Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Status of Infrared and Visible Light Fusion Methods
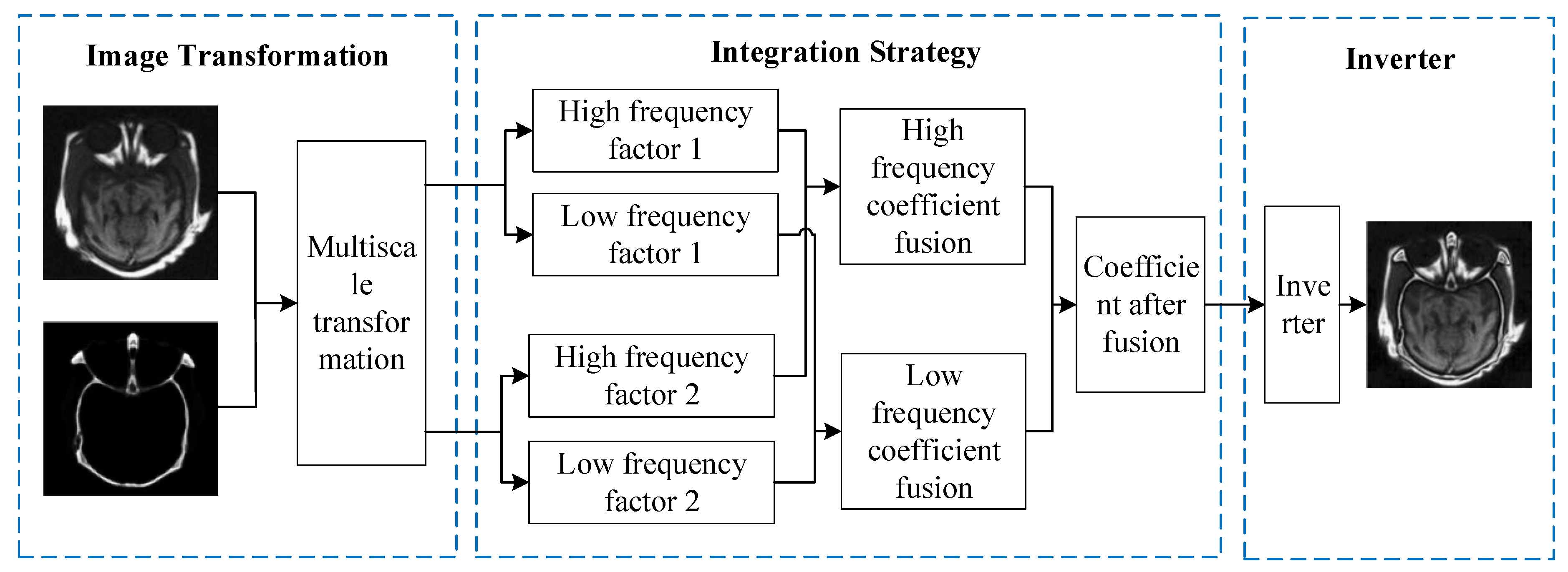
2.1. Multiscale Transform
2.2. Sparse Representation
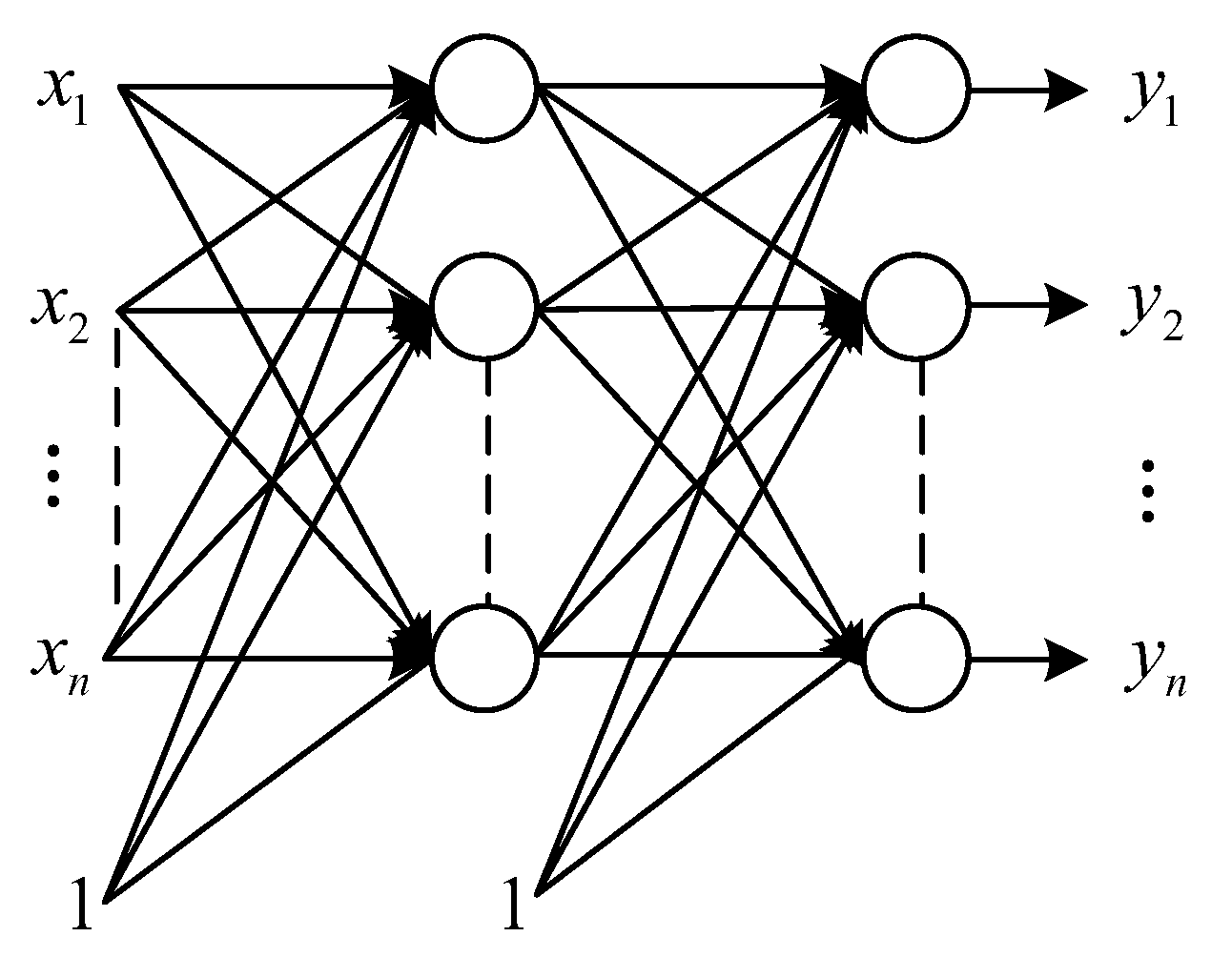
2.3. Subspace-Based
2.4. Automatic Encoder
2.5. Convolution Neural Network
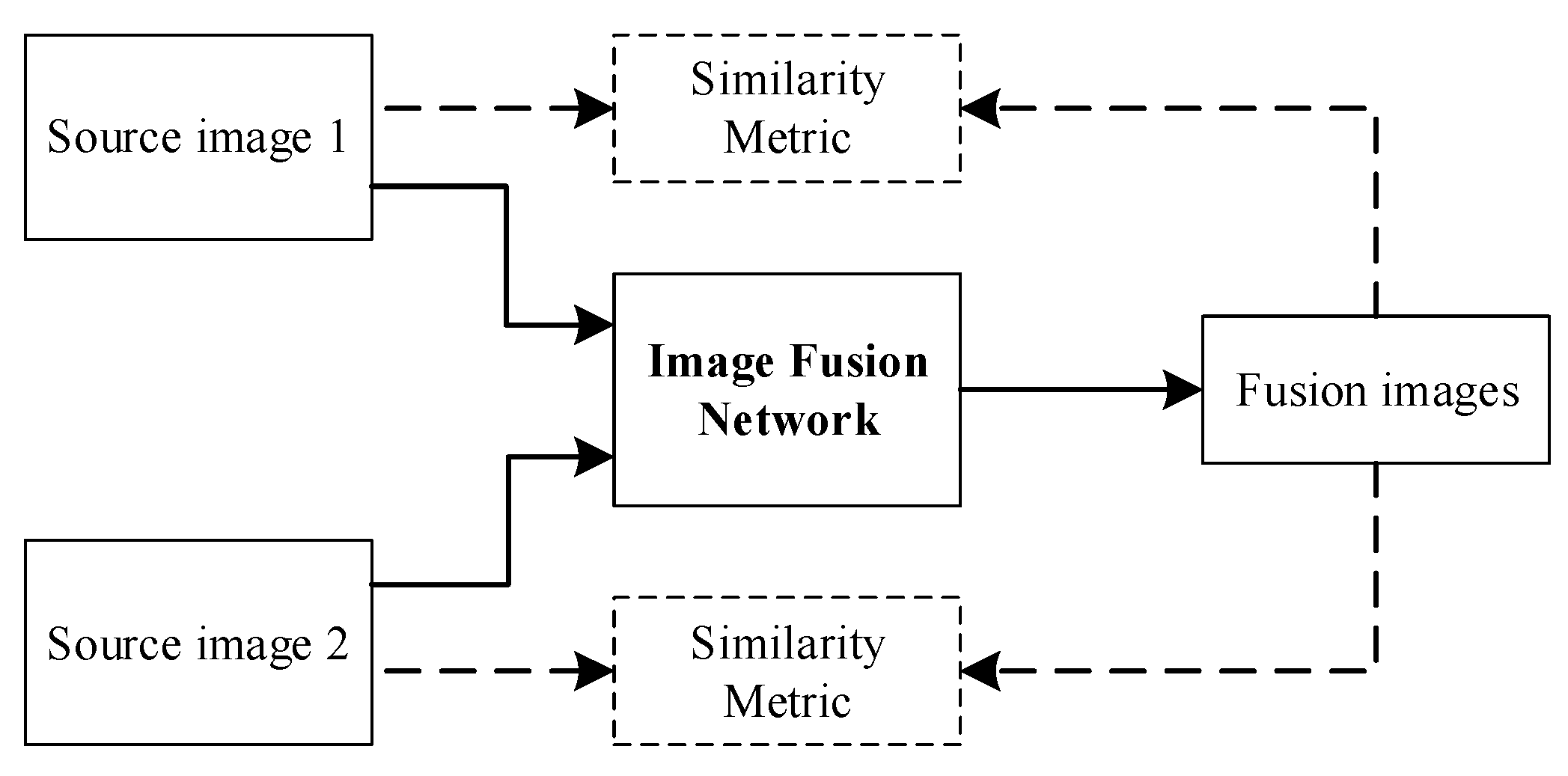
2.6. Generate Adversarial Network
2.7. Hybrid Model
3. Application of Image Fusion Technology in Different Fields
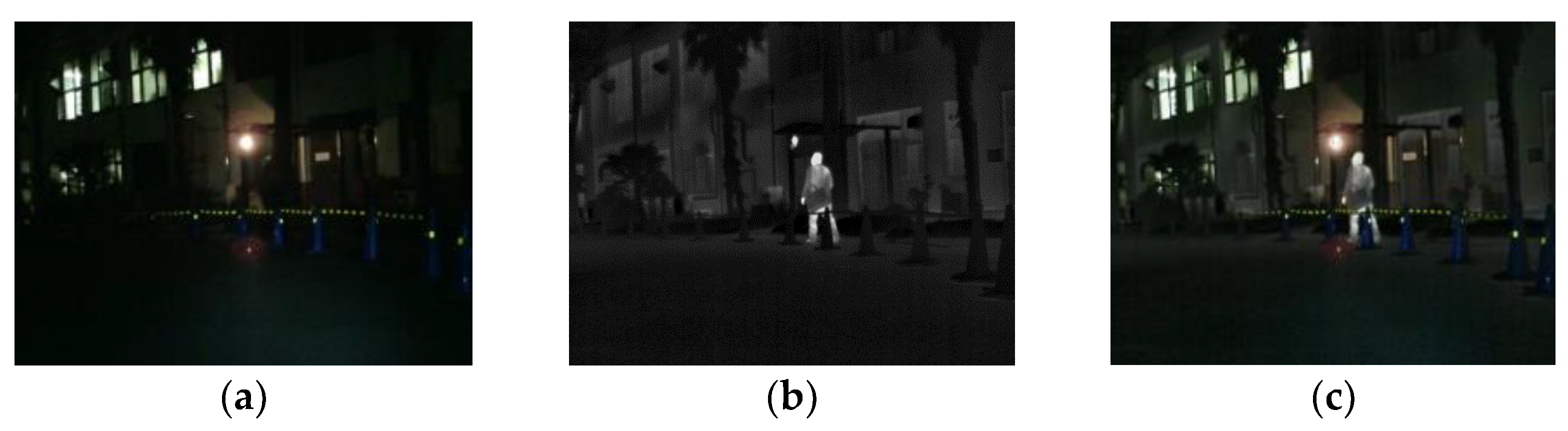
3.1. Robot Vision Field
3.2. Field of Medical Imaging
3.3. Agricultural Remote Sensing Field
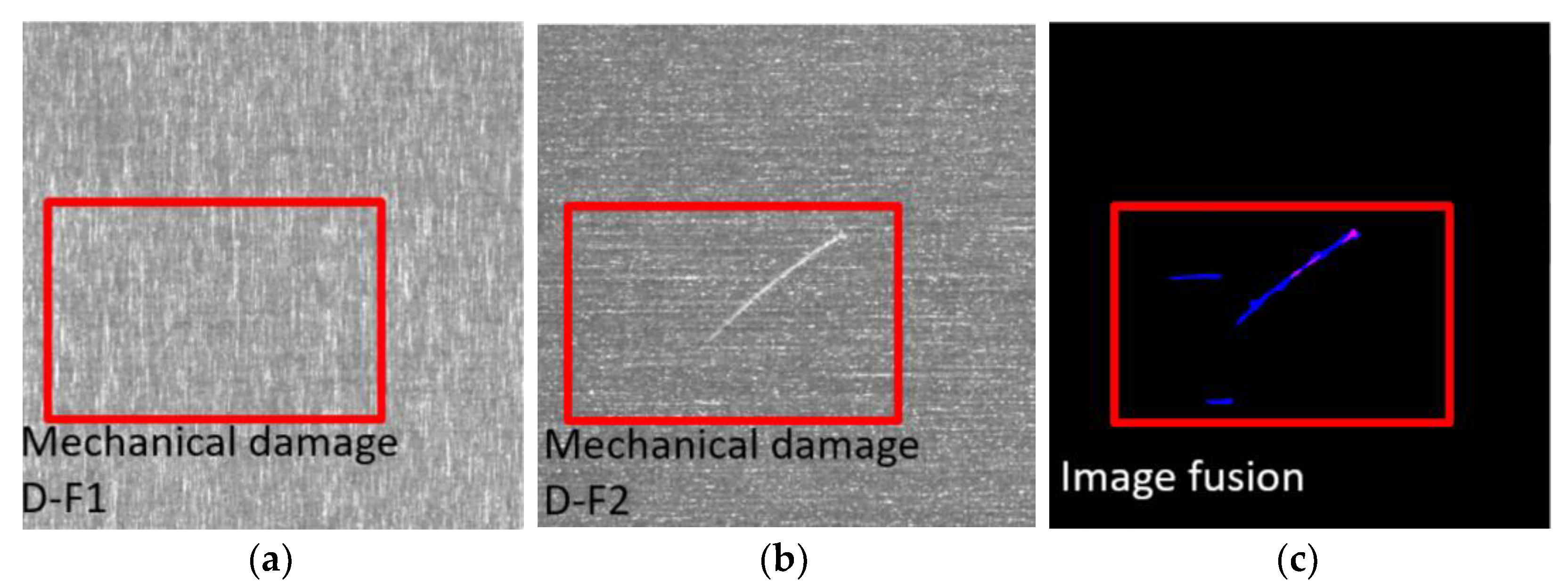
3.4. Industrial Defect Detection Field
4. Main Evaluation Indexes of Image Fusion
4.1. Subjective Evaluation
4.2. Objective Evaluation
5. Qualitative and Quantitative Testing of Mainstream Image Fusion Technology
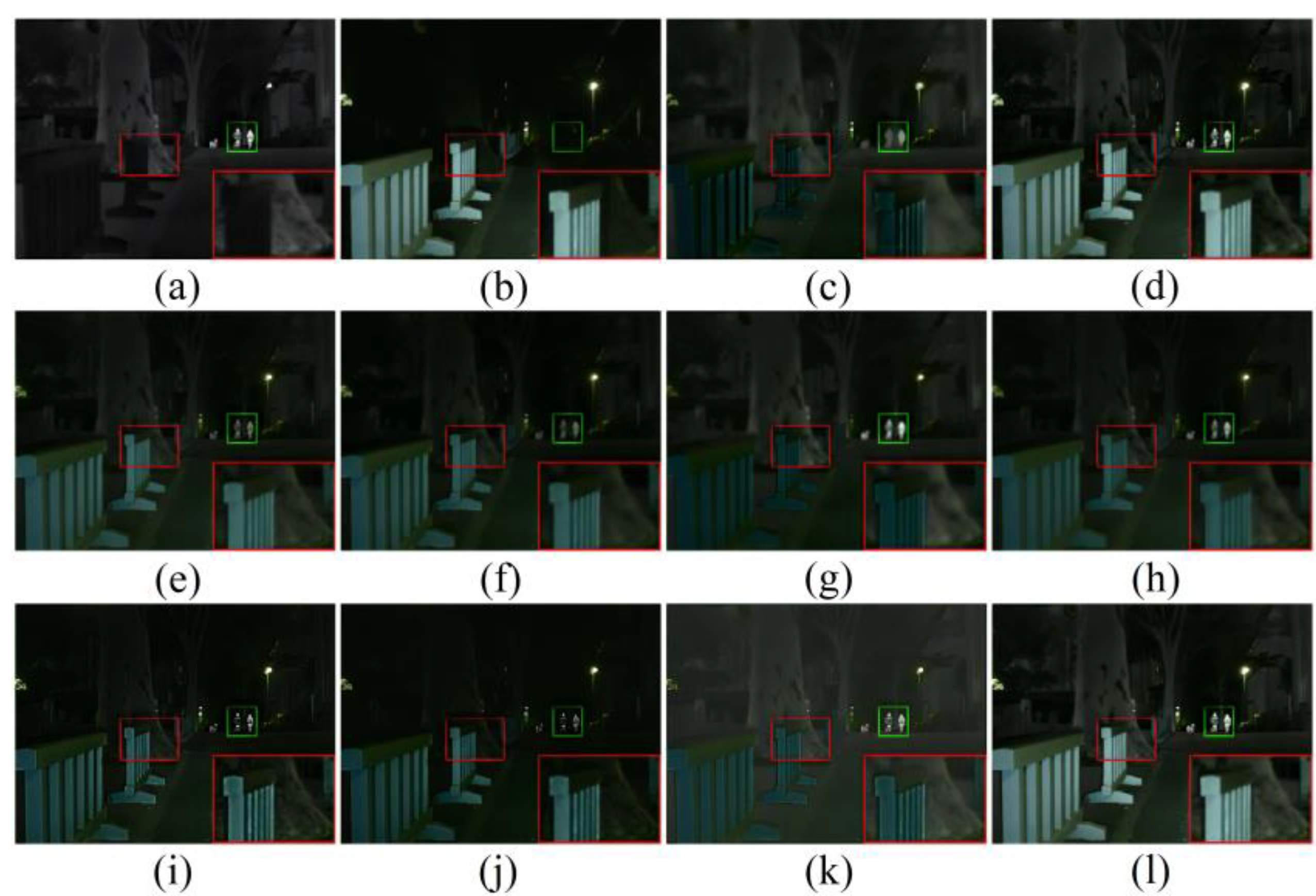
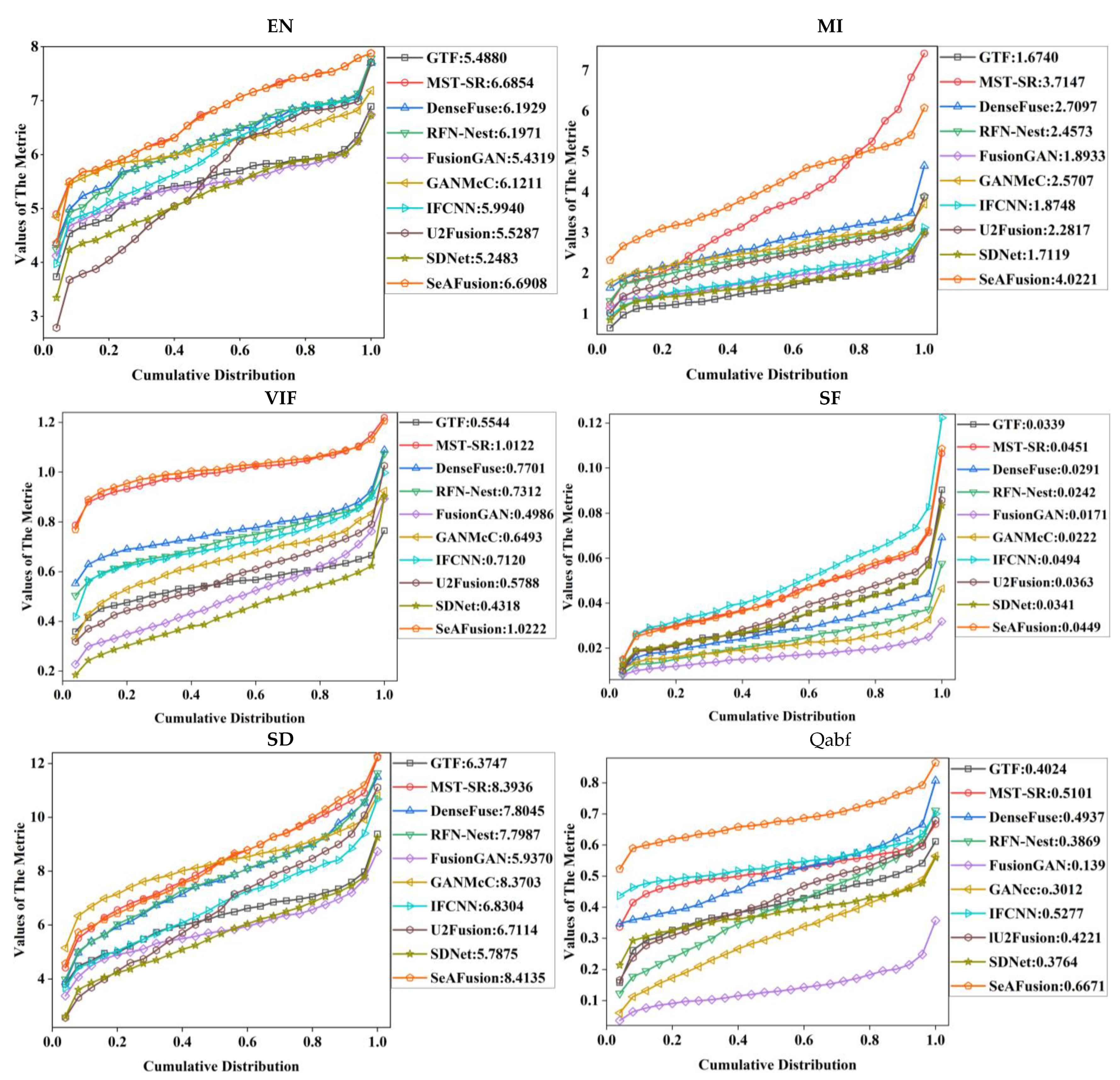
5.1. Qualitative Results
5.2. Quantitative Results
6. Future Prospects for Image Fusion Technology
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Xie, H.; Yan, W.; Chang, Y.; Qu, X. Detection of Road Objects with Small Appearance in Images for Autonomous Driving in Various Traffic Situations Using a Deep Learning Based Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 211164–211172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, X. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Inf. Fusion 2017, 42, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2016, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, F.E.Z.A.; Elmogy, M.; Atwan, A. Current trends in medical image registration and fusion. Egypt. Inform. J. 2016, 17, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2014, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A Generative Adversarial Network with Multiclassification Constraints for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zeng, M.; Huang, X. SDnet: Contextualized attention-based deep network for conversational question answering. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.03593. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yang, F.; Yin, M.; Mo, X.; Zhong, C. A review of multimodal medical image fusion techniques. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 8279342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pure, A.A.; Gupta, N.; Shrivastava, M. An overview of different image fusion methods for medical applications. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Li, W.; Lu, K.; Xiao, B. An overview of multi-modal medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 215, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermessi, H.; Mourali, O.; Zagrouba, E. Multimodal medical image fusion review: Theoretical background and recent advances. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, C.; Kang, X.; Han, D. An overview on pixel-level image fusion in remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Jinan, China, 18–21 August 2007; pp. 2339–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, C.; van Genderen, J. Remote sensing image fusion: An update in the context of Digital Earth. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Stein, A. Spatiotemporal Image Fusion in Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, D.; Shen, Y. An overview of image fusion metrics. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Singapore, 5–7 May 2009; pp. 918–923. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, Z.; Stathaki, T. Image fusion: An overview. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation, Langkawi, Malaysia, 27–29 January 2014; pp. 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, A.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Recent Advances in Sparse Representation Based Medical Image Fusion. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2021, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. In Readings in Computer Vision; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Dong, X. Region level based multi-focus image fusion using quaternion wavelet and normalized cut. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mei, W.; Du, H. Structure tensor and nonsubsampled shearlet transform based algorithm for CT and MRI image fusion. Neurocomputing 2017, 235, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Maldague, X. An adaptive fusion approach for infrared and visible images based on NSCT and compressed sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 74, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A Novel Decomposition Method for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image Fusion with Convolutional Sparse Representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. Image fusion by a ratio of low-pass pyramid. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1989, 9, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A.; Van Ruyven, L.J.; Valeton, J.M. Merging thermal and visual images by a contrast pyramid. Opt. Eng. 1989, 28, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. A morphological pyramidal image decomposition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1989, 9, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, W.T.; Adelson, E.H. The design and use of steerable filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 9, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy Functions into Square Integrable Wavelets of Constant Shape. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Cunha, A.L.; Zhou, J.; Do, M.N. The Non-subsampled Contourlet Transform: Theory, Design, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Ren, J.; Chen, Q.; Sui, X. A false color image fusion method based on multi-resolution color transfer in normalization YCBCR space. Optik 2014, 125, 6010–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Qi, Y. Fusion of infrared and visual images based on contrast pyramid directional filter banks using clonal selection optimizing. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 027002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Study on image fusion based on different fusion rules of wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering (ICACTE), Chengdu, China, 20–22 August 2010; Volume 3, pp. 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Selesnick, I.W.; Baraniuk, R.G.; Kingsbury, N.C. The dual-tree complex wavelet transform. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, T. Visible and infrared image fusion using the lifting wavelet. Telkomnika Indones. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 11, 6290–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cao, L.; Tan, Q.; Jin, G. Infrared and visible image fusion based on NSCT and fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Xi’an, China, 4–7 August 2010; pp. 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.X.; Zhu, T.H.; Zhao, J.J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on region of interest detection and nonsubsampled contourlet transform. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2013, 1, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Labate, D. Optimally Sparse Multidimensional Representation Using Shearlets. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2007, 39, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, H. Adaptive fusion method of visible light and infrared images based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and fast non-negative matrix factorization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2014, 67, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Y.; Shutao, L. Multifocus Image Fusion and Restoration with Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 884–892. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, R.; Zibulevsky, M.; Elad, M. Double Sparsity: Learning Sparse Dictionaries for Sparse Signal Approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.S.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, C.; Ganguly, D.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Bhattacharya, U.; Hou, Y. Privacy-aware supervised classification: An informative subspace based multi-objective approach. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Y. Infrared and visible images fusion based on RPCA and NSCT. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 77, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-Based Multimodal Image Fusion Using ICA Bases. IEEE Sensors J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Ferreira, B.L.; Maggio, R.M. Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baviristti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejic, N.; Lewis, J.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Adaptive Region-Based Multimodal Image Fusion Using ICA Bases. In Proceedings of the 2006 9th International Conference on Information Fusion, Florence, Italy, 10–13 July 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.A.; Lee, S.Y. Hierarchical Representation Using NMF. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, J.; Gao, W.; Song, Z. Image fusion based on non-negative matrix factorization and infrared feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; He, T.; An, B.; Ma, X.; Wen, H.; Wang, F. VDFEFuse: A novel fusion approach to infrared and visible images. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 121, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Durrani, T. NestFuse: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Architecture Based on Nest Connection and Spatial/Channel Attention Models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9645–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Classification Saliency-Based Rule for Visible and Infrared Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H. A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J. Rethinking the Image Fusion: A Fast Unified Image Fusion Network based on Proportional Maintenance of Gradient and Intensity. Proc. Conf. AAAI Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12797–12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. SDNet: A Versatile Squeeze-and-Decomposition Network for Real-Time Image Fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2761–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8789–8797. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Learning a Generative Model for Fusing Infrared and Visible Images via Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with Dual Discriminators. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via detail preserving adversarial learning. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.-P. DDcGAN: A Dual-Discriminator Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Multi-Resolution Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiao, L. A fusion algorithm for infrared and visible based on guided filtering and phase congruency in NSST domain. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 97, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Song, M.; Guo, B.; Shi, R.; Shan, D. Image fusion based on object region detection and Non-Subsampled Contourlet Transform. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 62, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, X.; Pei, H.; Zhao, Y. A fusion algorithm for infrared and visible images based on saliency analysis and non-subsampled Shearlet transform. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 73, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, M.; Song, Y. Fusion of infrared and visible images based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform and sparse K-SVD dictionary learning. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Duan, P.; Liu, W.; Liang, X. A novel infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on shift-invariant dual-tree complex shearlet transform and sparse representation. Neurocomputing 2017, 226, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, B.D.; Roy, J.K.; Padhee, S. Recent advances in multifunctional sensing technology on a perspective of multi-sensor system: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Koundal, D.; Kadyan, V. Image Fusion Techniques: A Survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 4425–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Kong, L.; Dong, G.; Remani, A.; Leach, R. Defect inspection technologies for additive manufacturing. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2021, 3, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M. End-to-End Ship Detection in SAR Images for Complex Scenes Based on Deep CNNs. J. Sensors 2021, 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, S.S.; Vázquez, C.O.; García, J.G.; Ortega, J.G. Quality inspection of machined metal parts using an image fusion technique. Measurement 2017, 111, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.L.; Schnelle, S.R. Fusing concurrent visible and infrared videos for improved tracking performance. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 017004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piella, G. A general framework for multiresolution image fusion: From pixels to regions. Inf. Fusion 2003, 4, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toet, A.; IJspeert, J.K.; Waxman, A.M.; Aguilar, M. Fusion of visible and thermal imagery improves situational awareness. Displays 1997, 18, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A.; Franken, E.M. Perceptual evaluation of different image fusion schemes. Displays 2003, 24, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Lee, Y.; Matsuyama, E. Information entropy measure for evaluation of image quality. J. Digit. Imaging 2008, 21, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, R.; Bovik, C. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, S.; Xydeas, S. Gradient-based multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aardt, J. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, V.; Xydeas, C. Objective image fusion performance characterization. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05), Beijing, China, 17–20 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 1866–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. A Sparse Image Fusion Algorithm with Application to Pan-Sharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piella, G.; Heijmans, H. A new quality metric for image fusion. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No 03CH37429), Barcelona, Spain, 14–17 September 2003; Volume 3, p. 173. [Google Scholar]







| Methods | Typical Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyramid transformation | Laplace pyramid transformation; ratio low-pass pyramid [32]; contrast pyramid [33]; morphological pyramid [34]; controllable pyramid [35]. | Opens up the basic idea of multiscale transform pixel-level image fusion research with simple implementation and fast operation speed. | Non-directional, sensitive to noise, not stable when reconstructed, and redundant between pyramid layers. |
| Wavelet transform [36,37] | Discrete wavelet transform (DWT), dual-tree discrete wavelet transform (DTWT), and lifting wavelet transform (DWT). | Good time-frequency localization, directionality, no redundancy, and high utilization of image frequency band information. | Does not have direction selectivity and translation invariance, and is weak in extracting the edge information of the image. |
| Multiscale geometric analysis [38] | Non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT); non-subsampled shear wave transform (NSST). | The frequency localization, multi-directionality, high variance and sparsity of the image can be better approximated and described. | Does not have translational invariance, and is prone to pseudo-Gibbs phenomenon near the singularities, and high computational complexity. |
| Evaluation Index | Mathematical Models and Explanations | |
|---|---|---|
| EN [90] | (11) | |
| represents the normalized histogram of the corresponding gray level of the fused image. | ||
| MI [4] | (12) | |
| is the histogram statistical probability of images A and B, respectively, and L is the number of gray levels. | ||
| VIF [91] | (13) | |
| when considering multiple sub-bands. | ||
| SF [92] | (14) | |
| are the row and column frequencies of the image. | ||
| SD [93] | (15) | |
| where M, N are the width and height of the image, is the mean value, and F is the pixel value of the image at position i, j. | ||
| Qabf [94] | (16) | |
| is the cardinality of . | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, S.X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Li, Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020599
Ma W, Wang K, Li J, Yang SX, Li J, Song L, Li Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Weihong, Kun Wang, Jiawei Li, Simon X. Yang, Junfei Li, Lepeng Song, and Qifeng Li. 2023. "Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review" Sensors 23, no. 2: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020599
APA StyleMa, W., Wang, K., Li, J., Yang, S. X., Li, J., Song, L., & Li, Q. (2023). Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors, 23(2), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020599










