Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- ✓ Single-layer phase reconfigurable reflecting metasurface structure to address the design complexity;
- ✓ Good angular stability and polarization sensitivity to address the minimum coverage issue from existing RIS systems;
- ✓ Phase reconfiguration through an active device maintains the ideal phase difference between the unit cells.
Literature Survey
- ✓ For practical activities, that the RIS should use the least amount of power is essential;
- ✓ To reduce design complexity, the RIS should be configured;
- ✓ RIS can take all incoming waves regardless of their polarizations, and the RIS should handle angles of incidence. The maximum suggested RISs are sensitive to the angle of incidence and are not polarization independent.
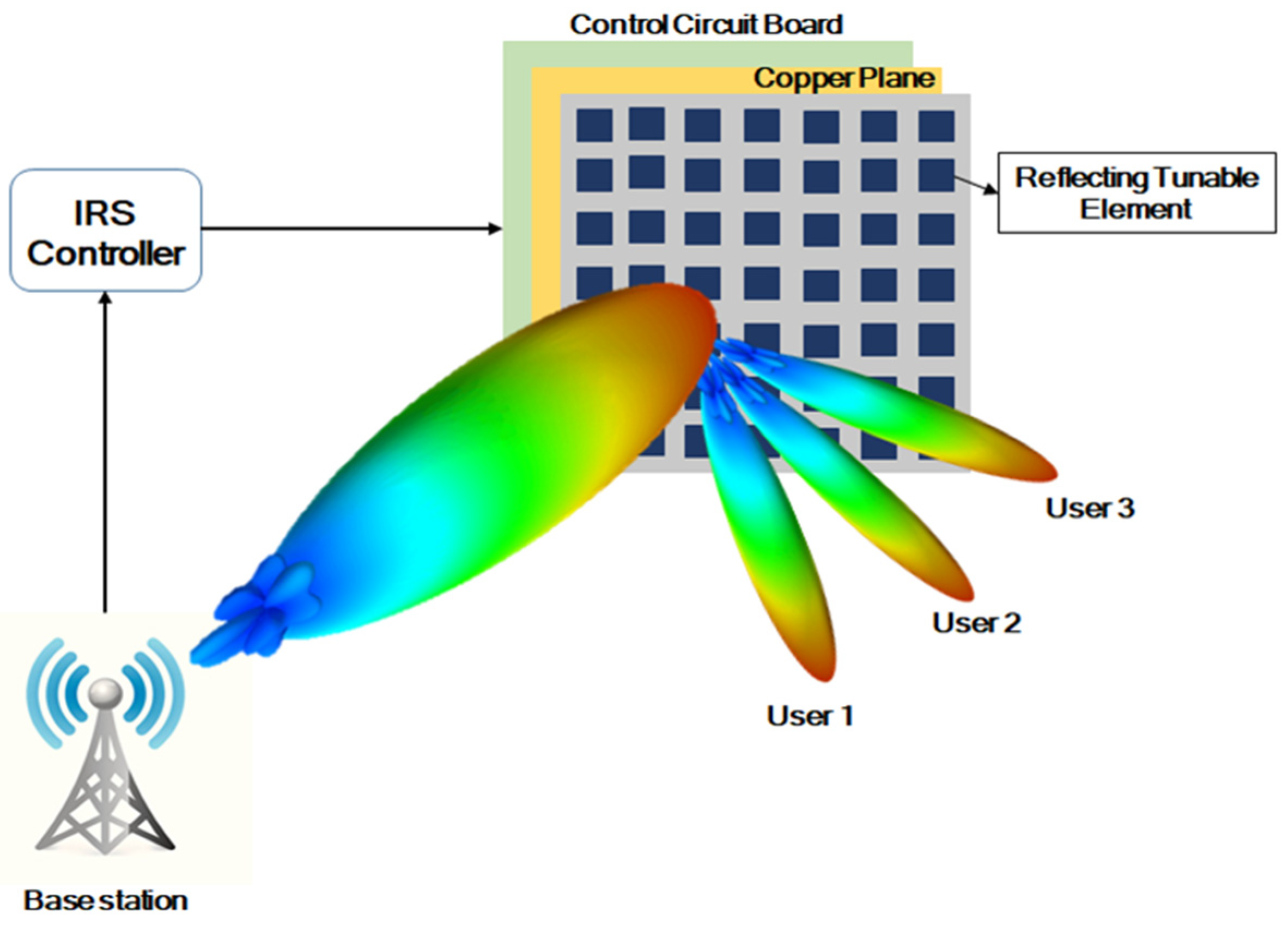
2. Design Flow of the Proposed Structure
2.1. Fundamental Architecture of Proposed Unit Cell
2.2. Reconfigurable Metasurface
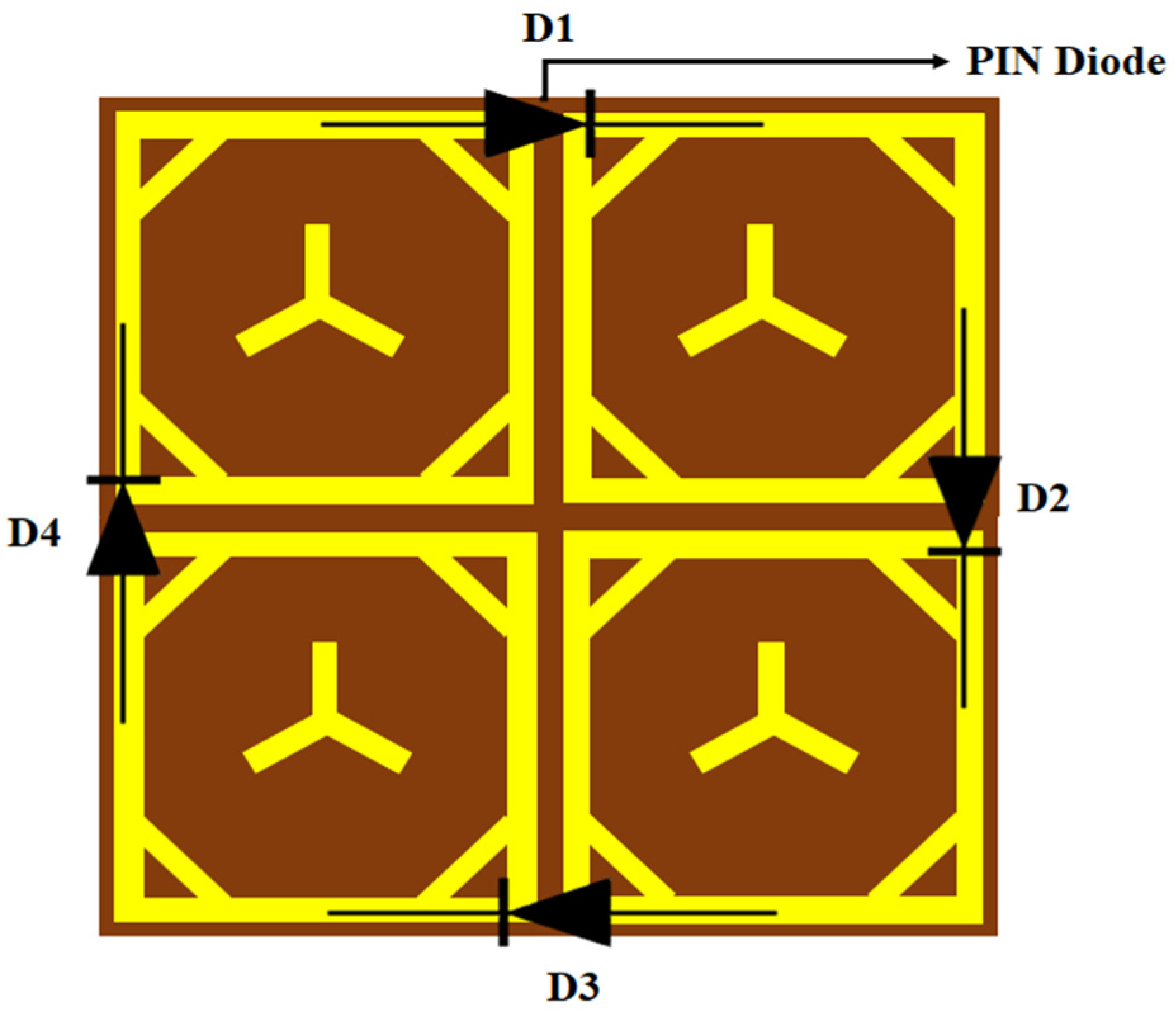
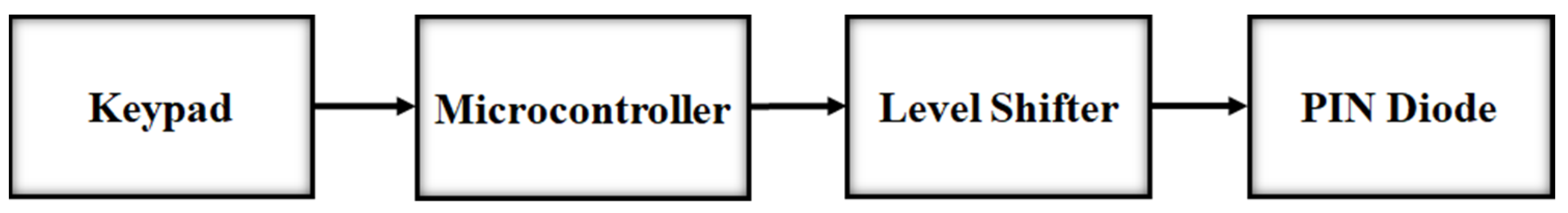
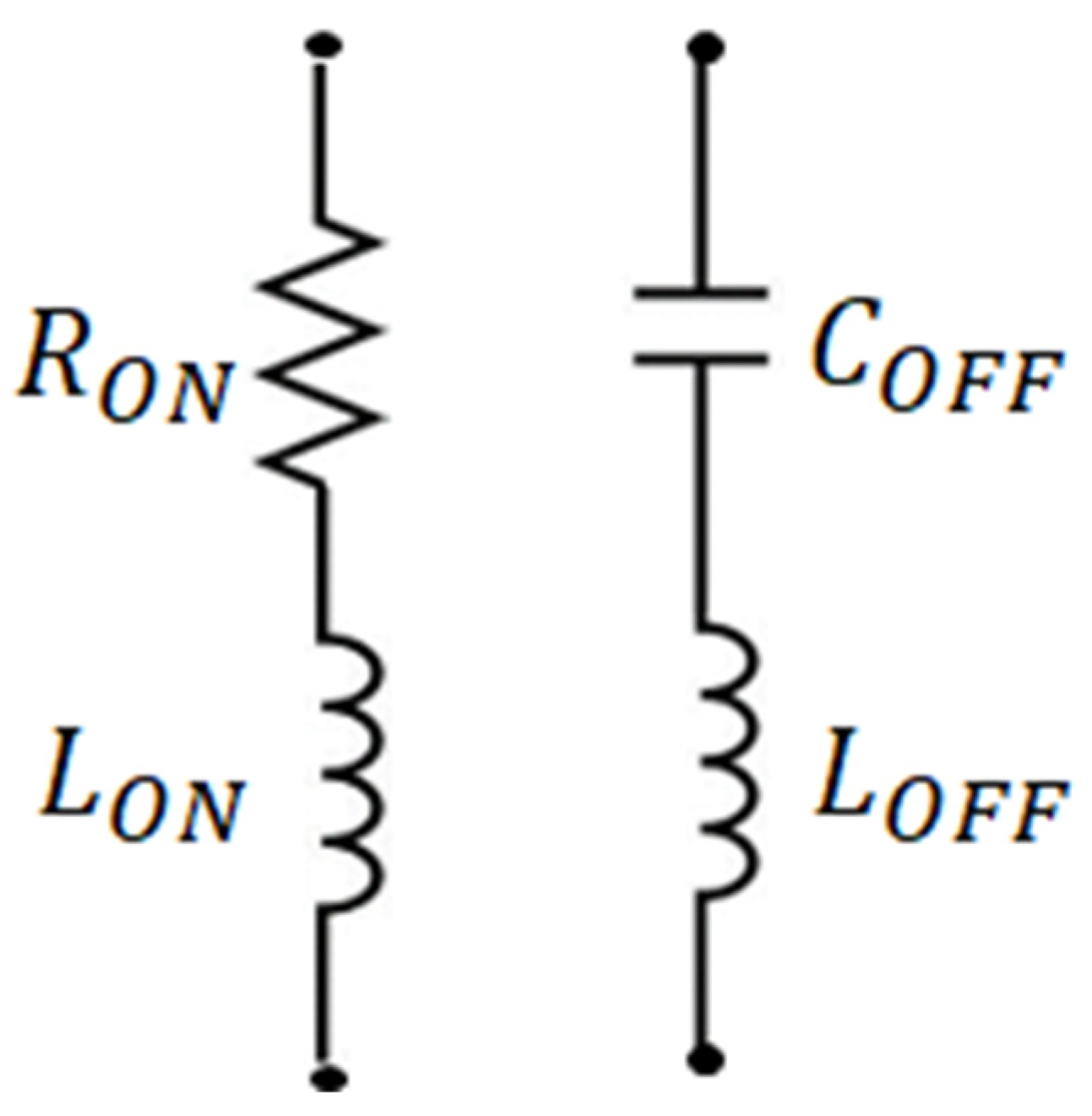
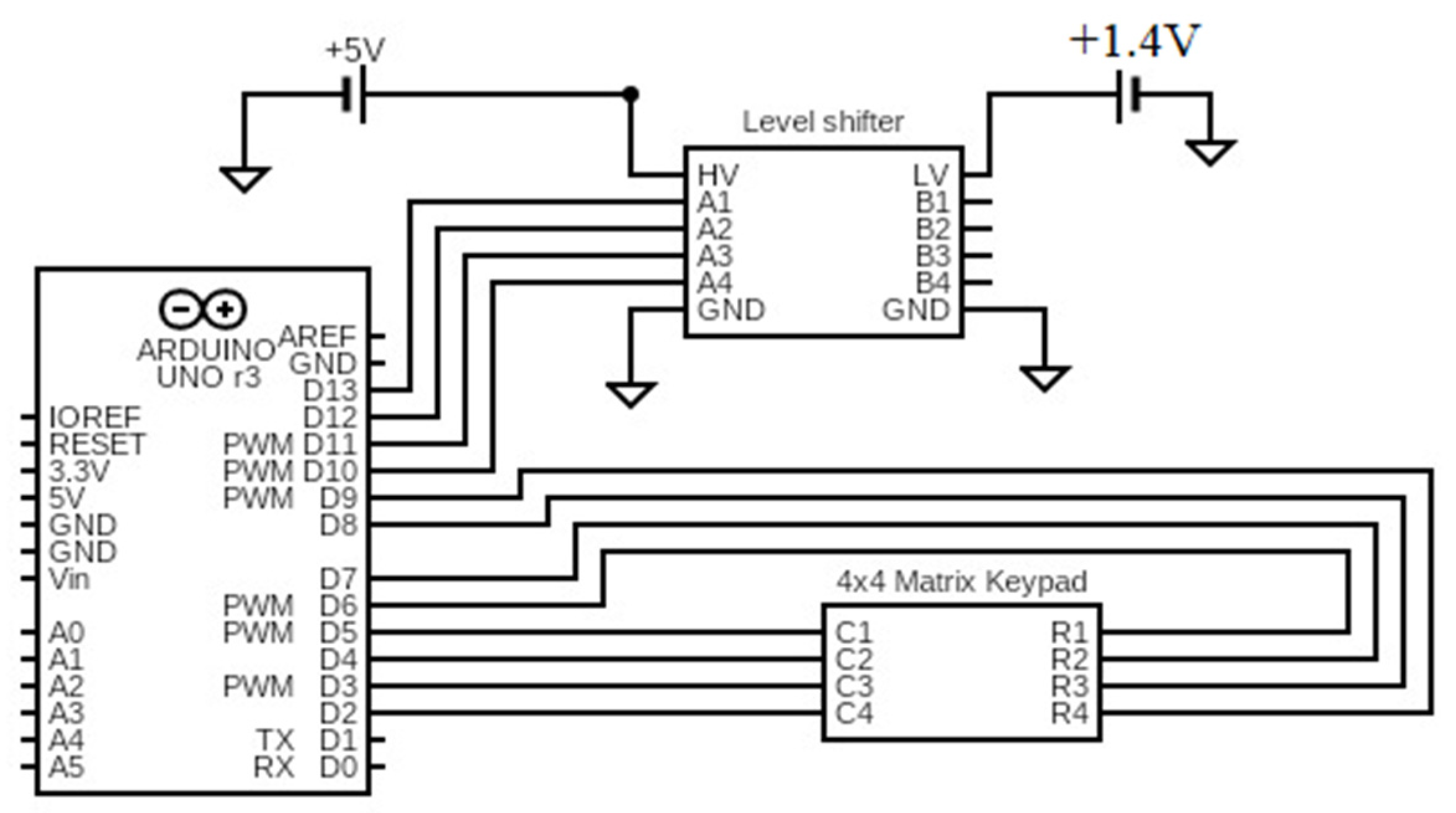
2.3. Switch Controller
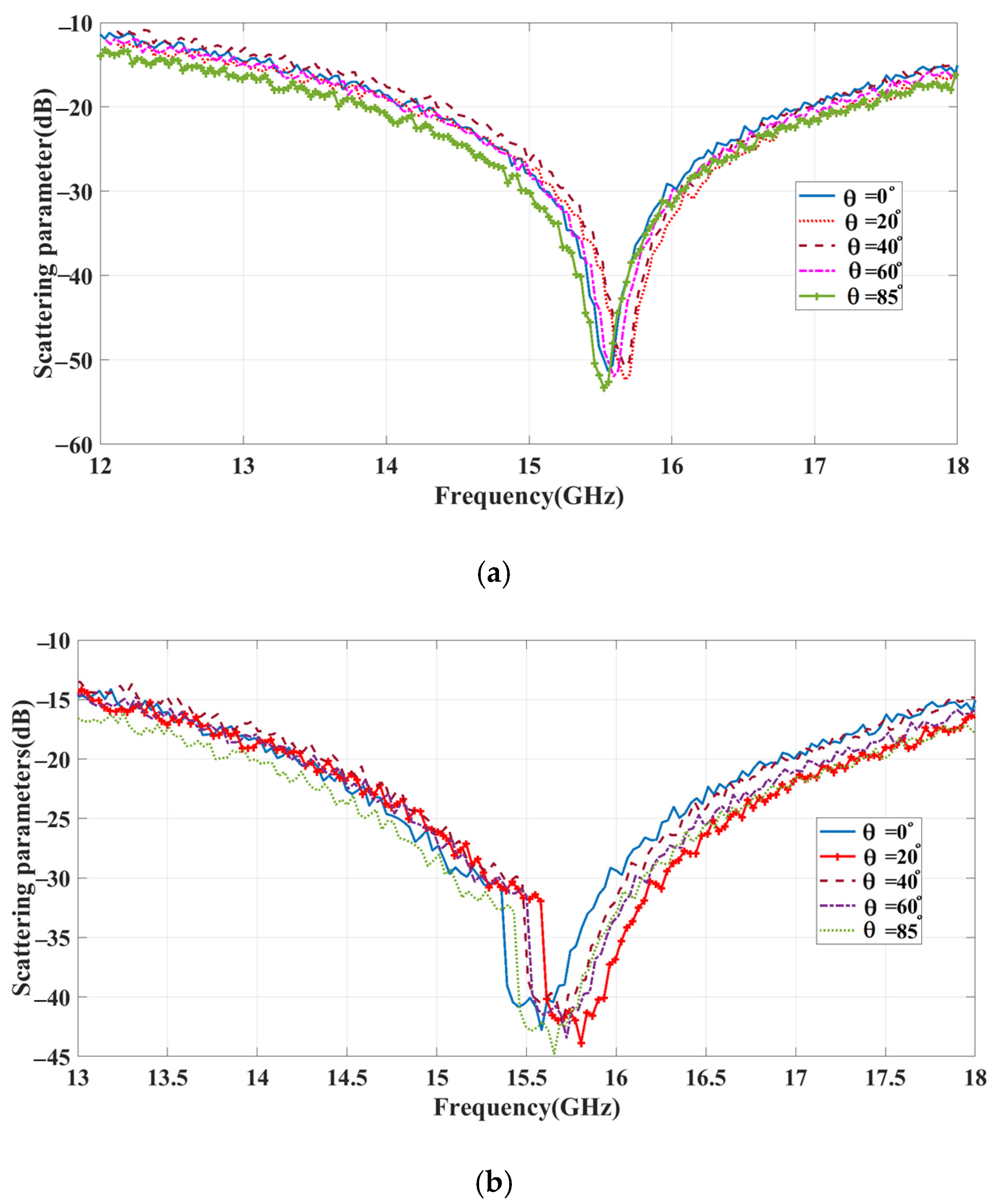
3. Performance Simulation
3.1. First Layer
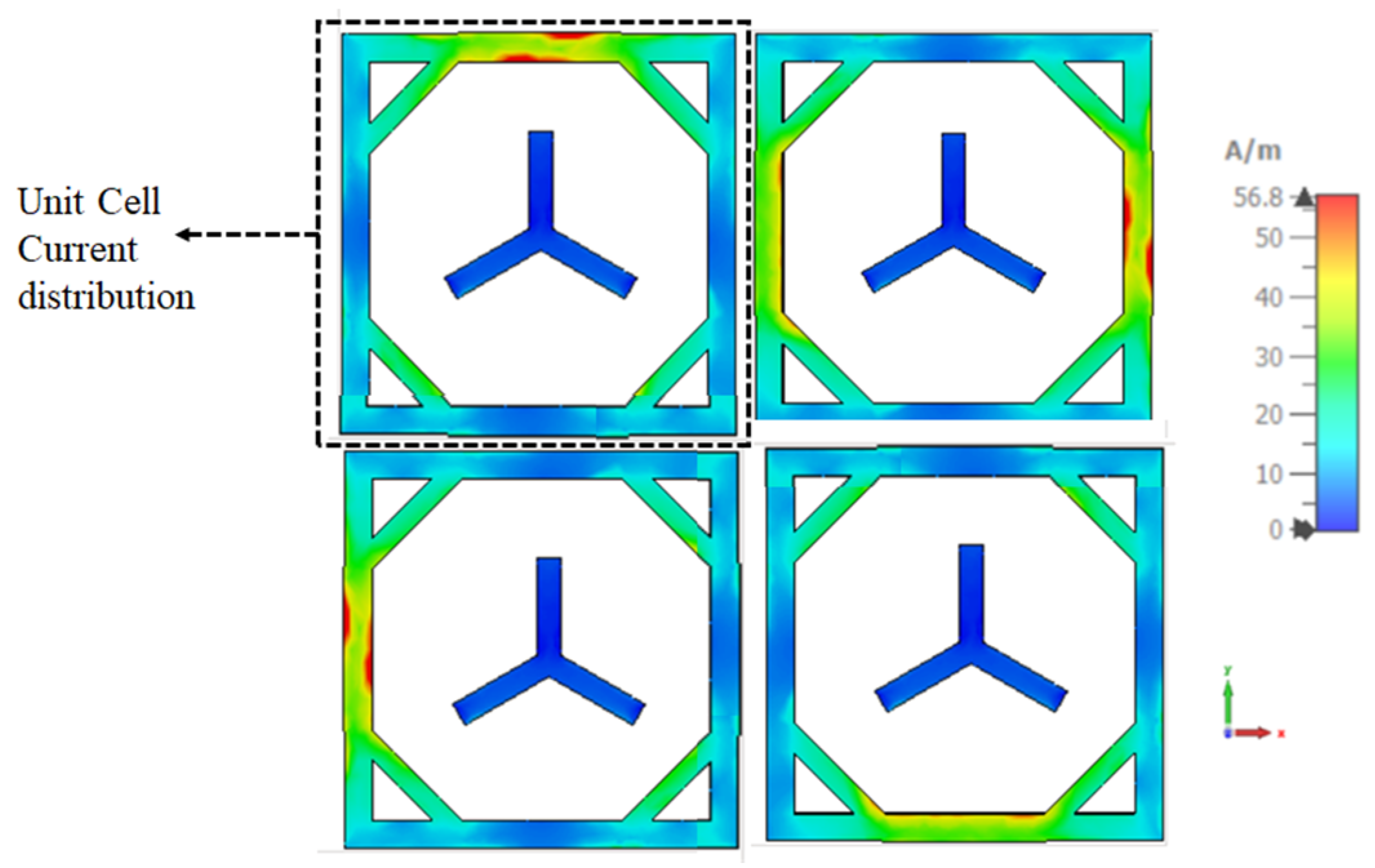
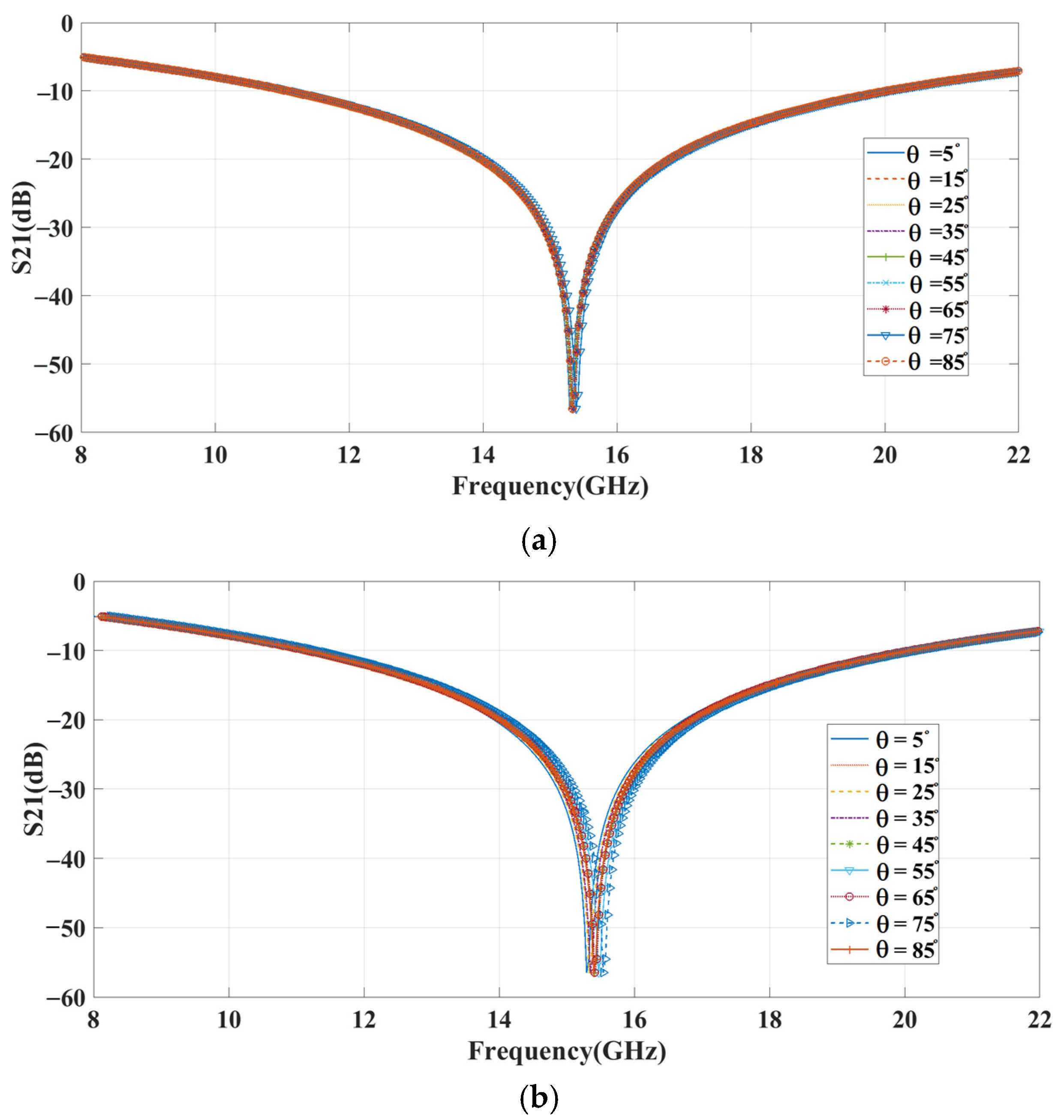
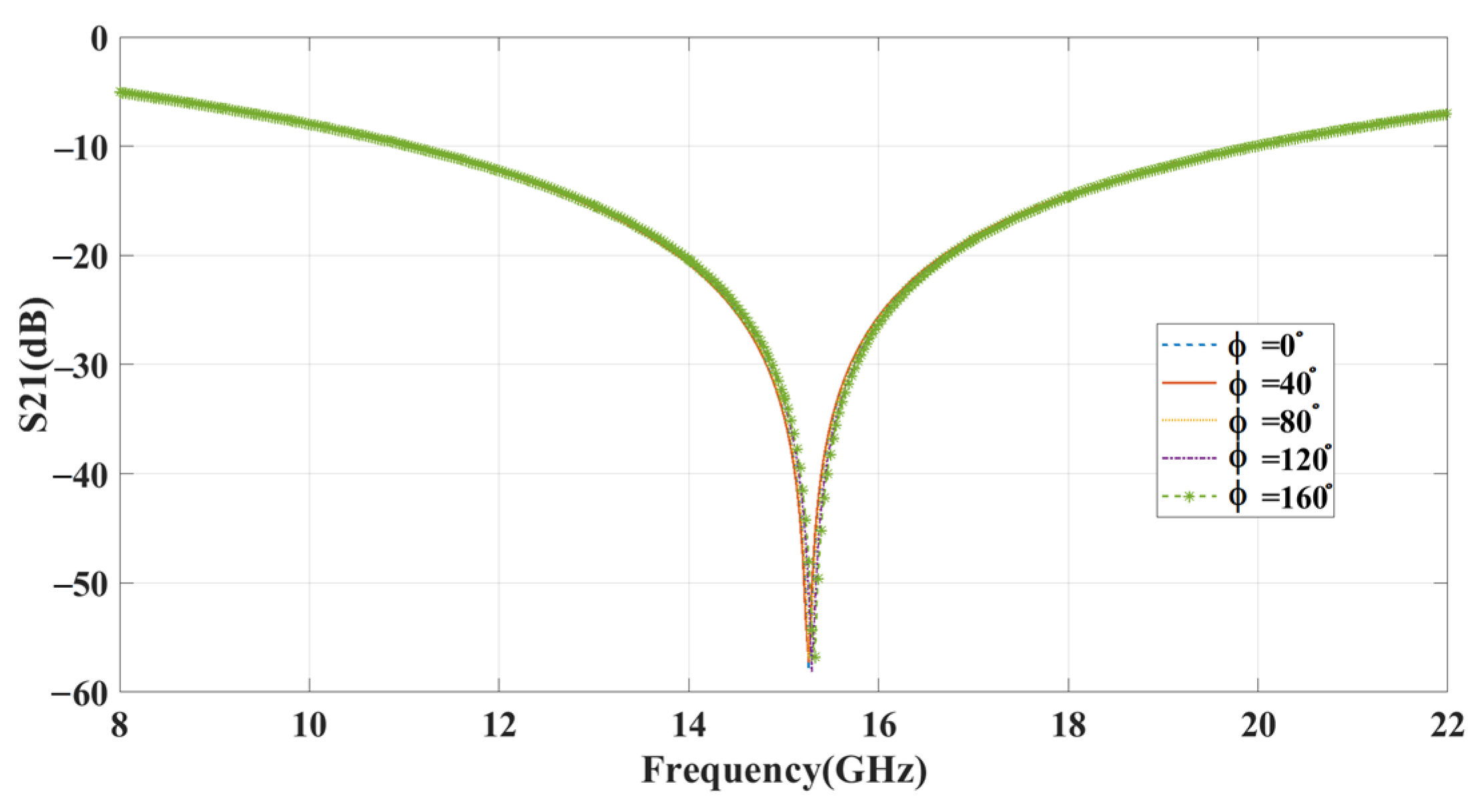
3.1.1. Investigation of Unit Cell
3.1.2. Investigation of Reconfigurable Metasurface
3.2. Second Layer
3.3. Third Layer
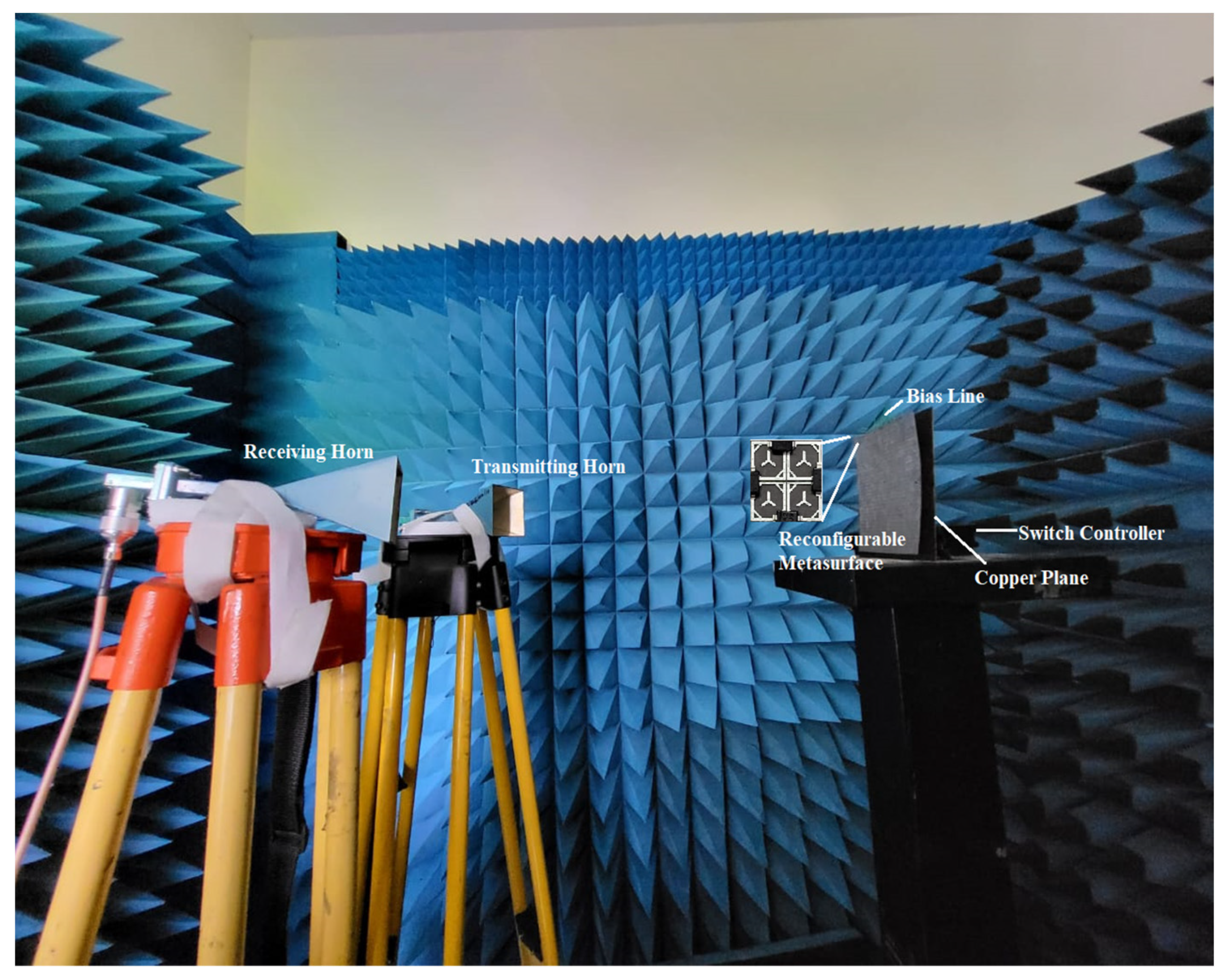
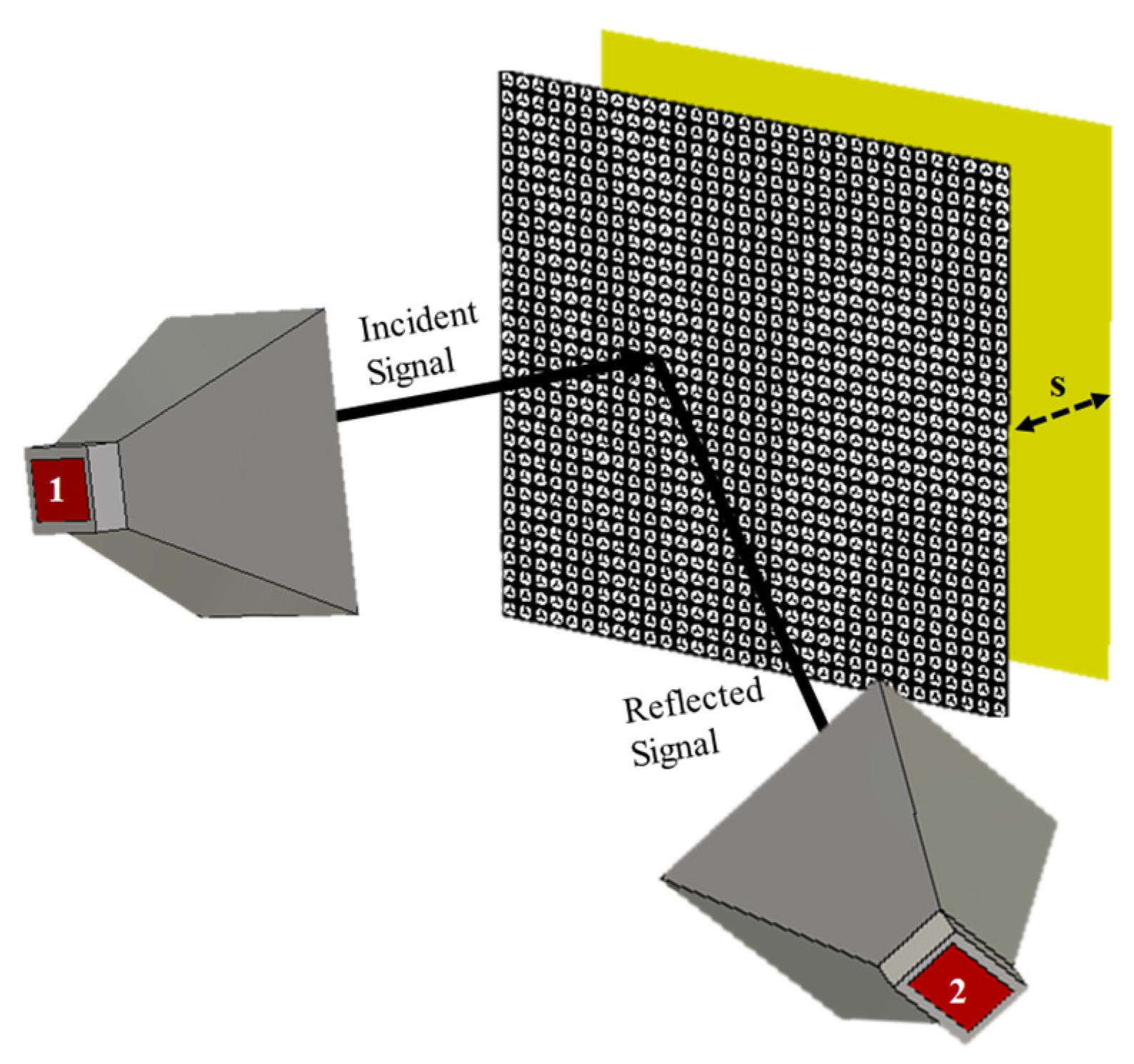
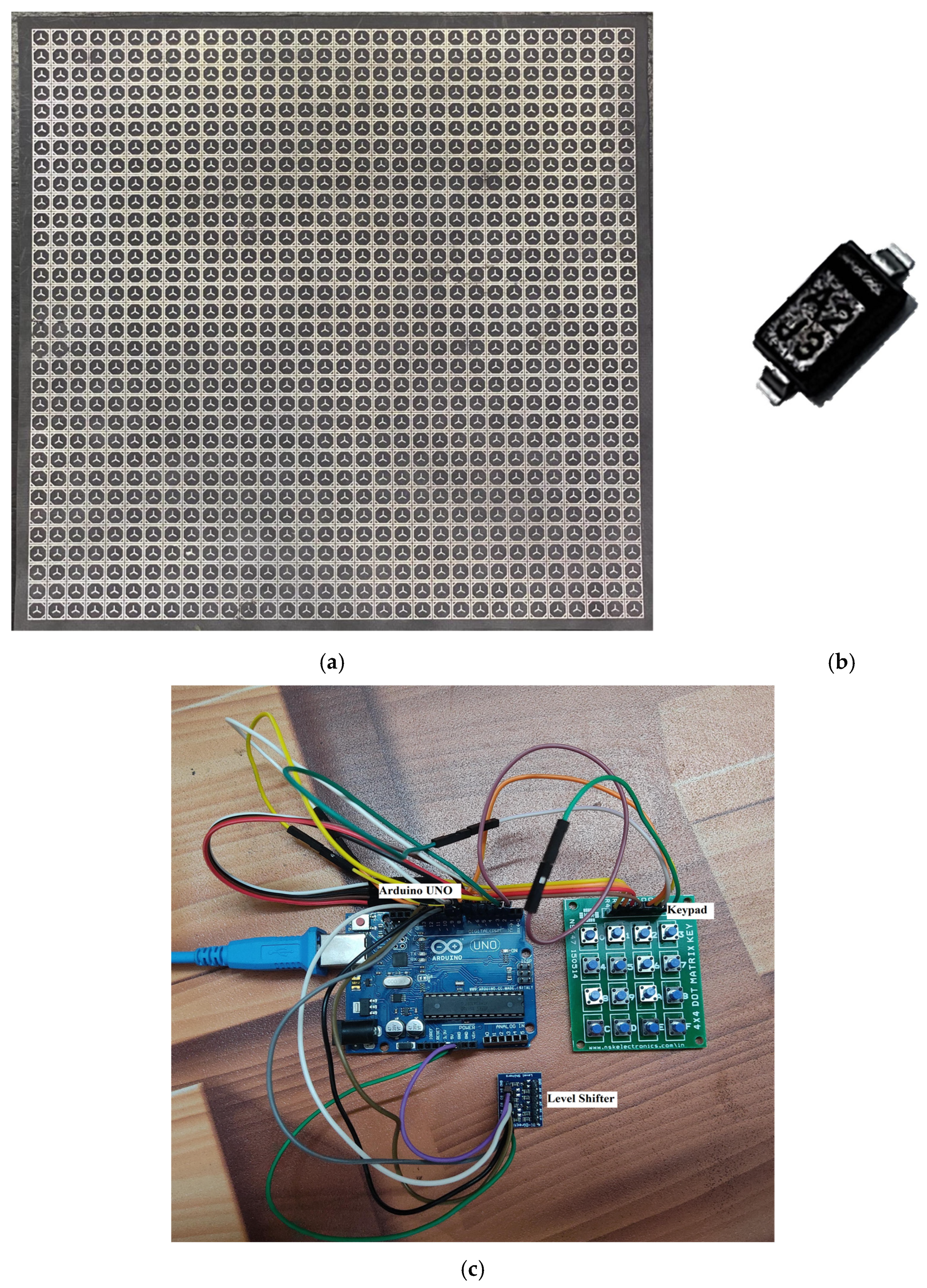
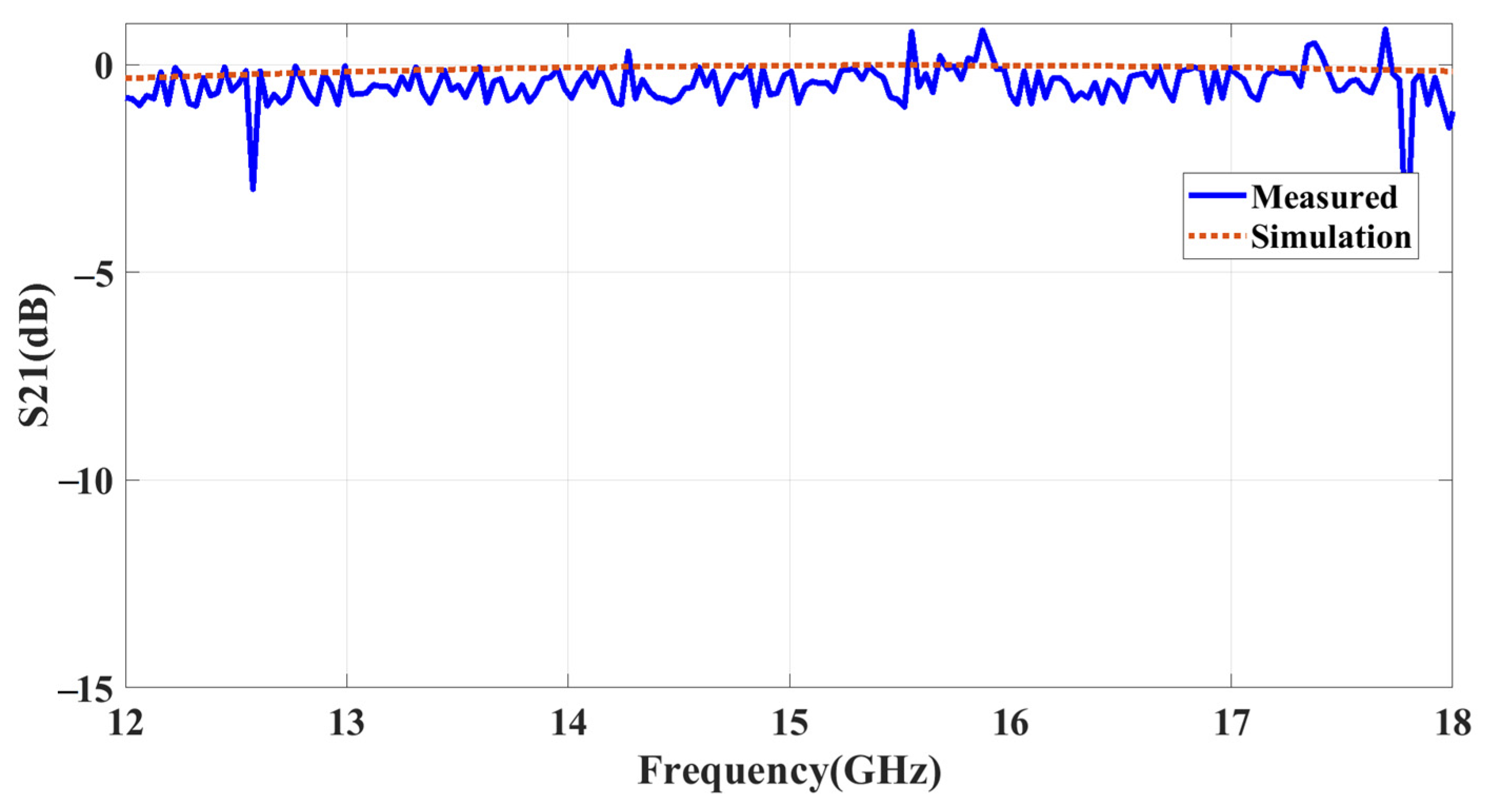
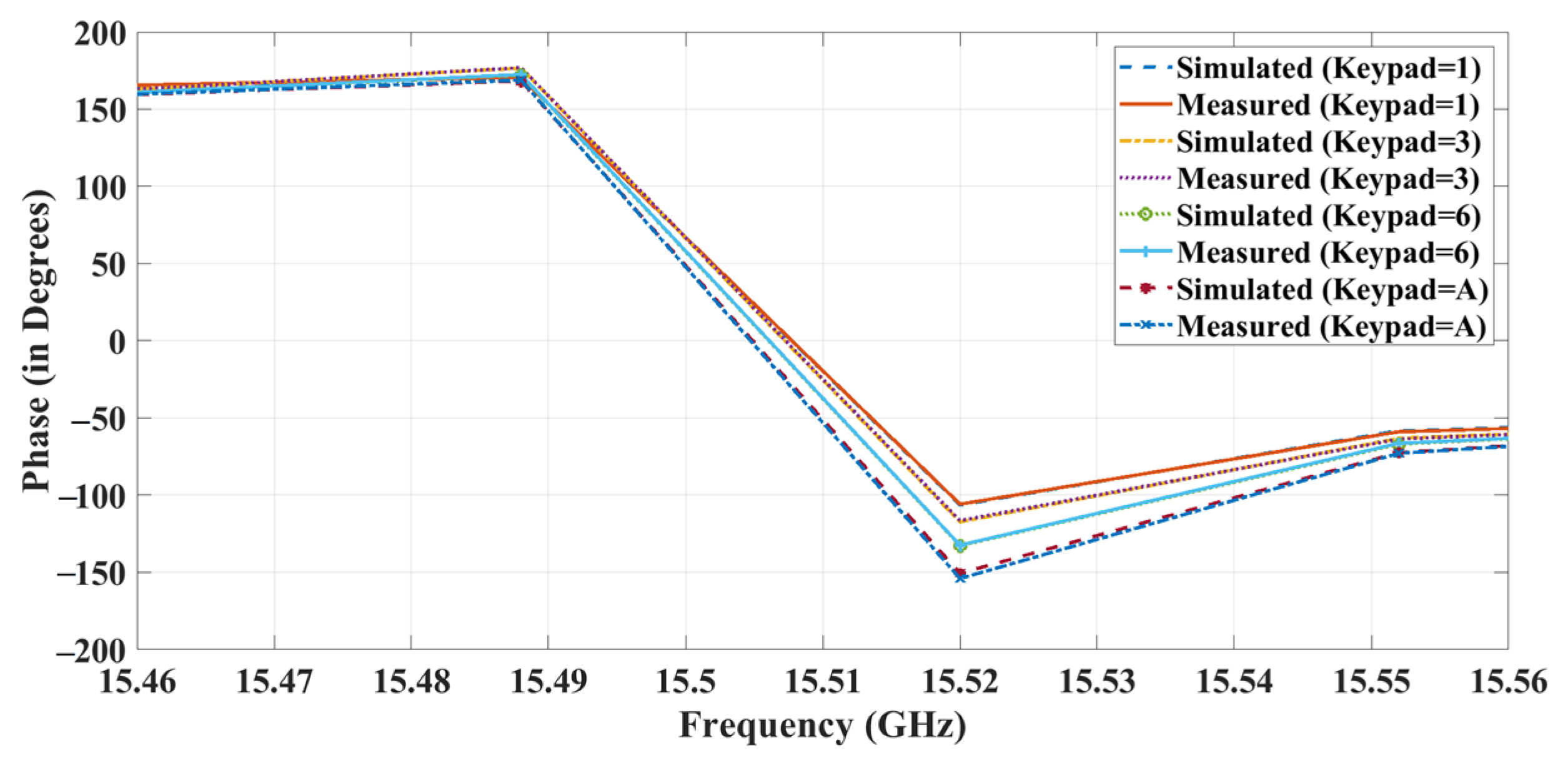
4. Experimental Validation and Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathur, H.; Deepa, T. A survey on advanced multiple access techniques for 5G and beyond wireless communications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 118, 1775–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Han, Y.; Liu, S.; Tao, F.; Zhang, G.; Fu, Z.; Li, C. Several key technologies for 6G: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2021, 5, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, E.; Mishra, K.V.; Soltanalian, M. IRS-aided radar: Enhanced target parameter estimation via intelligent reflecting surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Trondheim, Norway, 20–23 June 2022; pp. 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Weidong, M.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless networks: From single-reflection to multireflection design and optimization. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1380–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, L.; Niu, H.; An, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Al-Dhahir, N. Pain Without Gain: Destructive Beamforming from a Malicious RIS Perspective in IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Lin, Z.; Niu, H.; An, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Zheng, G.; Al-Dhahir, N. Secure satellite transmission with active reconfigurable intelligent surface. IEEE Commun. Lett 2022, 26, 3029–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, H.; An, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Chatzinotas, S.; Hu, Y. Refracting RIS-aided hybrid satellite-terrestrial relay networks: Joint beamforming design and optimization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehao, N.; Lin, Z.; An, K.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Wong, K.-K. Active RIS assisted rate-splitting multiple access network: Spectral and energy efficiency tradeoff. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 1452–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Holloway, C.L.; Mohamed, M.A.; Kuester, E.F.; Dienstfrey, A. Reflection and transmission properties of a metafilm: With an application to a controllable surface composed of resonant particles. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2005, 47, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.T.; Qi, M.Q.; Wan, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Q. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e218. [Google Scholar]
- Nadège, K.; Dupré, M.; Fink, M.; Lerosey, G. Hybridized resonances to design tunable binary phase metasurface unit cells. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 18881–18888. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.G.; Stephens, M.L. Distortion in variable-capacitance diodes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1975, 10, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievenpiper, D.F.; Schaffner, J.H.; Song, H.J.; Loo, R.Y.; Tangonan, G. Two-dimensional beam steering using an electrically tunable impedance surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2003, 51, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Khalily, M.; Safaei, M.; Bagheri, A.; Singh, V.; Wang, F.; Tafazolli, R. Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) in the sub-6 GHz band: Design, implementation, and real-world demonstration. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, X.; Yin, H.; Tan, L.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Bjornson, E. RIS-aided wireless communications: Prototyping, adaptive beamforming, and indoor/outdoor field trials. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 8627–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.G.; Xiao, P.; Cerqueira, A. A 2-bit tunable unit cell for 6G reconfigurable intelligent surface application. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Madrid, Spain, 27 March–1 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, F.; Ratajczak, P.; Phan-Huy, D.-T.; Ourir, A.; Di Renzo, M.; De Rosny, J. A prototype of reconfigurable intelligent surface with continuous control of the reflection phase. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 29, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tan, J.; Bi, S.; Xu, S.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Di Renzo, M.; et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-based wireless communications: Antenna design, prototyping, and experimental results. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 45913–45923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, J.-B.; Popov, V.; Odit, M.A.; Lenets, V.; Lerosey, G. A reconfigurable intelligent surface at mmWave based on a binary phase tunable metasurface. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, O.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Ren, J. Computer vision-aided reconfigurable intelligent surface-based beam tracking: Prototyping and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchu, L.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y.; Ren, X.; Xu, K.-D.; Yin, Y.-Z.; Shen, M. Design of Low-Cost Single-Layer 2-Bit Reflective Programmable Metasurface Based on Folded Ground. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar]
- Trichopoulos, G.C.; Theofanopoulos, P.; Kashyap, B.; Shekhawat, A.; Modi, A.; Osman, T.; Kumar, S.; Sengar, A.; Chang, A.; Alkhateeb, A. Design and evaluation of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in real-world environment. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2022, 3, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xintu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Mao, C.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, X.Y. High-accuracy reconfigurable intelligent surface using independently controllable methods. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition (iWEM), Guangzhou, China, 7–9 November 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Miftahul, A.M.; Tran, N.M.; Choi, K.W. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided wireless communications: Adaptive beamforming and experimental validations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 147442–147457. [Google Scholar]
- Jungi, J.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, Y.; Wi, S.-H. An improved path-loss model for reconfigurable-intelligent-surface-aided wireless communications and experimental validation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 98065–98078. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Yu, W.; Tang, R.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J. A dual-band reconfigurable intelligent metasurface with beam steering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 24, 245002. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.M.; Saini, J. Multi-band and multi-parameter reconfigurable slotted patch antenna with embedded biasing network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.M.; Saini, J. Dual Frequency Electronically Controlled Radiation Beam Reconfigurable slotted Antenna for Detection of a Stationary or Nonstationary Target. Def. Sci. J. 2020, 70, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Rathod, P. Webinar on 6G Usage Scenarios, Key Capabilities and Potential Technologies. National Telecommunication Institute for Policy Research, Innovation & Training. 2023. Available online: https://www.telecomhall.net/t/webinar-on-6g-usage-scenarios-key-capabilities-and-potential-technologies/25668 (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Unlocking Spectrum Innovations for 5G Advanced and 6G to Support Future Wireless Growth. Available online: https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2023/05/unlocking-spectrum-innovations-for-5g-advanced-and-6g-to-support-future-wireless-growth (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Faruque, M.R.I.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M.T. Tree-shaped fractal meta-surface with left-handed characteristics for absorption application. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2018, 124, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, D.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Mo, J. A miniaturized quad-stopband frequency selective surface with convoluted and interdigitated stripe based on equivalent circuit model analysis. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar]
- Karvounis, A.; Gholipour, B.; MacDonald, K.F.; Zheludev, N.I. All-dielectric phase-change reconfigurable metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

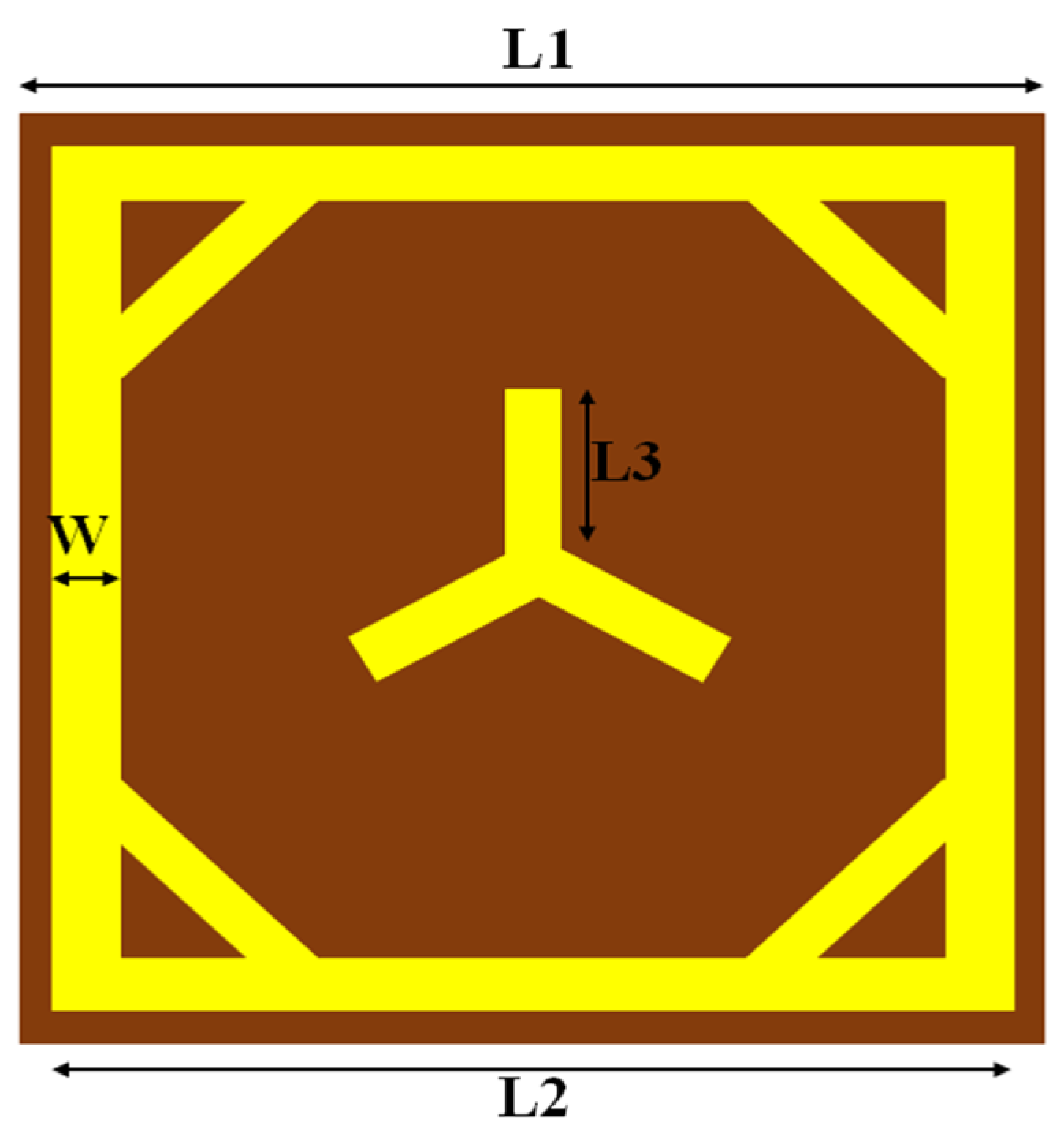






| Parameter | L1 | L2 | W | L3 | t |
| Dimensions (mm) | 4.5 | 4.3 | 0.3 | 1.075 | 0.508 |
| State | Frequency (GHz) | Phase Change (In Degrees) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15.48 | −102 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15.53 | −106 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 15.53 | −111 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 15.48 | −117 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 14.47 | −123 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 15.48 | −132 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 15.47 | −136 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15.48 | −140 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15.48 | −145 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15.53 | −153 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 15.47 | −157 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 15.48 | −166 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 15.47 | −170 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 15.48 | −180 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 15.48 | −189 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15.53 | −196 |
| Keypad | States | Phase Change (In Degrees) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | ||
| 0 | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | −102 |
| 1 | OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | −106 |
| 2 | OFF | OFF | ON | OFF | −111 |
| 3 | OFF | OFF | ON | ON | −117 |
| 4 | OFF | ON | OFF | OFF | −123 |
| 5 | OFF | ON | OFF | ON | −132 |
| 6 | OFF | ON | ON | OFF | −136 |
| 7 | OFF | ON | ON | ON | −140 |
| 8 | ON | OFF | OFF | OFF | −145 |
| 9 | ON | OFF | OFF | ON | −153 |
| A | ON | OFF | ON | OFF | −157 |
| B | ON | OFF | ON | ON | −166 |
| C | ON | ON | OFF | OFF | −170 |
| D | ON | ON | OFF | ON | −180 |
| E | ON | ON | ON | OFF | −189 |
| F | ON | ON | ON | ON | −196 |
| Keypad | Simulation Results | Experimental Results |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | −102 | −103 |
| 1 | −106 | −105 |
| 2 | −111 | −111 |
| 3 | −117 | −116 |
| 4 | −123 | −125 |
| 5 | −132 | −132 |
| 6 | −136 | −135 |
| 7 | −140 | −140 |
| 8 | −145 | −144 |
| 9 | −153 | −150 |
| A | −157 | −156 |
| B | −166 | −165 |
| C | −170 | −172 |
| D | −180 | −181 |
| E | −189 | −189 |
| F | −196 | −200 |
| Ref. | Unit Cell Type | Layer | Control Mechanism | Angular Stability | Polarization Insensitivity | Coding Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | Patch | Multi-layer | PIN diode | 60° | N/A | 2-bit |
| [19] | Patch | Single layer | PIN diode | N/A | N/A | 2-bit |
| [21] | 2-bit | Multi-layer | Two PIN diode | 60° | N/A | 2-bit |
| [22] | Patch with parasitic patch | Multi-layer | PIN diode | 60° | N/A | 1-bit |
| [23] | 2-bit | Multi-layer | PIN diode | 35° | N/A | 2-bit |
| [24] | Patch | Multi-layer | PIN diode | 50° | N/A | 1-bit |
| [25] | Cross-dipole-shaped | Multi-layer | PIN diode | N/A | N/A | 2-bit |
| This work | Combined loop with tripole | Single Layer | PIN Diode | 85° | Yes | 4-bit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvaraj, M.; Vijay, R.; Anbazhagan, R.; Rengarajan, A. Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications. Sensors 2023, 23, 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229166
Selvaraj M, Vijay R, Anbazhagan R, Rengarajan A. Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications. Sensors. 2023; 23(22):9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229166
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvaraj, Monisha, Ramya Vijay, Rajesh Anbazhagan, and Amirtharajan Rengarajan. 2023. "Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications" Sensors 23, no. 22: 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229166
APA StyleSelvaraj, M., Vijay, R., Anbazhagan, R., & Rengarajan, A. (2023). Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications. Sensors, 23(22), 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229166










