Path Loss Characterization in an Outdoor Corridor Environment for IoT-5G in a Smart Campus University at 850 MHz and 3.5 GHz Frequency Bands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurements Campaign
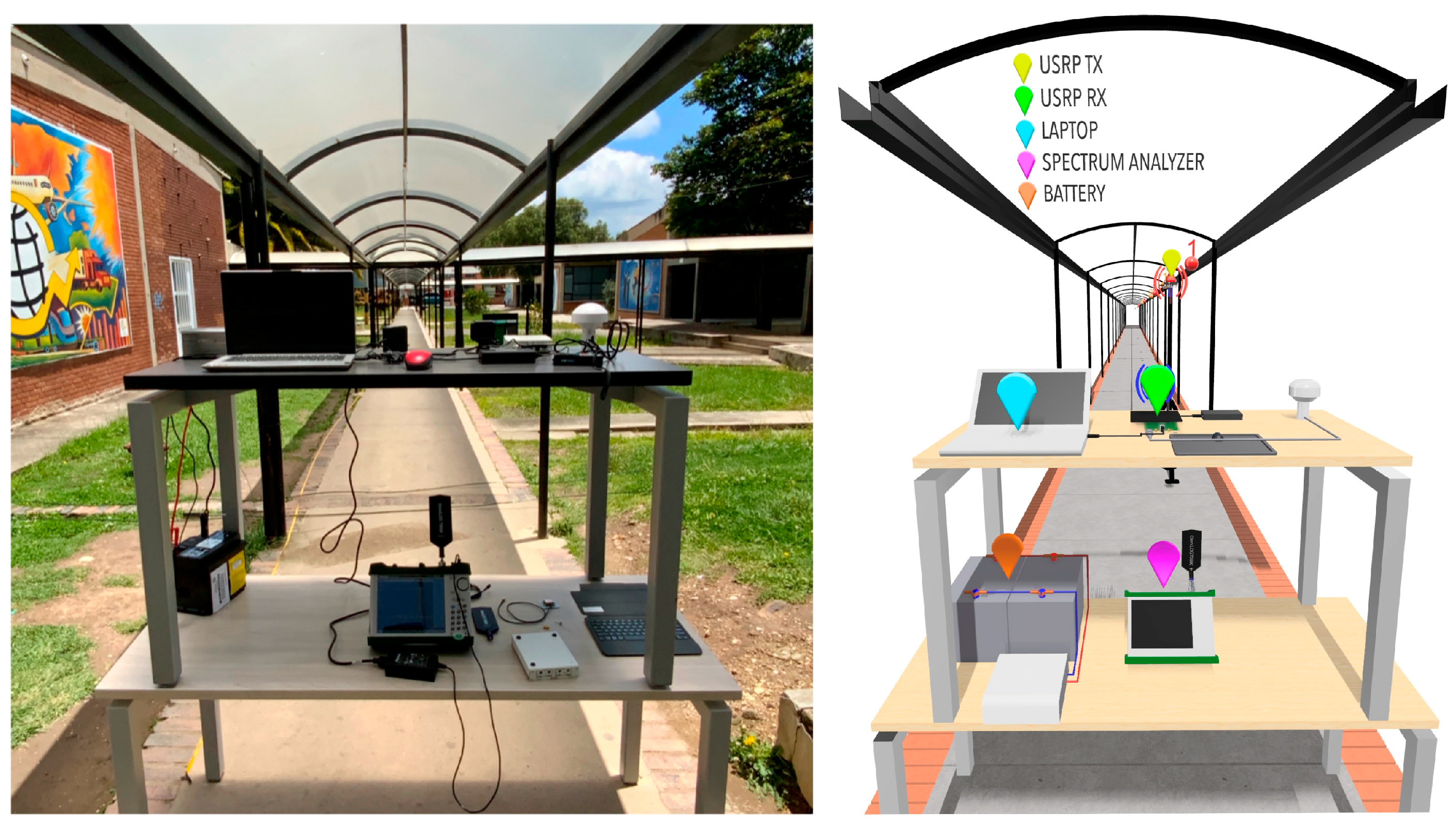
2.1. Propagation Environment
2.2. Equipment and Measurement Setup
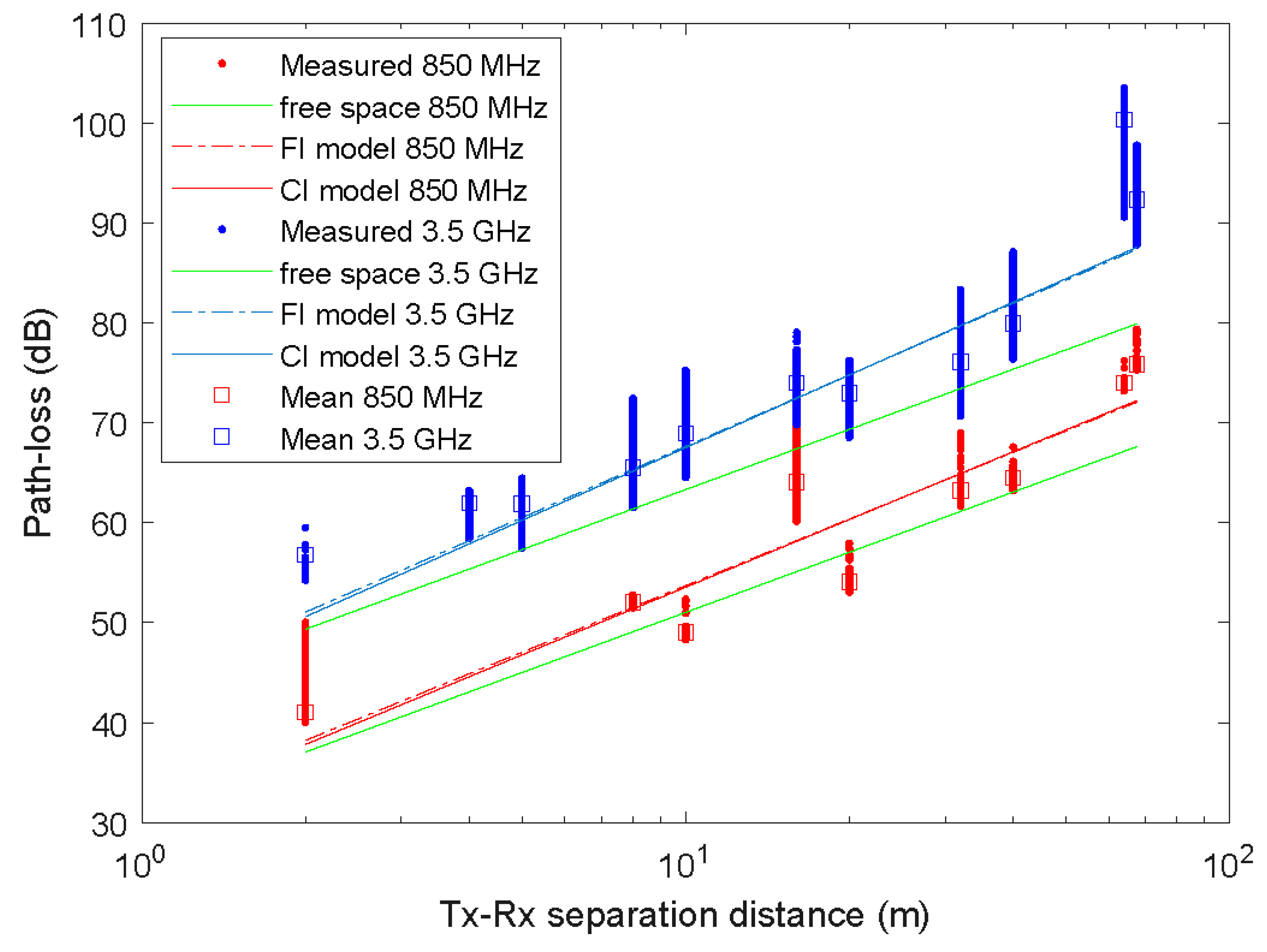
3. Large-Scale Path Loss Models
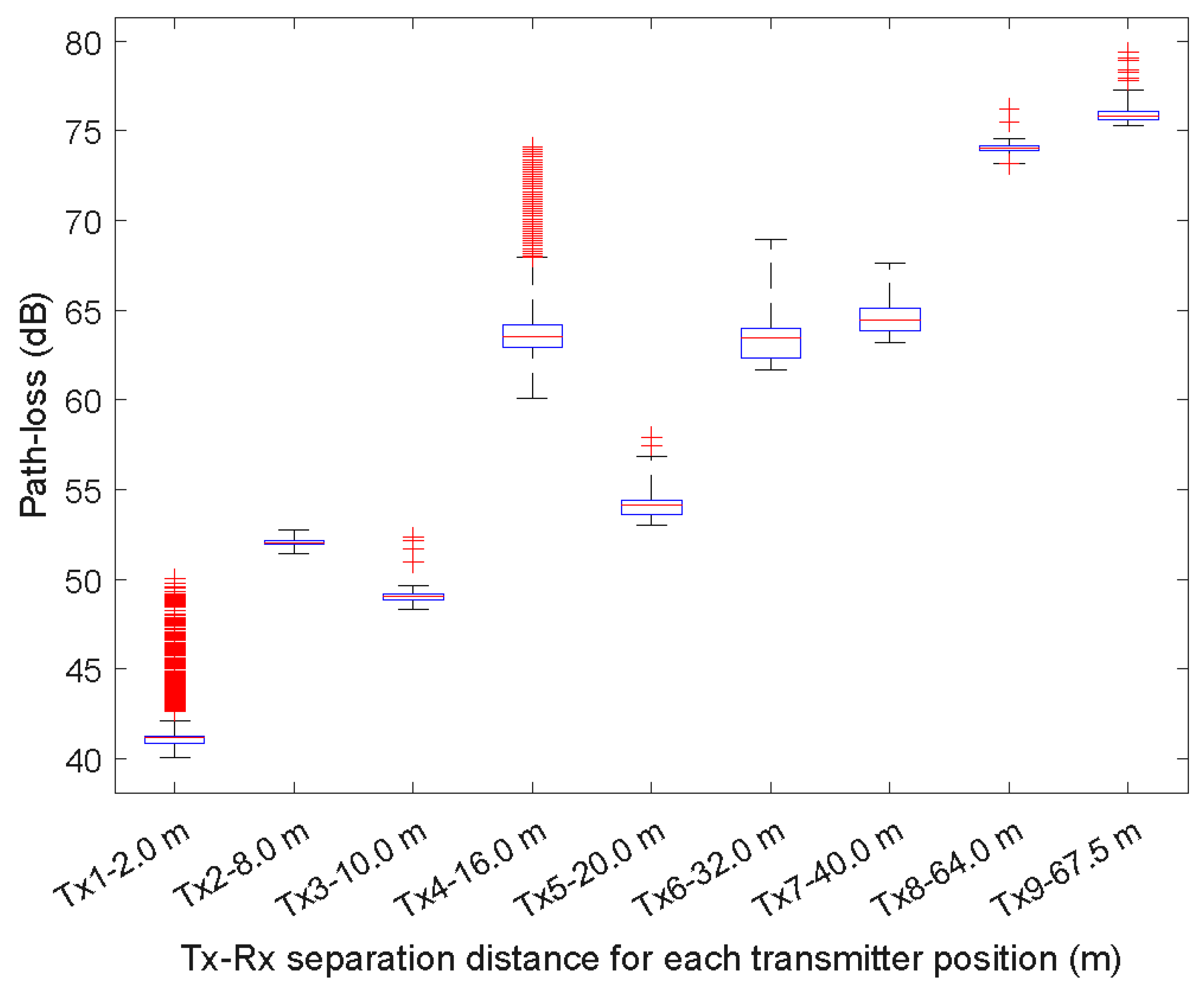
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federal Communications Commission. The FCC’s 5G FAST Plan. Available online: https://www.fcc.gov/5G (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Copyright 2019 5G Americas. 5G Americas White Paper, 5G Spectrum Vision; 5G Americas: Bellevue, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ITU. M.2150: Detailed Specifications of the Terrestrial Radio Interfaces of International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020). Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-M.2150-1-202202-I/en (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Ikpehai, A.; Adebisi, B.; Rabie, K.M.; Anoh, K.; Ande, R.E.; Hammoudeh, M.; Gacanin, H.; Mbanaso, U.M. Low-power wide area network technologies for Internet-of-Things: A comparative review. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 2225–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, K.; Khawaja, B.A.; Sabir, F.; Qazi, S.; Mustaqim, M. Internet of things (IoT) for next-generation smart systems: A review of current challenges, future trends and prospects for emerging 5G-IoT scenarios. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 23022–23040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Xing, Y.C.; MacCartney, G.R.; Molisch, A.F.; Mellios, E.; Zhang, J.H. Overview of Millimeter Wave Communications for Fifth-Generation (5G) Wireless Networks-With a Focus on Propagation Models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6213–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.; Peñarrocha, V.M.R.; Cabedo-Fabres, M.; Bernardo-Clemente, B.; Reig, J.; Fernández, H.; Pérez, J.R.; Torres, R.P.; Valle, L.; Fernández, Ó. Millimeter-Wave Channel Measurements and Path Loss Characterization in a Typical Indoor Office Environment. Electronics 2023, 12, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samman, A.M.; Rahman, T.A.; Azmi, M.H. Indoor corridor wideband radio propagation measurements and channel models for 5G millimeter wave wireless communications at 19 GHz, 28 GHz, and 38 GHz bands. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 6369517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Batalha, I.; Lopes, A.V.R.; Araújo, J.P.L.; Castro, B.L.S.; Barros, F.J.B.; Cavalcante, G.P.D.S.; Pelaes, E.G. Indoor corridor and office propagation measurements and channel models at 8, 9, 10 and 11 GHz. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55005–55021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhik, D.; Du, J.; Feick, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Castro, G.; Valenzuela, R.A. Path loss and directional gain measurements at 28 GHz for non-line-of-sight coverage of indoors with corridors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4820–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezughi, M.K.; Afullo, T.J.; Oyie, N.O. Performance study of path loss models at 14, 18, and 22 GHz in an indoor corridor environment for wireless communications. SAIEE Afr. Res. J. 2021, 112, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, M.A.; Diba, F.D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, D.-Y. Results of Large-Scale Propagation Models in Campus Corridor at 3.7 and 28 GHz. Sensors 2021, 21, 7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAl-Samman, A.M.; Rahman, T.A.; Al-Hadhrami, T.; Daho, A.; Hindia, M.N.; Azmi, M.H.; Dimyati, K.; Alazab, M. Comparative Study of Indoor Propagation Model Below and Above 6 GHz for 5G Wireless Networks. Electronics 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G Americas White Paper, Mid-Band Spectrum Update; 5G Americas: Bellevue, WA, USA, 2023.
- Bouzidi, M.; Mohamed, M.; Dalveren, Y.; Moldsvor, A.; Cheikh, F.A.; Derawi, M. Propagation Measurements for IQRF Network in an Urban Environment. Sensors 2022, 22, 7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.; Sharma, R.P.; Tripathi, S.; Kumar, C.; Ramesh, D. 2.4 GHz RF Received Signal Strength Based Node Separation in WSN Monitoring Infrastructure for Millet and Rice Vegetation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18298–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, G.; Alay, Ö.; De Nardis, L.; Brunstrom, A.; Neri, M.; Di Benedetto, M.-G. Empirical Models for NB-IoT Path Loss in an Urban Scenario. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13774–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Sciancalepore, V.; Banchs, A.; Costa-Pérez, X. LOKO: Localization-Aware Roll-Out Planning for Future Mobile Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 22, 5359–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.R.; Barati, H.; Barati, A. An efficient gray system theory-based routing protocol for energy consumption management in the Internet of Things using fog and cloud computing. Computing 2022, 104, 1307–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.R.; Barati, H.; Barati, A. An overlapping routing approach for sending data from things to the cloud inspired by fog technology in the large-scale IoT ecosystem. Wirel. Netw. 2022, 28, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiamansouri, E.; Barati, H.; Barati, A. A two-level clustering based on fuzzy logic and content-based routing method in the internet of things. Peer Peer Netw. Appl. 2022, 15, 2142–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad, M.A.; Barati, H.; Barati, A. An Authentication-Based Secure Data Aggregation Method in Internet of Things. J. Grid Comput. 2022, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 5G Use Cases | Services | Spectrum–Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| eMMB | Areas with limited connectivity, remote offices, teleworking, commerce, indoor environments, immersive technologies, and public transport. | Low and mid bands Medium and long range |
| mMTC | Massive IoT: smart cities, buildings, sensor networks for agriculture, and industry. | Mid band Medium long range |
| URLLC | Autonomous vehicles, Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), Vehicular-to-Everything (V2X), Industries 4.0, and smart grid. | High bands Short and medium range |
| Model | (dB) | (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FI | 31.55 (31.53–31.58) | 2.215 (2.214–2.217) | 3.959 |
| CI | 31.03 | 2.252 (2.251–2.252) | 3.963 |
| Model | (dB) | (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FI | 43.90 (43.87–43.92) | 2.376 (2.374–2.378) | 4.433 |
| CI | 43.32 | 2.419 (2.418–2.420) | 4.438 |
| Value | Tx1 | Tx2 | Tx3 | Tx4 | Tx5 | Tx6 | Tx7 | Tx8 | Tx9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | 42.13 | 52.75 | 49.63 | 67.97 | 56.84 | 68.95 | 67.59 | 74.56 | 77.26 |
| 75th percentile | 41.30 | 52.19 | 49.18 | 64.21 | 54.43 | 64.01 | 65.11 | 74.14 | 76.07 |
| Median | 41.18 | 52.03 | 49.06 | 63.53 | 54.16 | 63.43 | 64.48 | 74.03 | 75.81 |
| 25th percentile | 40.86 | 51.95 | 48.84 | 62.96 | 53.62 | 62.33 | 63.87 | 73.90 | 75.62 |
| Lower | 40.04 | 51.45 | 48.31 | 60.11 | 53.03 | 61.70 | 63.19 | 41.04 | 75.32 |
| Data points | 94,945 | 94,056 | 97,555 | 97,530 | 97,519 | 97,513 | 97,498 | 97,529 | 97,557 |
| Outliers | 449 | 0 | 5 | 6256 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 7 |
| Value | Tx1 | Tx2 | Tx3 | Tx4 | Tx5 | Tx6 | Tx7 | Tx8 | Tx9 | Tx10 | Tx11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | 56.27 | 63.22 | 63.84 | 67.02 | 70.74 | 76.30 | 76.09 | 77.29 | 82.86 | 103.55 | 97.45 |
| 75th percentile | 54.98 | 60.69 | 60.47 | 63.99 | 67.26 | 72.62 | 71.69 | 74.40 | 78.63 | 100.71 | 91.30 |
| Median | 54.65 | 59.67 | 60.14 | 63.40 | 66.74 | 71.97 | 70.72 | 74.01 | 77.82 | 98.63 | 90.15 |
| 25th percentile | 54.50 | 59.21 | 59.34 | 62.98 | 66.10 | 71.36 | 70.22 | 73.43 | 77.22 | 96.12 | 89.25 |
| Lower | 54.21 | 58.41 | 57.46 | 61.45 | 64.54 | 69.78 | 68.55 | 70.66 | 76.36 | 90.58 | 87.78 |
| Data points | 97,517 | 93,222 | 97,578 | 93,922 | 94,012 | 97,517 | 97,516 | 97,462 | 97,496 | 73,337 | 94,340 |
| Outliers | 19 | 0 | 7 | 653 | 2681 | 48 | 6 | 2914 | 802 | 0 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz, J.; Mancipe, D.; Fernández, H.; Rubio, L.; Rodrigo Peñarrocha, V.M.; Reig, J. Path Loss Characterization in an Outdoor Corridor Environment for IoT-5G in a Smart Campus University at 850 MHz and 3.5 GHz Frequency Bands. Sensors 2023, 23, 9237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229237
Muñoz J, Mancipe D, Fernández H, Rubio L, Rodrigo Peñarrocha VM, Reig J. Path Loss Characterization in an Outdoor Corridor Environment for IoT-5G in a Smart Campus University at 850 MHz and 3.5 GHz Frequency Bands. Sensors. 2023; 23(22):9237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229237
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz, Juan, David Mancipe, Herman Fernández, Lorenzo Rubio, Vicent M. Rodrigo Peñarrocha, and Juan Reig. 2023. "Path Loss Characterization in an Outdoor Corridor Environment for IoT-5G in a Smart Campus University at 850 MHz and 3.5 GHz Frequency Bands" Sensors 23, no. 22: 9237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229237
APA StyleMuñoz, J., Mancipe, D., Fernández, H., Rubio, L., Rodrigo Peñarrocha, V. M., & Reig, J. (2023). Path Loss Characterization in an Outdoor Corridor Environment for IoT-5G in a Smart Campus University at 850 MHz and 3.5 GHz Frequency Bands. Sensors, 23(22), 9237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229237









