3 W | 915 MHz | 11 m | 1 W |
| King TV tower [30] | 960 kW | 674–680 MHz | 4.1 km | 60 W |
| Reference | Focus | Objectives | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verma et al. [19] | Hardware design issues |
| 2016 |
| Mukminin et al. [20] | RF energy sources |
| 2020 |
| Lu et al. [21] | RF powered wireless networks |
| 2015 |
| Nintanavongsan et al. [22] | Circuit and protocol design |
| 2014 |
| Sidhu et al. [23] | energy harvesting sources |
| 2019 |
| Soyata et al. [24] | Trade-offs and methodologies on RF harvesting for embedded systems |
| 2016 |
| Tran et al. [25] | Design methodologies and applications for RF harvesting |
| 2017 |
| Srininvasu et al. [26] | Conceptualization of RF energy Harvesting |
| 2019 |
| Clerckx et al. [31] | Future Networks With Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting |
| 2022 |
| This Survey | Application domains and performance determinants of RF powered systems |
| 2022 |
| Application Domain | Coverage | Transmission Frequency | Operational Cost | Energy Efficiency | Latency | Network Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internet of Things | Varies * | Medium | Medium | Varies * | Medium | WAN |
| Industrial Automation | Medium | High | High | Low | Medium | WAN |
| Healthcare Informatics | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | PAN |
| Radio Frequency Identification | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | PAN |
| Smart Buildings/Structural Health Monitoring | Medium | Low | Low | High | Low | WAN |
| Band | Frequency Range (MHz) | Average Power Density (nW/cm) | Maximum Power Density (nW/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DTV [95] | 470–610 | 0.89 | 460 |
| GSM900 (MTx) [95] | 880–915 | 0.45 | 39 |
| GSM900 (BTx) [95] | 925–960 | 36 | 1930 |
| GSM1800 (MTx) [95] | 1710–1785 | 0.5 | 20 |
| GSM1800 (BTx) [95] | 1805–1880 | 84 | 6390 |
| 3G (MTx) [103] | 1920–1980 | 0.46 | 66 |
| 3G (BTx) [103] | 2110–2170 | 12 | 240 |
| Wi-Fi [103] | 2400–2500 | 0.18 | 6 |
| Antenna Proposal | Feature | PL * | HR ** | Frequency (GHz) | Bandwidth (MHz) | Gain (dBi)/ Effic (%) | RC † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polarization reconfigurable monopole antenna [133] | Circular patch with reconfigurable feed antenna | 1 LP, 2 CP | No | 5.07–5.86 | 0.79 | 3 | Yes |
| T-shaped slot wideband antenna [134] | T-shaped conductor line connected to path | CP | Yes | 2–3.5 | 1.5 | 5.5 | No |
| Metamaterial based multiband antenna [135] | Antenna loaded with interdigital capacitor slots | LP | No | OFF: 7–8.5 ON: 3.8–4.2, 5.5–6, 6.8–8.5 | OFF: 1.5 ON: 0.4, 0.5, 1.7 | OFF: 1.93 ON: 1.78, 1.63, 2.32 | Yes |
| Switchable Filtenna [136] | 3-loop resonators in UWB antenna | LP | Yes | OFF: 3.2–11 ON: 3–3.5, 4–5.7, 6.2–11 | 7 | OFF: 4.33, ON: 3.8 96% | Yes |
| Off center fed dipole antenna [137] | Dipoles are modified into bow tie stubs | CP | No | 1.8, 2.5 | 0.7 | 3.5 | No |
| Reference | Antenna Type * | Frequency Band | Power Conversion Efficiency, PCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mhatre et al. [71] | SB | 2.4 GHz | 30% |
| Sun et al. [140] | SB | GSM-1800 MHz and UMTS-2100 MHz | 40% @ 5 k |
| Singh et al. [144] | DB | 2.8 GHz and 5.8 GHz | 79% and 86% @ 1 k |
| Arrawatia et al. [146] | BB | 850 MHz to 1.94 GHz | 60% and 17% @ 500 |
| Song et al. [147] | BB | 1.8 to 2.5 GHz | 55% @ −10 dBm |
| Singh et al. [149] | BB | 22.5 GHz to 27.5 GHz | 80% @ 5 dBm & 5 k |
| saranya et al. [151] | BB | 5.8 GHz to 5.85 GHz | 88% @ 1 k |
| Singh et al. [153] | MB | C-band (4–8 GHz) | 84% |
| Chandra et al. [154] | TB | 2 GHz, 2.5 GHz, and 3.5 GHz | 53%, 31%, 15.5% |
| Hameed et al. [161] | SB | 902–928 MHz | 31% @ 1 M |
| Agrawal et al. [163] | SB | 900 MHz | 79% @ 50 k |
| Ref. | RF Energy Emission | Ambient/Dedicated Harvesting | Medium-Access Method (Radio) | Maximization Parameters | Experimentally Validated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [179] | Constantly | Ambient | CSMA (IEEE802.15.4) | Throughput, Fairness | Yes |
| [181] | On demand | Dedicated | CSMA | Throughput | Yes |
| [182] | Constantly | Ambient (LTE) | CSMA (IEEE802.15.4) | Throughput | No |
| [183] | Harvest-then-transmit | Dedicated (WiFi) | CSMA (IEEE802.11) | Throughput | No |
| [186] | When no data | Dedicated | CSMA | Harvesting energy | No |
| [184] | Harvest-then-transmit | Dedicated | TDMA | Throughput, Fairness | No |
| Section | Challenges and Open Issues | Future Directions |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluation metrics for RF power harvesting |
|
|
| Applications of RF energy harvesting |
|
|
| Dedicated vs. Ambient RF energy Harvesting |
|
|
| Energy propagation models |
|
|
| Rectenna Architecture for RF energy Harvesters |
|
|
| MAC Protocols for RF power Harvesting |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherazi, H.H.R.; Zorbas, D.; O’Flynn, B. A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting: Applications and Performance Determinants. Sensors 2022, 22, 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082990
Sherazi HHR, Zorbas D, O’Flynn B. A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting: Applications and Performance Determinants. Sensors. 2022; 22(8):2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082990
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherazi, Hafiz Husnain Raza, Dimitrios Zorbas, and Brendan O’Flynn. 2022. "A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting: Applications and Performance Determinants" Sensors 22, no. 8: 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082990
APA StyleSherazi, H. H. R., Zorbas, D., & O’Flynn, B. (2022). A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting: Applications and Performance Determinants. Sensors, 22(8), 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082990






