Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation with Limited Communication Resources: A Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
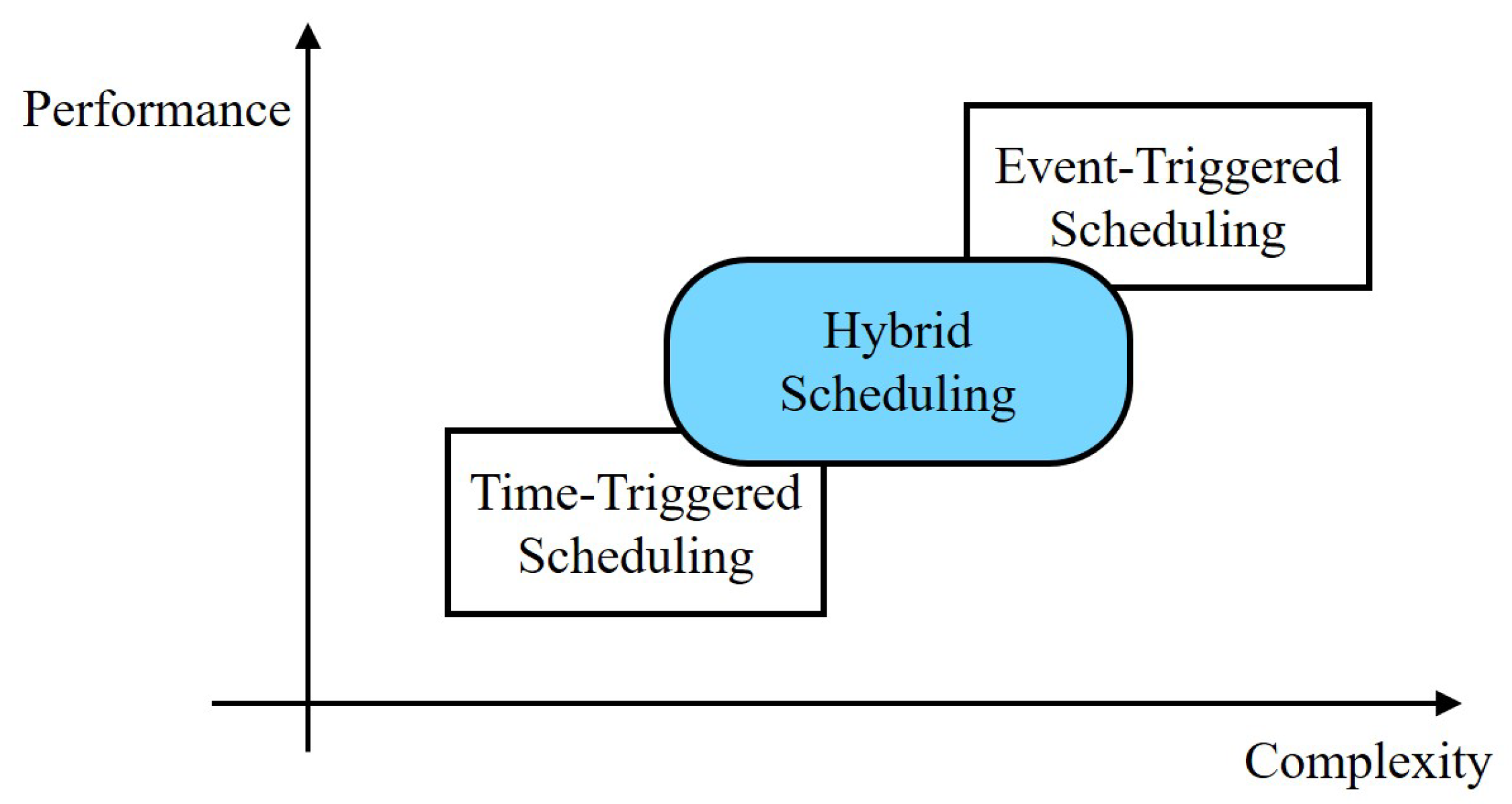
- In this work, we develop a hybrid scheduling for remote state estimation with a smart sensor. We combine a stochastic event trigger with an optimal periodic time trigger to enhance the estimation performance while preserving the communication rate.
- Under the proposed hybrid scheduling, the Gaussian property of the state estimator is preserved, and we derive the MMSE state estimator. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time that an MMSE state estimator has been developed for the combination of a stochastic event trigger and an optimal periodic time trigger.
- For the proposed hybrid scheduling, we provide the upper bound of the state estimation error covariance. Moreover, for the stable system, we characterize the transmission probability at the scheduled time, which is decided by the original optimal time trigger. The stochastic transmission implies the communication resource preservation brought by the stochastic event trigger.
2. Preliminaries
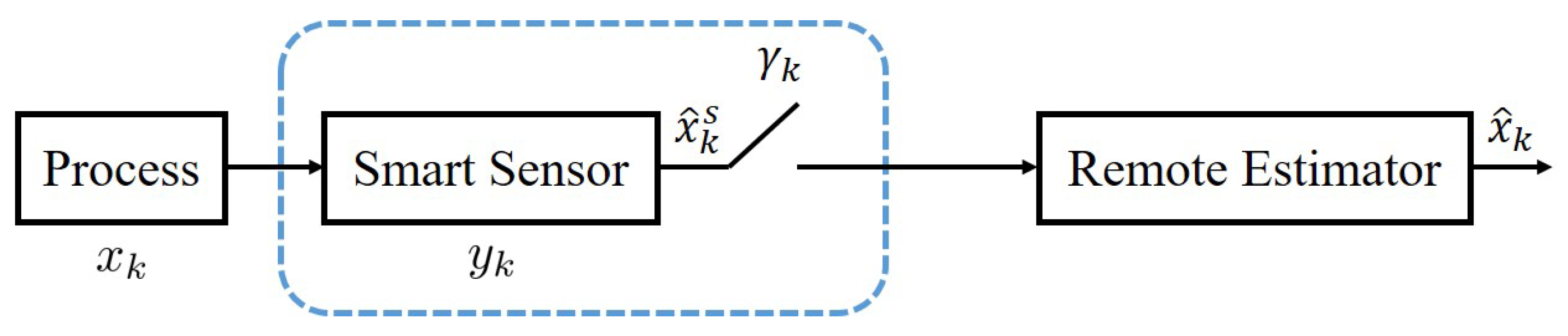
2.1. Process and Smart Sensor
2.2. Transmission with Limited Communication Resources
2.3. Remote Estimator
2.4. Problem of Interest
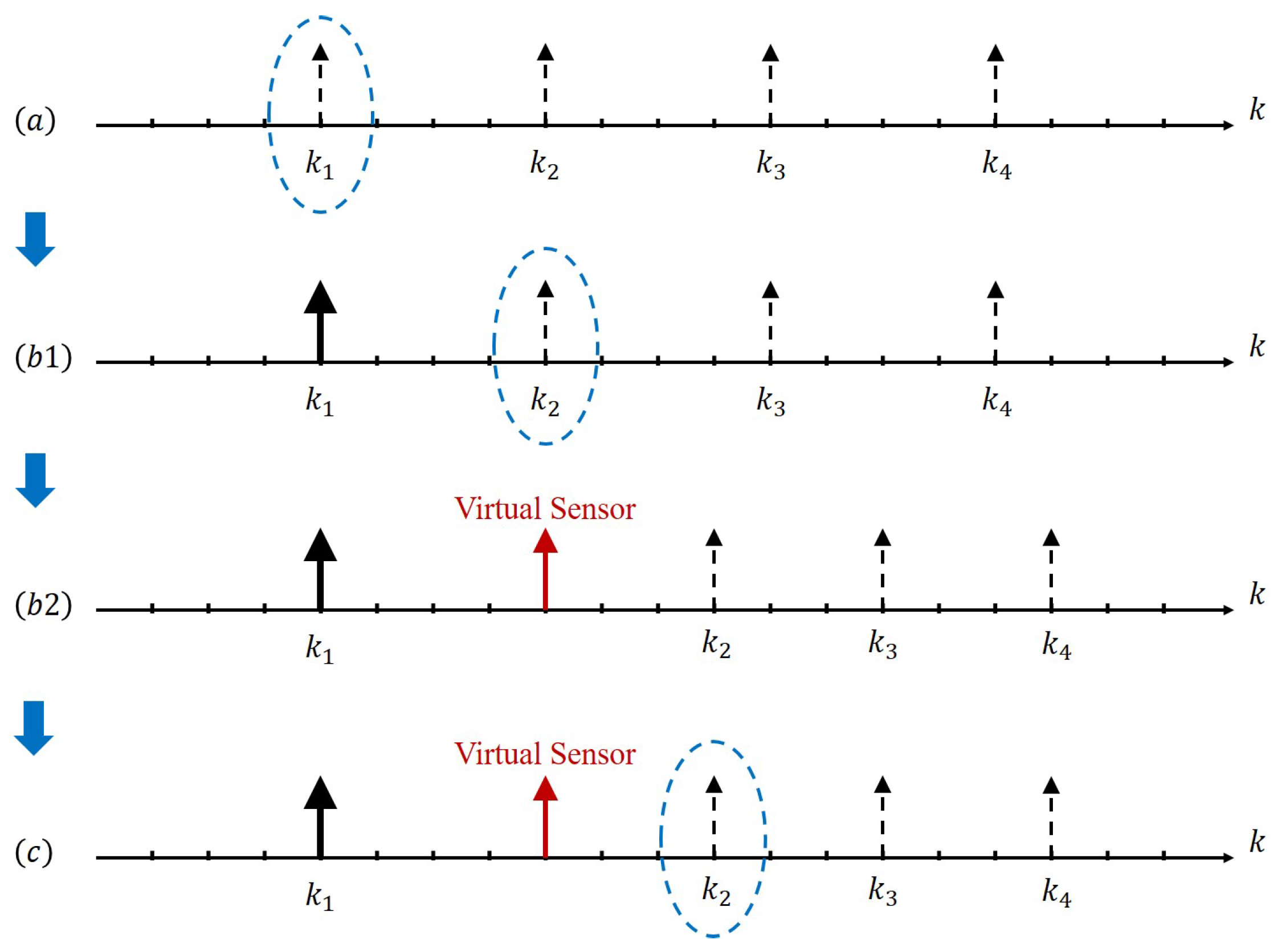
3. Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Sensor Scheduling
3.1. Optimal Time-Triggered Scheduling
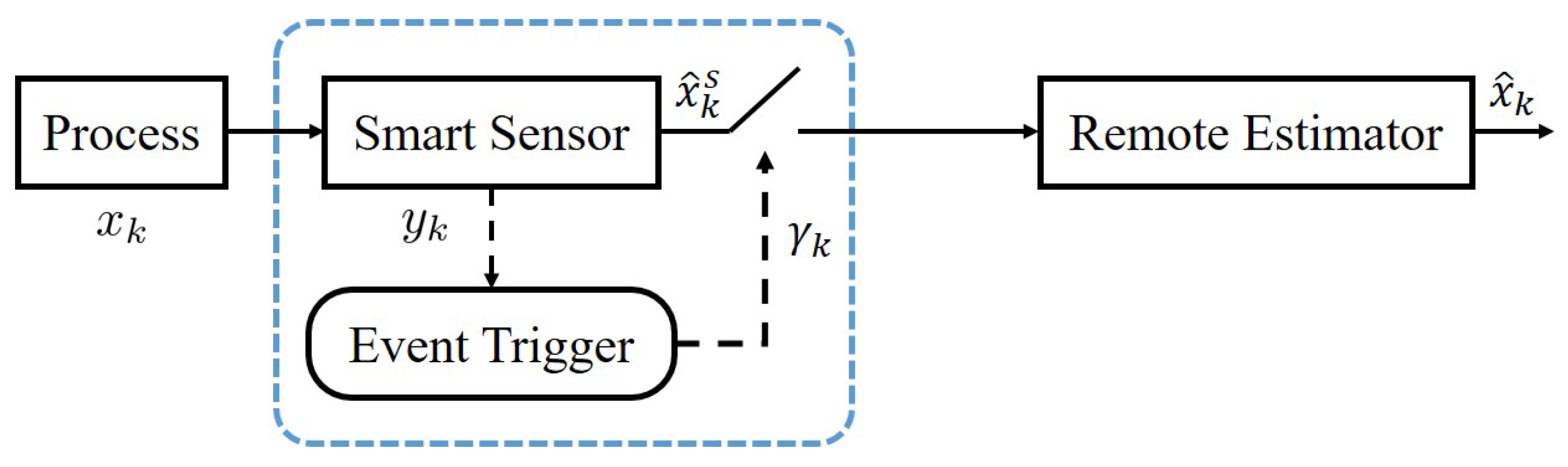
3.2. Stochastic Event-Triggered Scheduling
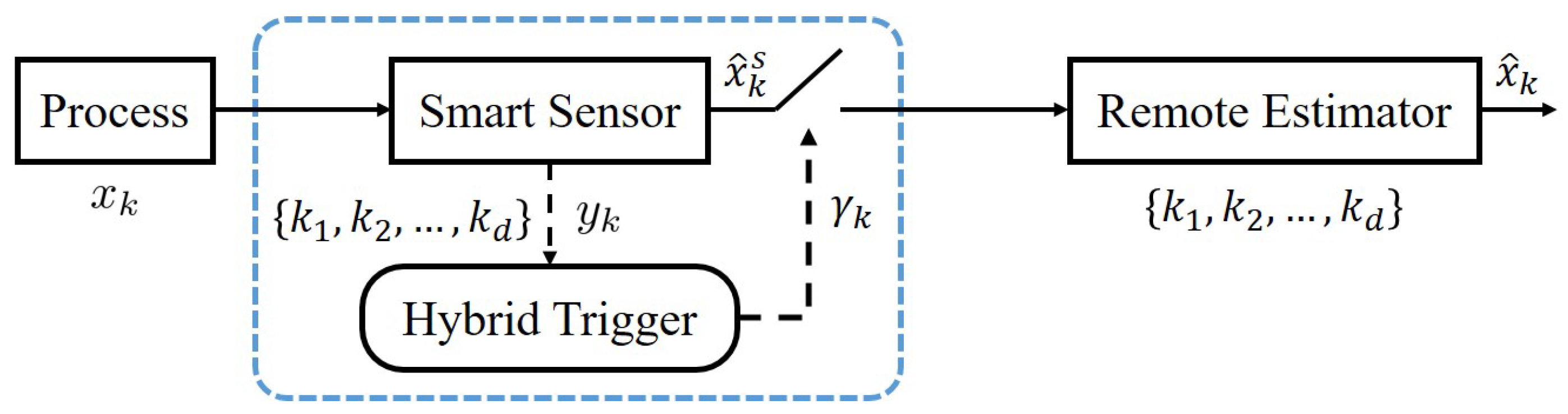
3.3. Hybrid Scheduling
| Algorithm 1 Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Sensor Scheduling and Estimation |
|
3.4. Performance Analysis
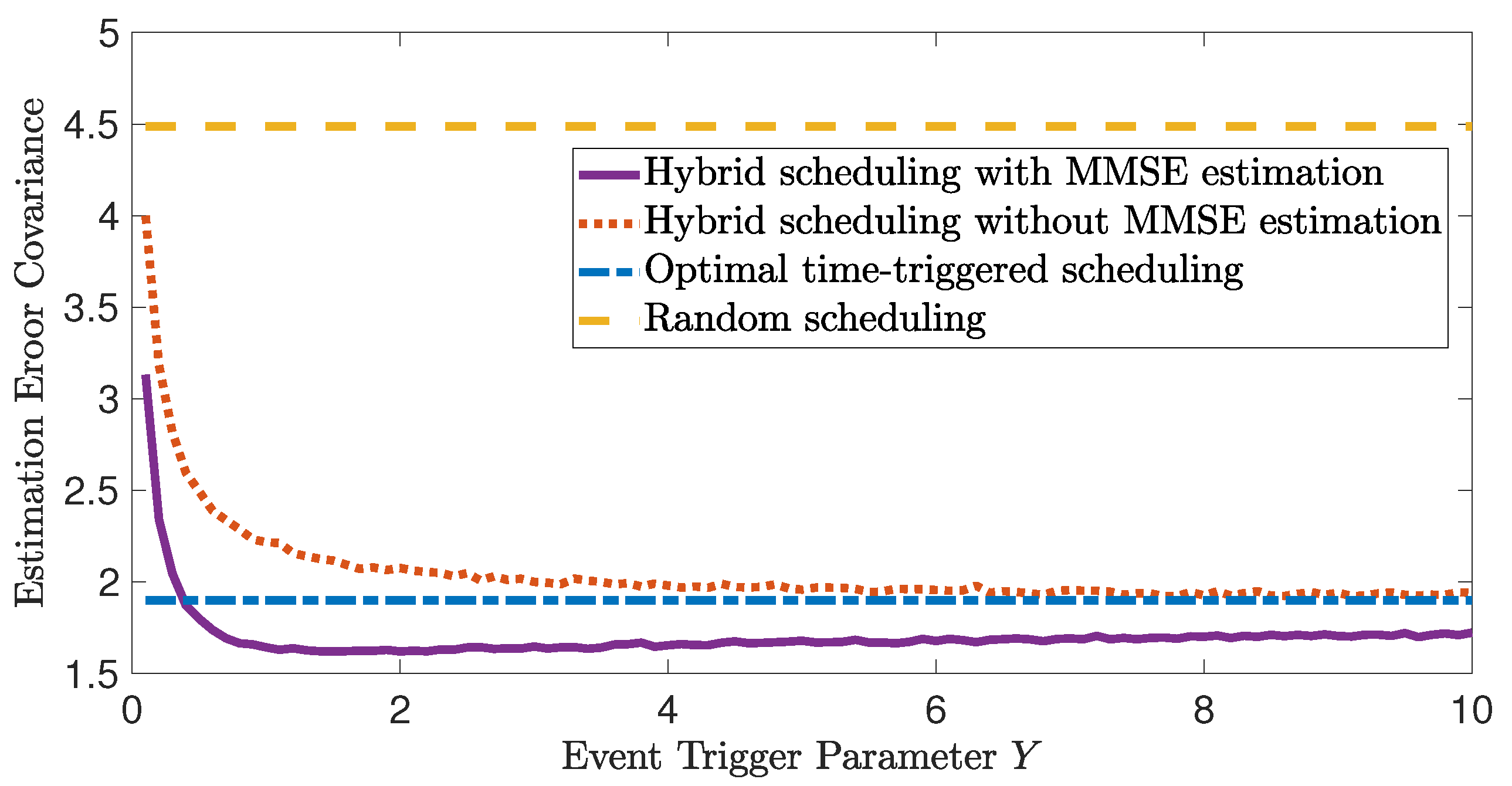
4. Simulation Examples
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Lemma 2
References
- Hespanha, J.P.; Naghshtabrizi, P.; Xu, Y. A survey of recent results in networked control systems. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.Y.; Xie, L.H. Survey of recent progress in networked control systems. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Han, Q.L.; Ge, X.; Ding, D.; Ding, L.; Yue, D.; Peng, C. Networked control systems: A survey of trends and techniques. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, P.A.M.; Hussin, F.A.; Ibrahim, R.; Bingi, K.; Khanday, F.A. A survey on the application of WirelessHART for industrial process monitoring and control. Sensors 2021, 21, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, B.; Liu, F. Localization of indoor mobile robot using minimum variance unbiased FIR filter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.O.; La Scala, B.F. Optimal scheduling of scalar Gauss-Markov systems with a terminal cost function. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cheng, P.; Chen, J. Optimal periodic sensor scheduling with limited resources. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, L. Deterministic sensor data scheduling under limited communication resource. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 5050–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Sun, X. Energy-aware scheduling of surveillance in wireless multimedia sensor networks. Sensors 2010, 10, 3100–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Jia, Q.S.; Johansson, K.H.; Shi, L. Event-based sensor data scheduling: Trade-off between communication rate and estimation quality. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Mo, Y.; Wu, J.; Weerakkody, S.; Sinopoli, B.; Shi, L. Stochastic event-triggered sensor schedule for remote state estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 2661–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.P.; Jia, C.; Williams, J. Event-triggered recursive state estimation for dynamical networks under randomly switching topologies and multiple missing measurements. Automatica 2020, 115, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H. Event-triggered robust state estimation for nonlinear networked systems with measurement delays against DoS attacks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Gu, Z.; Park, J.H.; Xie, X. Adaptive memory-event-triggered static output control of T–S fuzzy wind turbine systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 3894–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Shi, P.; Yue, D.; Ding, Z. Decentralized adaptive event-triggered H∞ filtering for a class of networked nonlinear interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinopoli, B.; Schenato, L.; Franceschetti, M.; Poolla, K.; Jordan, M.I.; Sastry, S.S. Kalman filtering with intermittent observations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2004, 49, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyavej, V.; Savkin, A.V. The problem of optimal robust Kalman state estimation via limited capacity digital communication channels. Syst. Control Lett. 2005, 54, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, G.; Gao, X. Variance-constrained robust estimation for discrete-time systems with communication constraints. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 980753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.D.; Moore, J.B. Optimal Filtering; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schenato, L. Optimal estimation in networked control systems subject to random delay and packet drop. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Johansson, K.H.; Qiu, L. Time and event-based sensor scheduling for networks with limited communication resources. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 13263–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, L.; Ma, W.J. A study of estimation and communication tradeoff using an event-based approach. In Proceedings of the 47th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L. How can online schedules improve communication and estimation tradeoff? IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Mo, Y.; Wu, J.; Sinopoli, B.; Shi, L. Stochastic event-triggered sensor scheduling for remote state estimation. In Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Firenze, Italy, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 6079–6084. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Epstein, M.; Murray, R.M. Kalman filtering over a packet-dropping network: A probabilistic perspective. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, P.; Shi, L.; Chen, J. Optimal denial-of-service attack scheduling with energy constraint. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Patton, R.J. Robust Model-Based Fault Diagnosis for Dynamic Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni , Y.; Liu , X.; Yang , C. Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation with Limited Communication Resources: A Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Approach. Sensors 2023, 23, 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218667
Ni Y, Liu X, Yang C. Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation with Limited Communication Resources: A Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Approach. Sensors. 2023; 23(21):8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218667
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi , Yuqing, Xiaochen Liu , and Chao Yang . 2023. "Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation with Limited Communication Resources: A Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Approach" Sensors 23, no. 21: 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218667
APA StyleNi , Y., Liu , X., & Yang , C. (2023). Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation with Limited Communication Resources: A Time- and Event-Triggered Hybrid Approach. Sensors, 23(21), 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218667





