A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
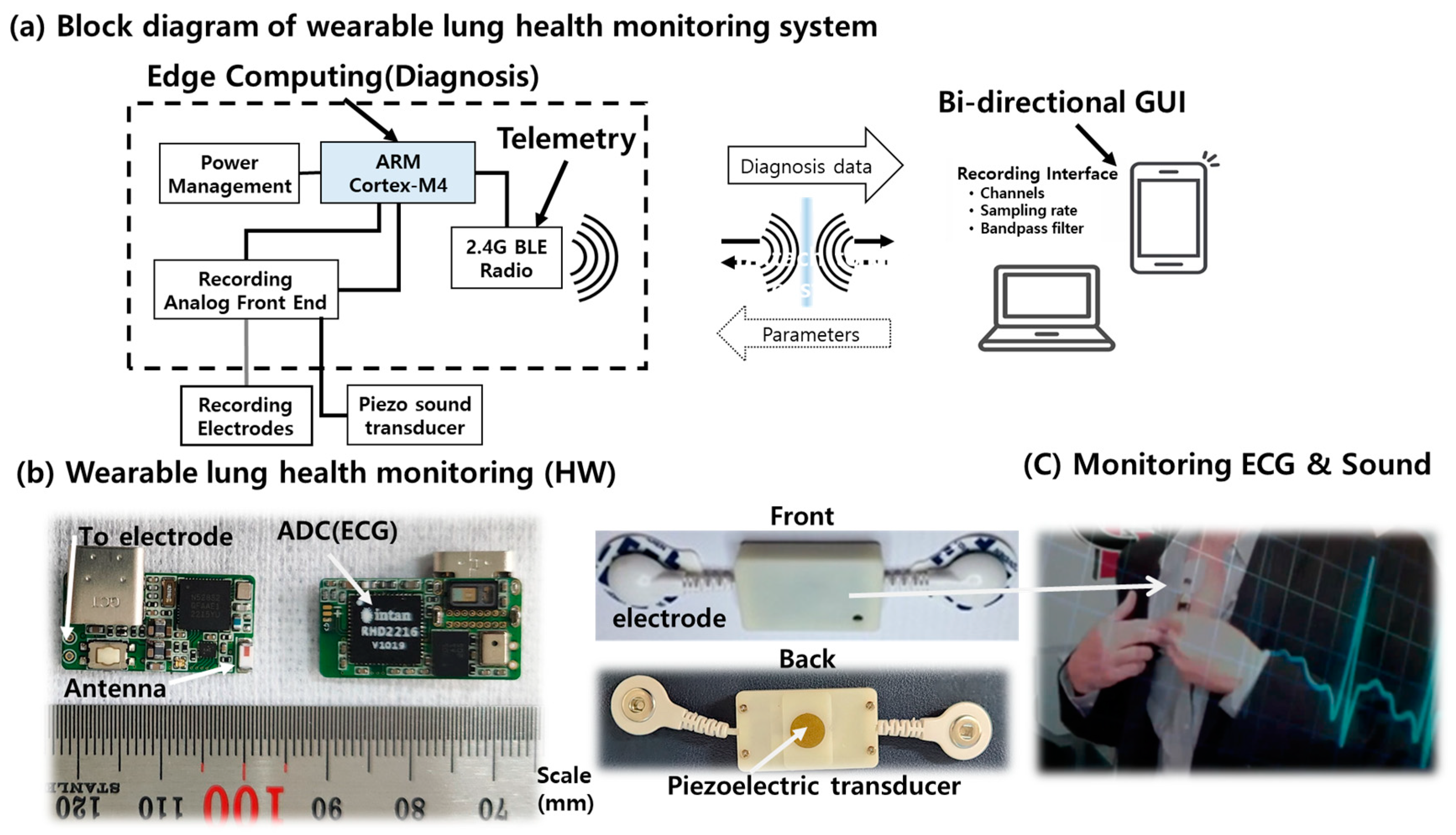
2. Wearable Lung Health Monitoring System and Experimental Setup
3. Modeling of Respiration Function
3.1. Sound Signal Modeling
3.2. ECG Signal Modeling
4. Lung Sound and ECG Sensor Signal Fusion
- Determining the cumulative AUC from lung sound and ECG signals using a seventh-order polynomial curve fit;
- Transformation of the AUCs into a series of signature matrices;
- Classification of the signature matrices’ characteristic respiration patterns.
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- do Nascimento, L.M.S.; Bonfati, L.V.; Freitas, M.L.B.; Mendes Junior, J.J.A.; Siqueira, H.V.; Stevan, S.L., Jr. Sensors and systems for physical rehabilitation and health monitoring—A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.K.; Sangkaew, S.; Chanh, H.Q.; Nhat, P.T.H.; Yacoub, S.; Georgiou, P.; Holmes, A.H. Continuous physiological monitoring using wearable technology to inform individual management of infectious diseases, public health and outbreak responses. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braman, S.S. The global burden of asthma. Chest 2006, 130, 4S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Asthma Facts—CDC’s National Asthma Control Program Grantees; US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bellia, V.; Scichilone, N.; Battaglia, S. Asthma in the elderly. Eur. Respir. Mon. 2009, 43, 56–76. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Khalidi, F.Q.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D.; Elphick, H.; Tan, S. Respiration rate monitoring methods: A review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 46, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siqueira, A.; Spirandeli, A.F.; Moraes, R.; Zarzoso, V. Respiratory waveform estimation from multiple accelerometers: An optimal sensor number and placement analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidhani, A.; Moon, K.S.; Ozturk, Y.; Lee, S.Q.; Youm, W. Extraction and analysis of respiratory motion using wearable inertial sensor system during trunk motion. Sensors 2017, 17, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Fan, Z.; Yao, P.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang Yadong Cao, Y.; Tai, H. Power generation humidity sensor based on NaCl/halloysite nanotubes for respiratory patterns monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.M.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Xie, L.X.; Li, Z. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator in wearable self-powered active sensor for respiration and healthcare monitoring. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 32, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, E.J.; Gómez, B.; Monsalve, E.; Aqueveque, P. Wireless Low–Cost Bioimpedance Measurement Device for Lung Capacity Screening. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1187–1190. [Google Scholar]
- George, U.Z.; Moon, K.S.; Lee, S.Q. Extraction and Analysis of Respiratory Motion Using a Comprehensive Wearable Health Monitoring System. Sensors 2021, 21, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenbein, E.; Firoozabadi, R.; Chien, S.; Carlson, E.; Babaeizadeh, S. Development of three methods for extracting respiration from the surface ECG: A review. J. Electrocardiol. 2014, 47, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuma, F.; Hayano, J. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Why does the heartbeat synchronize with respiratory rhythm? Chest 2004, 125, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Bonnici, T.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A.; Beale, R.; Watkinson, P.J. An assessment of algorithms to estimate respiratory rate from the electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, J.; Reljin, N.; Bailón, R.; Gil, E.; Noh, Y.; Laguna, P.; Chon, K.H. Electrocardiogram derived respiratory rate using a wearable armband. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzel, T.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Bartsch, R.P.; Riedl, M.; Kraemer, J.F.; Wessel, N.; Garcia, C.; Glos, M.; Fietze, I.; Schöbel, C. Modulations of heart rate, ECG, and cardio-respiratory coupling observed in polysomnography. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varon, C.; Morales, J.; Lázaro, J.; Orini, M.; Deviaene, M.; Kontaxis, S.; Testelmans, D.; Buyse, B.; Borzée, P.; Sörnmo, L. A Comparative Study of ECG-derived Respiration in Ambulatory Monitoring using the Single-lead ECG. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, H. Development of a respiratory inductive plethysmography module supporting multiple sensors for wearable systems. Sensors 2012, 12, 13167–13184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piuzzi, E.; Pisa, S.; Pittella, E.; Podestà, L.; Sangiovanni, S. Low-cost and portable impedance plethysmography system for the simultaneous detection of respiratory and heart activities. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Cai, M.; Shi, Y.; Ren, S.; Xu, W.; Gao, W.; Luo, Z.; Reinhardt, J.M. A novel method for automatic identification of breathing state. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, K.; WooSub, Y. An Interactive Health-Monitoring Platform for Wearable Wireless Sensor Systems. U.S. Patent Application 17/635,696, 15 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, D.J. Acoustical Respiratory Monitoring in the Time Domain. Open Anesth. J. 2019, 13, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Khandakar, A.; Alzoubi, K.; Mansoor, S.; MTahir, A.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Al-Emadi, N. Real-time smart-digital stethoscope system for heart diseases monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faezipour, M.; Abuzneid, A. Smartphone-based self-testing of COVID-19 using breathing sounds. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 26, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, M.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.D. Detection of sputum by interpreting the time-frequency distribution of respiratory sound signal using image processing techniques. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayward, N.; Shaban, M.; Badger, J.; Jones, I.; Wei, Y.; Spencer, D.; Isichei, S.; Knight, M.; Otto, J.; Rayat, G. A capaciflector provides continuous and accurate respiratory rate monitoring for patients at rest and during exercise. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2022, 36, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Sacchetti, M.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E. Contact-based methods for measuring respiratory rate. Sensors 2019, 19, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, C.; Nicolò, A.; Innocenti, L.; Sacchetti, M.; Schena, E.; Massaroni, C. Design and Testing of a Smart Facemask for Respiratory Monitoring during Cycling Exercise. Biosensors 2023, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, E.; Lasshofer, M.; Genitrini, M.; Schwameder, H. Enhanced breathing pattern detection during running using wearable sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.; Schaffarczyk, M.; Gronwald, T. Estimation of Respiratory Frequency in Women and Men by Kubios HRV Software Using the Polar H10 or Movesense Medical ECG Sensor during an Exercise Ramp. Sensors 2022, 22, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardi, G.; Massaroni, C.; Saccomandi, P.; Schena, E. Experimental assessment of a variable orifice flowmeter for respiratory monitoring. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 752540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prigent, G.; Aminian, K.; Rodrigues, T.; Vesin, J.-M.; Millet, G.P.; Falbriard, M.; Meyer, F.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A. Indirect estimation of breathing rate from heart rate monitoring system during running. Sensors 2021, 21, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degtyarenko, I.; Slyusarenko, K.; Omelchenko, A.; Riabov, V.; Chyzhyk, S. Low-power Continuous Heart and Respiration Rates Monitoring on Wearable Devices. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1298–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Dieffenderfer, J.; Goodell, H.; Mills, S.; McKnight, M.; Yao, S.; Lin, F.; Beppler, E.; Bent, B.; Lee, B.; Misra, V. Low-power wearable systems for continuous monitoring of environment and health for chronic respiratory disease. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, A.; Massaroni, C.; Schena, E.; Sacchetti, M. The importance of respiratory rate monitoring: From healthcare to sport and exercise. Sensors 2020, 20, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Bansal, S.; Ahuja, S.; Dubey, R.K.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Dey, N. Transfer learning–based ensemble support vector machine model for automated COVID-19 detection using lung computerized tomography scan data. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2021, 59, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Di Tocco, J.; Bravi, M.; Carnevale, A.; Presti, D.L.; Sabbadini, R.; Miccinilli, S.; Sterzi, S.; Formica, D.; Schena, E. Respiratory monitoring during physical activities with a multi-sensor smart garment and related algorithms. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Rhoades, R.D.; Kim, D.-Y.; Wu, N.; Liang, J.; Chae, J. Machine-learning enabled wireless wearable sensors to study individuality of respiratory behaviors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, P.; Badwal, J.; Alkhatib, F.; Singh, D.K.; Lindenauer, P.K.; Knee, A.; Lagu, T. Spirometry utilization among patients with asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Specification | Description | Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sound transducer | piezoelectric plate | 10 mm diameter | Sound from lung |
| ECG electrodes | Disposable Ag/AgCl standard pre-gelled and self-adhesive | (20 × 20) mm | Low impedance pre-gelled electrode |
| Front-end circuit | Intan Tech Chip | 10 mV, 16 bit, 8 ch | High resolution and low noise |
| Onboard CPU | ARM Cortex M4 | 4096 Hz sampling rate, onboard computing | Real-time data processing |
| Wireless Data transmission | NRF 52X, BLE5.0 | 2.4 GHz Carrier, 1 Mbps data rate in 2 m distance | Enable Wearable service |
| Power source | rechargeable battery | 8 h/charging | Internal battery for daytime |
| Experiment | Tidal Volume | Breathing Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| I—Deep breathing | 1000 mL | 4 s |
| II—Moderate breathing | 750 mL | 4 s |
| III—Shallow breathing | 500 mL | 4 s |
| IV—Coughing | Over 1000 mL | 4 s |
| Tidal Volume | F-Value (Sound) | p-Value (Sound) | F-Value (ECG) | p-Value (ECG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 mL vs. 500 mL | 18.22 (4.11) | 0.003 (0.07) | 3.04 (26.86) | 0.12 (0.0004) |
| 1000 mL vs. Cough | 128.81 | 0.003 | 34.93 | 0.004 |
| Critical value | 5.318 (4.965) | 0.05 (0.05) | 5.318 (4.965) | 0.05 (0.05) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, K.S.; Lee, S.Q. A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156790
Moon KS, Lee SQ. A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156790
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Kee S., and Sung Q Lee. 2023. "A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156790
APA StyleMoon, K. S., & Lee, S. Q. (2023). A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis. Sensors, 23(15), 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156790






