Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Case Presentation
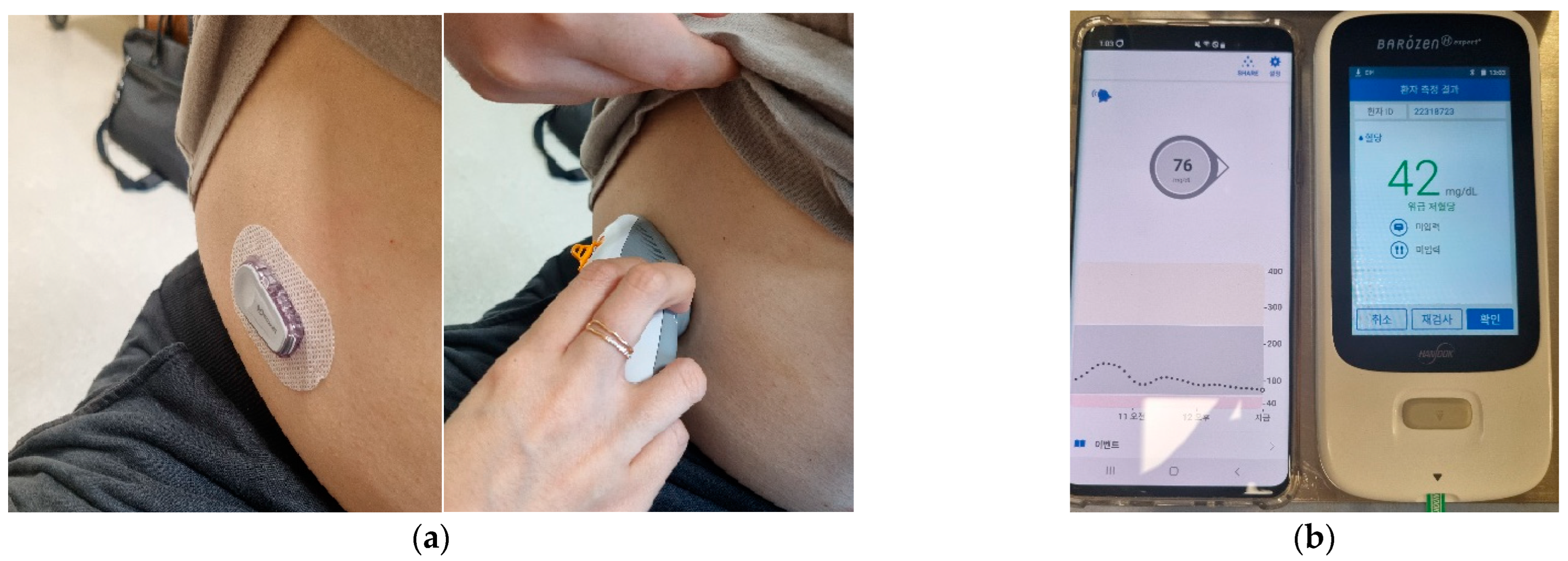
3.1. Case 1
3.2. Case 2
3.3. Case 3
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.H.; Chae, H.W.; Chin, S.O.; Ku, C.R.; Park, K.H.; Lim, D.J.; Kim, K.J.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, G.; Choi, Y.M.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molitch, M.E.; Clemmons, D.R.; Malozowski, S.; Merriam, G.R.; Vance, M.L.; Endocrine, S. Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1587–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Yoo, H.W.; Choi, J.H. Efficacy of growth hormone therapy in adults with childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 19, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, M.J. Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in human. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 22, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuen, K.C.J. Growth Hormone Stimulation Tests in Assessing Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, C.; Meinel, T.; Lahner, H.; Mann, K.; Petersenn, S. Recovery of pituitary function in the late-postoperative phase after pituitary surgery: Results of dynamic testing in patients with pituitary disease by insulin tolerance test 3 and 12 months after surgery. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laffel, L.M.; Kanapka, L.G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergamo, K.; Clements, M.A.; Criego, A.; DeSalvo, D.J.; Goland, R.; Hood, K.; Liljenquist, D.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H. Current status of continuous glucose monitoring among Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 25, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klupa, T.; Czupryniak, L.; Dzida, G.; Fichna, P.; Jarosz-Chobot, P.; Gumprecht, J.; Mysliwiec, M.; Szadkowska, A.; Bomba-Opon, D.; Czajkowski, K.; et al. Expanding the Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Modern Diabetes Care Beyond Type 1 Disease. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 1241–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, R.; Bloch, W.; Brinkmann, C. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Healthy Adults-Possible Applications in Health Care, Wellness, and Sports. Sensors 2022, 22, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Levi, A.M.; Rubio-Herrera, M.A.; Matia-Martin, P.; Perez-Ferre, N.; Marcuello, C.; Sanchez-Pernaute, A.; Torres-Garcia, A.J.; Calle-Pascual, A.L. Mixed Meal Tolerance Test Versus Continuous Glucose Monitoring for an Effective Diagnosis of Persistent Post-Bariatric Hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadwa, R.P.; Laffel, L.M.; Shah, V.N.; Garg, S.K. Accuracy of a Factory-Calibrated, Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring System During 10 Days of Use in Youth and Adults with Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeliosof, O.; Gangat, M. Diagnosis and management of hypopituitarism. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aken, M.O.; Lamberts, S.W. Diagnosis and treatment of hypopituitarism: An update. Pituitary 2005, 8, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Agreement between methods of measurement with multiple observations per individual. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2007, 17, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersenn, S.; Quabbe, H.J.; Schofl, C.; Stalla, G.K.; von Werder, K.; Buchfelder, M. The rational use of pituitary stimulation tests. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, P.; Dwyer, A.A.; Anghel, E.; Bouloux, P.M.; Khoo, B.; Chew, S.; Wernig, F.; Carroll, P.; Aylwin, S.J.B.; Baldeweg, S.E.; et al. A Comparison of the Blood Glucose, Growth Hormone, and Cortisol Responses to Two Doses of Insulin (0.15 U/kg vs. 0.10 U/kg) in the Insulin Tolerance Test: A Single-Centre Audit of 174 Cases. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 7360282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, Z.; Grossman, A.; Kelestimur, F. Investigation of the Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis: A contemporary synthesis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.R.; Graves, D.F.; Tacker, D.H.; Okorodudu, A.O.; Mohammad, A.A.; Cardenas, V.J., Jr. Comparison of POCT and central laboratory blood glucose results using arterial, capillary, and venous samples from MICU patients on a tight glycemic protocol. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 396, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, J.H.; Lorenzi, M.; Young, C.W.; Burns, A.D.; Prosser, P.R.; Grodsky, G.M.; Galante, M.; Forsham, P.H. Feedback-controlled dextrose infusion during surgical management of insulinomas. Am. J. Med. 1979, 66, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajjan, R.A.; Cummings, M.H.; Jennings, P.; Leelarathna, L.; Rayman, G.; Wilmot, E.G. Accuracy of flash glucose monitoring and continuous glucose monitoring technologies: Implications for clinical practice. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.N.; Laffel, L.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Garg, S.K. Performance of a Factory-Calibrated Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Utilizing an Automated Sensor Applicator. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tauschmann, M.; Forlenza, G.; Hood, K.; Cardona-Hernandez, R.; Giani, E.; Hendrieckx, C.; DeSalvo, D.J.; Laffel, L.M.; Saboo, B.; Wheeler, B.J.; et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Diabetes technologies: Glucose monitoring. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1390–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.I.G.; DeVries, J.H.; Hess-Fischl, A.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kirkman, M.S.; Klupa, T.; Ludwig, B.; Norgaard, K.; Pettus, J.; Renard, E.; et al. The Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Adults. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2589–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, C.; Brooks, A.; Basudev, N.; Lincoln, P. Continuous glucose monitoring for adults and children with diabetes: Summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ 2022, 379, o2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visavachaipan, N.; Aledo, A.; Franklin, B.H.; Brar, P.C. Continuous glucose monitoring: A valuable monitoring tool for management of hypoglycemia during chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothong, C.; Singh, L.G.; Satyarengga, M.; Spanakis, E.K. Continuous glucose monitoring in the hospital: An update in the era of COVID-19. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worth, C.; Dunne, M.; Ghosh, A.; Harper, S.; Banerjee, I. Continuous glucose monitoring for hypoglycaemia in children: Perspectives in 2020. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.L.; Battin, M.R.; Weston, P.J.; Harding, J.E. Continuous glucose monitoring in newborn babies at risk of hypoglycemia. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.E.; Fanelli, J.E.; Aloi, J.A.; Anzola, S.C.; Vishneski, S.R.; Saha, A.K.; Woody, C.C.; Segal, S. Feasibility of intraoperative continuous glucose monitoring: An observational study in general surgery patients. J. Clin. Anesth. 2023, 87, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, T.G.; Sargent, C.; Roach, G.D. Glucose Concentrations from Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Compared to Those from Blood Plasma during an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Healthy Young Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberer, F.; Hajnsek, M.; Rumpler, M.; Zenz, S.; Baumann, P.M.; Elsayed, H.; Puffing, A.; Treiber, G.; Pieber, T.R.; Sourij, H.; et al. Evaluation of subcutaneous glucose monitoring systems under routine environmental conditions in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worth, C.; Dunne, M.J.; Salomon-Estebanez, M.; Harper, S.; Nutter, P.W.; Dastamani, A.; Senniappan, S.; Banerjee, I. The hypoglycaemia error grid: A UK-wide consensus on CGM accuracy assessment in hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1016072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeropoulou, M.S.; Iglesias-Platas, I.; Beardsall, K. Should continuous glucose monitoring be used to manage neonates at risk of hypoglycaemia? Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, T.; Heinemann, L.; Kolassa, R.; Thomas, A. Discrepancies Between Blood Glucose and Interstitial Glucose-Technological Artifacts or Physiology: Implications for Selection of the Appropriate Therapeutic Target. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Peak | Baseline | Peak | Baseline | Peak | |
| Insulin tolerance test | ||||||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 48 | 87 | 80 | |||
| GH (ng/mL) | 0.08 | <0.04 | 0.06 | 1.08 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Cortisol (ug/dL) | 20.05 | 35.25 | 10.42 | 22.57 | 0.22 | 0.38 |
| IGF-I (ng/mL) | 121 | 61.12 | 133 | |||
| TRH stimulation test | ||||||
| TSH (mIU/L) | 1 | 3.8 | 2.56 | 13.92 | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| fT4 (ng/dL) | 1.19 | 0.99 | 1.24 | |||
| Prolactin (ng/mL) | 11.58 | 22.05 | 4.41 | 31.25 | 1.04 | 2.82 |
| GnRH stimulation test | ||||||
| LH (mIU/mL) | 0.98 | 4.06 | 2.07 | 11.01 | 1.08 | 1.79 |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | 1.43 | 4.92 | 1.98 | 6.92 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 0.47 | - | - | - | 2.44 | - |
| E2 (pg/mL) | - | - | 245.7 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, S.Y.; Ahn, M.B. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests. Sensors 2023, 23, 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156892
Sim SY, Ahn MB. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156892
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, Soo Yeun, and Moon Bae Ahn. 2023. "Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156892
APA StyleSim, S. Y., & Ahn, M. B. (2023). Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests. Sensors, 23(15), 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156892






