Research on None-Line-of-Sight/Line-of-Sight Identification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network-Channel Attention Module
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A multilayer Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) combined with a Channel Attention Module (CAM) for the NLOS/LOS identification method is proposed. The method takes the One-dimensional CIR signal as input, uses three groups of convolution modules (Convolution + BN + ReLU + Max-pooling) and CAM for self-extraction of key features, and the global average pooling layer is used to replace the fully connected layer for feature integration and classification output, which achieves NLOS/LOS identification.
- Two schemes are proposed on how to determine the specific structure of the CNN-CAM network and how to determine the optimal parameters. In the first scheme, the proposed CNN-CAM model is compared with CNN and CNN-CAM models with different structures, and it aims to select the optimal model structure for NLOS/LOS identification. In the second scheme, the effect of different learning rates and batches on the identification accuracy is compared experimentally for the proposed model, and it aims to determine the optimal parameters of the model.
- A scheme on how to verify the superiority of the proposed CNN-CAM method is offered. Firstly, the public dataset of the European Horizon 2020 program project eWINE is visualized and analyzed to illustrate the feasibility of using this dataset for experiments. Then, comparative experiments of several machine learning and deep learning identification methods are conducted using the dataset to validate the state-of-the-art of the proposed CNN-CAM method.
2. Related Work
3. Preliminaries
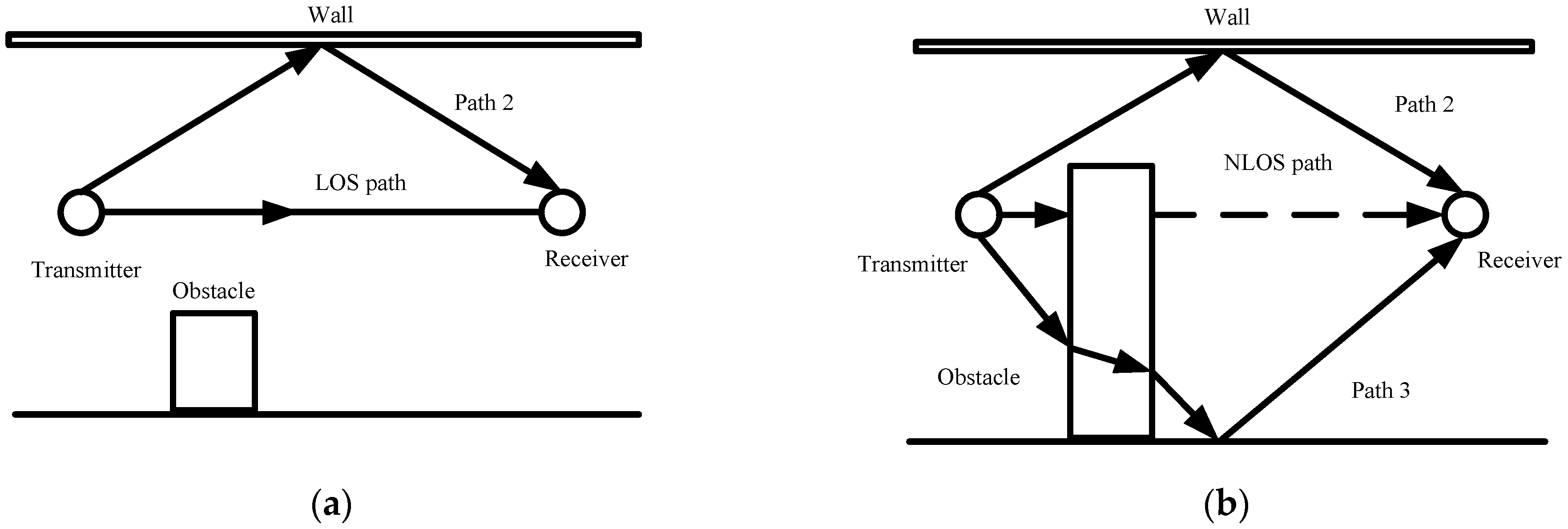
3.1. NLOS/LOS Problem Statement
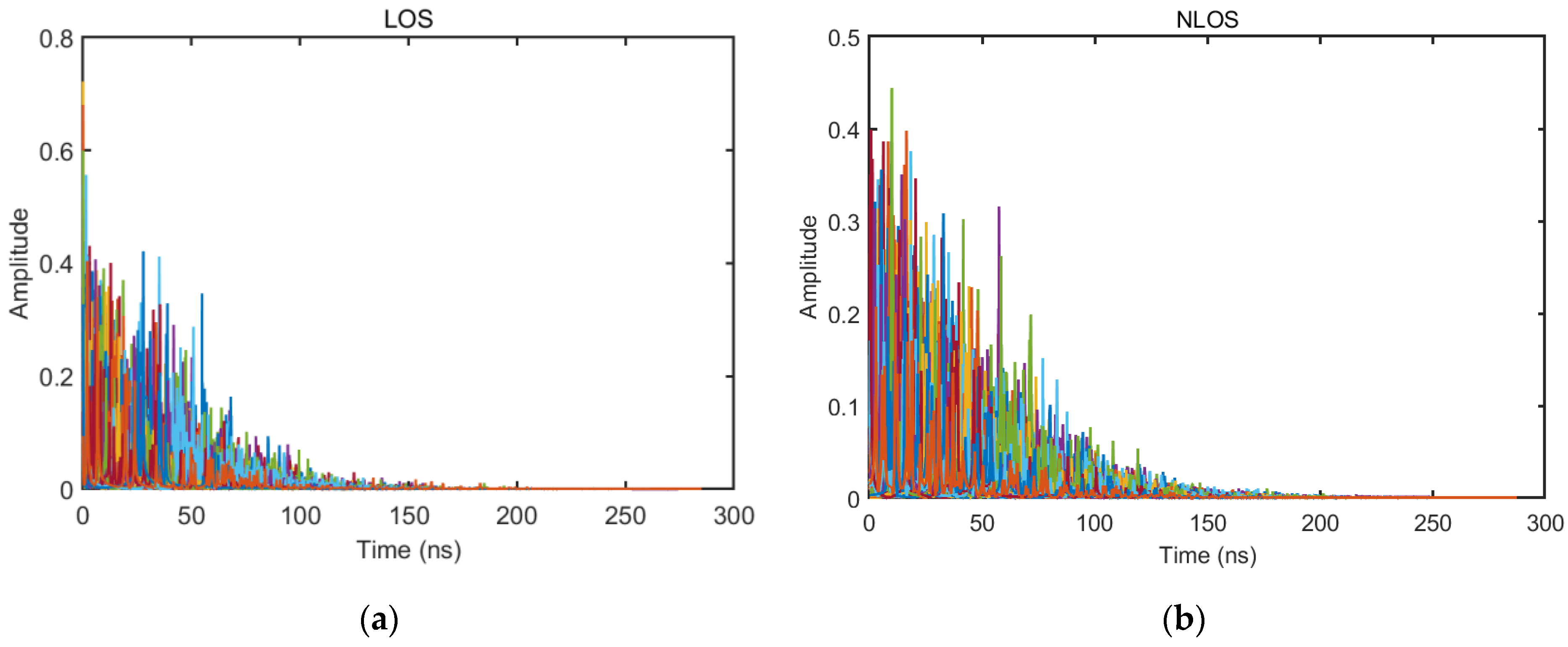
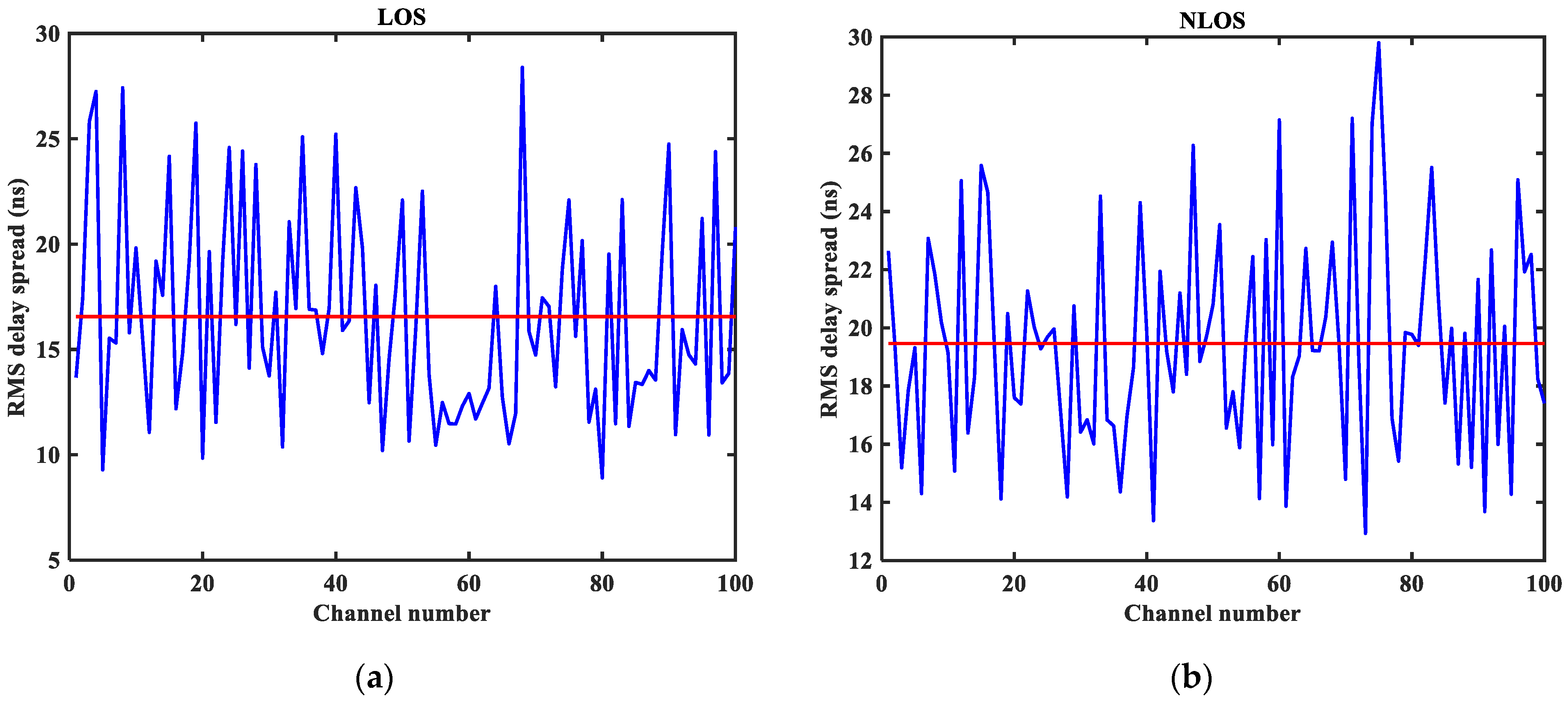
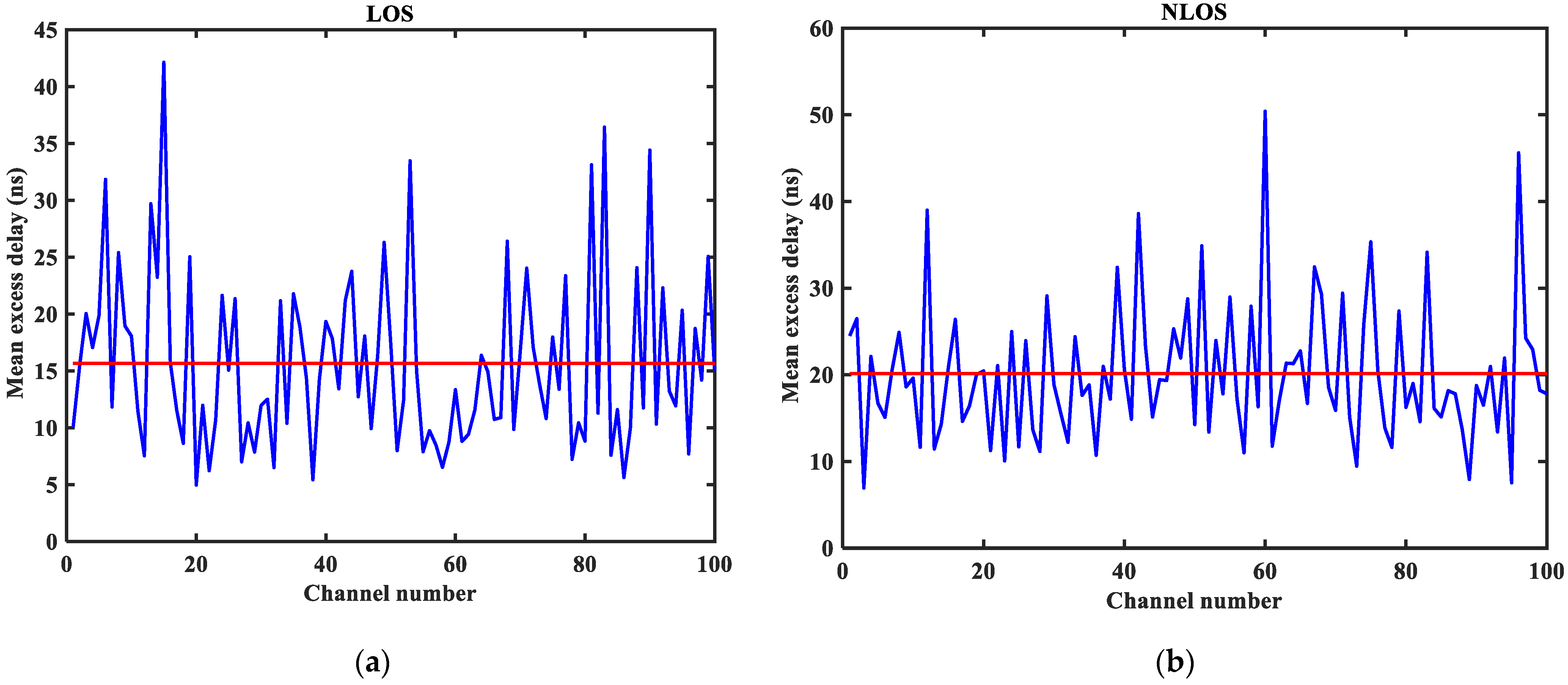
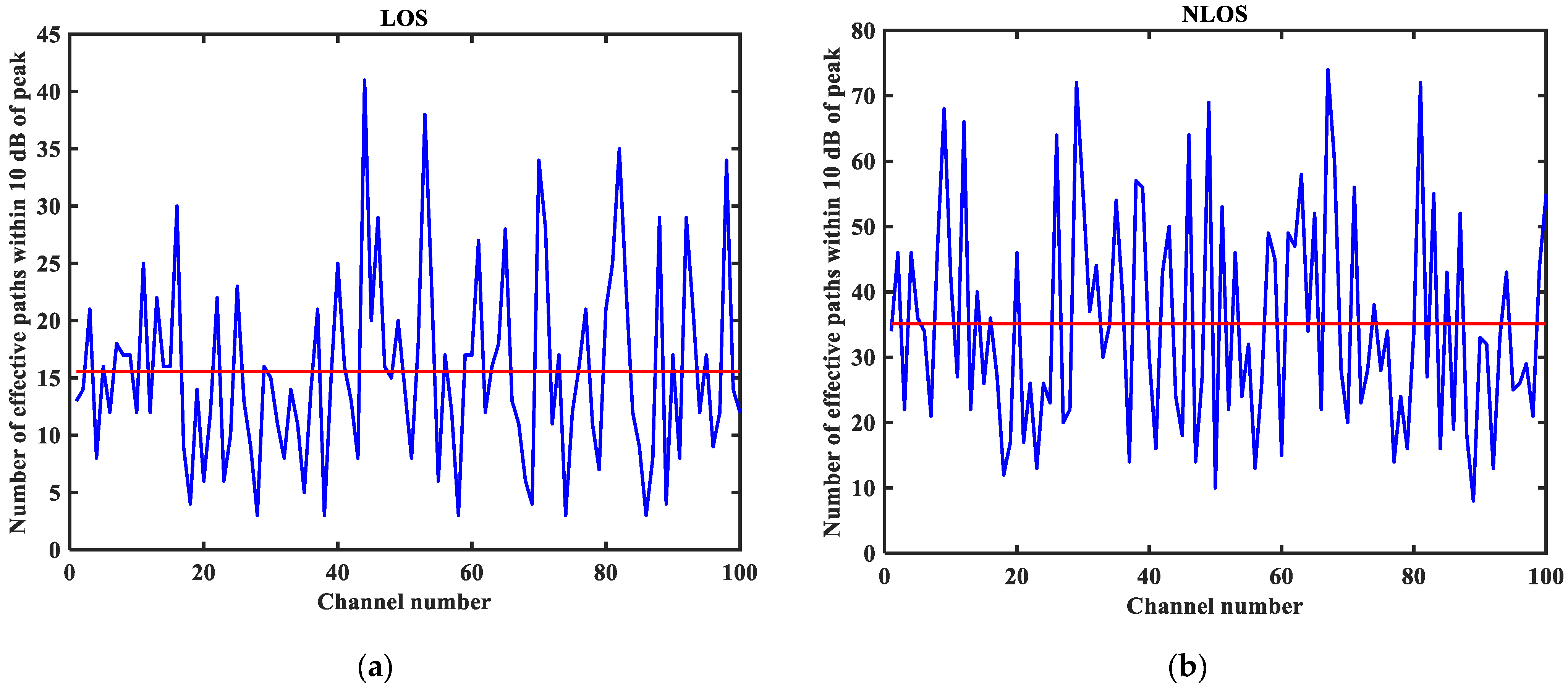
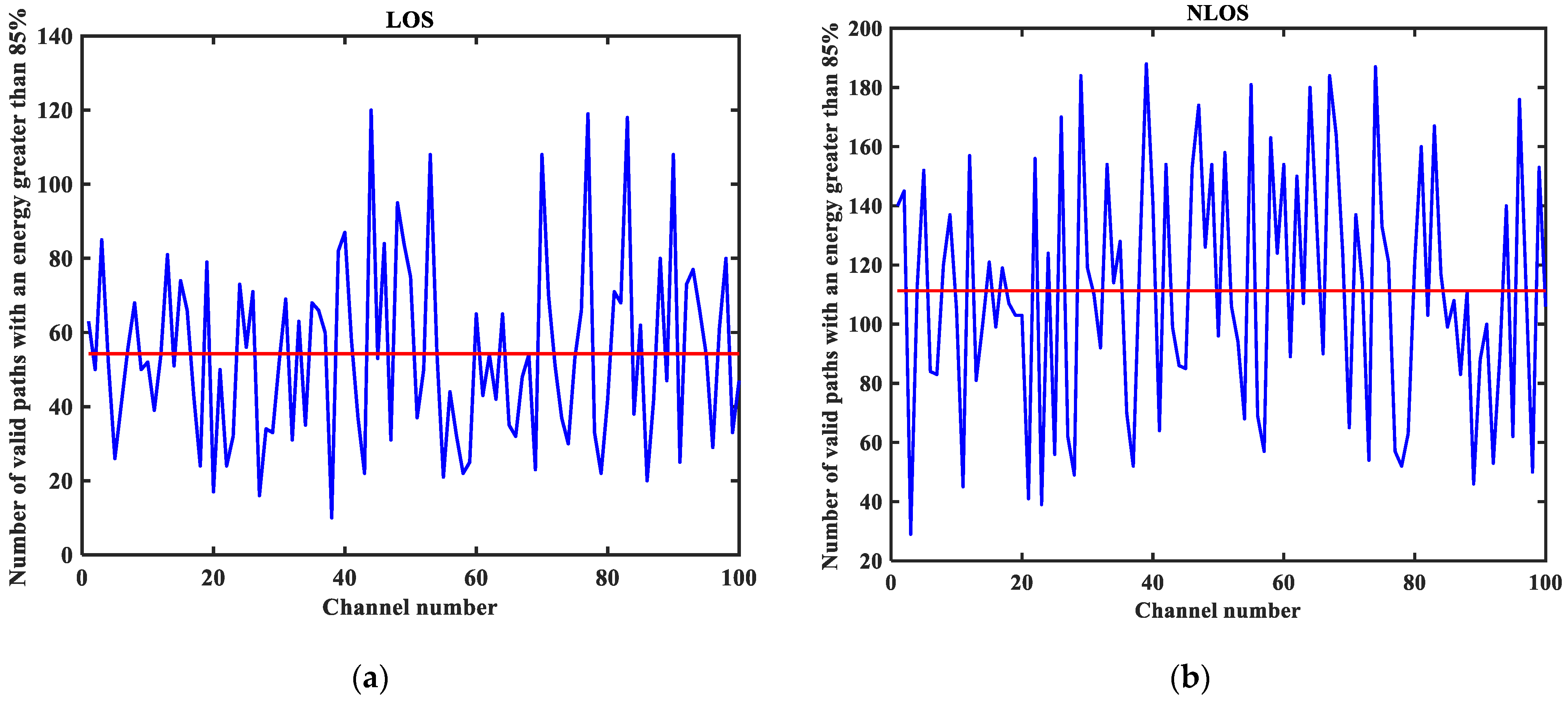
3.2. CIR Performance Analysis
4. Method
4.1. CNN Theory
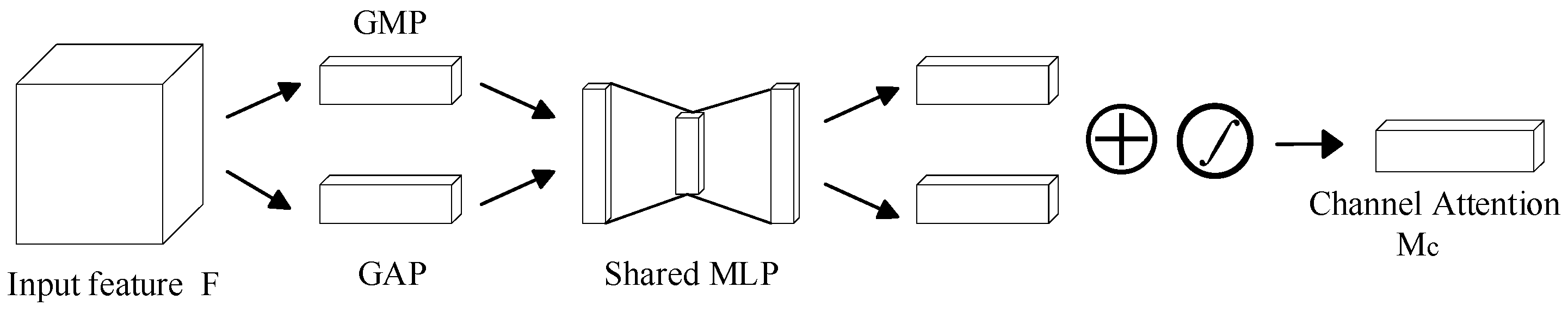
4.2. Attention Mechanism
4.3. NLOS/LOS Identification Method Based on CNN-CAM
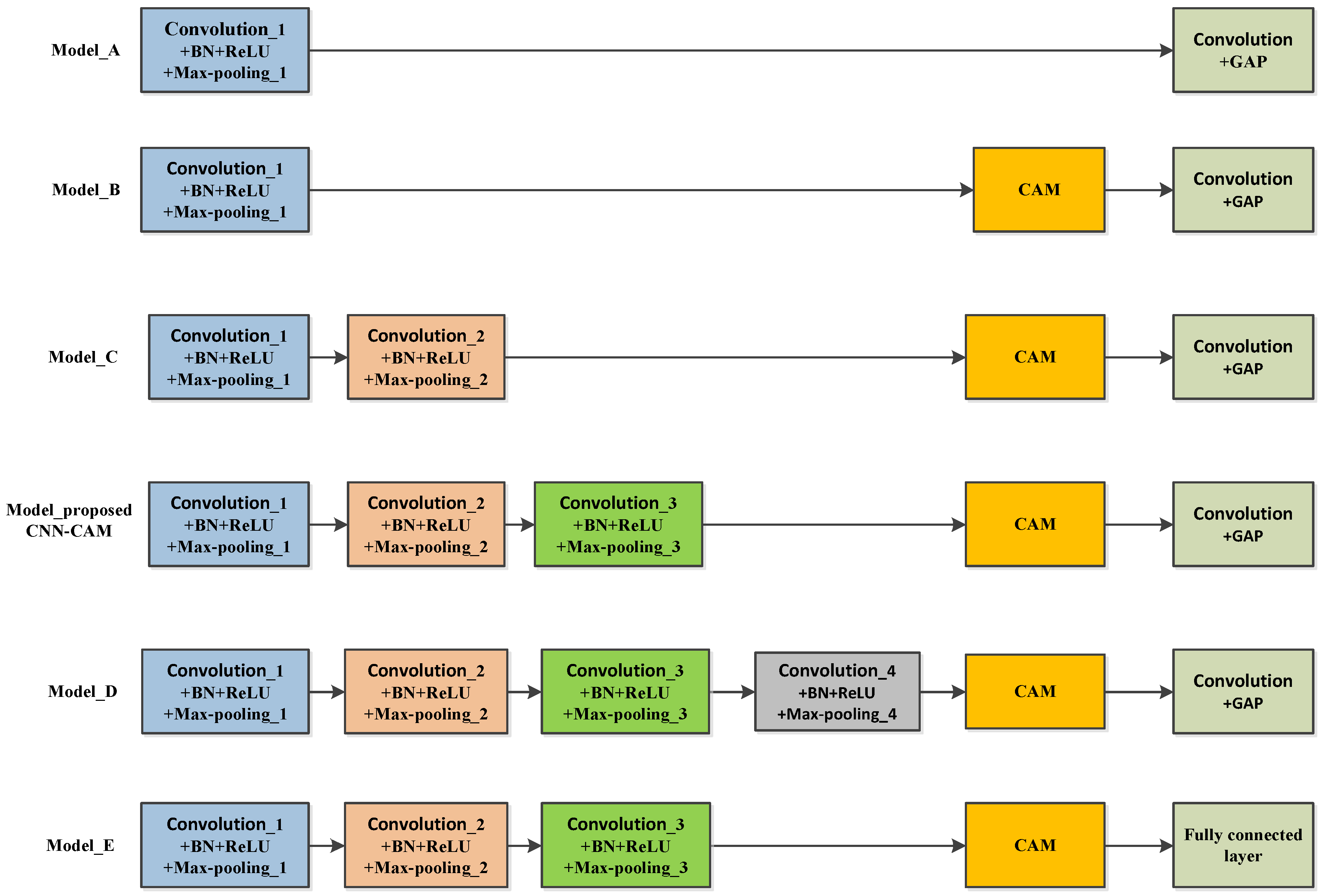
4.3.1. CNN-CAM Network Architecture
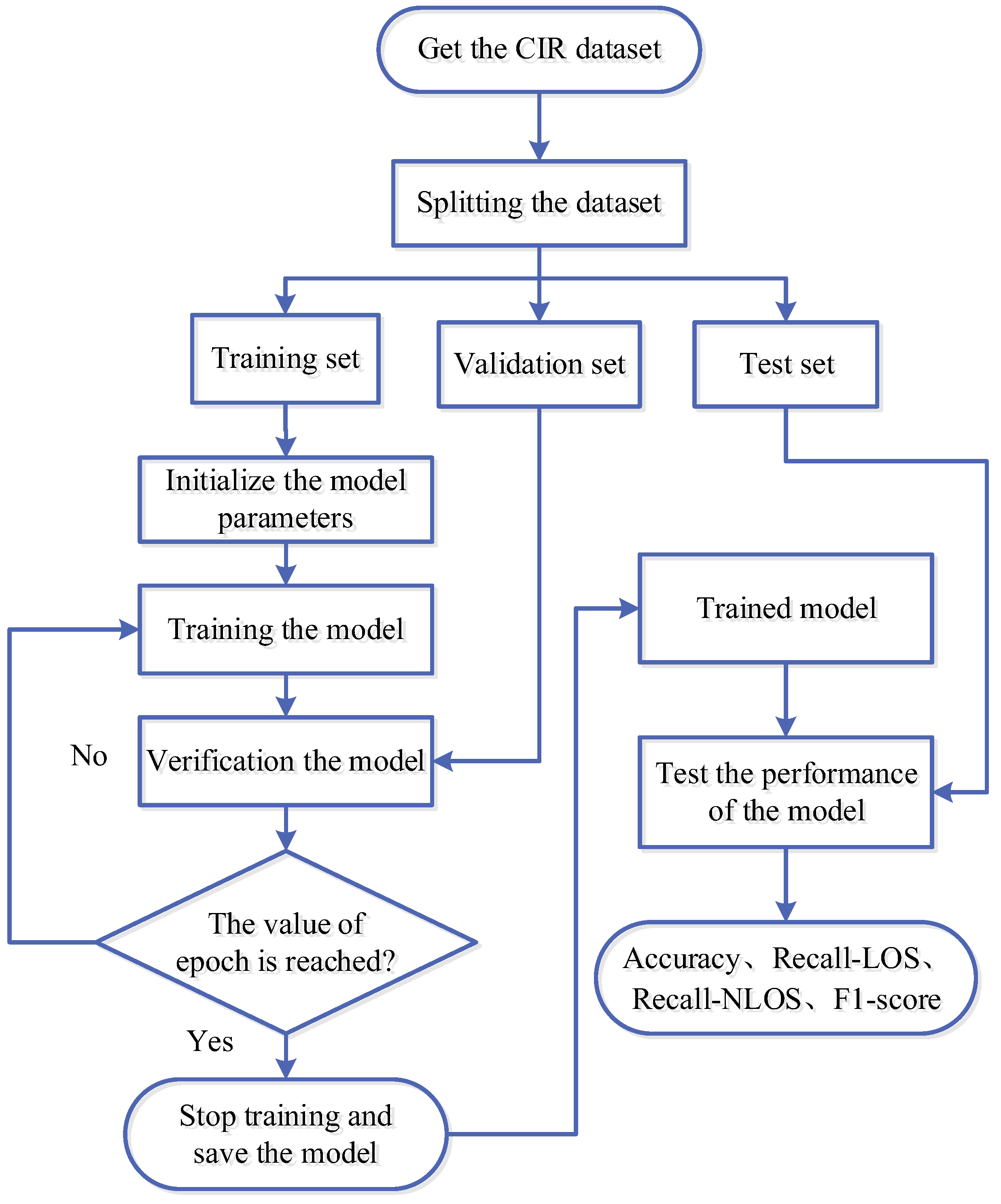
4.3.2. NLOS/LOS Identification Process
- The obtained CIR data is divided into training sets, validation sets, and test sets in the ratio of 7:2:1.
- Train the CNN-CAM model with the training sets and validate the performance of the trained model with the validation sets. Furthermore, the trained model is saved when the epoch is reached.
- The trained model is tested with test sets to obtain the final NLOS/LOS identification result.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Visual Analysis of Datasets
5.2. Experiments and Results
5.2.1. Parameter Analysis
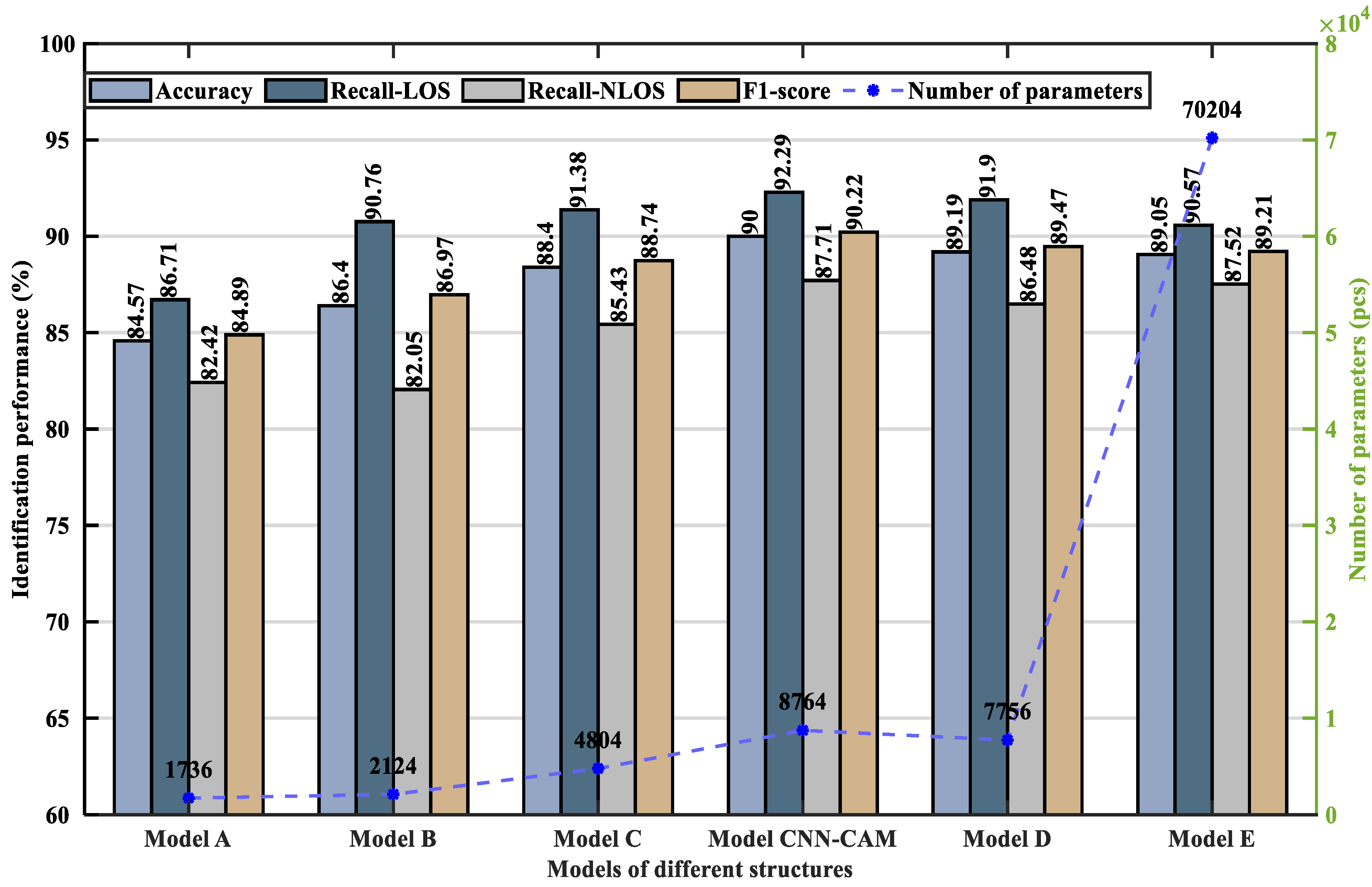
5.2.2. Performance Analysis
- (a)
- Comparative Experiments of Different Structural Models
- (b)
- Comparison Experiments of Different Identification Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Pei, L.; Guinness, R.; Kuusniemi, H. A hybrid smartphone indoor positioning solution for mobile LBS. Sensors 2012, 12, 17208–17233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Yu, B.; Du, S.; Li, J.; Jia, H.; Bi, J. Multi-Level Fusion Indoor Positioning Technology Considering Credible Evaluation Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, A.; Al-Salman, A.; Alsaleh, M.; Alnafessah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, S.; Al-Ammar, M.A.; Al-Khalifa, H.S. Ultra wideband indoor positioning technologies: Analysis and recent advances. Sensors 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B. Research on UWB Indoor Positioning Algorithm under the Influence of Human Occlusion and Spatial NLOS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X. Recognition of Blocking Categories for UWB Positioning in Complex Indoor Environment. Sensors 2020, 20, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wen, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K. A novel NLOS mitigation algorithm for UWB localization in harsh indoor environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchler, M.; Huber, A. An improved algorithm for UWB-bases positioning in a multi-path environment. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Zurich Seminar on Communications, Zurich, Switzerland, 22 February 2004–24 February 2006; pp. 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, M. UWB LOS/NLOS identification in multiple indoor environments using deep learning methods. Phys. Commun. 2022, 52, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Seow, C.K.; Sun, M.; Si, M.; Huang, L. UWB sensor-based indoor LOS/NLOS localization with support vector machine learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 2988–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Wang, Y.; Siljak, H.; Seow, C.; Yang, H. A lightweight CIR-based CNN with MLP for NLOS/LOS identification in a UWB positioning system. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvenç, İ.; Chong, C.C.; Watanabe, F.; Inamura, H. NLOS identification and weighted least-squares localization for UWB systems using multipath channel statistics. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 2008, 271984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, S.; Gifford, W.M.; Wymeersch, H.; Win, M.Z. NLOS identification and mitigation for localization based on UWB experimental data. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2010, 28, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wei, Z. Research on NLOS identification method based on CIR feature parameters. China Test. 2021, 47, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Bo, Y. An UWB channel impulse response de-noising method for NLOS/LOS classification boosting. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2513–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Bo, Y. UWB NLOS/LOS classification using deep learning method. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Wang, G. NLOS/LOS signal recognition model based on CNN-BiLSTM. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Beijing, China, 26–28 April 2022; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, X. FCN-Attention: A deep learning UWB NLOS/LOS classification algorithm using fully convolution neural network with self-attention mechanism. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Tian, S.; Cheng, J. LOS/NLOS identification for indoor UWB positioning based on Morlet wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 25, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, K.; Bu, J.; Lin, Y.; Han, S. Multi-classification of UWB signal propagation channels based on one-dimensional wavelet packet analysis and CNN. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 8534–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Huang, L. A new set of channel feature parameters for UWB indoor localization. J. Navig. Position. 2022, 10, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Molisch, A.F.; Cassioli, D.; Chong, C.C.; Emami, S.; Fort, A.; Kannan, B.; Kardeal, J.; Schantz, H.G.; Siwiak, K.; Win, M.Z. A comprehensive standardized model for ultrawideband propagation channels. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 3151–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhu, R.; Li, Y. HPIPS: A high-precision indoor pedestrian positioning system fusing WiFi-RTT, MEMS, and map information. Sensors 2020, 20, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Jung, S.-W.; Lee, S.; Oh, B.; Yang, S. Deep Learning-Based Evaluation of Ultrasound Images for Benign Skin Tumors. Sensors 2023, 23, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. SCA-CNN: Spatial and Channel-Wise Attention in Convolutional Networks for Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Remote Sensing Small Object Detection Network Based on Attention Mechanism and Multi-Scale Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bregar, K.; Mohorčič, M. Improving indoor localization using convolutional neural networks on computationally restricted devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17429–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Reference Distance (m) | Mean of Ranging Error (m) | Standard Deviation of Ranging Error (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0000 | 0.0790 | 0.0253 |
| 2.0000 | 0.0954 | 0.0232 |
| 3.0000 | 0.0959 | 0.0306 |
| 4.0000 | 0.0653 | 0.0270 |
| 5.0000 | 0.1040 | 0.0343 |
| 6.0000 | 0.0604 | 0.0305 |
| 7.0000 | 0.1198 | 0.0497 |
| 8.0000 | 0.0351 | 0.0289 |
| 9.0000 | 0.0377 | 0.0322 |
| Reference Distance (m) | Mean of Ranging Error (m) | Standard Deviation of Ranging Error (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.8023 | 0.1186 | 0.0275 |
| 2.5000 | 0.2348 | 0.0318 |
| 3.3541 | 0.5747 | 0.2456 |
| 4.272 | 0.3476 | 0.1922 |
| 5.2202 | 0.9203 | 0.6075 |
| 6.1847 | 2.0852 | 0.2191 |
| 7.159 | 1.9741 | 0.0469 |
| 8.1394 | 3.1719 | 0.3178 |
| 9.1241 | 2.7760 | 0.2898 |
| Network Composition | Designation | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Sequence Input | 1016 × 1 × 1 |
| Convolution_1 (stride) | 4 × 1 × 10 (2) | |
| BN, ReLU | —— | |
| Max-pooling_1 (stride) | 2 × 1 (2) | |
| Convolution_2 (stride) | 5 × 1 × 20 (2) | |
| BN, ReLU | —— | |
| Max-pooling_2 (stride) | 2 × 1 (2) | |
| Convolution_3 (stride) | 3 × 1 × 32 (2) | |
| BN, ReLU | —— | |
| Max-pooling_3 (stride) | 2 × 1 (2) | |
| Part 2 | GMP, GAP | —— |
| Convolution_4/Convolution_6 | 1 × 1 × 8 | |
| BN, ReLU/BN, ReLU | —— | |
| Convolution_5/Convolution_7 | 1 × 1 × 32 | |
| Part 3 | Convolution | 1 × 1 × 128 |
| GAP | —— | |
| Dropout | 0.5 | |
| Training | Epoch | 25 |
| Learning rate | 0.001 | |
| Batch size | 64 |
| Model Names | Number of Parameter | Accuracy (%) | Recall-LOS (%) | Recall-NLOS (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model_A | 1736 | 84.57 | 86.71 | 82.42 | 84.89 |
| Model_B | 2124 | 86.40 | 90.76 | 82.05 | 86.97 |
| Model_C | 4804 | 88.40 | 91.38 | 85.43 | 88.74 |
| Model_proposed CNN-CAM | 8764 | 90.00 | 92.29 | 87.71 | 90.22 |
| Model_D | 7756 | 89.19 | 91.90 | 86.48 | 89.47 |
| Model_E | 70,204 | 89.05 | 90.57 | 87.52 | 89.21 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Recall-LOS (%) | Recall-NLOS (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 84.94 | 84.91 | 84.97 | 84.93 |
| CNN-SVM | 86.12 | 85.67 | 86.57 | 86.06 |
| RF (single feature) | 54.52 | 54.08 | 54.96 | 54.10 |
| RF (multiple features) | 87.43 | 85.52 | 89.59 | 87.85 |
| CNN-CAM proposed | 90.00 | 92.29 | 87.71 | 90.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yi, Q.; Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, H. Research on None-Line-of-Sight/Line-of-Sight Identification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network-Channel Attention Module. Sensors 2023, 23, 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208552
Zhang J, Yi Q, Huang L, Yang Z, Cheng J, Zhang H. Research on None-Line-of-Sight/Line-of-Sight Identification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network-Channel Attention Module. Sensors. 2023; 23(20):8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208552
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingjing, Qingwu Yi, Lu Huang, Zihan Yang, Jianqiang Cheng, and Heng Zhang. 2023. "Research on None-Line-of-Sight/Line-of-Sight Identification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network-Channel Attention Module" Sensors 23, no. 20: 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208552
APA StyleZhang, J., Yi, Q., Huang, L., Yang, Z., Cheng, J., & Zhang, H. (2023). Research on None-Line-of-Sight/Line-of-Sight Identification Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network-Channel Attention Module. Sensors, 23(20), 8552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208552









