Measurement Technologies of Light Field Camera: An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
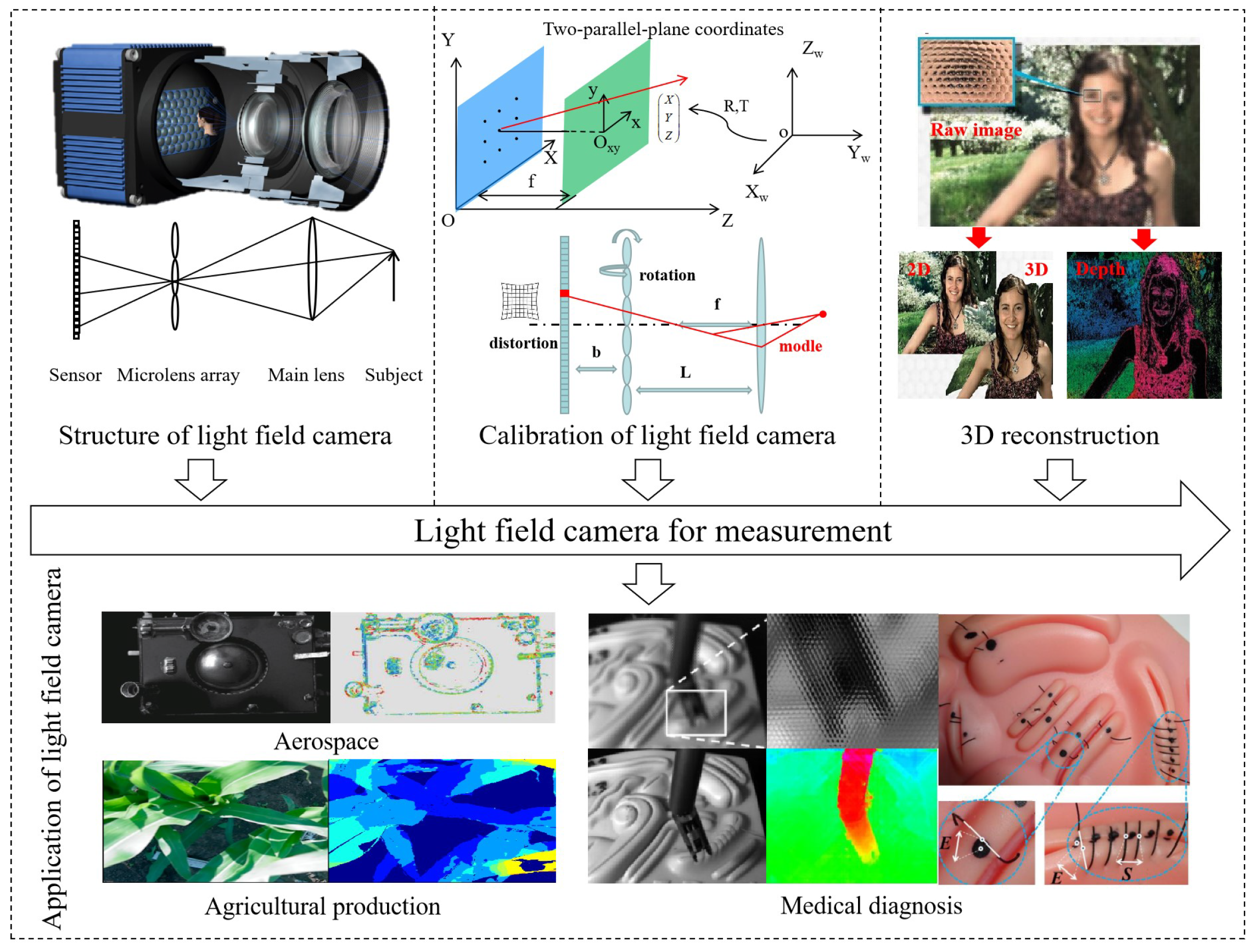
2. Imaging Principle of the Light Field Camera
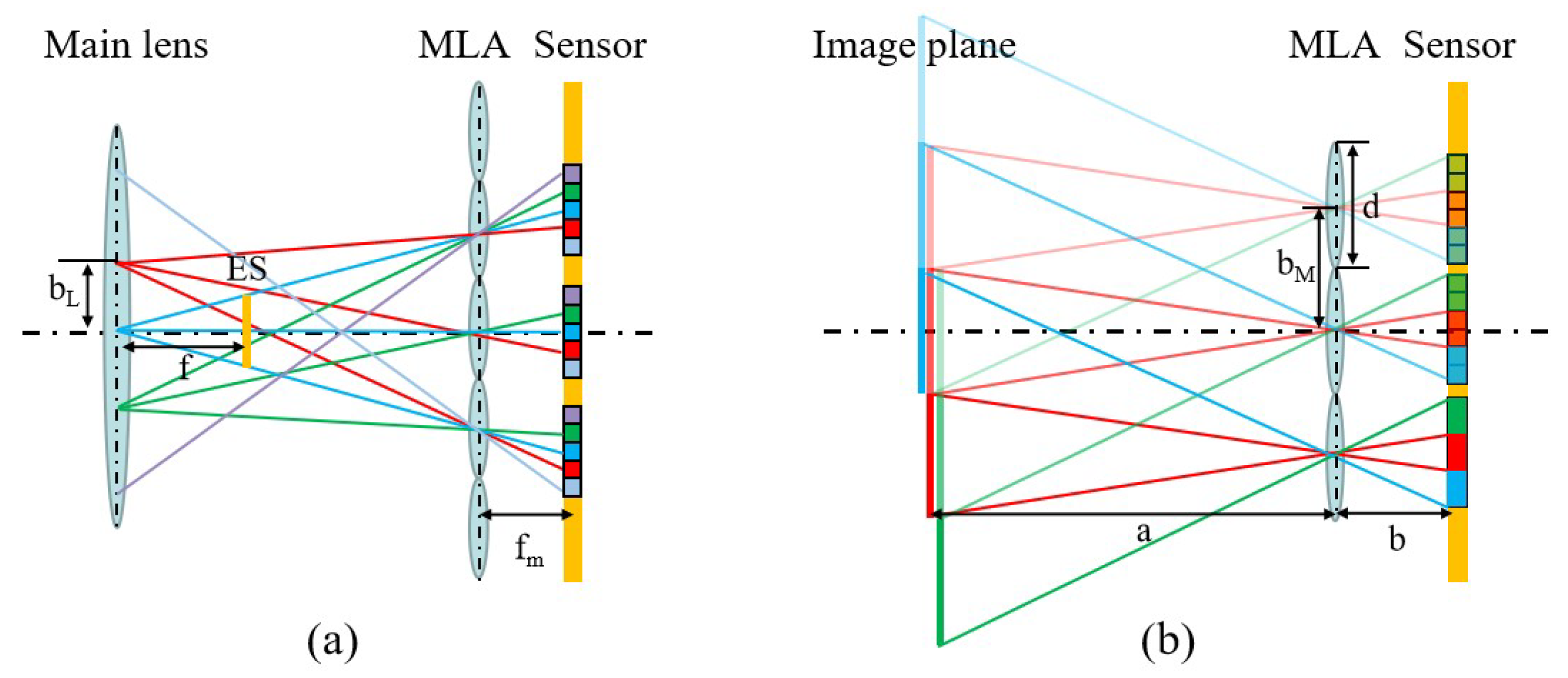
2.1. The Structure of the Light Field Camera
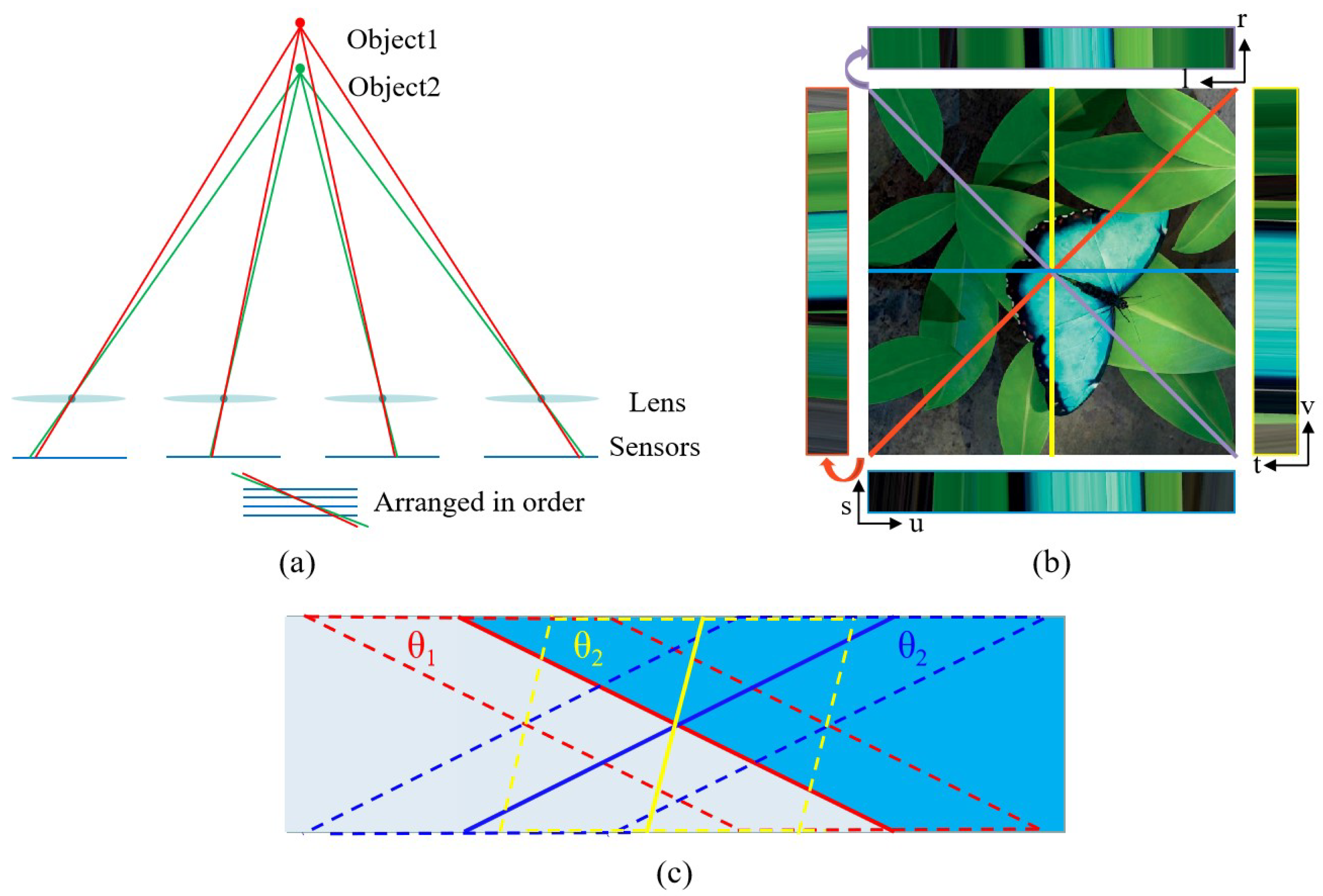
2.2. Measurement Fundamentals
2.3. Light Field Camera Design
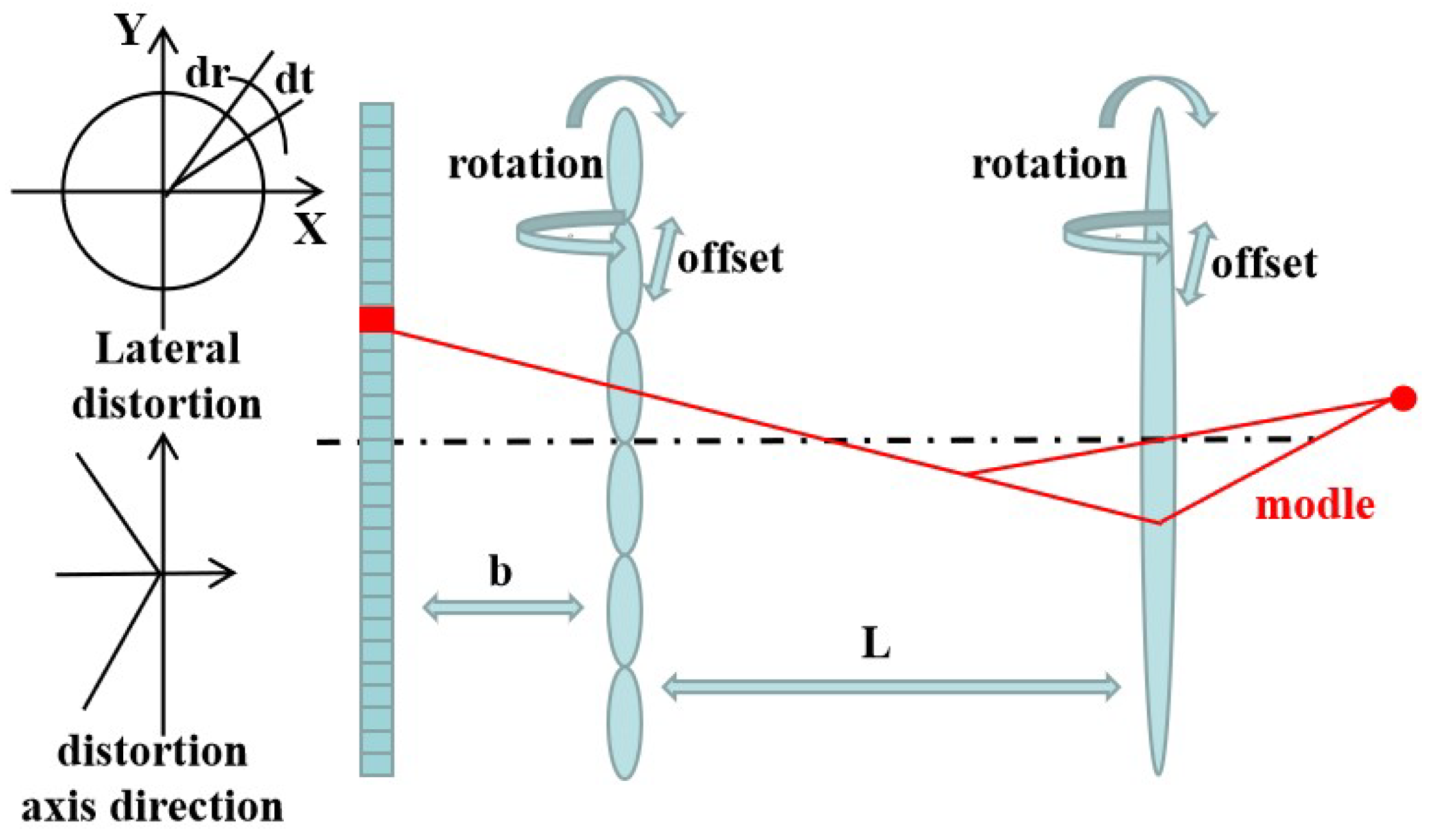
3. Calibration Technology of the Light Field Camera
4. Reconstruction Algorithms of the Light Field Camera
4.1. Light Field Reconstruction Based on Traditional Algorithms
4.2. Light Field Reconstruction Based on Deep Learning
4.3. Conclusions
5. Measurement Application of Light Field Camera
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Machine vision and applications. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2018, 457, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Kar, A.; Jha, S.; Khan, M. Machine vision system: A tool for quality inspection of food and agricultural products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marr, D. Vision: A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; He, Z.; Wu, C. Review on the machine vision measurement and control technology for intelligent manufacturing equipment. Control Theory Appl. 2015, 32, 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bodin, P.; Noteborn, R.; Larsson, R.; Karlsson, T.; D’Amico, S.; Ardaens, J.S.; Delpech, M.; Berges, J.-C. The prisma formation flying demonstrator: Overview and conclusions from the nominal mission. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 2012, 144, 441–460. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, J.A.; Cryan, S. A survey of lidar technology and its use in spacecraft relative navigation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control (GNC) Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 19–22 August 2013; p. 4641. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P. Research on comparison of lidar and camera in autonomous driving. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2093, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, A.; Grisleri, P.; Zani, P. Sensors technologies for intelligent vehicles perception systems: A comparison between vision and 3d-lidar. In Proceedings of the 16th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC 2013), The Hague, The Netherlands, 6–9 October 2013; pp. 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, R.; Levoy, M.; Brédif, M.; Duval, G.; Horowitz, M.; Hanrahan, P. Light Field Photography with a Hand-Held Plenoptic Camera. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Lu, S.; Hou, Y.; Shi, S. Accurate 3d geometry measurement for non-cooperative spacecraft with an unfocused light field camera. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2022, 33, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raytrix GmbH. Customer-Inspired Example Setups. Website. 2008. Available online: https://raytrix.de/examples/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Schima, R.; Mollenhauer, H.; Grenzdörffer, G.; Merbach, I.; Lausch, A.; Dietrich, P.; Bumberger, J. Imagine all the plants: Evaluation of a light field camera for on-site crop growth monitoring. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shademan, A.; Decker, R.S.; Opfermann, J.; Leonard, S.; Kim, P.C.; Krieger, A. Plenoptic cameras in surgical robotics: Calibration, registration, and evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Adelson, E.H.; Wang, J.Y. Single lens stereo with a plenoptic camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumsdaine, A.; Georgiev, T. The focused plenoptic camera. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–17 April 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, T.G.; Lumsdaine, A. Depth of field in plenoptic cameras. Eurographics 2009, 11814, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, T.; Lumsdaine, A. The multifocus plenoptic camera. In Digital Photography VIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8299, pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Lai, A.; Eaton, K.; Jin, P.; Gao, L. On the fundamental comparison between unfocused and focused light field cameras. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, A1–A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignard-Debise, L.; Restrepo, J.; Ihrke, I. A unifying first-order model for light field cameras: The equivalent camera array. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2017, 3, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahne, C.; Aggoun, A.; Velisavljevic, V.; Fiebig, S.; Pesch, M. Baseline and triangulation geometry in a standard plenoptic camera. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diebold, M.; Blum, O.; Gutsche, M.; Wanner, S.; Garbe, C.; Baker, H.; Jähne, B. Light-field camera design for high-accuracy depth estimation. In Videometrics, Range Imaging, and Applications XIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9528, p. 952803. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; New, T. Development and Application of Light-Field Cameras in Fluid Measurements; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, C.M.; Thurow, B.S.; Fahringer, T.W. Calibration of a microlens array for a plenoptic camera. In Proceedings of the 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014; p. 0396. [Google Scholar]
- Dansereau, D.G.; Pizarro, O.; Williams, S.B. Decoding, calibration and rectification for lenselet-based plenoptic cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, O.; Heinze, C.; Goldluecke, B.; Perwaß, C. On the calibration of focused plenoptic cameras. In Time-of-Flight and Depth Imaging. Sensors, Algorithms, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 302–317. [Google Scholar]
- Heinze, C.; Spyropoulos, S.; Hussmann, S.; Perwass, C. Automated robust metric calibration of multi-focus plenoptic cameras. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Pisa, Italy, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 2038–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Heinze, C.; Spyropoulos, S.; Hussmann, S.; Perwaß, C. Automated robust metric calibration algorithm for multifocus plenoptic cameras. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Q. Decoding and calibration method on focused plenoptic camera. Comput. Vis. Media 2016, 2, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Cai, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G. A two-step calibration method of lenslet-based light field cameras. Opt. Laser Eng. 2019, 115, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Mei, L.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Liu, N. A new imaging model of lytro light field camera and its calibration. Neurocomputing 2019, 328, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, Y.; Jeon, H.-G.; Kweon, I.S. Geometric calibration of micro-lens-based light field cameras using line features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Noury, C.-A.; Teulière, C.; Dhome, M. Light-field camera calibration from raw images. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Mo, F.; Aleksandrov, M.; Zlatanova, S.; Tao, P. Accurate calibration of standard plenoptic cameras using corner features from raw images. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, S.; Trumpf, J.; Ila, V.; Mahony, R. Calibrating light field cameras using plenoptic disc features. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 5–8 September 2018; pp. 286–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Ling, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J. A generic multi-projection-center model and calibration method for light field cameras. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2539–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, N.; Quint, F.; Stilla, U. Calibration and accuracy analysis of a focused plenoptic camera. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeller, N.; Quint, F.; Stilla, U. Depth estimation and camera calibration of a focused plenoptic camera for visual odometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 118, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, N.; Noury, C.; Quint, F.; Teulière, C.; Stilla, U.; Dhome, M. Metric calibration of a focused plenoptic camera based on a 3d calibration target. Proc. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahne, C.; Aggoun, A.; Haxha, S.; Velisavljevic, V.; Fernández, J.C.J. Light field geometry of a standard plenoptic camera. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 26659–26673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, N.B.; Barreto, J.P.; Gaspar, J.A. Standard plenoptic cameras mapping to camera arrays and calibration based on dlt. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 4090–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, Z.; Cai, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, G. Light field calibration and 3d shape measurement based on epipolar-space. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 10171–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, K.H.; Lingenauber, M. Stepwise calibration of focused plenoptic cameras. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 145, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. Light field camera self-calibration and registration. In Optoelectronic Imaging and Multimedia Technology IV; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 10020, pp. 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Gao, B.Z. Ray calibration and phase mapping for structured-light field 3d reconstruction. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7598–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lei, G.; Wang, T.; Xu, C. Improved blur circle detection method for geometric calibration of multifocus light field cameras. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 093101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Xie, B.; Wang, X. Geometric parameters calibration of focused light field camera based on edge spread information fitting. Photonics 2023, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Ai, H.-B.; Xu, B.; Sun, Y.-S.; Fan, Z.-L. Progress and prospect of 3d reconstruction based on light field cameras. Acta Electonica Sin. 2022, 50, 1774. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Hossain, M.M.; Xu, C.-L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.-M. A novel calibration method of focused light field camera for 3-d reconstruction of flame temperature. Opt. Commun. 2017, 390, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Ding, J.; New, T.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Volumetric calibration enhancements for single-camera light field piv. Exp. Fluids 2019, 60, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, S.; Goldluecke, B. Variational light field analysis for disparity estimation and super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Masia, B.; Jarabo, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Dai, Q.; Chai, T.; Liu, Y. Light field image processing: An overview. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 926–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, X.; Lin, H.; Lumsdaine, A.; Yu, J. Line assisted light field triangulation and stereo matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2792–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Heber, S.; Pock, T. Shape from light field meets robust pca. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 751–767. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, T.E.; Favaro, P. Plenoptic depth estimation from multiple aliased views. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 1622–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, T.E.; Favaro, P. Full-resolution depth map estimation from an aliased plenoptic light field. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 186–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sabater, N.; Drazic, V.; Seifi, M.; Sandri, G.; Pérez, P. Light-Field Demultiplexing and Disparity Estimation; HAL: Lyon, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sabater, N.; Seifi, M.; Drazic, V.; Sandri, G.; Pérez, P. Accurate disparity estimation for plenoptic images. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.-G.; Park, J.; Choe, G.; Park, J.; Bok, Y.; Tai, Y.-W.; Kweon, I.S. Accurate depth map estimation from a lenslet light field camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1547–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.W.; Hadap, S.; Malik, J.; Ramamoorthi, R. Depth from combining defocus and correspondence using light field cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 673–680. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.W.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Malik, J.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Ramamoorthi, R. Depth from shading, defocus, and correspondence using light field angular coherence. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1940–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Kang, S.B.; Yu, J. Depth recovery from light field using focal stack symmetry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3451–3459. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Lin, H.; Yu, Z.; Kang, S.B.; Yu, J. Light field stereo matching using bilateral statistics of surface cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1518–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.-C.; Efros, A.A.; Ramamoorthi, R. Occlusion-aware depth estimation using light field cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3487–3495. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J. Occlusion-model guided antiocclusion depth estimation in light field. IEEE J.-STSP 2017, 11, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williem, W.; Park, I.K. Robust light field depth estimation for noisy scene with occlusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4396–4404. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.K.; Lee, K.M. Robust Light Field Depth Estim. Using Occlusion-Noise Aware Data Costs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2484–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Bolles, R.C.; Baker, H.H.; Marimont, D.H. Epipolar-plane image analysis: An approach to determining structure from motion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1987, 1, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, S.; Goldluecke, B. Globally consistent depth labeling of 4d light fields. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Sheng, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z. Robust depth estimation for light field via spinning parallelogram operator. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 145, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D. Occlusion-aware depth estimation for light field using multi-orientation epis. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, S.A. Using color to separate reflection components. Color Res. Appl. 1985, 10, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.W.; Wang, T.-C.; Malik, J.; Ramamoorthi, R. Depth estimation for glossy surfaces with light field cameras. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 533–547. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.W.; Su, J.-C.; Wang, T.-C.; Malik, J.; Ramamoorthi, R. Depth estimation and specular removal for glossy surfaces using point and line consistency with light field cameras. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.-C.; Chandraker, M.; Efros, A.A.; Ramamoorthi, R. Svbrdf-invariant shape and reflectance estimation from light field cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5451–5459. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Murez, Z.; Cui, T.; Zhang, Z.; Kriegman, D.; Ramamoorthi, R. Depth and image restoration from light field in a scattering medium. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2401–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, O.; Honauer, K.; Goldluecke, B.; Alperovich, A.; Battisti, F.; Bok, Y.; Brizzi, M.; Carli, M.; Choe, G.; Diebold, M.; et al. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense light field depth estimation algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 82–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, C.; Jeon, H.-G.; Yoon, Y.; Kweon, I.S.; Kim, S.J. Epinet: A fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light field images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4748–4757. [Google Scholar]
- Heber, S.; Pock, T. Convolutional networks for shape from light field. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3746–3754. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-L.; Ouhyoung, M.; Chuang, Y.-Y. Attention-based view selection networks for light field disparity estimation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12095–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Fessler, J.A.; Norris, T.B.; Chun, I.Y. Light-field reconstruction and depth estimation from focal stack images using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 8648–8652. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Unsupervised depth estimation from light field using a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 5–8 September 2018; pp. 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Leng, Z.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Y. Cascade light field disparity estimation network based on unsupervised deep learning. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 25130–25146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Qi, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y. Temperature field reconstruction of 3d luminous flames based on light field tomography theory. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Ding, J.; New, T.H.; Soria, J. Light-field camera-based 3d volumetric particle image velocimetry with dense ray tracing reconstruction technique. Exp. Fluids 2017, 58, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VOMMA GmbH. Product Center. Website. 2020. Available online: http://www.vommatec.com/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Lingenauber, M.; Strobl, K.H.; Oumer, N.W.; Kriegel, S. Benefits of plenoptic cameras for robot vision during close range on-orbit servicing maneuvers. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
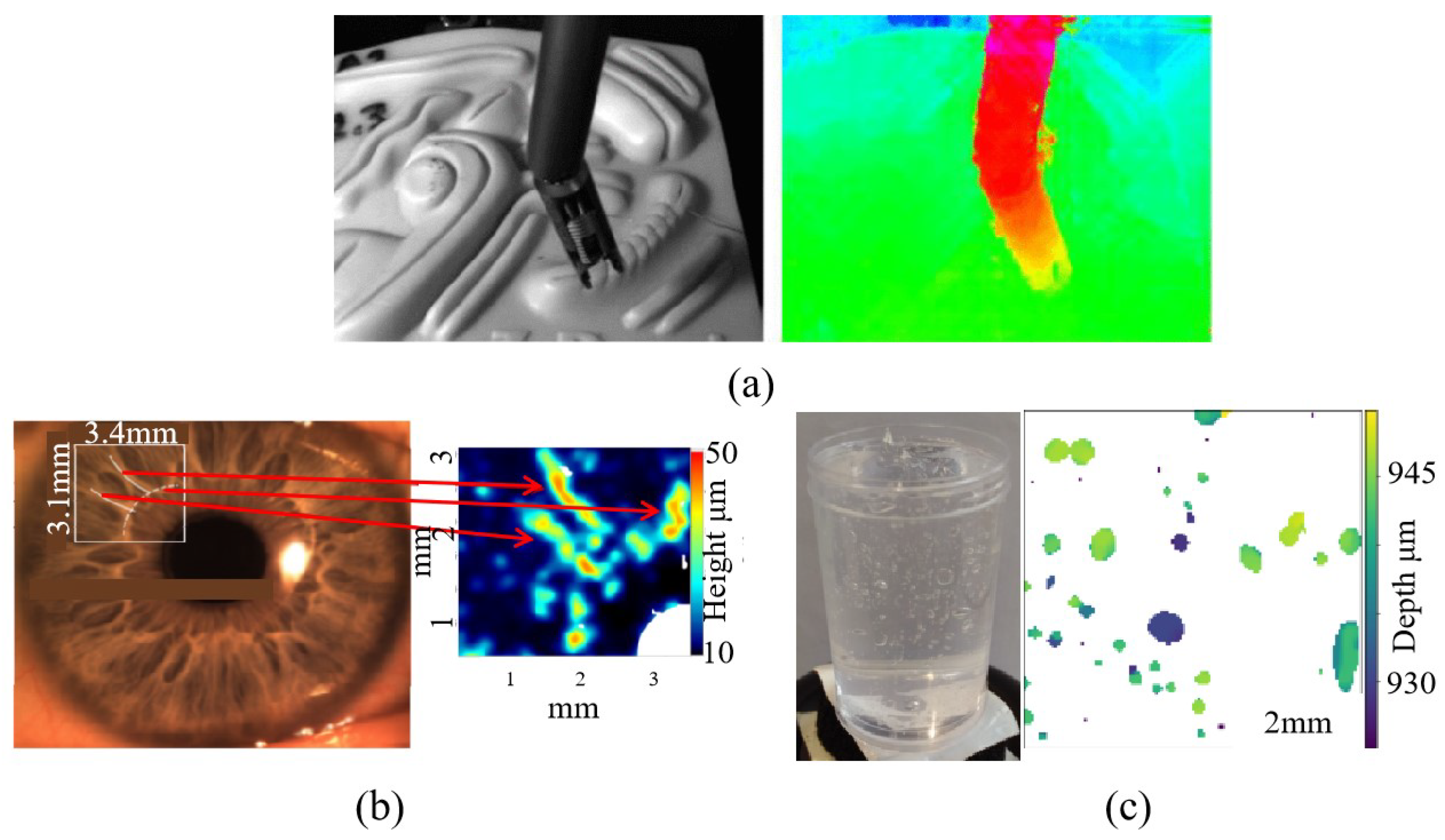
- Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B. A 3d measurement method of bubbles based on edge gradient segmentation of light field images. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139590. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, B.; Hossain, M.M.; Wang, S.; Qi, H.; Tan, H. Three-dimensional temperature field measurement of flame using a single light field camera. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luan, Y.; Mei, D.; Shi, S. Light-field multi-spectral radiation thermometry. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, X.; Quinn, M.K. 3d surface pressure measurement with single light field camera and pressure-sensitive paint. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D. Neuroimaging with light field microscopy: A mini review of imaging systems. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Woodward, M.A.; Burke, D.T.; Jeganathan, V.S.E.; Demirci, H.; Sick, V. Human iris three-dimensional imaging at micron resolution by a micro-plenoptic camera. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4514–4522. [Google Scholar]
- Viganò, N.; Lucka, V.; de La Rochefoucauld, O.; Coban, S.B.; van Liere, R.; Fajardo, M.; Zeitoun, P.; Batenburg, K.J. Emulation of X-ray light field cameras. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Yan, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhou, S.; Wei, R.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Snapshot compressive spectral-depth imaging based on light field. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2022, 6, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Thurow, B.S. Perspective on the development and application of light field cameras in flow diagnostics. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 101001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Chang, K.; Tang, J.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Huang, R.; Yu, J. Detection method of rice blast based on 4d light field refocusing depth information fusion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107614. [Google Scholar]
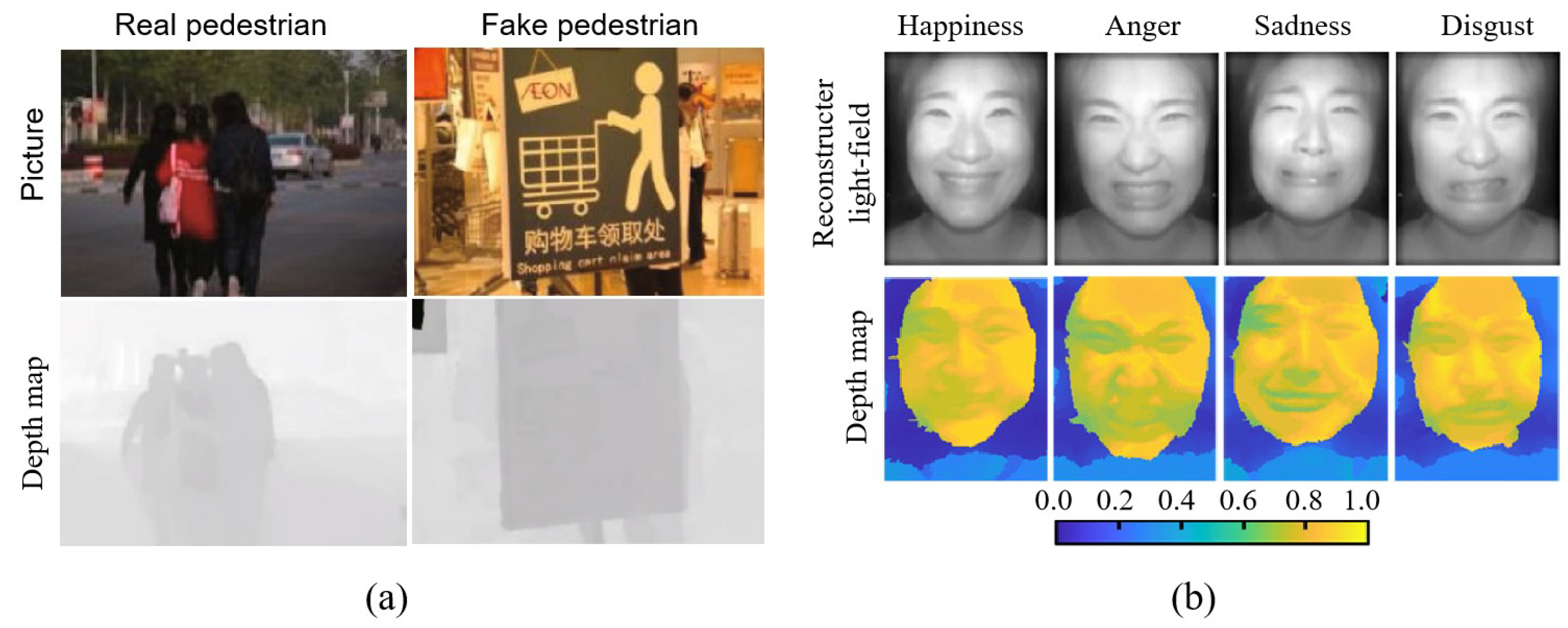
- Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhao, M. Light field imaging based on a parallel svm method for recognizing 2d fake pedestrians. Optoelectron. Lett. 2022, 18, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.-I.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.-M.; Kim, H.-K.; Jang, K.-W.; Lee, D.; Jeong, K.-H. Machine-learned light field camera that reads facial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3d facial images. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100182. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q. Review of state-of-the-art artificial compound eye imaging systems. Bioinspir. Biomimetics 2019, 14, 031002. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-B.; Jang, H.; Park, S.; Song, Y.M.; Lee, H.-N. Compu-eye: A high resolution computational compound eye. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, V.; Liu, H.-C.; Halioua, M. Automated phase-measuring profilometry of 3-d diffuse objects. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 3105–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Gao, Y.; He, H.; Lu, D.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Nerf: Neural radiance field in 3d vision, a comprehensive review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.00379. [Google Scholar]







| System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Single camera | Simple system, small size, and light weight | Poor depth recovery |
| Multi-view system | High measurement accuracy and retention of features such as color and texture | Cumbersome calibration and large system size |
| LiDAR | Long measuring distance, high measuring accuracy, and low influence by light | High cost and low sampling accuracy |
| Light field camera | Small size, light weight, good dynamic performance, and dense view | Low measurement accuracy and high data volume |
| Type of Light Field Camera | Angular Resolution (Depth Resolution) | Spatial Resolution (Lateral Resolution) | Depth of Field | Reconstruction Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | high | low | high | low |
| Focused | low | high | low | high |
| Wang | Williem | Shin | Tsai | Peng | Liu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buddha | 11.68/1.94 | 3.21/0.64 | 1.55/0.36 | 2.02/0.33 | 11.55/1.14 | 4.54/0.33 |
| Papillon | 29.97/0.83 | 7.33/0.65 | 35.56/6.12 | 34.96/5.07 | 30.30/5.32 | 27.10/1.06 |
| Stilllife | 59.45/84.61 | 14.4/1.26 | 11.37/2.43 | 11.78/14.01 | 42.05/17.28 | 8.97/5.52 |
| Avg | 33.7/29.13 | 8.31/0.85 | 16.16/2.97 | 16.25/6.47 | 27.97/7.91 | 13.54/2.30 |
| Algorithms | Precision | Efficiency | Stability | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | high | low | more stable | No |
| Deep learning | low | high | less stable | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Miao, L.; Fang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X. Measurement Technologies of Light Field Camera: An Overview. Sensors 2023, 23, 6812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156812
Hu X, Li Z, Miao L, Fang F, Jiang Z, Zhang X. Measurement Technologies of Light Field Camera: An Overview. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156812
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaoming, Zhuotong Li, Li Miao, Fengzhou Fang, Zhongjie Jiang, and Xiaodong Zhang. 2023. "Measurement Technologies of Light Field Camera: An Overview" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156812
APA StyleHu, X., Li, Z., Miao, L., Fang, F., Jiang, Z., & Zhang, X. (2023). Measurement Technologies of Light Field Camera: An Overview. Sensors, 23(15), 6812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156812