Individual Tree Species Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Multitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
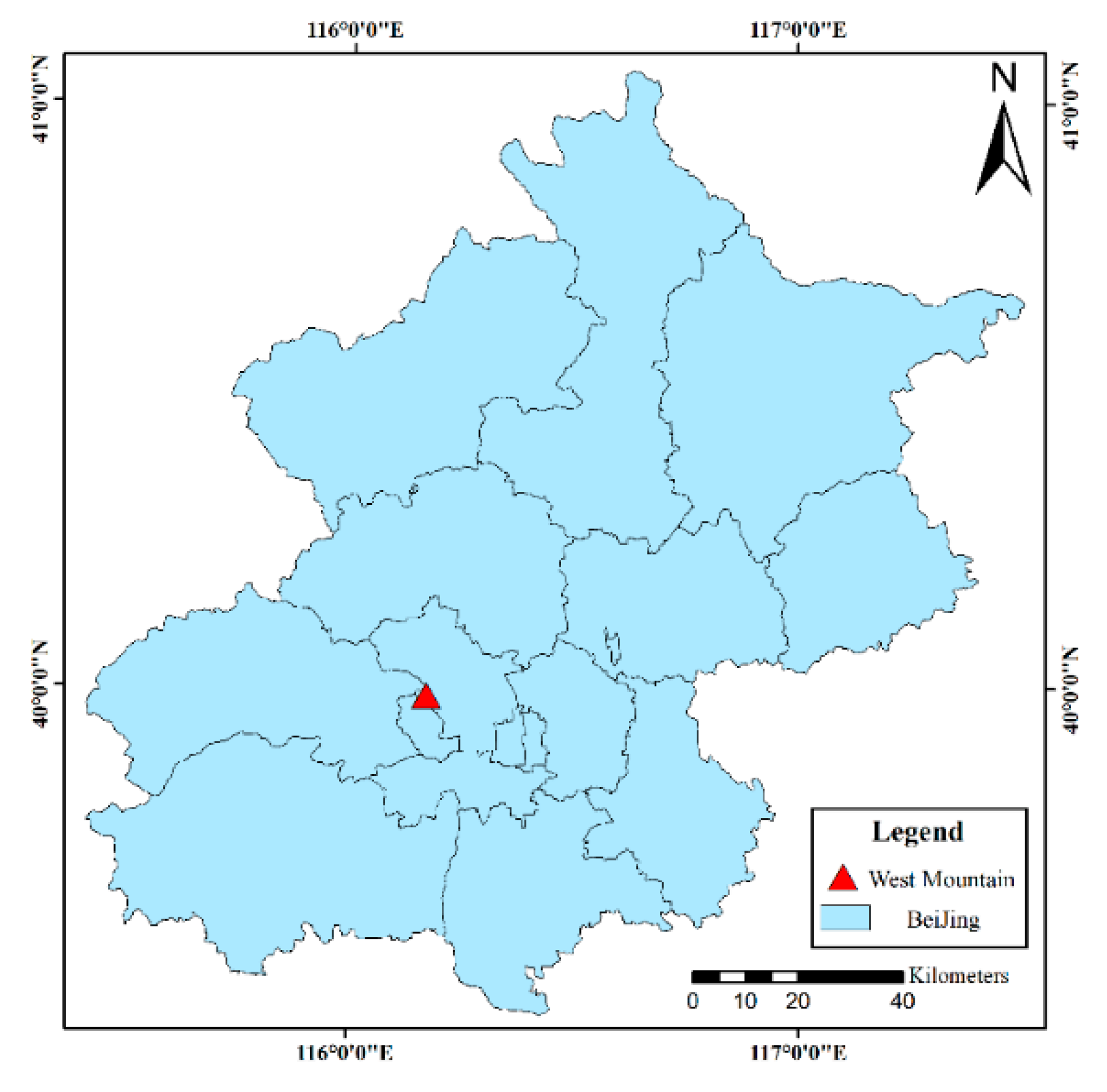
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Worldview-3
2.2.2. Google Earth
2.2.3. Field Sampling Points
2.3. ITS Sample Sets
2.3.1. Individual Tree Crown Delineation
2.3.2. Data Augmentation
2.3.3. Remote Sensing Imagery Sample Set of ITS
2.4. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.4.1. GoogLeNet
2.4.2. ResNet
2.4.3. DenseNet
2.4.4. Model Training
2.5. Random Forests
2.6. Accuracy Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Overall Classification Accuracy
3.1.1. Comparison of the Classification Accuracies of Worldview-3 and Google Earth Images
3.1.2. Comparison of Different CNN Models
3.1.3. Comparison of the Classification Accuracies of CNN Models and RF
3.2. Classification Accuracy of Tree Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gyamfi-Ampadu, E.; Gebreslasie, M. Two Decades Progress on The Application of Remote Sensing for Monitoring Tropical and Sub-Tropical Natural Forests: A Review. Forests 2021, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pause, M.; Schweitzer, C.; Rosenthal, M.; Keuck, V.; Bumberger, J.; Dietrich, P.; Heurich, M.; Jung, A.; Lausch, A. In Situ/Remote Sensing Integration to Assess Forest Health—A Review. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angela, L.; Erik, B.; Jan, B.; Peter, D.; Marco, H.; Andreas, H.; Reinhard, K.; Sonja, K.; Hannes, M.; Hendrik, P.; et al. Understanding Forest Health with Remote Sensing, Part III: Requirements for a Scalable Multi-Source Forest Health Monitoring Network Based on Data Science Approaches. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bambang, H.T.; David, P. A review of remote sensing applications in tropical forestry with a particular emphasis in the plantation sector. Geocarto Int. 2018, 35, 317–339. [Google Scholar]
- Wulder, M. Optical remote-sensing techniques for the assessment of forest inventory and biophysical parameters. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1998, 22, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, F.H.; Ferreira, M.P.; Sanchez, A.; Hirye, M.C.M.; Zortea, M.; Gloor, E.; Phillips, O.L.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Aragao, L.E.O.C. Individual tree crown delineation in a highly diverse tropical forest using very high-resolution satellite images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleoianu, A.I.; Stupariu, M.S.; Sandric, I.; Stupariu, I.; Drǎgu, L. Individual tree-crown detection and species classification in very high-resolution remote sensing imagery using a deep learning ensemble model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xie, D.; Yan, G. Realistic 3D-simulation of large-scale forest scene based on individual tree detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NäSi, R.; Honkavaara, E.; Blomqvist, M.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Hakala, T.; Viljanen, N.; Kantola, T.; Holopainen, M. Remote sensing of bark beetle damage in urban forests at individual tree level using a novel hyperspectral camera from UAV and aircraft. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 30, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stereńczak, K.; Kraszewski, B.; Mielcarek, M.; Piasecka, A.; Lisiewicz, M.; Heurich, M. Mapping individual trees with airborne laser scanning data in a European lowland forest using a self-calibration algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 93, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.Y.; Sanesi, G.; Lafortezza, R. Remote sensing in urban forestry: Recent applications and future directions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fassnacht, F.; Koch, B. Review of forestry oriented multi-angular remote sensing techniques. Int. For. Rev. 2012, 14, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Vastaranta, M.; Hilker, T.; Tompalski, P. Remote Sensing Technologies for Enhancing Forest Inventories: A Review. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surový, P.; Kuželka, K. Acquisition of Forest Attributes for Decision Support at the Forest Enterprise Level Using Remote-Sensing Techniques—A Review. Forests 2019, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Telmo, A.; Hruka, J.; Pádua, L.; Bessa, J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J. Hyperspectral Imaging: A Review on UAV-Based Sensors, Data Processing and Applications for Agriculture and Forestry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, R.R.; Hardin, P.J.; Hardin, A.J. Estimating urban leaf area index (LAI) of individual trees with hyperspectral data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yao, D.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J. A hyperspectral image classification method based on multi-discriminator generative adversarial networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dian, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, Y. Spectral and texture features combined for forest tree species classification with airborne hyperspectral imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2014, 43, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesset, E.; Dalponte, M.; Orka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Gianelle, D. Tree species classification in boreal forests with hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2632–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Julia, M.; Clement, A.; Markus, I. Individual tree crown segmentation and classification of 13 tree species using airborne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raczko, E.; Zagajewski, B. Comparison of support vector machine, random forest and neural network classifiers for tree species classification on airborne hyperspectral APEX images. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nezami, S.; Khoramshahi, E.; Nevalainen, O.; Pölönen, I.; Honkavaara, E. Tree species classification of drone hyperspectral and RGB imagery with deep learning convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Three-dimensional convolutional neural network model for tree species classification using airborne hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Neumann, C.; Förster, M.; Buddenbaum, H.; Ghosh, A.; Clasen, A.; Joshi, P.K.; Koch, B. Comparison of feature reduction algorithms for classifying tree species with hyperspectral data on three central european test sites. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.; Rivard, B.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, A. Classification of tree species based on longwave hyperspectral data from leaves, a case study for a tropical dry forest. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, A.T.; Evans, J.S.; Smith, A.S. LiDAR utility for natural resource managers. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 934–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterenczak, K.; Moskalik, T. Use of LIDAR-based digital terrain model and single tree segmentation data for optimal forest skid trail network. iForest—Biogeosci. For. 2014, 8, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechesne, C.; Mallet, C.; Bris, A.L.; Gouet-Brunet, V. Semantic segmentation of forest stands of pure species combining airborne lidar data and very high-resolution multispectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Pang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Z. Individual tree classification using airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data in a natural mixed forest of northeast china. Forests 2020, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrs, J.; Ni-Meister, W. Machine learning techniques for tree species classification using co-registered LiDAR and hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballanti, L.; Blesius, L.; Hines, E.; Kruse, B. Tree species classification using hyperspectral imagery: A comparison of two classifiers. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Xin, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, H. Characterizing tree species of a tropical wetland in southern china at the individual tree level based on convolutional neural network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, J.; Wang, H. An overview of applying high resolution remote sensing to natural resources survey. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2019, 31, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, A.; Korhonen, L.; Manninen, T.; Maltamo, M. Automatic segment-level tree species recognition using high resolution aerial winter imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, V.M.; Cattau, M.E.; Joseph, M.B.; Balch, J.K. Integrating national ecological observatory network (NEON) airborne remote sensing and In-Situ data for optimal tree species classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qin, R.; Chen, X. Unmanned aerial vehicle for remote sensing applications—A review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, S.E.; Ahmed, O.S. Deciduous tree species classification using object-based analysis and machine learning with unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5236–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Coops, N.C.; Wu, X. Tree species classification using UAS-based digital aerial photogrammetry point clouds and multispectral imageries in subtropical natural forests. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Eichel, J.; Wiser, S.; Burrow, L.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Schmidtlein, S. Convolutional Neural Networks accurately predict cover fractions of plant species and communities in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle imagery. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 6, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, X. An improved Res-UNet model for tree species classification using airborne high-resolution images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guimares, N.; Pádua, L.; Marques, P.; Silva, N.; Soura, J.J. Forestry remote sensing from unmanned aerial vehicles: A review focusing on the data, processing and potentialities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Colkesen, I.; Yomralioglu, T. Object-based classification with rotation forest ensemble learning algorithm using very-high-resolution WorldView-2 image. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, C.; Tshingomba, U.K.; Soti, V. Assessing Worldview-3 multispectral imaging abilities to map the tree diversity in semi-arid parklands. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 93, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ke, Y.H.; Gong, H.L.; Chen, B.B.; Zhu, L. Tree species classification based on WorldView-2 imagery in complex urban environment. In Proceedings of the 2014 Third International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Changsha, China, 11–14 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deur, M.; Gaparovi, M.; Balenovi, I. Tree species classification in mixed deciduous forests using very high spatial resolution satellite imagery and machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Mcneil, B.E.; Warner, T.A.; Maxwell, A.E.; Dahle, G.A.; Eutsler, E.; Li, J.J. Discriminating tree species at different taxonomic levels using multi-temporal WorldView-3 imagery in Washington D.C. USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.P.; Wagner, F.H.; Arago, L.E.O.C.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Filho, C.R.D.S. Tree species classification in tropical forests using visible to shortwave infrared WorldView-3 images and texture analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://s.visitbeijing.com.cn/attraction/101591 (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- Digital Globe. Worldview-3. Available online: http://worldview3.digitalglobe.com/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Li, H.; Jing, L.; Tang, Y.; Ding, H.F. An Improved Pansharpening Method for Misaligned Panchromatic and Multispectral Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Google Earth. Available online: https://earth.google.com/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Jing, L.; Noland, T.; Guo, H. Automated tree crown delineation from imagery based on morphological techniques. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Barea, F.J.; Jerez, J.M.; Franco, L. Improving classification accuracy using data augmentation on small data sets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Robinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.X.; Li, Q.; Jing, L.H. CNN-Based Individual Tree Species Classification Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Airborne LiDAR Data. Forests 2021, 12, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olli, N.; Eija, H.; Sakari, T.; Nikko, V.; Teemu, H.; Juha, H.; Heikki, S.; Pölönen, I.; Imai, N.N.; Tommaselli, A.M.G. Individual Tree Detection and Classification with UAV-Based Photogrammetric Point Clouds and Hyperspectral Imaging. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitris, S.; Eleni, D.; Ioannis, G.; Christo, K. Decision Fusion Based on Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellite Imagery for Accurate Forest Species Mapping. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6897–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majid, I.A.; Latif, Z.A.; Adnan, N.A. Tree species classification using worldview-3 data. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium (ICSGRC), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 8 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; An, H. Urban Greening Tree Species Classification Based on HSV Colour Space of WorldView-2. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S. Mapping urban tree species by integrating multi-seasonal high resolution pléiades satellite imagery with airborne LiDAR data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 53, 126675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonsela, S.; Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Mutanga, O.; Ramoelo, A.; Kaszta, Z.; Kerchove, R.V.D.; Wolff, E. Multi-phenology WorldView-2 imagery improves remote sensing of savannah tree species. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartling, S.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Carron, J. Urban Tree Species Classification Using a WorldView-2/3 and LiDAR Data Fusion Approach and Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaee, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mishra, R.; Tong, F.; Tong, H. Using a VGG-16 Network for Individual Tree Species Detection with an Object-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th IAPR Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing (PRRS), Beijing, China, 19–20 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.P.; Lotte, R.G.; D’Elia, F.V.; Stamatopoulos, C.; Kim, D.H.; Benjamin, A.R. Accurate mapping of Brazil nut trees (Bertholletia excelsa) in Amazonian forests using WorldView-3 satellite images and convolutional neural networks. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Band | Wavelength Range (nm) | Wavelength Center (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Panchromatic | 450–800 | 625 |
| Coastal | 400–450 | 425 |
| Blue | 450–510 | 480 |
| Green | 510–580 | 545 |
| Yellow | 585–625 | 605 |
| Red | 630–690 | 660 |
| Red Edge | 705–745 | 725 |
| NIR-1 | 770–895 | 832.5 |
| NIR-2 | 860–1040 | 950 |
| Name | Number of Samples | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Validation | Test | ||
| Cypress | 702 | 234 | 234 | 1170 |
| Pine | 432 | 144 | 144 | 720 |
| Locust | 324 | 108 | 108 | 540 |
| Maple | 252 | 84 | 84 | 420 |
| Oak | 360 | 120 | 120 | 600 |
| Ginkgo | 216 | 72 | 72 | 360 |
| Goldenrain tree | 216 | 72 | 72 | 360 |
| - | 2502 | 834 | 834 | 4170 |
| Sample Set | SprGE | AutGE | WV3 | WV3SprGE | WV3AutGE | WV3SprAutGE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Metrics | ||||||
| RF | Precision | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.57 |
| Recall | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.57 | |
| F1 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.57 | |
| GoogLeNet | Precision | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.80 | 0.75 |
| Recall | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.76 | 0.72 | |
| F1 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.78 | 0.73 | |
| ResNet_34 | Precision | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| Recall | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.73 | |
| F1 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.74 | |
| DenseNet_40 | Precision | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.78 |
| Recall | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.75 | |
| F1 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.76 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Li, H.; Jing, L.; Wang, P. Individual Tree Species Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Multitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093157
Guo X, Li H, Jing L, Wang P. Individual Tree Species Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Multitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Sensors. 2022; 22(9):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093157
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xianfei, Hui Li, Linhai Jing, and Ping Wang. 2022. "Individual Tree Species Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Multitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images" Sensors 22, no. 9: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093157
APA StyleGuo, X., Li, H., Jing, L., & Wang, P. (2022). Individual Tree Species Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Multitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Sensors, 22(9), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093157







