3D Scanner-Based Identification of Welding Defects—Clustering the Results of Point Cloud Alignment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A comprehensive discussion of the classification of weld defects is made based on image processing and data analysis, including the qualitative variation of each weld defect;
- A methodology is developed for the visualization of weld defects using computer-aided design (CAD) with a results-oriented approach;
- The point clouds processed by the 3D camera and modeled with CAD programs are determined (point feature histogram—PFH); the descriptive characteristics of the points prepares the clouds for coarse (FGR) and fine (ICP) matching;
- The weld defects are detected by density-based clustering (DBSCAN) by sorting the top distance between point pairs, and the clustered errors are aligned to the standard.
2. The Proposed CAD Model-Based Method of Generation and Analysis of Error Distributions
- The prepared welded parts are scanned with the 3D scanner. CAD parts with defects and a reference CAD workpiece are modeled (see Input block on Figure 1) and converted into a point cloud for the training and test set (Section 2.1).
- Sampling generates a point cloud from the models (mesh files) for the validation set (see Cloud points matching block on Figure 1). The point features should be calculated to compare the two point clouds (Section 2.2).
- After computing the point properties, the technique of matching the point clouds using the FGR and ICP algorithms (see Cloud points matching block on Figure 1) is described (Section 2.3).
- The optimal percentile value is selected for PFH to facilitate efficient clustering (see Clustering block on Figure 1). DBSCAN clustering is applied (Section 2.4).
2.1. Training and Validation Datasets
- Modeling the CAD models: is the 3D point-cloud of the masterpiece with () 3D points, where is the number of points; is the 3D point-cloud of the test piece with (), where is the point number in the cloud. For optimal point matching, sampling is required.
- Sampling the resulting point clouds: Sampling is the systematic selection of a relatively small number of representative elements or sub-clouds. After sampling, the point clouds and consisted of the same number of points necessary for a proper fit.
- 1.
- Tray calibration according to the size of the workpiece. The projection grid is projected by the projector onto the surface of the tray, followed by scanning of other details of the background (rotation table).
- 2.
- The flawless workpiece is placed in the center of the tray, adjusting the rotation angle, and the scanning process begins. The three-dimensional model, usually fused from six or seven images, can be exported as a mesh model in various (.stl/.obj) formats.
- 3.
- Since the scanned file is currently a mesh model consisting of 3D points and triangles (called surfaces), a point cloud is created from the models and used as the experimental subject (data source) for the study.
- 4.
- The process is repeated with the workpiece containing the weld defect, with recommended setup.
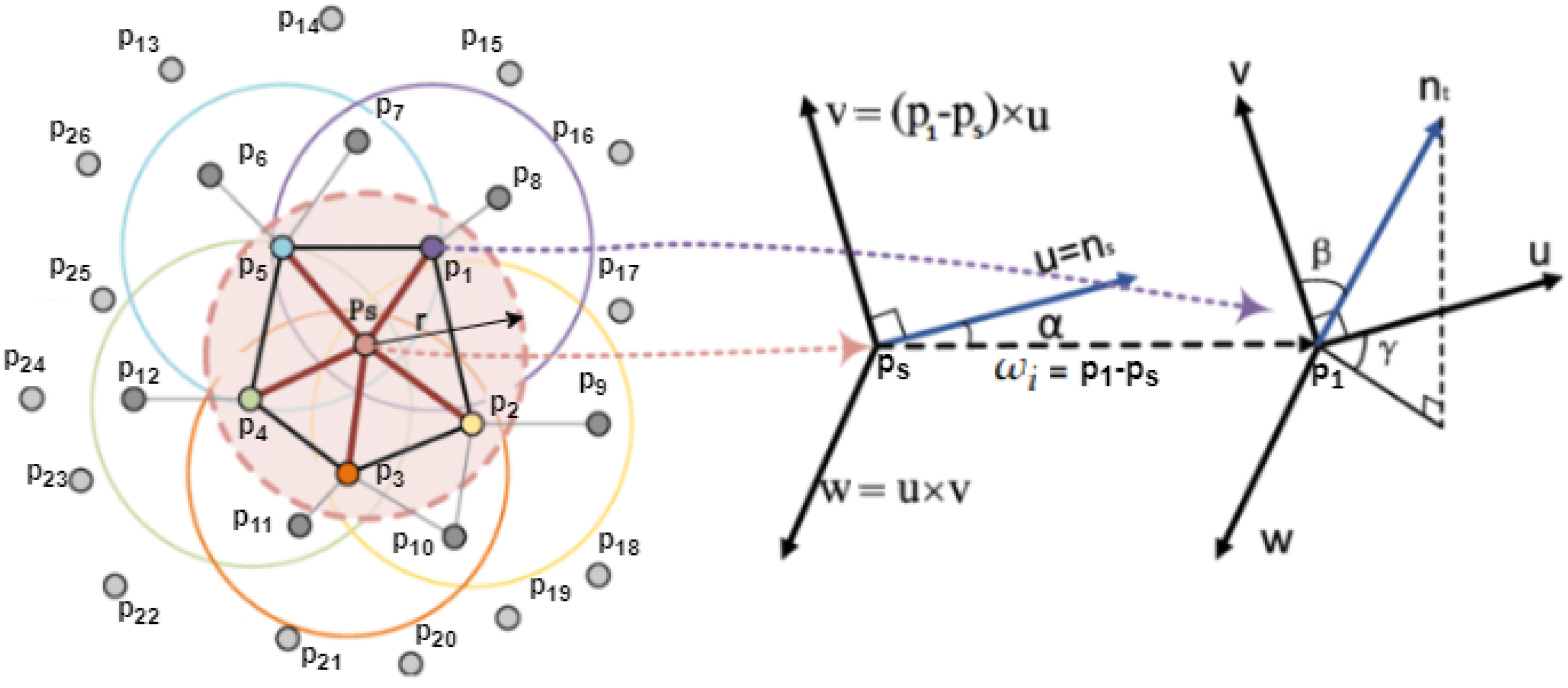
2.2. Determination of the Point Features
2.3. Fitting of the Point Clouds, FGR then ICP
- 1.
- Determination of correspondencesFirst, we search for a correspondence set C, which contains matching index pairs. For each point in the cloud, we search for its nearest neighbor from . Their indexes form a pair.
- 2.
- Transformation estimation
- 3.
- TransformationFinally, the translated and rotated point (in Equation (16)) can be obtained:
- 4.
- IterationSteps 1–3 are repeated, refining the transformation itself, getting closer to the overlap between the two point clouds so that the clouds fit together better.
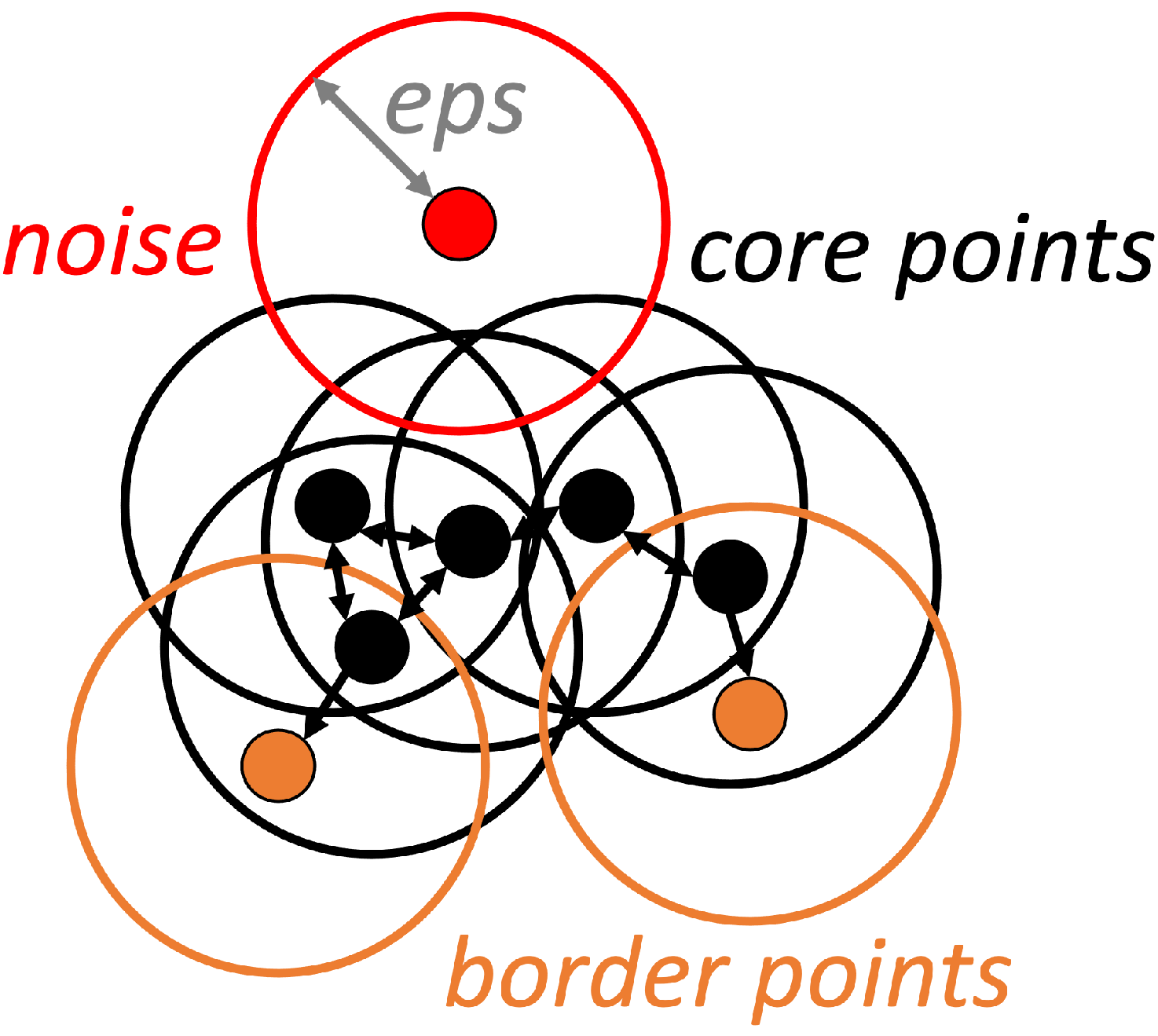
2.4. Clustering Based on Density
3. Application of the Developed Clustering Method for Welding Defects Identification
- 3D scanning: HP 3D Structured Light Scanner 5 Pro Edition scanner (0.05 mm maximum accuracy) with software (vers.: 5.2.0.790), HP Development Company, L.P., Germany
- CAD models: Solid Edge Academic Edition (vers.:221.00.00.114),
- Point clouds to creating: Meshlab (fpv2020.12),
- Algorithm environment: Python (vers.: 3.7.7),
- Visualization field: Open3D (vers.: 21.1.3).
3.1. Performing Tests on Generated Workpieces
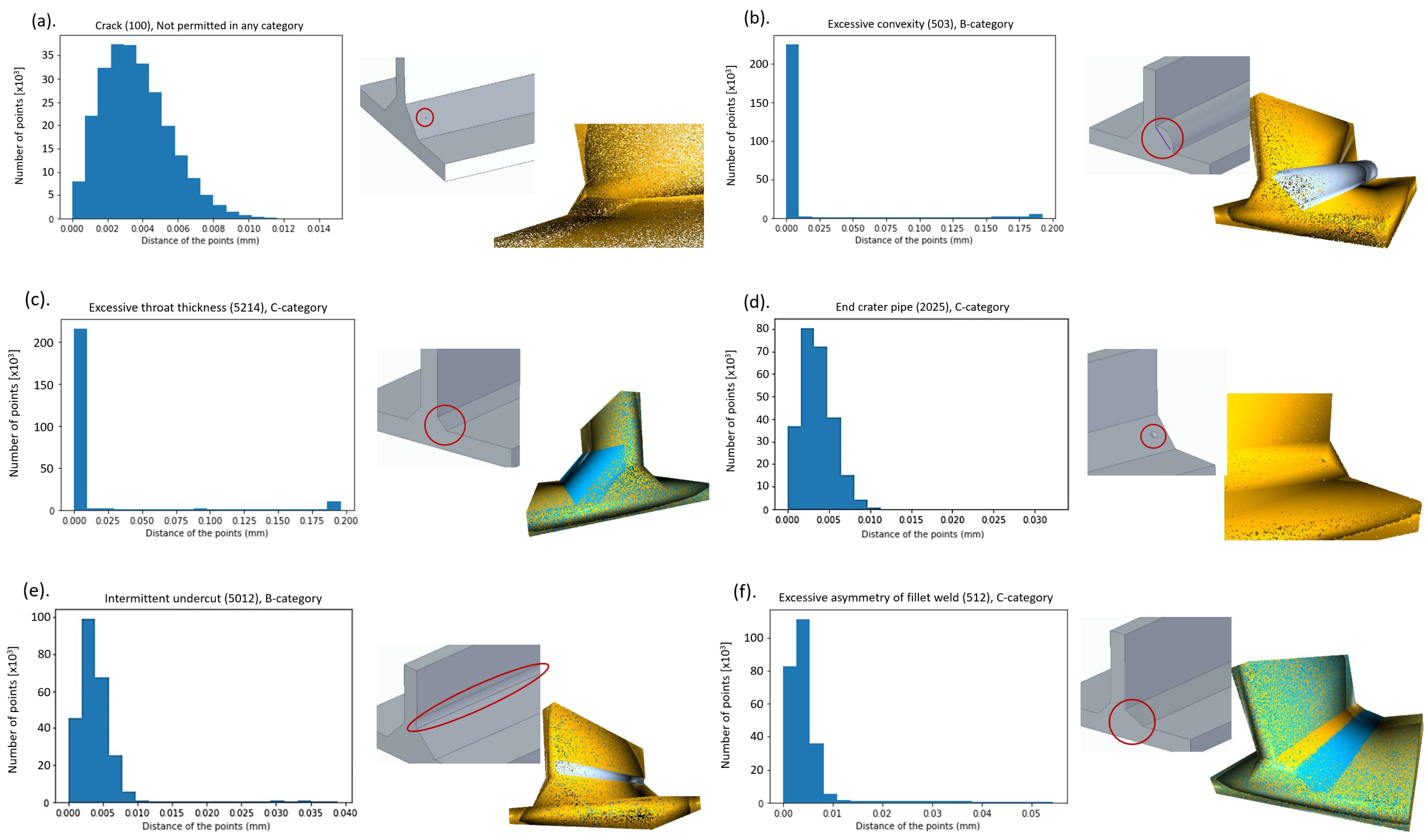
- Crack (number of imperfection 100): For the test, a “brick body cavity” of was created in the CAD model (Figure 5a). Regardless of the defect type, the system detects the same percentage of the parts remaining outside the scattered areas together with the cavitation defect cluster for both defect clusters ( points for ). The least sensitive group for the test, due to the size difference (100 points/ points), small and fragmented clusters are not visible to the system, and the test cannot detect clusters with such low scores.
- Excessive convexity (number of imperfection 503): (Figure 5b).
- In case of Imperfect shape (number of main imperfection 500):
- -
- Insufficient throat thickness (Smaller root size—number of imperfection 5213): detectable in categories C and D.
- -
- Excessive throat thickness (Larger root size—number of imperfection 5214): (Figure 5c) detectable in categories C and D.
- End crater pipe (number of imperfection 5012) (Figure 5d) and Intermittent undercut (number of imperfection 2025) (Figure 5e): In these cases, minus normal vector errors proportional to the reference point cloud are detected. The number of points in the cluster detected as an error decreases steadily, and at , the cluster product of the generated error contains 5700 points. The linear decrease is also true for the error group of the end craters, but the number of points in the cluster clouds is smaller, from 288 to 176.
- Excessive asymmetry of fillet weld (number of imperfection 512) and dimension: The most sensitive group of errors to analyze, the diversity of errors means that detection is roughly successful (Figure 5f). At this optimum percentage, the test detects five clusters (all the errors represented).
3.2. Performing Tests on Real Physical Workpieces
- It is inefficient for the framework of the CAD model to contain errors of too small a size; below a score of 200 (out of 250,000), no error is detectable. (Crack and end crater defects cannot be detected.)
- Sub-surface defects cannot be detected due to weld seam gassing, and additional investigations are needed.
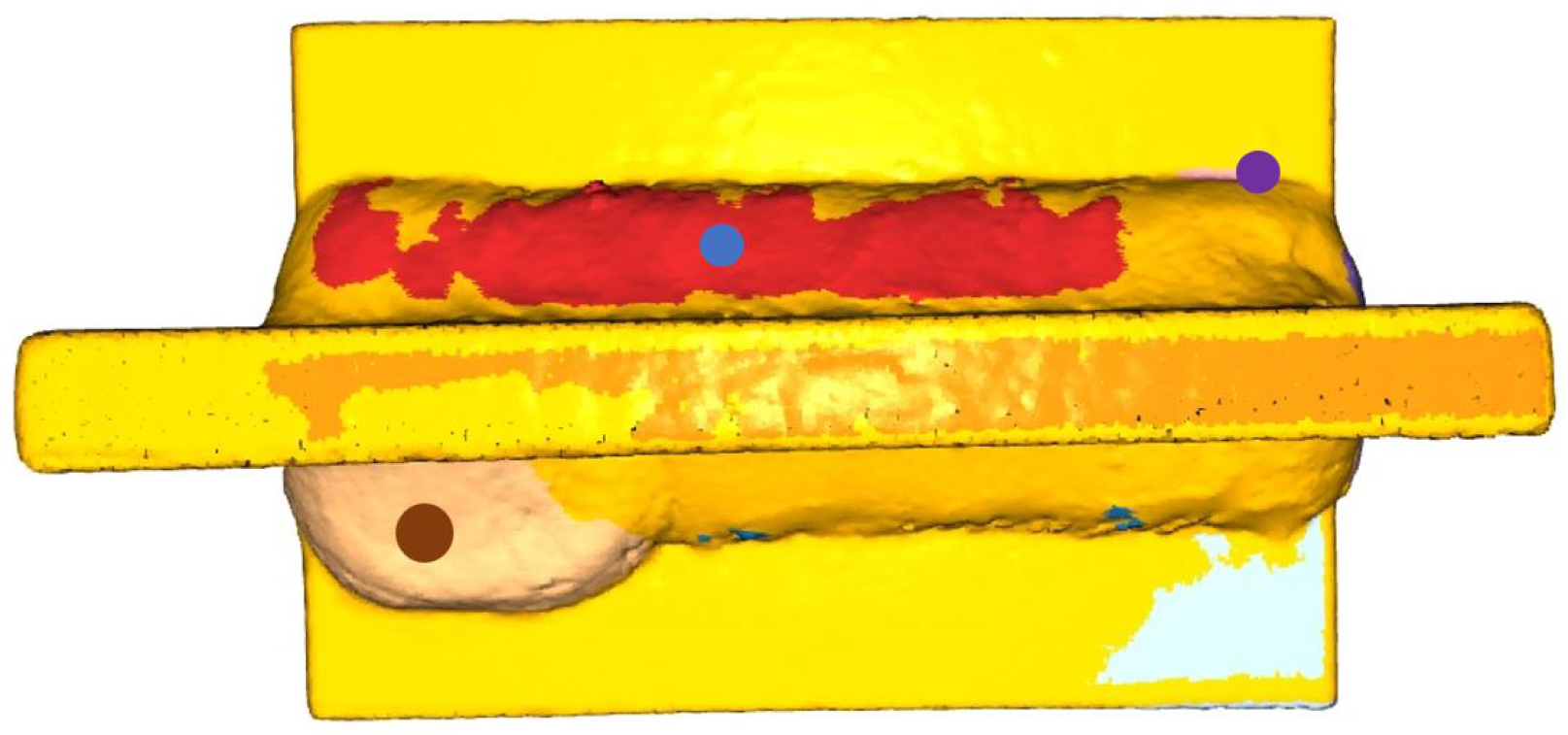
- Comparing the image of the CAD model with the image of the welded workpiece is unfortunate due to geometric differences, as differences not related to the weld scan are also considered errors. Dimensional differences caused by inaccurate cuts generate huge clusters.
- A glossy, transparent surface or all-black-and-white color will spoil the expected scanning result. However, environmental preparation is also essential (from the projector light, no brighter light in the room).
- Care had to be taken to fine-tune the scan in the setup, but it is highly hardware-dependent. Generating a 3D model from more than six (rotation angles less than 60 degrees) matching images makes the process slow.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Point pairs with angular features (FPFH) | |
| Query points (FPFH) | |
| Translation vector (ICP) | |
| These are subtracted the corresponding center of mass from every point of and | |
| (ICP) | |
| Translated and rotated points (ICP) | |
| Normal of (FPFH) | |
| Normal of (FPFH) | |
| Transformation matrix (ICP) | |
| Objective function by rotation matrix, and transformation vector (ICP) | |
| The nearest neighbor of from cloud (DBSCAN) | |
| The top ten percent of (DBSCAN) | |
| Master and test point clouds after sampling (CAD models) | |
| Cross-covariance matrix (ICP) | |
| Master and test point clouds (CAD models) | |
| C | Correspondence set (ICP) |
| The centers of mass of the correspondence points (ICP) | |
| Different angular features (FPFH) | |
| Fixed coordinate frame (FPFH) | |
| Distance between the query point and its neighbor (FPFH) | |
| The neighborhood of a query point (FPFH) | |
| The algorithm checks by radius for each point whether it has neighbors or not, | |
| according the parameter (DBSCAN) | |
| The minimum number of points per cluster (DBSCAN) | |
| The arithmetic mean of the distance between each point in the point cloud and its | |
| neighbors (DBSCAN) | |
| Root-mean-square error (DBSCAN) | |
| N | Number of the points after the sampling |
References
- Stavridis, J.; Papacharalampopoulos, A.; Stavropoulos, P. Quality assessment in laser welding: A critical review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 1825–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, F.; Lu, R.; Ni, X.; Zhu, W. Weld Feature Extraction Based on Semantic Segmentation Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.T.; Alfaro, S.C.A. Data analysis and modeling techniques of welding processes: The state-of-the-art. In Welding-Modern Topics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, K.; Elangovan, S.; Rathinasuriyan, C. Modeling and prediction of weld strength in ultrasonic metal welding process using artificial neural network and multiple regression method. Mater. Sci. Eng. Int. J. 2018, 2, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Balos, S.; Dramicanin, M.; Janjatovic, P.; Zabunov, I.; Pilić, B.; Goel, S.; Szutkowska, M. Suppressing the Use of Critical Raw Materials in Joining of AISI 304 Stainless Steel Using Activated Tungsten Inert Gas Welding. Metals 2019, 9, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostromęcka, M.; Szymański, M. Preparation of Specimens for Macro and Microscopic Examinations of Dissimilar Friction Welded Steel Joints and Their Evaluation According to Applicable Standards. Probl. Kolejnictwa Railw. Rep. 2022, 66, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacek, G.; Ozgowicz, A. The structure and properties of laser seam stepper system (LSS) welded the low alloy high strength steel DOCOL 1200M with martensitic structure. Mater. Sci. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2018, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ge, S.; Khyam, M.O.; Luo, C. Automatic Welding Seam Tracking and Identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7261–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhen, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, W. Welding Seam Detection and Tracking Based on Laser Vision for Robotic Arc Welding. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1650, 22030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hong, Y.; Gao, J.; Hong, B.; Li, X. Welding Seam Trajectory Recognition for Automated Skip Welding Guidance of a Spatially Intermittent Welding Seam Based on Laser Vision Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodea, M. Implementation of Artificial intelligence in welding technologies. In Proceedings of the Conferinta Sudura, Resita, Romania, 22–23 April 2021; Volume 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.N.; Yang, F.C.; Nguyen, V.T.T.; Vo, N.T.M. CFD Analysis and Optimum Design for a Centrifugal Pump Using an Effectively Artificial Intelligent Algorithm. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, P.S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Uyen, T.M.T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.T. Study on the Fatigue Strength of Welding Line in Injection Molding Products under Different Tensile Conditions. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Automated visual defect detection for flat steel surface: A survey. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Bornstein, M.M. Current applications, opportunities, and limitations of AI for 3D imaging in dental research and practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.; Yahyia, M.; Albasha, L.; Mortula, M.M.; Ali, T. Communication Network for Ultrasonic Acoustic Water Leakage Detectors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29954–29964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olympus, N. Phased array testing: Basic theory for industrial applications. Olympus NDT 2010, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Suh, D. Mannequin fabrication methodology using 3D-scanning, modeling and printing. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2021, 33, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcácer, V.; Cruz-Machado, V. Scanning the industry 4.0: A literature review on technologies for manufacturing systems. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.C.; Martill, D.M.; Smyth, R.S.; Byrne, R.; Simms, M.J. Chaperoning digital dinosaurs. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2021, 132, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Law, A.C.; Garcia, D.; Yang, S.; Kong, Z. Development of structured light 3D-scanner with high spatial resolution and its applications for additive manufacturing quality assurance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Deng, T.; Tang, D. Geometric Quality Assessment of Prefabricated Steel Box Girder Components Using 3D Laser Scanning and Building Information Model. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Peng, C.C. 3D face point cloud reconstruction and recognition using depth sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, R.; Jagan, A.; Pavithran, L.; Shrivastava, A.; Selvaraj, S.K. Intelligent welding by using machine learning techniques. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 7402–7410. [Google Scholar]
- Boumchich, A.; Picaut, J.; Bocher, E. Using a Clustering Method to Detect Spatial Events in a Smartphone-Based Crowd-Sourced Database for Environmental Noise Assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SO 5817:2014; IWelding—Fusion-Welded Joints in Steel, Nickel, Titanium and Their Alloys (Beam Welding Excluded)—Quality Levels for Iimperfections. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Wu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, F.; Peng, T.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, F. Fast Registration of Point Cloud Based on Custom Semantic Extraction. Sensors 2022, 22, 7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, Z. Virtual Namesake Point Multi-Source Point Cloud Data Fusion Based on FPFH Feature Difference. Sensors 2021, 21, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balta, H.; Velagic, J.; Beglerovic, H.; De Cubber, G.; Siciliano, B. 3D registration and integrated segmentation framework for heterogeneous unmanned robotic systems. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, D.; Xia, C.; He, Q. A Point Cloud Registration Method Based on Histogram and Vector Operations. Electronics 2022, 11, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M. Clustering Validation. Ph.D. Thesis, Itä-Suomen yliopisto, Kuopio, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perafan-Lopez, J.C.; Ferrer-Gregory, V.L.; Nieto-Londoño, C.; Sierra-Pérez, J. Performance Analysis and Architecture of a Clustering Hybrid Algorithm Called FA+ GA-DBSCAN Using Artificial Datasets. Entropy 2022, 24, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6520-1:2007; Welding and Allied Processes—Classification of Geometric Imperfections in Metallic Materials—Part 1: Fusion welding. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Wang, C.; Ji, M.; Wang, J.; Wen, W.; Li, T.; Sun, Y. An improved DBSCAN method for LiDAR data segmentation with automatic Eps estimation. Sensors 2019, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lang, J. Semi-Supervised Training for Positioning of Welding Seams. Sensors 2021, 21, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




 | 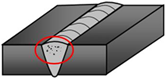 | 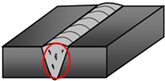 |
| 100—Crack, example: transverse crack in the parent material (1024) | 200—Cavity, example: gas cavity (2011) | 300—Solid inclusion, example: slag inclusion (301) |
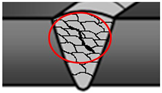 |  | 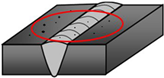 |
| 400—Lack of fusion and penetration, example: lack of inter-run fusion (4012) | 500—mperfect shape, example: inter-run undercut (5014) | 600—Miscellaneous imperfection, example: spatter (602) |
| Limit Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Imperfections | B | C | D |
| Crack (100) (Figure 5a) | not permitted | not permitted | not permitted |
| Excessive convexity (503) (Figure 5b) | 3 mm | 4 mm | 5 mm |
| Insufficient (5213) (Figure 5c) | not permitted | 1 mm | 2 mm |
| Excessive throat thickness (5214) (Figure 5c) | 3 mm | 4 mm | 5 mm |
| Endcrater pipe (2025) (Figure 5d) | not permitted | 1 mm | 2 mm |
| Intermittent undercut (5012) (Figure 5e) | 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm | 1 mm |
| Excessive asymmetry of fillet weld (512) (Figure 5f) | 2.25 mm | 2.75 mm | 3 mm |
| Cluster ID | Number of Points | RMSE | Center of the Mass in Case of Excessive Convexity Defect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3824 | 3.165 | 127.278, −57.460, 146.059 |
| 1 | 8433 | 2.089 | 160.334, −55.132, 107.931 |
| 2 | 6058 | 1.742 | 114.276, −64.487, 146.245 |
| 3 | 618 | 1.487 | 151.439, −61.352, 104.103 |
| 4 | 3741 | 1.106 | 144.248, −31.916, 121.838 |
| 5 | 172 | 0.832 | 130.808, −57.191, 124.218 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hegedűs-Kuti, J.; Szőlősi, J.; Varga, D.; Abonyi, J.; Andó, M.; Ruppert, T. 3D Scanner-Based Identification of Welding Defects—Clustering the Results of Point Cloud Alignment. Sensors 2023, 23, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052503
Hegedűs-Kuti J, Szőlősi J, Varga D, Abonyi J, Andó M, Ruppert T. 3D Scanner-Based Identification of Welding Defects—Clustering the Results of Point Cloud Alignment. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052503
Chicago/Turabian StyleHegedűs-Kuti, János, József Szőlősi, Dániel Varga, János Abonyi, Mátyás Andó, and Tamás Ruppert. 2023. "3D Scanner-Based Identification of Welding Defects—Clustering the Results of Point Cloud Alignment" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052503
APA StyleHegedűs-Kuti, J., Szőlősi, J., Varga, D., Abonyi, J., Andó, M., & Ruppert, T. (2023). 3D Scanner-Based Identification of Welding Defects—Clustering the Results of Point Cloud Alignment. Sensors, 23(5), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052503









