Smartphone Photogrammetric Assessment for Head Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
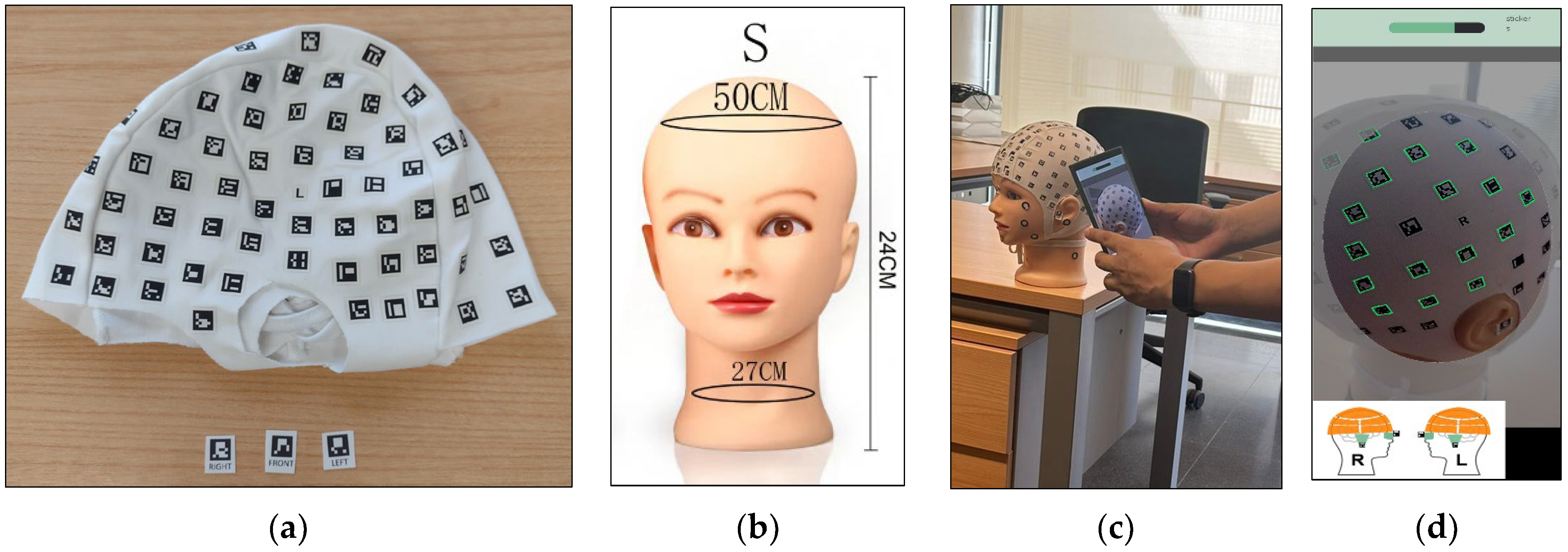
2.1. PhotoMeDAS App
2.2. Smartphones
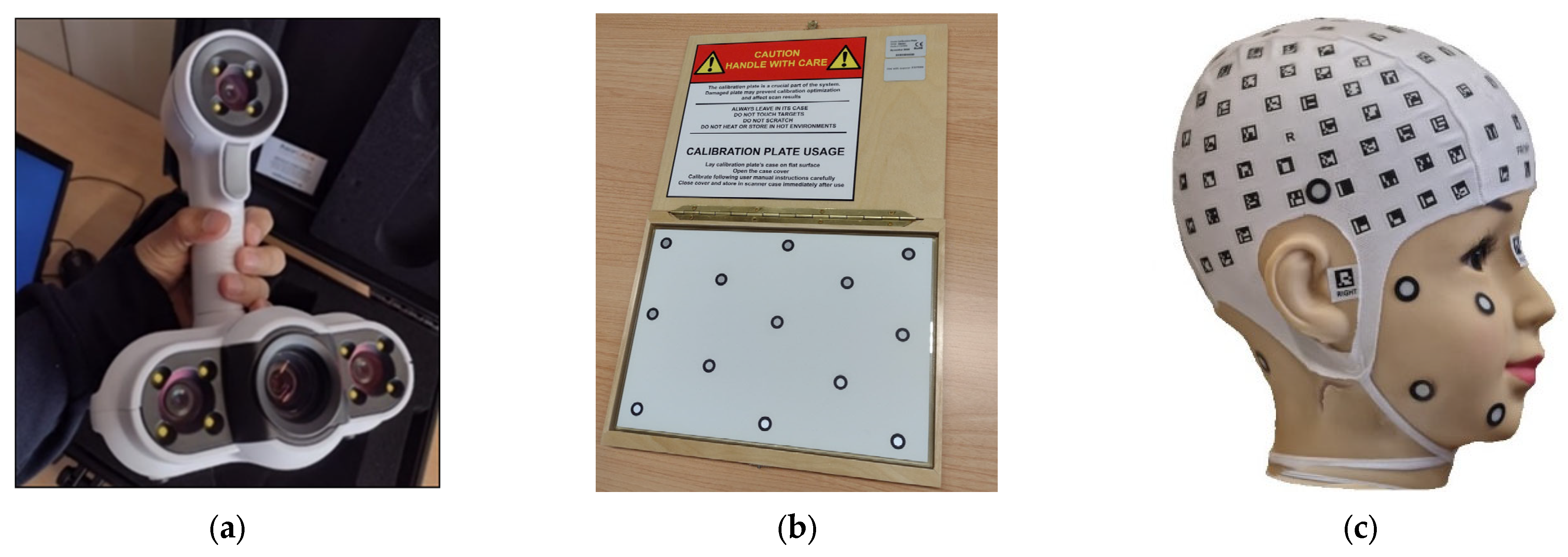
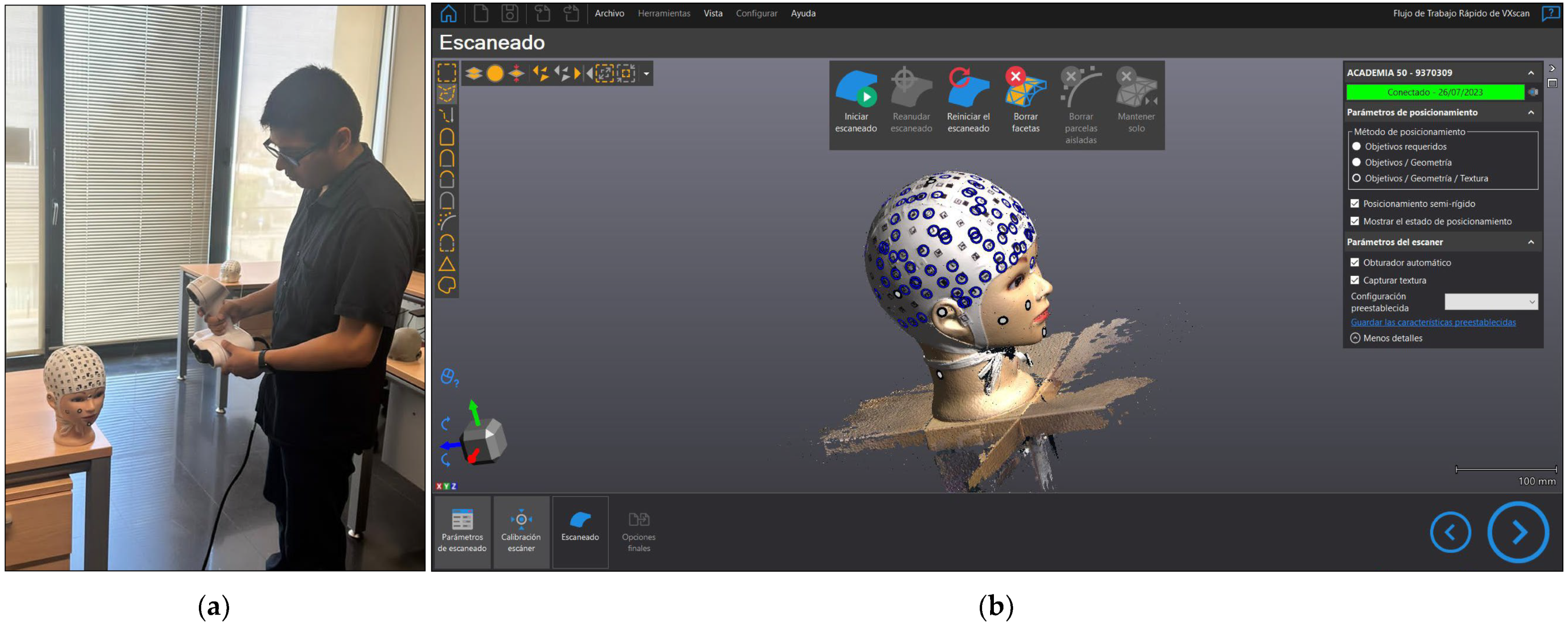
2.3. 3D Scanner
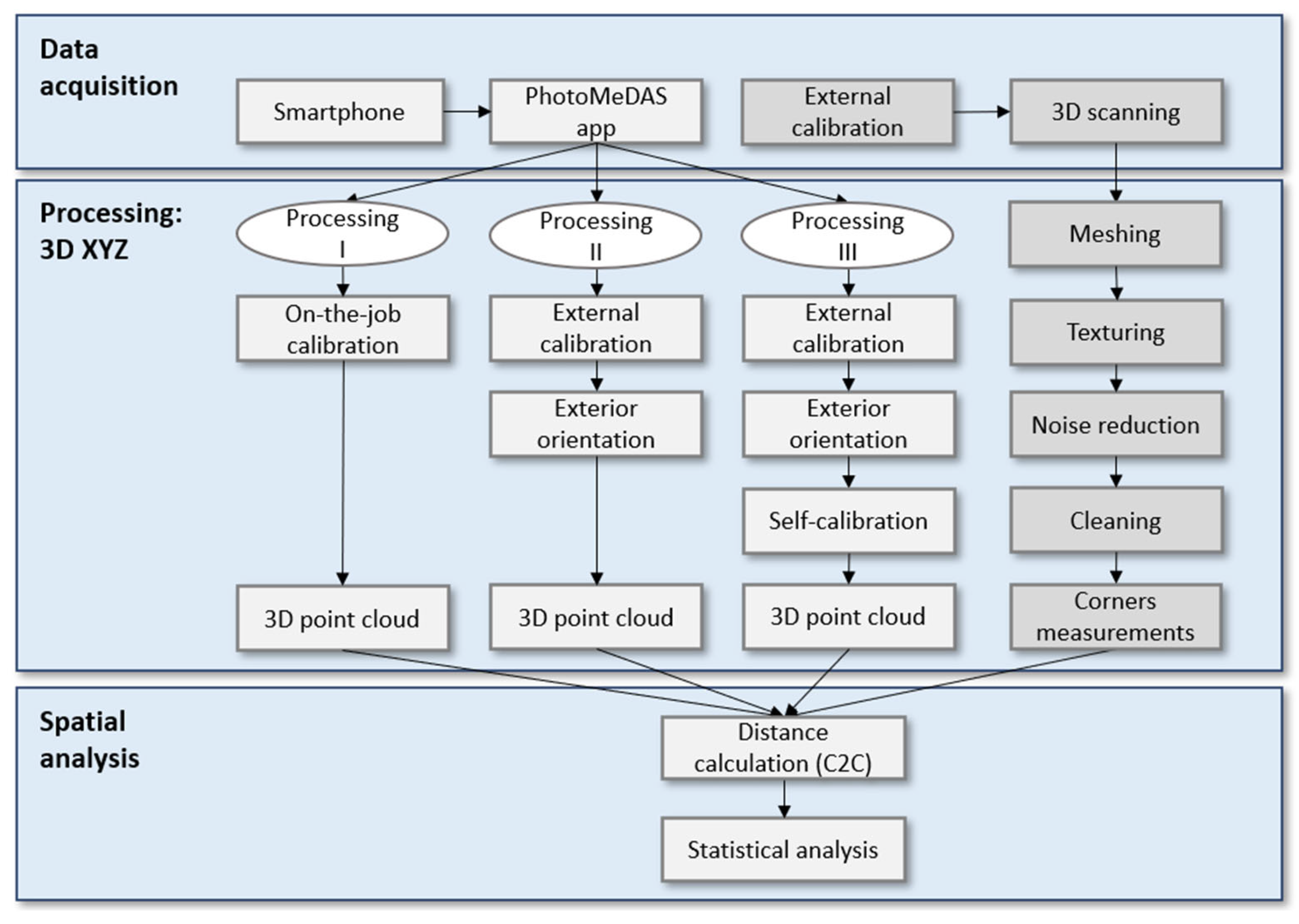
2.4. Workflow
2.5. Processing
2.5.1. Processing I
2.5.2. Processing II
2.5.3. Processing III
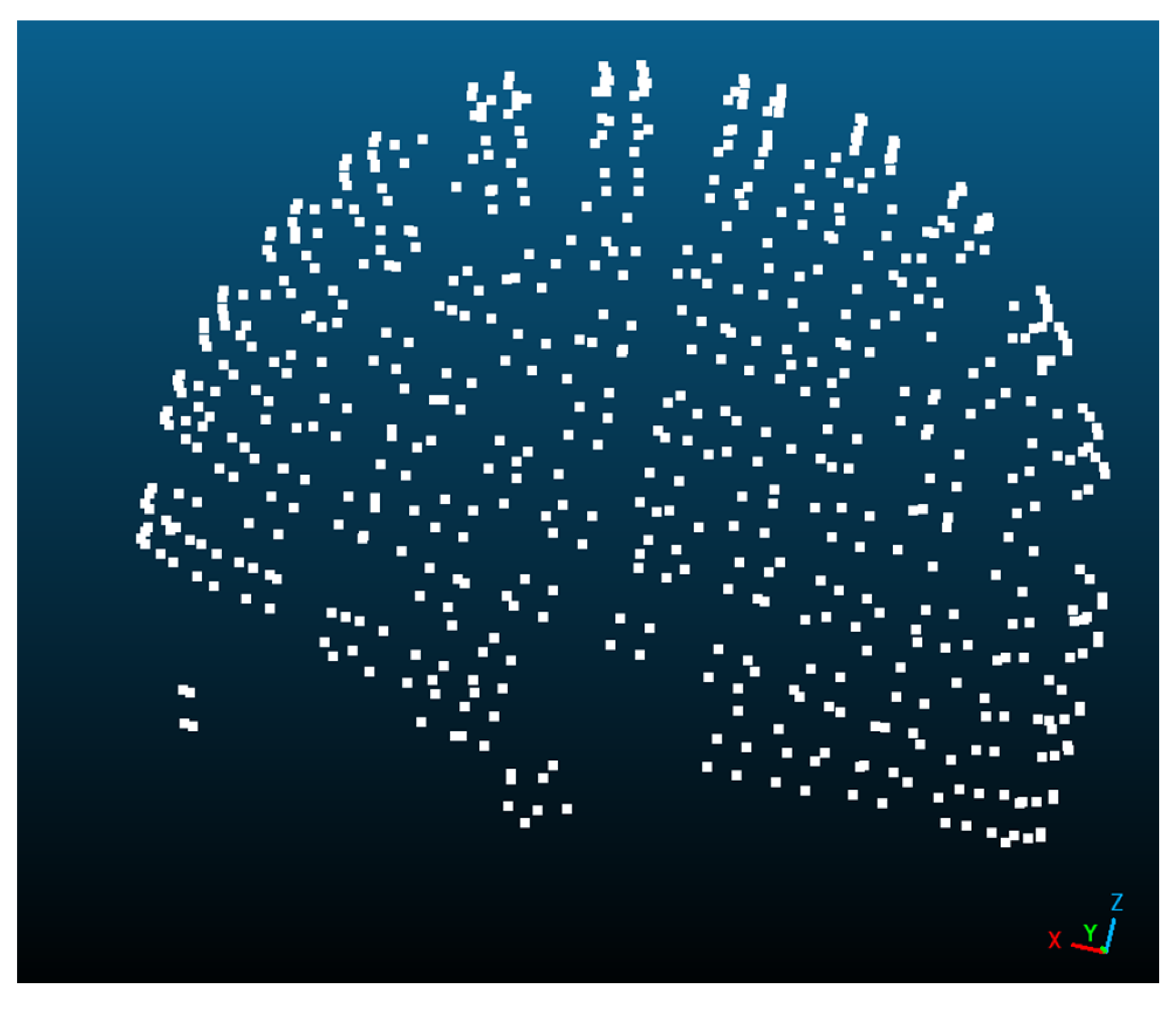
2.6. 3D Scanning
2.6.1. Data Capture with the 3D Scanner
2.6.2. Three-Dimensional Scanning Handling
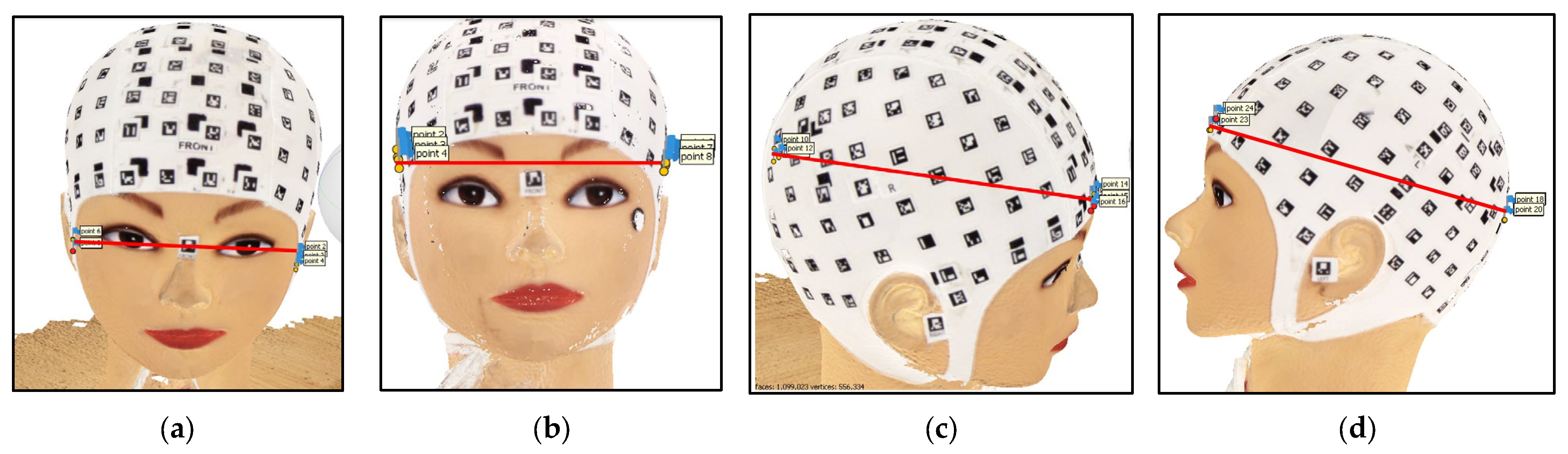
2.6.3. Calculation of 3D Distances
3. Results
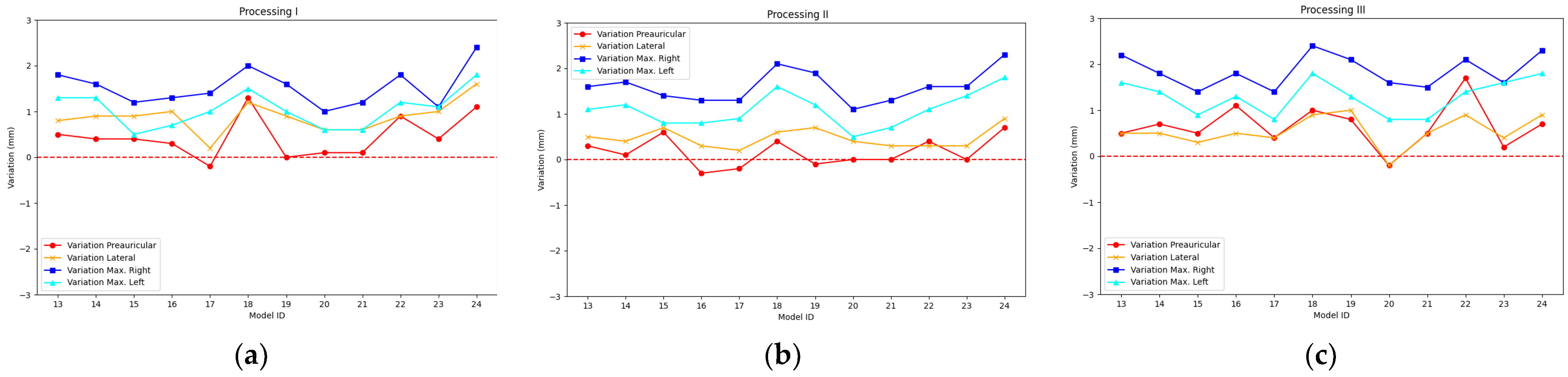
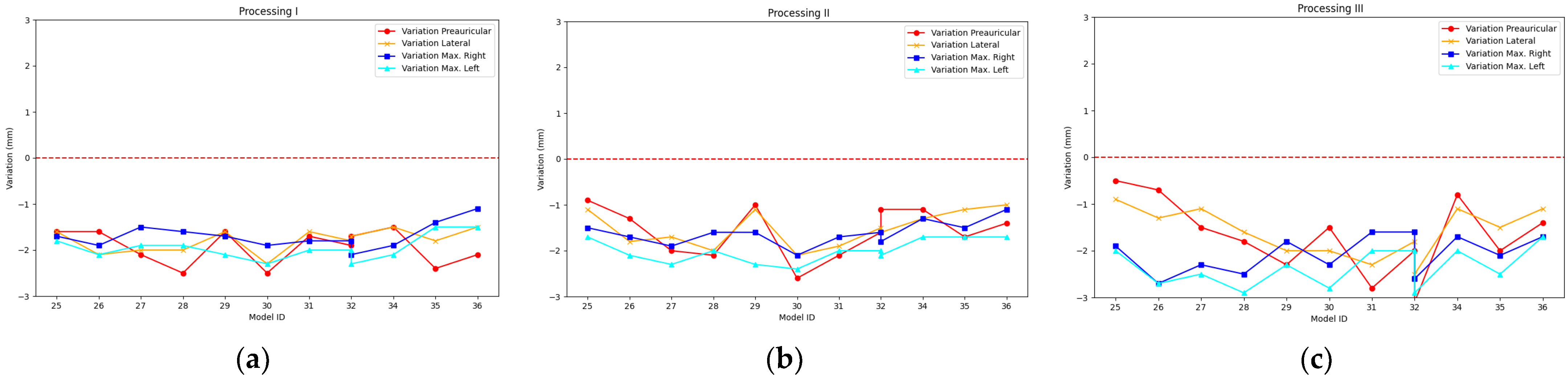
3.1. Comparative Analysis
3.2. Precision Calculation
3.3. Accuracy Calculation
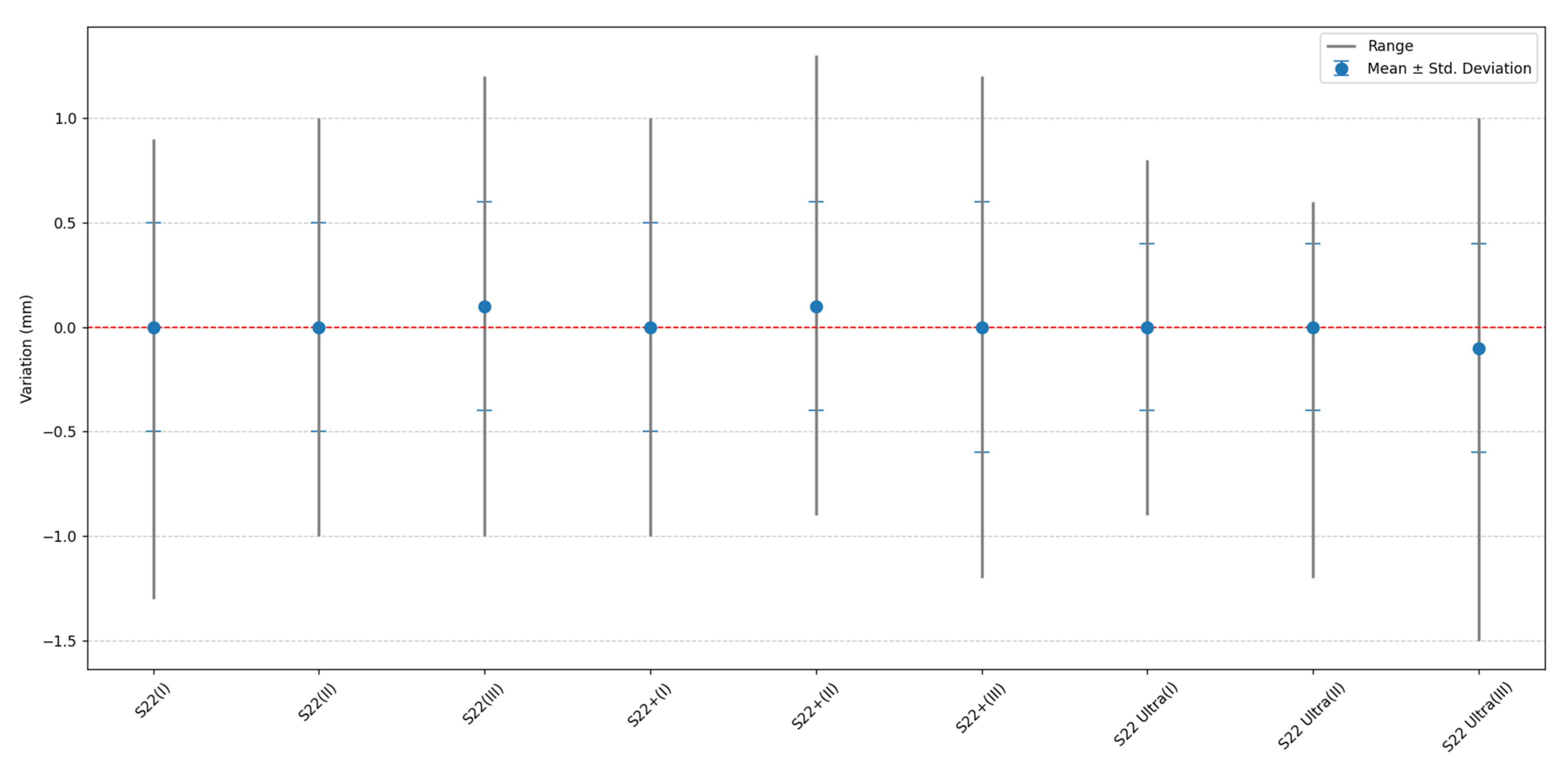
3.4. Relationship between Scaling Factors for S22, S22+, and S22 Ultra
3.5. t-Student Test
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Smartphone Model and Photogrammetric Processing
4.2. Evaluation of Precision and Accuracy
4.3. Evaluation of Scaling Factor
4.4. Limitations and Future Areas of Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedetti, A.T.; De Albuquerque, C.E. Morfologia craniana e a relação com tempo de parto em neonatos em uma ala materno infantil no Hospital Universitário do Oeste do Paraná. Fag J. Health 2021, 3, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawji, A.; Vollman, A.R.; Hatfield, J.; McNeil, D.A.; Sauvé, R. The incidence of positional plagiocephaly: A cohort study. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialocerkowski, A.E.; Vladusic, S.L.; Ng, C.W. Prevalence, risk factors, and natural history of positional plagiocephaly: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2008, 50, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballardini, E.; Sisti, M.; Basaglia, N.; Benedetto, M.; Baldan, A.; Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Garani, G. Prevalence and characteristics of positional plagiocephaly in healthy full-term infants at 8–12 weeks of life. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, B.R.; Wallace, E.R.; Kartin, D.; Cunningham, M.L.; Speltz, M.L. Cognitive outcomes and positional plagiocephaly. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegenthaler, M.H. Methods to Diagnose, Classify, and Monitor Infantile Deformational Plagiocephaly and Brachycephaly: A Narrative Review. J. Chiropr. Med. 2015, 14, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbrand, J.F.; Wilbrand, M.; Pons-Kuehnemann, J.; Blecher, J.C.; Christophis, P.; Howaldt, H.P.; Schaaf, H. Value and reliability of anthropometric measurements of cranial deformity in early childhood. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 39, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.B.; Luximon, Y. Review on 3D scanners for head and face modeling. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, C.A.A.; Knoops, P.G.M.; Borghi, A.; Jeelani, N.U.O.; Koudstaal, M.J.; Schievano, S.; Dunaway, D.J.; Rodriguez-Florez, N. Three-dimensional surface scanners compared with standard anthropometric measurements for head shape. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminati, E.; Talamas, D.C.; Young, M.; Twiste, M.; Dhokia, V.; Bilzon, J.L.J. Validity and reliability of a novel 3D scanner for assessment of the shape and volume of amputees’ residual limb models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsaxner, C.; Wallner, J.; Chen, X.; Zemann, W.; Egger, J. Facial model collection for medical augmented reality in oncologic cranio-maxillofacial surgery. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazmiño-Armijos, A.O.; Pozo-Safla, E.R.; Medina-Quintero, E.H. Obtención del modelo geométrico de un socket para prótesis infantiles utilizando ingeniería inversa y modelamiento mediante software CAD. Cienc. Técnicas Apl. Artículo Investig. 2019, 5, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Baselga, S.; Mora-Navarro, G.; Lerma, J.L. Assessment of Cranial Deformation Indices by Automatic Smartphone-Based Photogrammetric Modelling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, A.; Lee, J.; Toews, M.; Gilardino, M.S. Smartphone Integration of Artificial Intelligence for Automated Plagiocephaly Diagnosis. Plast Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, E.L.; Agarwal, S.; Hallac, R.R.; Daescu, O.; Kane, A.A. A Role for Artificial Intelligence in the Classification of Craniofacial Anomalies. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, F.; Zeitvogel, S.; Meder, C.; Stoevesandt, K.; Wernet, C.; Laubenheimer, A. Feedback Mechanisms of an iOS App to Record RGBD Data for AI-Based Diagnosis and Monitoring of Infant Head Deformation. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference and Exhibition on 3D Body Scanning and Processing Technologies, Lugano, Switzerland, 27–28 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieb, J.; Barbero-García, I.; Lerma, J.L. Spherical harmonics to quantify cranial asymmetry in deformational plagiocephaly. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupnik, E.; Daakir, M.; Deseilligny, M.P. MicMac—A free, open-source solution for photogrammetry. Open Geospat. Data Softw. Stand. 2017, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbrand, J.F.; Szczukowski, A.; Blecher, J.C.; Pons-Kuehnemann, J.; Christophis, P.; Howaldt, H.P.; Schaaf, H. Objectification of cranial vault correction for craniosynostosis by three-dimensional photography. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Steinmacher, S.; Bächli, H.; Somlo, E.; Hoffmann, J.; Engel, M. Metopic synostosis: Measuring intracranial volume change following fronto-orbital advancement using three-dimensional photogrammetry. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, T.; Nagano, N.; Kato, R.; Hashimoto, S.; Saito, K.; Miyabayashi, H.; Sasano, M.; Sumi, K.; Yoshino, A.; Morioka, I. Natural-course evaluation of infants with positional severe plagiocephaly using a three-dimensional scanner in japan: Comparison with those who received cranial helmet therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabayashi, H.; Nagano, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Saito, K.; Kato, R.; Noto, T.; Sasano, M.; Sumi, K.; Yoshino, A.; Morioka, I. Evaluating Cranial Growth in Japanese Infants Using a Three-dimensional Scanner: Relationship between Growth-related Parameters and Deformational Plagiocephaly. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2022, 62, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, R.; Nagano, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Saito, K.; Miyabayashi, H.; Noto, T.; Morioka, I. Three-Dimensional Versus Two-Dimensional Evaluations of Cranial Asymmetry in Deformational Plagiocephaly Using a Three-Dimensional Scanner. Children 2022, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühlman, D.C.; Almuzian, M.; Coppini, C.; Alzoubi, E.E. Accuracy (trueness and precision) of four tablet-based applications for three-dimensional facial scanning: An in-vitro study. J. Dent. 2023, 135, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.P.; Jiménez-Castellanos, E.; Martínez-de-Fuentes, R.; Fernandez, A.A.V.; Chu, S. Perception of maxillary dental midline shift in asymmetric faces. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2015, 10, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





| Characteristic | S22 | S22+ | S22 Ultra |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | CPU Speed: 1.8 GHz; CPU Type: Octa-Core | ||
| Rear camera—Ultra wide angle | 12 MP F2.2 [FF], FOV 120°, 1/2.55”, 1.4 µm | 12 MP F2.2 [FF], FOV 120°, 1/2.55”, 1.4 µm | 12 MP F2.2 [Dual Pixel AF], FOV 120°, 1/2.55”, 1.4 µm |
| Rear camera—Wide Angle | 50 MP F1.8 [Dual Pixel AF], OIS, FOV 85°, 1/1.56”, 1.0 µm with Adaptive Pixel | 50 MP F1.8 [Dual Pixel AF], OIS, FOV 85°, 1/1.56”, 1.0 µm with Adaptive Pixel | 108 MP F1.8 [PDAF], OIS, FOV 85°, 1/1.33”, 0.8 µm with Adaptive Pixel |
| Rear CAMERA—Telephoto lens | 10 MP F2.4 [3x, PDAF], OIS FOV 36°, 1/3.94”, 1.0 µm | 10 MP F2.4 [3x, PDAF], OIS FOV 36°, 1/3.94”, 1.0 µm | 10 MP F2.4 [3x, Dual Pixel AF], OIS, FOV 36°, 1/3.52”, 1.12 µm |
| Physical specifications | Dimentions: 146.0 mm × 70.6 mm × 7.6 mm; Weight: 167 g | Dimentions: 157.4 mm × 75.8 mm × 7.6 mm; Weight: 195 g | Dimentions: 163.3 mm × 77.9 mm × 8.9 mm; Weight: 228 g |
| Screen | Resolution: 2340 × 1080 (FHD+); Size: 153.9 mm (6.1” full rectangle)/149.9 mm (5.9” rounded corners) Technology: Dynamic AMOLED 2X Number of colours: 16 M | Resolution: 2340 × 1080 (FHD+) Size: 166.5 mm (6.6” full rectangle)/162.1 mm (6.4” rounded corners) Technology: Dynamic AMOLED 2X Number of colours: 16 M | Resolution: 3088 × 1440 (Quad HD+); Size: 173.1 mm (6.8” full rectangle)/172.5 mm (6.8” rounded corners) Technology: Dynamic AMOLED 2X Number of colours: 16 M |
| Battery | Internet usage time (4G): Up to 15 h; Battery capacity: 3700 mAh | Internet usage time (4G): Up to 19 h; Battery capacity: 4500 mAh | Internet usage time (4G): Up to 19 h; Battery capacity: 5000 mAh |
| Session | Preauricular Distance (mm) | Max. Length Distance Right (mm) | Max. Length Distance Left (mm) | Maximum Width Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Session 1 | 127.224 | 170.814 | 169.473 | 140.279 |
| Session 2 | 127.176 | 170.845 | 169.510 | 140.226 |
| Session 3 | 127.239 | 170.878 | 169.528 | 140.251 |
| Session 4 | 127.165 | 170.845 | 169.504 | 140.111 |
| Session 5 | 127.130 | 170.930 | 169.469 | 140.110 |
| Session 6 | 127.193 | 170.669 | 169.491 | 140.127 |
| Minimum | 127.130 | 170.669 | 169.469 | 140.110 |
| Maximum | 127.239 | 170.930 | 169.528 | 140.279 |
| Mean | 127.188 | 170.830 | 169.496 | 140.184 |
| Standard deviation | 0.040 | 0.088 | 0.023 | 0.076 |
| Smartphone | Process | Overall Results of Distance Differences | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | σ (mm) | Minimum (mm) | Maximum (mm) | ||
| S22 | Processing I | −1.2 | 0.5 | −2.5 | −0.1 |
| Processing II | −1.1 | 0.5 | −2.3 | 0.1 | |
| Processing III | −1.1 | 0.6 | −2.3 | 0.3 | |
| S22+ | Processing I | 1.0 | 0.6 | −0.2 | 2.4 |
| Processing II | 0.8 | 0.6 | −0.3 | 2.3 | |
| Processing III | 1.1 | 0.7 | −0.2 | 2.4 | |
| S22 Ultra | Processing I | −1.8 | 0.3 | −2.5 | −1.2 |
| Processing II | −1.7 | 0.4 | −2.6 | −0.9 | |
| Processing III | −1.9 | 0.6 | −3.1 | −0.5 | |
| Smartphone | Distance | Processing I | Processing II | Processing III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | σ (mm) | RSD (%) | (mm) | σ (mm) | RSD (%) | (mm) | σ (mm) | RSD (%) | ||
| S22 | Preauricular | 128.2 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 128.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 127.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Lateral | 141.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 141.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 141.3 | 0.5 | 0.4 | |
| Max right | 172.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 172.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 172.0 | 0.6 | 0.3 | |
| Max left | 170.9 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 170.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 170.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 | |
| Mean RSD | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |||||||
| S22+ | Preauricular | 126.8 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 127.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 126.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Lateral | 139.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 139.7 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 139.7 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| Max right | 169.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 169.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 169.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| Max left | 168.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 168.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 168.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| Mean RSD | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |||||||
| S22 Ultra | Preauricular | 129.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 128.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 128.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| Lateral | 142.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 141.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 141.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | |
| Max right | 172.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 172.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 172.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| Max left | 171.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 171.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 171.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| Mean RSD | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |||||||
| Smartphone | Distance | Processing I | Processing II | Processing III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | AD (mm) | RD (%) | (mm) | AD (mm) | RD (%) | (mm) | AD (mm) | RD (%) | ||
| S22 | Preauricular | 128.2 | 1.0 | 0.79 | 128.1 | 0.9 | 0.71 | 127.9 | 0.5 | 0.39 |
| Lateral | 141.1 | 0.9 | 0.64 | 141.4 | 1.2 | 0.86 | 141.3 | 1.1 | 0.78 | |
| Max right | 172.2 | 1.4 | 0.82 | 172.0 | 1.2 | 0.70 | 172.0 | 1.2 | 0.70 | |
| Max left | 170.9 | 1.4 | 0.83 | 170.7 | 1.2 | 0.71 | 170.7 | 1.2 | 0.71 | |
| Mean | 1.2 | 0.77 | 1.1 | 0.74 | 1.1 | 0.65 | ||||
| S22+ | Preauricular | 126.8 | 0.4 | 0.31 | 127.0 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 126.5 | 0.9 | 0.71 |
| Lateral | 139.3 | 0.9 | 0.64 | 139.7 | 0.5 | 0.36 | 139.7 | 0.5 | 0.36 | |
| max right | 169.3 | 1.5 | 0.88 | 169.2 | 1.6 | 0.94 | 169.0 | 1.8 | 1.05 | |
| max left | 168.5 | 1.0 | 0.59 | 168.4 | 1.1 | 0.65 | 168.2 | 1.3 | 0.77 | |
| Mean | 0.9 | 0.61 | 0.9 | 0.52 | 1.1 | 0.72 | ||||
| S22 Ultra | Preauricular | 129.1 | 1.9 | 1.49 | 128.8 | 1.6 | 1.26 | 128.9 | 1.5 | 1.18 |
| Lateral | 142.0 | 1.8 | 1.28 | 141.7 | 1.5 | 1.07 | 141.8 | 1.6 | 1.14 | |
| Max right | 172.5 | 1.7 | 1.00 | 172.4 | 1.6 | 0.94 | 172.9 | 2.1 | 1.23 | |
| Max left | 171.5 | 2.0 | 1.18 | 171.5 | 2 | 1.18 | 171.8 | 2.3 | 1.36 | |
| Mean | 1.9 | 1.24 | 1.7 | 1.11 | 1.9 | 1.23 | ||||
| Smartphone | Processing | Variation Preauricular | Variation Lateral | Variation Max Right | Variation Max Left | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S22 | Processing I | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.993 |
| Processing II | 0.993 | 0.992 | 0.993 | 0.993 | 0.993 | |
| Processing III | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.993 | 0.993 | 0.993 | |
| S22+ | Processing I | 1.003 | 1.006 | 1.009 | 1.006 | 1.006 |
| Processing II | 1.001 | 1.003 | 1.009 | 1.006 | 1.005 | |
| Processing III | 1.005 | 1.004 | 1.011 | 1.008 | 1.007 | |
| S22 Ultra | Processing I | 0.985 | 0.988 | 0.99 | 0.989 | 0.988 |
| Processing II | 0.988 | 0.989 | 0.991 | 0.988 | 0.989 | |
| Processing III | 0.987 | 0.989 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.988 |
| Smartphone | Processing | Overall Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | σ (mm) | Minimum (mm) | Maximum (mm) | ||
| S22 | Processing I | 0.0 | 0.5 | −1.3 | 0.9 |
| Processing II | 0.0 | 0.5 | −1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Processing III | 0.0 | 0.6 | −1.2 | 1.2 | |
| S22+ | Processing I | 0.0 | 0.5 | −1.0 | 1.0 |
| Processing II | 0.1 | 0.5 | −0.9 | 1.3 | |
| Processing III | 0.1 | 0.5 | −1.0 | 1.2 | |
| S22 Ultra | Processing I | 0.1 | 0.5 | −1.0 | 1.2 |
| Processing II | 0.0 | 0.4 | −1.2 | 0.6 | |
| Processing III | −0.1 | 0.5 | −1.5 | 1.0 | |
| Smartphone | Processing | p Value of 2 Queues | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without Scaling | After Scaling | ||
| S22 | Processing I | <0.001 | 0.512 |
| Processing II | <0.001 | 0.896 | |
| Processing III | <0.001 | 0.872 | |
| S22+ | Processing I | <0.001 | 0.490 |
| Processing II | <0.001 | 0.548 | |
| Processing III | <0.001 | 0.794 | |
| S22 Ultra | Processing I | <0.001 | 0.118 |
| Processing II | <0.001 | 0.830 | |
| Processing III | <0.001 | 0.192 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quispe-Enriquez, O.C.; Valero-Lanzuela, J.J.; Lerma, J.L. Smartphone Photogrammetric Assessment for Head Measurements. Sensors 2023, 23, 9008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23219008
Quispe-Enriquez OC, Valero-Lanzuela JJ, Lerma JL. Smartphone Photogrammetric Assessment for Head Measurements. Sensors. 2023; 23(21):9008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23219008
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuispe-Enriquez, Omar C., Juan José Valero-Lanzuela, and José Luis Lerma. 2023. "Smartphone Photogrammetric Assessment for Head Measurements" Sensors 23, no. 21: 9008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23219008
APA StyleQuispe-Enriquez, O. C., Valero-Lanzuela, J. J., & Lerma, J. L. (2023). Smartphone Photogrammetric Assessment for Head Measurements. Sensors, 23(21), 9008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23219008







