A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Acoustic Emission (AE)
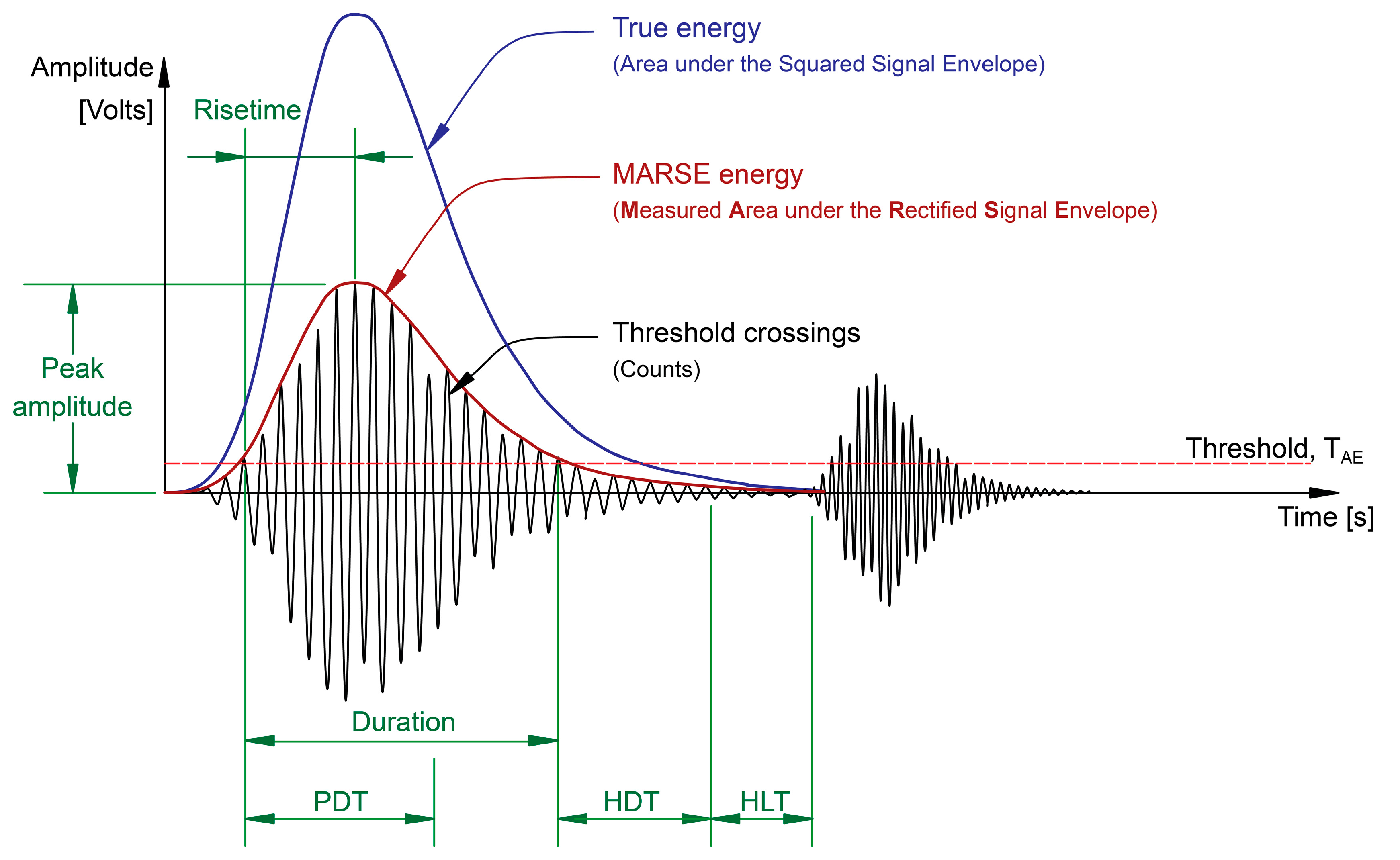
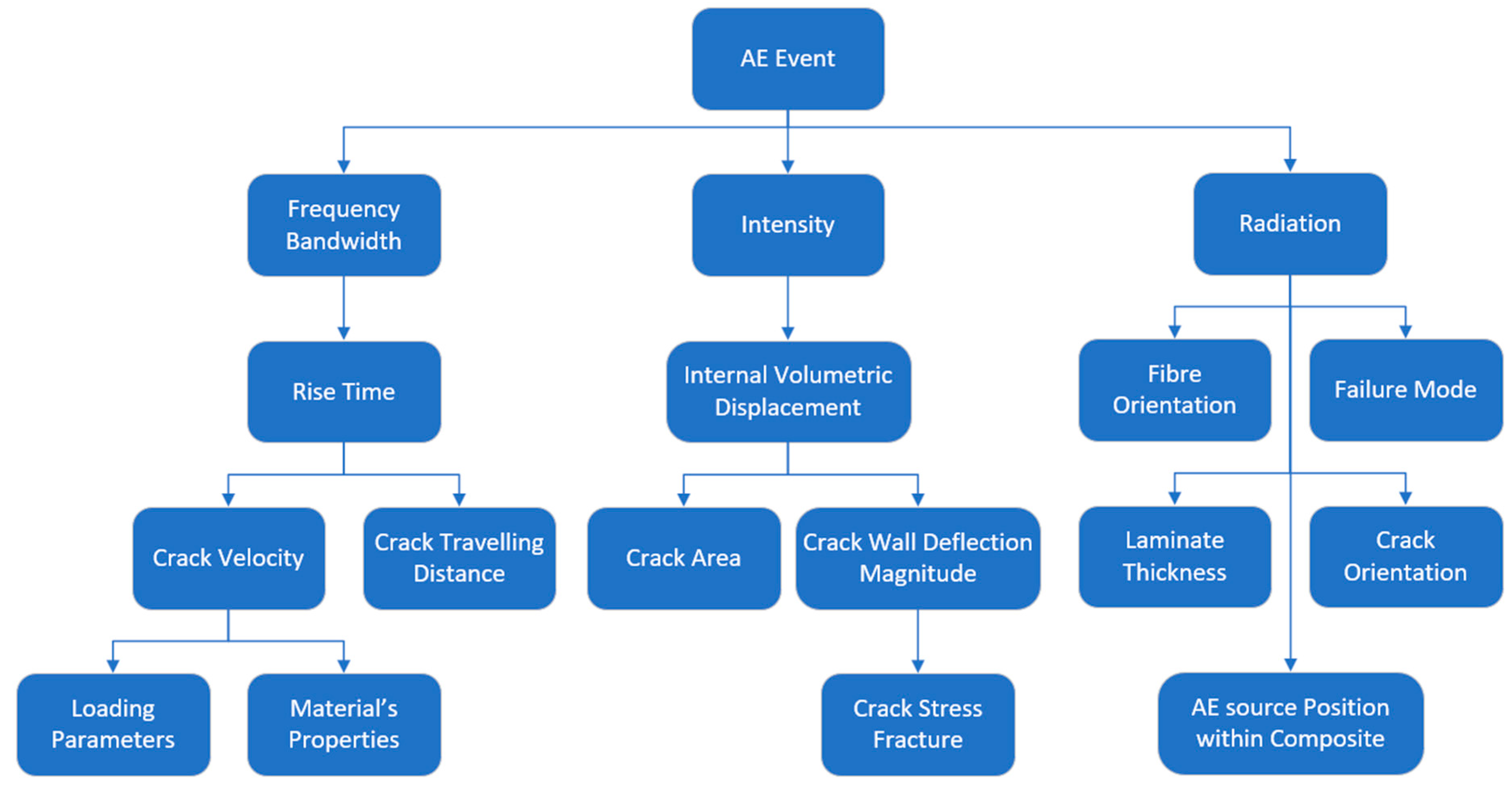
2.1. AE Parametric Features
2.2. AE Sources
2.2.1. Composite Mechanical Loading
- -
- Matrix cracking can be distinguished by low amplitude, low energy, and a slow rise time.
- -
- Fibre-matrix debonding has a higher amplitude, higher energy, and shorter rise time.
- -
- Fibre breakage has a quicker rise time, a short duration, a higher amplitude, and a higher energy.
- -
- Delamination has a slow rise time, a much longer duration, and higher energy.
- -
- Core damage is characterised by a short rise time, a short time, and low amplitude and energy.
- -
- Resin cracking is characterised by a slower rise time and higher energy and amplitude.
- -
- Interfacial debonding waveforms have a slow rise time, a long duration, and a higher amplitude and energy.
- -
- Fibre-breaking signals have a quick rise time, an extremely short time, and a very high amplitude and energy.
2.2.2. Physical Contact
2.2.3. Noise
2.3. Artificial AE Sources
2.3.1. Pencil Lead Breaking
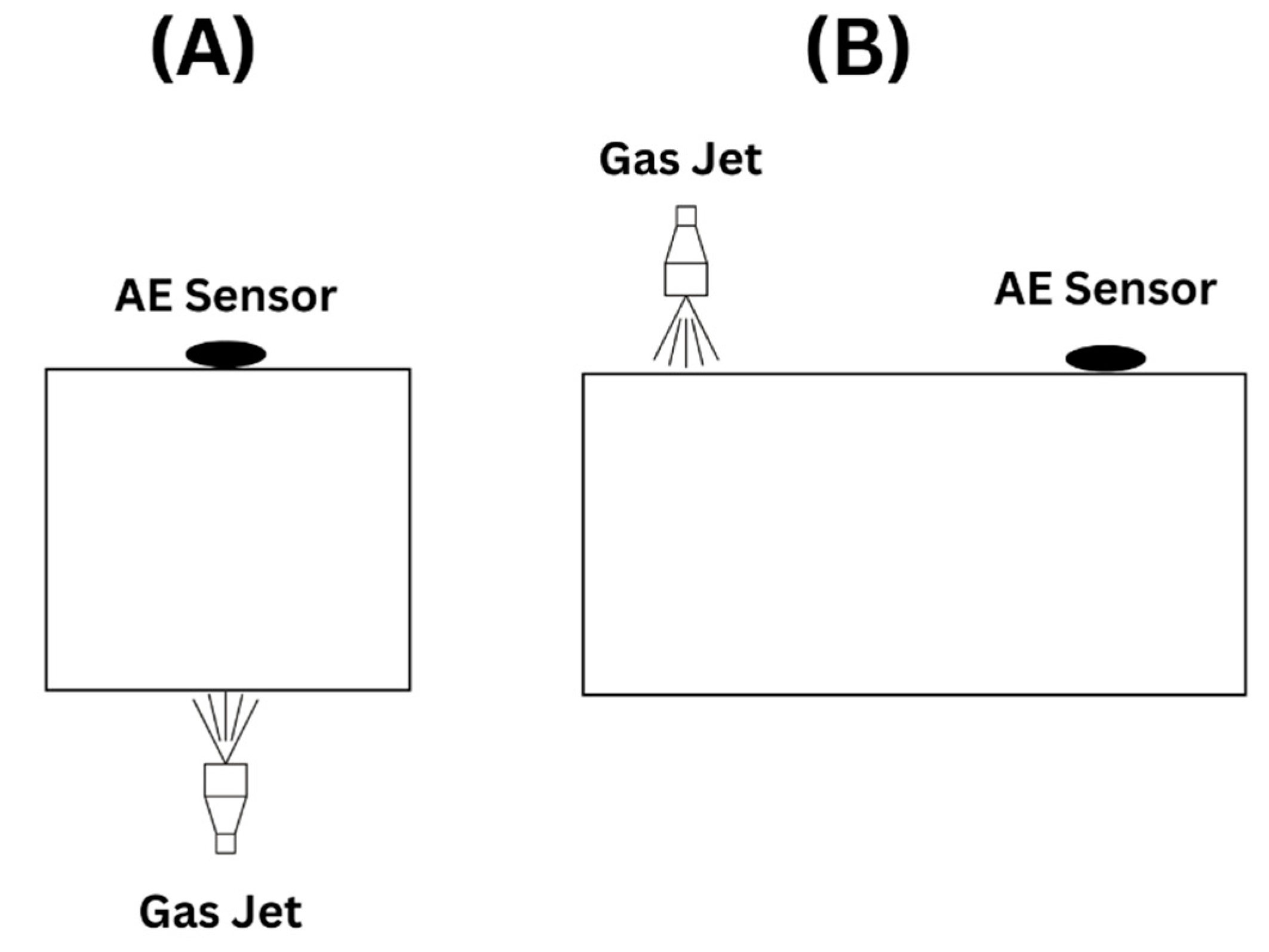
2.3.2. Gas Jet
2.3.3. Transducer
2.4. AE Details in Composites
2.4.1. Bandwidth Response
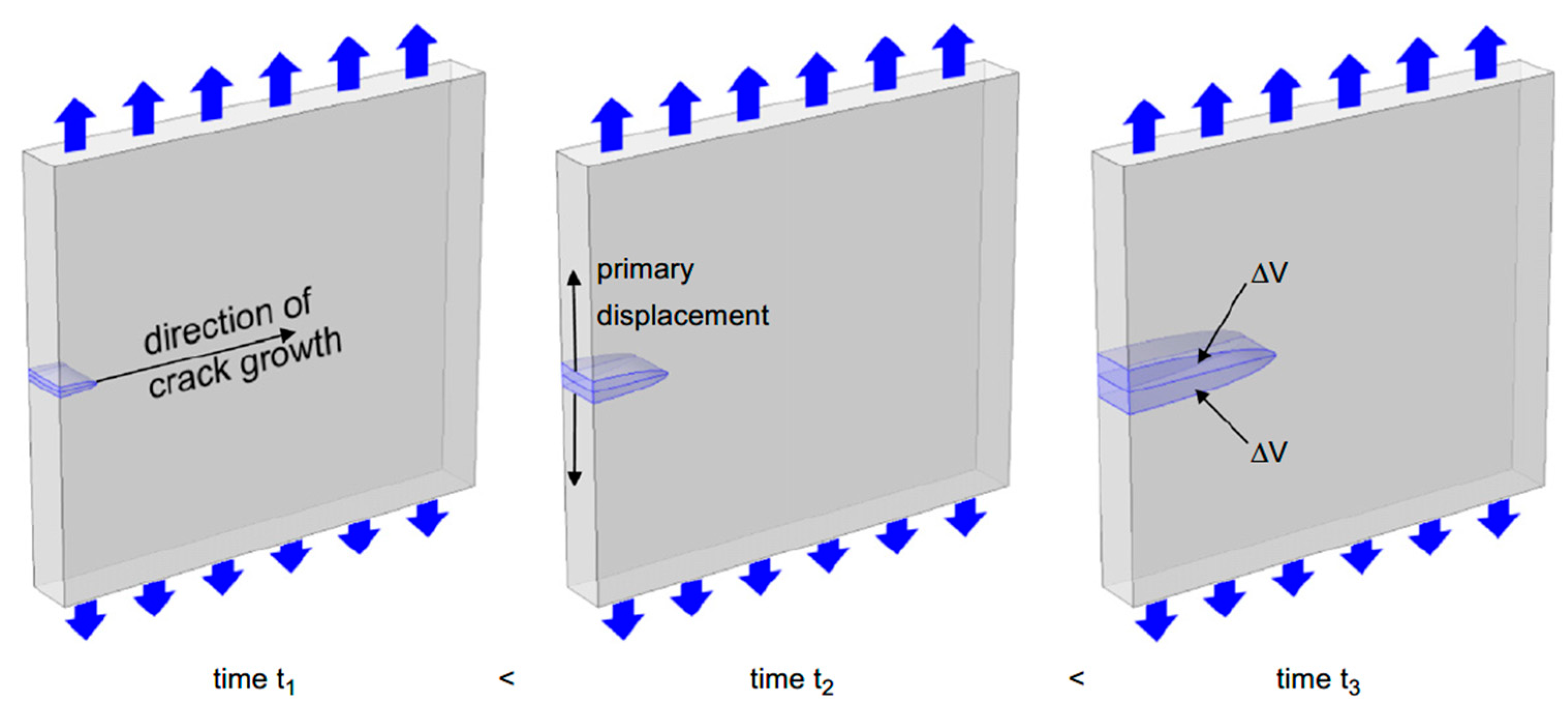
2.4.2. The Intensity of the AE Signal
2.4.3. Radiation through the Material
2.5. The Signal-Shaping Chain
2.5.1. Propagation of the Wave
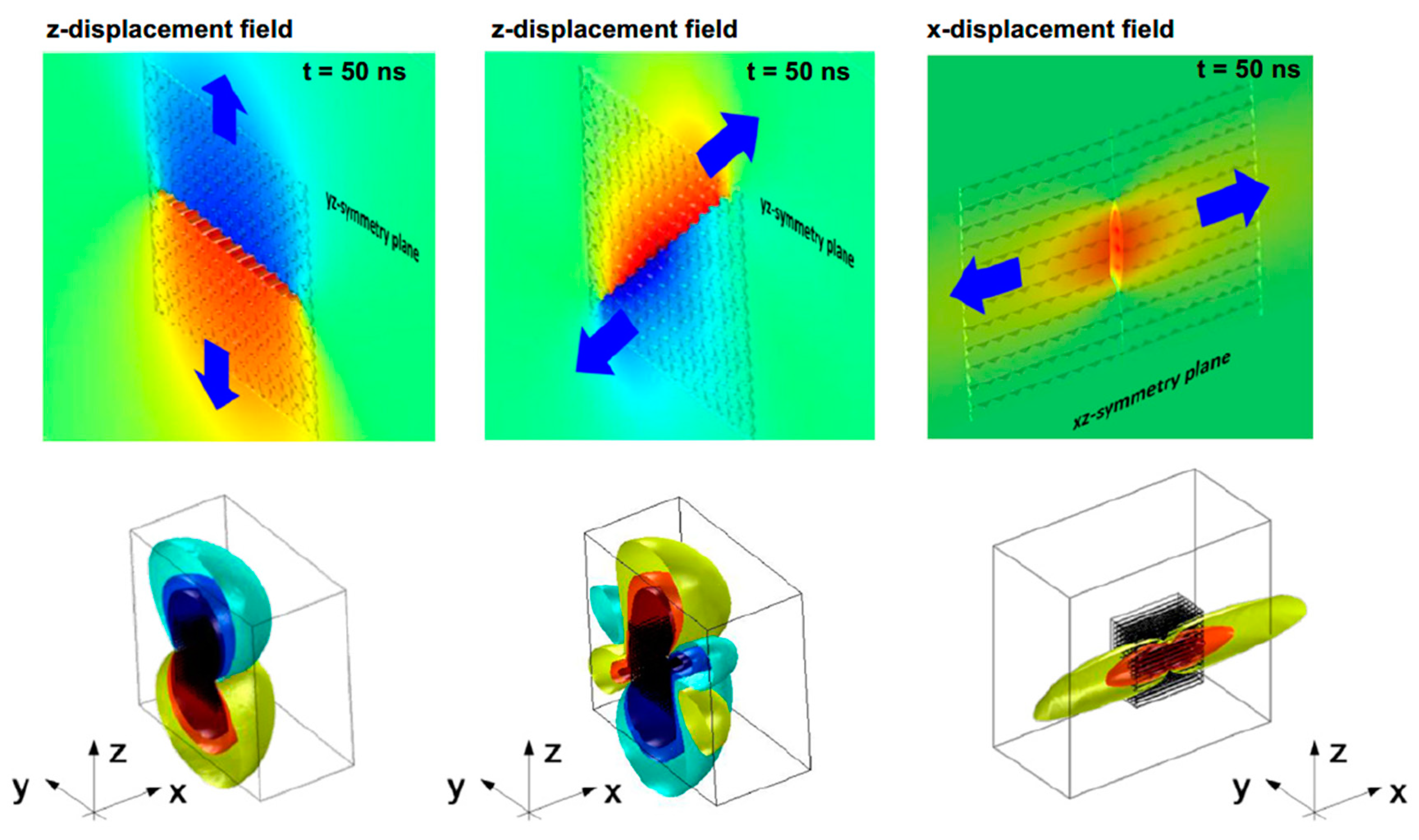
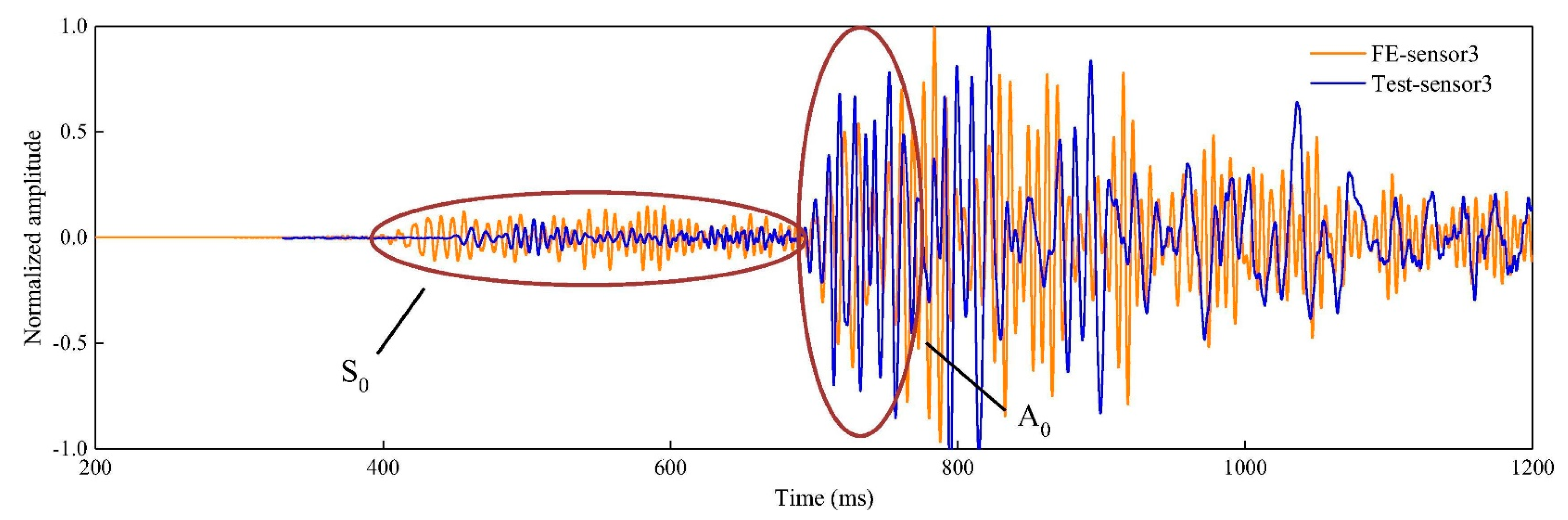
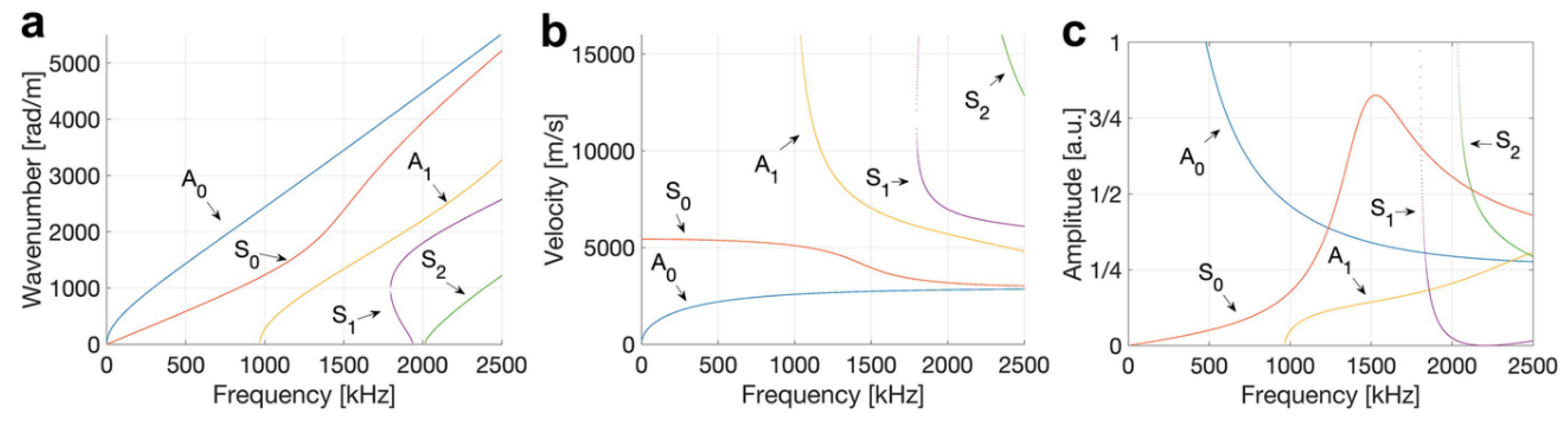
2.5.2. Wave Modes [35]
2.5.3. Attenuation [35]
2.6. Couplant
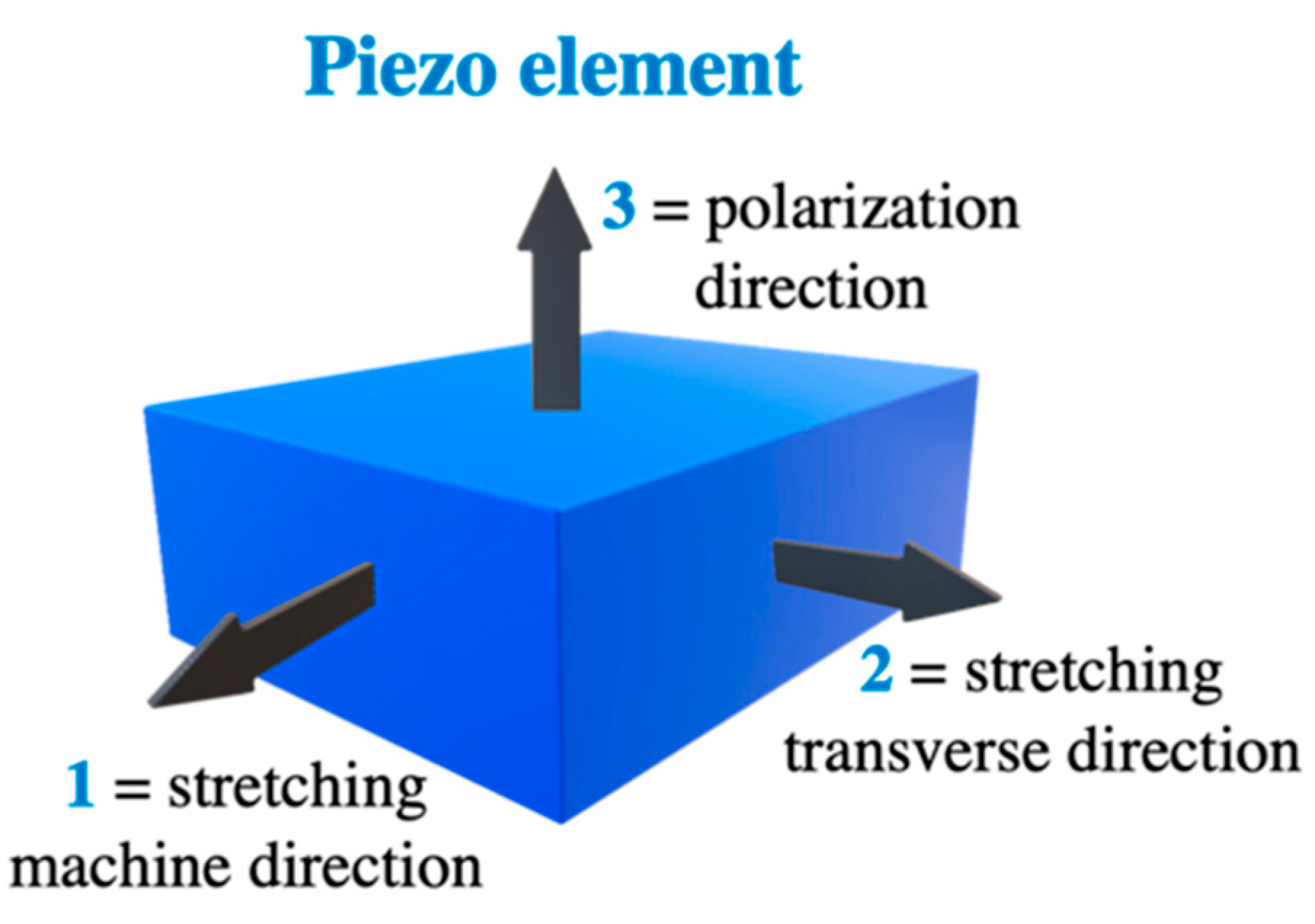
2.7. Piezoelectric-Based Acoustic Emission Sensors
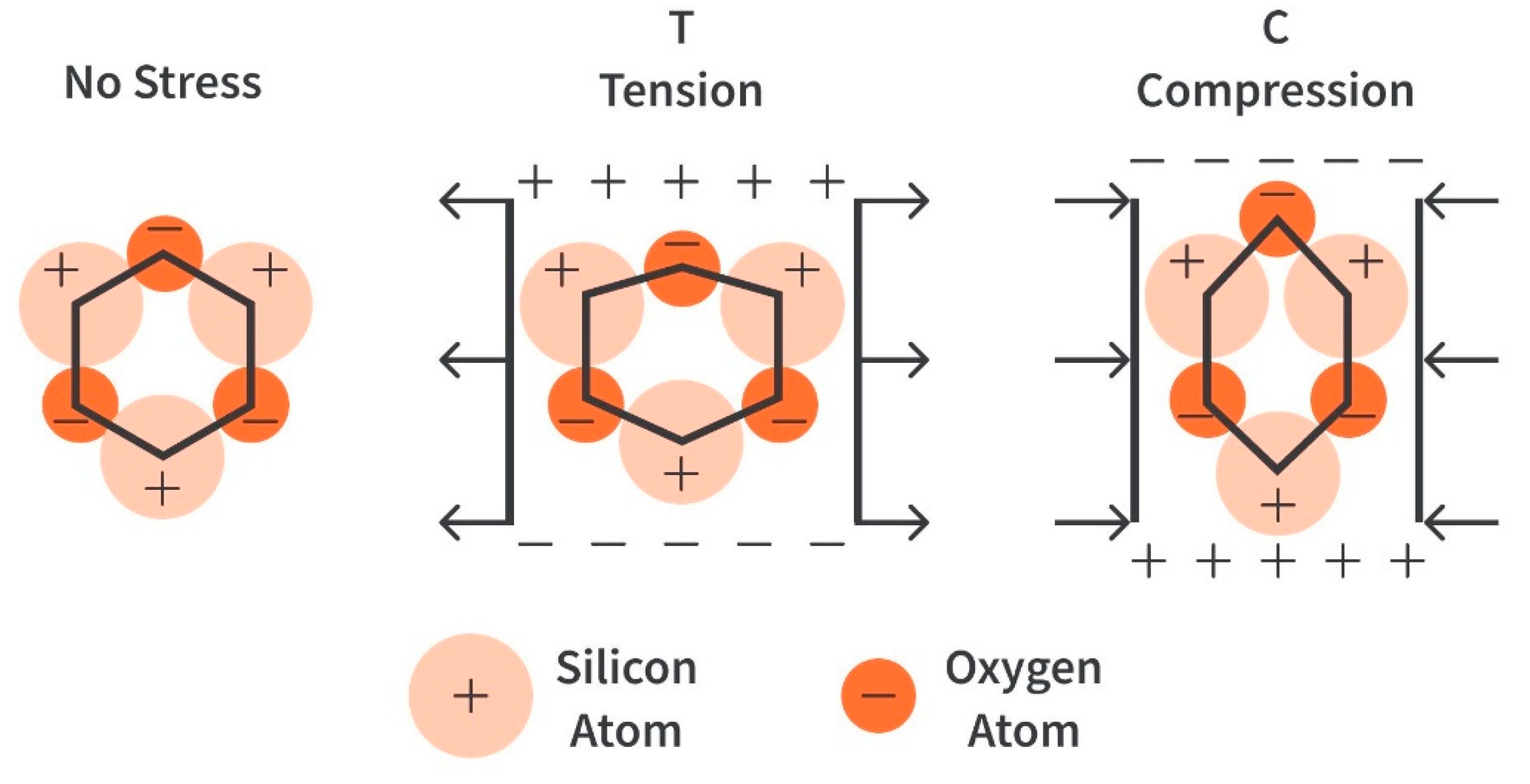
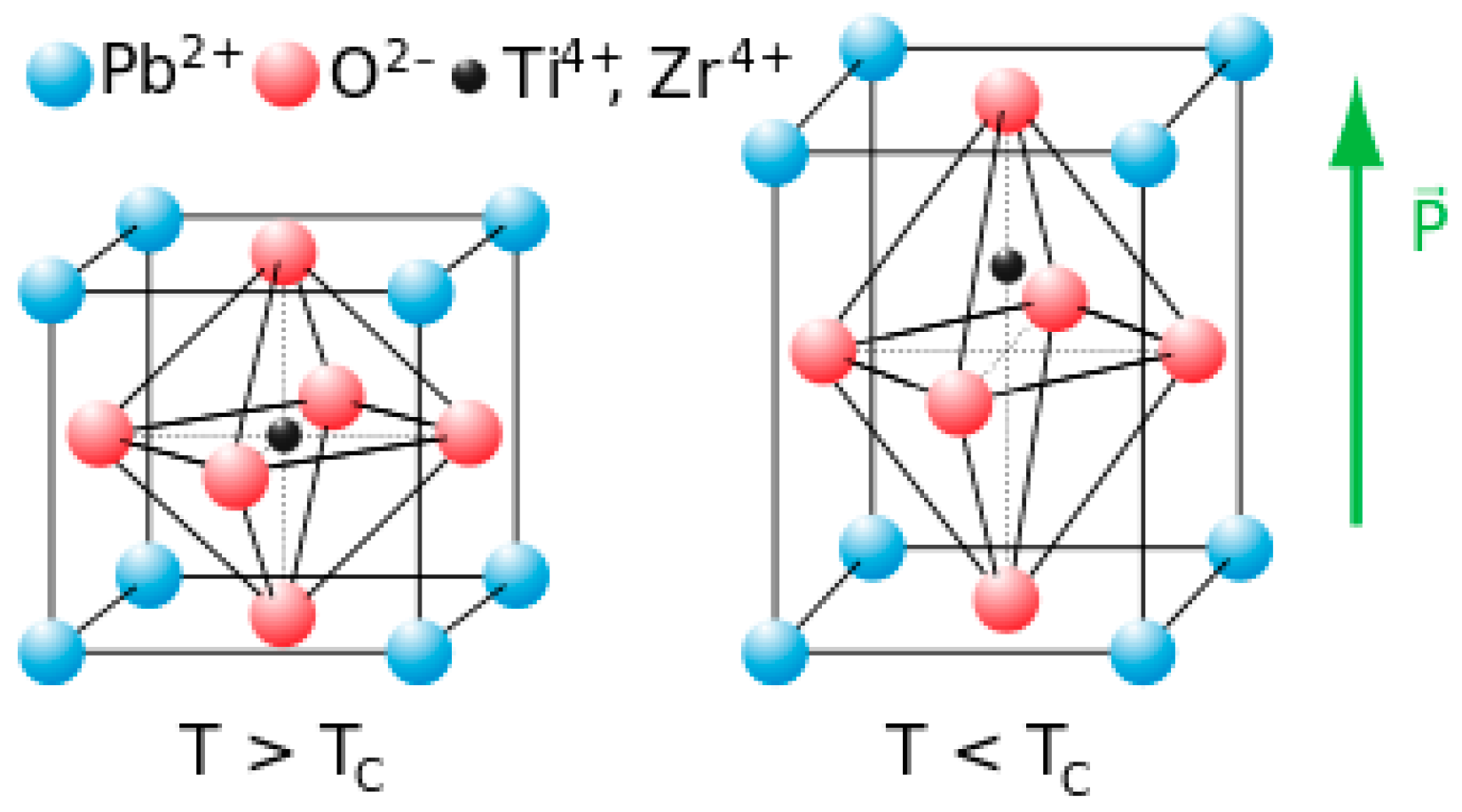
2.7.1. Piezoceramic Discs (PZT)
2.7.2. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Sensor

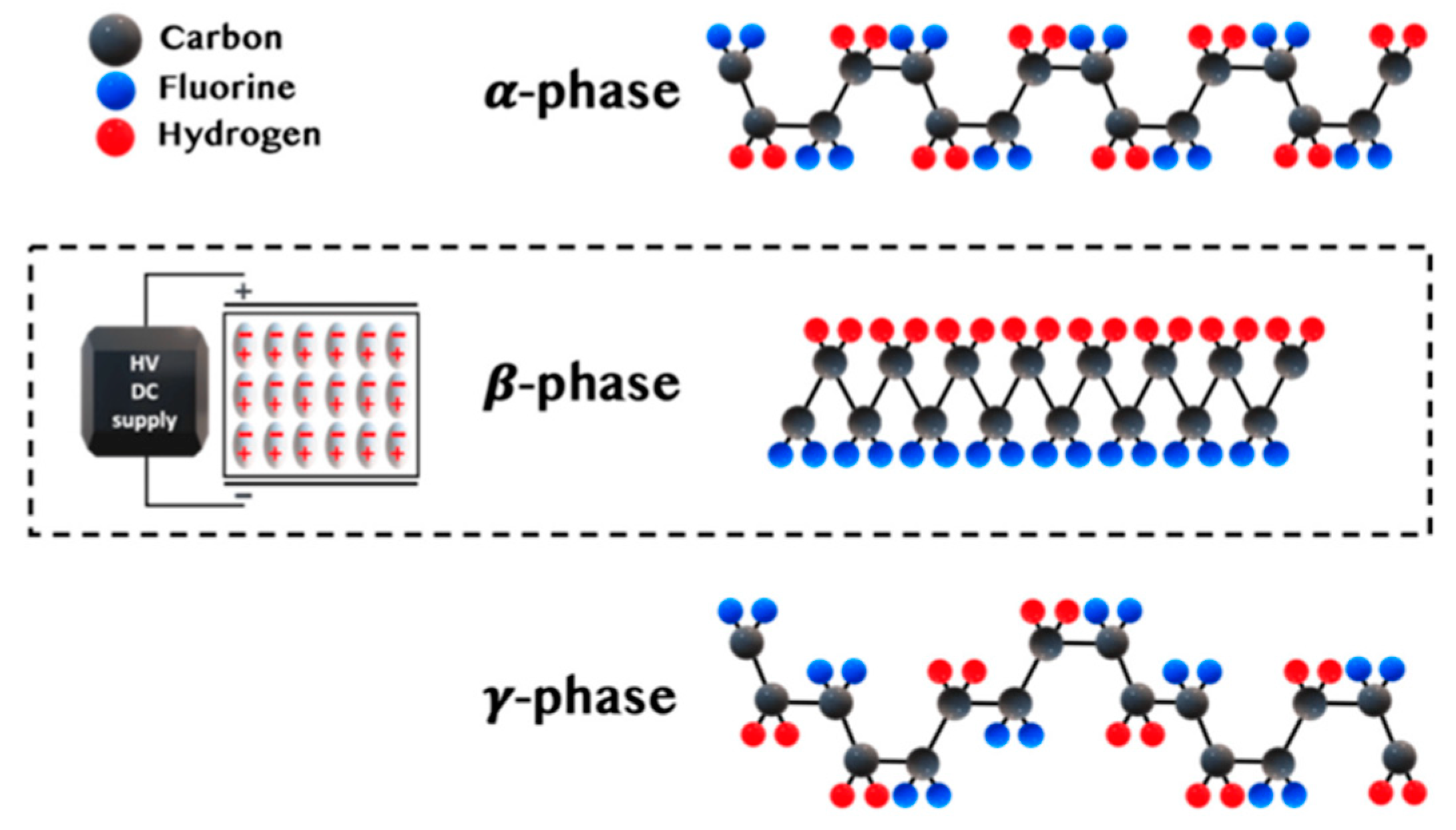
2.8. Fibre Optic Acoustic Emission Sensors (FOAES)
2.8.1. Fused Tapered Couplers
2.8.2. Intensity-Modulated Fibre Optic Sensors
2.8.3. Fibre Bragg Grating
2.9. Wave Velocity Inside the Material
2.9.1. Experimental Calculation of Wave Velocity
2.9.2. Theoretical Wave Velocity Inside the Material [70]
2.10. AE Source Location Identification Using Time of Arrival (TOA) [20]
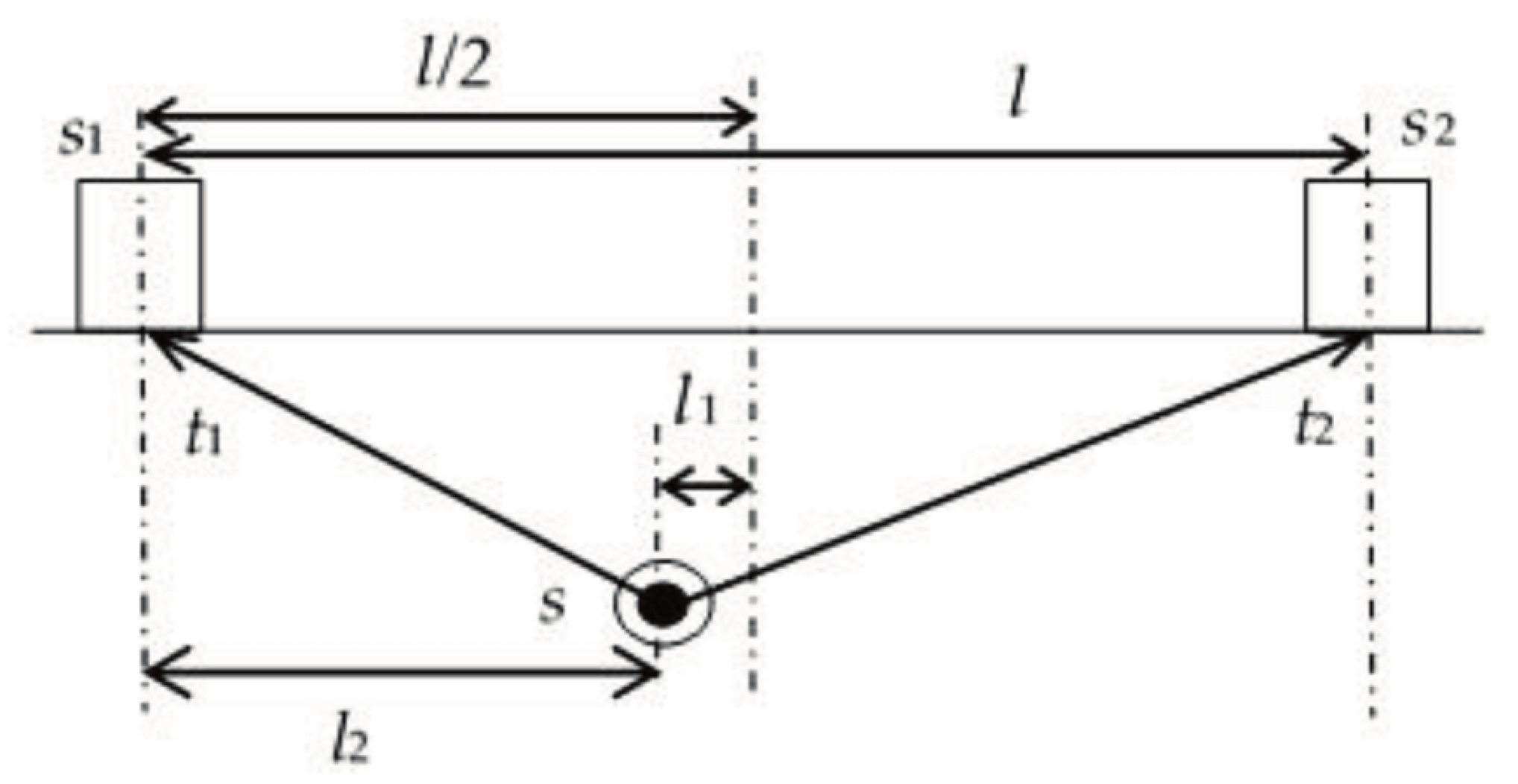
2.10.1. Linear Source Location Technique [20]
2.10.2. Two-Dimensional Source Location Technique [20,77]
2.11. Determination of the Time of Arrival (Onset Picking)
2.11.1. Amplitude Threshold Picker
2.11.2. Short-Time Average/Long-Time Average Ratio (STA/LTA)
2.11.3. Akaike Information Criteria (AIC)
2.12. Embedding Sensors
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, M.; Kumar, A.; Beard, S.J.; Qing, X. Built-in structural diagnostic with the SMART LayerTM and SMART suitcaseTM. Smart Mater. Bull. 2001, 2001, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. An introduction to structural health monitoring. In CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, Courses and Lectures; Springer International Publishing: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S.; El Guerjouma, R. Structural health monitoring by acoustic emission of smart composite laminates embedded with piezoelectric sensor. In Design and Modeling of Mechanical Systems; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, J. Designing with Active Materials: An Impedance Based Approach; Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute: Troy, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, C.A. U.S. Army Research Office Workshop on Smart Materials, Structures and Mathematical Issues Held in Blacksburg, Virginia on 15-16 September 1988; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Technomic Publishing Co.: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1989; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rytter, A. Vibrational Based Inspection of Civil Engineering Structures. Department of Building Technology and Structural Engineering, Aalborg University. 1993. Available online: https://vbn.aau.dk/en/publications/vibrational-based-inspection-of-civil-engineering-structures (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Cawley, P. Structural health monitoring: Closing the gap between research and industrial deployment. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleischer, C. How Piezoelectricity Works|EAGLE|Blog. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/eagle/blog/piezoelectricity/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Maestre, S. What is Piezoelectric Effect? CircuitBread. 2022. Available online: https://www.circuitbread.com/ee-faq/what-is-piezoelectric-effect (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Matsouka, D.; Vassiliadis, S.; Bayramol, D.V. Piezoelectric textile fibres for wearable energy harvesting systems. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 65508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennett, C.A.; Choens, R.C.; Taylor, C.A.; Heckman, N.M.; Ingraham, M.D.; Robinson, D.; Boyce, B.L.; Short, M.P.; Hattar, K. Listening to Radiation Damage In Situ: Passive and Active Acoustic Techniques. JOM 2020, 72, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qing, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H. Piezoelectric Transducer-Based Structural Health Monitoring for Aircraft Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.P.; Beard, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Ooi, T.K.; Chang, F.-K. Built-in Sensor Network for Structural Health Monitoring of Composite Structure. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2007, 18, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güemes, A.; Fernandez-Lopez, A.; Pozo, A.R.; Sierra-Pérez, J. Structural Health Monitoring for Advanced Composite Structures: A Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, R.K.; McIntire, P. Nondestructive Testing Handbook: Acoustic Emission Testing, 5th ed.; ASNT: Columbus, OH, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Unnþórsson, R. Hit Detection and Determination in AE Bursts. In Acoustic Emission—Research and Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggelis, D.G.; Sause, M.G.R.; Packo, P.; Pullin, R.; Grigg, S.; Kek, T.; Lai, Y.K. Acoustic Emission. Springer Aerospace Technology; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 175–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, M. Acoustic emission sensors for assessing and monitoring civil infrastructures. In Sensor Technologies for Civil Infrastructures; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precision Acoustics Student Pack of PVDF—Precision Acoustics. Available online: https://www.acoustics.co.uk/product/students-datasheet/ (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Khan, M.T.I. Structural Health Monitoring by Acoustic Emission Technique. In Structural Health Monitoring from Sensing to Processing; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellier, C.J. Acoustic emission testing. In Handbook of Nondestructive Evaluation; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 543–582. Available online: https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9781260441437/toc-chapter/chapter10/section/section2 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Giurgiutiu, V. Impact and Acoustic Emission Monitoring for Aerospace Composites SHM. In Structural Health Monitoring of Aerospace Composites; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 317–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumsey, M.A.; Paquette, J.A. Structural Health Monitoring of Wind Turbine Blades. In Proceedings of the Smart Sensor Phenomena, Technology, Networks, and Systems 2008, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson, C. Acoustic Emission Monitoring of the DC-XA Composite Liquid Hydrogen Tank During Structural Testing. Alabama: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); 1996. 12p. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19970001260/downloads/19970001260.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Srivastava, L.; Krishnanand, L.; Kishore Nath, N.; Hirwani, C.K.; Babu, M.R.M. Online structural integrity monitoring of high-performance composite rocket motor casing. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunhofer Institute for Ceramic Technologies and Systems IKTS Acoustic Emission Testing on Composite Structures for Damage Detection—Fraunhofer IKTS. Available online: https://www.ikts.fraunhofer.de/en/departments/electronics_microsystems_biomedicine/condition_monitoring_non-destructive_testing/acoustic_emission_testing_on_composite_structures_for_damage_detection.html (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Godin, N.; Huguet, S.; Gaertner, R. Integration of the Kohonen’s Self-Organising Map and k-Means Algorithm for the Segmentation of the AE Data Collected during Tensile Tests on Cross-Ply Composites. NDT E Int. 2005, 38, 299–309. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00436801 (accessed on 23 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Moevus, M.; Godin, N.; R’Mili, M.; Rouby, D.; Reynaud, P.; Fantozzi, G.; Farizy, G. Analysis of damage mechanisms and associated acoustic emission in two SiCf/ [Si-B-C] composites exhibiting different tensile behaviours. Part II: Unsupervised acoustic emission data clustering. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S. Use of piezoelectric as acoustic emission sensor for in situ monitoring of composite structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 80, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, R.; Arumugam, V.; Santulli, C.; Kumar, S.; Stanley, A. Investigation of the strength of the failure modes in GFRP laminates using acoustic emission monitoring. Int. J. Poly Technol. 2011, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshtizadeh, N.; Mostafapour, A.; Davoodi, S. Three point bending test of glass/epoxy composite health monitoring by acoustic emission. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, M.; Heidary, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Pashmforoush, F. Characterization of composite materials damage under quasi-static three-point bending test using wavelet and fuzzy C-means clustering. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht, M.; Yousefi, J.; Hosseini-Toudeshky, H.; Minak, G. Delamination evaluation of composite laminates with different interface fiber orientations using acoustic emission features and micro visualization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 113, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ding, Z. jun Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals and deformation measurement for delaminated glass fiber epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 195, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellier, C.J. The Signal-Shaping Chain, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9781260441437/toc-chapter/chapter10/section/section23 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Pollock, A.A. Acoustic Emission Inspection, Physical Acoustics Corporation; Technical Report TR-103-96-12/89; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Awerbuch, J.; Ozevin, D.; Khanolkar, A.; Tan, T.-M. Damage Identification Using Acoustic Emission Data Obtained from Large Composite Structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2015, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
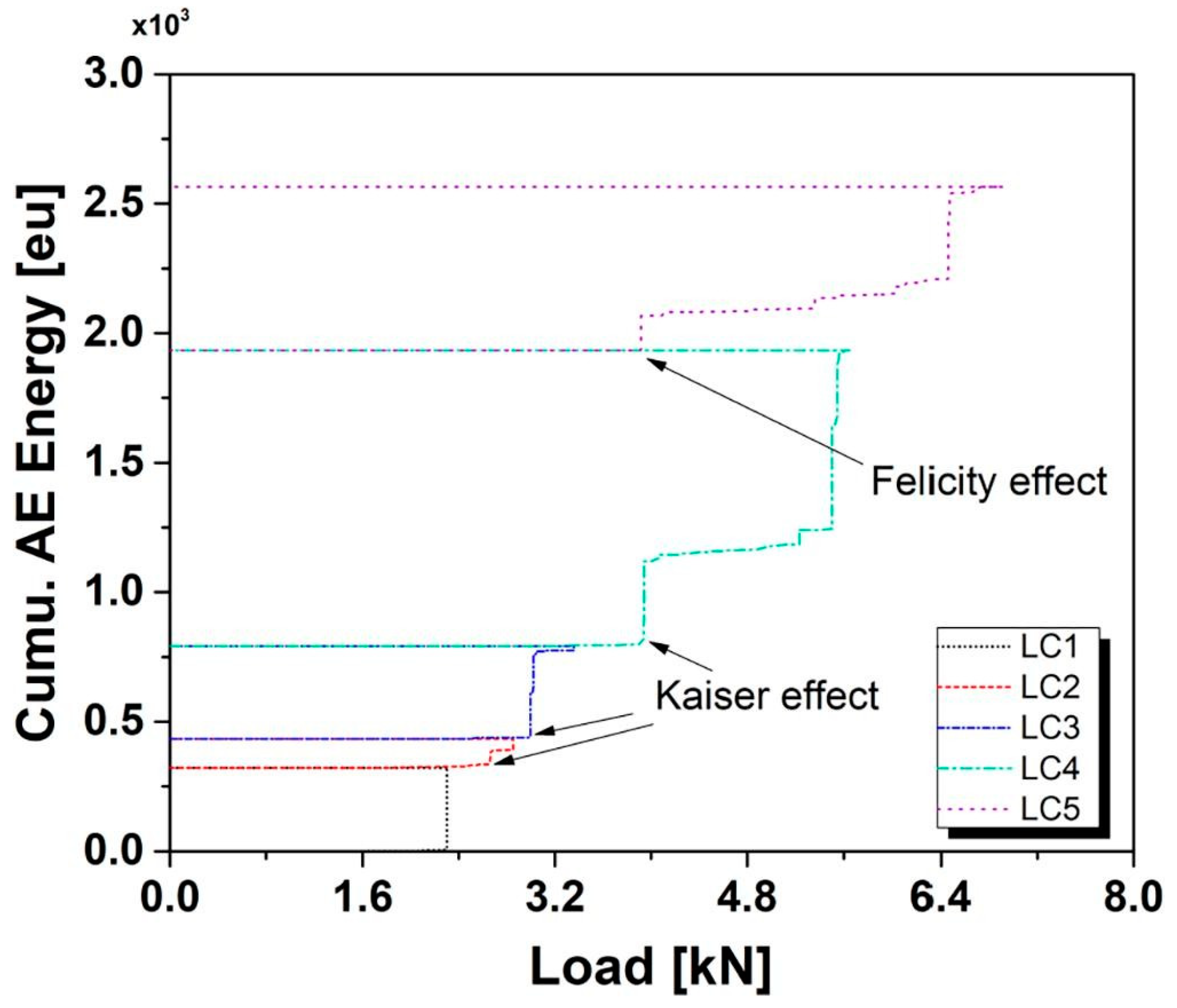
- Kaiser, J. Untersuchungen Uber Das Auftreten Gereausen bein Zugersuch. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hutchshule, Munich, Germany, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedifar, M.; Mansvelder, J.; Mohammadi, R.; Zarouchas, D. Using passive and active acoustic methods for impact damage assessment of composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2019, 226, 111252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellier, C.J. Overview of Acoustic Emission, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9781260441437/toc-chapter/chapter10/section/section3 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Sause, M.; Hamstad, M. Acoustic emission analysis. In Comprehensive Composite Materials II; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 291–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard Guide for Determining the Reproducibility of Acoustic Emission Sensor Response. 2015. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e0976-10.html (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Sause, M. Investigation of Pencil-Lead Breaks as Acoustic Emission Sources. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2011, 29, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Ohtsu, M. A generalized theory of acoustic emission and Green’s functions in a half space. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1984, 3, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsu, M.; Ono, K. The Generalized Theory and Source Representation of Acoustic Emission. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1986, 5, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Physics A de. Lamb Waves. 2007. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lamb_waves#/media/File:Lamb_Waves_2_Modes.jpg (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Cheng, L.; Xin, H.; Groves, R.M.; Veljkovic, M. Acoustic emission source location using Lamb wave propagation simulation and artificial neural network for I-shaped steel girder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, W.H.; Hamstad, M.A.; Gary, J.; OGallagher, A.; Hamstad, M.A.; Gary, J.; OGallagher, A. Reflections of AE Waves in Finite Plates: Finite Element Modeling and Experimental Measurements. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1999, 17, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Samaitis, V.; Jasiūnienė, E.; Packo, P.; Smagulova, D. Ultrasonic Methods. Springer Aerospace Technology; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 87–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Laliberte, J.; Martinez, M. Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) of Composite Aerospace Structures Using Lamb Waves. In Proceedings of the ICCM19—The 19th International Conference on Composite Materials, Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 July–2 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Higo, Y.; Inaba, H. The General Problems of AE Sensors. In ASTM Special Technical Publication; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1991; pp. 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E650/E650M-12; ASTM Standard Guide for Mounting Piezoelectric Acoustic Emission Sensors. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Theobald, P.; Zeqiri, B.; Avison, J. Couplants and their influence on ae sensor sensitivity. J. Acoust. Emiss. 2008, 26, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- APC International PZT Properties & PZT Manufacturing. Available online: https://www.americanpiezo.com/piezo-theory/pzt.html (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- PI PZT Ceramics Manufacturing Process: Piezo Tutorial: Ceramic Materials. Available online: https://www.pi-usa.us/en/products/piezo-motors-stages-actuators/piezo-motion-control-tutorial/tutorial-4-16/ (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- LibreTexts. 6.3: Crystal Structure Chemistry. Available online: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Douglas_College/DC%3A_Chem_2330_%28O%27Connor%29/6%3A_Solids/6.3%3A_Crystal_Structure (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Sappati, K.K.; Bhadra, S. Piezoelectric Polymer and Paper Substrates: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirohi, J.; Chopra, I. Piezoceramic Actuators and Sensors. Encycl. Aerosp. Eng. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuldina, G.; Turdakyn, N.; Abay, I.; Medeubayev, A.; Nurpeissova, A.; Adair, D. A Review of Piezoelectric PVDF Film by Electrospinning and Its Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Electroactive and Magnetoactive Materials—Structural Health Monitoring with Piezoelectric Wafer Active Sensors, 2nd ed.; O’Reilly UK Ltd: London, UK, 2014; pp. 21–49. Available online: https://learning.oreilly.com/library/view/structural-health-monitoring/9780124186910/xhtml/chp002.xhtml (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- De Rosa, I.M.; Sarasini, F. Use of PVDF as acoustic emission sensor for in situ monitoring of mechanical behaviour of glass/epoxy laminates. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RS 1-1002908-0|TE Connectivity Vibration Sensor 0°C → +70°C, Dimensions 41 (mm) × 16 (mm) × 40 (μm)|RS Components. Available online: https://uk.rs-online.com/web/p/vibration-sensors/8937301 (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Ueberschlag, P. PVDF piezoelectric polymer. Sens. Rev. 2001, 21, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willberry, J.O.; Papaelias, M. Structural health monitoring using fibre optic acoustic emission sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Sui, Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, D.; Sai, Y. Development of high temperature acoustic emission sensing system using fiber Bragg grating. Photonic Sens. 2018, 8, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Fiber-Optic Sensors. In Structural Health Monitoring of Aerospace Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 249–296. [Google Scholar]
- Wevers, M.; Rippert, L.; Papy, J.; van Huffe, S. Damage in CFRP composite materials monitored with intensity modulated fiber optic sensors. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Non-Destructive Testing, Thessaloniki, Greece, 26–28 May 2003; Hemelrijck, D., Anastaopoulos, A., Melanitis, N.E., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2003; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Takuma, M.; Hisada, S.; Saitoh, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kadono, A.; Murata, A.; Iwata, S.; Sasaki, T. Acoustic emission measurement by fiber bragg grating glued to cylindrical sensor holder. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 274071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonigen, E. Detection of Crack Initiation in Fire Protection Coating Materials Using Acoustic Emissions; Cranfield University: Cranfield, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Perrin, M.; Pastor, M.L.; Casari, P.; Gong, X. On the determination of acoustic emission wave propagation velocity in composite sandwich structures. Compos. Struct. 2021, 259, 113231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Kundu, T. Acoustic source localization in a highly anisotropic plate with unknown orientation of its axes of symmetry and material properties with numerical verification. Ultrasonics 2020, 100, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, N.; Kundu, T. A new wave front shape-based approach for acoustic source localization in an anisotropic plate without knowing its material properties. Ultrasonics 2018, 87, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kundu, T.; Nakatani, H.; Takeda, N. Acoustic source localization in anisotropic plates. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Gawroński, M.; Packo, P.; Uhl, T.; Kundu, T.; Sen, N. Square-shaped sensor clusters for acoustic source localization in anisotropic plates by wave front shape-based approach. MSSP 2021, 153, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cui, Z.; Kundu, T. Acoustic source localization in anisotropic plates with “Z” shaped sensor clusters. Ultrasonics 2018, 84, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.G.; Lee, W.G.; Kim, J.; Kwon, H. A Point Crack Source Location Method without Velocity Information in Anisotropic Plates. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Khan, T.I.; Hasemura, Y.; Islam, M. Performance investigation of Two AE source location techniques on a planar multilayer structure. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2020, 25, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESGsolutions Event Detection & Triggering|ESG Solutions. Available online: https://www.esgsolutions.com/technical-resources/microseismic-knowledgebase/event-detection-and-triggering (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Zhou, Z.; Cheng, R.; Rui, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H. An Improved Automatic Picking Method for Arrival Time of Acoustic Emission Signals. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 75568–75576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ren, H.W.; Dong, B.Q.; Xing, F. Acoustic Emission Behavior of Early Age Concrete Monitored by Embedded Sensors. Materials 2014, 7, 6908–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kong, Q.; Ho, S.C.M.; Lim, I.; Mo, Y.L.; Song, G. Feasibility study of using smart aggregates as embedded acoustic emission sensors for health monitoring of concrete structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogordato, M.; Taylor, M.; Taylor, A.; Browne, M. Real time monitoring of progressive damage during loading of a simplified total hip stem construct using embedded acoustic emission sensors. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuloup, C.; Harizi, W.; Aboura, Z.; Meyer, Y. Integration of piezoelectric transducers (PZT and PVDF) within polymer-matrix composites for structural health monitoring applications: New success and challenges. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2020, 11, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S.; El Guerjouma, R. Mechanical behavior and health monitoring by Acoustic Emission of unidirectional and cross-ply laminates integrated by piezoelectric implant. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 86, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; El Guerjouma, R. Mechanical behaviour and health monitoring by acoustic emission of sandwich composite integrated by piezoelectric implant. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S.; Guerjouma, R. El Structural integrity of laminated composite with embedded piezoelectric sensors. In Design and Modeling of Mechanical Systems—II; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 789, pp. 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S. Fatigue behaviour and structural health monitoring by acoustic emission of E-glass/epoxy laminates with piezoelectric implant. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 108, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S. Effect of Piezoelectric Implant on the Structural Integrity of Composite Laminates Subjected to Tensile Loads. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seychal, G.; Ramasso, E.; Le Moal, P.; Bourbon, G.; Gabrion, X.; Placet, V. Towards in-situ acoustic emission-based health monitoring in bio-based composites structures: Does embedment of sensors affect the mechanical behaviour of flax/epoxy laminates? Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 236, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneva, C.; De Rosa, I.M.; Sarasini, F. Monitoring of Impacted Aramid-Reinforced Composites by Embedded PVDF Acoustic Emission Sensors. Strain 2008, 44, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Minajagi, S.; Dange, E.; Bhover, S.U.; Dharanendra, Y.T. Impact and acoustic emission performance of polyvinylidene fluoride sensor embedded in glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite structure. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzo, F.; Huang, Y.; Nemat-Nasser, S. Onset of Resin Micro-Cracks in Unidirectional Glass Fiber Laminates with Integrated SHM Sensors: Experimental Results. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2009, 8, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
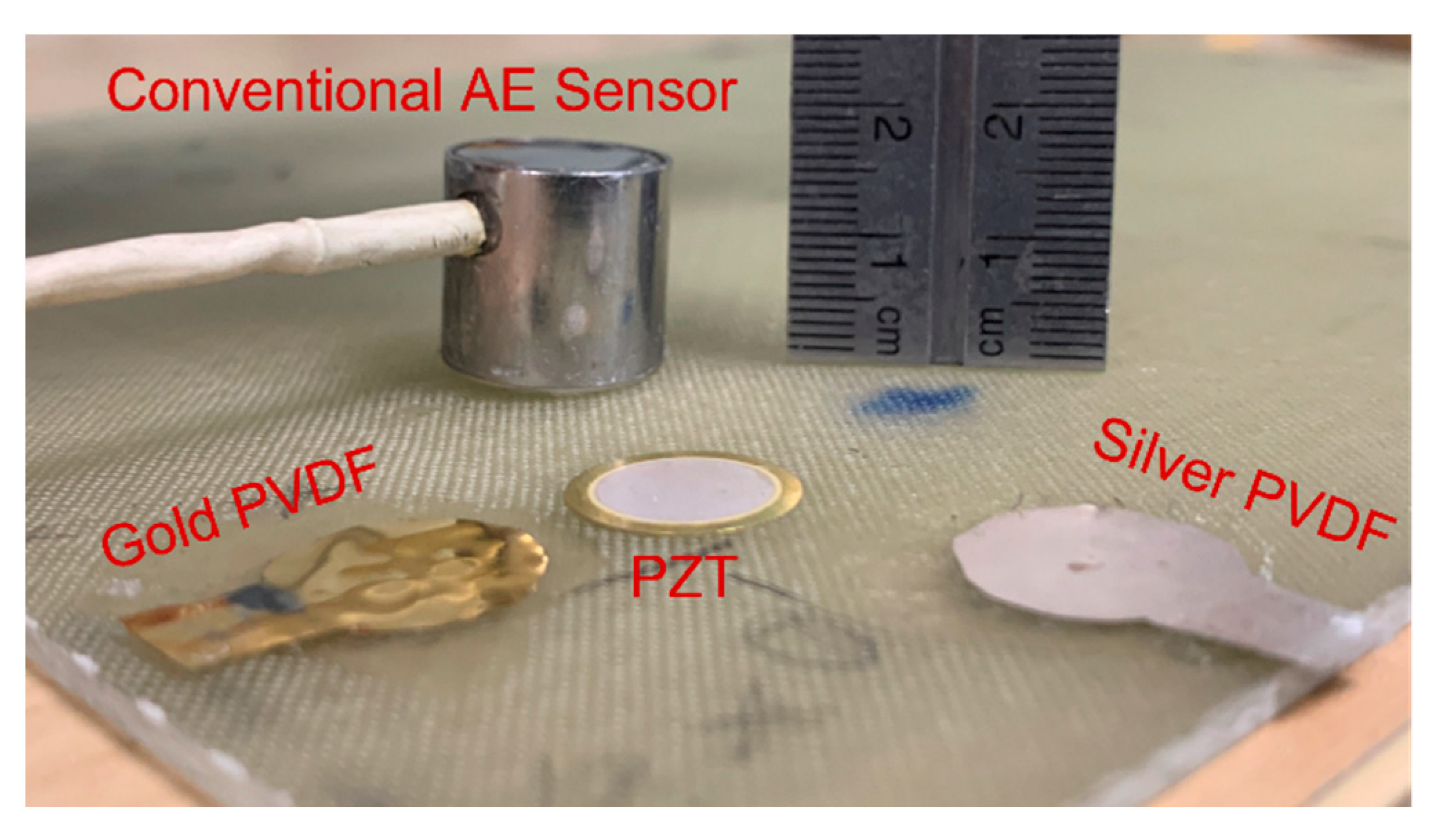






| Reference | Thickness (mm) | Frequency Response (kHz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix Cracking | Fibre-Matrix Cracking | Delamination | Fibre Fracture | ||
| [30] | 2.78 | 90–110 | - | 130–200 | 250–280 |
| [31] | 4 | 62.5–125 | 125–187.5 | - | 187.5–250 |
| [32] | 5 | 100–190 | 200–320 | - | 380–430 |
| [33] | 4.8 | 60–180 | 190–250 | - | 350–500 |
| [34] | 4.8 | 11–93 | 82–210 | - | 160–281 |
| Damage Mechanism | Form of Signal |
|---|---|
| Matrix cracking (A class) |  |
| Fibre-matrix debonding (B class) |  |
| Fibres breaking (C class) |  |
| Delamination (D class) |  |
| Property | Units | PVDF film | PZT(PbZrTiO3) | BaTiO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | kg/m3 | 1780 | 7500 | 5700 |
| Relative permittivity | 12 | 1200 | 1700 | |
| d31 | 10−12 C/N | 23 | 110 | 78 |
| g31 | 10−3 Vm/N | 216 | 10 | 5 |
| k31 | at 1 kHz | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.21 |
| Young’s modulus | GPa | ~3 | ~60 | ~110 |
| Acoustic impedance | 106 kg/m2-sec | 2.7 | 30 | 30 |
| Gold PVDF [19] | Silver PVDF [62] | |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness (t) | 28, 52 and 110 µm | 28, 52 and 110 µm (+12 µm for the protective film) |
| Maximum operating temperature (T) | 70 °C | 70 °C |
| Piezo strain constant ( | 22 pC/N | 23 pC/N |
| Piezo strain constant ( | 3 pC/N | N/A |
| Piezo strain constant ( | −30 pC/N | −33 pC/N |
| Number of AE Sensors Required | The Dimension of the Source Location |
|---|---|
| Two AE sensors | Single (one) degree of source location |
| Three AE sensor | Two-dimensional source location |
| Four or more AE sensors | Three-dimensional source location |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghadarah, N.; Ayre, D. A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites. Sensors 2023, 23, 6945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156945
Ghadarah N, Ayre D. A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156945
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhadarah, Noor, and David Ayre. 2023. "A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156945
APA StyleGhadarah, N., & Ayre, D. (2023). A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites. Sensors, 23(15), 6945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156945






