Estimation of One-Repetition Maximum, Type, and Repetition of Resistance Band Exercise Using RGB Camera and Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Exercise
2.3. Experimental Setup
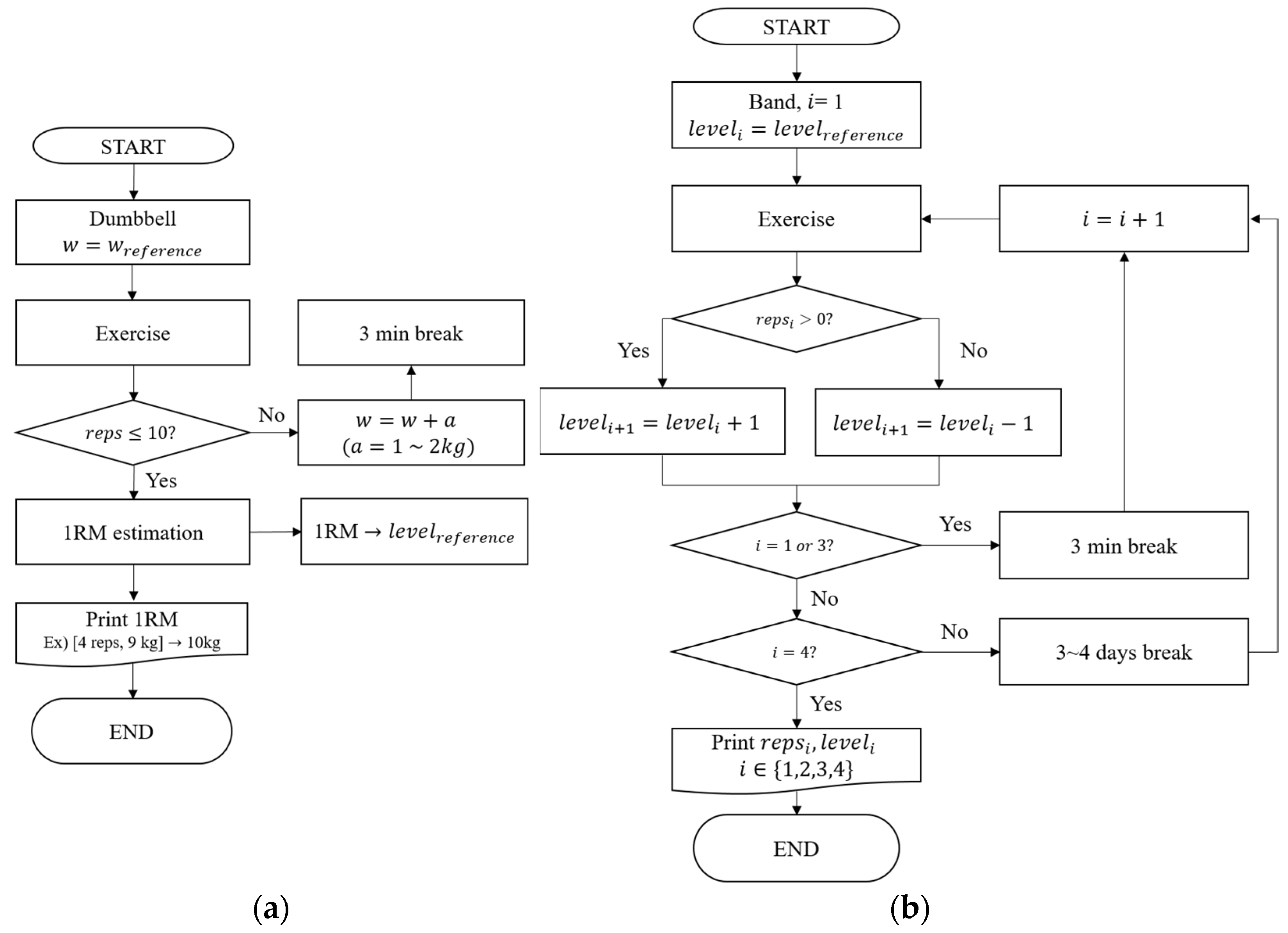
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.4.1. Dumbbell 1−RM Estimation
2.4.2. Band Force Test
2.5. Data Acquisition
2.5.1. Dumbbell 1−RM Estimation
2.5.2. IMU sensor
2.5.3. RGB Camera and Pose Estimation
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. Statistical Analysis
2.6.2. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Architecture
2.6.3. Repetition-Counting Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. RM Regression Equation
3.1.1. Comparison between Dumbbell RM and BF
3.1.2. Analysis of Chest Press Regression
3.1.3. Analysis of Shoulder Press Regression
3.1.4. Regression Analysis of Seated Row
3.1.5. Regression Analysis of Biceps Curl
3.1.6. Analysis of Overhead Triceps Extension Regression
3.2. Convolution Neural Networks
3.2.1. IMU Input Model
3.2.2. Joint Position Input Model
3.2.3. Upper Joint Position Input Model
3.2.4. IMU and Joint Position Input Model
3.3. Repetition-Counting Algorithm
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Regression Expression for Each Exercise
4.2. CNN Model F1-Score Analysis
4.3. Counting Algorithm
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Regression Analysis Model Reduction
| Exercise | Model | Parameter | Order | Coefficient | p-Value | Residual Standard Error | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest press | 1 | Intercept | 1 | 3.516284 | 0.30212 | 1.996 | 0.8939 |
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | −0.621192 | 0.00141 ** | ||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.586614 | 0.00221 ** | ||||
| Repetition2, (reps) | 1 | 0.293881 | 0.03966 * | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.025779 | 0.00689 ** | ||||
| 2 | Intercept | 1 | 5.061241 | 0.1627 | 2.154 | 0.8764 | |
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | −0.545342 | 0.0059 ** | ||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.493515 | 0.0104 * | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.031559 | 0.0017 ** | ||||
| 3 | Intercept | 1 | 13.905680 | 0.0000 *** | 2.44 | 0.8415 | |
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | −0.924192 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.053651 | 0.0000 *** |
| Exercise | Model | Parameter | Order | Coefficient | p-Value | Residual Standard Error | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder press | 1 | Intercept | 1 | −1.986427 | 0.06882 | 1.076 | 0.9245 |
| Band Force1, (kgf) | 1 | 1.030632 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| 2 | 0.021399 | 0.00816 ** | |||||
| Repetition2, (reps) | 1 | 0.665331 | 0.07708 | ||||
| 2 | 0.056737 | 0.10476 | |||||
| Repetition2*Band Force2, | 1 | 0.040959 | 0.02954 * | ||||
| 2 | Intercept | 1 | −1.049199 | 0.2621 | 1.117 | 0.9187 | |
| Band Force1, (kgf) | 1 | 1.028001 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| 2 | 0.020626 | 0.0127 * | |||||
| Repetition2, (reps) | 1 | 0.133151 | 0.4655 | ||||
| Repetition2*Band Force2, | 1 | −0.040203 | 0.0381 * | ||||
| 3 | Intercept | 1 | −0.629601 | 0.3842 | 1.107 | 0.9202 | |
| Band Force1, (kgf) | 1 | 0.992013 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| 2 | 0.020787 | 0.0111 * | |||||
| Repetition2*Band Force2, | 1 | −0.029686 | 0.0160 * |
| Exercise | Model | Parameter | Order | Coefficient | p-Value | Residual Standard Error | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seated row | 1 | Intercept | 1 | 19.57982 | 0.00810 ** | 2.158 | 0.8688 |
| Band Force1, (kgf) | 1 | −1.87319 | 0.00880 ** | ||||
| 2 | 0.03177 | 0.08346 | |||||
| 2 | −0.04833 | 0.00720 ** | |||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.55397 | 0.04243 * | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.07482 | 0.00761 ** | ||||
| 2 | Intercept | 1 | 11.29618 | 0.03383 * | 2.361 | 0.8429 | |
| Band Force1, (kgf) | 1 | −1.10259 | 0.03913 * | ||||
| 2 | −0.05265 | 0.00625 ** | |||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.84785 | 0.00120 ** | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.07982 | 0.00779 ** | ||||
| 3 | Intercept | 1 | 2.15774 | 0.48092 | 2.697 | 0.7951 | |
| 2 | −0.01846 | 0.02173 * | |||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.59555 | 0.00952 ** | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.02565 | 0.03092 * |
| Exercise | Model | Parameter | Order | Coefficient | p-Value | Residual Standard Error | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biceps curl | 1 | Intercept | 1 | 3.896989 | 0.0000 *** | 0.9036 | 0.8843 |
| 2 | 0.011323 | 0.0136 * | |||||
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | 0.183714 | 0.0973 | ||||
| 2 | 0.031916 | 0.0000 *** | |||||
| 2 | −0.003096 | 0.2522 | |||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | −0.028959 | 0.0312 * | ||||
| 2 | Intercept | 1 | 3.710290 | 0.0000 *** | 1.107 | 0.8827 | |
| 2 | 0.010340 | 0.0211 * | |||||
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | 0.150178 | 0.1586 | ||||
| 2 | 0.032720 | 0.0000 *** | |||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | −0.025419 | 0.0507 | ||||
| 3 | Intercept | 1 | 4.432227 | 0.0000 *** | 1.129 | 0.8778 | |
| 2 | 0.005706 | 0.0515 | |||||
| 2 | 0.031340 | 0.0000 *** | |||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 3.710290 | 0.0000 *** |
| Exercise | Model | Parameter | Order | Coefficient | p-Value | Residual Standard Error | Adjusted R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overhead triceps extension | 1 | Intercept | 1 | 0.47045 | 0.617542 | 0.8043 | 0.9305 |
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | −0.13721 | 0.090012 | ||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.94210 | 0.002390 ** | ||||
| 2 | −0.03053 | 0.093832 | |||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.05062 | 0.000577 *** | ||||
| 2 | Intercept | 1 | 1.48852 | 0.05922 | 0.8365 | 0.9249 | |
| Repetition1, (reps) | 1 | −0.09673 | 0.22120 | ||||
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.49041 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.04835 | 0.00118 ** | ||||
| 3 | Intercept | 1 | 0.642109 | 0.0689 | 0.8457 | 0.9232 | |
| Band Force2, (kgf) | 1 | 0.063498 | 0.0000 *** | ||||
| Repetition1*Band Force1, | 1 | 0.006473 | 0.0000 *** |
Appendix B. Goodness-of-Fit Plots for Regression Equations





Appendix C. Confusion Matrices for CNN Models




References
- Strasser, B. Importance of assessing muscular fitness in secondary care. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 583810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, M.; Breen, L.; Hamilton, D.L.; Philp, A. Live strong and prosper: The importance of skeletal muscle strength for healthy ageing. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco-García, J.M.; Rodal, M.; Gutiérrez-Horrillo, R.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Nobari, H.; Ardigò, L.P.; Gianikellis, K. Shoulder Kinematics and Symmetry at Different Load Intensities during Bench Press Exercise. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hislop, H.J. Daniels and Worthingham’s Muscle Testing: Techniques of Manual Examination; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 182–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bye, E.; Glinsky, J.; Yeomans, J.; Hungerford, A.; Patterson, H.; Chen, L.; Harvey, L. The inter-rater reliability of the 13-point manual muscle test in people with spinal cord injury. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2021, 37, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, N.B. Muscle and Sensory Testing-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Bermejo, L.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Manzano, F.; Collado-Mateo, D.; Villafaina, S.; Adsuar, J.C. Reliability of isokinetic knee strength measurements in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Katoh, M.; Gomi, M.; Arai, S. Validity and reliability of isometric knee extension muscle strength measurements using a belt-stabilized hand-held dynamometer: A comparison with the measurement using an isokinetic dynamometer in a sitting posture. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2020, 32, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croteau, F.; Robbins, S.M.; Pearsall, D. Hand-held shoulder strength measures correlate with isokinetic dynamometry in elite water polo players. J. Sport Rehabil. 2021, 30, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadalupe-Grau, A.; Carnicero, J.A.; Gómez-Cabello, A.; Gutiérrez Avila, G.; Humanes, S.; Alegre, L.M.; Castro, M.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; García-García, F.J. Association of regional muscle strength with mortality and hospitalisation in older people. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, R.; Donath, L.; Kurz, E.; Zahner, L.; Faude, O. Absolute and relative reliability of isokinetic and isometric trunk strength testing using the IsoMed-2000 dynamometer. Phys. Ther. Sport 2017, 24, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrázulas, J.A.; Estrázulas, J.A.; de Jesus, K.; de Jesus, K.; da Silva, R.A.; Dos Santos, J.O. Evaluation isometric and isokinetic of trunk flexor and extensor muscles with isokinetic dynamometer: A systematic review. Phys. Ther. Sport 2020, 45, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.I.; Harrington, S.E. Research round-up. Rehabil. Oncol. 2015, 33, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Cheng, M.S.; Smith, A.R.; Kolber, M.J. Intrarater reliability of hand held dynamometry in measuring lower extremity isometric strength using a portable stabilization device. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 27, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Lim, D.H.; Cho, Y.H. Analysis of the reliability of the make test in young adults by using a hand-held dynamometer. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2238–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jared, V.; Joseph, D. Muscle Performance Testing: Create Your Own Dynamometer. The Movement System. 2019. Available online: https://athletemovementsystem.com/muscle-performance-testing-create-your-own-dynamometer/ (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Grgic, J.; Lazinica, B.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Pedisic, Z. Test–retest reliability of the one-repetition maximum (1−RM) strength assessment: A systematic review. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramos, A.; Barboza-González, P.; Ulloa-Díaz, D.; Rodriguez-Perea, A.; Martinez-Garcia, D.; Guede-Rojas, F.; Hinojosa-Riveros, H.; Chirosa-Ríos, L.J.; Cuevas-Aburto, J.; Janicijevic, D.; et al. Reliability and validity of different methods of estimating the one-repetition maximum during the free-weight prone bench pull exercise. J. Sport. Sci. 2019, 37, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.L.; Vinstrup, J.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Sundstrup, E. Validity and reliability of elastic resistance bands for measuring shoulder muscle strength. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldsson, B.T.; Andersen, C.H.; Erhardsen, K.T.; Zebis, M.K.; Micheletti, J.K.; Pastre, C.M.; Andersen, L.L. Submaximal elastic resistance band tests to estimate upper and lower extremity maximal muscle strength. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.S.S.; Machado, A.F.; Micheletti, J.K.; De Almeida, A.C.; Cavina, A.P.; Pastre, C.M. Effects of training with elastic resistance versus conventional resistance on muscular strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119831116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aidar, F.J.; Clemente, F.M.; de Lima, L.F.; de Matos, D.G.; Ferreira, A.R.P.; Marçal, A.C.; Moreira, O.C.; Bulhões-Correia, A.; de Almeida-Neto, P.F.; Díaz-de-Durana, A.L.; et al. Evaluation of training with elastic bands on strength and fatigue indicators in paralympic powerlifting. Sports 2021, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.V.A.; Miguel, H. Elastic resistance training: Resistance exercise alternative in the home environment during Covid-19 pandemic. Interamerican J. Med. Health 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market Decipher. Available online: https://www.marketdecipher.com/report/resistance-bands-market (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Ma, J.; Hogervorst, E.; Magistro, D.; Chouliaras, V.; Zecca, M. Development of sensorised resistance band for objective exercise measurement: Activities classification trial. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 3942–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Liang, J.; Jeong, J.; Xu, T. Monitoring the training dose and acute fatigue response during elbow flexor resistance training using a custom-made resistance band. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Neto, F.; Guanais, P.; Dornelas, E.; Coutinho, A.C.B.; Costa, R.R.G. Validity of one-repetition maximum predictive equations in men with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A. Predictability of a Linear Model of Repetition Maximums in the Bench Press v. Traditional Conversion Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, The William Paterson University of New Jersey, Wayne, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Kim, J.; Hwang, B.; Shim, G.; Kim, J. Estimation of 1-repetition maximum using a hydraulic bench press machine based on User’s lifting speed and load weight. Sensors 2022, 22, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.A.; Lu, Y.C.; You, C.H.; Chiang, C.K. Deep learning for sensor-based rehabilitation exercise recognition and evaluation. Sensors 2019, 19, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crema, C.; Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Sisinni, E.; Haslwanter, T.; Salzmann, S. IMU-based solution for automatic detection and classification of exercises in the fitness scenario. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Glassboro, NJ, USA, 13–15 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, A.; Brunner, G.; Tanner, S.; Wattenhofer, R. Recognition and repetition counting for complex physical exercises with deep learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skawinski, K.; Montraveta Roca, F.; Findling, R.D.; Sigg, S. Workout type recognition and repetition counting with CNNs from 3D acceleration sensed on the chest. In Proceedings of the International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Gran Canaria, Spain, 12–14 June 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J. Motion recognition based on deep learning and human joint points. Comp. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1826951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strength Level, Weightlifting Strength Standards. Available online: https://strengthlevel.com/strength-standards/ (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Patterson, R.M.; Stegink Jansen, C.W.; Hogan, H.A.; Nassif, M.D. Material properties of thera-band tubing. Phys. Ther. 2001, 81, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richens, B.; Cleather, D.J. The relationship between the number of repetitions performed at given intensities is different in endurance and strength trained athletes. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, T.; Joo, H.; Matthews, I.; Sheikh, Y. Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4645–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatiah, T.; Chen, C. Recognizing exercises and counting repetitions in real time. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.03194. [Google Scholar]






| Exercise | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Chest press (Ex1) | ×0.20 | ×0.10 |
| Shoulder press (Ex2) | ×0.15 | ×0.10 |
| Seated row (Ex3) | ×0.20 | ×0.10 |
| Biceps curl (Ex4) | ×0.10 | ×0.05 |
| Overhead triceps extension (Ex5) | ×0.05 | ×0.05 |
| Definition of Variables | Dataset 1 | Dataset 2 |
|---|---|---|
| BF () | ||
| Repetition () | ||
| () | ||
| Square of repetition () | ||
| Interaction between BF and repetition () |
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error Mean | 95% Confidence | Significance (2-Tailed) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| BF1–RM1 | 0.34445 | 1.04577 | 0.19093 | –0.04605 | 0.73495 | 0.082 |
| BF1–RM2 | 0.16000 | 0.67361 | 0.12298 | –0.09153 | 0.41153 | 0.204 |
| BF1–RM3 | –0.03757 | 0.67295 | 0.12286 | –0.28885 | 0.21372 | 0.762 |
| BF1–RM4 | –0.13733 | 0.61292 | 0.11190 | –0.36620 | 0.09154 | 0.230 |
| BF1–RM5 | –4.48081 | 2.77822 | 0.50723 | –5.51821 | –3.44340 | 0.000 * |
| Reps of Ex1 | Reps of Ex2 | Reps of Ex3 | Reps of Ex4 | Reps of Ex5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Available | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Not available | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mean | 16.87 | 7.40 | 17.53 | 15.17 | 8.83 | |
| Standard deviation | 4.125 | 3.892 | 4.108 | 5.160 | 4.639 | |
| Sum | 506 | 222 | 526 | 455 | 265 | |
| Layer | Output Shape | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Conv 2D _1 | (None, 10, 60, 32) | 832 |
| Max_pooling2D_1 | (None, 5, 30, 32) | 0 |
| Conv 2D _2 | (None, 5, 30, 64) | 8256 |
| Max_pooling2D_2 | (None, 2, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 2, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Flatten | (None, 1920) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | (None, 1000) | 1,921,000 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 1000) | 0 |
| Dense_2 | (None, 6) | 6006 |
| Input Data Type (Size) | Exercise | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMU: quaternion, gyro, acceleration () | Chest press | 0.97385784 | 0.99923362 | 0.98638255 |
| Shoulder press | 0.99199688 | 0.99257812 | 0.99228742 | |
| Seated row | 0.94417599 | 0.99946157 | 0.9710325 | |
| Biceps curl | 0.99695321 | 0.92098914 | 0.95746682 | |
| Overhead triceps extension | 0.99134948 | 0.98841794 | 0.98988154 | |
| Non-exercise | 0.99252037 | 0.96032567 | 0.97615764 |
| Layer | Output Shape | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Conv 2D _1 | (None, 50, 60, 32) | 832 |
| Max_pooling2D_1 | (None, 25, 30, 32) | 0 |
| Conv 2D _2 | (None, 25, 30, 64) | 8256 |
| Max_pooling2D_2 | (None, 12, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 12, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Flatten | (None, 11,520) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | (None, 1000) | 11,521,000 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 1000) | 0 |
| Dense_2 | (None, 6) | 6006 |
| Input Data Type (Size) | Exercise | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint position () | Chest press | 0.99246873 | 0.99310257 | 0.99278555 |
| Shoulder press | 0.9978308 | 0.98828125 | 0.99303307 | |
| Seated row | 0.98130469 | 0.99623099 | 0.98871151 | |
| Biceps curl | 0.99528495 | 0.97607559 | 0.98558668 | |
| Overhead triceps extension | 0.99270807 | 0.97289305 | 0.98270068 | |
| Non-exercise | 0.9725975 | 0.98617214 | 0.97933778 |
| Layer | Output Shape | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Conv 2D _1 | (None, 16, 60, 32) | 832 |
| Max_pooling2D_1 | (None, 8, 30, 32) | 0 |
| Conv 2D _2 | (None, 8, 30, 64) | 8256 |
| Max_pooling2D_2 | (None, 4, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 4, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Flatten | (None, 3840) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | (None, 1000) | 3,841,000 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 1000) | 0 |
| Dense_2 | (None, 6) | 6006 |
| Input Data Type (Size) | Exercise | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper joint position () | Chest press | 0.98885512 | 0.99731767 | 0.99306836 |
| Shoulder press | 0.97651588 | 0.99082031 | 0.98361609 | |
| Seated row | 0.97405847 | 0.99569256 | 0.98475671 | |
| Biceps curl | 0.99483258 | 0.96763168 | 0.98104362 | |
| Overhead triceps extension | 0.99612503 | 0.95022178 | 0.97263211 | |
| Non-exercise | 0.97730204 | 0.97932282 | 0.97831139 |
| Layer | Output Shape | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Conv 2D _1 | (None, 60, 60, 32) | 832 |
| Max_pooling2D_1 | (None, 30, 30, 32) | 0 |
| Conv 2D _2 | (None, 30, 30, 64) | 8256 |
| Max_pooling2D_2 | (None, 15, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 | (None, 15, 15, 64) | 0 |
| Flatten | (None, 14,400) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | (None, 1000) | 14,401,000 |
| Dropout_2 | (None, 1000) | 0 |
| Dense_2 | (None, 6) | 6006 |
| Input Data Type (Size) | Exercise | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMU and joint position () | Chest press | 0.99262368 | 0.99693447 | 0.99477441 |
| Shoulder press | 0.99529227 | 0.99101562 | 0.99314934 | |
| Seated row | 0.9822681 | 0.99919235 | 0.99065795 | |
| Biceps curl | 0.99467976 | 0.97728187 | 0.98590407 | |
| Overhead triceps extension | 0.97402282 | 0.98866437 | 0.98128898 | |
| Non-exercise | 0.98898216 | 0.97441199 | 0.98164302 |
| Exercise | MAE | MRE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest press | 1.5841 | 17.21% | 46.02% | 76.11% | 82.30% |
| Shoulder press | 1.0089 | 26.58% | 41.07% | 84.82% | 92.86% |
| Seated row | 0.8803 | 6.09% | 59.83% | 85.47% | 91.45% |
| Biceps curl | 2.9806 | 37.85% | 12.62% | 42.72% | 60.19% |
| Overhead triceps extension | 3.2099 | 34.68% | 12.35% | 44.44% | 61.73% |
| Exercise | Regression Equation |
|---|---|
| Chest press | |
| Shoulder press | |
| Seated row | |
| Biceps curl | |
| Overhead triceps extension |
| Classification Models | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|
| CNN models in this study | IMU (N = 10) | 97.86% |
| Joint position (N = 50) | 98.71% | |
| Upper body joint position (N = 16) | 98.32% | |
| IMU + joint position (N = 60) | 98.83% | |
| Soro et al. (2019) [32] | All (hand and foot) | 99.96% |
| Hand | 95.90% | |
| Foot | 86.30% | |
| Skawinski et al. (2019) [33] | 90.60% | |
| Alatiah et al. (2020) [40] | 98.40% | |
| Repetition Counting | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| Repetition-counting algorithm in this study | Chest press | 1.58 |
| Shoulder press | 1.01 | |
| Seated row | 0.88 | |
| Biceps curl | 2.98 | |
| Overhead triceps extension | 3.21 | |
| Soro et al. (2019) [32] | 0.70 | |
| Alatiah et al. (2020) [40] | 1.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, B.; Shim, G.; Choi, W.; Kim, J. Estimation of One-Repetition Maximum, Type, and Repetition of Resistance Band Exercise Using RGB Camera and Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23021003
Hwang B, Shim G, Choi W, Kim J. Estimation of One-Repetition Maximum, Type, and Repetition of Resistance Band Exercise Using RGB Camera and Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23021003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Byunggon, Gyuseok Shim, Woong Choi, and Jaehyo Kim. 2023. "Estimation of One-Repetition Maximum, Type, and Repetition of Resistance Band Exercise Using RGB Camera and Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors" Sensors 23, no. 2: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23021003
APA StyleHwang, B., Shim, G., Choi, W., & Kim, J. (2023). Estimation of One-Repetition Maximum, Type, and Repetition of Resistance Band Exercise Using RGB Camera and Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors. Sensors, 23(2), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23021003








