Reliable Fast (20 Hz) Acquisition Rate by a TD fNIRS Device: Brain Resting-State Oscillation Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
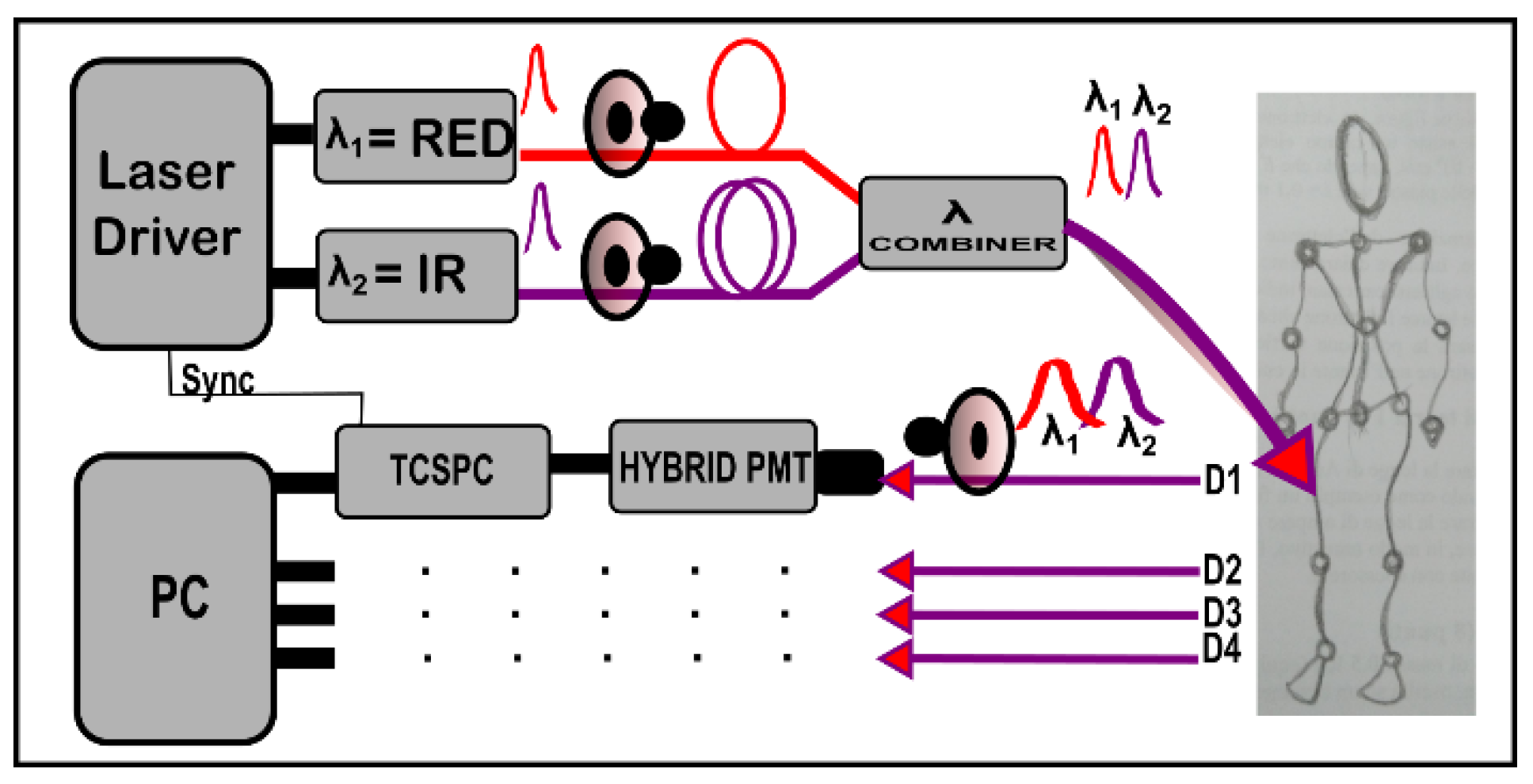
2. Instrument Description
3. Characterization Protocols
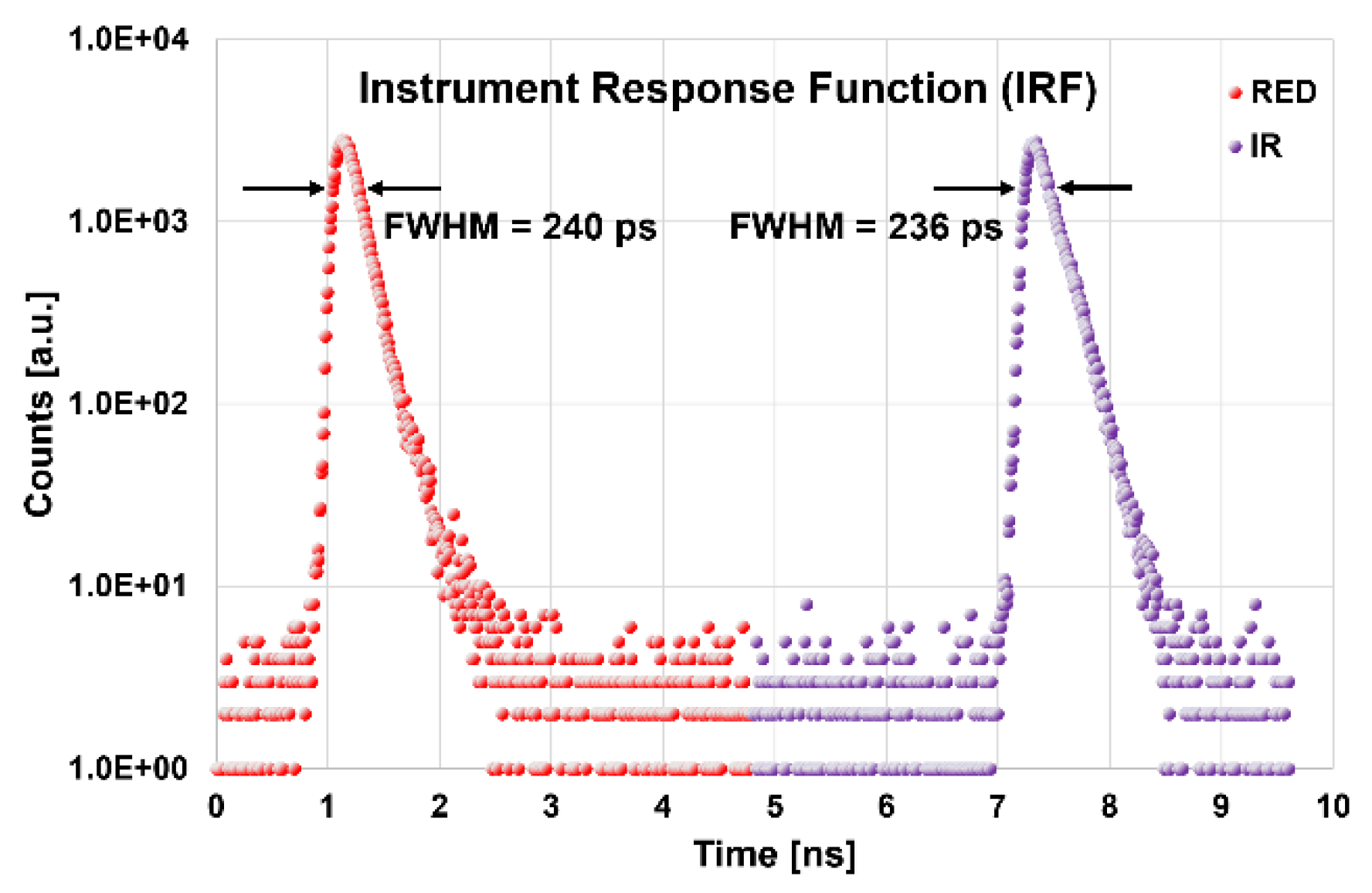
3.1. Basic Instrumental Performance (BIP)
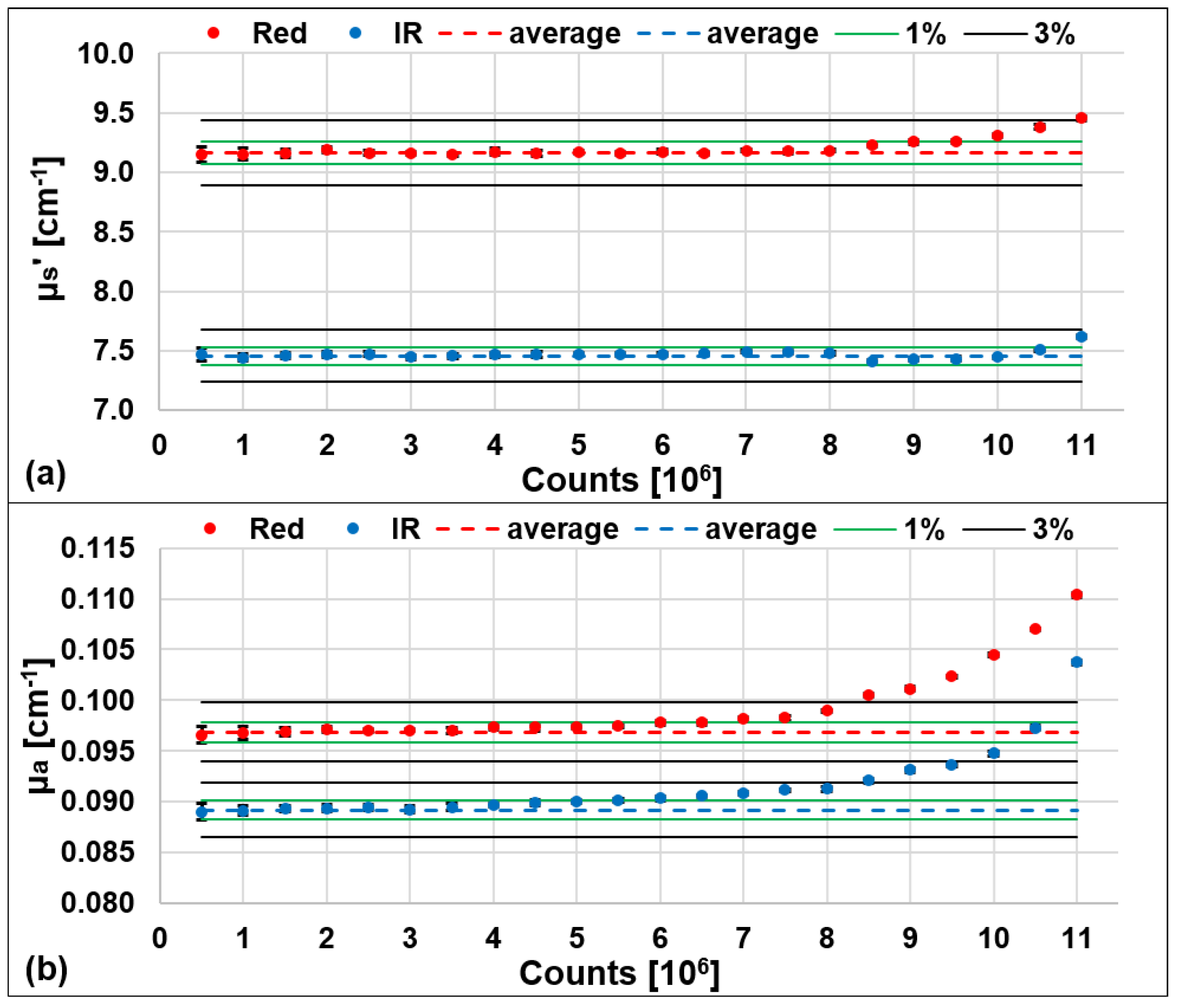
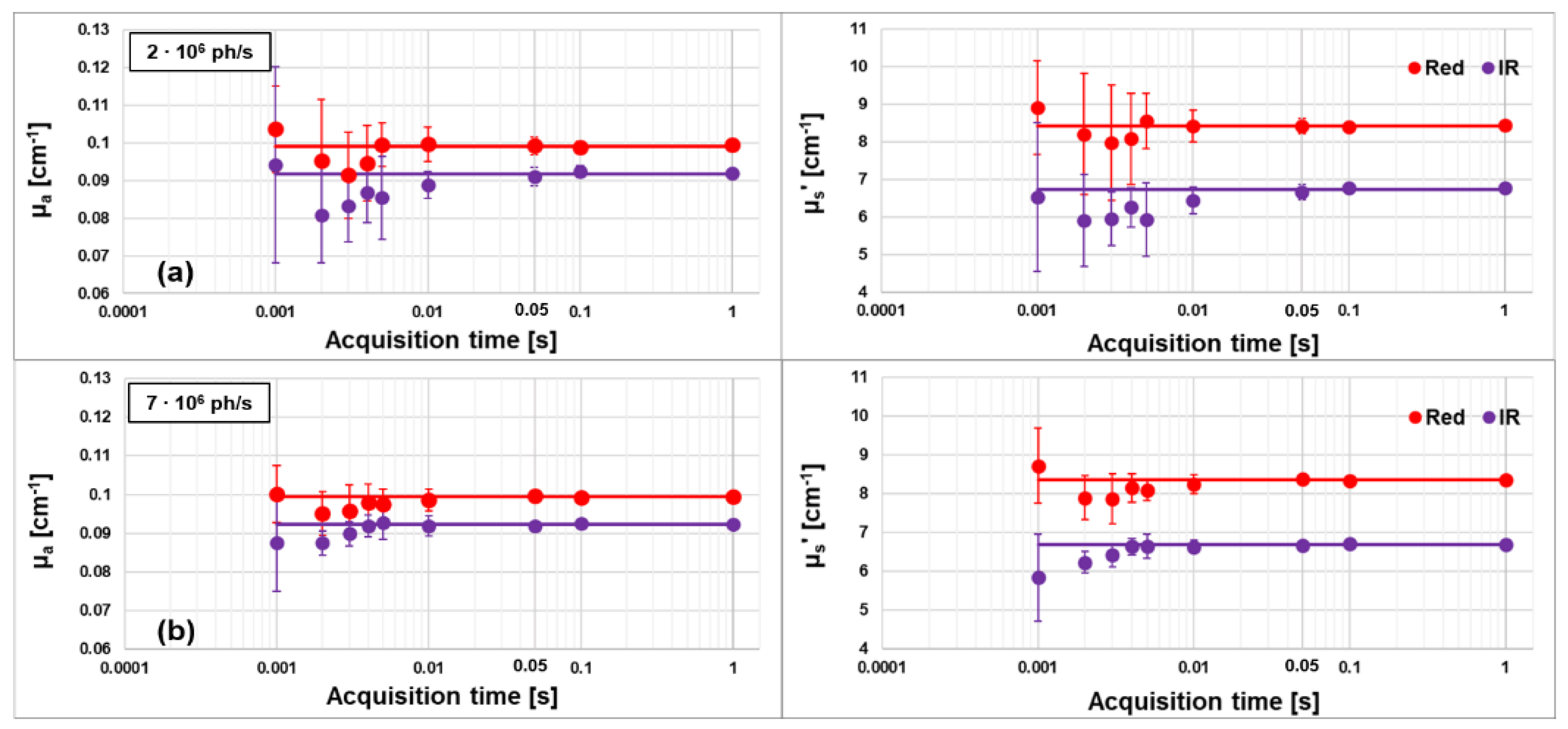
3.2. Assessment of the Maximum Count Rate and Acquisition Rate
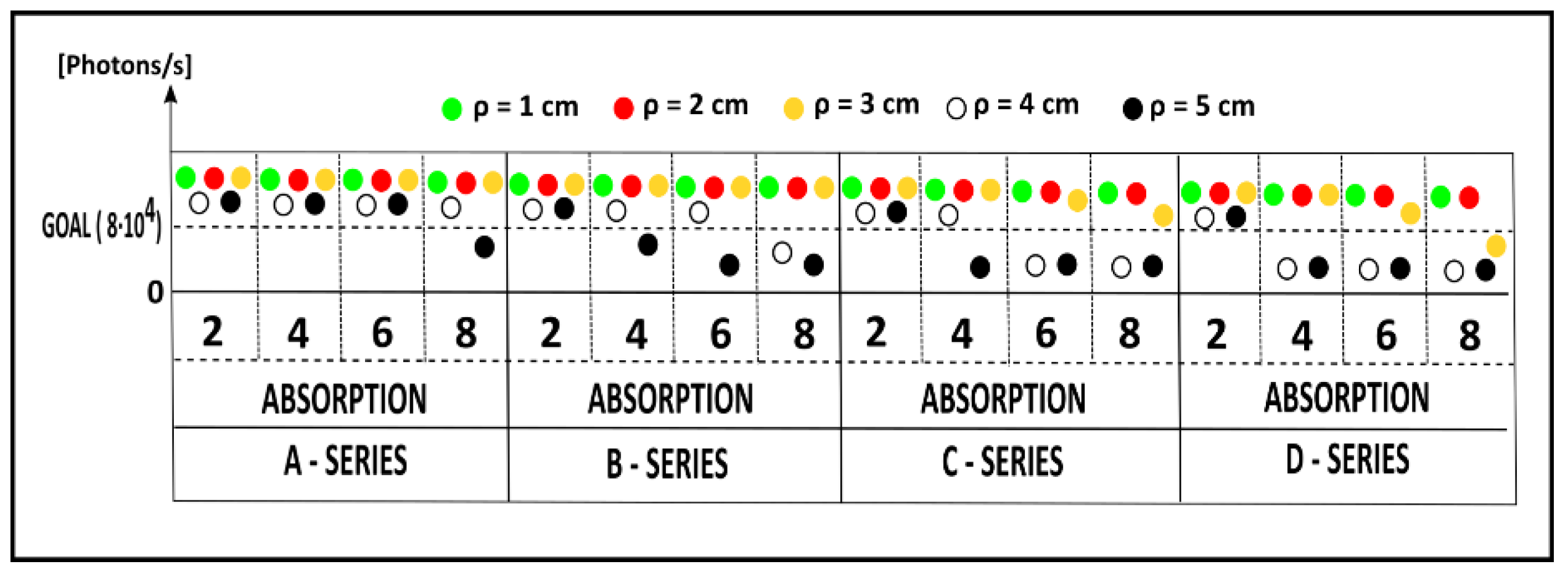
3.3. Further Characterizations
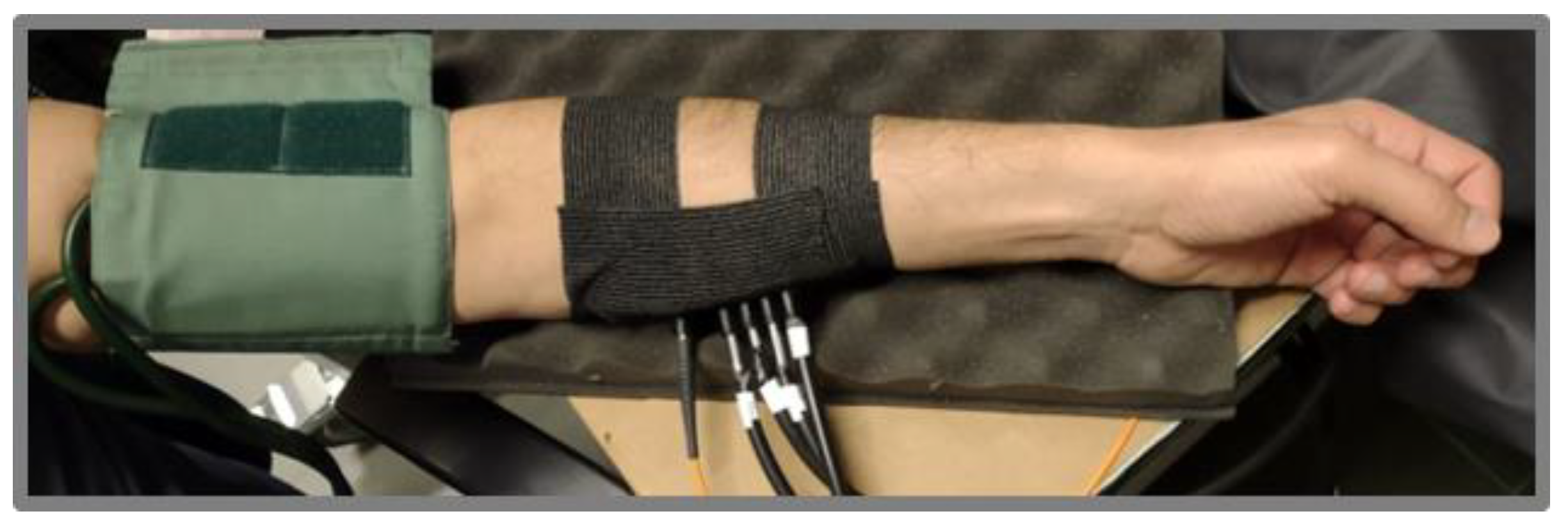
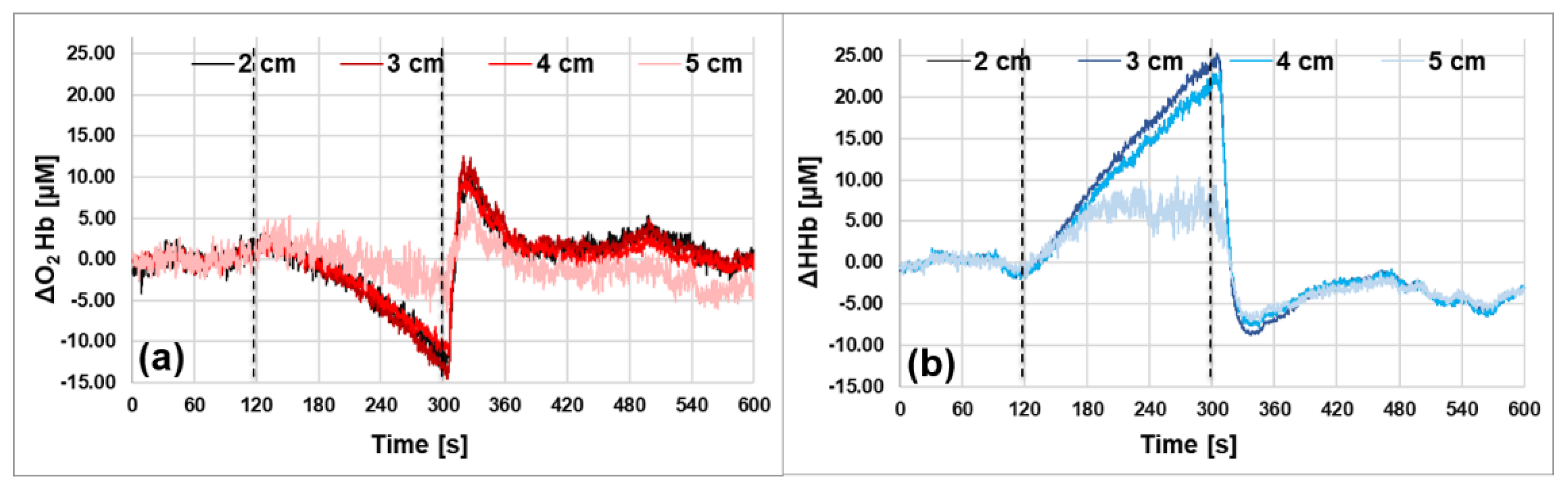
3.4. In Vivo Characterization Protocol: Arm Muscle Arterial Occlusion
4. Cortical Resting-State Oscillations: Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torricelli, A.; Contini, D.; Pifferi, A.; Caffini, M.; Re, R.; Zucchelli, L.; Spinelli, L. Time domain functional NIRS imaging for human brain mapping. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinciute, S. Translating the hemodynamic response: Why focused interdisciplinary integration should matter for the future of functional neuroimaging. PeerJ 2019, 2019, e6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; He, Y. Resting-state functional brain connectivity: Lessons from functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deco, G.; Jirsa, V.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Emerging concepts for the dynamical organization of resting-state activity in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 12, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villringer, A.; Planck, J.; Hock, C.; Schleinkofer, L.; Dirnagl, U. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS): A new tool to study hemodynamic changes during activation of brain function in human adults. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 154, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hong, K.S. Quantitative Assessment of Resting-State for Mild Cognitive Impairment Detection: A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Deep Learning Approach. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 80, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.H.; Bhattacharya, M.; Møller, K.; Kjeldsen, S.; Grand, J.; Kjaergaard, J.; Dutta, A.; Kondziella, D. Resting-State NIRS–EEG in Unresponsive Patients with Acute Brain Injury: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 34, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindra, J.; Pham, P.; Aneman, A.; Chuan, A.; Jaeger, M. Non-invasive Monitoring of Dynamic Cerebrovascular Autoregulation Using Near Infrared Spectroscopy and the Finometer Photoplethysmograph. Neurocrit. Care 2016, 24, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, S.; Homae, F.; Watanabe, H.; Taga, G. Frequency-specific functional connectivity in the brain during resting state revealed by NIRS. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrig, H.; Neufang, M.; Wenzel, R.; Kohl, M.; Steinbrink, J.; Einhäupl, K.; Villringer, A. Spontaneous Low Frequency Oscillations of Cerebral Hemodynamics and Metabolism in Human Adults. Neuroimage 2000, 12, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Deb Frederick, B. Time lag dependent multimodal processing of concurrent fMRI and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) data suggests a global circulatory origin for low-frequency oscillation signals in human brain. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham, T.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Fantini, S. Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics. Photonics 2019, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yamashita, Y. Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Imaging: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabnitz, H.; Jelzow, A.; Mazurenka, M.; Steinkellner, O.; MacDonald, R.; Milej, D.; Zołek, N.; Kacprzak, M.; Sawosz, P.; Maniewski, R.; et al. Performance assessment of time-domain optical brain imagers, part 2: NEUROPt protocol. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 086012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEC 60825-1:2007; Safety or Laser Products—Part1: Equipment Classification and Requirements. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Koga, S.; Barstow, T.J.; Okushima, D.; Rossiter, H.B.; Kondo, N.; Ohmae, E.; Poole, D.C. Validation of a high-power, time-resolved, near-infrared spectroscopy system for measurement of superficial and deep muscle deoxygenation during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Mata, A.D.C.; Lindner, S.; Lindner, S.; Lindner, S.; Charbon, E.; Wolf, M.; Kalyanov, A. 2.5 Hz sample rate time-domain near-infrared optical tomography based on SPAD-camera image tissue hemodynamics. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, H.Y.; Barrett, G.M.; Borisevich, A.; Chaturvedi, A.; Dahle, J.L.; Dehghani, H.; Dubois, J.; Field, R.M.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Gundran, A.; et al. Kernel Flow: A high channel count scalable time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy system. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 074710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Themelis, G.; Selb, J.; Thaker, S.; Stott, J.J.; Custo, A.; Boas, D.; Franceschini, M.A. Depth of arterial oscillation resolved with NIRS time and frequency domain. In Biomedical Topical Meeting; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. WF2. [Google Scholar]
- Kacprzak, M.; Sawosz, P.; Weigl, W.; Milej, D.; Gerega, A.; Liebert, A. Frequency analysis of oscillations in cerebral hemodynamics measured by time domain near infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Contini, D.; Caffini, M.; Cubeddu, R.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A. A compact time-resolved system for near infrared spectroscopy based on wavelength space multiplexing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, C.; Lacerenza, M.; Pirovano, I.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Cubeddu, R.; Torricelli, A.; Re, R. Optical characterization of 3D printed PLA and ABS filaments for diffuse optics applications. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Martelli, F.; Zaccanti, G. Photon migration through a turbid slab described by a model based on diffusion approximation I Theory. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wabnitz, H.; Taubert, D.R.; Mazurenka, M.; Steinkellner, O.; Jelzow, A.; Macdonald, R.; Milej, D.; Sawosz, P.; Kacprzak, M.; Liebert, A.; et al. Performance assessment of time-domain optical brain imagers, part 1: Basic instrumental performance protocol. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 086010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Muthalib, M.; Zucchelli, L.; Perrey, S.; Contini, D.; Caffini, M.; Spinelli, L.; Kerr, G.; Torricelli, A. Multichannel time domain fNIRS mapping of cortical activation and superficial systemic responses during neuromuscular electrical stimulation. In Proceedings of the Optics InfoBase Conference Papers; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Martinenghi, E.; Mora, A.D.; Contini, D.; Pifferi, A.; Torricelli, A. Probe-hosted silicon photomultipliers for time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy: Phantom and in vivo tests. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pirovano, I.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A. Time domain near infrared spectroscopy device for monitoring muscle oxidative metabolism: Custom probe and in vivo applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, L.; Martelli, F.; Farina, A.; Pifferi, A.; Torricelli, A.; Cubeddu, R.; Zaccanti, G. Accuracy of the nonlinear fitting procedure for time-resolved measurements on diffusive phantoms at NIR wavelengths. In Optical Tomography and Spectroscopy of Tissue VII; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 7174. [Google Scholar]
- Advanced Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Applications; Becker, W., Ed.; Springer Series in Chemical Physics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 111, ISBN 978-3-319-14928-8. [Google Scholar]
- Avanzi, E.; Behera, A.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Dalla Mora, A.; Di Sieno, L. Effects and correctability of pile-up distortion using established figures of merit in time-domain diffuse optics at extreme photon rates. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, A.; Torricelli, A.; Bassi, A.; Taroni, P.; Cubeddu, R.; Wabnitz, H.; Grosenick, D.; Möller, M.; Macdonald, R.; Swartling, J.; et al. Performance assessment of photon migration instruments: The MEDPHOT protocol. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Contini, D.; Turola, M.; Spinelli, L.; Zucchelli, L.; Caffini, M.; Cubeddu, R.; Torricelli, A. Multi-channel medical device for time domain functional near infrared spectroscopy based on wavelength space multiplexing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeck, M.; Koessler, L.; Bast, T.; Leijten, F.; Michel, C.; Baumgartner, C.; He, B.; Beniczky, S. The standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchelli, L.; Contini, D.; Re, R.; Torricelli, A.; Spinelli, L. Method for the discrimination of superficial and deep absorption variations by time domain fNIRS. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Hocke, L.M.; Licata, S.C.; Frederick, B.D. Low-frequency oscillations measured in the periphery with near-infrared spectroscopy are strongly correlated with blood oxygen level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging signals. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, M.A.; Selb, J.; Aasted, C.M.; Lin, P.; Borsook, D.; Becerra, L.; Boas, D.A.; Kvernmo, H.D.; Stefanovska, A.; Bracic, M.; et al. Mayer waves reduce the accuracy of estimated hemodynamic response functions in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, M.L.; Schmiedel, O.; Von Cramon, D.Y. Spontaneous low-frequency oscillations decline in the aging brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassaroli, A.; Pierro, M.; Bergethon, P.R.; Fantini, S. Low-Frequency Spontaneous Oscillations of Cerebral Hemodynamics Investigated With Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2012, 18, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intaglietta, M. Vasomotion and flowmotion: Physiological mechanisms and clinical evidence. Vasc. Med. Rev. 1990, vmr-1, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, G.H.; Li, T.-Q.; Ress, D. Image-Based Method for Retrospective Correction of Physiological Motion Effects in fMRI: Retroicor. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, R.C.; Franceschini, M.A.; Boas, D.A.; Murphy, K.; Birn, R.M.; Handwerker, D.A.; Jones, T.B.; Bandettini, P.A.; Arieli, A.; Sterkin, A.; et al. Functional connectivity in single and multislice echoplanar imaging using resting-state fluctuations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 37, 184–192. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Re, R.; Pirovano, I.; Contini, D.; Amendola, C.; Contini, L.; Frabasile, L.; Levoni, P.; Torricelli, A.; Spinelli, L. Reliable Fast (20 Hz) Acquisition Rate by a TD fNIRS Device: Brain Resting-State Oscillation Studies. Sensors 2023, 23, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010196
Re R, Pirovano I, Contini D, Amendola C, Contini L, Frabasile L, Levoni P, Torricelli A, Spinelli L. Reliable Fast (20 Hz) Acquisition Rate by a TD fNIRS Device: Brain Resting-State Oscillation Studies. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010196
Chicago/Turabian StyleRe, Rebecca, Ileana Pirovano, Davide Contini, Caterina Amendola, Letizia Contini, Lorenzo Frabasile, Pietro Levoni, Alessandro Torricelli, and Lorenzo Spinelli. 2023. "Reliable Fast (20 Hz) Acquisition Rate by a TD fNIRS Device: Brain Resting-State Oscillation Studies" Sensors 23, no. 1: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010196
APA StyleRe, R., Pirovano, I., Contini, D., Amendola, C., Contini, L., Frabasile, L., Levoni, P., Torricelli, A., & Spinelli, L. (2023). Reliable Fast (20 Hz) Acquisition Rate by a TD fNIRS Device: Brain Resting-State Oscillation Studies. Sensors, 23(1), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010196








