The Suspended Sediment Flux in Winter in the South of Chengshantou, between the North and South Yellow Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
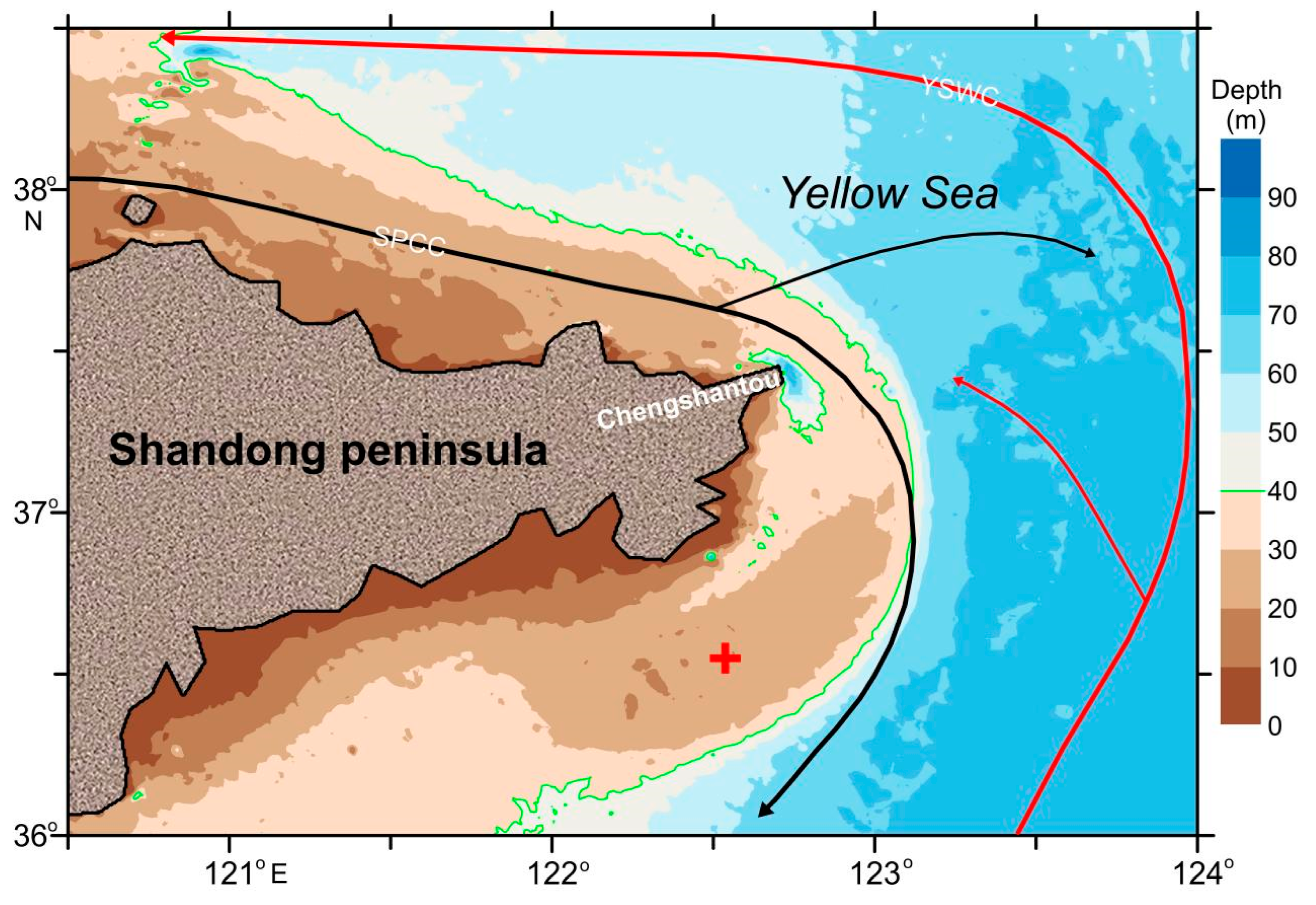
2. Methods
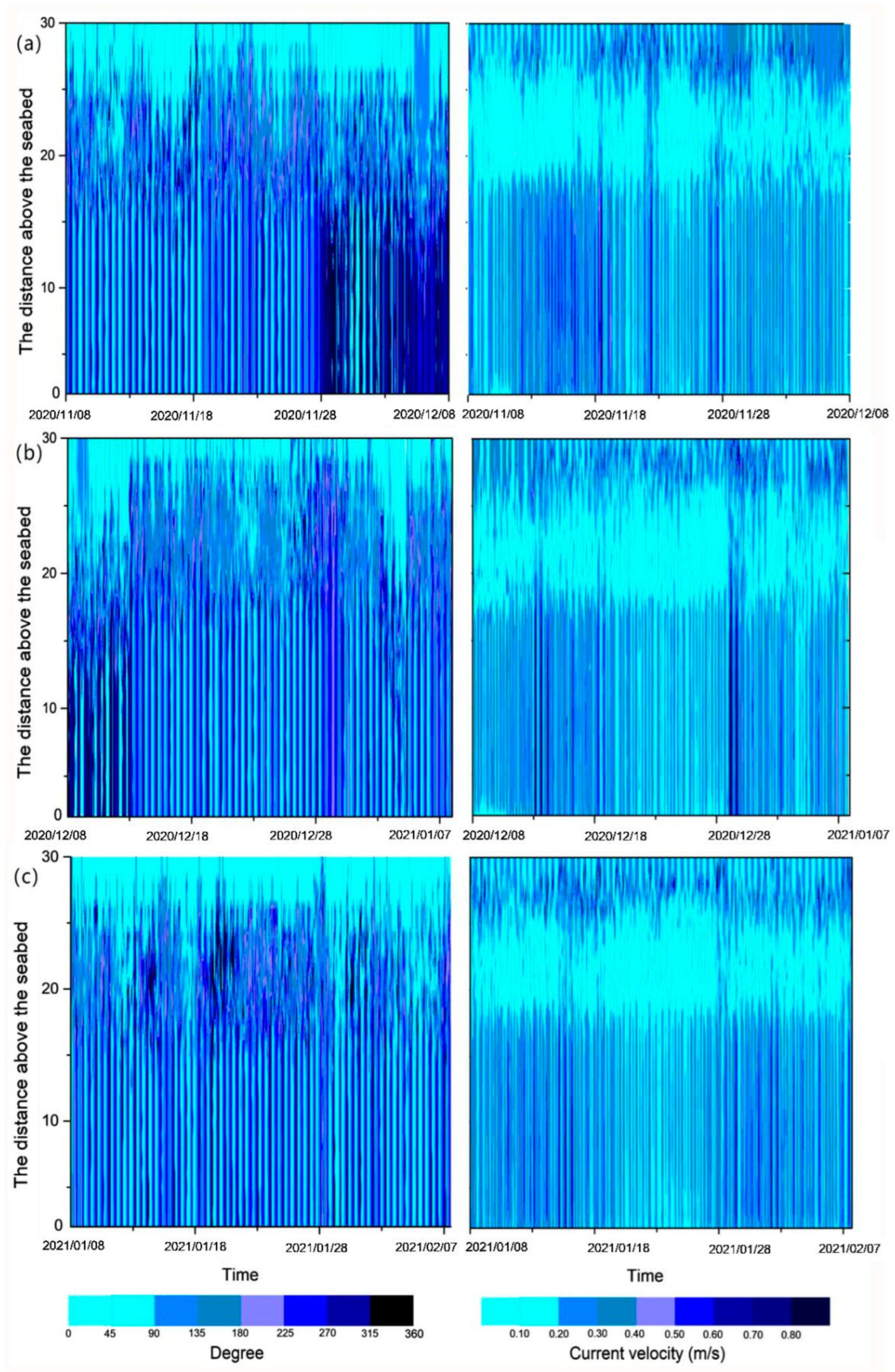
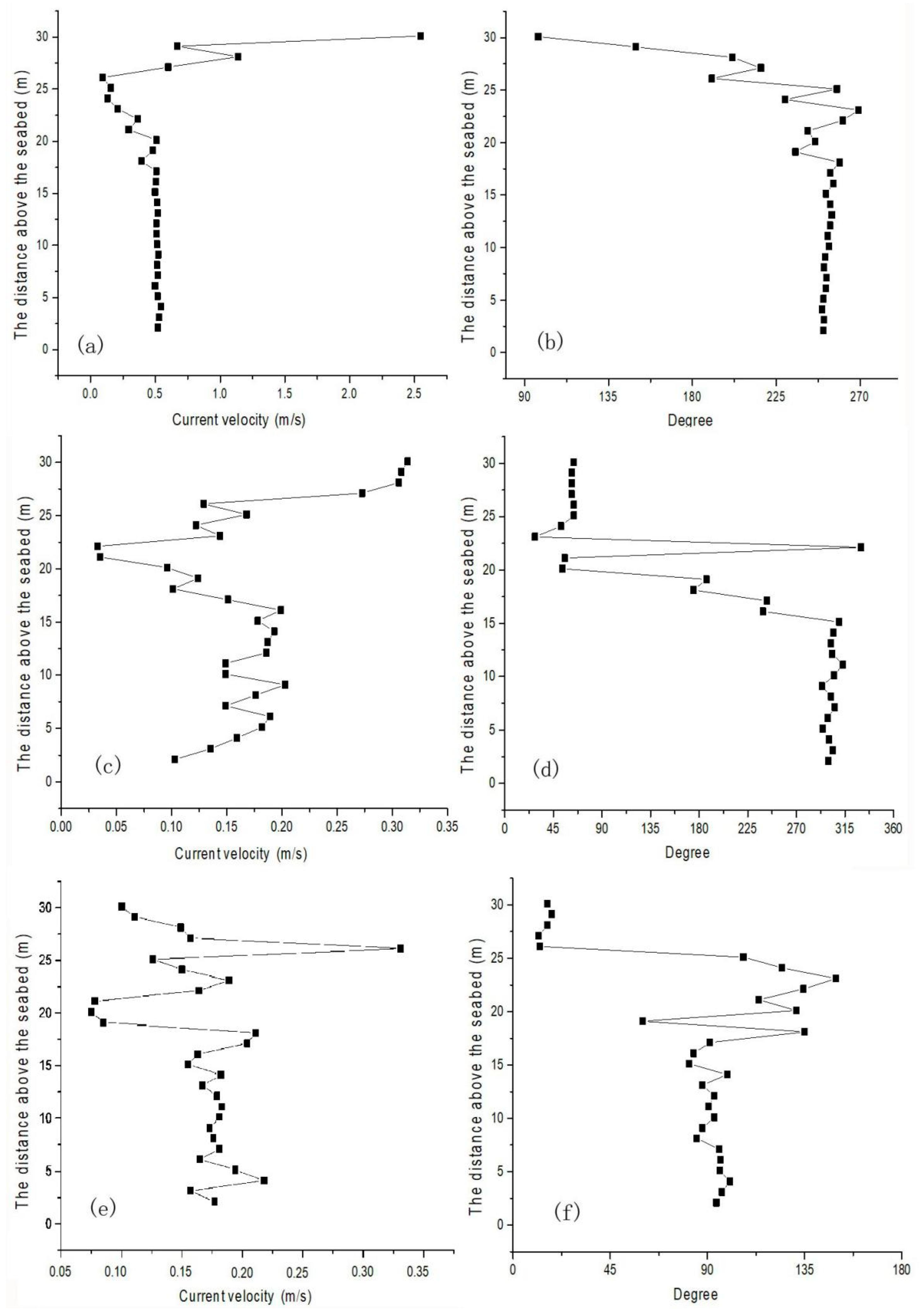
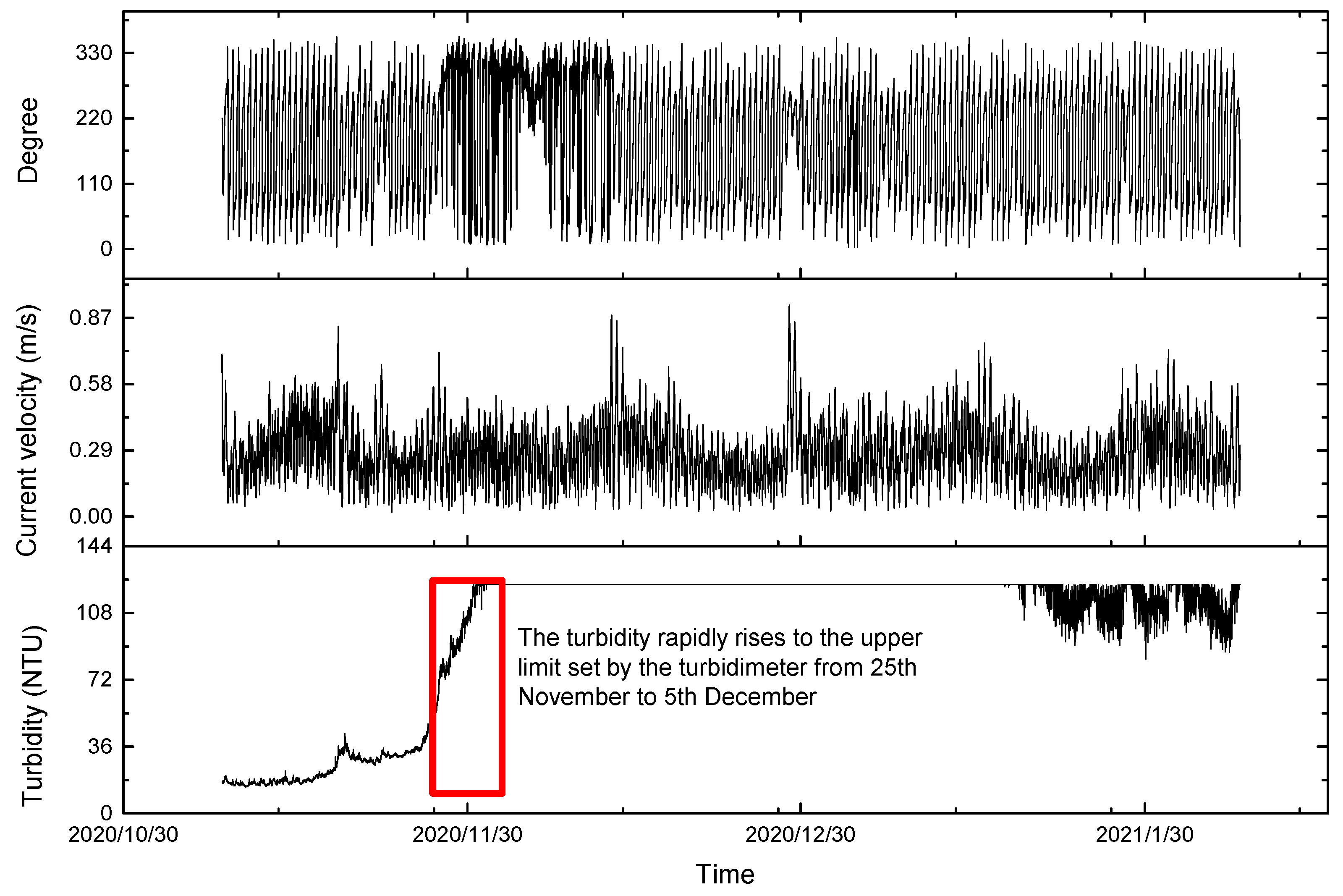
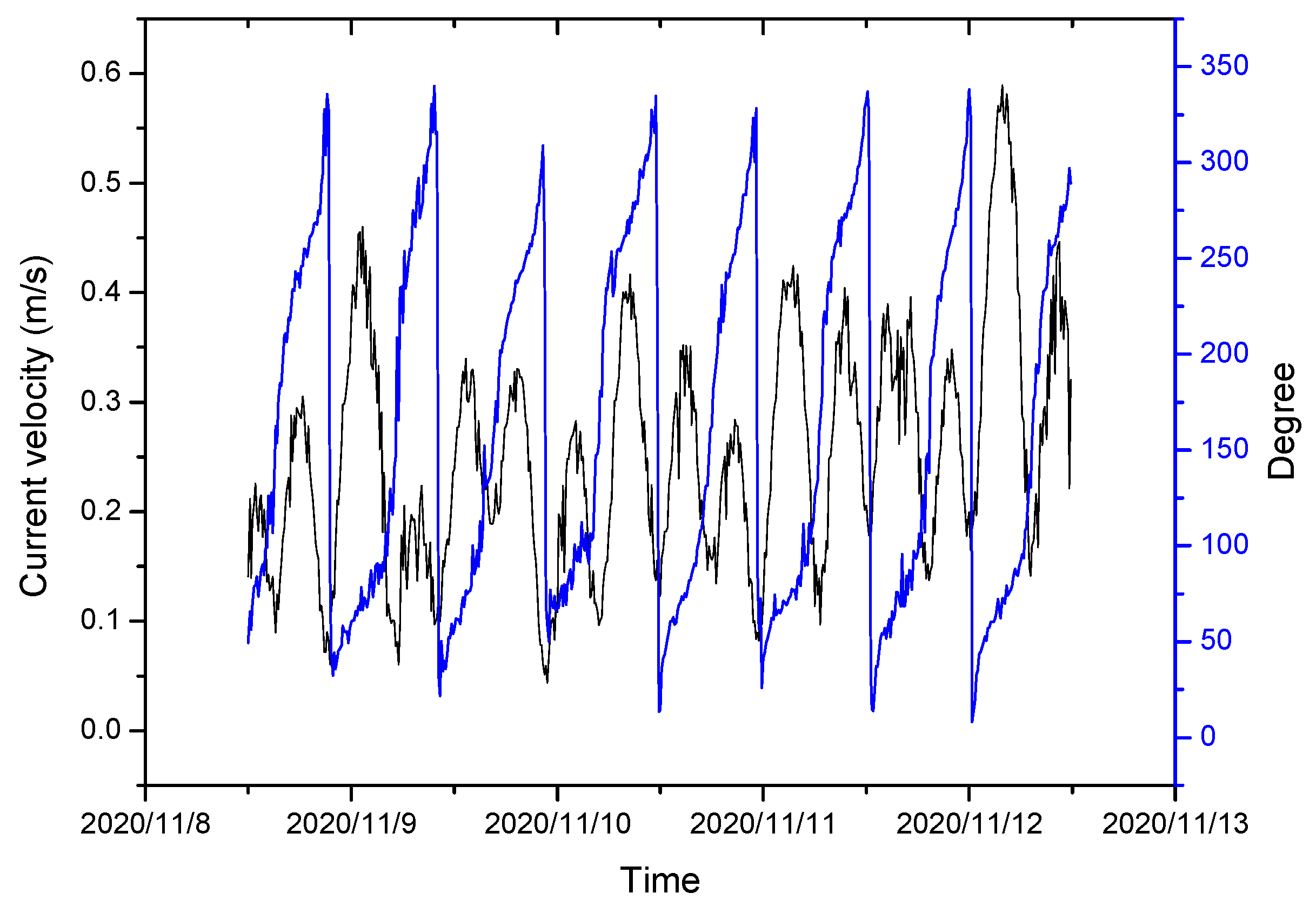
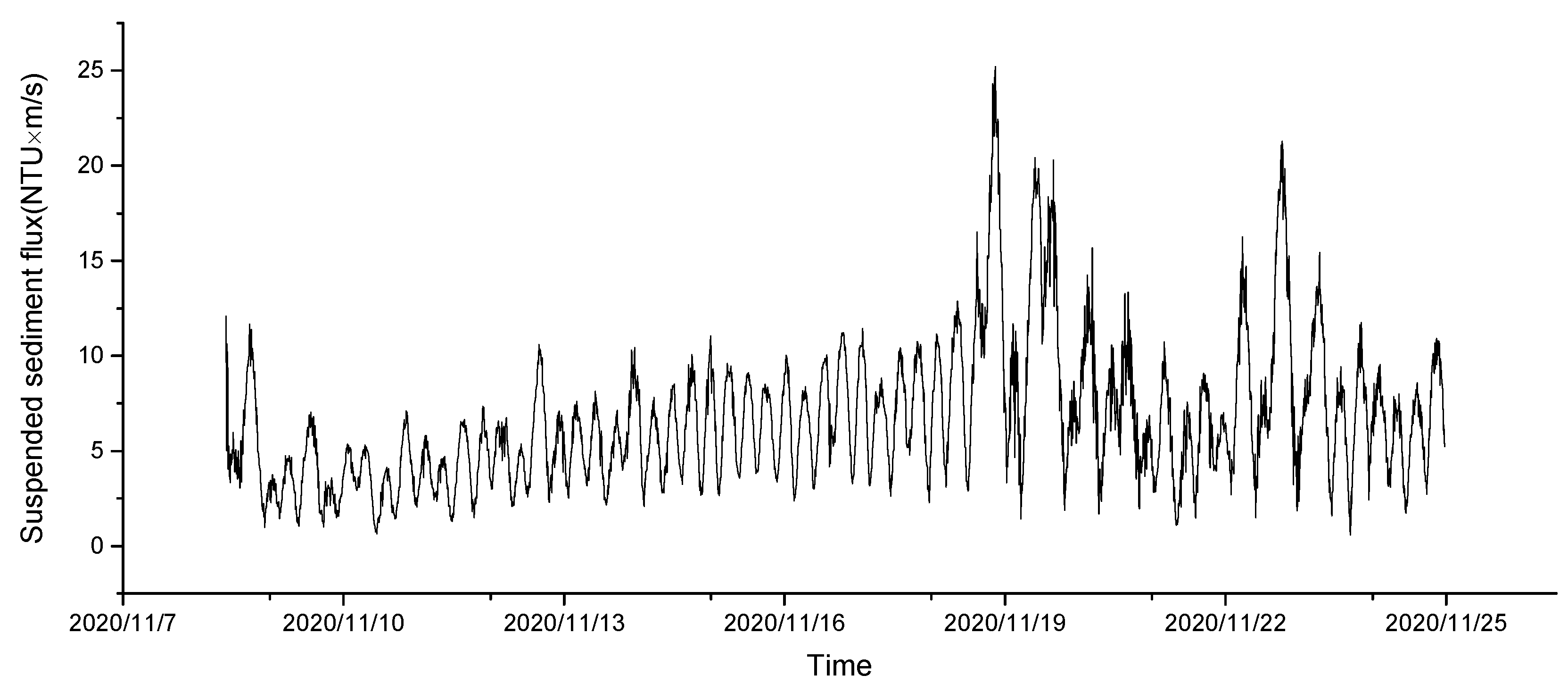
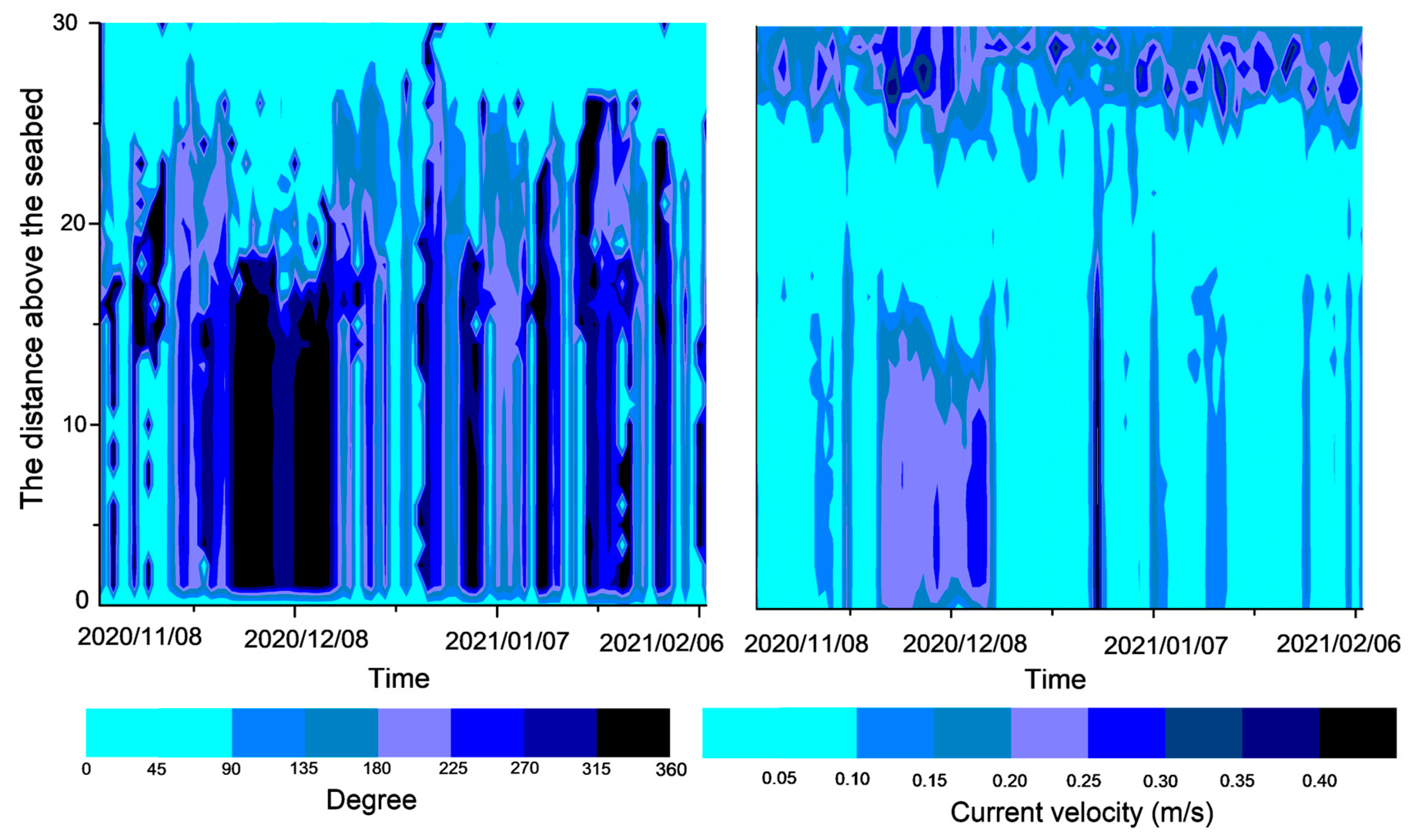
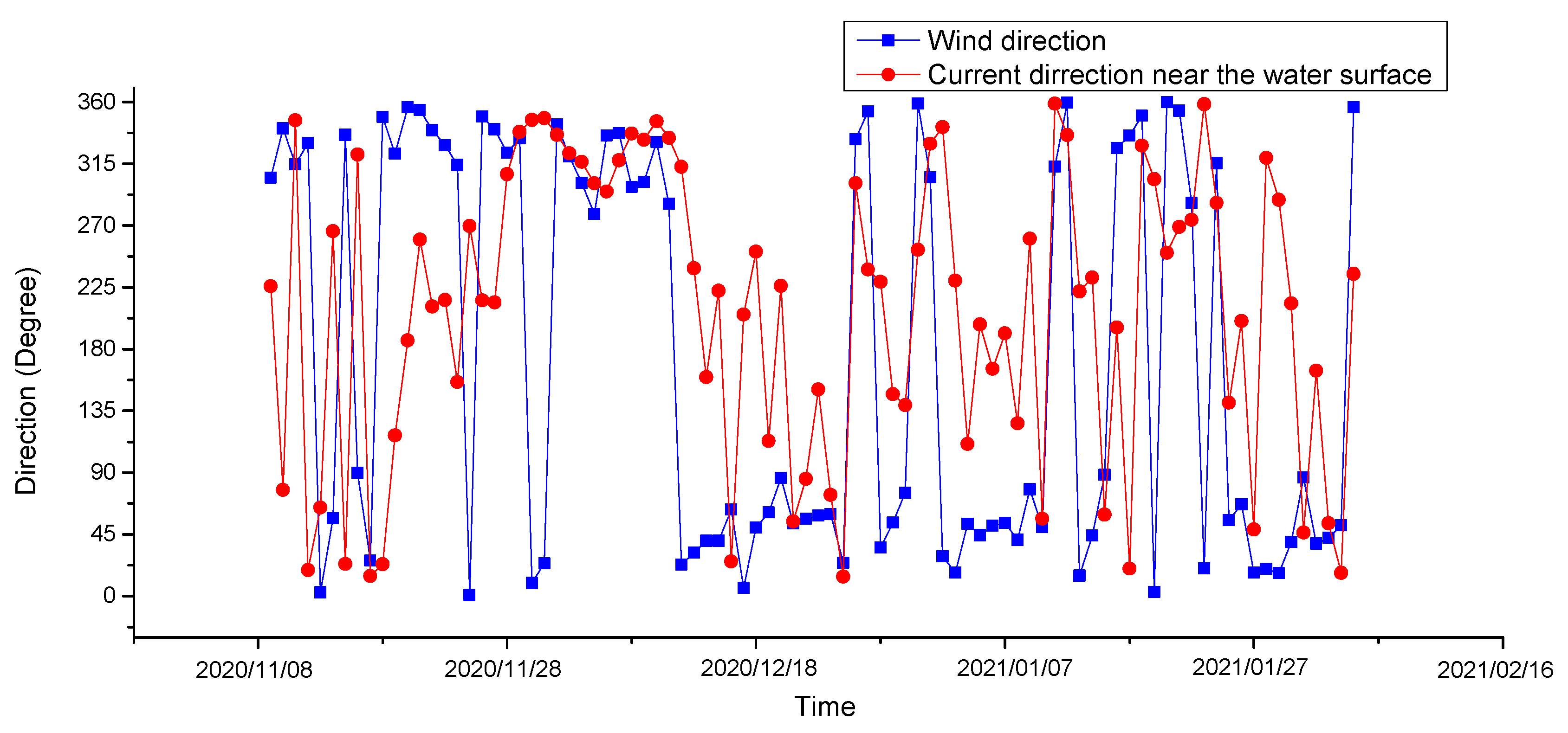
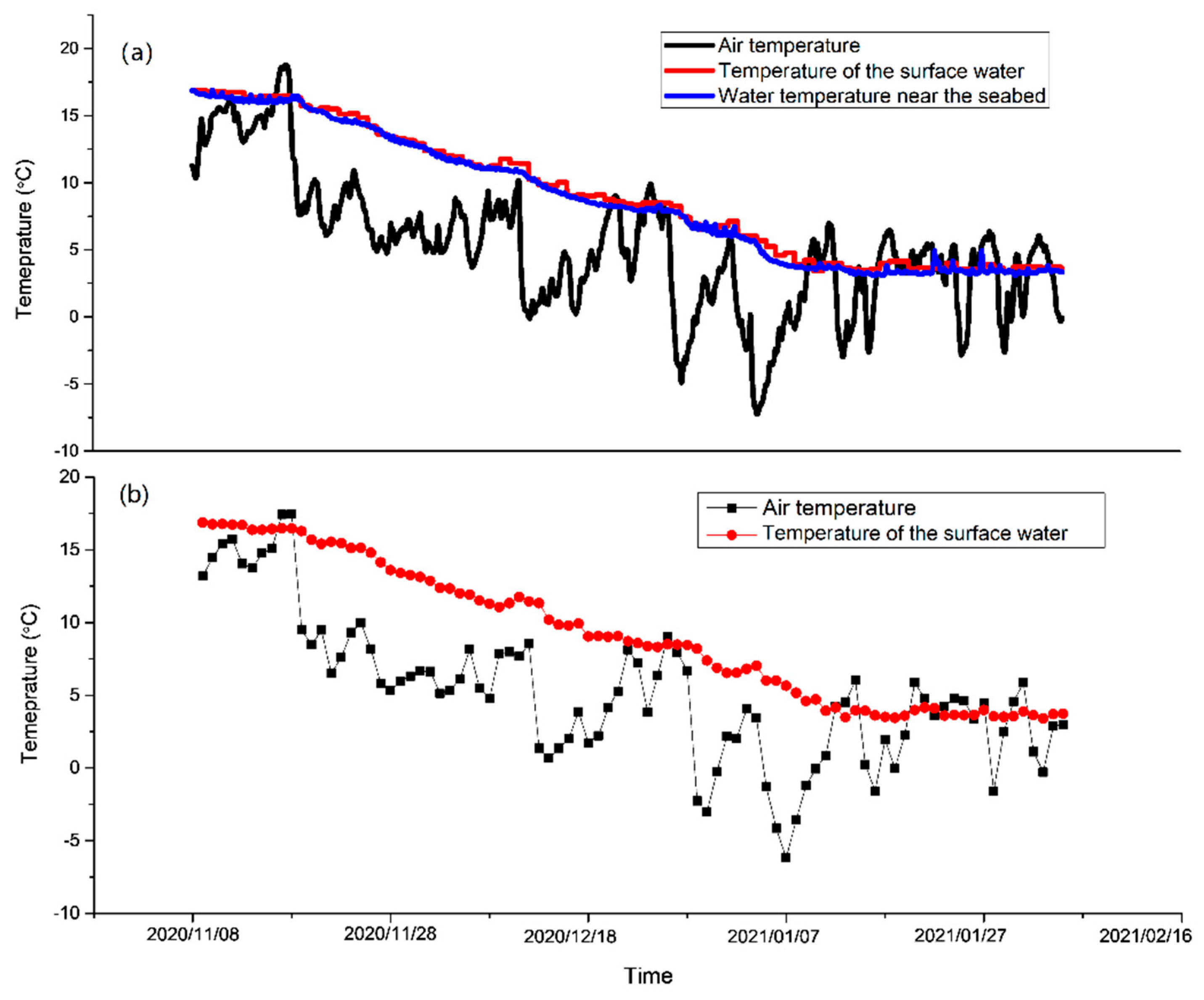
3. Results
4. Discussion
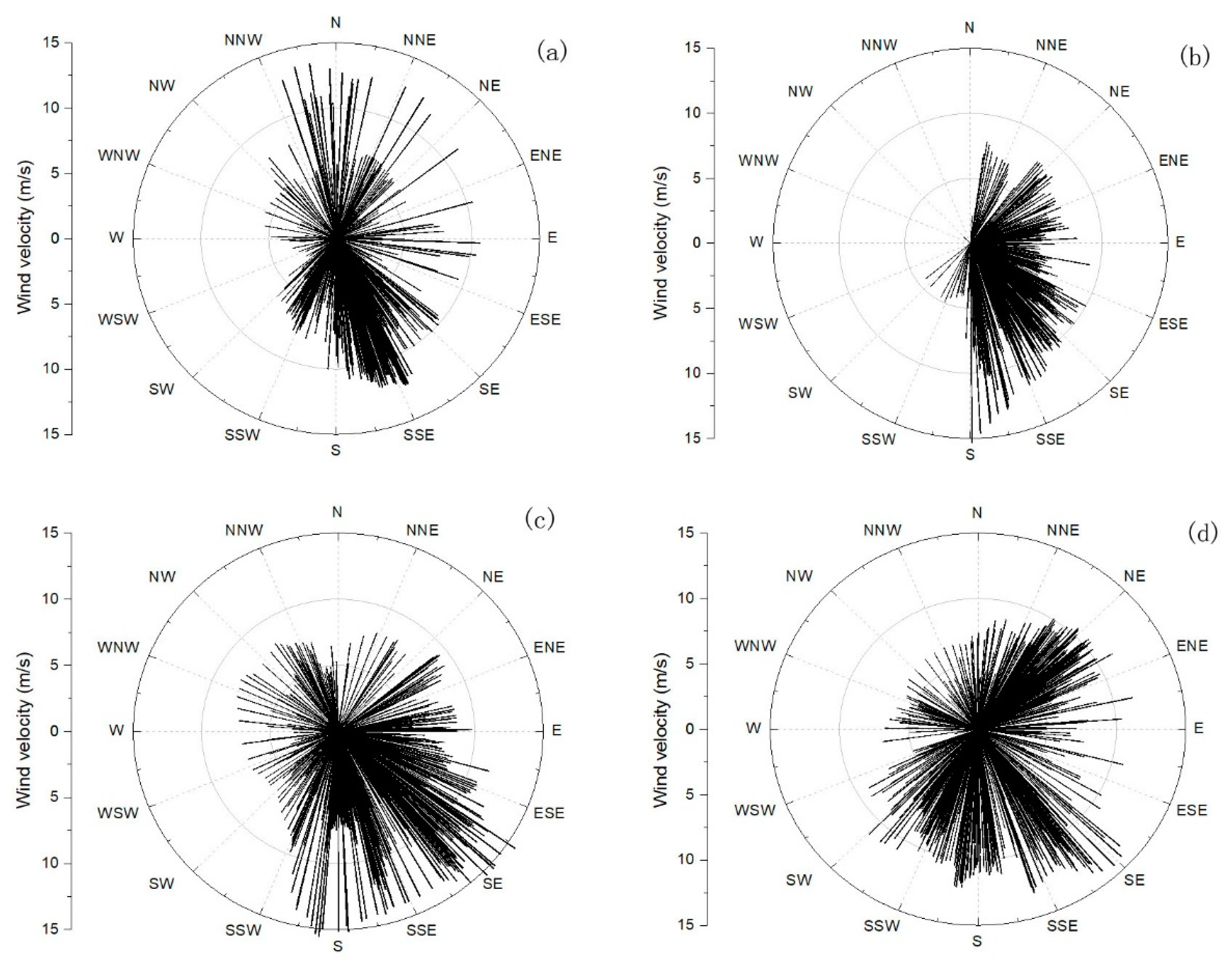
4.1. Suspended Sediment Fluxes
4.2. Resuspended Sediment Transport
4.3. Current Stratification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Zhang, G.L.; Zheng, L.X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, J. Seasonal variation of fluxes and distributions of dissolved methane in the North Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.Z.; Chen, H.T.; Hong, G.H.; Wei, H.; Wu, Q.M. Inventory of nutrient compounds in the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Q. Distribution features of nutrients and nutrient structure in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea in spring and autumn. Donghai Mar. Sci. 2004, 22, 38–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Feng, Z.Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, G.Z.; Fan, J.F. Phytoplankton community in the North Yellow Sea in spring and yearly variation. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 182–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.X. Sediment source and its bearing on marine sedimentation. Mar. Geol. Front. 2011, 27, 8–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.A.; Khim, B.K. Origin and dispersal of recent clay minerals in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 1992, 104, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Chough, S.K. Sediment distribution, dispersal and budget in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 1989, 87, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.E.; Shi, Y.L. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River (China) and its effect on the sedimentation of the Bohai and Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1986, 5, 785–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; Milliman, J.D. Characteristics of sediment transport of Changjiang river and its deposition in the east china sea. J. Shandong Coll. Oceanol. 1984, 13, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Qiao, F.; Lu, J.; Gong, F. The tuibidity maxima of the northern Jiangsu shoal-water in the Yellow Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Qiao, L. Seasonal distribution and relationship of water mass and suspended load in North Yellow Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2009, 27, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Pang, L.; Yoon, J. Response of the Changjiang diluted water around Jeju Island to external forcings: A modeling study of 2002 and 2006. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, N. Sediment distribution features in the North Yellow Sea during Summer and Winter. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 2, 48–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Qiao, L.L.; Yang, Z.S.; Bao, X.W. Research on suspended sediment transport mechanisms along northeast coast of Shandong Peninsula in summer and in winter. J. Sediment Res. 2012, 30, 49–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Ju, X.; Qiao, L.L.; Bao, X.W. Water turbidity in the northern yellow sea in summer and winter. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2014, 45, 928–937. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, S.; Milliman, J.; Limeburner, R. Suspended matter in the south yellow sea. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 1989, 20, 101–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Qin, Y.S.; Milliman, J.D. Suspended solids in the South Yellow Sea in summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. (In Chinese). 1990, 12, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.T. Statistical analysis of hydrodynamic factors dominating the distribution of suspended matter in the south yellow sea. Mar. Sci. 1995, 5, 59–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Weng, X.C.; Gu, H.K., Guo. New Progress in the Joint Study of Oceanography in the Yellow Sea between China and South Korea. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. (In Chinese). 1996, 27, 657–662. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Qiao, F.L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, W.J.; Teng, Y.; Xia, C.S. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, H.; Bi, N.; Wu, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal variation of suspended sediment in the bohai and yellow sea and the pathway of sediment transport. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2015, 35, 11–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Milliman, J.D.; Fan, L.; Yiyang, Z.; Tiemin, Z.; Limeburner, R. Suspended matter regime in the Yellow Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 1986, 17, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Qiao, L.L.; Yang, Z.S.; Bao, X.W.; Zhao, M.X.; Wang, G.S. Suspended Sediment Transport and Deposition due to Strong Regional Shear Current Front: An example from the shelf waters off eastern Shandong Peninsula. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2013, 31, 486–496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Z.; Xue, Z.G.; Bi, N.; Yao, Z.; Wu, X.; Ge, Q.; Wang, H. Seasonal and Intra-seasonal Variations of Suspended-Sediment Distribution in the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 148, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.L.; Zhu, J.R.; Li, C.Y. Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 70, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.X.; Guan, W.B.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.H.; Liu, X.H.; Zeng, X.M. Sediment transport in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.S.; Li, F.; Zheng, T.M.; Xu, S.M. A study on total suspended matter in winter in the south yellow sea. Mar. Sci. 1986, 10, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xu, S.M.; Jiang, X.M. Suspended-cline and lower turbid water in seawater in the soute yellow sea. Mar. Sci. 1991, 5, 43–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.X. Vertical distribution patterns of suspended matter and near bottom turbid water layer in the south yellow sea. Stud. Mar. Sin. 1996, 37, 33–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.S.; Liu, L.; Zang, J.Y.; Ran, X.B. The distribution and transport of suspended matter in the southern Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 34, 73–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Q.; Li, T.G.; Chen, J. High resolution unsaturated alkenones sea surface temperature records in the Yellow Sea during the period of 3500–1300 cal. yr BP. Quat. Int. 2017, 441, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.T.; Yan, H.; Zou, L.; Bai, F.L.; Xu, F.J.; Yin, X.B.; Wei, G.J. Sr-N disotopic geochemistry of Holocene sediments from the South Yellow Sea: Implications for provenance and monsoon variability. Chem. Geol. 2018, 479, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.R.; Sun, B.Y. The distribution and seasonal change of dissolved oxygen in the south yellow sea. J. Shandong Coll. Oceanol. 1980, 1980, 10–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Zheng, C.Z. Horizontal distributions and transportation of nutrients in the southern Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1999, 21, 124–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, W. Exploring seasonal acidification in the Yellow Sea. Sci China Earth Sci 2018, 61, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.X. Distribution feature of dissolved oxygen in Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2001, 20, 9–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Liu, F. Distribution features of the chemical parameters in the Southern Yellow Sea in spring. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1998, 17, 45–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.D. Vertical profiles and transportation of nutrients in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1999, 18, 13–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.T. Chemical oceanography of bioactive elements in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2000, 19, 68–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, J.H.; Sheng, H.; Du, J.; Jia, J.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Li, J.; Bai, F.L.; Chen, Y.N. Cross-Front Sediment Transport Induced by Quick Oscillation of the Yellow Sea Warm Current: Evidence From the Sedimentary Record. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 45, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M. Field survey and analysis of water flux and salinity gradients considering the effects of sea ice coverage and rubber dam: A case study of the Liao River Estuary, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1154150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, H. Numerical Study of Hydrodynamic and Solute Transport with Discontinuous Flows in Coastal Water. Environ. Model Assess 2018, 23, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.H. Preliminary assessment of Tidal Current Energy on Chengshantou area. Ocean Technol. 2010, 29, 98–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Qiao, L.; Dong, P.; Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Ding, D.; et al. Hydrodynamic condition and suspended sediment diffusion in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6204–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Equipment | Main Function | Main Index |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature and salt depth turbidimeter | Observes parameters such as temperature, salinity, pressure, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and oxygen redox potential (ORP) | The accuracy of the temperature and salt sensor is 0.002 degrees; the salinity accuracy is 0.003 ms/cm. The accuracy of the pressure sensor is 0.05% of the water depth. The accuracy of the optical dissolved oxygen sensor is 5%. The accuracy of the ORP sensor is 0.01 V. The accuracy of the turbidity sensing is 2%. |
| 600 K HZ ADCP | Velocity profile (upward) | The blind zone is 2.11 m. The distance is 2 m per layer and 17 frequencies are emitted every 600 s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Xiong, X.; Duan, B.; Wang, D.; Yu, L. The Suspended Sediment Flux in Winter in the South of Chengshantou, between the North and South Yellow Sea. Sensors 2023, 23, 7771. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187771
Li B, Xiong X, Duan B, Wang D, Yu L. The Suspended Sediment Flux in Winter in the South of Chengshantou, between the North and South Yellow Sea. Sensors. 2023; 23(18):7771. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187771
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bowen, Xuejun Xiong, Baichuan Duan, Daolong Wang, and Long Yu. 2023. "The Suspended Sediment Flux in Winter in the South of Chengshantou, between the North and South Yellow Sea" Sensors 23, no. 18: 7771. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187771
APA StyleLi, B., Xiong, X., Duan, B., Wang, D., & Yu, L. (2023). The Suspended Sediment Flux in Winter in the South of Chengshantou, between the North and South Yellow Sea. Sensors, 23(18), 7771. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187771





