Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Meat Samples
2.3. Reagents and Antibodies
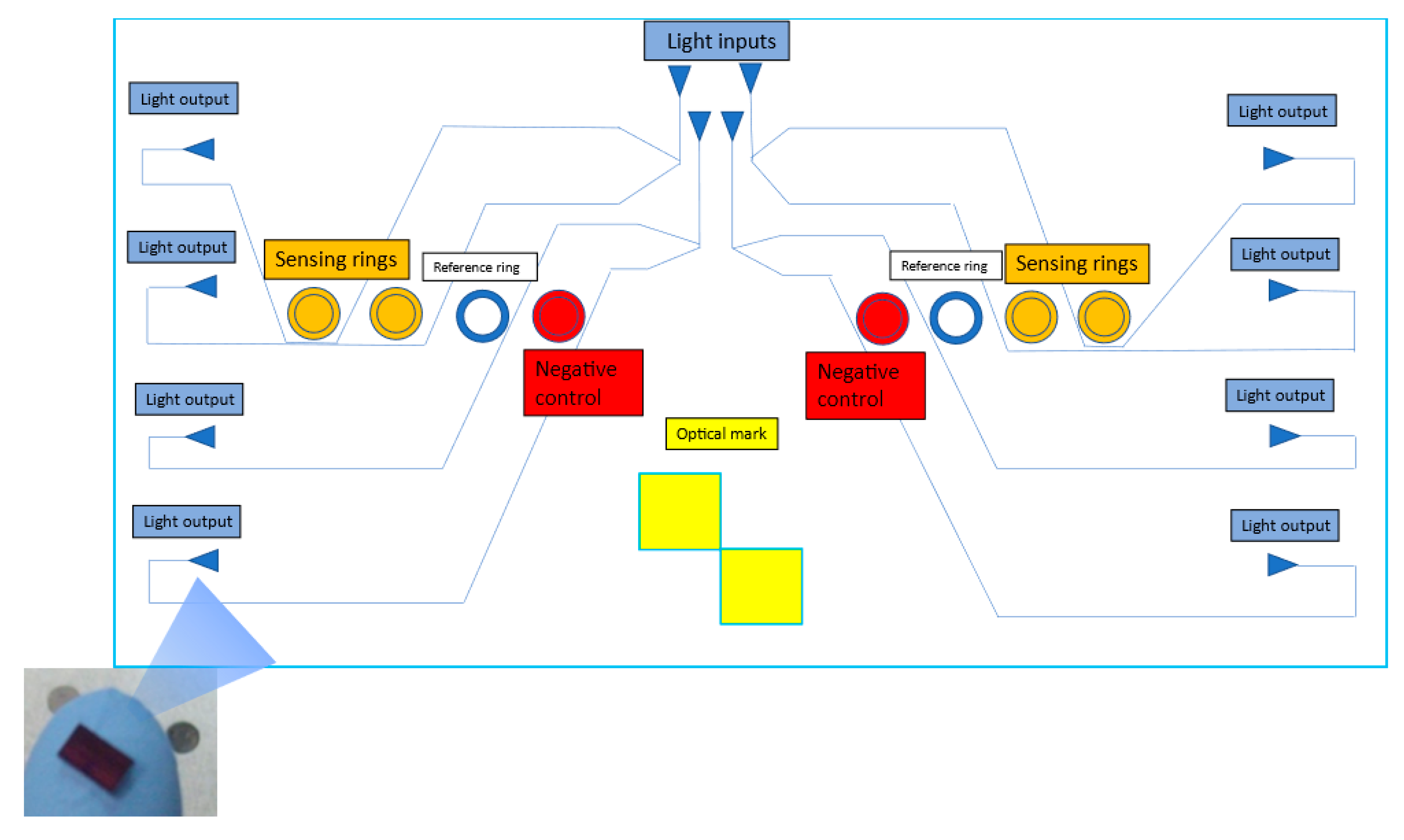
2.4. Antibody Array or Immobilization Control Test
2.5. iELISA (Indirect ELISA)
Polyclonal Antibody Anti-Listeria iELISA
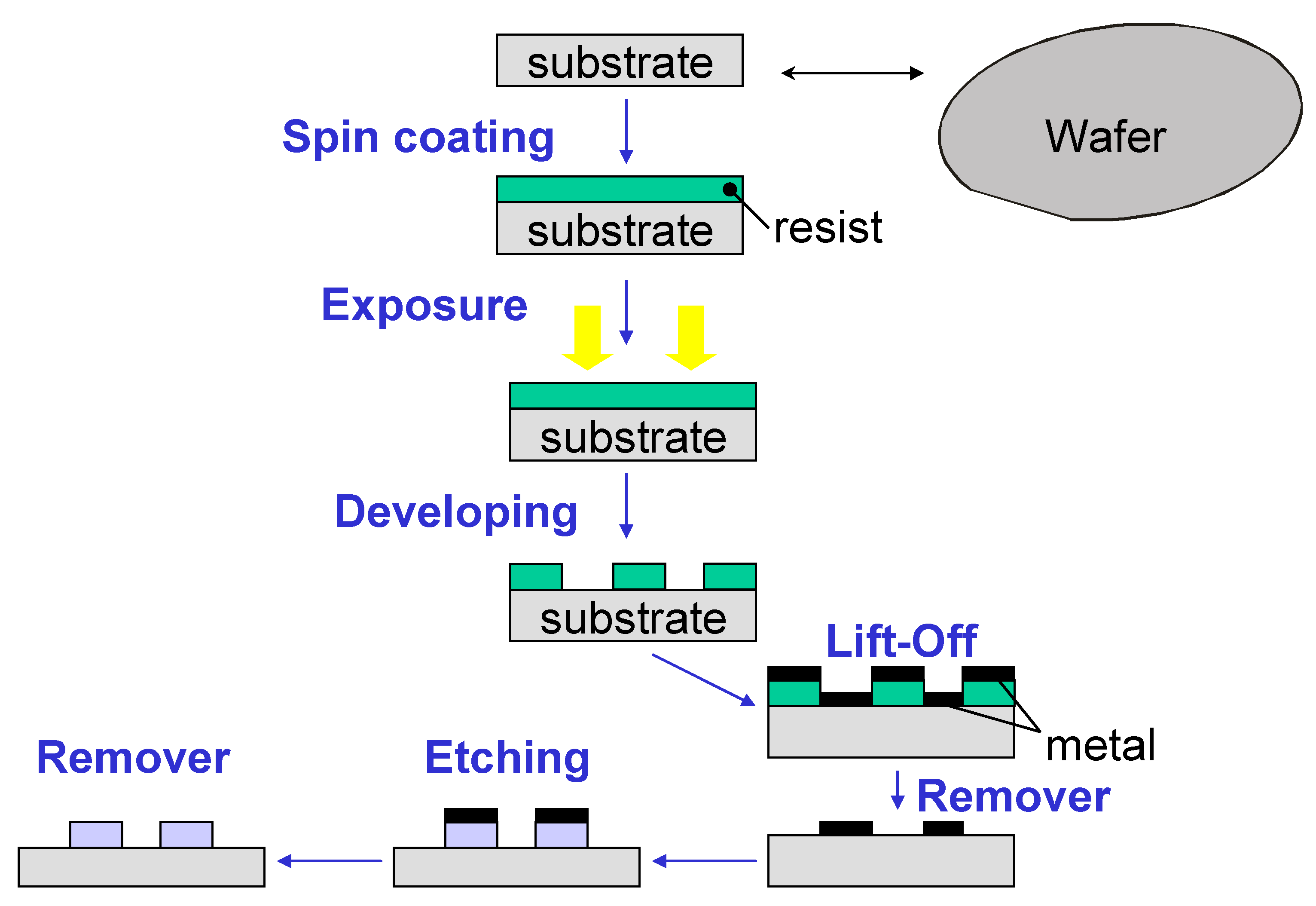
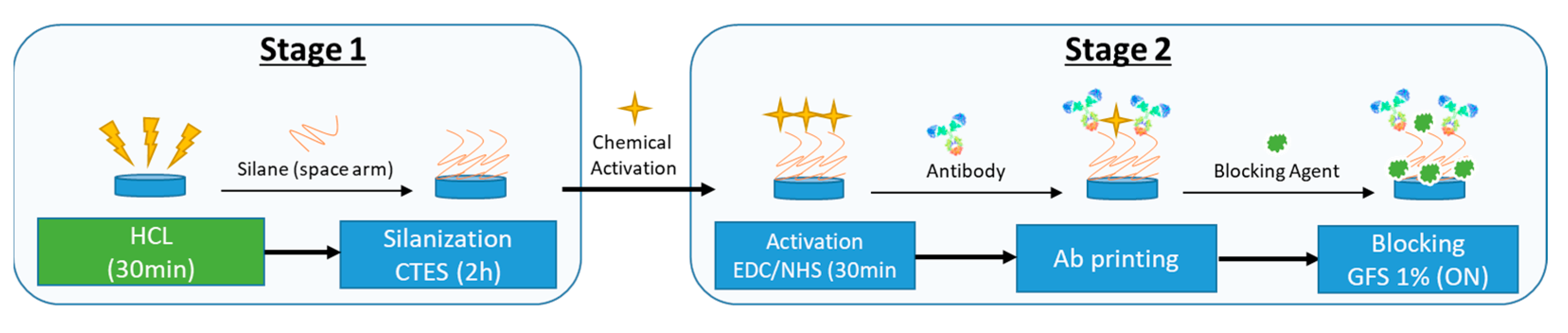
2.6. Optical PIC Functionalization
2.7. Microbiological Quantification
2.8. Detection Method for L. monocytogenes
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antibody Microarray Detection of L. monocytogenes
3.2. iELISA for the Detection of L. monocytogenes and Sensitivity Studies
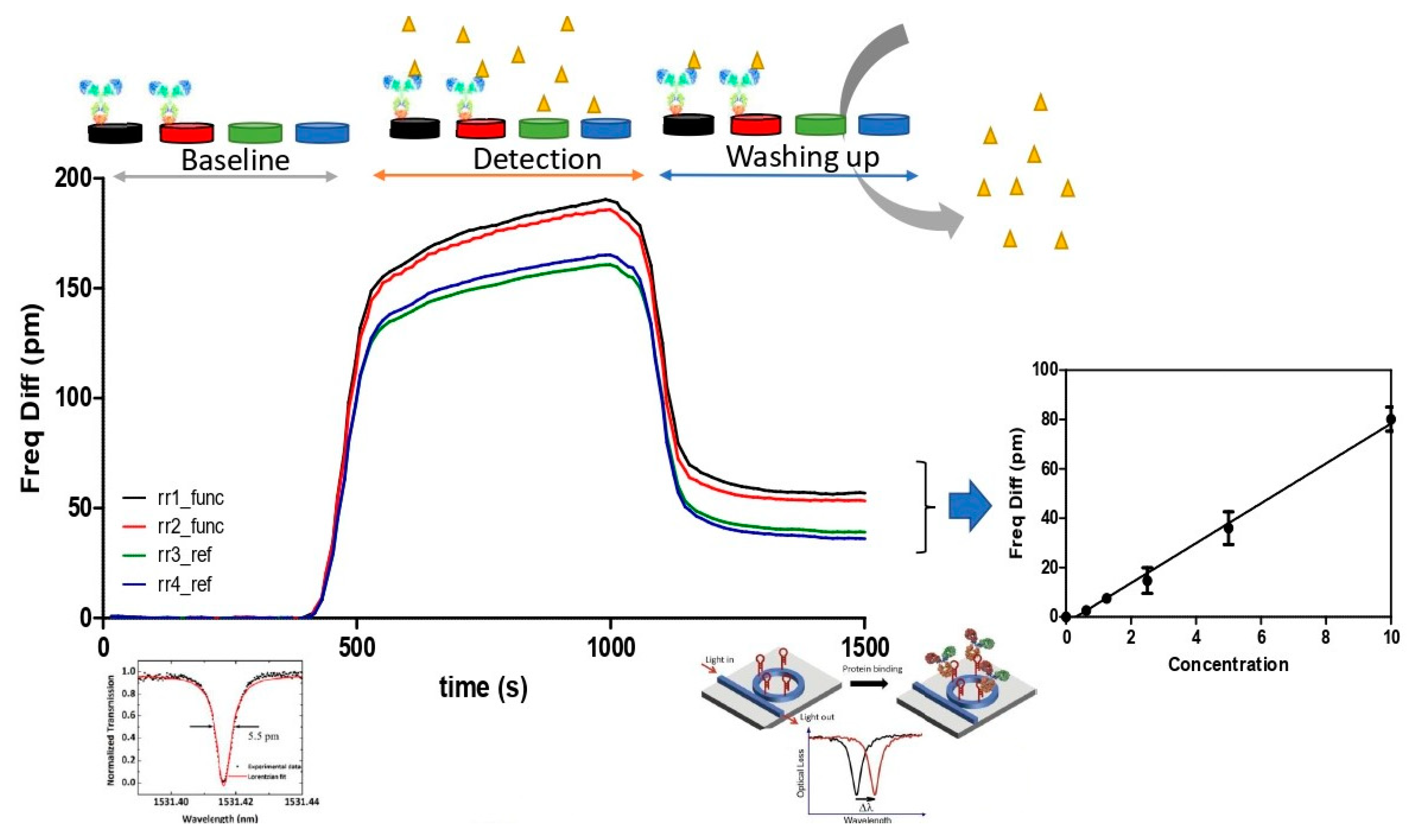
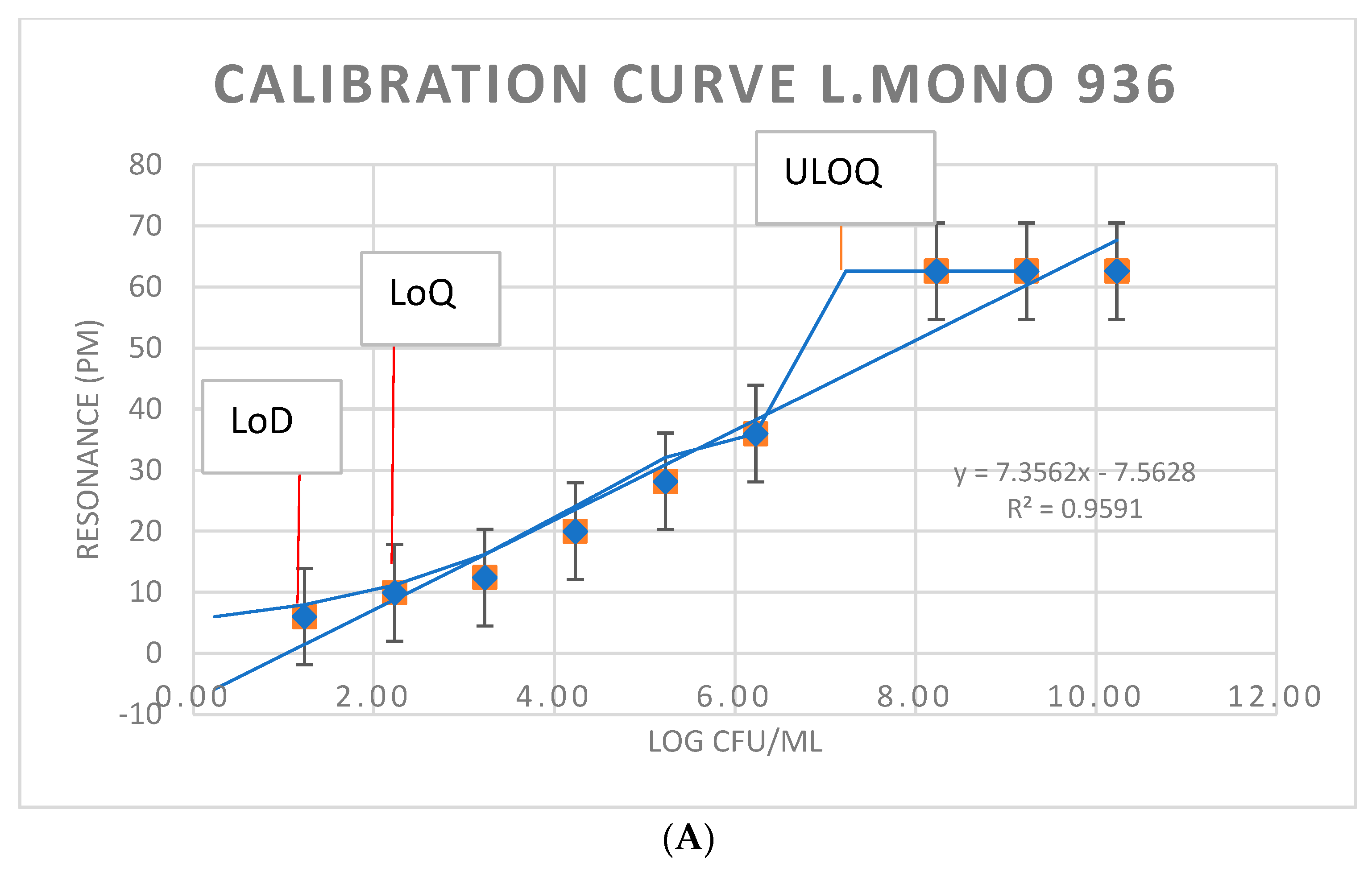
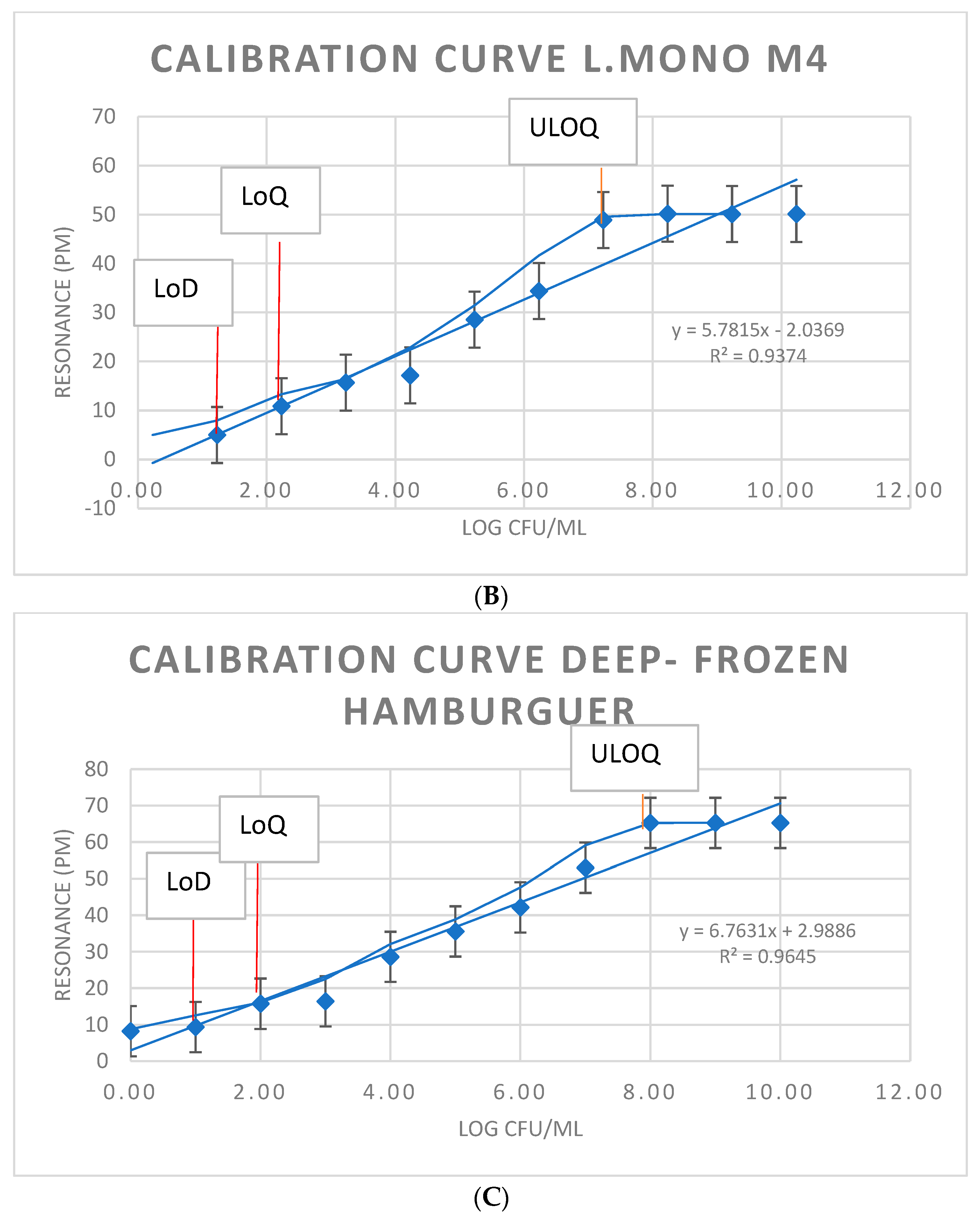
3.3. Immunosensor Detection of L. monocytogenes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuchat, A.; Swaminathan, B.; Broome, C.V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 4, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrada, H.; Soriano, J.; Picó, Y.; Mañes, J. Quantification of Listeria monocytogenes in salads by real time quantitative PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 107, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Bacillus: A Biological Tool for Crop Improvement through Bio-Molecular Changes in Adverse Environments. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, L.; Ebel, E.D.; Kause, J.R. Draft FSIS Risk Assessment for Listeria, Ready-to-eat Meat and Poultry Products; Food Safety and Inspection Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EC). No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, L338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Lombard, B.; Smith, H.; Rzezutka, A.; D’Agostino, M.; Helmuth, R.; Schroeter, A.; Malorny, B.; Miko, A.; Guerra, B.; et al. Trends in analytical methodology in food safety and quality: Monitoring microorganisms and genetically modified organisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.F.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Prin-ciples, applications, advantages, and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 11290-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria Mono-Cytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. ISO Standards: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Rodriguez-Lazaro, D.; Gonzalez-García, P.; Gattuso, A.; Gianfranceschi, M.V.; Hernandez, M. Reducing time in the analysis of Listeria monocytogenes in meat, dairy and vegetable products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 184, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimaglia, F.; De Lorenzis, E.; Mezzolla, V.; Rossi, F.; Poltronieri, P. Detection of L. monocytogenes in Enrichment Cultures by Immunoseparation and Immunosensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7045–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, P.; Mezzolla, V.; Primiceri, E.; Maruccio, G. Biosensors for the Detection of Food Pathogens. Foods 2014, 3, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, J.A.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lee, J.; Gehring, A.G. Detection of pathogenic bacteria in large volume food samples using an enzyme-linked immunoelectrochemical biosensor. Food Control 2020, 119, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, P. Innovations in Detection of Deliberate or Accidental Contamination with Biological Agents in Environment and Foods. Challenges 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrne, B.; Stack, E.; Gilmartin, N.; O’Kennedy, R. Antibody-Based Sensors: Principles, Problems and Potential for Detection of Pathogens and Associated Toxins. Sensors 2009, 9, 4407–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, M.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Chuong, P.D.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoon, B.S.; Hwang, K.K.; Lim, Y.K. Development of a sandwich ELISA for the detection of Listeria spp. using specific flagella antibodies. J. Veter-Sci. 2005, 6, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banada, P.P.; Bhunia, A.K. Antibodies and immunoassays for detection of bacterial pathogens. In Principles of Bacterial Detection: Biosensors Recognition Receptors and Microsystems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 567–602. [Google Scholar]
- Hearty, S.; Leonard, P.; Quinn, J.; O’Kennedy, R. Production, characterisation and potential application of a novel monoclonal antibody for rapid identification of virulent Listeria monocytogenes. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 66, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Kim, K.P.; Gomez, R.; Sherman, D.M.; Bashir, R.; Ladisch, M.R.; Bhunia, A.K. Expression of cellular antigens of Listeria monocytogenes that react with monoclonal anti-bodies C11E9 and EM-7G1 under acid-, salt- or temperature-induced stress environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahm, B.-K.; Bhunia, A. Effect of environmental stresses on antibody-based detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vytřasova, J.; Zachová, I.; Červenka, L.; Štěpanková, J.; Pejchalová, M. Non-specific reactions during immunomagnetic sepa-ration of Listeria. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 43, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Poltronieri, P.; de Blasi, M.; D’Urso, O. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes through real-time PCR and biosensor methods. Plant Soil Environ. 2009, 55, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Urso, O.F.; De Blasi, M.D.; Manera, M.G.; Latronico, M.F.; Rella, R.; Poltronieri, P. Listeria monocytogenes detection with surface plasmon resonance and protein arrays. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2008 IEEE, Lecce, Italy, 26–29 October 2008; pp. 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.W.; Inerowicz, H.D.; Regnier, F.E.; Reifenberger, R. Patterned Protein Microarrays for Bacterial Detection. Langmuir 2002, 19, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Reddy, P.J.; Srivastava, S. Protein microarrays and novel detection platforms. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2011, 8, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Banada, P.P.; Chatni, M.R.; Lim, K.S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Ladisch, M.; Bashir, R. A multifunctional micro-fluidic system for dielectrophoretic concentration coupled with immuno-capture of low numbers of Listeria monocytogenes. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, B. Lab-on-a-chip pathogen sensors for food safety. Sensors 2012, 12, 10713–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarocka, U.; Wasowicz, M.; Radecka, H.; Malinowski, T.; Michalczuk, L.; Radecki, J. Impedimetric immunosensor for detection of plum pox virus in plant extracts. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocka, U.; Sawicka, R.; Góra-Sochacka, A.; Sirko, A.; Zagórski-Ostoja, W.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H. Immunosensor based on antibody binding fragments attached to gold nanoparticles for detection of avian influenza virus H5N1. Sensors 2014, 14, 15714–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- David, S.; Polonschii, C.; Gheorghiu, M.; Bratu, D.; Dobre, A.; Gheorghiu, E. Assessment of pathogenic bacteria using periodic actuation. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primiceri, E.; Chiriacò, M.S.; De Feo, F.; Santovito, E.; Fusco, V.; Maruccio, G. A multipurpose biochip for food pathogen de-tection. Anal. Methods 2016, 88, 3055–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotter, R.; Lee, L.; Wilson, D. Sensor Technologies for Monitoring Metabolic Activity in Single Cells—Part I: Optical Methods. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, F.P.; Alocilja, E.C. Photon based sensing of pathogens in food. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2002 IEEE, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–14 June 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, R.K.; Cavallaro, N.D.; Pola, C.C.; Danyluk, M.D.; McLamore, E.S.; Gomes, C.L. Planar Interdigitated Aptasensor for Flow-Through Detection of Listeria spp. in Hydroponic Lettuce Growth Media. Sensors 2020, 20, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etty, M.C.; D’Auria, S.; Fraschini, C.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. Effect of the optimized selective enrichment medium on the ex-pression of the p60 protein used as Listeria monocytogenes antigen in specific sandwich ELISA. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, D.J.; Pavesi, L. Silicon Fundamentals for Photonics Applications. Silicon Photonics Top. Appl. Phys. 2004, 94, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.G.; Bonneau, D.; Silverstone, J.W. III Chapter—Silicon Quantum Photonics Home. In Silicon Photonics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 41–82. [Google Scholar]
- Burbano, E.; Carrascal, A.; Mercado, M.; Poutou, R. Validación de PCR para Listeria monocytogenes en Leches. Normas Calid. 2003, 57, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Reyes, C.N.; Becker, C.A.; Katsumoto, T.R.; Ma, J.; Wolf, A.J.; Bose, N.; Chan, A.S.H.; Magee, A.S.; Danielson, M.E.; et al. Activation of the innate immune receptor Dectin-1 upon formation of a ‘phagocytic synapse’. Nature 2011, 472, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, P.; Biswas, A.; Choi, K.; Pal, U. Methods for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogens: An Overview. Am. J. Food Technol. 2011, 6, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aznar, R.; Alarcón, B. On the Specificity of PCR Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Food: A Comparison of Published Primers. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 25, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm-Stecher, B.F.; Johnson, E.A. Rapid Methods for Detection of Listeria; Food Science Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 161, p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Manessis, G.; Mourouzis, C.; Griol, A.; Zurita-Herranz, D.; Peransi, S.; Sanchez, C.; Giusti, A.; Gelasakis, A.I.; Bossis, I. Integration of Microfluidics, Photonic Integrated Circuits and Data Acquisition and Analysis Methods in a Single Platform for the Detection of Swine Viral Diseases. Animals 2021, 11, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, S.K.; Santacruz, N.A.; Pham, D.; Luo, J.; Hsieh, C.-S. Antigen-specific peripheral shaping of the natural regulatory T cell population. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapsford, K.; Shubin, Y.; Delehanty, J.; Golden, J.; Taitt, C.; Shriver-Lake, L.; Ligler, F. Fluorescence-based array biosensors for detection of biohazards. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, R.; Krüger, J.; Moynihan, S. A miniaturised image based fluorescence detection system for point-of-care-testing of cocaine abuse. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.J.; Morley Hutchinson, J.S. Hormone Assays in Biological Fluids. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Fraser, W.D., Ed.; Springer: Houston, TX, USA, 2006; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Hornbeck, P. Double-Immunodiffusion Assay for Detecting Specific Antibodies. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2017, 116, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.T. Immunoassay. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1991, 2, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plested, J.S.; Coull, P.A.; Gidney, M.A.J. ELISA. Methods Mol. Med. 2003, 71, 243–261. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, C.; Kyriakides, A. Listeria: A Practical Approach to the Organism and Its Control in Foods, 2nd ed.; Practical Food Microbiology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Coutu, J.; Morissette, C.; D’auria, S.; Lacroix, M. Development of a highly specific sandwich ELISA for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes, an important foodborne pathogen. Microbiol. Res. Int. 2014, 2, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, R.L.T.; Lee, H.; Hall, J.C. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes and the toxin listeriolysin O in food. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 64, 141–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Yang, C.; Yu, L.; Korostynska, O.; Stasiak, K.O.; Adley, C. Label-free detection of Bacillus cereus DNA hybridization using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for food quality monitoring application. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Limerick, Ireland, 23–25 February 2010; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Poon, A.W. Silicon-Nitride-Based Integrated Optofluidic Biochemical Sensors Using a Coupled-Resonator Optical Waveguide. Front. Mater. 2015, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, E.; Long, M.; Zeng, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Hu, W.; Ni, Z.; et al. High Responsivity Phototransistors Based on Few-Layer ReS2for Weak Signal Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; White, I.M.; Shopova, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Suter, J.D.; Sun, Y. Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, K.; Bartolozzi, I.; Schacht, E.; Bienstman, P.; Baets, R. Silicon-on-Insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7610–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, L.; Vivien, G.; Sattler, A.; Kaźmierczak, B.; Sanchez, K.B.; Gylfason, A.; Griol, D.; Marris-Morini, E.; Cassan, D.; Giannone, H.; et al. High efficiency silicon nitride surface grating couplers. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castelló-Pedrero, L.; Gómez-Gómez, M.I.; García-Rupérez, J.; Griol, A.; Martínez, A. Performance improvement of a silicon nitride ring resonator biosensor operated in the TM mode at 1310 nm. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Guerrero, A.B.; Dante, S.; Duval, D.; Osmond, J.; Lechuga, L.M. Advanced photonic biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scotter, S.L.; Langton, S.; Lombard, B.; Schulten, S.; Nagelkerke, N.; In’t Veld, P.H.; Rollier, P.; Lahellec, C. Validation of ISO Method 11290 Part Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 64, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, R.R.; Hazeleger, V.C. Listeria monocytogenes: Diagnostic Problems. FEMS Inmunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 35, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.J.; King, R.K.; Burchak, J.; Gannon, V.P. Sensitive and specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk and ground beef with the polymerase chain reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 2576–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingianni, A.; Floris, M.; Palomba, P.; Madeddu, M.; Quartuccio, M.; Pompei, R. Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in foods, by a combination of PCR and DNA probe. Mol. Cell. Probes 2001, 15, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Cocolin, L.; Ferroni, P.; Cantoni, C.; Comi, G. A simple and fast PCR protocol to detect Listeria monocytogenes from meat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaclíková, E.; Pangallo, D.; Drahovská, H.; Oravcová, K.; Kuchta, T. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food, equivalent to ISO 11290-1 or ISO 10560, by a three days Polymerase Chain Reaction-based method. Food Control 2003, 14, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

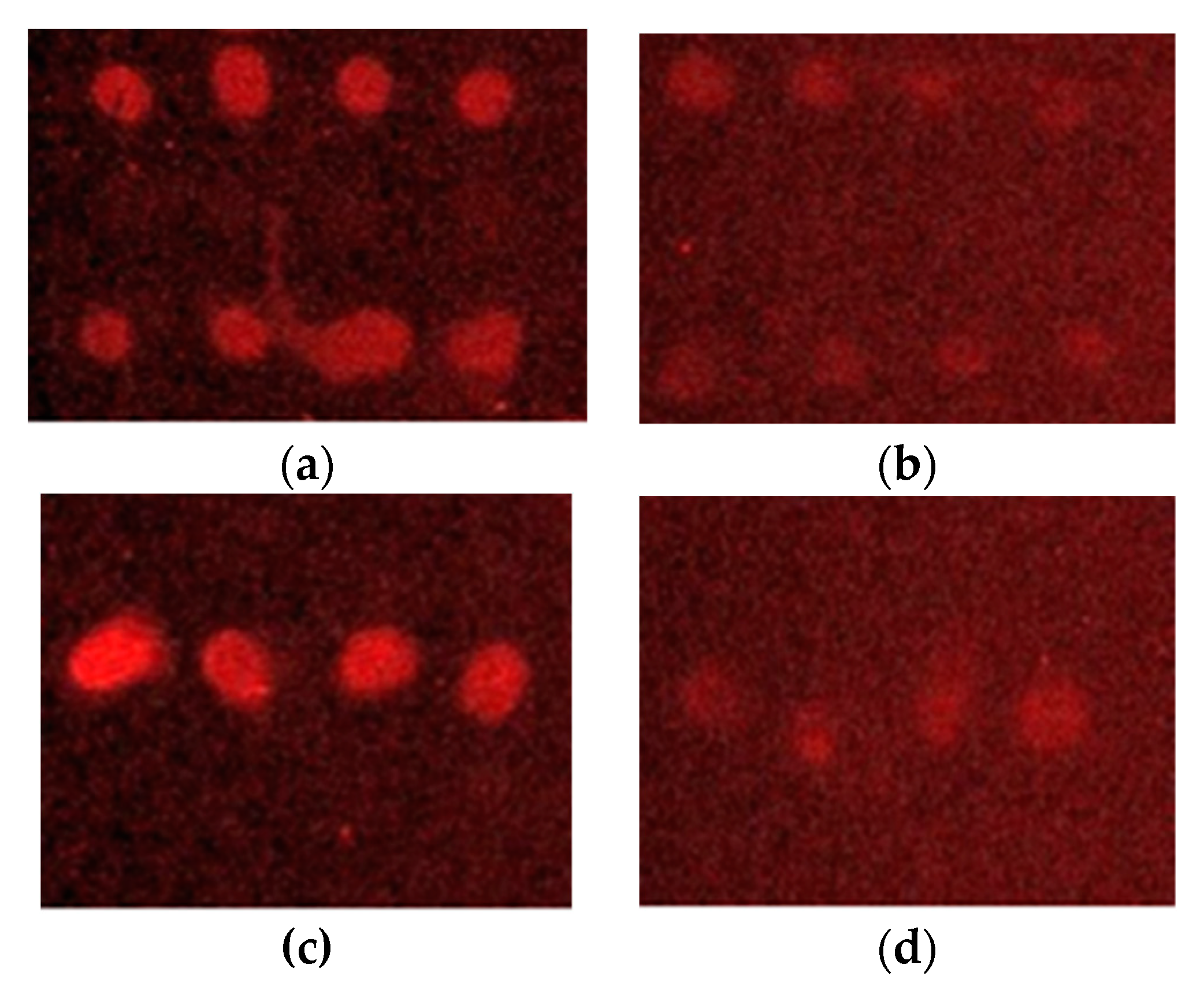
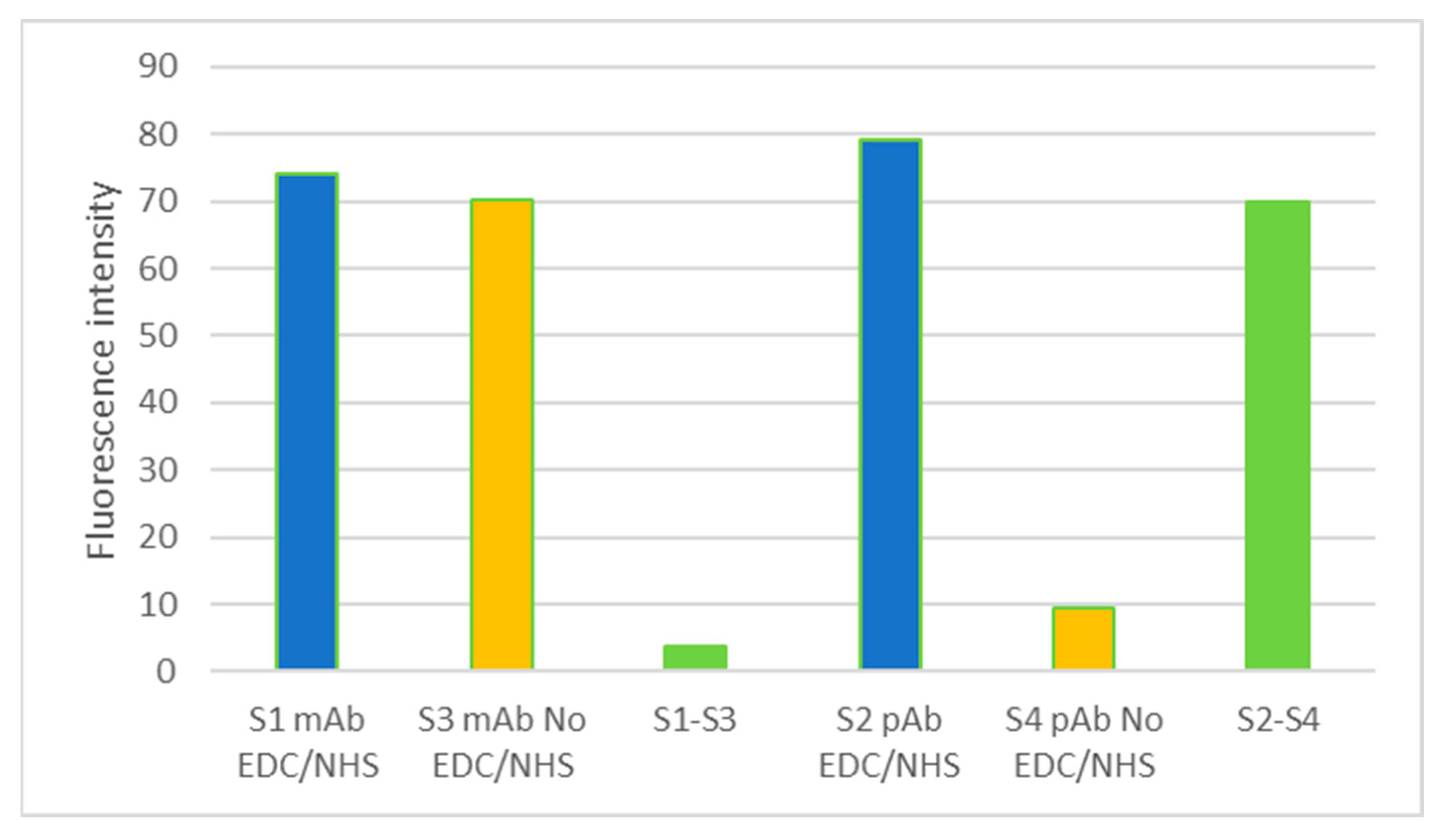


| Target Species/Sample * | Inmunosensor Response ** | Count on Selective Agar (CFU/mL) *** |
|---|---|---|
| L. monocytogenes CECT933 04/2022 | + | 1 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT911 04/2022 | − | 0 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 04/2022 | + | >108 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 05/2022 | + | 1.4 × 1010 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 05/2022 | + | 4.1 × 109 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 05/2022 | + | 3.5 × 108 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 05/2022 | + | 2.1 × 107 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 05/2022 | + | 2.1 × 107 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 06/2022 | + | 6.4 × 108 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 06/2022 | + | 1.7 × 108 |
| L. monocytogenes CECT936 07/2022 | + | 1.4 × 1010 |
| L. innocua CECT910 04/2022 | − | 9.5 × 109 |
| L. innocua CECT910 04/2022 | − | 9.5 × 108 |
| L. innocua CECT910 05/2022 | − | 8 × 107 |
| L. innocua CECT910 06/2022 | − | 4.5 × 106 |
| L. innocua CECT910 07/2022 | − | 1 × 102 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 05/2022 | + | 9 × 1010 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 05/2022 | + | 3.0 × 102 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 05/2022 | + | 4.0 × 106 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 06/2022 | + | 1.7 × 108 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 06/2022 | + | 8.4 × 107 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 07/2022 | + | 1 × 1010 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 07/2022 | + | 1 × 102 |
| L. monocytogenes M4 07/2022 | + | 1 × 101 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 04/2022 | + | 2 × 101 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 04/2022 | + | 2 × 108 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 04/2022 | + | 2 × 109 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 04/2022 | + | 2 × 1010 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 05/2022 | − | 0 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 06/2022 | + | 6.5 × 105 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 06/2022 | + | 6.5 × 106 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 07/2022 | + | 6.5 × 1010 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 09/2022 | + | <103 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 10/2022 | + | 1.2 × 107 |
| Deep-frozen hamburger 11/2022 | + | 1.1 × 103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández Blanco, A.; Hernández Pérez, M.; Moreno Trigos, Y.; García-Hernández, J. Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food. Sensors 2023, 23, 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23125570
Fernández Blanco A, Hernández Pérez M, Moreno Trigos Y, García-Hernández J. Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food. Sensors. 2023; 23(12):5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23125570
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández Blanco, Ana, Manuel Hernández Pérez, Yolanda Moreno Trigos, and Jorge García-Hernández. 2023. "Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food" Sensors 23, no. 12: 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23125570
APA StyleFernández Blanco, A., Hernández Pérez, M., Moreno Trigos, Y., & García-Hernández, J. (2023). Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food. Sensors, 23(12), 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23125570






