Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Based on Residual Attention Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The article proposes a multi-task residual attention network, which introduces a residual attention module to perform end-to-end multi-task learning. The MTAN [9] uses a soft attention mask to extract features of interest from shared features, and we also use an additive operation to emphasize global features before extracting features of interest using the CBAM, and the residual connectivity is added to improve the training speed and accuracy.
- To keep the loss of tasks on a controllable scale and prevent the training process from being dominated by specific tasks, a random-weighted strategy is added to the IMTL method. In this way, the losses and gradients are further balanced impartially and dynamically.
- The experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Meanwhile, some comparison experiments are carried out with other related methods.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multi-Task Learning
2.2. Residual Attention
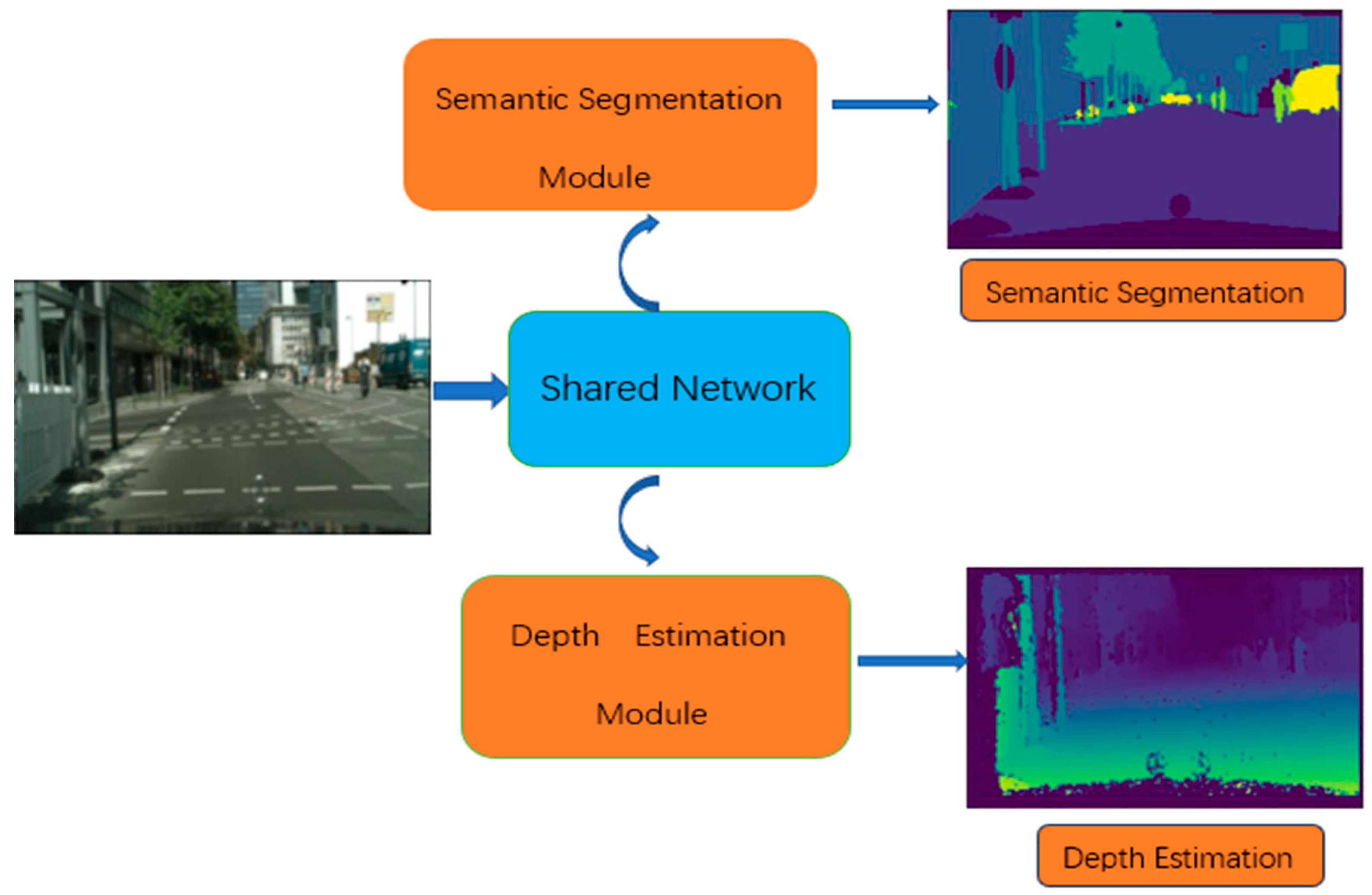
3. Methods
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Task-Sharing Network
3.3. Task-Specific Networks with Residual Attention
- (1)
- Semantic segmentation network
- (2)
- Depth estimation network
3.4. Model Training
| Algorithm 1 IMTL-G algorithm with random-weighted multi-task losses |
| Input: Initialized task-shared/specific parameters / and learning rate Output: 1. for t = 1 to T do 2. compute task scaled loss: ,… 3. compute weight: ~Dirichlet 4. compute total loss: = 5. compute gradient of shared feature: = 6. compute unit-norm gradient = 7. end for 8. = (1−I,), where I = (1,…,1), IMTL-G 9. update task-shared parameters = − () 10. for t = 1 to T do 11. update task-specific parameters = 12. end for |
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Training Setup
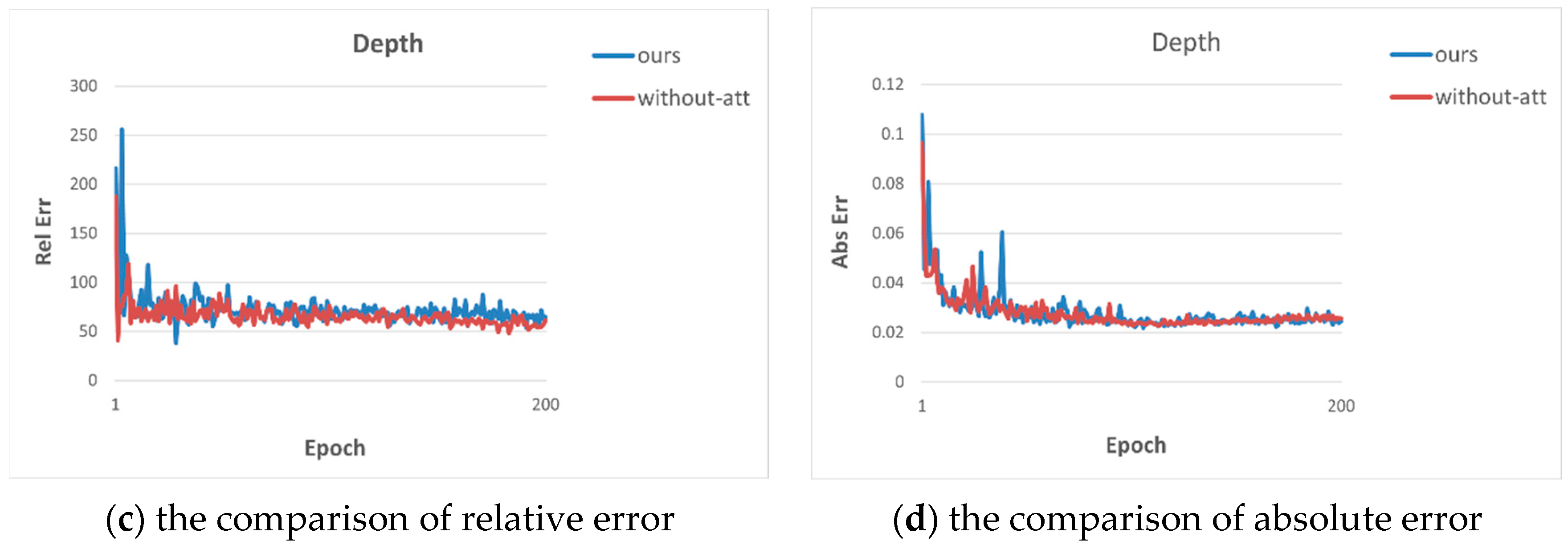
4.3. Ablation Studies
- (1)
- Effectiveness of residual attention
- (2)
- Ablation experiments of optimization algorithms
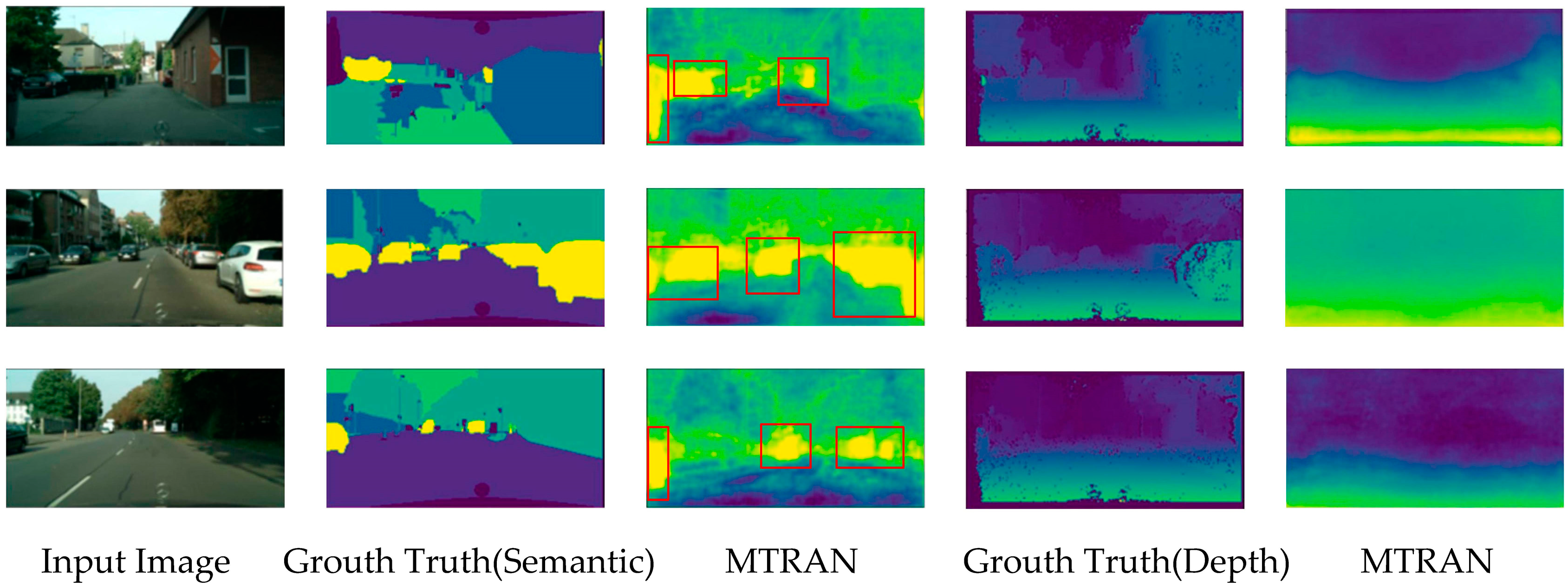
4.4. Visualization Results
4.5. Comparison Results
4.5.1. Comparison of Network Structure
4.5.2. Comparison between Task Balance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, T.; He, Y. HROM: Learning high-resolution representation and object-aware masks for visual object tracking. Sensors 2020, 20, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulwahab, S.; Rashwan, H.A.; Sharaf, N.; Khalid, S.; Puig, D. Deep Monocular Depth Estimation Based on Content and Contextual Features. Sensors 2023, 23, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Shao, M.; Liang, H.; Ren, J. ESAMask: Real-Time Instance Segmentation Fused with Efficient Sparse Attention. Sensors 2023, 23, 6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Qian, F. Monocular depth estimation based on deep learning: An overview. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1612–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context encoding for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7151–7160. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Tang, H.; Liu, H.; Sebe, N.; Ricci, E. Structured attention guided convolutional neural fields for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3917–3925. [Google Scholar]
- Guizilini, V.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Ambrus, R.; Gaidon, A. Semantically-guided representation learning for self-supervised monocular depth. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.12319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, Z.; Xu, C.; Yan, Y.; Sebe, N.; Yang, J. Pattern-affinitive propagation across depth, surface normal and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4106–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Johns, E.; Davison, A.J. End-to-end multi-task learning with attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1871–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Lee, C.Y.; Rabinovich, A. Gradnorm: Gradient normalization for adaptive loss balancing in deep multitask networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 794–803. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, O.; Koltun, V. Multi-task learning as multi-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y.; Cipolla, R. Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7482–7491. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Xue, J.-H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, W. Towards impartial multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bilen, H.; Vedaldi, A. Integrated perception with recurrent multi-task neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, D.; Fergus, R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2650–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. Usr-mtl: An unsupervised sentence representation learning framework with multi-task learning. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 3506–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, J.X.; Hu, Q.V.; He, L. Is position important? deep multi-task learning for aspect-based sentiment analysis. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, M.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Ji, W. Spatial and temporal saliency based four-stream network with multi-task learning for action recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 132, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; Luo, P.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, H. Universal instance perception as object discovery and retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 15325–15336. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Z. End to end multi-task learning with attention for multi-objective fault diagnosis under small sample. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, Z.; Xu, C.; Jie, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Joint task-recursive learning for semantic segmentation and depth estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Wei, W.; Cai, Z.; Fan, Z.; Xie, S.Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q. CI-Net: A joint depth estimation and semantic segmentation network using contextual information. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 18167–18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, R. CSART: Channel and spatial attention-guided residual learning for real-time object tracking. Neurocomputing 2021, 436, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Guan, W.; Li, P.; Ikeda, N.; Hirasawa, K.; Lu, H. Residual multi-task learning for facial landmark localization and expression recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwinda, D.; Paradisa, R.H.; Bustamam, A.; Anggia, P. Deep learning in image classification using residual network (ResNet) variants for detection of colorectal cancer. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 179, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Kanervisto, A.; Miura, J.; Hautamaki, V. Multi-task learning with attention for end-to-end autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2902–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Silberman, N.; Hoiem, D.; Kohli, P.; Fergus, R. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; Proceedings Part V 12. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 746–760. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Wei, Z. Multi-task learning based on geometric invariance discriminative features. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 3505–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, I.; Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, A.; Hebert, M. Cross-stitch networks for multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 3994–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Stone, P.; Liu, Q. Conflict-averse gradient descent for multi-task learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 18878–18890. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, A.; Levine, S.; Hausman, K.; Finn, C. Gradient surgery for multi-task learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 5824–5836. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ngiam, J.; Huang, Y.; Luong, T.; Kretzschmar, H.; Chai, Y.; Anguelov, D. Just pick a sign: Optimizing deep multitask models with gradient sign dropout. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar]



| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| MTRAN | 1.605 × 107 | 79.25 | 94.87 | 0.0218 | 38.0849 |
| Without-att | 1.602 × 107 | 79.22 | 94.81 | 0.0228 | 41.1473 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| MTRAN | 1.605 × 107 | 35.43 | 61.03 | 0.5278 | 0.2489 |
| Without-att | 1.602 × 107 | 35.14 | 60.25 | 0.5556 | 0.2675 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| MTRAN | 1.605 × 107 | 35.43 | 61.03 | 0.5278 | 0.2489 |
| MTAN [9] | 4.121 × 107 | 17.72 | 55.32 | 0.5906 | 0.2577 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| MTRAN | 1.605 × 107 | 79.25 | 94.87 | 0.0218 | 38.0849 |
| Remove residuals | 1.605 × 107 | 79.14 | 94.83 | 0.0220 | 52.3582 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| MTRAN with IMTL-RWL | 1.605 × 107 | 79.25 | 94.87 | 0.0218 | 38.0849 |
| MTRAN with IMTL | 1.605 × 107 | 79.26 | 95.03 | 0.0225 | 48.3591 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| Single-Task | 9.45 × 106 | 77.94 | 94.38 | 0.0223 | 49.5168 |
| MTAN [9] | 4.121 × 107 | 53.86 | 91.11 | 0.0144 | 33.63 |
| Multi-Task | 9.49 × 106 | 78.03 | 94.48 | 0.0261 | 34.0978 |
| DAMAN [34] | - | 55.45 | 92.07 | 0.0146 | 26.33 |
| Cross-Stitch [35] | 2.163 × 107 | 74.48 | 93.54 | 0.0257 | 47.9483 |
| MTRAN | 1.605 ×107 | 79.25 | 94.87 | 0.0218 | 38.0849 |
| Architecture | #P | Segmentation | Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU↑ | Pix Acc↑ | Abs Err↓ | Rel Err↓ | ||
| IMTL-RWL | 1.605 × 107 | 79.25 | 94.87 | 0.0218 | 38.0849 |
| MGD [11] | 1.605 × 107 | 78.46 | 94.66 | 0.0220 | 53.3083 |
| CAG [36] | 1.605 × 107 | 79.25 | 94.86 | 0.0217 | 48.4214 |
| PCG [37] | 1.605 × 107 | 79.01 | 94.76 | 0.0220 | 55.1992 |
| GradDrop [38] | 1.605 × 107 | 79.47 | 94.92 | 0.0220 | 48.7384 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, N.; Dong, H.; Meng, F.; Pang, L. Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Based on Residual Attention Mechanism. Sensors 2023, 23, 7466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177466
Ji N, Dong H, Meng F, Pang L. Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Based on Residual Attention Mechanism. Sensors. 2023; 23(17):7466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177466
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Naihua, Huiqian Dong, Fanyun Meng, and Liping Pang. 2023. "Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Based on Residual Attention Mechanism" Sensors 23, no. 17: 7466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177466
APA StyleJi, N., Dong, H., Meng, F., & Pang, L. (2023). Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Based on Residual Attention Mechanism. Sensors, 23(17), 7466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177466





