Pre-Trained Joint Model for Intent Classification and Slot Filling with Semantic Feature Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1).
- Proposing an effective semantic feature fusion layer that improves the utilization of semantic features and mutual information between tasks, leading to better sentence-level accuracy than other models;
- (2).
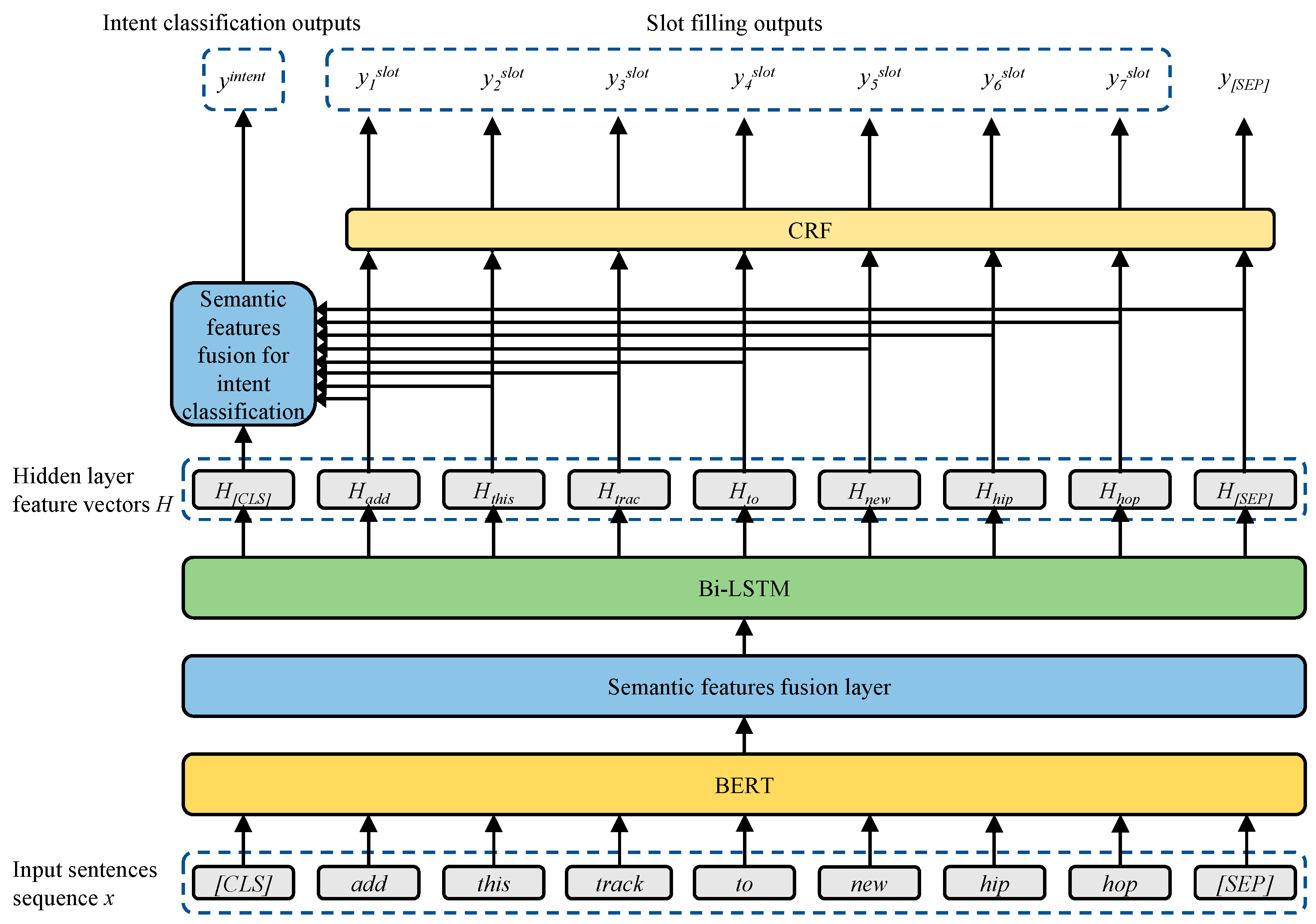
- Introducing the Joint Model based on BERT with Semantic Fusion (JMBSF), which employs the pre-trained BERT and semantic fusion layer to combine multi-layer contextual semantic features extracted by BERT;
- (3).
- Demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed model structure and identifying the optimal value for the semantic feature fusion layer parameter K through ablation experiments;
- (4).
- Achieving state-of-the-art performance in two public datasets, especially in terms of sentence-level accuracy.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. BERT
3.2. The BERT-Semantic Feature Fusion Layer
3.3. Bi-LSTM
3.4. Conditional Random Field
3.5. Intent Classification
3.6. Slot Filling
3.7. Datasets
4. Experiments
4.1. Evaluation Indicators
4.2. Training Setup and Procedure
4.3. Results and Analysis
4.4. Ablation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, M. Review of intent detection methods in the human-machine dialogue system. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1267, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhuo, Z.; Wang, W. Bert for joint intent classification and slot filling. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10909. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Du, N.; Fan, W.; Yu, P.S. Joint slot filling and intent detection via capsule neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.09471. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanand, J.; Bhavsar, K.; Pedanekar, N. Wishful thinking-finding suggestions and ’buy’ wishes from product reviews. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2010 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Analysis and Generation of Emotion in Text, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5 June 2010; pp. 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, B. Statistical Methods for Spoken Dialogue Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yongtao, H.; Zhixiang, Y.; Weiming, X.; Xiao, Z. Slot filling and intent recognition based on BLSTM-CNN-CRF model [J/OL]. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, D.; Sekine, S. A survey of named entity recognition and classification. Lingvisticae Investig. 2007, 30, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Hakanni-Tür, D.; Tur, G.; Celikyilmaz, A.; Guo, J.; Deng, L. Syntax or semantics? Knowledge-guided joint semantic frame parsing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), San Diego, CA, USA, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H. A joint model of intent determination and slot filling for spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-16), New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 2993–2999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lane, I. Attention-based recurrent neural network models for joint intent detection and slot filling. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH 2016), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, K.J.; Lakshmi, K.S. Joint slot filling and intent prediction for natural language understanding in frames dataset. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 11–12 July 2018; pp. 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lane, I. Recurrent neural network structured output prediction for spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the NIPS Workshop on Machine Learning for Spoken Language Understanding and Interactions, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Yao, M.; Wang, T.; Li, S. Bidirectional Association Model for Intent Detection and Slot Filling. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2021, 3, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lixian, H.O.U.; Yanling, L.I.; Min LI, N.; Chengcheng, L.I. Joint Recognition of Intent and Semantic Slot Filling Combining Multiple Constraints. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 1545. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training. 2018; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Che, W.; Li, Y.; Wen, H.; Liu, T. A stack-propagation framework with token-level intent detection for spoken language understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.02188. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Z. A Typed Iteration Approach for Spoken Language Understanding. Electronics 2022, 11, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- LazyAdam a Variant of Adam Optimizer. Available online: https://tensorflow.org/addons/api_docs/python/tfa//optimizers//La-zyAdam (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Tur, G.; Hakkani-Tür, D.; Heck, L. What is left to be understood in ATIS? In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop, Berkeley, CA, USA, 12–15 December 2010; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Coucke, A.; Saade, A.; Ball, A.; Bluche, T.; Caulier, A.; Leroy, D.; Doumouro, C.; Gisselbrecht, T.; Caltagirone, F.; Lavril, T.; et al. Snips voice platform: An embedded spoken language understanding system for private-by-design voice interfaces. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10190. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.01991. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Qiu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X. How to fine-tune bert for text classification? In Chinese Computational Linguistics: 18th China National Conference, CCL 2019, Kunming, China, 18–20 October 2019; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 194–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann, G.; Yimam, S.M.; Biemann, C. UHH-LT at SemEval-2020 task 12: Fine-tuning of pre-trained transformer networks for offensive language detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11493. [Google Scholar]
- Hakkani-Tür, D.; Tür, G.; Celikyilmaz, A.; Chen, Y.N.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.Y. Multi-domain joint semantic frame parsing using bi-directional rnn-lstm. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Bidirectional LSTM networks for improved phoneme classification and recognition. In Artificial Neural Networks: Formal Models and Their Applications–ICANN 2005: 15th International Conference, Warsaw, Poland, 11–15 September 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, C.; Riccardi, G. Generative and discriminative algorithms for spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2007—8th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Anvers, Belgium, 27–31 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F.C. Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Machine Learning 2001 (ICML 2001), San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Settles, B. Biomedical named entity recognition using conditional random fields and rich feature sets. In Proceedings of the International Joint Workshop on Natural Language Processing in Biomedicine and Its Applications (NLPBA/BioNLP), Geneva, Switzerland, 28–29 August 2004; pp. 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Hang, C.W.; Sil, A.; Potdar, S. Improved text classification via contrastive adversarial training. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 11130–11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Ramakrishnan, G. Bae: Bert-based adversarial examples for text classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.01970. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, C.; McCallum, A. An introduction to conditional random fields. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2012, 4, 267–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, C.W.; Gao, G.; Hsu, Y.K.; Huo, C.L.; Chen, T.C.; Hsu, K.W.; Chen, Y.N. Slot-gated modeling for joint slot filling and intent prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Volume 2, pp. 753–757. [Google Scholar]




| Sample | Add | This | Track | To | New | Hip | Hop |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slot | O | O | B-music_item | O | B-playlist | I-playlist | I-playlist |
| Intent | AddToPlaylist | ||||||
| Dataset | ATIS | SNIPS |
|---|---|---|
| Vocabulary size | 722 | 11,241 |
| Intents | 21 | 7 |
| Slots | 120 | 72 |
| Training samples | 4478 | 13,084 |
| Validation samples | 500 | 700 |
| Models | ATIS | Snips | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | |
| Atten-BiRNN [10] | 91.10 | 94.20 | 78.90 | 96.70 | 87.80 | 74.10 |
| Joint seq [27] | 92.60 | 94.30 | 80.70 | 96.90 | 87.30 | 73.20 |
| Slot-gated [35] | 94.10 | 95.20 | 82.60 | 97.00 | 88.80 | 75.50 |
| BiAss-Gate [13] | 97.09 | 95.80 | 86.56 | 98.29 | 93.62 | 84.43 |
| Joint BERT [2] | 97.58 | 95.83 | 88.12 | 98.77 | 96.18 | 90.89 |
| Stack-propagation + BERT [17] | 97.30 | 96.10 | 88.20 | 98.60 | 96.70 | 91.80 |
| Typed abstraction mechanism + BERT [18] | 98.10 | 96.20 | 88.70 | 98.90 | 96.70 | 92.20 |
| JMBSF | 98.80 | 98.25 | 93.40 | 99.71 | 97.24 | 93.57 |
| Models | ATIS | Snips | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | |
| BERT + CRF | 97.40 | 97.87 | 90.60 | 98.57 | 95.50 | 89.43 |
| BERT + CRF + Bi-LSTM | 97.62 | 98,12 | 91.2 | 98.77 | 96.30 | 90.29 |
| BERT + CRF + merge_layer * | 97.80 | 97.72 | 91.8 | 98.83 | 95.78 | 90.71 |
| JMBSF * | 98.00 | 98.16 | 92.00 | 99.11 | 96.52 | 92.14 |
| JMBSF | 98.80 | 98.25 | 93.40 | 99.71 | 97.24 | 93.57 |
| JMBSF | ATIS | Snips | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | Intent Acc | Slot F1 | Sen Acc | |
| K = 1 | 98.00 | 98.16 | 92.00 | 99.11 | 96.52 | 92.14 |
| K = 2 | 98.32 | 98.19 | 93.12 | 99.54 | 96.93 | 92.74 |
| K = 3 | 98.80 | 98.25 | 93.40 | 99.71 | 97.24 | 93.57 |
| K = 4 | 98.85 | 98.09 | 93.22 | 99.80 | 97.07 | 93.28 |
| K = 5 | 98.89 | 97.93 | 93.06 | 99.83 | 96.96 | 93.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Luo, Z. Pre-Trained Joint Model for Intent Classification and Slot Filling with Semantic Feature Fusion. Sensors 2023, 23, 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052848
Chen Y, Luo Z. Pre-Trained Joint Model for Intent Classification and Slot Filling with Semantic Feature Fusion. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052848
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yan, and Zhenghang Luo. 2023. "Pre-Trained Joint Model for Intent Classification and Slot Filling with Semantic Feature Fusion" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052848
APA StyleChen, Y., & Luo, Z. (2023). Pre-Trained Joint Model for Intent Classification and Slot Filling with Semantic Feature Fusion. Sensors, 23(5), 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052848





