Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Biomarkers and Analytical Tools
2. AD Immunosensors Detecting Autoantibodies
3. AD Immunosensors Detecting Other Protein Biomarkers
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical biosensors for autoantibodies in autoimmune and cancer diseases. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, K.; Hundt, J.E.; Yu, X.; Ehlers, M.; Petersen, F.; Karsten, C.M.; Köhl, J.; Kridin, K.; Kalies, K.; Kasprick, A.; et al. Autoimmune pre-disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, F.; Abbaszadeh, H.; Mehdizadeh, A.; Ebrahimi-Warkiani, M.; Rashidi, M.-R.; Yousefi, M. Biosensors and nanobiosensors for rapid detection of autoimmune diseases: A review. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrin, T.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Walker, L.S.K. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2023, 401, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038, Erratum in Lancet 2016, 388, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, K.; Shahbaz, S.K.; Keshavarz, M.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Gold Nanoparticles: Multifaceted Roles in the Management of Autoimmune Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.F.G.; Pirko, I.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis: Where do we stand? Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.; Kitamura, N.; Nagasawa, Y.; Tsuzuki, H.; Iwata, M.; Nagatsuka, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Imai, K.; Fujiwara, S. Are Viral Infections Key Inducers of Autoimmune Diseases? Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldan, S.S.; Lieberman, P.M. Epstein–Barr virus and multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 21, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnberg, T.; Lichtensteiger, C.; Ali, O.H.; Pop, O.T.; Jochum, A.-K.; Risch, L.; Brugger, S.D.; Velic, A.; Bomze, D.; Kohler, P.; et al. Pulmonary Surfactant Proteins Are Inhibited by Immunoglobulin A Autoantibodies in Severe COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Castagnoli, R.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A.; Brambilla, I. COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases: Is there a connection? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.Y.; Mao, T.; Klein, J.; Dai, Y.; Huck, J.D.; Jaycox, J.R.; Liu, F.; Zhou, T.; Israelow, B.; Wong, P.; et al. Diverse Functional Autoantibodies in Patients with COVID-19. medRxiv Prepr. Serv. Health Sci. 2021, 595, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Ling, G.S.; Cao, X. Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: From immunopathology to therapeutic target. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 132, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staruszkiewicz, M.; Pituch-Noworolska, A.; Skoczen, S. Uncommon types of autoantibodies—Detection and clinical associations. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Murphy, C.; Loscher, C.E.; O’kennedy, R. Autoantibodies—Enemies, and/or potential allies? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 953726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoganathan, K.; Stevenson, A.; Tahir, A.; Sadler, R.; Radunovic, A.; Malek, N. Bedside and laboratory diagnostic testing in myasthenia. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.V.; Schett, G.; Steffen, U. Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Historical Background and Novel Findings. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 63, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yan, Y.; Xie, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Gopinath, S.C.; Anbu, P.; He, S.; Zhang, L. Immunosensing the rheumatoid arthritis biomarker through bifunctional aldehyde-amine linkers on an iron oxide nanoparticle seeded voltammetry sensor. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2022, 12, 18479804221085103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, I.; Sanmartí, R.; Gómara, M.J. Implications of Post-Translational Modifications in Autoimmunity with Emphasis on Citrullination, Homocitrullination and Acetylation for the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Prognosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.C.; Park, M.-C.; Kim, Y.-G. Interleukin-32 as a biomarker in rheumatic diseases: A narrative review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1140373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ai, W.; Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Yuan, S.; Xie, Y.; Mo, X.; Li, W.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Inflammatory markers and risk factors of RA patients with depression and application of different scales in judging depression. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, J. Microfluidic electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of interleukin-6 based on hybrid of AuNPs and graphene. Talanta 2021, 240, 123173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Mujahid, M. Recent Advances in Electrochemical and Optical Biosensors Designed for Detection of Interleukin 6. Sensors 2020, 20, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zambrano, A.; Lin, Z.-T.; Xing, Y.; Rippy, J.; Wu, T. Immunosensors for Biomarker Detection in Autoimmune Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 65, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Krishnan, S. Electrochemical and surface plasmon insulin assays on clinical samples. Analyst 2018, 143, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, R.; Koohi, F.; Rasouli, M.; Rezaei, K.; Abbasgholinejad, E.; Bekeschus, S.; Doroudian, M. Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents. Vaccines 2023, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmaj, K.W.; Mycko, M.P.; Furlan, R.; Rejdak, K. Fluid phase biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Luo, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Z. Emerging Roles of Exosomes in T1DM. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 593348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, H. Construction and Potential Applications of Biosensors for Proteins in Clinical Laboratory Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, M.; Aydin, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Chapter One—Advances in immunosensor technology. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 102, pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Karachaliou, C.-E.; Koukouvinos, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.; Livaniou, E.; Petrou, P. Recent Developments in the Field of Optical Immunosensors Focusing on a Label-Free, White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy-Based Immunosensing Platform. Sensors 2022, 22, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasuki, S.; Varsha, V.; Mithra, R.; Dharshni, S.; Abinaya, R.; Dharshini, N.; Sivarajasekar, N. Thermal Biosensors and Their Applications. Am. Int. J. Res. Sci. Technol. Eng. Math 2019, 1, 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.V.P.; Chuang, Y.-S.; Li, C.; Wu, C.-C. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Immunosensors with Nanomaterial Assistance for Signal Amplification. Biosensors 2023, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, M.; Janani, R.; Deepa, C.; Rajeshkumar, L. Nanotechnology-Enabled Biosensors: A Review of Fundamentals, Design Principles, Materials, and Applications. Biosensors 2022, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobeissy, F.H.; Gulbakan, B.; Alawieh, A.; Karam, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guingab-Cagmat, J.D.; Mondello, S.; Tan, W.; Anagli, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Post-Genomics Nanotechnology Is Gaining Momentum: Nanoproteomics and Applications in Life Sciences. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2014, 18, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florea, A.; Melinte, G.; Simon, I.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases. Biosensors 2019, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serin, M.; Kara, P. Biosensing strategies (approaches) for diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis. Talanta 2023, 252, 123794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirdöğen, B.C. A literature review of biosensors for multiple sclerosis: Towards personalized medicine and point-of-care testing. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 48, 102675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K. Advances in the detection of rheumatoid arthritis related biomarker by highly sensitive electrochemical sensors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andréasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, K.Y.; Silva-Junior, A.G.; Pitta, M.G.; Errachid, A.; Oliveira, M.D.; Andrade, C.A. Nanoimmunosensor for the electrochemical detection of oncostatin M receptor and monoclonal autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Talanta 2023, 256, 124285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Cho, S. Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis Biomarker: Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody in Human Serum Based on Avidin-Biotin System. Sensors 2021, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, P.; Debiec, H. Molecular Pathogenesis of Membranous Nephropathy. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2020, 15, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hampitak, P.; Jowitt, T.A.; Melendrez, D.; Fresquet, M.; Hamilton, P.; Iliut, M.; Nie, K.; Spencer, B.; Lennon, R.; Vijayaraghavan, A. A Point-of-Care Immunosensor Based on a Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Graphene Biointerface for Antibody Assay. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3520–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, T.; Kohanim, Y.K.; Toledano, Y.; Alon, U. Autoimmune thyroid diseases as a cost of physiological autoimmune surveillance. Trends Immunol. 2023, 44, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlov, A.; Pushkarev, A.; Znoyko, S.; Novichikhin, D.; Bragina, V.; Gorshkov, B.; Nikitin, P. Multiplex label-free biosensor for detection of autoantibodies in human serum: Tool for new kinetics-based diagnostics of autoimmune diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Park, J.; Abbasi, M.A.; Cho, S. Label-free electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor for sensitive detection of IgM rheumatoid factor in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veigas, B.; Matias, A.; Calmeiro, T.; Fortunato, E.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Antibody modified gold nanoparticles for fast colorimetric screening of rheumatoid arthritis. Analyst 2019, 144, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catassi, C.; Verdu, E.F.; Bai, J.C.; Lionetti, E. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtamu, H.B.; Not, T.; De Leo, L.; Longo, S.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Nanoelectrode Ensembles for the Serological Analysis of IgG-type Tissue Transglutaminase. Sensors 2019, 19, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, Q.A.; Hill, A.; Berentsen, S. Defining autoimmune hemolytic anemia: A systematic review of the terminology used for diagnosis and treatment. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moraes, M.; Lima, L.R.; Vicentini-Oliveira, J.C.; De Souza, A.V.G.; Oliveira, O.N.; Deffune, E.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. Immunosensor for the Diagnostics of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) Based on Immobilization of a Monoclonal Antibody on a Layer of Silk Fibroin. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3772–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raos, M.; Lukic, M.; Pulanic, D.; Vodanovic, M.; Cepulic, B.G. The role of serological and molecular testing in the diagnostics and transfusion treatment of autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Blood Transfus. Trasfus. Sangue 2022, 20, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurt, F.G.; Bose, K.; Hammoud, B.; Brandt, S.; Bernhardt, A.; Gross, C.; Mertens, P.R.; Chatzikyrkou, C. Old known and possible new biomarkers of ANCA-associated vasculitis. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 133, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H.; Ding, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, M. PtCo nanocubes/reduced graphene oxide hybrids and hybridization chain reaction-based dual amplified electrochemiluminescence immunosensing of antimyeloperoxidase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagúndez, P.; Brañas, G.; Cairoli, E.; Laíz, J.; Tosar, J.P. An electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of anti-dsDNA antibodies in absolute scale. Analyst 2018, 143, 3874–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, M.; Bianchi, V.; Gentili, S.; Fortunati, S.; De Munari, I.; Careri, M. An integrated IoT-Wi-Fi board for remote data acquisition and sharing from innovative immunosensors. Case of study: Diagnosis of celiac disease. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Fang, C.; Yan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Tu, Y. A label-free electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for glutamate decarboxylase antibody detection on AuNPs supporting interface. Talanta 2018, 186, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, N.M.D.; Juste-Dolz, A.; Grau-García, E.; Román-Ivorra, J.A.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A.; Morais, S.; Gimenez-Romero, D. Label-free piezoelectric biosensor for prognosis and diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Rivera, L.C.; Dulay, S.; Lozano-Sánchez, P.; Katakis, I.; Acero-Sánchez, J.L.; O’sullivan, C.K. Disulfide-modified antigen for detection of celiac disease-associated anti-tissue transglutaminase autoantibodies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3799–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, M.; Mattarozzi, M.; Umiltà, E.; Manfredi, A.; Quaglia, S.; Careri, M. An amperometric immunosensor for diagnosis of celiac disease based on covalent immobilization of open conformation tissue transglutaminase for determination of anti-tTG antibodies in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkus, B.; Emregul, E.; Yucesan, C.; Emregul, K.C. Myelin basic protein immunosensor for multiple sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 46, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.M.; González-García, M.B.; Nouws, H.P.; Costa-García, A. Celiac disease detection using a transglutaminase electrochemical immunosensor fabricated on nanohybrid screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dulay, S.; Lozano-Sánchez, P.; Iwuoha, E.; Katakis, I.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Electrochemical detection of celiac disease-related anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies using thiol based surface chemistry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.d.G.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C.; Haro, I.; Gomara, M.J.; Sanmartí, R.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Mendoza, E. Carbon nanotube composite peptide-based biosensors as putative diagnostic tools for rheumatoid arthritis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 27, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouvalakis, K.A.; Bangsaruntip, S.; Hueber, W.; Kozar, L.G.; Utz, P.J.; Dai, H. Peptide-coated nanotube-based biosensor for the detection of disease-specific autoantibodies in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balkenhohl, T.; Lisdat, F. Screen-printed electrodes as impedimetric immunosensors for the detection of anti-transglutaminase antibodies in human sera. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullin, R.F.; Vinter, V.G.; Zamaleeva, A.I.; Matveeva, M.V.; Kourbanov, R.A.; Temesgen, B.K.; Ishmuchametova, D.G.; Abramova, Z.I.; Konovalova, O.A.; Salakhov, M.K. Quartz crystal microbalance immunosensor for the detection of antibodies to double-stranded DNA. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Sim, S.J. Enhanced performance of a surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for detecting Ab–GAD antibody based on the modified self-assembled monolayers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.; Wajs, E.M.; Fragoso, A.; O’Sullivan, C.K. A bienzymatic amperometric immunosensor exploiting supramolecular construction for ultrasensitive protein detection. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Rivera, L.; Acero-Sánchez, J.; Lozano-Sánchez, P.; Katakis, I.; O’Sullivan, C. Electrochemical immunosensor detection of antigliadin antibodies from real human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkenhohl, T.; Lisdat, F. An impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of autoantibodies directed against gliadins. Analyst 2007, 132, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, O.K.; Ngqinambi, A.; Mashazi, P.N. Ultrasensitive detection of anti-p53 autoantibodies based on nanomagnetic capture and separation with fluorescent sensing nanobioprobe for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsounidi, D.; Tsaousis, V.; Xenos, N.; Kroupis, C.; Moutsatsou, P.; Christianidis, V.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.; Petrou, P. Simultaneous determination of procalcitonin and interleukin-6 in human serum samples with a point-of-care biosensing device. Talanta 2023, 258, 124403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhil, A.; Bansal, R.; Anupam, K.; Tandon, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Latest insight into etiopathogenesis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo, B.; Blázquez-García, M.; Valverde, A.; Serafín, V.; Montero-Calle, A.; Solís-Fernández, G.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J. Simultaneous electrochemical immunosensing of relevant cytokines to diagnose and track cancer and autoimmune diseases. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, B.; Blázquez-García, M.; Valverde, A.; Serafín, V.; Montero-Calle, A.; Solís-Fernández, G.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Binary MoS2 nanostructures as nanocarriers for amplification in multiplexed electrochemical immunosensing: Simultaneous determination of B cell activation factor and proliferation-induced signal immunity-related cytokines. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, S.; Sánchez-Tirado, E.; Agüí, L.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Development of an Electrochemical CCL5 Chemokine Immunoplatform for Rapid Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, S.; Sánchez-Tirado, E.; Agüí, L.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J. Simultaneous determination of CXCL7 chemokine and MMP3 metalloproteinase as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta 2021, 234, 122705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.; Queirós, R.; Abreu, C.M.; Barata, C.; Fernandes, R.; Silva, R.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Soares-Dos-Reis, R.; Guimarães, J.; Sá, M.J.; et al. Electrochemical Immunosensor for TNFα-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Screening. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2676–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Dong, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Ueda, H.; Dong, J. Quench-Release-Based Fluorescent Immunosensor for the Rapid Detection of Tumor Necrosis Factor α. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31009–31016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkus, B.; Bozkurt, P.A.; Tulu, M.; Emregul, K.C.; Yucesan, C.; Emregul, E. Simultaneous quantification of Myelin Basic Protein and Tau proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of Multiple Sclerosis patients using nanoimmunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Krishnan, S. Voltammetric Immunosensor Assembled on Carbon-Pyrenyl Nanostructures for Clinical Diagnosis of Type of Diabetes. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2648–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhavsar, K.; Fairchild, A.; Alonas, E.; Bishop, D.K.; La Belle, J.T.; Sweeney, J.; Alford, T.; Joshi, L. A cytokine immunosensor for Multiple Sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy using electroplated printed circuit board electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Su, S.; Zhao, L.; Hu, C. Development of a novel method to measure macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by combined electrochemical immunosensor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Belle, J.T.; Bhavsar, K.; Fairchild, A.; Das, A.; Sweeney, J.; Alford, T.; Wang, J.; Bhavanandan, V.P.; Joshi, L. A cytokine immunosensor for multiple sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štros, M.; Polanská, E.V.; Hlaváčová, T.; Skládal, P. Progress in Assays of HMGB1 Levels in Human Plasma—The Potential Prognostic Value in COVID-19. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatunova, E.A.; Korolev, M.A.; Omelchenko, V.O.; Kurochkina, Y.D.; Davydova, A.S.; Venyaminova, A.G.; Vorobyeva, M.A. Aptamers for Proteins Associated with Rheumatic Diseases: Progress, Challenges, and Prospects of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Kim, S.-K.; Youn, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Jeong, J.; Mok, J.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, H.-S.; Ban, C. A highly sensitive and selective impedimetric aptasensor for interleukin-17 receptor A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blind, M.; Blank, M. Aptamer Selection Technology and Recent Advances. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-J.; Ma, X.-H.; Li, J.-P. An Insulin Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Epitope Imprinting. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.L.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Precision medicine in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, C.; Dutra, L.A.; dos Reis-Neto, E.T.; Castro, C.H.D.M.; Fritzler, M.J.; Andrade, L.E.C. The Role of Autoantibody Testing in Modern Personalized Medicine. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 63, 251–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Han, M.; Li, D.; Hao, R.; Guo, X.; Sang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Jin, H.; Xing, Z.; et al. A cost-effective smartphone-based device for rapid C-reaction protein (CRP) detection using magnetoelastic immunosensor. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K.; Noumani, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Solanki, P.R. FRET Based Biosensor: Principle Applications Recent Advances and Challenges. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunati, S.; Giannetto, M.; Giliberti, C.; Bolchi, A.; Ferrari, D.; Locatelli, M.; Bianchi, V.; Boni, A.; De Munari, I.; Careri, M. Smart Immunosensors for Point-of-Care Serological Tests Aimed at Assessing Natural or Vaccine-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Immunity. Sensors 2022, 22, 5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Verma, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Solanki, P. The perspectives of biomarker-based electrochemical immunosensors, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Medical Things toward COVID-19 diagnosis and management. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 20, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
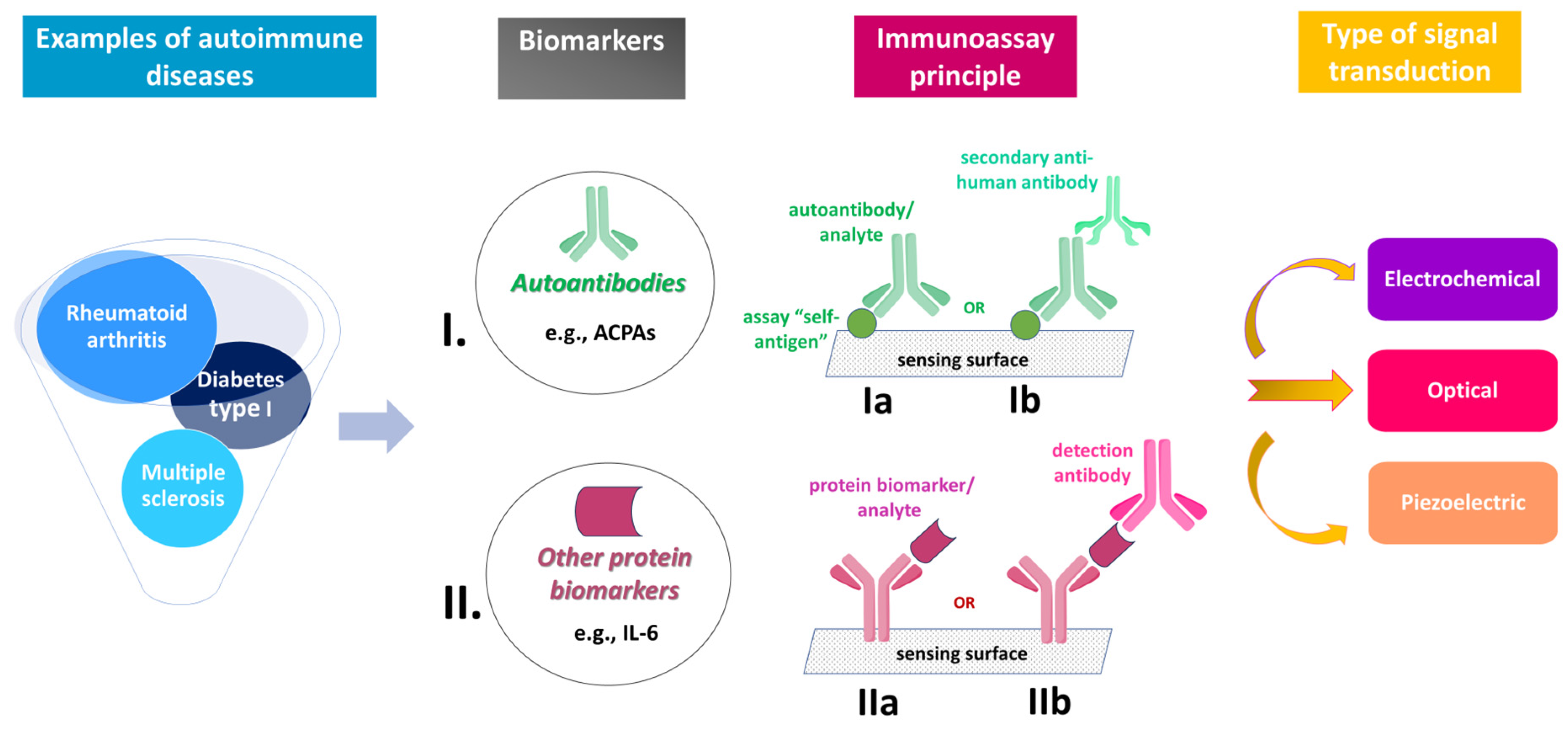

| Type of Signal Transduction | Immunoassay Principle—Use of Secondary Antibody | Autoantibody-Biomarker | Limit of Detection (LoD)/ Concentration Range | Autoimmune Disease | Biological Sample | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical (Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-oncostatin-M receptor autoantibodies | - | Systemic sclerosis (SSc) | Human serum from healthy individuals and SSc patients | [41] |
| Electrochemical (Voltammetry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-citrullinated peptide/protein autoantibodies (ACPAs) | 15 pg mL−1/ 8–250 pg mL−1 | Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) | Human serum (spiked) | [18] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | ACPAs | 0.82 IU ** mL−1/ 1–800 IU mL | RA | Human serum (spiked) | [42] |
| Optical (Spectral correlation interferometry—SCI) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a non-labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-thyroglobulin (anti-TG) and anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) autoantibodies | 6 IU mL−1 (anti-TG) 1.7 IU mL−1 (anti-TPO)/ 6–400 IU mL−1 (anti-TG) 1.7–860 IU mL−1 (anti-TPO) | Autoimmune thyroid diseases | Patients’ serum | [46] |
| Piezoelectric quartz-crystal microbalance | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (anti-PL2R) autoantibodies | 0.1 μg mL−1/ 0.5–100 μg mL−1 | Primary membranous nephropathy (pMN) | Patients’ serum | [44] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Immunoglobulin M—rheumatoid factor (IgM-RF) | 0.22 IU mL−1/ 10–200 IU mL−1 | RA | Human serum (spiked) | [47] |
| Electrochemical (Voltammetry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tissue transglutaminase (anti-tTG) autoantibodies | 1.8 ng mL−1/ 0.005–1 μg mL−1 | Celiac disease (CD) | Serum from healthy individuals and CD patients | [50] |
| Electrochemical (Impedance spectroscopy and square wave voltammetry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Autoantibodies on red blood cells (RBCs) | - | Autoimmune hemolytic anemia | Healthy and “sick” RBCs (i.e., RBCs from healthy and affected individuals) | [52] |
| Optical (Colorimetry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | IgM-RF | 4.15 IU mL−1 | RA | Human plasma (spiked) | [48] |
| Electrochemical (Electro-chemiluminescence—ECL) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay *; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-myeloperoxidase (anti-MPO) autoantibodies | 15.68 fg mL−1/ 50 fg mL−1–1 ng mL−1 | Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides | Human serum (spiked) | [55] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay *; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) autoantibodies | 8 μg mL−1 | Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) | Patients’ serum | [56] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies (IgG and IgA) | 1.4 AU ** mL−1 (IgG) and 3.2 AU mL−1 (IgA)/ up to 30 AU mL−1 (IgG and IgA) | CD | Patients’ serum LOD: 3.2 AU **/mL (IgA), 1.4 AU/mL (IgG) | [57] |
| Electrochemical (Electro-chemiluminescence—ECL) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-glutamate decarboxylase (anti-GAD) autoantibodies | 0.10 ng mL−1/ 0.30–50 ng mL−1 | Type-1 diabetes (T1D) or latent autoimmune diabetes in adult | Patients’ serum | [58] |
| Piezoelectric Quartz-crystal microbalance | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-TRIM21 and anti-TROVE2 autoantibodies | 0.01 U ** mL−1 (anti-TRIM21) 0.005 U mL−1 (anti-TROVE2)/ 0.32–7.17 U mL−1 (anti-TRIM21) 0.07–1.46 U mL−1 (anti-TROVE2) | SLE | Serum from healthy individuals and SLE patients | [59] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies | 0.26 μg mL−1/ 0.26–6.9 μg mL−1 | CD | Serum from CD patients | [60] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies (IgA and IgG) | 1.7 AU mL−1 (IgA) and 2.7 AU mL−1 (IgG)/ Up to 30 AU mL−1 (IgA and IgG) | CD | Serum from pediatric patients | [61] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-Myelin Basic Protein (anti-MBP) autoantibodies | 0.1495 ng mL−1/ 0.4875–2500 ng mL−1 | Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum from relapsing/remitting MS patients | [62] |
| Electrochemical (CV) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies | - | CD | Serum from CD patients | [63] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay *; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies | 390 ng mL−1 | CD | Serum from CD patients | [64] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay *; a labeled secondary antibody was used | ACPAs | - | RA | Serum from RA patients | [65] |
| Piezoelectric Quartz-crystal microbalance | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | ACPAs | - | RA | Serum from RA patients | [66] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay; a labeled secondary antibody was used | Anti-tTG autoantibodies | - | CD | Serum from CD patients | [67] |
| Piezoelectric Quartz-crystal microbalance | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-dsDNA autoantibodies | - | SLE | Serum from healthy individuals and patients with bronchial asthma and SLE | [68] |
| Optical (Surface plasmon resonance–SPR) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Anti-GAD autoantibodies | - | T1D | (Buffer) | [69] |
| Type of Signal Transduction | Immunoassay Principle | Protein-Biomarker | LoD/ Concentration Range | Autoimmune Disease | Biological Sample | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical (Multi Area Reflectance Spectroscopy—MARS) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | Procalcitonin and interleukin-6 (IL-6) | 2.0 ng mL−1 (PCT) and 0.01 ng mL−1 (IL-6)/ up to 100.0 ng mL−1 (PCT) and up to 10.0 ng mL−1 (IL-6) | Various inflammatory/autoimmune diseases | Human serum | [74] |
| Electrochemical (Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Oncostatin-M receptor (sOSMR) protein | 0.42 pg mL−1/ 0.005–500 pg mL−1 | Systemic sclerosis (SSc) | Serum from healthy individuals and SSc patients | [41] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | B cell activation factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-induced ligand (APRIL) | 0.33 pg mL−1 (BAFF) and 16.4 pg mL−1 (APRIL) / 1.1–100 pg mL−1 (BAFF) and 0.05–20 ng mL−1 (APRIL) | Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) | Serum from healthy individuals and SLE patients | [76] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | B cell activation factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-induced ligand (APRIL) | 0.08 ng mL−1 (BAFF) and 0.06 ng mL−1 (APRIL) / 0.24–120 ng mL−1 (BAFF) and 0.19–25 ng mL−1 (APRIL) | SLE | Serum from SLE patients | [77] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | CCL5 chemokine | 40 pg mL−1/ 0.1–300 ng mL−1 | Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Serum from healthy individuals and MS patients | [78] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | IL-6 | 0.42 pg mL−1/ 0.97–250 pg mL−1 | Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) | Human serum (spiked) | [22] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, sandwich-type assay | CXCL7 chemokine and MMP3 metalloproteinase | 0.8 ng mL−1 (CXCL7) and 1.2 pg mL−1 (MMP3)/ 1–75 ng mL−1 (CXCL7) and 2.0–2000 pg mL−1 (MMP3) | RA | Serum from healthy individuals and RA patients | [79] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) | 0.085 pg mL−1/ 1–25 pg mL−1 | Various inflammatory/autoimmune diseases | Serum and tears from healthy individuals; cerebrospinal fluid (CFS) from patients undergone routine lumbar puncture | [80] |
| Electrochemical (Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) and Tau proteins | 0.30 nM (MBP) and 0.15 nM (Tau) | MS | CSF and serum from MS patients | [82] |
| Electrochemical (Voltammetry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Insulin | 5 pM/ 5–200 pM | Diabetes types I and II | Serum from diabetic patients | [83] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Interleukin-12 (IL-12) | 3.5 pg mL−1/ 0.1–500 pg mL−1 | MS | Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | [84] |
| Electrochemical (Amperometry) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) | 0.02 ng mL−1/ 0.03–230 ng mL−1 | RA | Serum from RA patients | [85] |
| Electrochemical (EIS) | Non-competitive, direct-type assay | IL-12 | <100 fM | MS | (Buffer) | [86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karachaliou, C.-E.; Livaniou, E. Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 6770. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156770
Karachaliou C-E, Livaniou E. Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6770. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156770
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarachaliou, Chrysoula-Evangelia, and Evangelia Livaniou. 2023. "Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6770. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156770
APA StyleKarachaliou, C.-E., & Livaniou, E. (2023). Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review. Sensors, 23(15), 6770. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156770







