Terahertz Time-of-Flight Ranging with Adaptive Clock Asynchronous Optical Sampling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
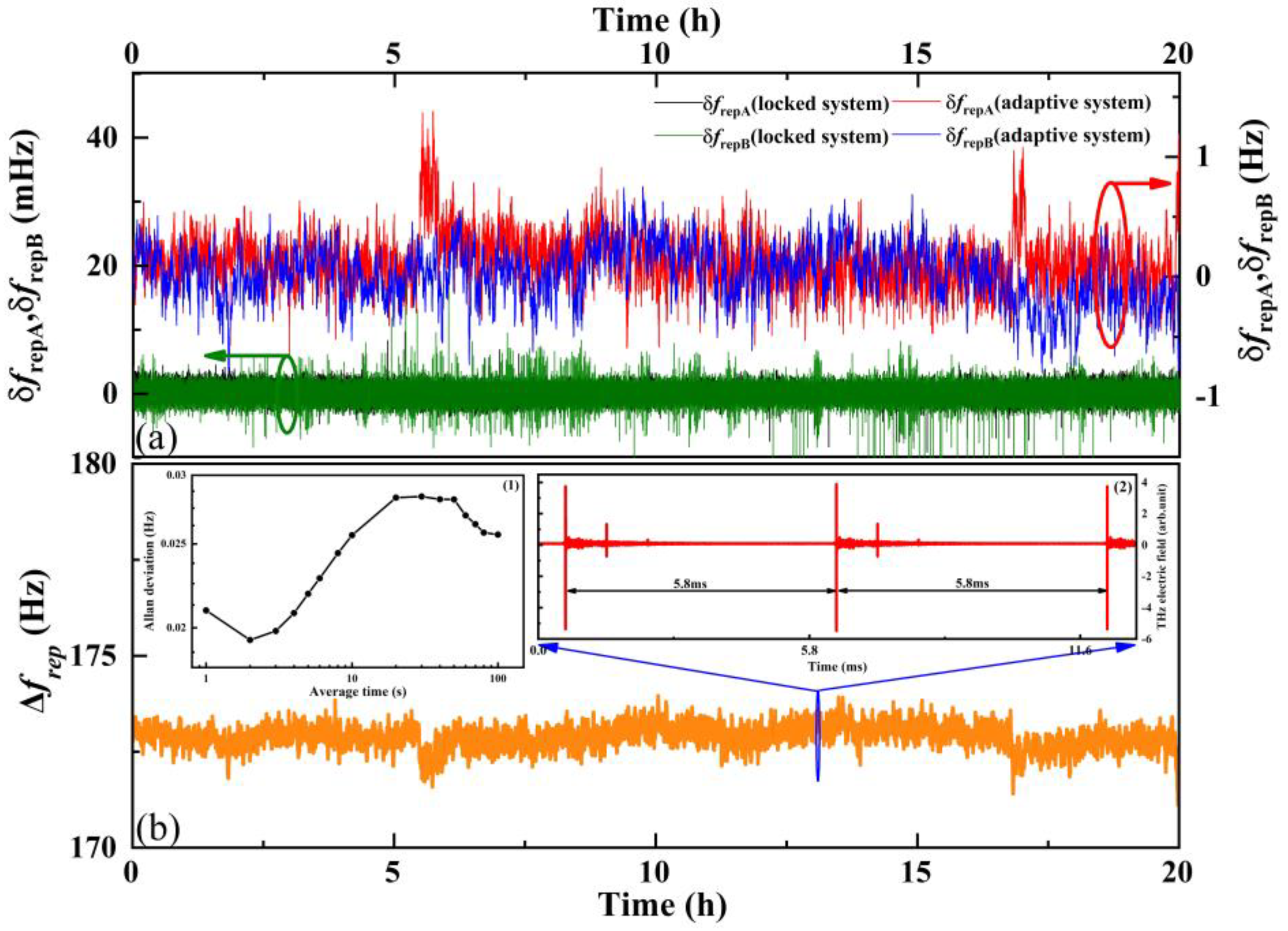
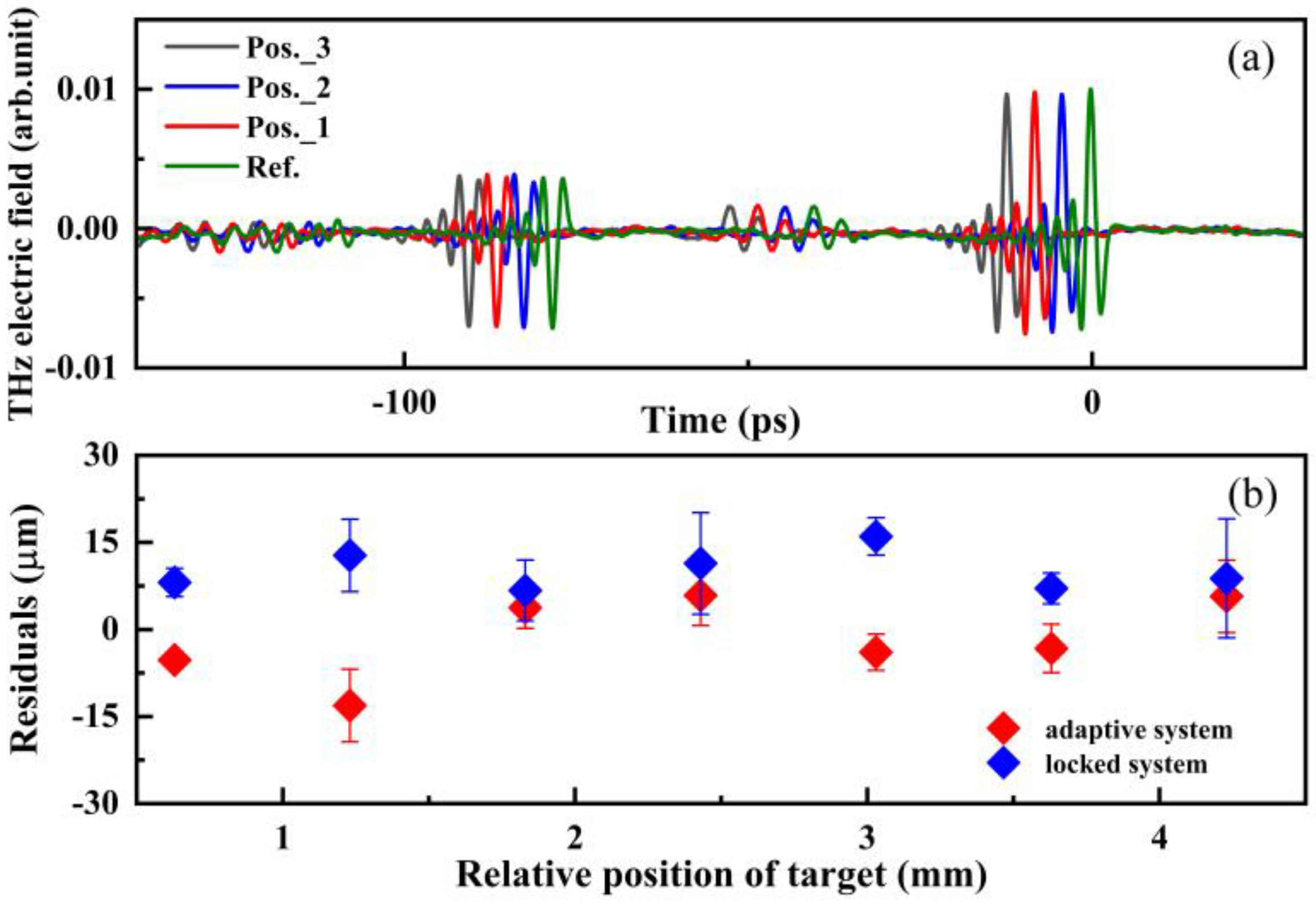
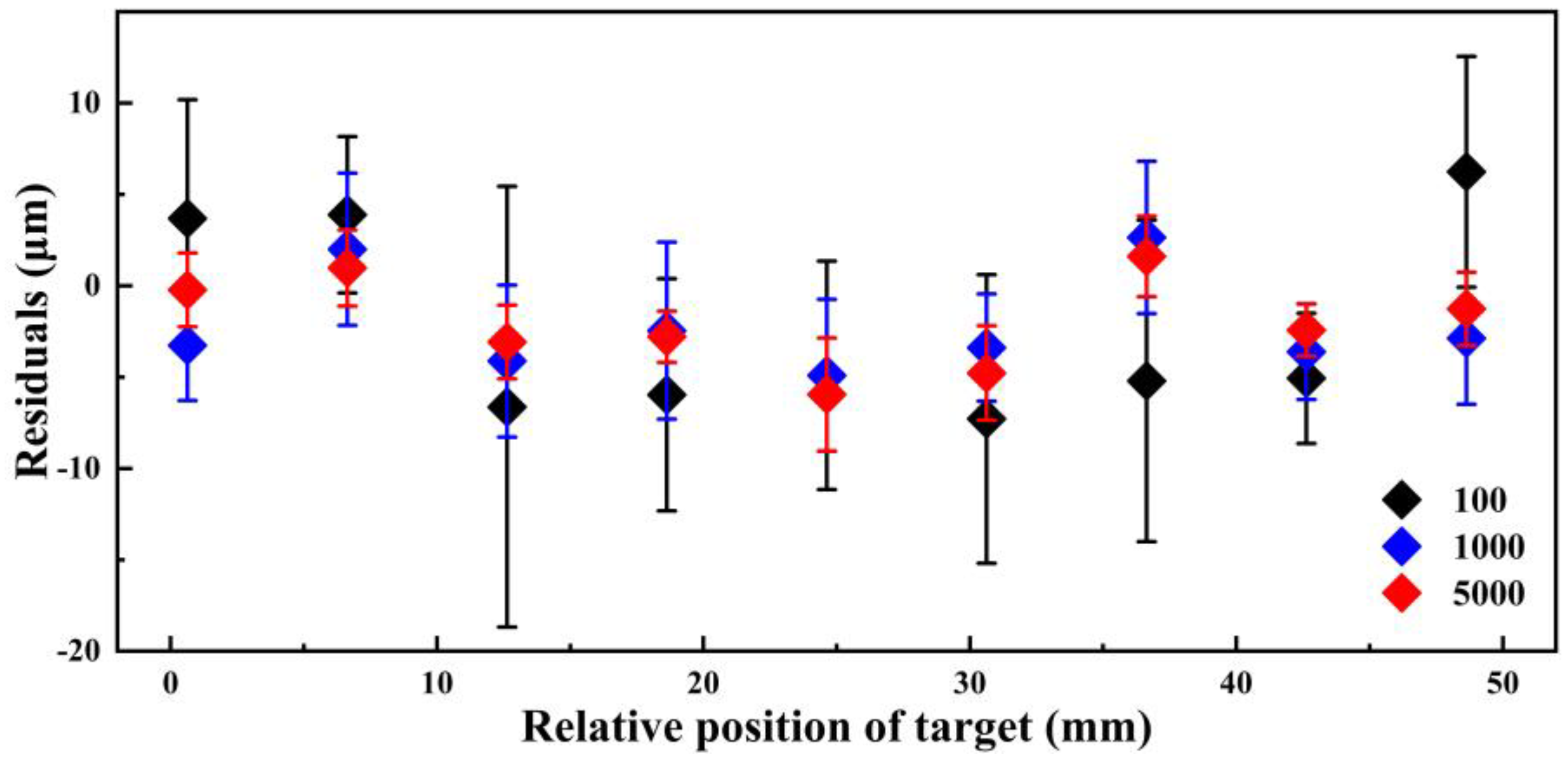
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cuypers, W.; Van Gestel, N.; Voet, A.; Kruth, J.P.; Mingneau, J.; Bleys, P. Optical measurement techniques for mobile and large-scale dimensional metrology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2009, 47, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eitel, J.U.H.; Hofle, B.; Vierling, L.A.; Abellan, A.; Asner, G.P.; Deems, J.S.; Glennie, C.L.; Joerg, P.C.; LeWinter, A.L.; Magney, T.S.; et al. Beyond 3-D: The new spectrum of lidar applications for earth and ecological sciences. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.; Martins, R.J.; Jang, J.; Badloe, T.; Khadir, S.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Genevet, P.; Rho, J. Nanophotonics for light detection and ranging technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.X.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.C.; Wu, J.Q.; Zheng, Y.C.; Wu, D.Y. Detection and tracking of pedestrians and vehicles using roadside LiDAR sensors. Transp. Res. Pt. C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 100, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.C. Progress in terahertz nondestructive testing: A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 14, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Hajeb, P.; Ara, P.; Ehsani, R.J. A Comprehensive Review on Food Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1563–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.S.; Lee, J.W. Internal Non-Destructive Examination of XLPE Insulation for Power Cables with a Terahertz Imaging System. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2020, 40, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valusis, G.; Lisauskas, A.; Yuan, H.; Knap, W.; Roskos, H.G. Roadmap of Terahertz Imaging 2021. Sensors 2021, 21, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Park, H.; Moon, K.; Lim, M.; Do, Y.; Han, H.; Choi, H.J.; Min, B.H.; Kim, S.; Park, I.; et al. THz Time-Domain Spectroscopic Imaging of Human Articular Cartilage. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, Z.D.; Singh, R.S.; Bennett, D.B.; Tewari, P.; Kealey, C.P.; Bajwa, N.; Culjat, M.O.; Stojadinovic, A.; Lee, H.; Hubschman, J.P.; et al. THz Medical Imaging: In vivo Hydration Sensing. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Kawase, K.; Murate, K. Highly sensitive multi-stage terahertz parametric detector. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 3901–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.H.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, L.F.; Ni, K.; Zeng, X.H.; Li, Y. Experimental optimization of the repetition rate difference in dual-comb ranging system. Appl. Phys. Express 2014, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.B.; Xu, G.Y.; Ni, K.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, G.H. Synthetic-wavelength-based dual-comb interferometry for fast and precise absolute distance measurement. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 5747–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuse, N.; Ozawa, A.; Kobayashi, Y. Static FBG strain sensor with high resolution and large dynamic range by dual-comb spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 11141–11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wei, H.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Yang, H.L.; Li, Y. Absolute distance measurement by dual-comb nonlinear asynchronous optical sampling. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6597–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.D.; Yardimci, N.T.; Ou, Y.H.; Kieu, K.; Jarrahi, M. Self-triggered Asynchronous Optical Sampling Terahertz Spectroscopy using a Bidirectional Mode-locked Fiber Laser. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.Q.; Mizuguchi, T.; Oe, R.; Nitta, K.; Zhao, X.; Minamikawa, T.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z.; Yasui, T. Dual terahertz comb spectroscopy with a single free-running fibre laser. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Jiang, X.L.; Wu, J.R.; Qiu, L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Guo, X.G.; Zhu, Y.M. Terahertz dual-comb spectroscopy: A comparison between time- and frequency-domain operation modes. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 115, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M.; Watanabe, S. Triggerless data acquisition in asynchronous optical-sampling terahertz time-domain spectroscopy based on a dual-comb system. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 39613–39623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, J.T.; Holland, D.B.; Finneran, I.A.; Carroll, P.B.; Kelley, M.J.; Blake, G.A. A decade-spanning high-resolution asynchronous optical sampling terahertz time-domain and frequency comb spectrometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Kabetani, Y.; Ohgi, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Araki, T. Absolute distance measurement of optically rough objects using asynchronous-optical-sampling terahertz impulse ranging. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5262–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideguchi, T.; Poisson, A.; Guelachvili, G.; Picqué, N.; Hänsch, T.W. Adaptive real-time dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.S.; Song, Y.J.; Liang, F.; Xu, L.M.; Hu, M.L.; Wang, C.Y. Effect of timing jitter on time-of-flight distance measurements using dual femtosecond lasers. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 14057–14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Hsieh, Y.D.; Hayashi, K.; Cahyadi, H.; Hindle, F.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Iwata, T.; Mizutani, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Adaptive sampling dual terahertz comb spectroscopy using dual free-running femtosecond lasers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebert, N.B.; Genest, J.; Deschenes, J.D.; Bergeron, H.; Chen, G.Y.; Khurmi, C.; Lancaster, D.G. Self-corrected chip-based dual-comb spectrometer. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 8168–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finneran, I.A.; Good, J.T.; Holland, D.B.; Carroll, P.B.; Allodi, M.A.; Blake, G.A. Decade-Spanning High-Precision Terahertz Frequency Comb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fellinger, J.; Winkler, G.; Aldia, P.E.C.; Mayer, A.S.; Shumakova, V.; Perner, L.W.; Pecile, V.F.; Martynkien, T.; Mergo, P.; Soboń, G.; et al. Simple approach for extending the ambiguity-free range of dual-comb ranging. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3677–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.J.; Li, Z.P.; Liao, X.Y.; Guan, W.; Ma, X.H.; Zhou, K.; Cao, J.C.; Li, H. Improved comb and dual-comb operation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers utilizing a symmetric thermal dissipation. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 29412–29422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danylov, A.A.; Goyette, T.M.; Waldman, J.; Coulombe, M.J.; Gatesman, A.J.; Giles, R.H.; Goodhue, W.D.; Qian, X.F.; Nixon, W.E. Frequency stabilization of a single mode terahertz quantum cascade laser to the kilohertz level. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 7525–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.P.; Wan, W.J.; Zhou, K.; Liao, X.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, C.J.; Cao, J.C.; Zeng, H.P. Toward Compact and Real-Time Terahertz Dual-Comb Spectroscopy Employing a Self-Detection Scheme. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.L.; Yan, M.; Hao, Q.; Yang, K.W.; Zeng, H.P. Adaptive Dual-Comb Spectroscopy With 1200-h Continuous Operation Stability. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Yan, M.; Hao, Q.; Yang, K.W.; Shen, X.L.; Zeng, H.P. Rapid thermal sensors with high resolution based on an adaptive dual-comb system. Front. Inform. Technol. Elect. Eng. 2019, 20, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, G. Dual-Comb Ranging. Engineering 2018, 4, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Xiong, S.L.; Ni, K.; Zhu, Z.B.; Zhou, Q. Parameter optimization of a dual-comb ranging system by using a numerical simulation method. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32044–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Xia, Y.; He, M.; Yang, K.; Yuan, S.; Yan, M.; Huang, K.; Zeng, H. Terahertz Time-of-Flight Ranging with Adaptive Clock Asynchronous Optical Sampling. Sensors 2023, 23, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020715
Li M, Liu Z, Xia Y, He M, Yang K, Yuan S, Yan M, Huang K, Zeng H. Terahertz Time-of-Flight Ranging with Adaptive Clock Asynchronous Optical Sampling. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020715
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Min, Zheng Liu, Yu Xia, Mingyang He, Kangwen Yang, Shuai Yuan, Ming Yan, Kun Huang, and Heping Zeng. 2023. "Terahertz Time-of-Flight Ranging with Adaptive Clock Asynchronous Optical Sampling" Sensors 23, no. 2: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020715
APA StyleLi, M., Liu, Z., Xia, Y., He, M., Yang, K., Yuan, S., Yan, M., Huang, K., & Zeng, H. (2023). Terahertz Time-of-Flight Ranging with Adaptive Clock Asynchronous Optical Sampling. Sensors, 23(2), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020715









