Traffic Noise Assessment Using Intelligent Acoustic Sensors (Traffic Ear) and Vehicle Telematics Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
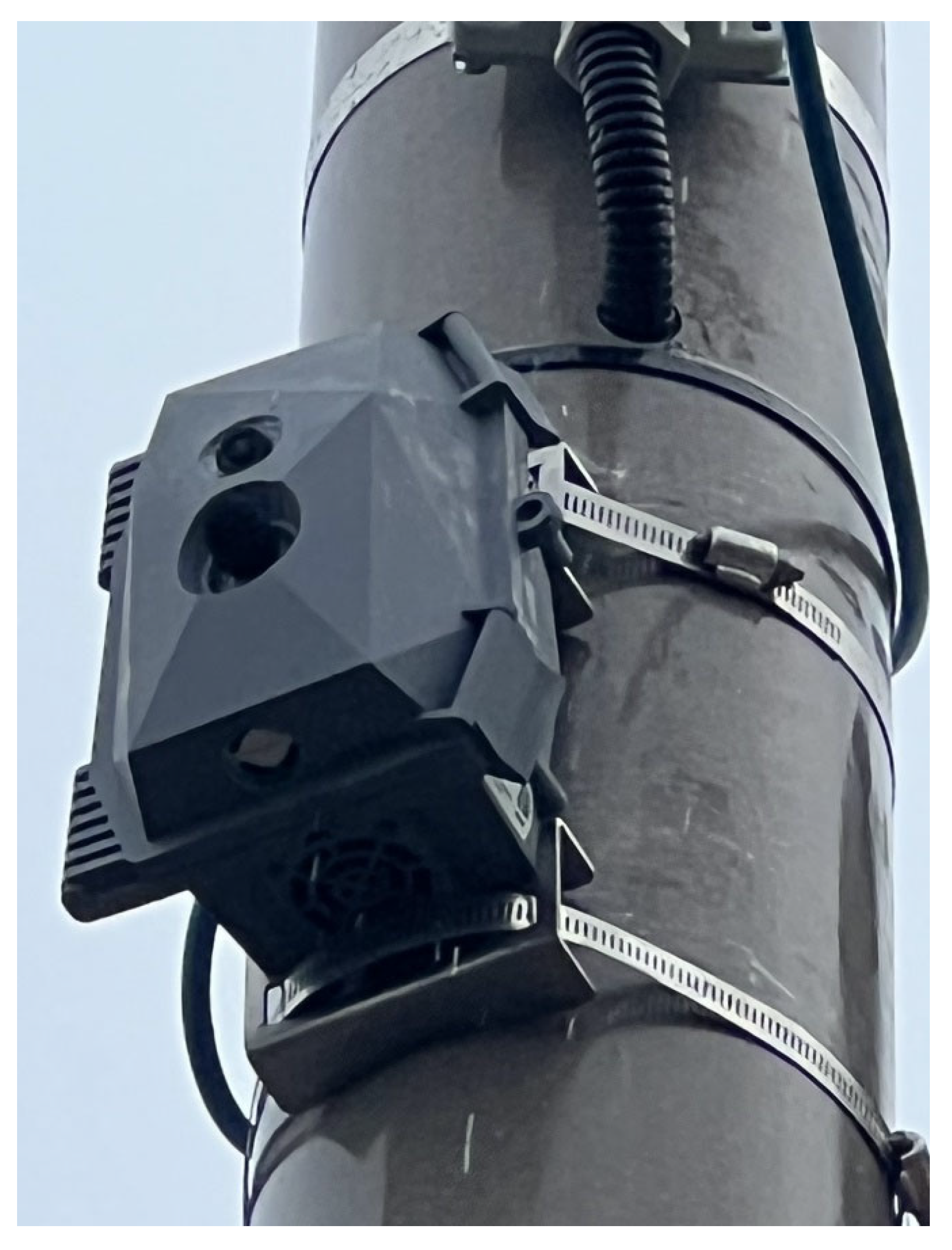
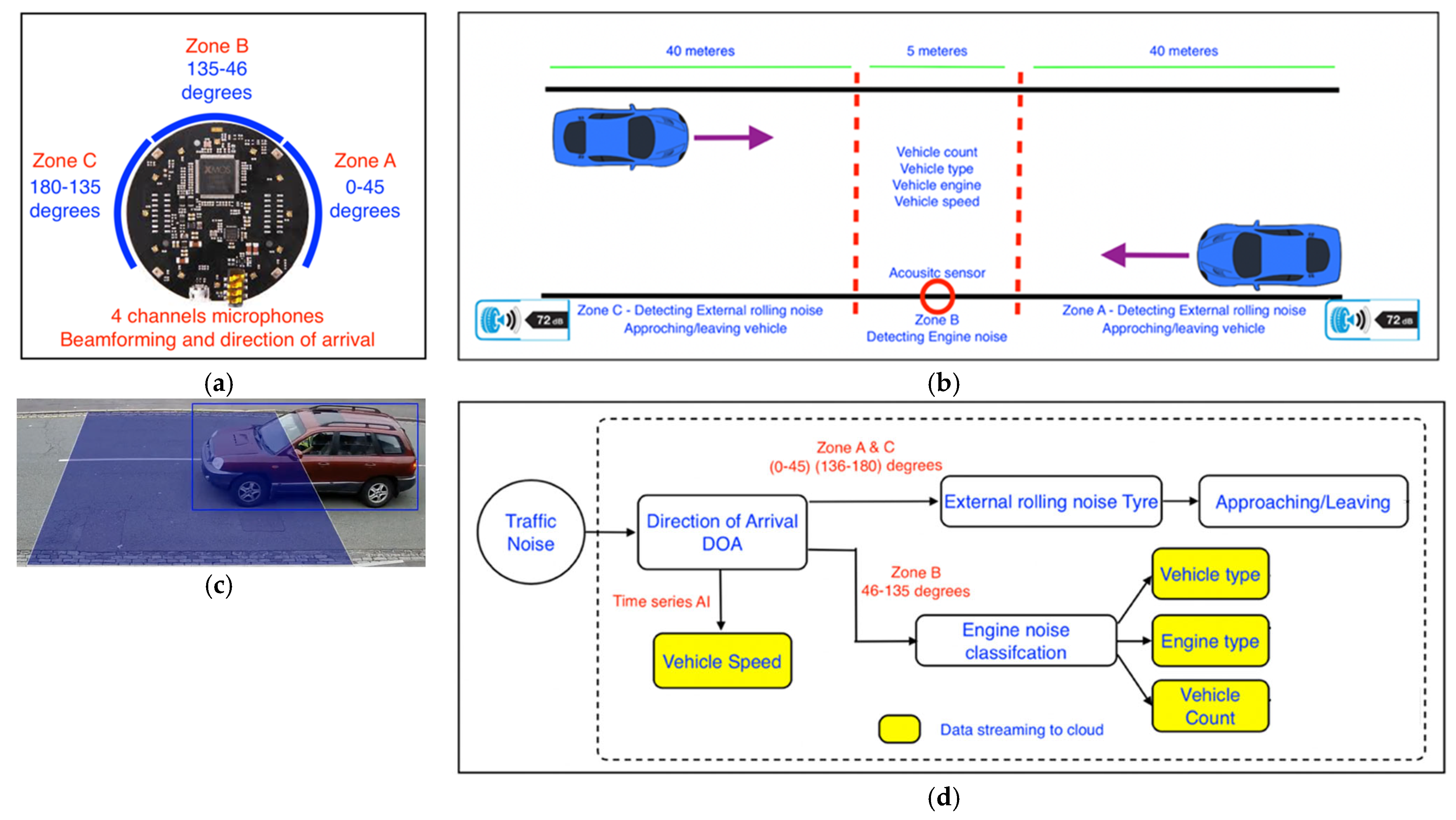
2.1. Acoustic Sensors and Traffic Ear
2.1.1. Literature Review
2.1.2. Traffic Ear
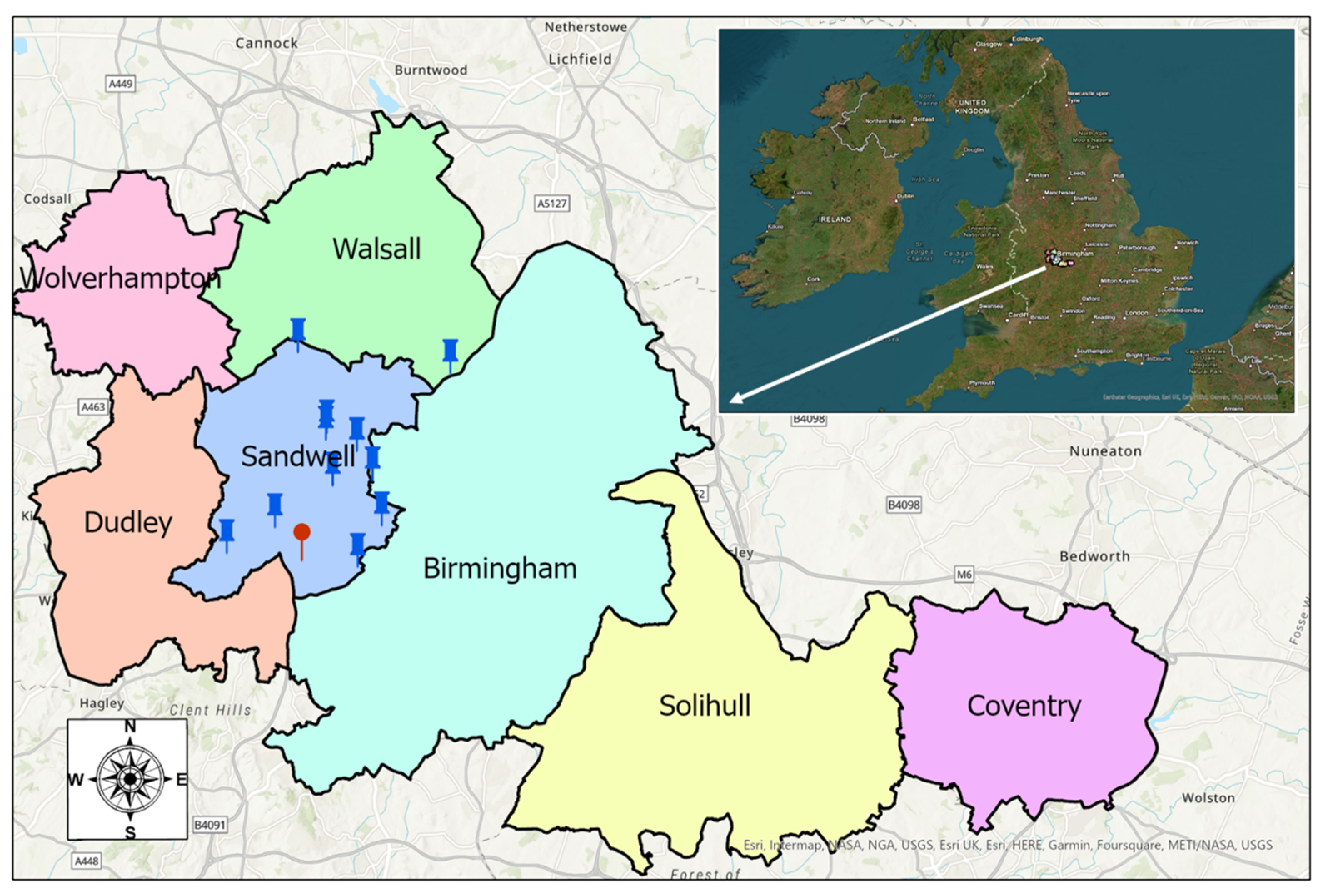
2.2. The Spatial Scope of the Study and the Locations of the Measurements
2.3. Vehicle Telematics Data and the Method of GeoSTMUM
2.4. Fleet Composition
2.5. Noise Map Development
2.6. Rush/Non-Rush Hour and Weekday/Weekend Effects Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
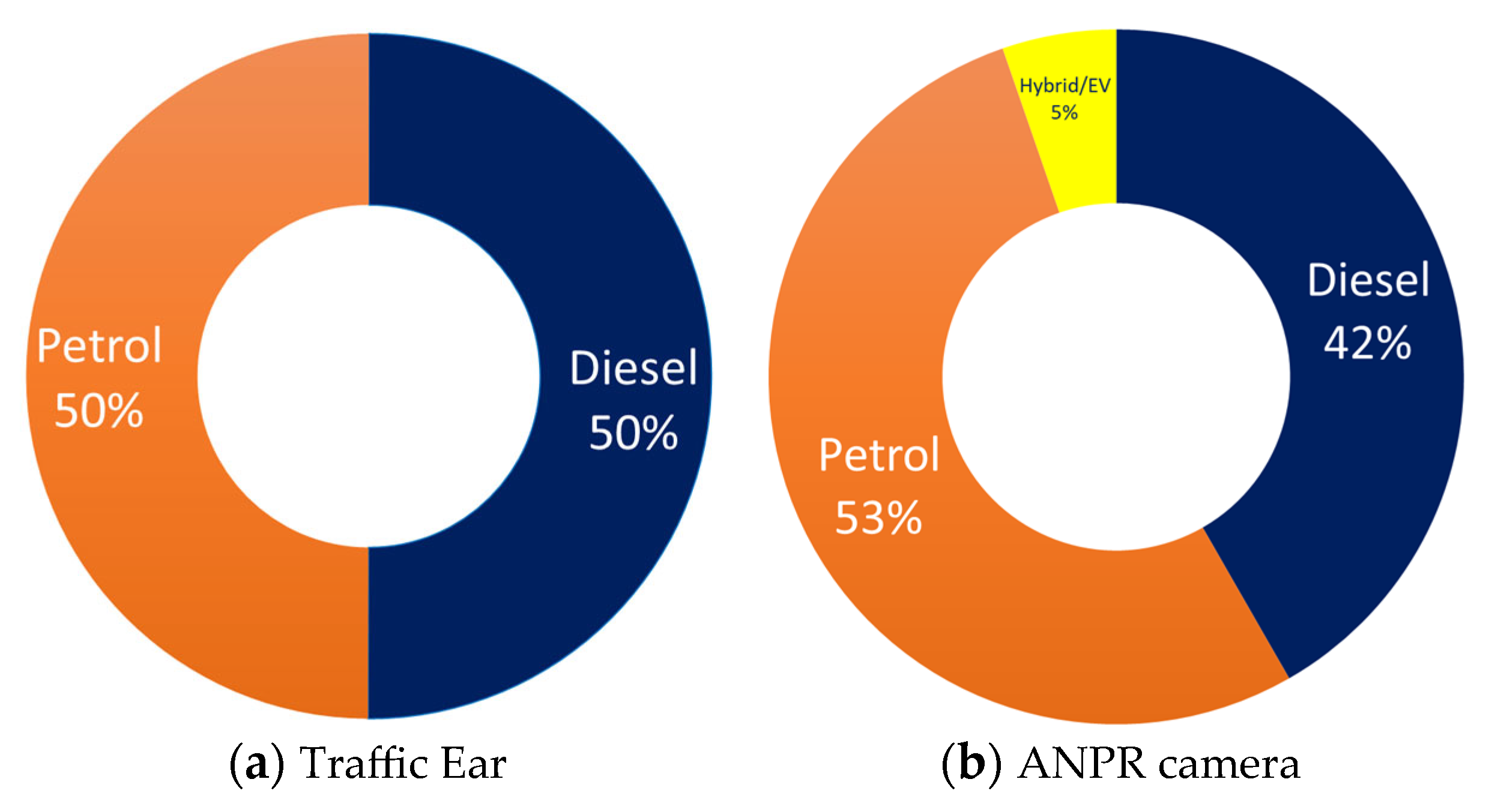
3.1. Fleet Composition
3.2. Traffic Noise Assessment on a Per-Vehicle Basis
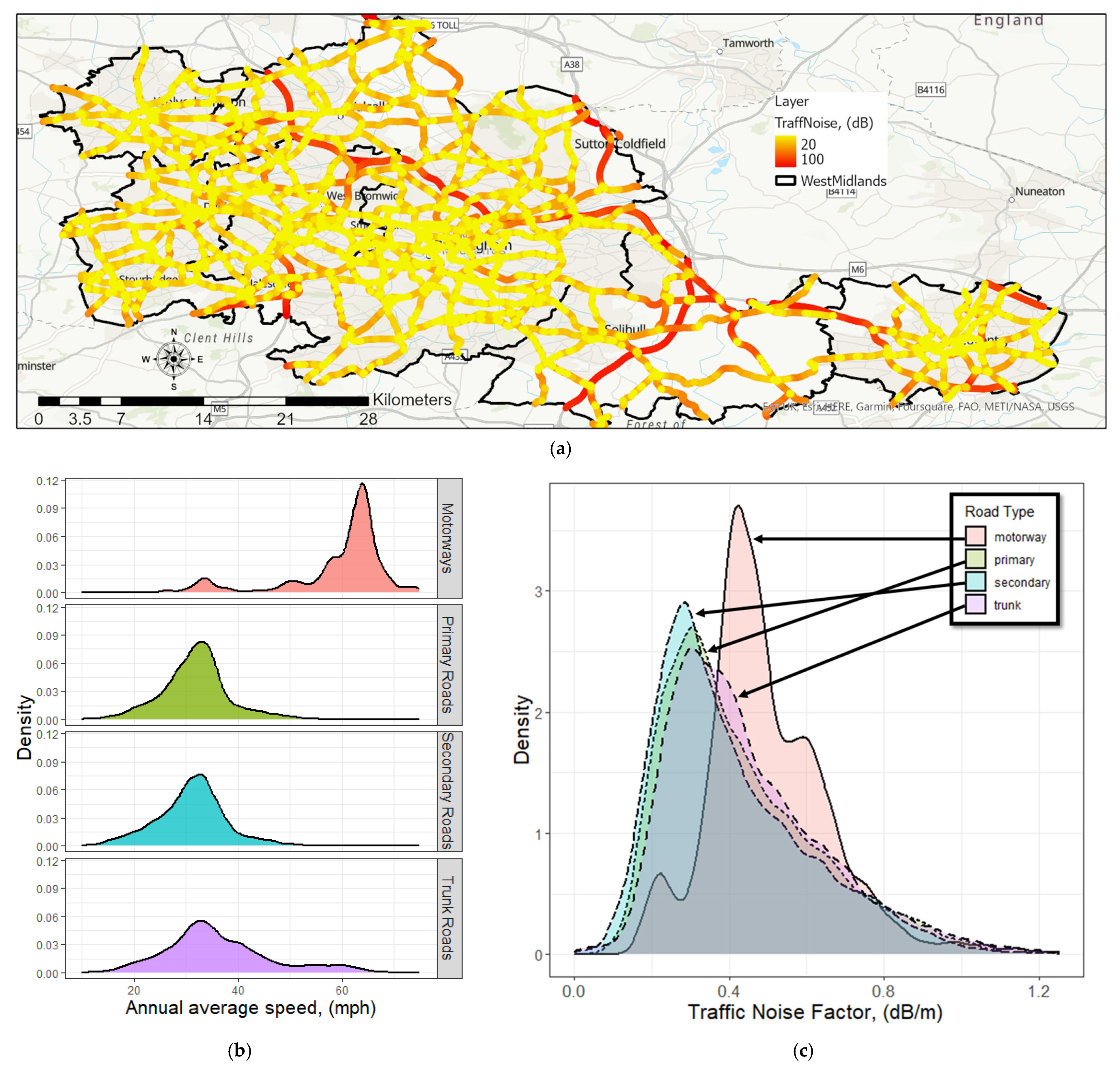
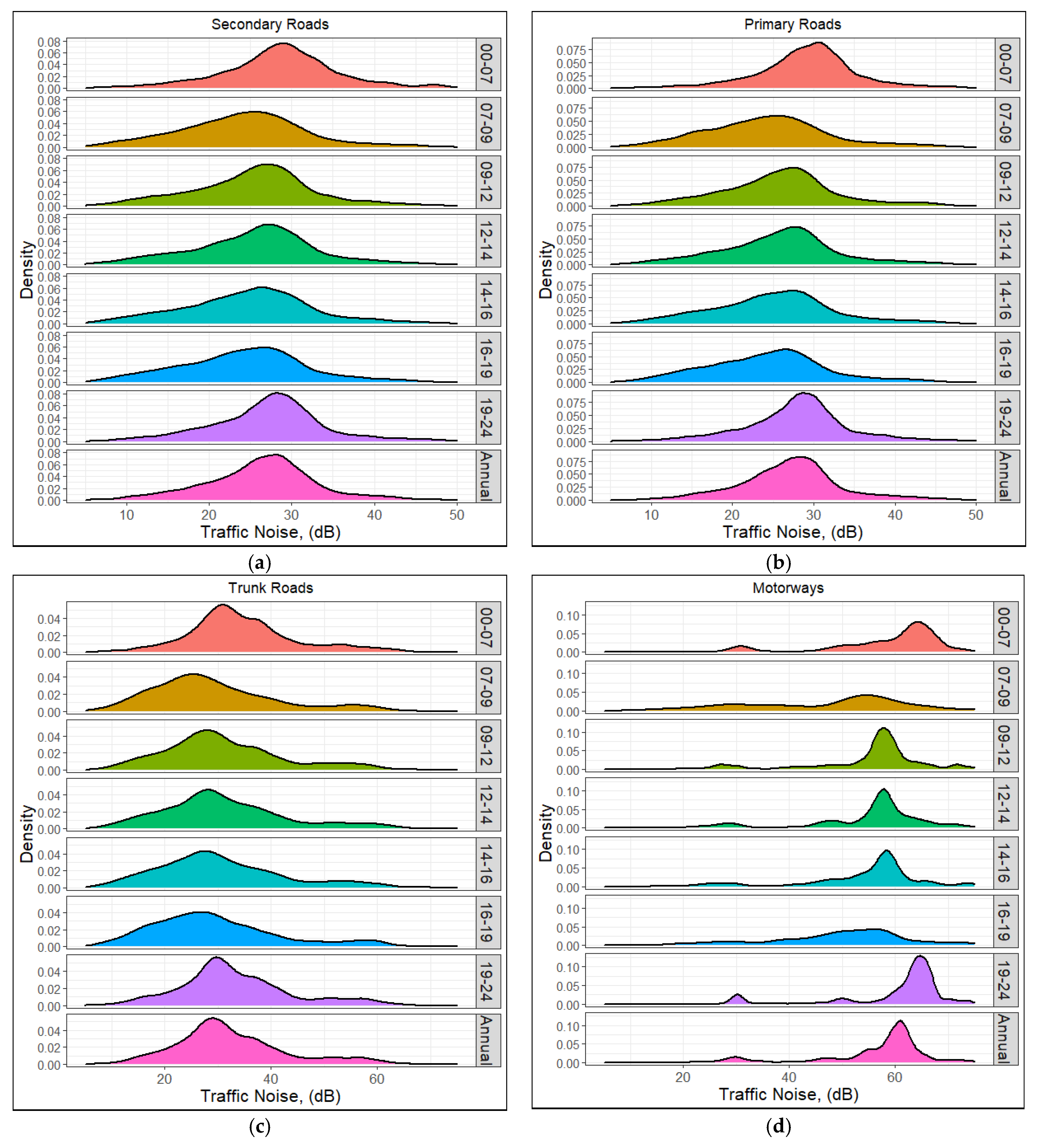
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of the Traffic Noise
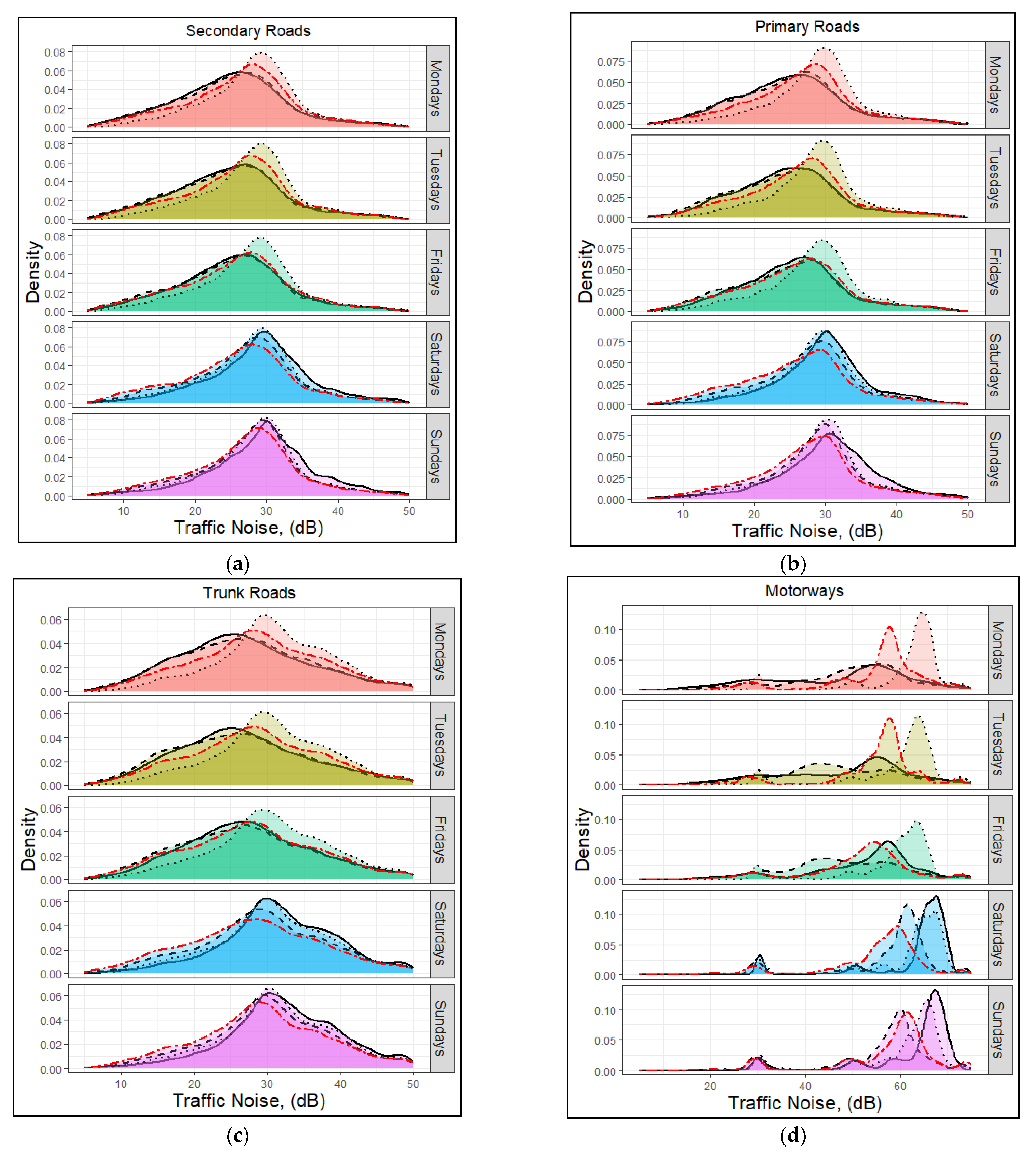
3.4. Rush/Non-Rush Hour and Weekday/Weekend Effects
4. Summary, Conclusions, and Future Research Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EUC. EU Transport in Figures: Statistical Pocketbook 2021; European Commission Directorate-General for Mobility Transport: Brussel, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue, J.P.; Comtois, C.; Slack, B. The Geography of Transport Systems; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Deng, Z.; Davis, S.J.; Giron, C.; Ciais, P. Monitoring Global carbon emissions in 2021. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrigón Morillas, J.M.; Rey Gozalo, G.; Montes González, D.; Sánchez-Fernández, M.; Bachiller León, A. A comprehensive experimental study of the influence of temperature on urban road traffic noise under real-world conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibili, F.; Owolabi, A.O.; Ackaah, W.; Massaquoi, A.B. Statistical Modelling for Urban Roads Traffic Noise Levels. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.-W.; Xue, W.-X.; Jiang, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.-X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Dong, G.-H.; Cai, M.; Chen, Y.-J. Exposure to road traffic noise and behavioral problems in Chinese schoolchildren: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M.; Poulsen, A.H.; Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Brandt, J.; Frohn, L.M.; Ketzel, M.; Christensen, J.H.; Im, U.; Khan, J.; Münzel, T.; et al. Air pollution, road traffic noise and lack of greenness and risk of type 2 diabetes: A multi-exposure prospective study covering Denmark. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmanian, M.; Sakhvidi, M.J.; Mehrparvar, A.H.; Sakhvidi, F.Z.; Dadvand, P. Association between occupational noise exposure and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health 2023, 252, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.; Smith, R.B.; Bou Karim, Y.; Shen, C.; Drummond, K.; Teng, C.; Toledano, M.B. Noise pollution and human cognition: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of recent evidence. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Cai, M. Dynamic traffic noise maps based on noise monitoring and traffic speed data. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 94, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive, E. Directive 2002/49/EC of the European parliament and the Council of 25 June 2002 relating to the assessment and management of environmental noise. Off. J. Eur. Communities L 2002, 189, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, E.; Faulkner, J.P.; Douglas, O. Current State-of-the-Art and New Directions in Strategic Environmental Noise Mapping. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFRA. Strategic Noise Mapping: Explaining Which Noise Sources Were Included in 2017 Noise Maps; Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Van Renterghem, T.; De Coensel, B.; Botteldooren, D. Dynamic noise mapping: A map-based interpolation between noise measurements with high temporal resolution. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 101, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Cai, M. Evaluation of an urban traffic Noise–Exposed population based on points of interest and noise maps: The case of Guangzhou. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benocci, R.; Confalonieri, C.; Roman, H.E.; Angelini, F.; Zambon, G. Accuracy of the dynamic acoustic map in a large city generated by fixed monitoring units. Sensors 2020, 20, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benocci, R.; Molteni, A.; Cambiaghi, M.; Angelini, F.; Roman, H.E.; Zambon, G. Reliability of Dynamap traffic noise prediction. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 156, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, G.; Roman, H.E.; Smiraglia, M.; Benocci, R. Monitoring and prediction of traffic noise in large urban areas. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, K.-T.; Lin, M.-D.; Chen, Y.-H. Noise mapping in urban environments: A Taiwan study. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.A.; Akpan, P.E.; Effiong, A.E.; Babatunde, I.O. The effect of station density in geostatistical prediction of air temperatures in Sweden: A comparison of two interpolation techniques. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 11, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zou, J.; Xie, J.; Ma, X. Road traffic noise mapping in Guangzhou using GIS and GPS. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 87, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, G.; Benocci, R.; Bisceglie, A.; Roman, H.E.; Bellucci, P. The LIFE DYNAMAP project: Towards a procedure for dynamic noise mapping in urban areas. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 124, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Evaluation of road traffic noise exposure based on high-resolution population distribution and grid-level noise data. Build. Environ. 2019, 147, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; He, C.; Cai, M. Urban road traffic noise spatiotemporal distribution mapping using multisource data. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Feng, T.; Wu, R. Flexible distributed heterogeneous computing in traffic noise mapping. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adulaimi, A.A.A.; Pradhan, B.; Chakraborty, S.; Alamri, A. Traffic Noise Modelling Using Land Use Regression Model Based on Machine Learning, Statistical Regression and GIS. Energies 2021, 14, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Fallah-Shorshani, M.; McConnell, R.; Fruin, S.; Franklin, M. Predicting Fine Spatial Scale Traffic Noise Using Mobile Measurements and Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12860–12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Shorshani, M.; Yin, X.; McConnell, R.; Fruin, S.; Franklin, M. Estimating traffic noise over a large urban area: An evaluation of methods. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Dong, C.; Li, W.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J. Urban road traffic flow prediction: A graph convolutional network embedded with wavelet decomposition and attention mechanism. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 608, 128274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, F.; González, C.M.; Trejos, E.M.; López, L.D.; Sandoval, F.J.; Cuellar, O.A.; Mangones, S.C.; Rojas, N.Y.; Aristizábal, B.H. Comparison of Top-Down and Bottom-Up Road Transport Emissions through High-Resolution Air Quality Modeling in a City of Complex Orography. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpasand, O.; Talaie, M.R.; Ahmadikia, H.; Khozani, A.T.; Shalamzari, M.D. A high-resolution spatial and temporal on-road vehicle emission inventory in an Iranian metropolitan area, Isfahan, based on detailed hourly traffic data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Uchino, M.; Li, C.; Tagashira, S.; Fukuda, A. Design of acoustic vehicle detector with steady-noise suppression. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, M.; Ishida, S.; Kubo, K.; Tagashira, S.; Fukuda, A. Initial design of acoustic vehicle detector with wind noise suppressor. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Kyoto, Japan, 11–15 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Czyżewski, A.; Kotus, J.; Szwoch, G. Estimating traffic intensity employing passive acoustic radar and enhanced microwave doppler radar sensor. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotus, J.; Szwoch, G. Estimation of average speed of road vehicles by sound intensity analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwoch, G.; Kotus, J. Acoustic Detector of Road Vehicles Based on Sound Intensity. Sensors 2021, 21, 7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, R.C.; Forster, C.H.Q. Audio-based machine learning model for traffic congestion detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 7200–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygert, S.; Czyżewski, A. Vehicle detection with self-training for adaptative video processing embedded platform. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, N.; Chen, X.; Beauseroy, P.; Zhu, M. Traffic flow estimation using acoustic signal. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Sarradj, E.; Fernández, M.D.; Geyer, T.; Ballesteros, M.J. Noise source identification with Beamforming in the pass-by of a car. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 93, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Sarradj, E.; Fernandez Berlanga, M.; Geyer, T.; Ballesteros, M. Methodology for Pass-By Measurements with Beamforming on Cars. In Proceedings of the 5th Berlin Beamforming Conference, Berlin, Germany, 19–20 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sarradj, E.; Fritzsche, C.; Geyer, T. Silent Owl Flight: Bird Flyover Noise Measurements. AIAA J. 2011, 49, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjono, B.; Tjahyadi, H.; Rhizma, M.G.; Widjaja, A.E.; Kondorura, R.; Halim, A.M. Vehicle counting quantitative comparison using background subtraction, viola jones and deep learning methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, S.H.; Milan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Dick, A.; Reid, I. Joint probabilistic data association revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; He, S.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. SINet: A scale-insensitive convolutional neural network for fast vehicle detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Göksu, H. Engine Speed–Independent Acoustic Signature for Vehicles. Meas. Control 2018, 51, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Department for Transport. Road Traffic Statistics; Estimated Motor Vehicle Traffic; Department for Transport: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ONS. Population and Household Estimates, England and Wales: Census 2021; Office for National Statistics, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffarpasand, O.; Burke, M.; Osei, L.K.; Ursell, H.; Chapman, S.; Pope, F.D. Vehicle Telematics for Safer, Cleaner and More Sustainable Urban Transport: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F. Telematics data for geospatial and temporal mapping of urban mobility: New insights into the travel characteristics and vehicle specific power. Preprint for the time being, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F.D. Telematics data for geospatial and temporal mapping of urban mobility: Fuel consumption, and air pollutant and climate-forcing emissions of passenger cars. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei, L.K.; Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F.D. Real-World Contribution of Electrification and Replacement Scenarios to the Fleet Emissions in West Midland Boroughs, UK. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Borough | Birmingham | Sandwell | Walsall | Wolverhampton | Solihull | Dudley | Coventry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (%) | 39 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 11 | 12 |
| Road length (%) | 33 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 11 |
| Vehicle miles (%) | 35 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 14 | 10 | 11 |
| Vehicle Class | A (dB h/km) | b (dB) | R-Square | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrol cars | 1.45 | −5.45 | 0.87 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Diesel cars | 1.45 | −5.47 | 0.87 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Vans | 1.3 | −1.15 | 0.77 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Buses | 1.4 | −5.05 | 0.85 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| HGVs | 1.3 | −4.4 | 0.86 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Cars | Vans | Buses | HGVs | NA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic Ear | 78 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| ANPR camera | 82 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Motorways | Secondary Roads | Primary Roads | Trunk Roads | Weighted Average * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rush/non-rush hour effect | 18% | 9% | 10.3% | 10% | 8.4% |
| Weekday/weekend effect | 5.3% | 4.5% | 5.4% | 4.7% | 4.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaffarpasand, O.; Almojarkesh, A.; Morris, S.; Stephens, E.; Chalabi, A.; Almojarkesh, U.; Almojarkesh, Z.; Pope, F.D. Traffic Noise Assessment Using Intelligent Acoustic Sensors (Traffic Ear) and Vehicle Telematics Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 6964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156964
Ghaffarpasand O, Almojarkesh A, Morris S, Stephens E, Chalabi A, Almojarkesh U, Almojarkesh Z, Pope FD. Traffic Noise Assessment Using Intelligent Acoustic Sensors (Traffic Ear) and Vehicle Telematics Data. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156964
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaffarpasand, Omid, Anwar Almojarkesh, Sophie Morris, Elizabeth Stephens, Alaa Chalabi, Usamah Almojarkesh, Zenah Almojarkesh, and Francis D. Pope. 2023. "Traffic Noise Assessment Using Intelligent Acoustic Sensors (Traffic Ear) and Vehicle Telematics Data" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156964
APA StyleGhaffarpasand, O., Almojarkesh, A., Morris, S., Stephens, E., Chalabi, A., Almojarkesh, U., Almojarkesh, Z., & Pope, F. D. (2023). Traffic Noise Assessment Using Intelligent Acoustic Sensors (Traffic Ear) and Vehicle Telematics Data. Sensors, 23(15), 6964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156964









