Highly Stable Spatio-Temporal Prediction Network of Wavefront Sensor Slopes in Adaptive Optics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
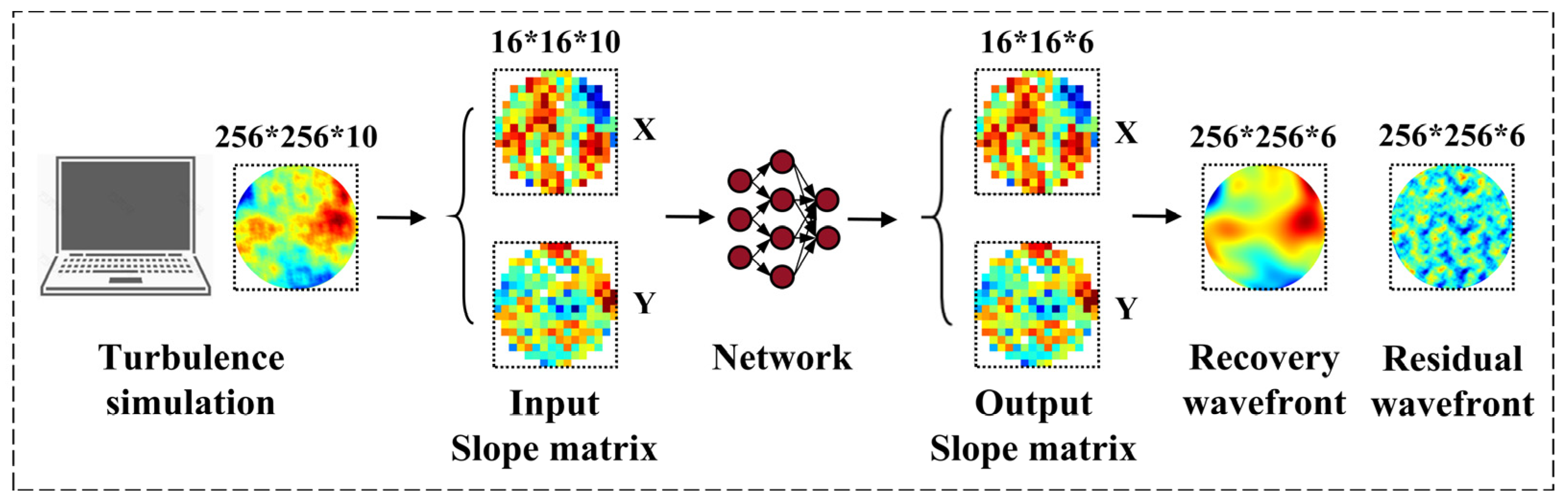
2. Methodology
2.1. Atmospheric Turbulence Data Set Generation
2.2. Network Model Settings
3. Results and Discussion
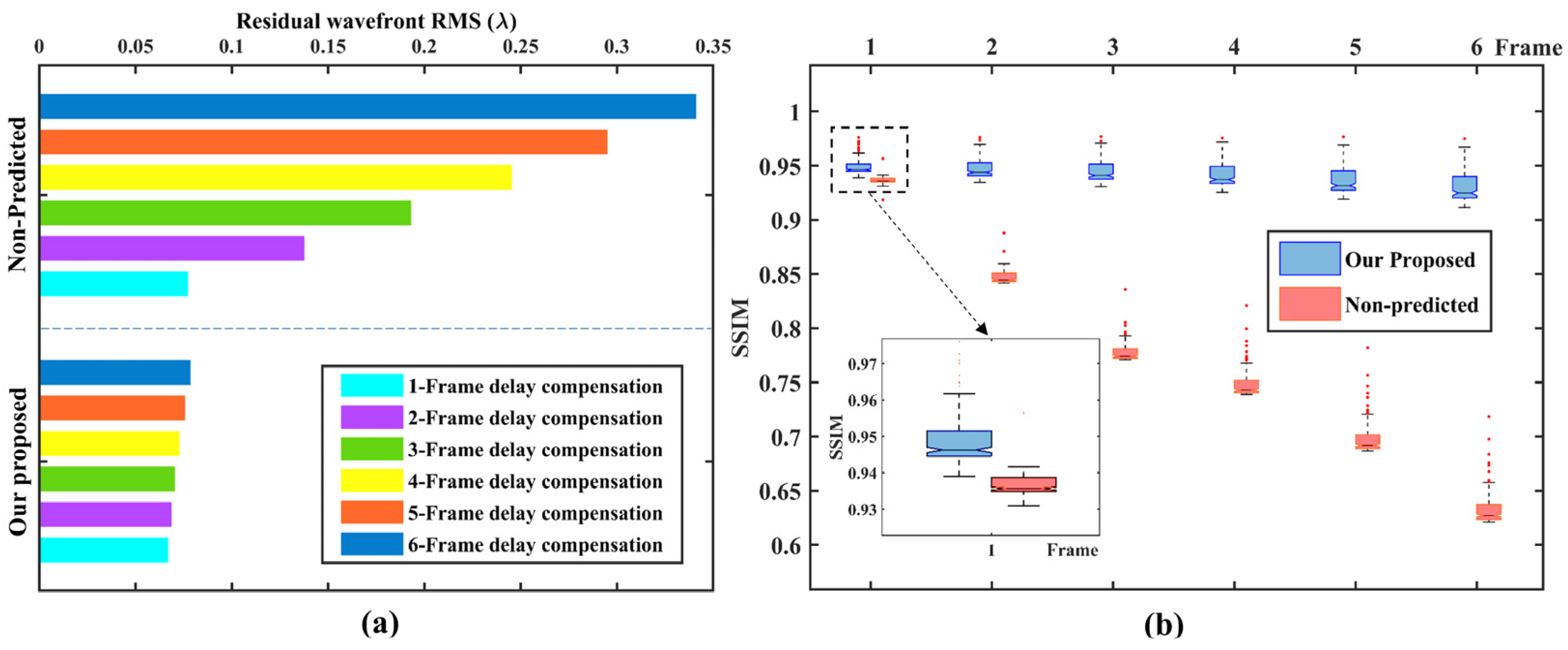
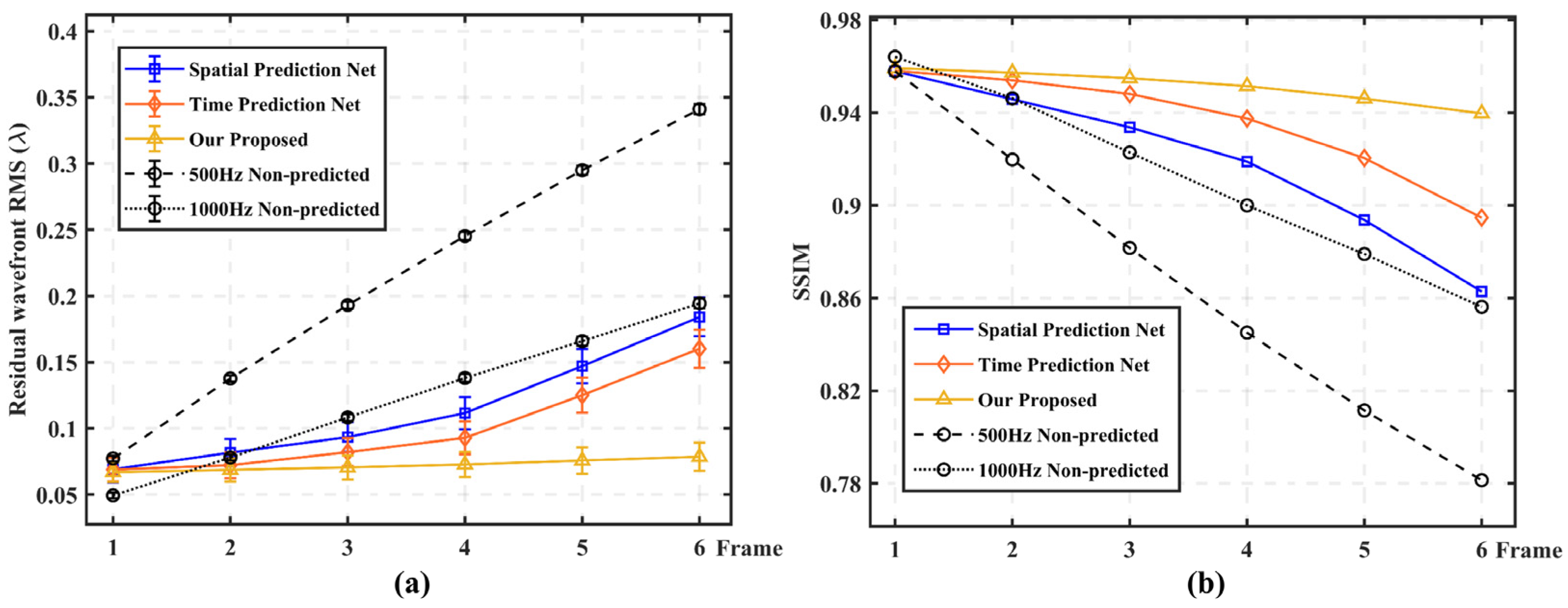
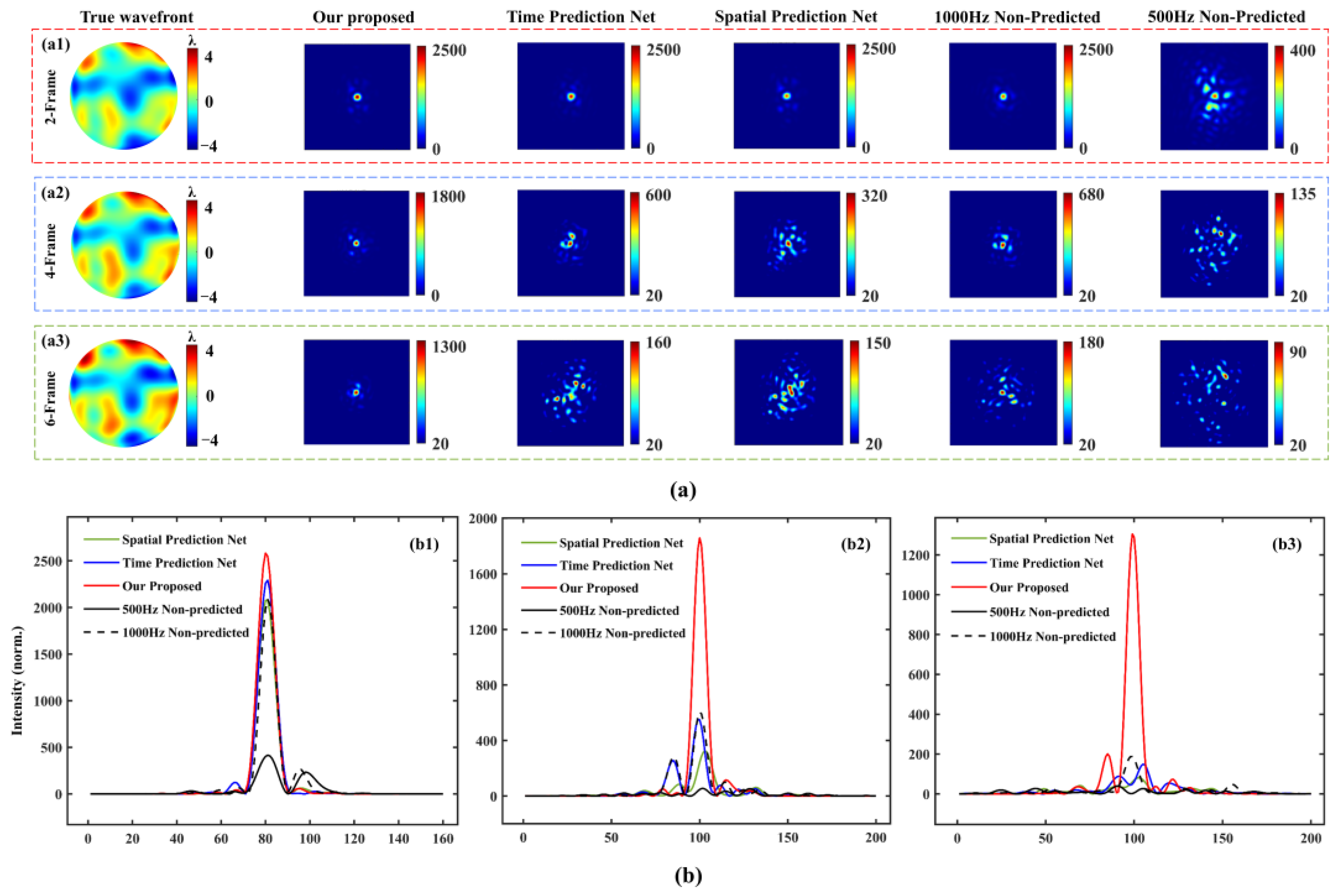
3.1. Simulation Data Analysis
- i.
- RMSe: Residual wavefront RMS;
- ii.
- SSIM: Structural similarity index.
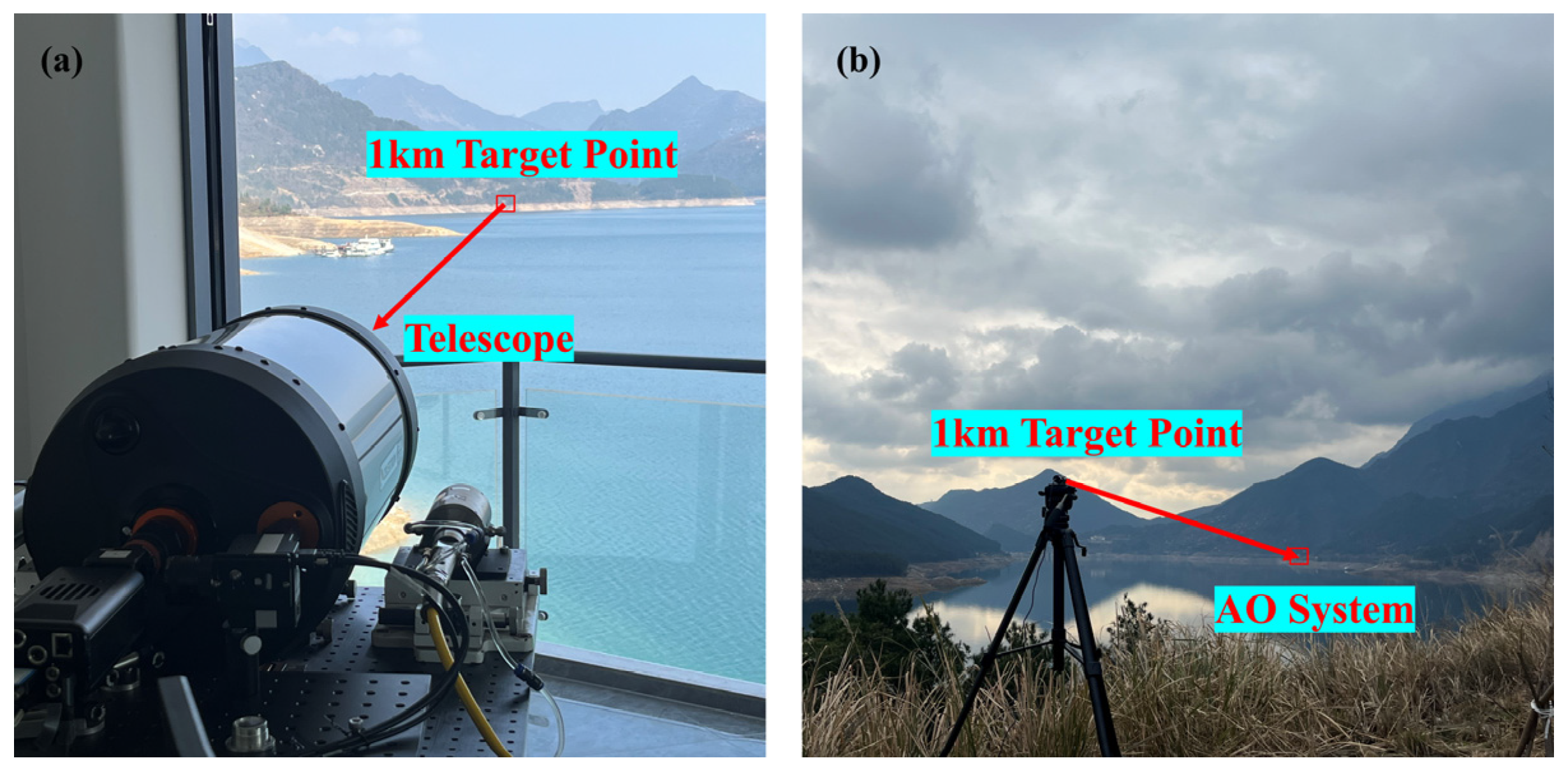
3.2. Experimental Data Verification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fried, D.L. Time-delay-induced mean-square error in adaptive optics. JOSA A 1990, 7, 1224–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivo, G.; Kulcsár, C.; Conan, J.M. First on-sky SCAO validation of full LQG control with vibration mitigation on the CANARY pathfinder. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 23565–23591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcsár, C.; Raynaud, H.F.; Petit, C.; Conan, J.M. Minimum variance prediction and control for adaptive optics. Automatica 2012, 48, 1939–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Effective bandwidth analysis of adaptive optics control system. Acta Opt. Sin. 1997, 17, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Analysis of the residual servo variance for an adaptive optics system. Acta Opt. Sin. 2000, 20, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Page, K.A.; Schöck, M. Analysis of atmospheric turbulence with applications to linear predictions. Eur. South. Obs. Conf. Workshop Proc. 2002, 58, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Rao, C. Numerical simulation of a prediction control algorithm for close-loop adaptive optical system. Acta Opt. 2011, 31, 0101003. [Google Scholar]
- Beghi, A.; Cenedese, A.; Masiero, A. Atmospheric turbulence prediction: A PCA approach. In Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 566–571. [Google Scholar]
- Fraanje, R.; Doelman, N. Modeling and prediction of turbulence induced wavefront distortions. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 June–2 July 2010; Volume 7736, pp. 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, C.; Raynaud, H.F.; Kulcsár, C.; Conan, J.M. On the optimal reconstruction and control of adaptive optical systems with mirror dynamics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2010, 27, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, D.M.; Max, C.E.; Gavel, D.T. A spatial non-dynamic LQG controller: Part I, Application to adaptive optics. In Proceedings of the 2004 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37601), Nassau, Bahamas, 14–17 December 2004; pp. 3326–3332. [Google Scholar]
- Wiberg, D.M.; Max, C.E.; Gavel, D.T. A spatial non-dynamic LQG controller: Part II, theory. In Proceedings of the 2004 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37601), Nassau, Bahamas, 14–17 December 2004; pp. 3333–3338. [Google Scholar]
- Looze, D.P. Linear-quadratic-Gaussian control for adaptive optics systems using a hybrid model. JOSA A 2009, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Quiros-Pacheco, F.; Conan, J.M.; Kulcsar, C.; Raynaud, H.F.; Fusco, T.; Rousset, G. Kalman-filter-based control for adaptive optics. In Advancements in Adaptive Optics; SPIE Digital Library: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 1414–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M.; Petit, C.; Rodionov, S.; Bocquet, M.; Bertino, L.; Ferrari, M.; Fusco, T. Local ensemble transform Kalman filter, a fast non-stationary control law for adaptive optics on ELTs: Theoretical aspects and first simulation results. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 20894–20913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.P.; Norris, B.R.; Tuthill, P.G.; Scalzo, R.; Lozi, J.; Vievard, S.; Guyon, O. Predictive control for adaptive optics using neural networks. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2021, 7, 019001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Guo, S.; Wang, N.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, P. Research Progress of Laser Adaptive Optics Based on Machine Learning. Chin. J. Lasers 2023, 50, 1101008. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Li, X. Neural network prediction algorithm for control voltage of deformable mirror in adaptive optical system. Acta Opt. Sin. 2010, 30, 911–916. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Z.; Li, X. Predicting control voltages of deformable mirror in adaptive optical system. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2012, 24, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, S. Analysis and demonstration of PID algorithm based on arranging the transient process for adaptive optics. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2013, 11, 110101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Morris, T.; Saunter, C.; de Cos Juez, F.J.; González-Gutiérrez, C.; Bardou, L. Wavefront prediction using artificial neural networks for open loop adaptive optics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Shah, V.; Liu, L. Performance of a U-Net-based neural network for predictive adaptive optics. Opt. Letters 2021, 46, 2513–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Ma, S.; Zhao, W.; Ge, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, P. Deep Learning-Based Prediction Algorithm on Atmospheric Turbulence Induced Wavefront for Adaptive Optics. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Di, J.; Hu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J. PredictionNet: A long short-term memory-based attention network for atmospheric turbulence prediction in adaptive optics. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 3687–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.; Lamb, M.; Correia, C.; Sivanandam, S.; Kutulakos, K. Wavefront reconstruction and prediction with convolutional neuralnetworks. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Austin, TX, USA, 10–15 June 2018; Volume 10703, pp. 481–490. [Google Scholar]
- Schöck, M.; Spillar, E.J. Method for a quantitative investigation of the frozen flow hypothesis. JOSA A 2000, 17, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyneer, L.; van Dam, M.; Véran, J.P. Experimental verification of the frozen flow atmospheric turbulence assumption with use of astronomical adaptive optics telemetry. JOSA A 2009, 26, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, E.; Léna, P. Single layer atmospheric turbulence demonstrated by adaptive optics observations. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1996, 239, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, B.; Laurence, T.A.; Martin, C.; Dimotakis, P.E. Dimotakis. Temporal coherence of individual turbulent patterns in atmospheric seeing. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 4879–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large reynolds numbers. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1991, 434, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K.; Woo, W.C. Convolutional lstm network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]





| Methods | 4-Frame Delay | 6-Frame Delay | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Hz Non-predicted | Our proposed | 70.0% | 76.8% |
| Spatial Prediction Net | 54.3% | 62.0% | |
| Time Prediction Net | 46.0% | 53.1% | |
| 1000 Hz Non-predicted | Our proposed | 47.1% | 59.3% |
| Spatial Prediction Net | 18.8% | 32.6% | |
| Time Prediction Net | 5.2% | 17.5% |
| Simulation Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 0.28 m |
| SHWS lens let array | 16 × 16 |
| CCD | 256 × 256 pixels |
| Wavelength | 1064 nm |
| r0 | 1.49 cm |
| Wind Speeds | 3.0–5.5 m/s |
| Wind Directions | R [0–360°] |
| Transmit/Receive Altitude | 10 m |
| Transmission Distance | 1 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, Q.; Ge, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, P. Highly Stable Spatio-Temporal Prediction Network of Wavefront Sensor Slopes in Adaptive Optics. Sensors 2023, 23, 9260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229260
Wang N, Zhu L, Yuan Q, Ge X, Gao Z, Wang S, Yang P. Highly Stable Spatio-Temporal Prediction Network of Wavefront Sensor Slopes in Adaptive Optics. Sensors. 2023; 23(22):9260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Licheng Zhu, Qiang Yuan, Xinlan Ge, Zeyu Gao, Shuai Wang, and Ping Yang. 2023. "Highly Stable Spatio-Temporal Prediction Network of Wavefront Sensor Slopes in Adaptive Optics" Sensors 23, no. 22: 9260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229260
APA StyleWang, N., Zhu, L., Yuan, Q., Ge, X., Gao, Z., Wang, S., & Yang, P. (2023). Highly Stable Spatio-Temporal Prediction Network of Wavefront Sensor Slopes in Adaptive Optics. Sensors, 23(22), 9260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229260








