Computer Vision Algorithms of DigitSeis for Building a Vectorised Dataset of Historical Seismograms from the Archive of Royal Observatory of Belgium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Motivation
1.3. Related Work
1.4. Contribution
2. Materials and Methods
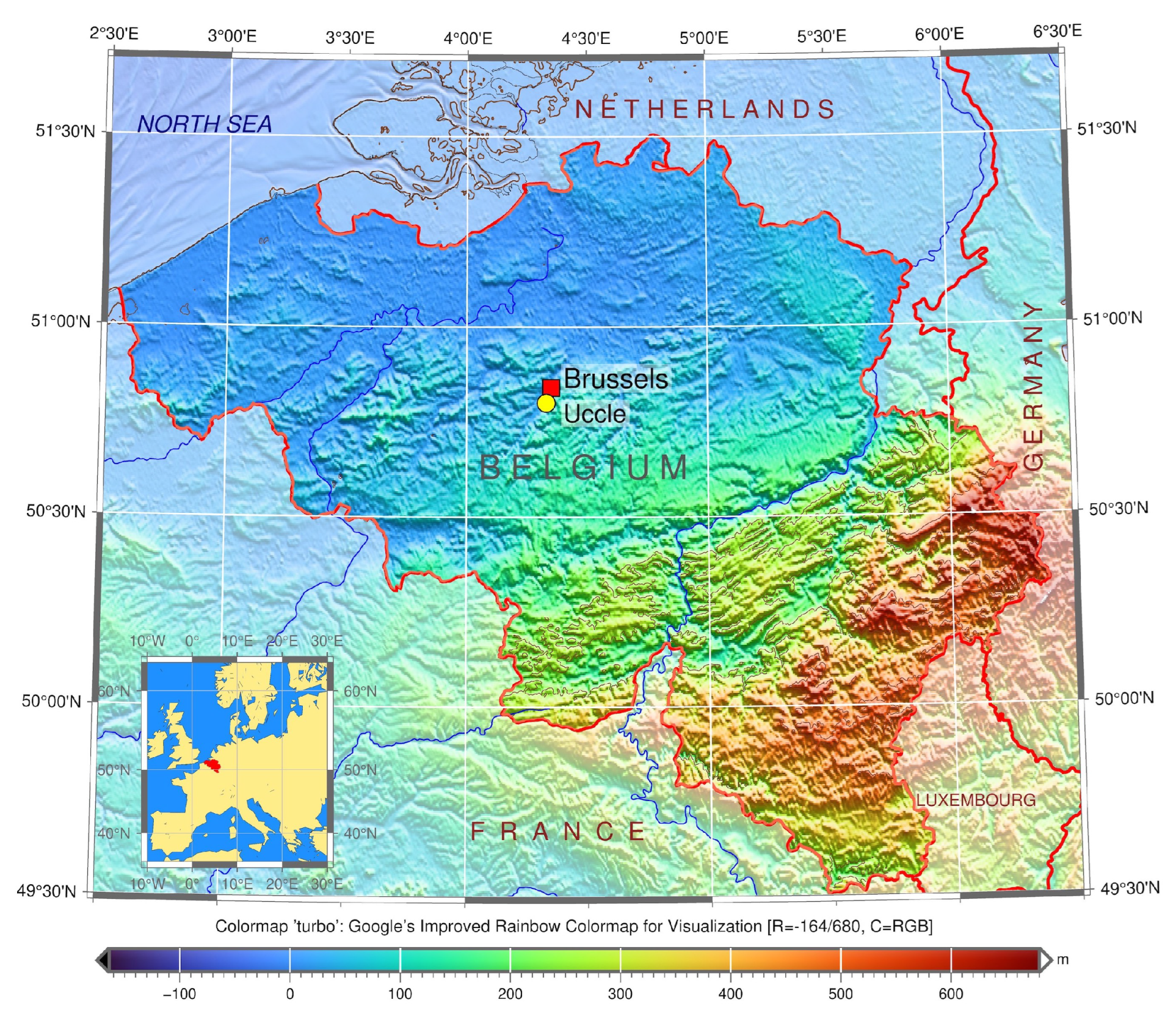
2.1. Study Area
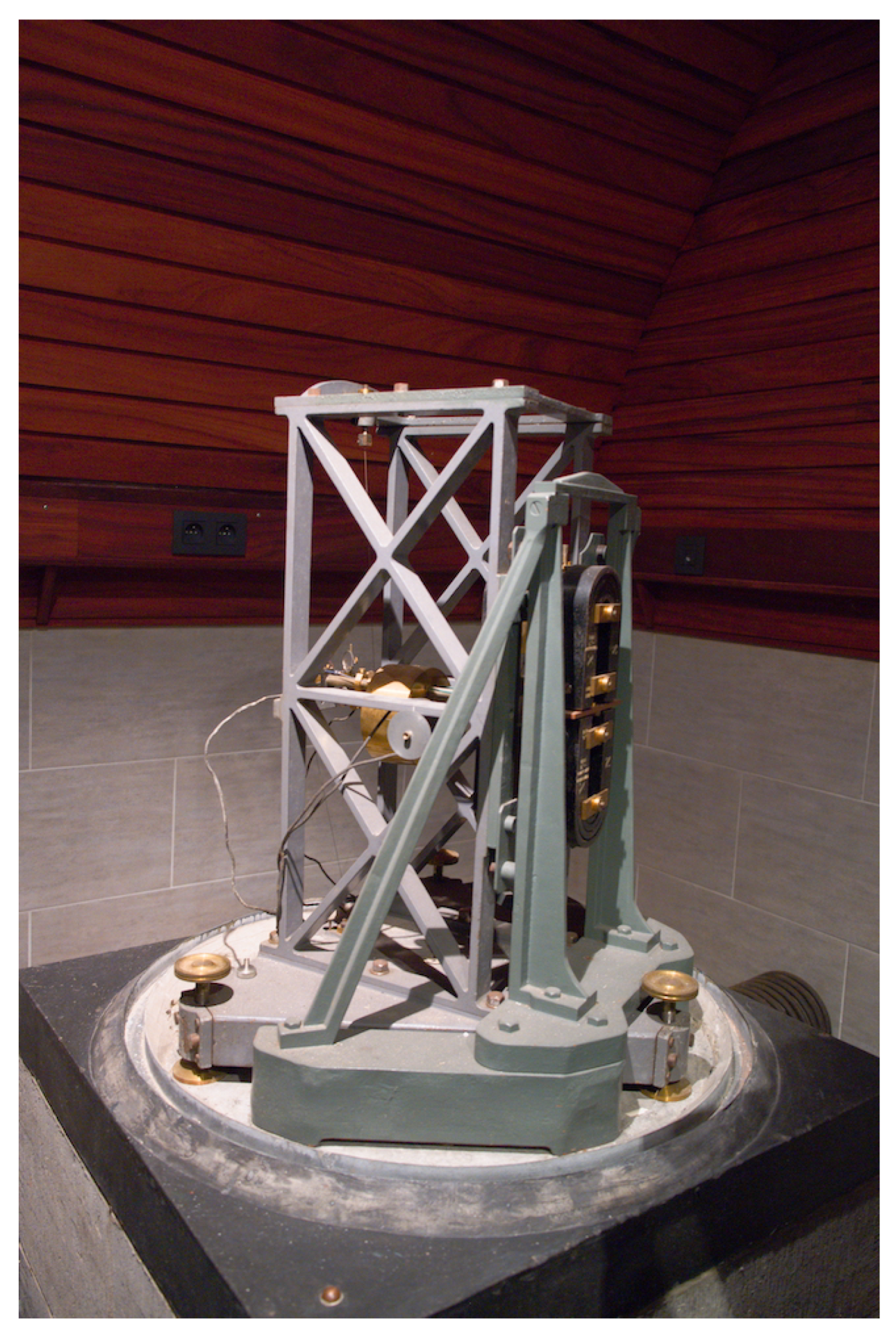
2.2. Instrument
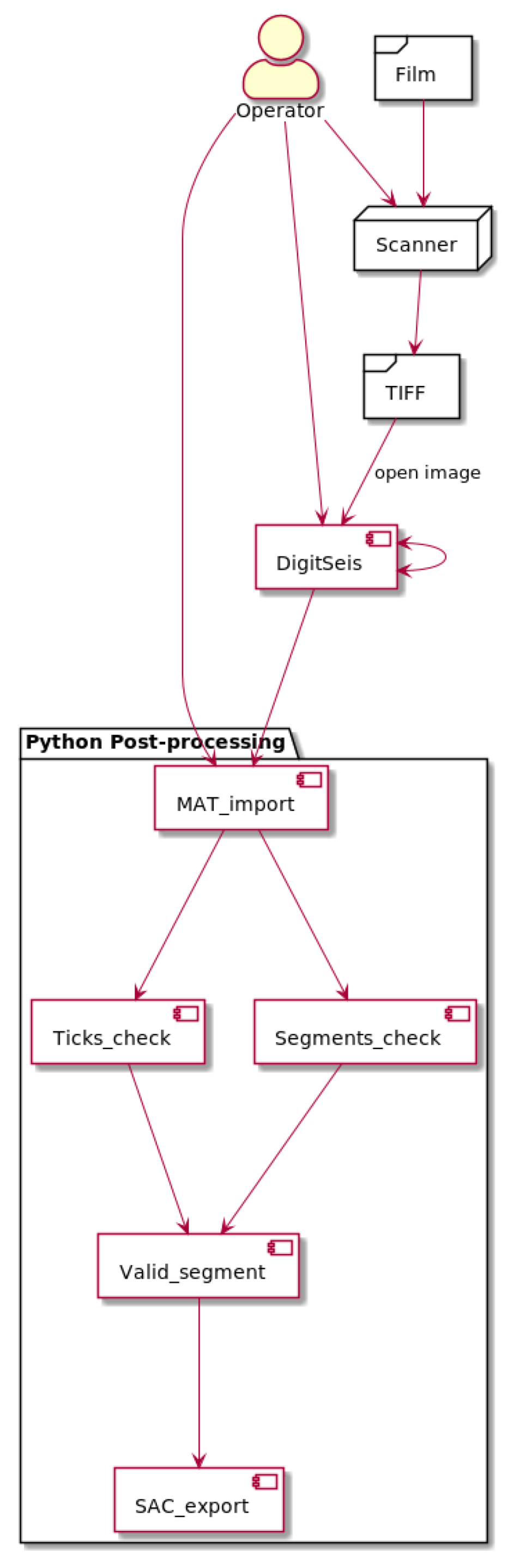
2.3. Workflow
2.4. Data
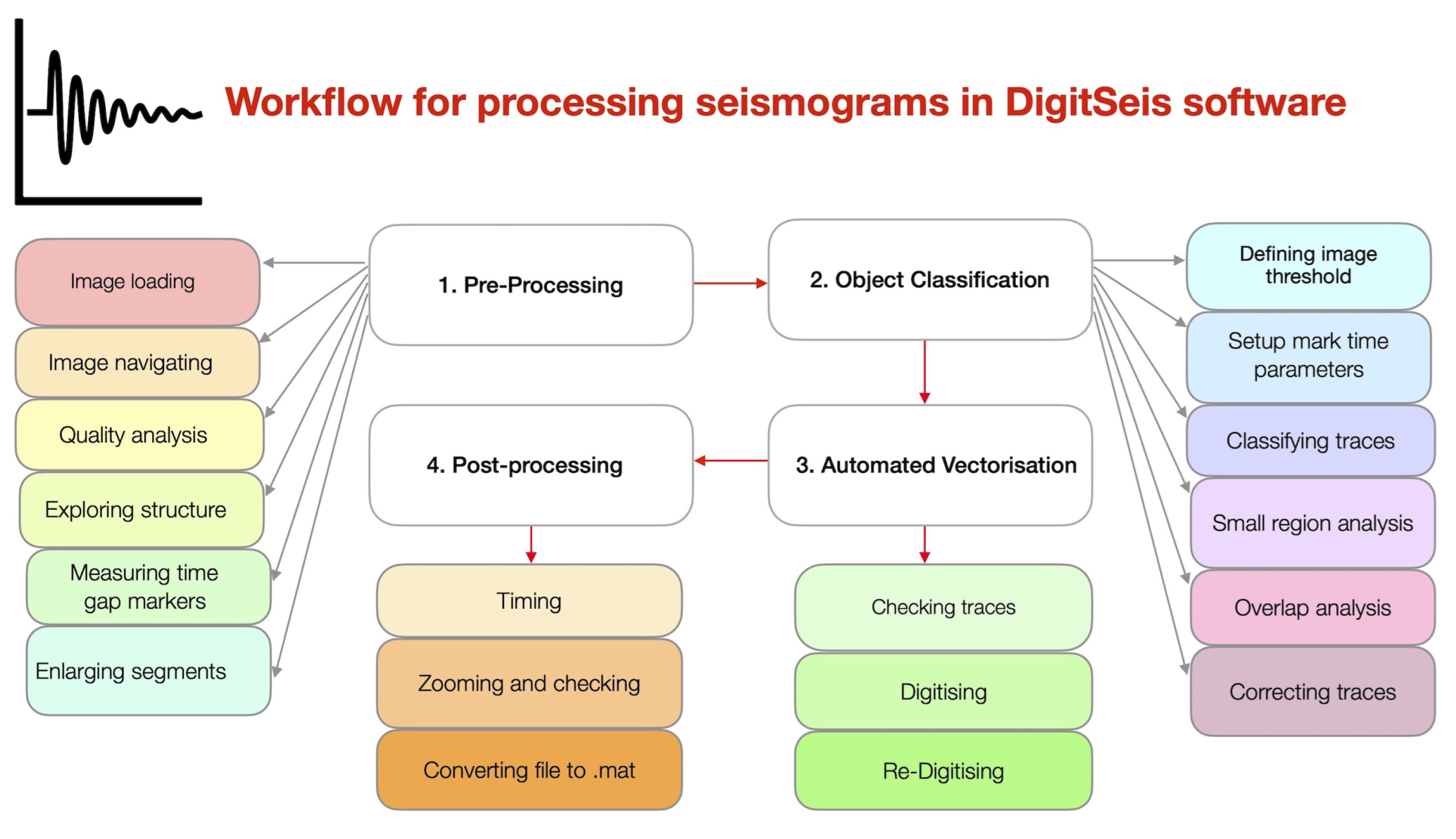
2.5. Software and Workflow
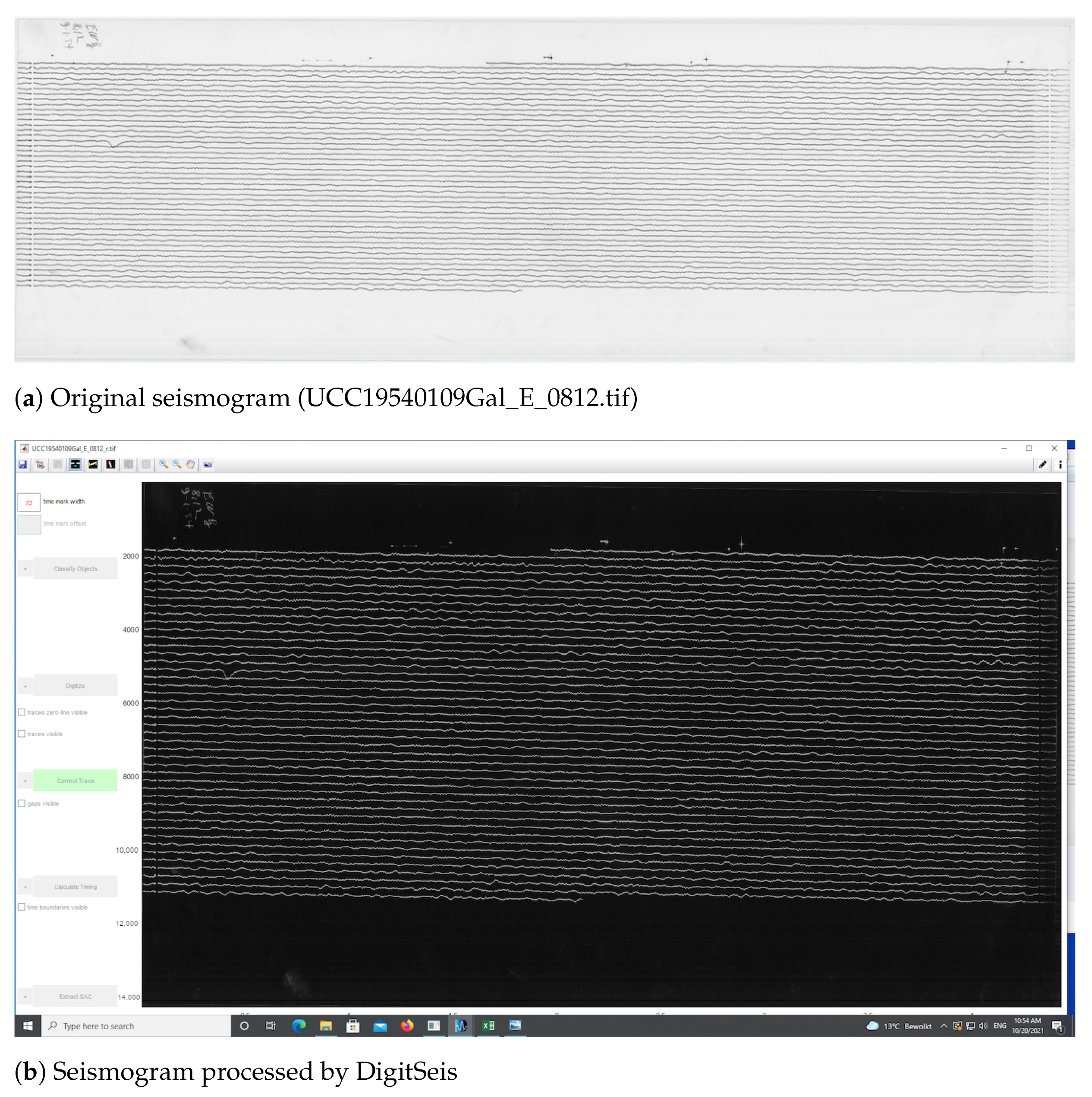
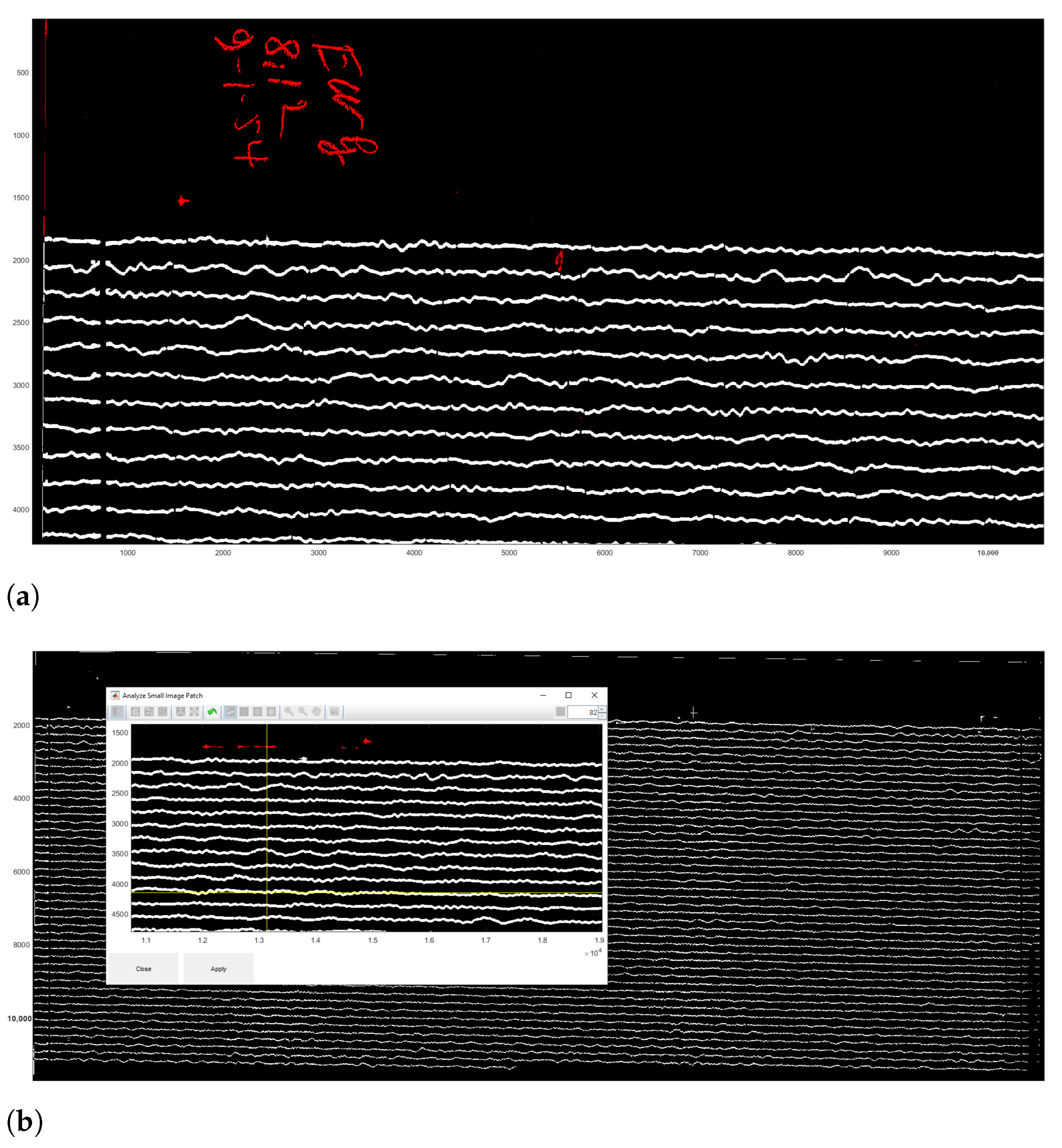
2.5.1. Image Preprocessing
2.5.2. Identifying theTime Gaps
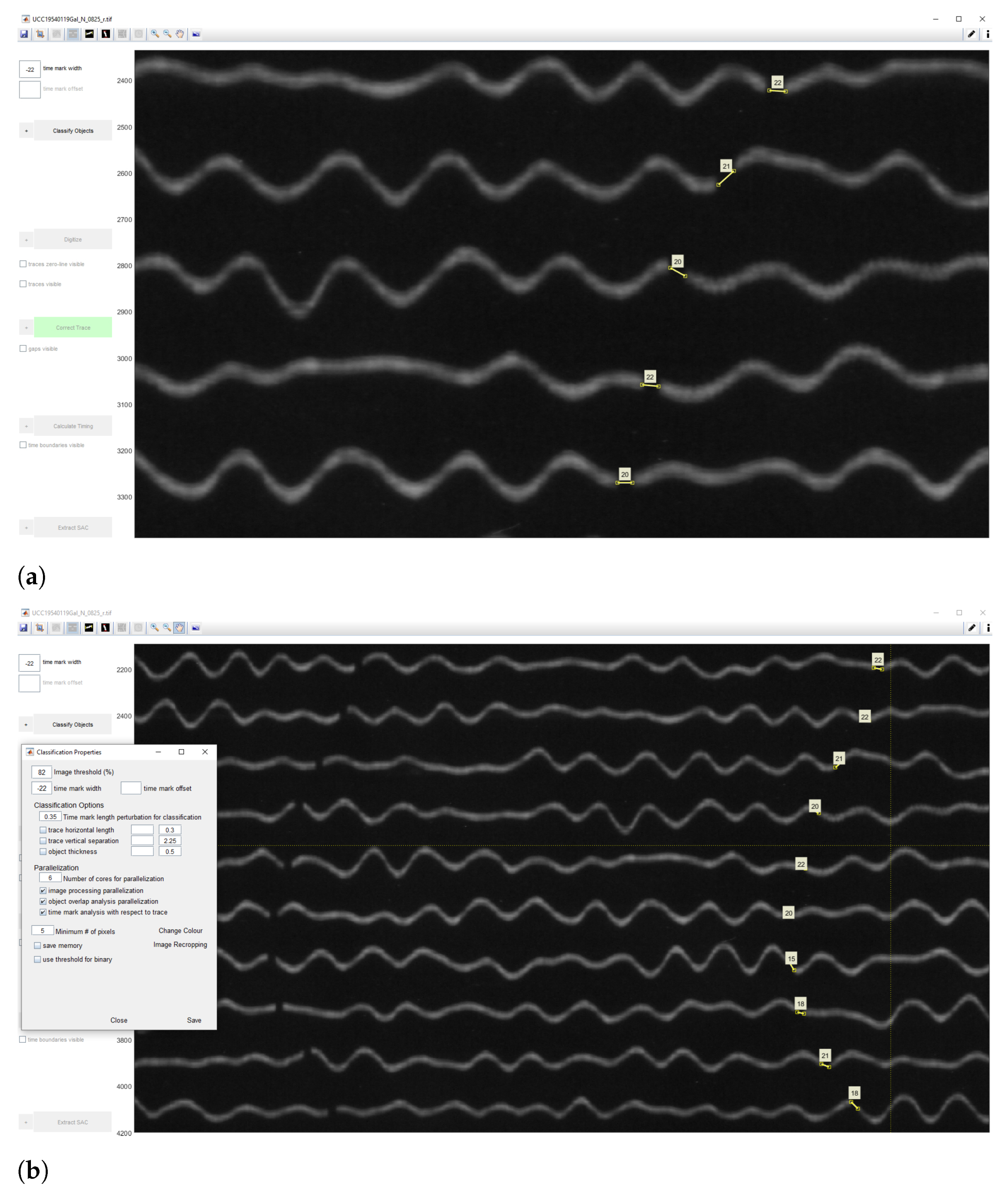
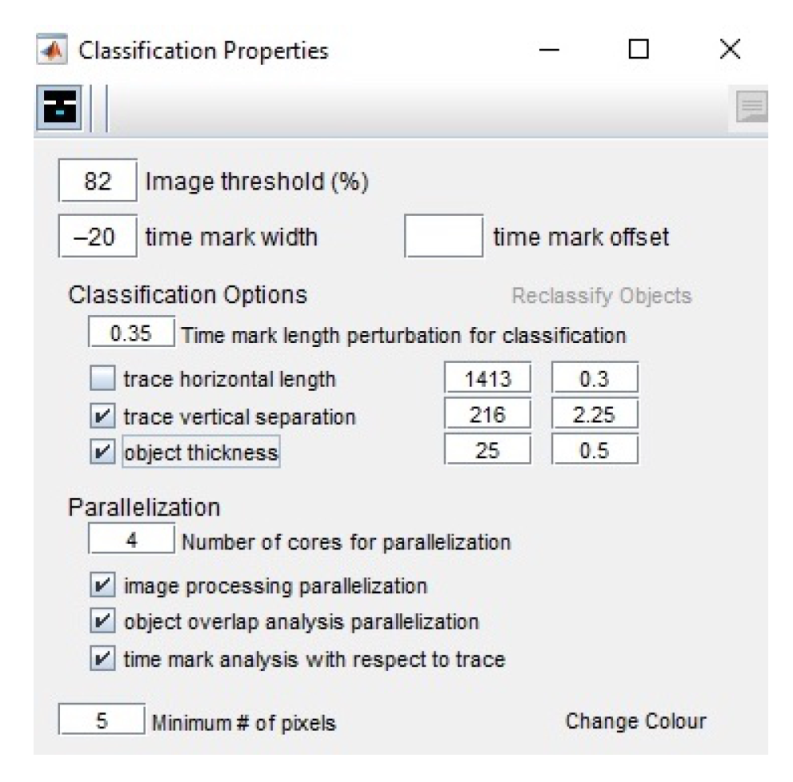
2.5.3. Classification
3. Results
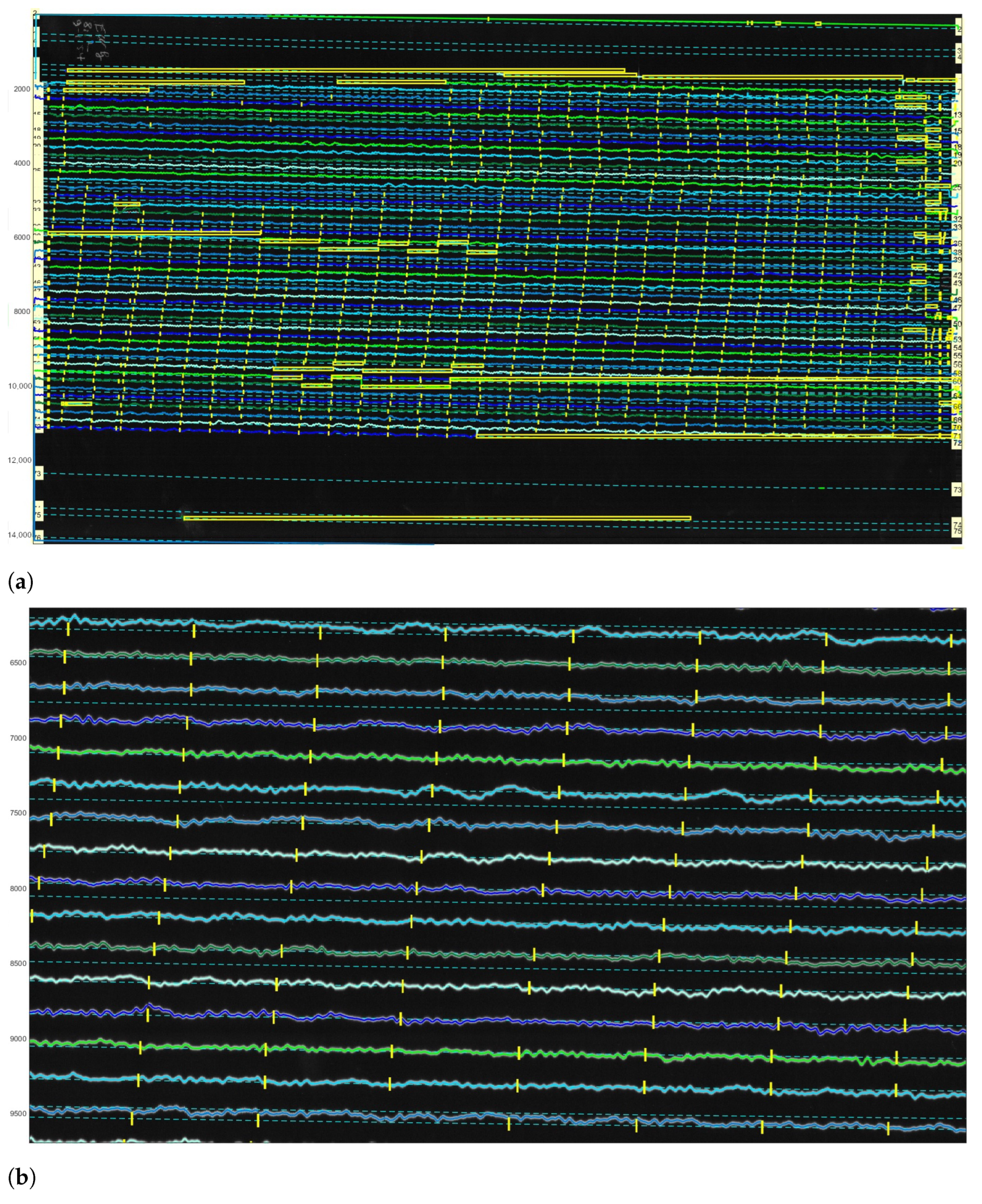
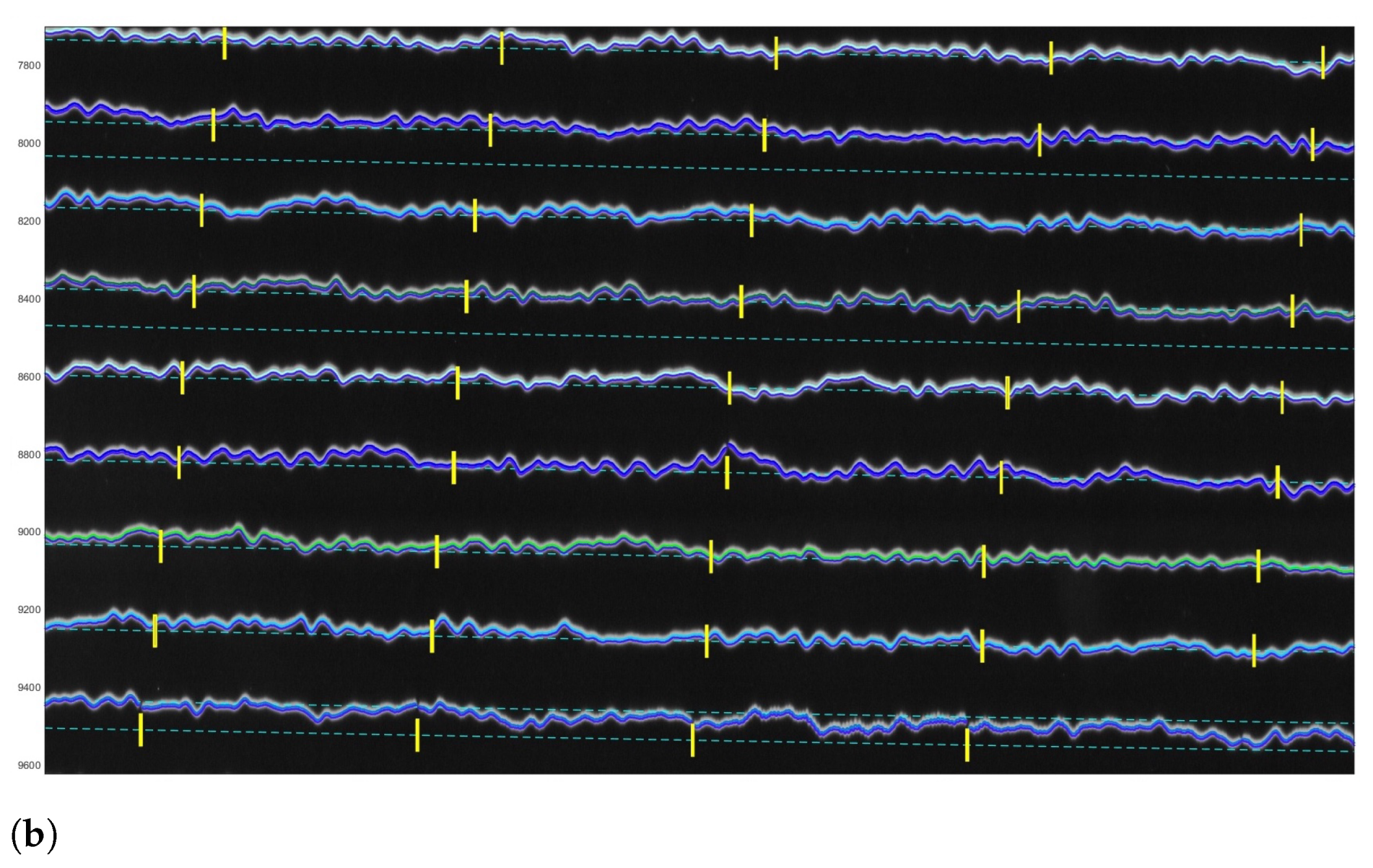
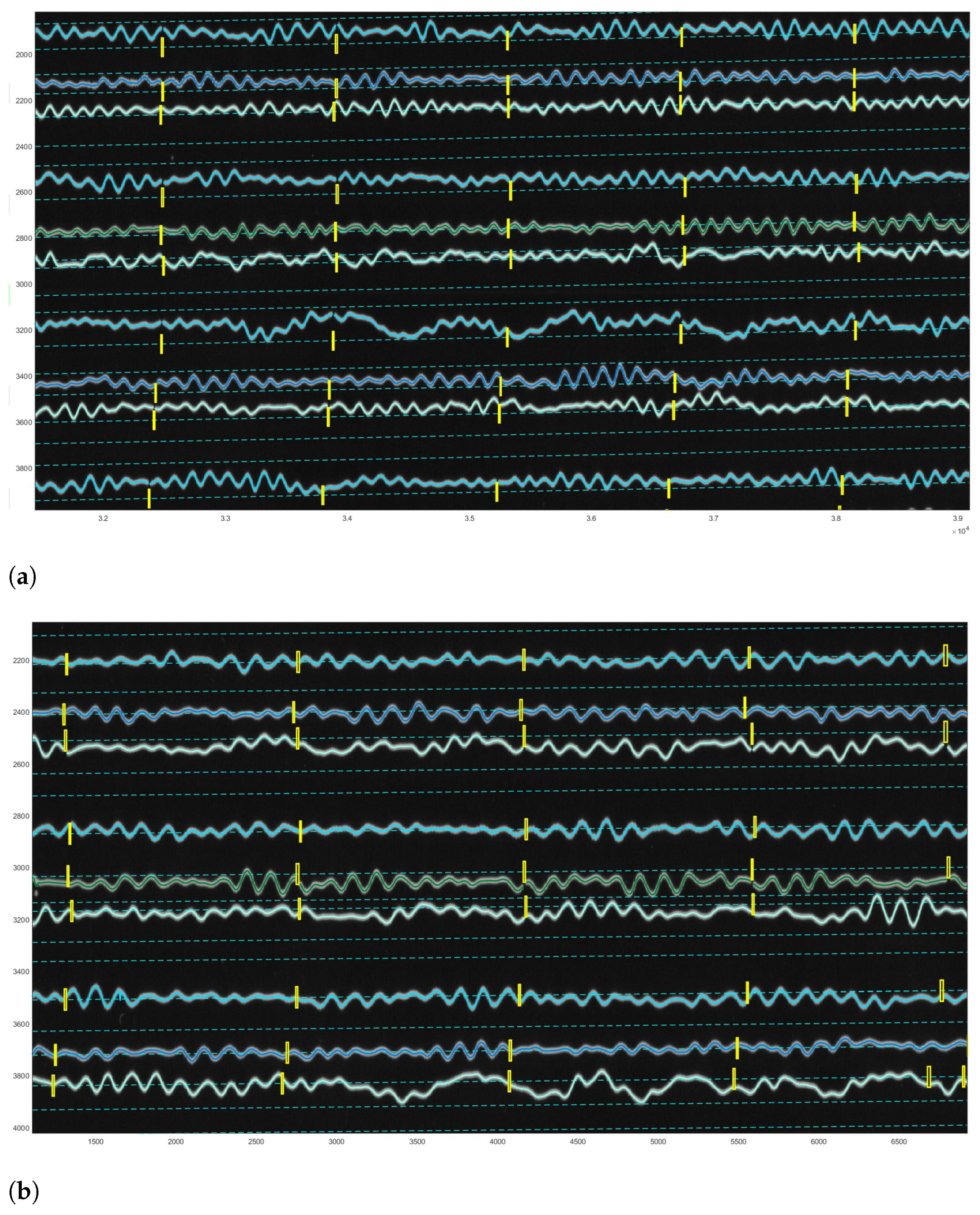
3.1. Vectorisation
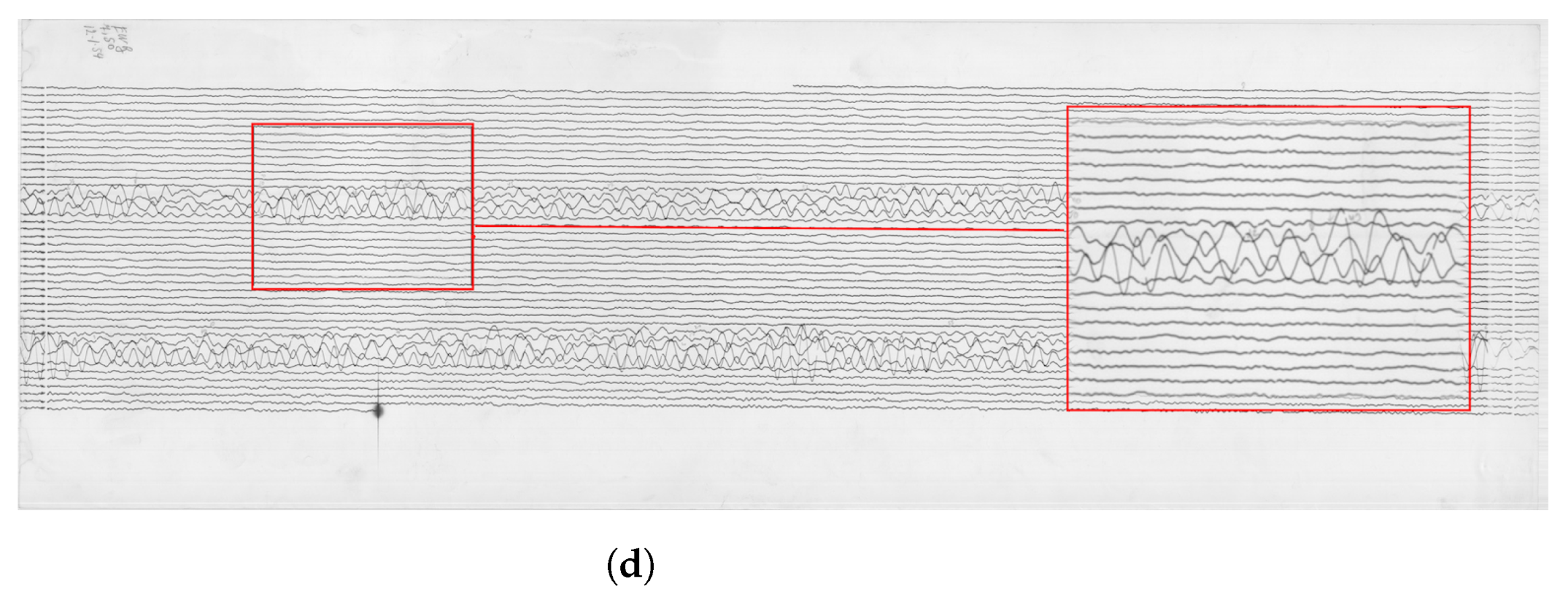
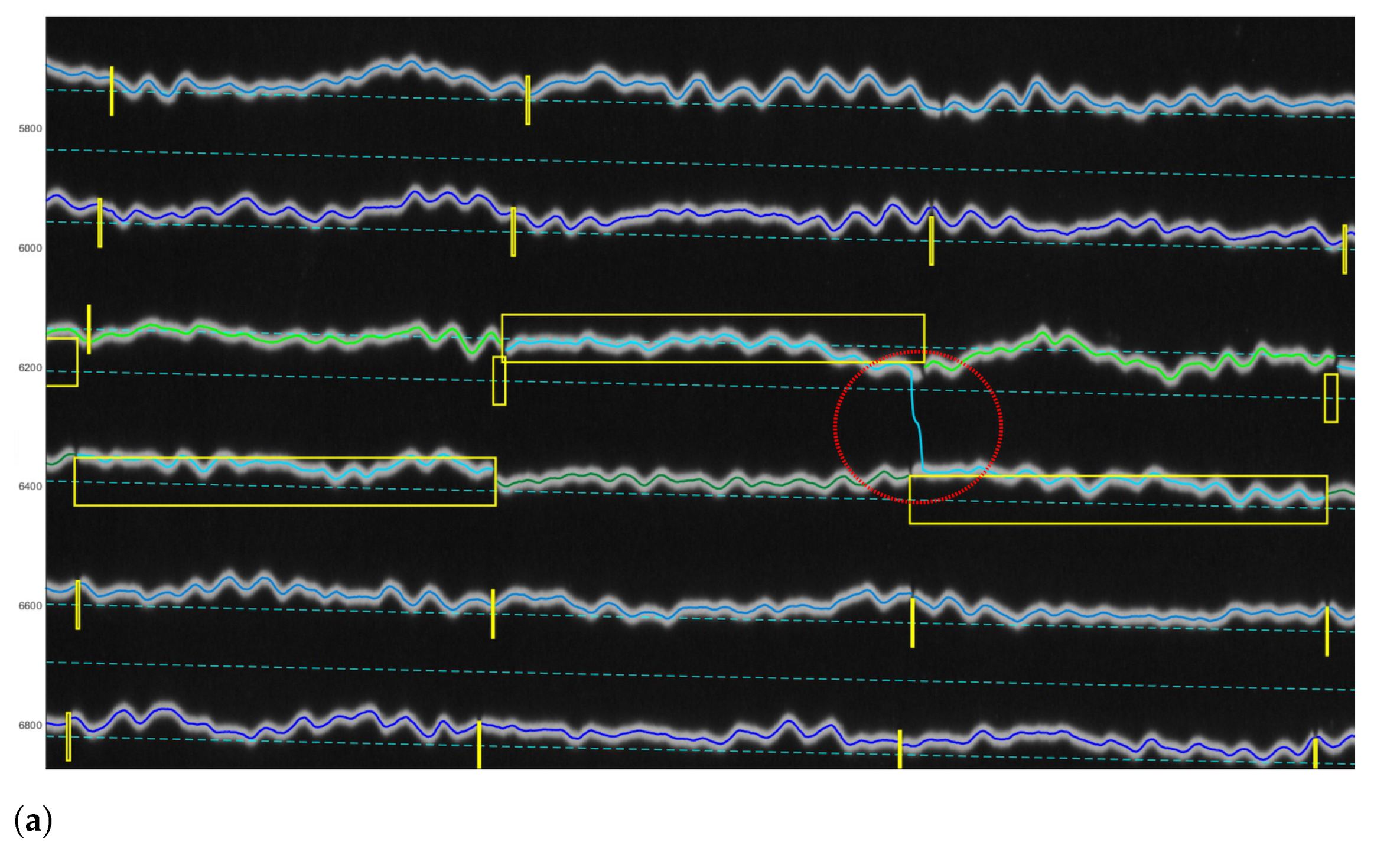
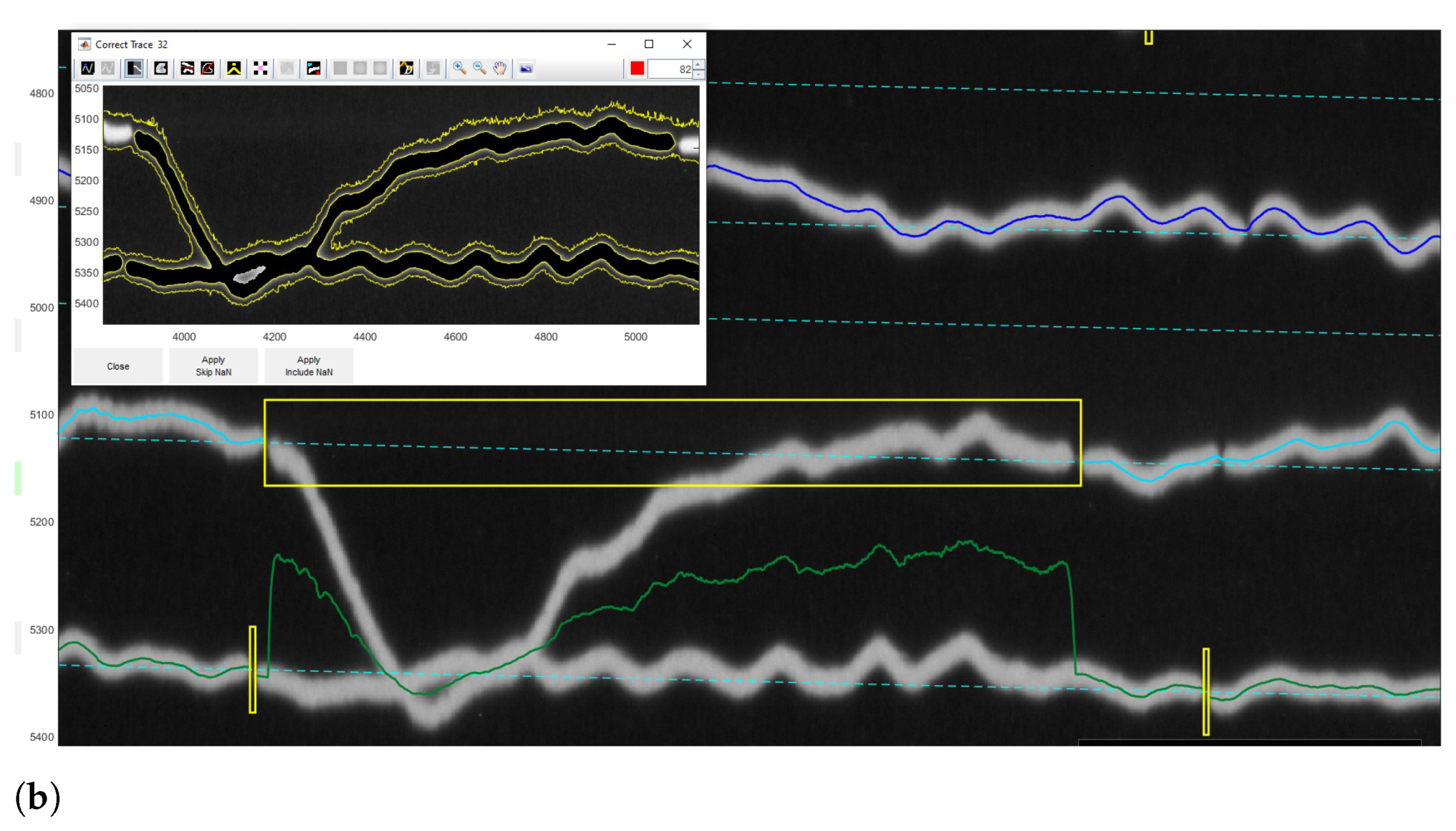
3.2. Post-Processing: Correcting Traces
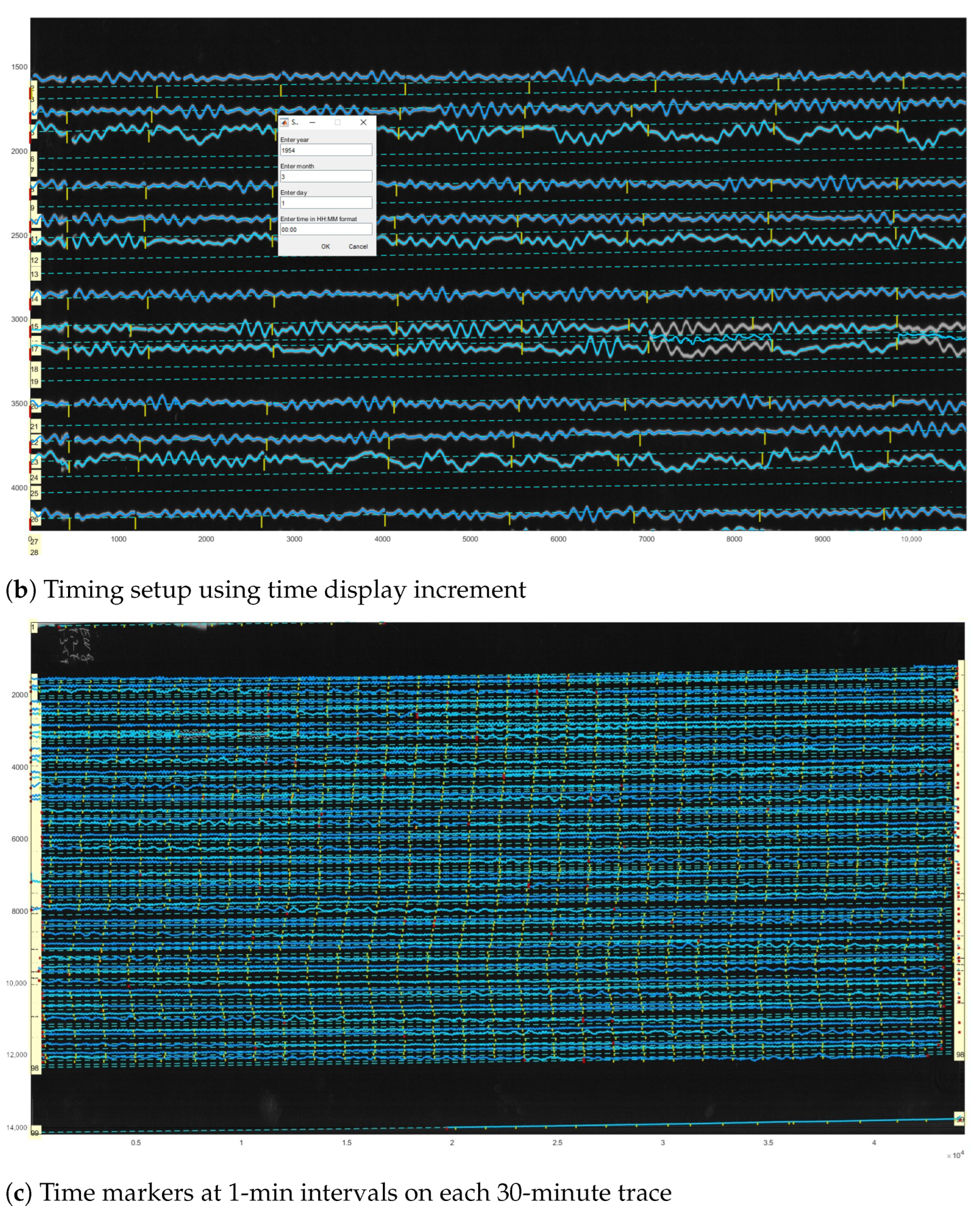
3.3. Timing and Converting
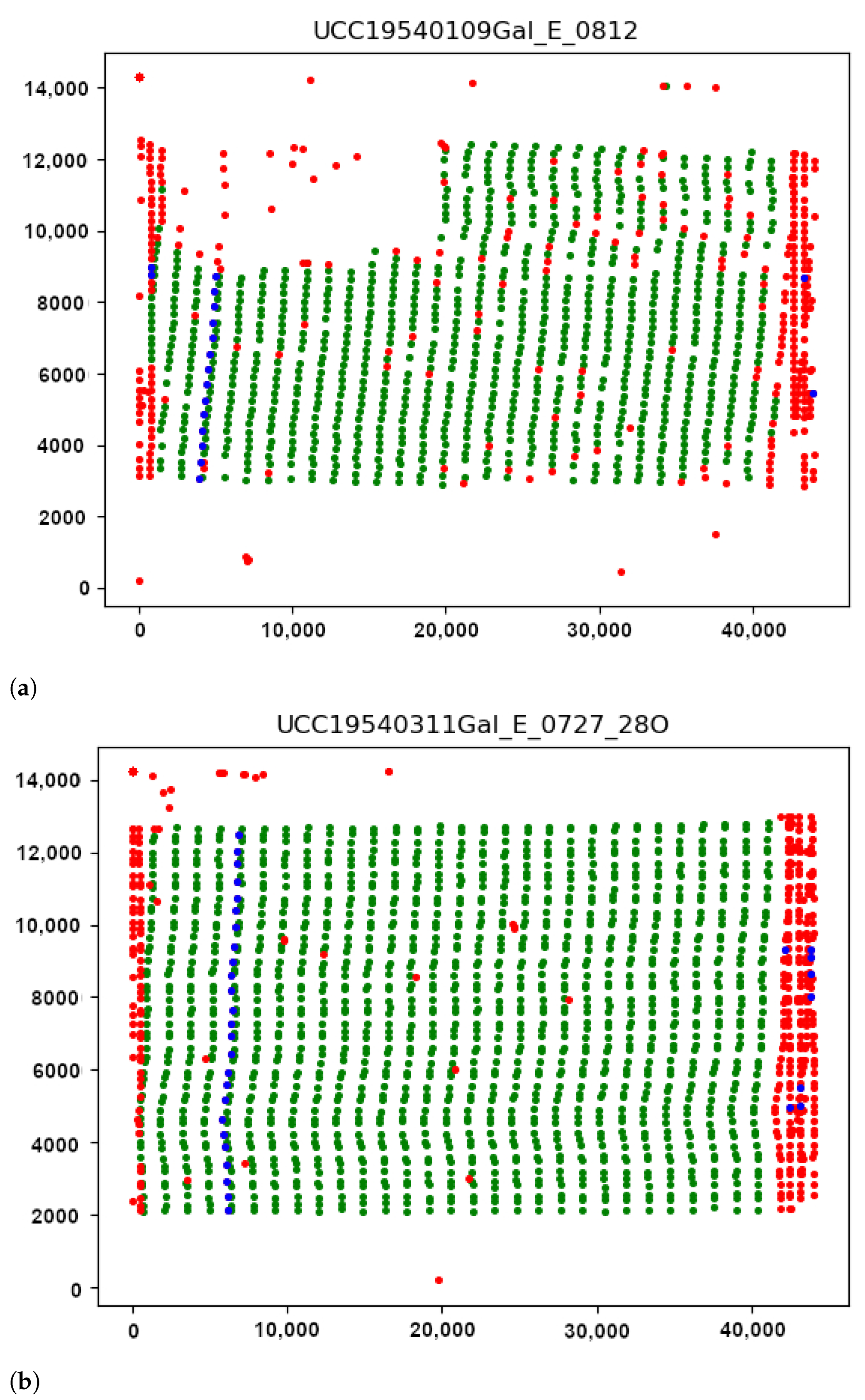
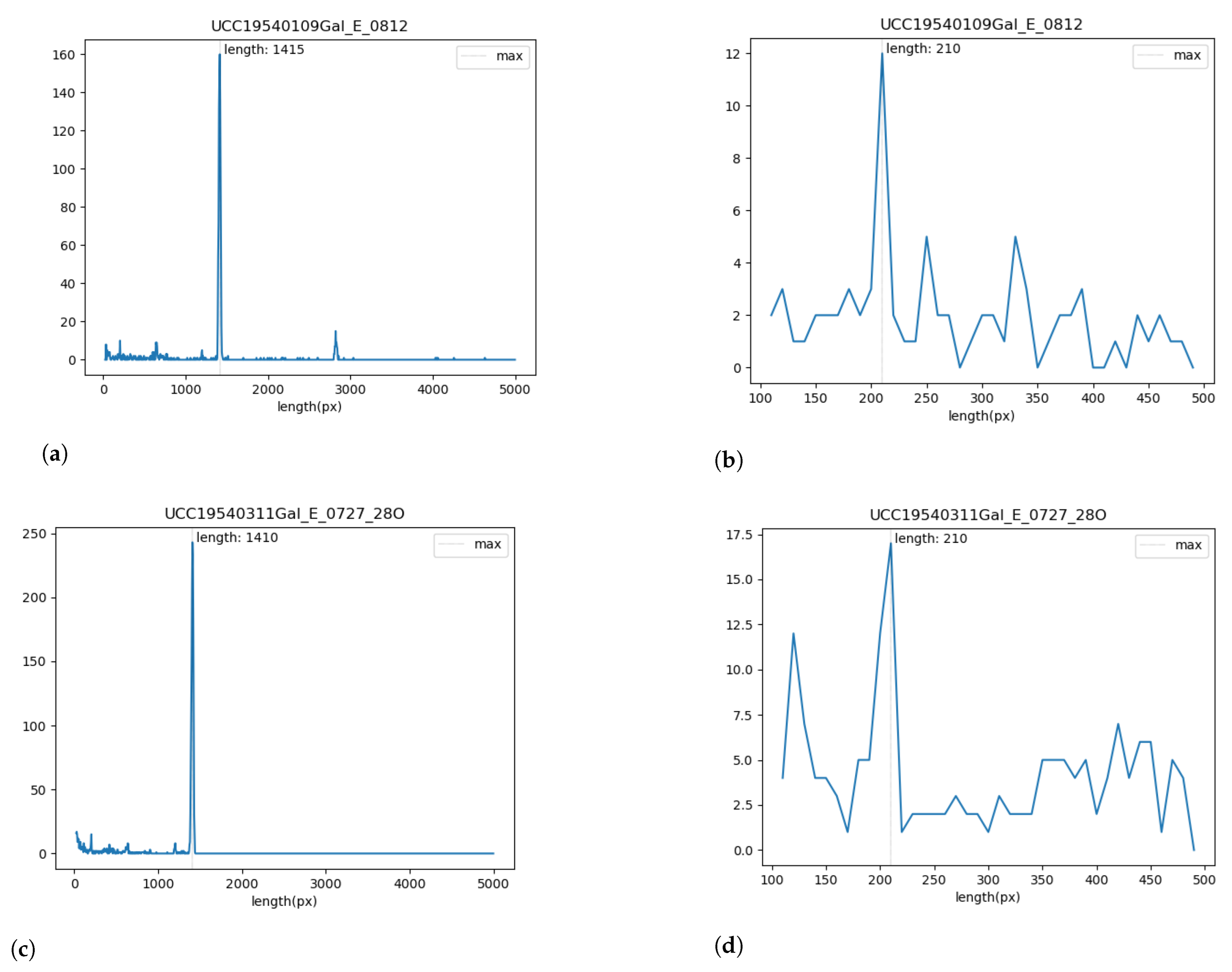
3.4. Validating theResults UsingPython
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| WWSSN | World-Wide Standardized Seismograph Network |
| EO | Earth Observation |
| IRIS | Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology |
| GMT | Generic Mapping Tools |
| UCC | Uccle seismic station |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| DFT | Discrete Fourier Transform |
| IFT | Inverse Fourier Transform |
| HSV | Hue, Saturation, Value |
| ROB | Royal Observatory of Belgium |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
References
- Gutenberg, B.; Richter, C.F. Seismicity of the Earth and Associated Phenomena; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Shearer, P. Introduction to Seismology, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udías, A.; Buforn, E. Principles of Seismology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakata, N.; Gualtieri, L.; Fichtner, A. Introduction. In Seismic Ambient Noise; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. xx–xxviii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.; Byerly, P. The history of seismometry to 1900. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1979, 11, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Agnew, D.C. History of seismology. In International Handbook of Earthquake and Engineering Seismology; Lee, W.H.K., Kanamori, H., Jennins, P.C., Kisslinger, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 81A, pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer, J.; Lee, W. 88—Old Seismic Bulletins to 1920: A Collective Heritage from Early Seismologists. In International Handbook of Earthquake and Engineering Seismology, Part B. International Geophysics; Lee, W.H., Kanamori, H., Jennings, P.C., Kisslinger, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 81, pp. 1665–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlló, J.; Stich, D.; Macià, R. Quantitative Analysis of Early Seismograph Recordings. In Historical Seismology. Modern Approaches in Solid Earth Sciences; Fréchet, J., Meghraoui, M., Stucchi, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, J.; Yu, X.; Lin, N.; Feng, S.; Liu, C. A New Waveform Mosaic Algorithm in the Vectorization of Paper Seismograms. Sens. Transduc. 2014, 182, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- An, V.A.; Ovtchinnikov, V.M.; Kaazik, P.B.; Adushkin, V.V.; Sokolova, I.N.; Aleschenko, I.B.; Mikhailova, N.N.; Kim, W.Y.; Richards, P.G.; Patton, H.J.; et al. A digital seismogram archive of nuclear explosion signals, recorded at the Borovoye Geophysical Observatory, Kazakhstan, from 1966 to 1996. GeoResJ 2015, 6, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engdahl, E.R.; Villaseñor, A. Global seismicity: 1900–1999. In International Handbook of Earthquake and Engineering Seismology; Lee, W.H.K., Jennings, P., Kisslinger, C., Kanamori, H., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 665–690. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.; Murphy, L. WWNSS: Seismology’s Global Network of Observing Stations. Science 1971, 174, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammon, C.J.; Lay, T.; Simpson, D.W. Great Earthquakes and Global Seismic Network. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2010, 81, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiner, I. Computational Seismology: A Practical Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori, H.; Rivera, L.; Lee, W.H.K. Historical seismograms for unravelling a mysterious earthquake: The 1907 Sumatra Earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 183, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bungum, H.; Pettenati, F.; Schweitzer, J.; Sirovich, L.; Faleide, J.I. The 23 October 1904 MS 5.4 Oslofjord earthquake: Reanalysis based on macroseismic and instrumental data. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 2836–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, H.; Rivera, L.; Ye, L.; Lay, T.; Murotani, S.; Tsumura, K. New constraints on the 1922 Atacama, Chile, earthquake from Historical seismograms. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 219, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomnitz, C. Major Earthquakes of Chile: A Historical Survey, 1535–1960. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2004, 75, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambraseys, N.N. Notes on historical seismicity. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, C.J.; Velasco, A.A.; Lay, T.; Wallace, T.C. Seismogram interpretation and processing. In Foundations of Modern Global Seismology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Chapter 5; pp. 141–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhánek, O. Anatomy of seismograms. In Developments in Solid Earth Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lecocq, T.; Ardhuin, F.; Collin, F.; Camelbeeck, T. On the Extraction of Microseismic Ground Motion from Analog Seismograms for the Validation of Ocean-Climate Models. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampin, S.; Peacock, S. A review of the current understanding of seismic shear-wave splitting in the Earth’s crust and common fallacies in interpretation. Wave Motion 2008, 45, 675–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.A. 31—Using Earthquakes for Continental Tectonic Geology. Int. Geophys. 2002, 81, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, S.; Lucazeau, F.; d’Acremont, E.; Watremez, L.; Autin, J.; Rouzo, S.; Bellahsen, N.; Tiberi, C.; Ebinger, C.; Beslier, M.O.; et al. Contrasted styles of rifting in the eastern Gulf of Aden: A combined wide-angle, multichannel seismic, and heat flow survey. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, D.W. Macroseismic Effects of the Liège Earthquake with Particular Reference to Industrial Installations. In Seismic Activity in Western Europe; NATO ASI Series (Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences); Melchior, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 144, pp. 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilecki, Z.; Isakow, Z.; Czarny, R.; Pilecka, E.; Harba, P.; Barnaśa, M. Capabilities of seismic and georadar 2D/3D imaging of shallow subsurface of transport route using the Seismobile system. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 143, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzeja, J. Seismometric monitoring in the area of the Piekary Śląskie junction of the A1 motorway in terms of recording the vibrations resulting from mining tremors. J. Sustain. Min. 2017, 16, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahorner, L.; Camelbeeck, T.; De Becker, M.; Flick, J.; Ritsema, R.; Houtgast, G.; Vogt, J. Macroseismic Map of the Liège Earthquake of November 8, 1983. In Seismic Activity in Western Europe; NATO ASI Series (Seriec C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences); Melchior, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 144, pp. 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, R.; Seydoux, L.; Beaucé, E.; Campillo, M. Hierarchical exploration of continuous seismograms with unsupervised learning. Earth Space Sci. Open Arch. 2021, 127, e2021JB022455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorèse, D.; Benjumea, J.; Cara, M. Source parameters of the 1926 and 1927 Jersey earthquakes from historical, instrumental, and macroseismic data. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2020, 300, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomnitz, C. Fundamentals of Earthquake Prediction; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yuliatmoko, R.S.; Kurniawan, T.; Vita, A.N.; Rohadi, S.; Riama, N.F.; Gunawan, I.; Karnawati, D.K. Estimation site effect from the seismogram. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2320, 040023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzo, E.D. Chapter 13 Seismic Wave Scattering in Volcanoes. Adv. Geophys. 2008, 50, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratdomopurbo, A.; Poupinet, G. Monitoring a temporal change of seismic velocity in a volcano: Application to the 1992 eruption of Mt. Merapi (Indonesia). Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordret, A.; Mikesell, T.D.; Harig, C.; Lipovsky, B.P.; Prieto, G.A. Monitoring southwest Greenland’s ice sheet melt with ambient seismic noise. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemenkova, P.; Debeir, O. Seismotectonics of Shallow-Focus Earthquakes in Venezuela with Links to Gravity Anomalies and Geologic Heterogeneity Mapped by a GMT Scripting Language. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenguier, F.; Campillo, M.; Takeda, T.; Aoki, Y.; Shapiro, N.; Briand, X.; Emoto, K.; Miyake, H. Mapping pressurized volcanic fluids from induced crustal seismic velocity drops. Science 2014, 345, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. GEBCO Gridded Bathymetric Datasets for Mapping Japan Trench Geomorphology by Means of GMT Scripting Toolset. Geod. Cartogr. 2020, 46, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszus, B.; Goes, S.; Allen, R.; Rietbrock, A.; Collier, J.; Harmon, N.; Henstock, T.; Hicks, S.; Rychert, C.A.; Maunder, B.; et al. Subduction history of the Caribbean from upper-mantle seismic imaging and plate reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P.; Debeir, O. Satellite Image Processing by Python and R Using Landsat 9 OLI/TIRS and SRTM DEM Data on Côte d’Ivoire, West Africa. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. NOAA Marine Geophysical Data and a GEBCO Grid for the Topographical Analysis of Japanese Archipelago by Means of GRASS GIS and GDAL Library. GEomatics Environ. Eng. 2020, 14, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kind, R.; Priestley, K.; Sobolev, S.V.; Tilmann, F.; Yuan, X.; Weber, M. Mapping the Hawaiian plume conduit with converted seismic waves. Nature 2000, 405, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhuin, F.; Stutzmann, E.; Schimmel, M.; Mangeney, A. Ocean wave sources of seismic noise. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucan, J.; Ardhuin, F. Infragravity waves in the deep ocean: An upward revision. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3435–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peureux, C.; Ardhuin, F. Ocean bottom pressure records from the Cascadia array and short surface gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 2862–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, T.; Rajendran, C.P.; Kumar, S. Dynamic terranes: Surface deformation, seismicity, and climate change. Quat. Int. 2021, 585, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, G.; Takenaka, H.; Kanao, M.; Tsuboi, S.; Tono, Y. Numerical modeling of seismic waves for estimating the influence of the Greenland ice sheet on observed seismograms. Polar Sci. 2015, 9, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromirski, P.D.; Flick, R.E.; Graham, N. Ocean wave height determined from inland seismometer data: Implications for investigating wave climate changes in the NE Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 20753–20766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.F.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.R.; Magalhaes, R.; Vanthillo, R.; Zhan, Z.; González-Herráez, M.; Martins, H.F. Distributed sensing of microseisms and teleseisms with submarine dark fibers. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, J.; Cadiot, B.; Lambert, J. Problèmes de sismicité historique: Exemples de faux séismes, de séismes méconnus et de séismes réinterprétés dans l’ensemble Allemagne/Belgique/Nord-Ouest de la France/Sud de Grande-Bretagne. In Seismic Activity in Western Europe with Particular Consideration to the Liège Earthquake of 8 November 1983; NATO ASI Series, Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; Volume 144, pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teves-Costa, P.; Borges, J.F.; Rio, I.; Ribeiro, R.; Marreiros, C. Source parameters of old earthquakes: Semi-automatic digitization of analog records and seismic moment assessment. Nat. Hazards 1999, 19, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, A. Historical seismometry database project: A comprehensive relational database for historical seismic records. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okal, E.A. Historical seismograms: Preserving an endangered species. GeoResJ 2015, 6, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandre, P. La séismicité historique du Hainaut, de la Flandre et de l’Artois de 700 à 1800. Tecton. Actuelle Récente Belg. Ann. Soc. Géol. Belg. 1990, 112, 329–344. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre, P. Catalogue des Séismes Survenus au Moyen Age en Belgique et dans les Regions Voisines. In Seismic Activity in Western Europe; NATO ASI Series (Seriec C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences); Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 144, pp. 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, P. Les Séismes en Europe Occidentale de 394 à 1259. Nouveau Catalogue Critique; Série Géophysique, Bruxelles; Hors-série; Observatoire Royal de Belgique: Uccle, Belgium, 1990; pp. 1–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori, H. Importance of Historical Seismograms for Geophysical Research. In Historical Seismograms and Earthquakes of the World; Lee, W.H.K., Meyers, H., Shimazaki, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Claerbout, J.F. Earth Soundings Analysis: Processing Versus Inversion; Blackwell Scientific: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosch, H. Automatic Digitization of Seismograms. Geophys. J. Int. 1975, 42, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, W.M.; Allen, D.C. Reading seismograms with digital computers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, W.P.; Latchman, J.L. A Microprocessor-Based System for Digitizing Seismic Events from Magnetic-Tape Recordings. Comput. Geosci. 1983, 9, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, C.B.; Matuschka, T. Digitization noise and accelerograph pen offset associated with Japanese accelerograms. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbaum, F. Inverse and simulation filtering of digital seismograms. In Of Poles and Zeros. Fundamentals of Digital Seismology. Modern Approaches in Geophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 15, pp. 132–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlund, U.; Griffiths, C.M. Automatic Construction of Two- and Three-Dimensional Chronostratigraphic Sections from Digitized Seismic Data. Comput. Geosci. 1993, 19, 1185–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, T.M. High-resolution marine reflection profiling for engineering and environmental purposes. Part B: Digitizing analogue seismic signals. J. Appl. Geophys. 1995, 33, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Harjes, H.P.; Jost, M.L.; Schweitzer, J.; Gestermann, N. Automatic Seismogram Analysis at GERESS. Comput. Geosci. 1993, 19, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbaum, F. Analog-to-digital conversion. In Of Poles and Zeros. Fundamentals of Digital Seismology. Modern Approaches in Geophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 15, pp. 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbaum, F. The measurement of wavelet parameters from digital seismograms. In Of Poles and Zeros. Fundamentals of Digital Seismology. Modern Approaches in Geophysics; Scherbaum, F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 15, pp. 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhao, G.; Han, B. Digitalizing Seismograms Using a Neighborhood Backtracking Method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management (KSEM 2016), Passau, Germany, 5–7 October 2016; Lehner, F., Fteimi, N., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9983, pp. 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Ishii, H.; Bernier, B.; Bulat, E. Efforts to Recover and Digitize Analog Seismograms from Harvard-Adam Dziewoński Observatory. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2015, 86, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenke, H.W.; Lemenkova, P. Zur Frage der Meeresboden-Kartographie: Die Nutzung von AutoTrace Digitizer für die Vektorisierung der Bathymetrischen Daten in der Petschora-See. Hydrogr. Nachrichten 2008, 81, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunac, M.D.; Lee, V.W.; Todorovska, M.I. Common problems in automatic digitization of strong motion accelerograms. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1999, 18, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoutas, I.G.; Kalogeras, I.S.; Kourouzidis, M.; Panopoulou, G. A modern technique for the retrieval and processing of historical seismograms in Greece. Nat. Hazards 2000, 21, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, R. Practical Python Syntax. In Earth Observation Using Python; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 2021; Chapter 4; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzillard, J.M. Taxonomy-Focused Natural Product Databases for Carbon-13 NMR-Based Dereplication. Analytica 2021, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenkova, P. Statistical Analysis of the Mariana Trench Geomorphology Using R Programming Language. Geod. Cartogr. 2019, 45, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemenkova, P. AWK and GNU Octave Programming Languages Integrated with Generic Mapping Tools for Geomorphological Analysis. GeoSci. Eng. 2019, 65, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemenkov, V.; Lemenkova, P. Using TeX Markup Language for 3D and 2D Geological Plotting. Found. Comput. Decis. Sci. 2021, 46, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.A.; Brown, W.J.; Billingham, L.; Holme, R. MagPySV: A Python Package for Processing and Denoising Geomagnetic Observatory Data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 3347–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoneback, R.A.; Burrell, A.G.; Klenzing, J.; Depew, M.D. PYSAT: Python Satellite Data Analysis Toolkit. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 5271–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemenkova, P. Testing Linear Regressions by StatsModel Library of Python for Oceanological Data Interpretation. Aquat. Sci. Eng. 2019, 34, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.F., II; Gerstoft, P.; Bianco, M.J.; Bromirski, P.D. Unsupervised Deep Clustering of Seismic Data: Monitoring the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB021716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, T.H.; Xu, Y.C. Clipping Noise Compensation with Neural Networks in OFDM Systems. Signals 2020, 1, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Decaestecker, C. Data augmentation for training deep regression for in vitro cell detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fifth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Tripoli, Lebanon, 17–19 October 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Morris, B. HalluciNet-ing Spatiotemporal Representations Using a 2D-CNN. Signals 2021, 2, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Adanja, I.; Warzee, N.; Van Ham, P.; Decaestecker, C. Phase contrast image segmentation by weak watershed transform assembly. In Proceedings of the 2008 5th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Paris, France, 14–17 May 2008; pp. 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucart, A.; Debeir, O.; Decaestecker, C. SNOW: Semi-Supervised, Noisy And/Or Weak Data For Deep Learning in Digital Pathology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 1869–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Almasri, F.; Decaestecker, C. Deep-shift phase contrast cell detection and tracking. Poster, 2019. In Proceedings of the ISBI 2019, IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Venise, Italy, 8–11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pintore, S.; Quintiliani, M.; Franceschi, D. Teseo: A vectoriser of historical seismograms. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 31, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Huang, M. A new program on digitizing analog seismograms. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 93, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, T. An interactive program on digitizing historical seismograms. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 63, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromirski, P.D.; Chuang, S. SeisDig User’s Manual; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.A.; Akhter, G.; Ahmad, Z. DigiSeis—A software component for digitizing seismic signals using the PC sound card. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 43, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Yu, N.; Zhang, T.; Pan, J. A seismogram digitization and database management system. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2001, 14, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogiatzis, P.; Ishii, M. DigitSeis: A new digitization software for analog seismograms. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2016, 87, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camelbeeck, T. Some Notes Concerning the Seismicity in Belgium—Magnitude Scale—Detection Capability of the Belgian Seismological Stations. In Seismic Activity in Western Europe; NATO ASI Series (Seriec C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences); Melchior, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 144, pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somville, O. Constantes des Sismographes Galitzine; Annales de l’Observatoire Royal de Belgique: Uccle, Belgium, 1922; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Somville, O. Sur la Methode d’Enregistrement Galvanometrique Appliquee aux Sismographes Galitzine; Annales de l’Observatoire Royal de Belgique: Uccle, Belgium, 1922; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wgg, G.G. The Galitzin Seismograph. Nature 1910, 84, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, F. Sensitivity controls on Galitzin-type seismographs. Eos Trans. AGU 1956, 37, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.K.; Tandon, A.N. Calibration of electromagnetic seismographs satisfying galitzin conditions. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynton, C.A. Overview of TIFF 5.0. In Image Processing and Interchange: Implementation and Systems; Arps, R.B., Pratt, W.K., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992; Volume 1659, pp. 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J. Sequential minimax search for a maximum. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1953, 4, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Section 10.2. Golden Section Search in One Dimension, 3rd ed.; Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L., Jr. Python Reference Manual; Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemenkova, P.; De Plaen, R.; Lecocq, T.; Debeir, O. Computer Vision Algorithms of DigitSeis for Building a Vectorised Dataset of Historical Seismograms from the Archive of Royal Observatory of Belgium. Sensors 2023, 23, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010056
Lemenkova P, De Plaen R, Lecocq T, Debeir O. Computer Vision Algorithms of DigitSeis for Building a Vectorised Dataset of Historical Seismograms from the Archive of Royal Observatory of Belgium. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemenkova, Polina, Raphaël De Plaen, Thomas Lecocq, and Olivier Debeir. 2023. "Computer Vision Algorithms of DigitSeis for Building a Vectorised Dataset of Historical Seismograms from the Archive of Royal Observatory of Belgium" Sensors 23, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010056
APA StyleLemenkova, P., De Plaen, R., Lecocq, T., & Debeir, O. (2023). Computer Vision Algorithms of DigitSeis for Building a Vectorised Dataset of Historical Seismograms from the Archive of Royal Observatory of Belgium. Sensors, 23(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010056




