The Enzymatic Doped/Undoped Poly-Silicon Nanowire Sensor for Glucose Concentration Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
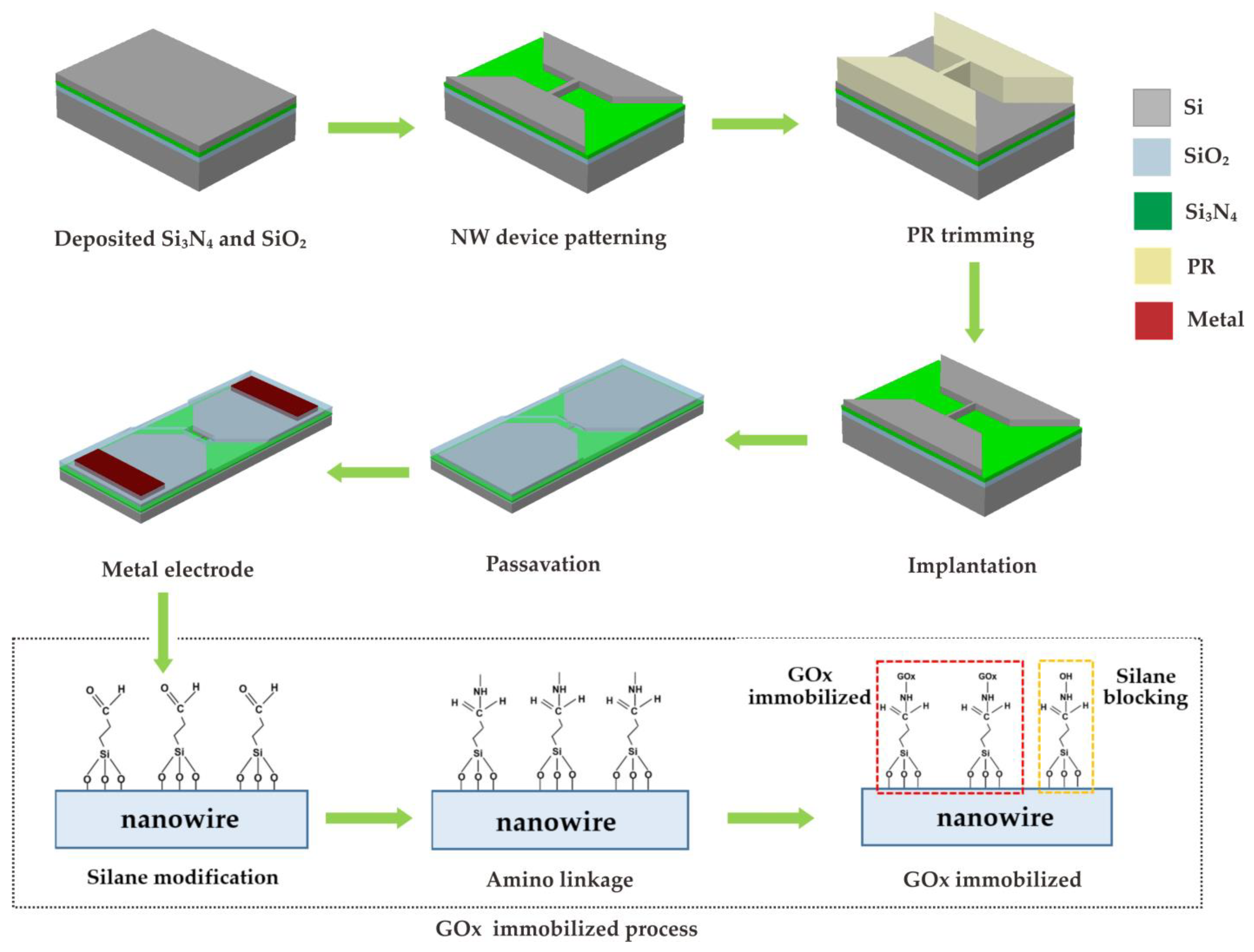
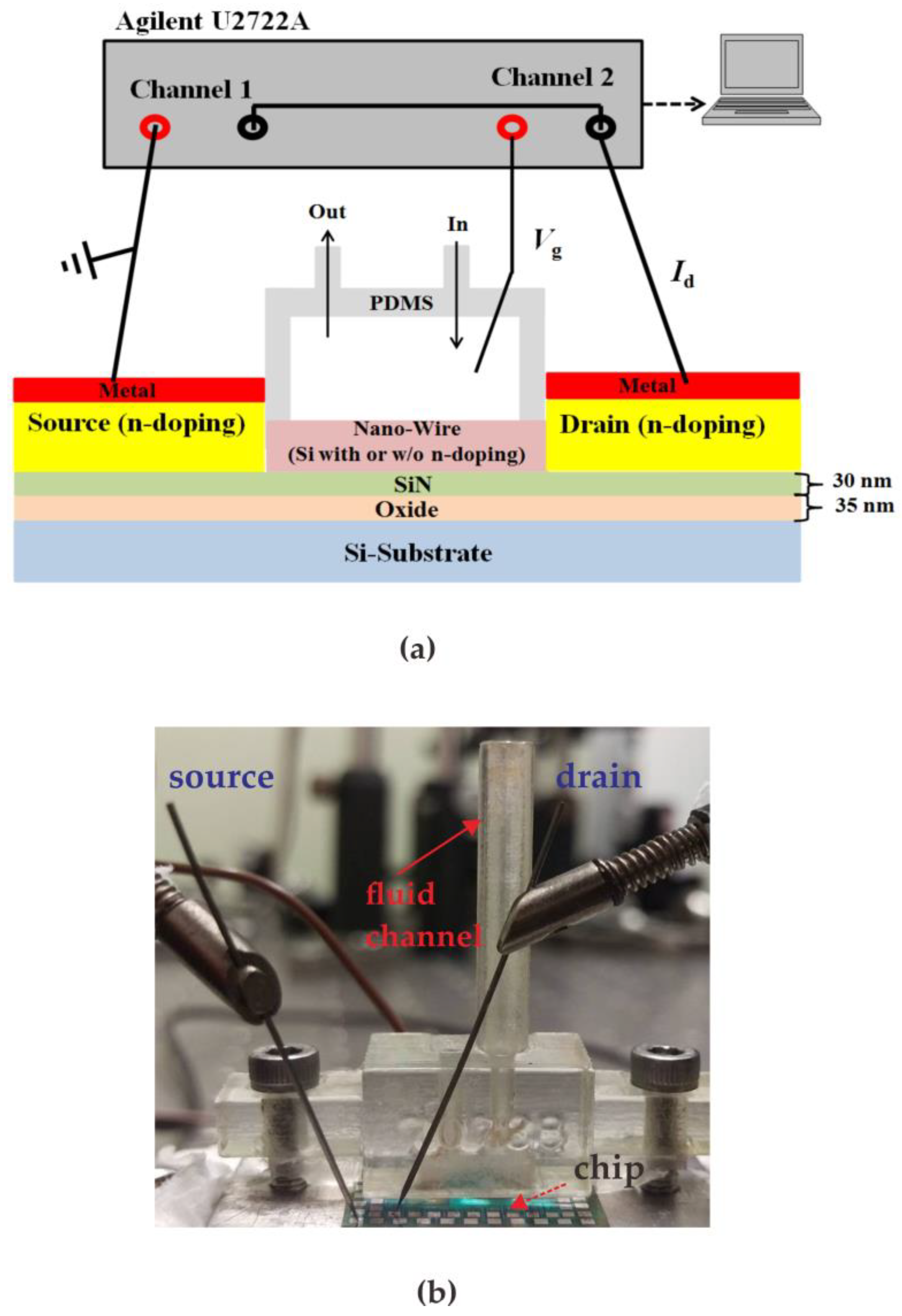
2. Fabrication Procedure for the Enzymatic Poly-Silicon Nanowire Glucose Sensor
3. Theoretical Simulation
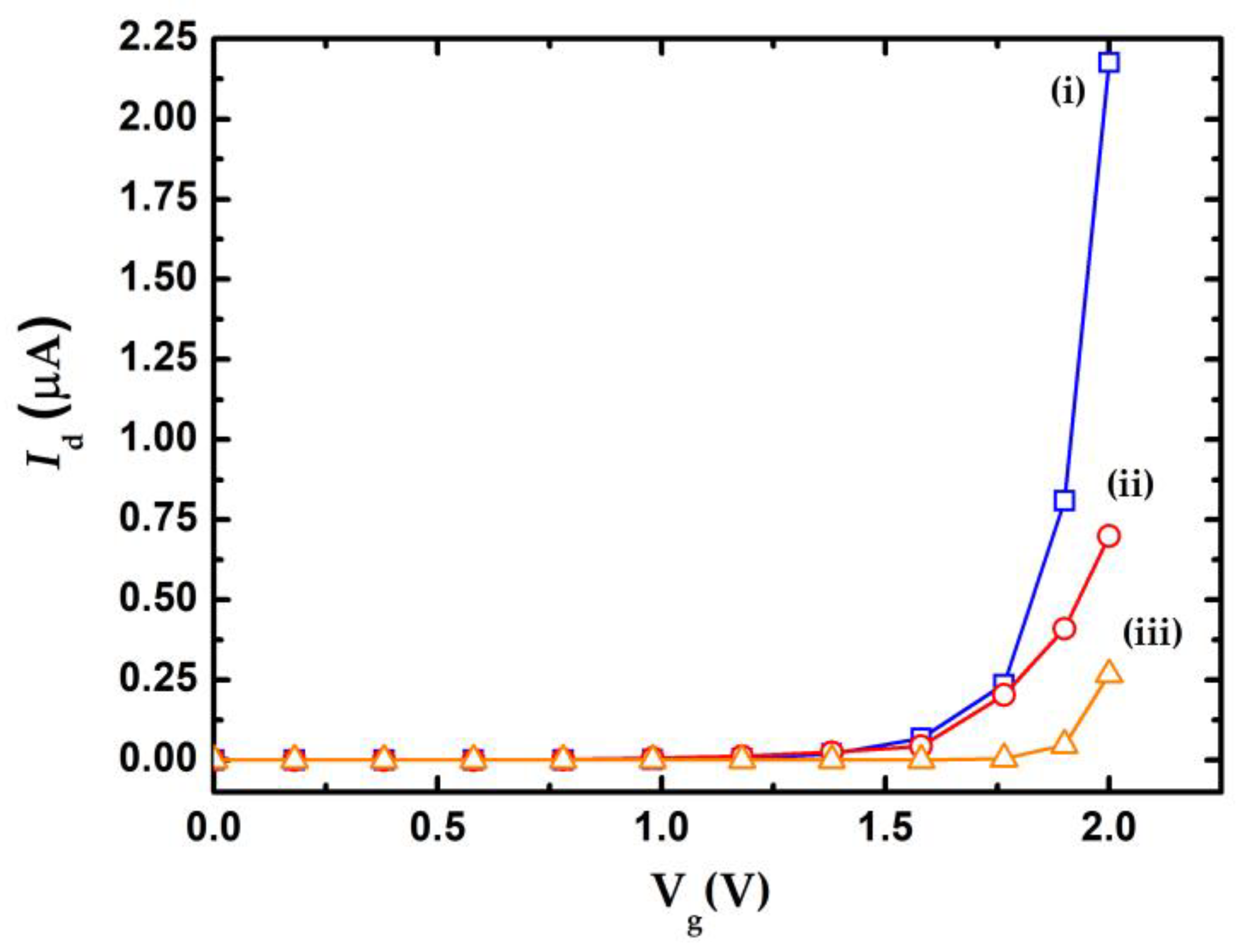
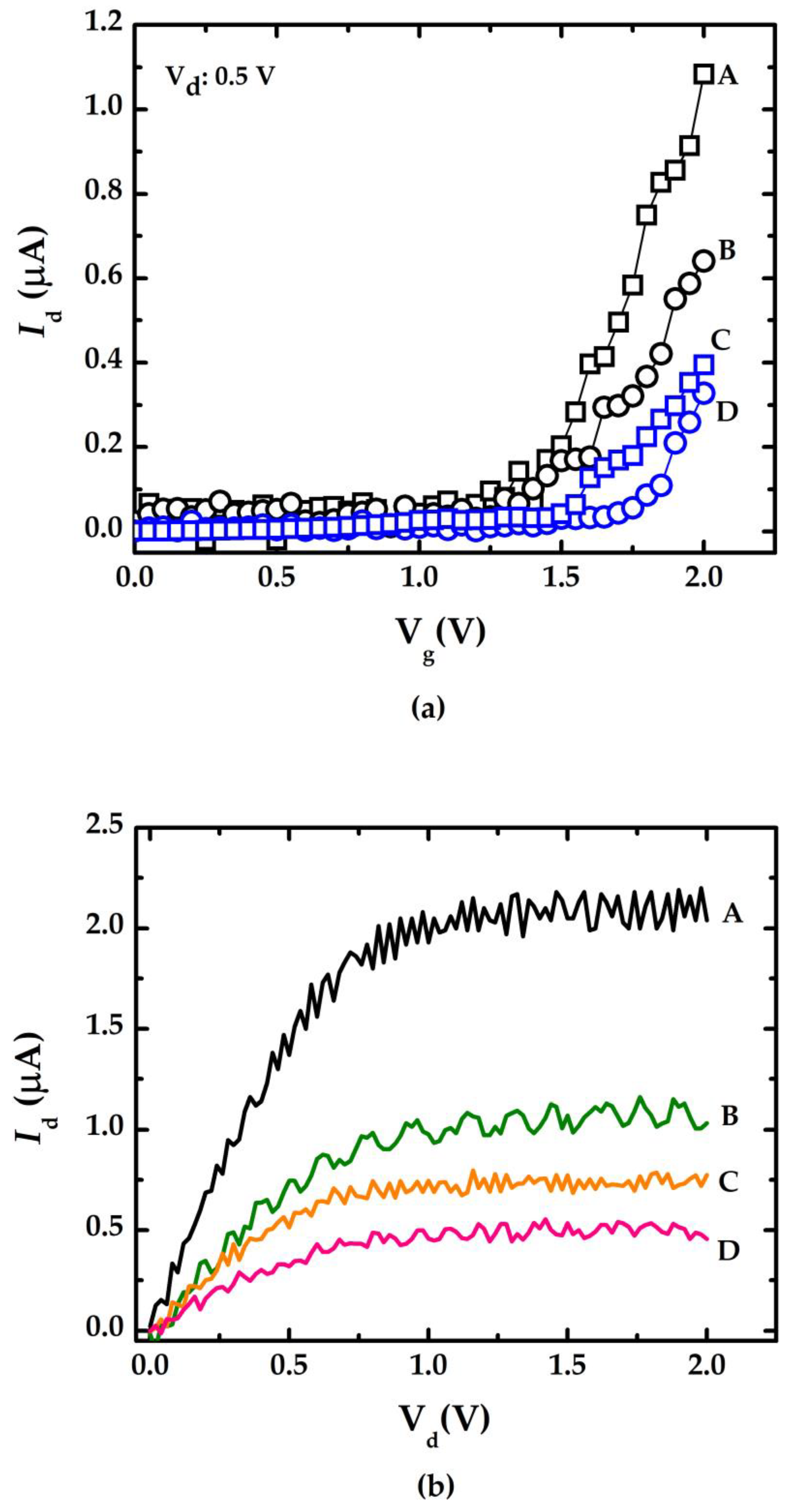
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2020 Edition. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- IDF Diabetes Atlas, 2015 Edition. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/previous/files/7/IDF%20Diabetes%20Atlas%207th.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, P.; Vasa, N.J.; Sujatha, N. Glucose sensing in the anterior chamber of the human eye model using supercontinuum source based dual wavelength low coherence interferometry. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2019, 23, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouiganon, S.; Thammakhet, C.; Thavrungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Buranachai, C. An application of optical coherence tomography and a smart polymer gel to construct an enzyme-free sugar sensor. Appl. Phys. B 2016, 122, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esenaliev, R.O.; Larin, K.V.; Larina, I.V. Noninvasive monitoring of glucose concentration with optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Q.; Lu, Y.L.; Hsu, C.C. Fabrication of glucose fiber sensor based on immobilized GOD technique for rapid measurement. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 27560–27566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Hung, S.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Wu, M.R. In vitro glucose concentration measurement by a reusable enzymatic glucose sensor and a highly stable circular heterodyne polarimeter. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 5004–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Yang, X.; Gao, J. Enhancing intensity and refractive index sensing capability with infrared plasmonic perfect absorbers. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 3185–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehit, E.; Altintas, Z. Significance of nanomaterials in electrochemical glucose sensors: An updated review (2016–2020). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.M.; Lee, M.K. Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Elfstrom, N.; Juhasz, R.; Sychugov, I.; Engfeldt, T.; Karlstrom, A.E.; Linnros, J. Surface charge sensitivity of silicon nanowires: Size dependence. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.I.; Li, B.R.; Chen, Y.T. Silicon nanowire field-effect transistor-based biosensors for biomedical diagnosis and cellular recording investigation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, A.J.S.; Jin, J.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.J. A comprehensive review of glucose biosensors based on nanostructured metal-oxides. Sensors 2010, 10, 4855–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Wong, N.B.; Lee, S.T. Silicon nanowire sensors for bioanalytical applications: Glucose and hydrogen peroxide detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Karevan, M.; Armini, A. Prickly nickel nanowires grown on Cu substrate as a supersensitive enzyme-free electrochemical glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 204, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, X.; Tang, J.; Lan, M.; Zhao, H. A comparative study of nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on Pt-Pd nanotube and nanowire arrays. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, Y.Y.; Hsu, Y.K.; Ganguly, A.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, L.C. Direct-growth of polyaniline nanowires for enzyme-immobilization and glucose detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, K.; Baudequin, M.; O’Riordan, A. Single on-chip gold nanowires for electrochemical biosensing of glucose. Analyst 2011, 136, 4507–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Liao, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yeh, H.I.; Wu, C.C. Multiple silicon nanowires with enzymatic modification for measuring glucose concentration. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Lai, C.J.; Dai, C.L. Optimization of reusable polysilicon nanowire sensor for salt concentration measurement. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 104, 06JE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, X.; Hu, J.; Lieber, C.M. Doping and electrical transport in silicon nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 5213–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Development, operation, and application of the ion-sensitive-field-effect transistor as a tool for electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, 19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, W.L.; Cox, D.; Gonder-Frederick, L.A.; Carter, W.; Pohl, S.L. Evaluating clinical accuracy of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 1987, 10, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Test Systems for Over-the-Counter Use: Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff; Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018.
- Eggins, B.R. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, P.W. A Study on Polycrystalline-Silicon Nanowire Tunnel Thin-Film Transistor with Raised Source/Drain. Master’s Thesis, Department of Electronphysics, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Design considerations of silicon nanowire biosensors. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2007, 54, 3400–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; To, S.; You, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of nanowire number, diameter, and doping density on nano-FET biosensor sensitivity. ACS Nano 2011, 8, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


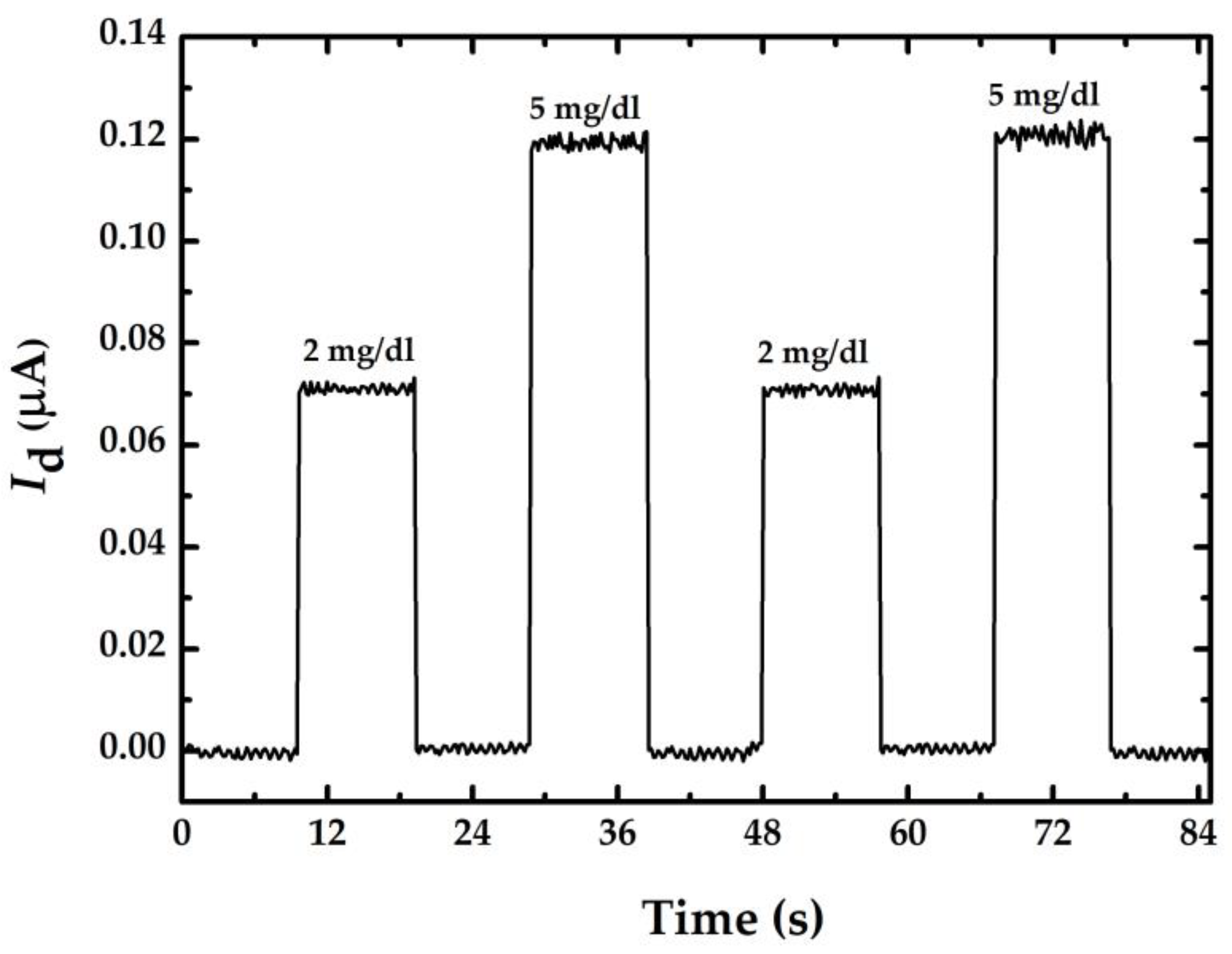
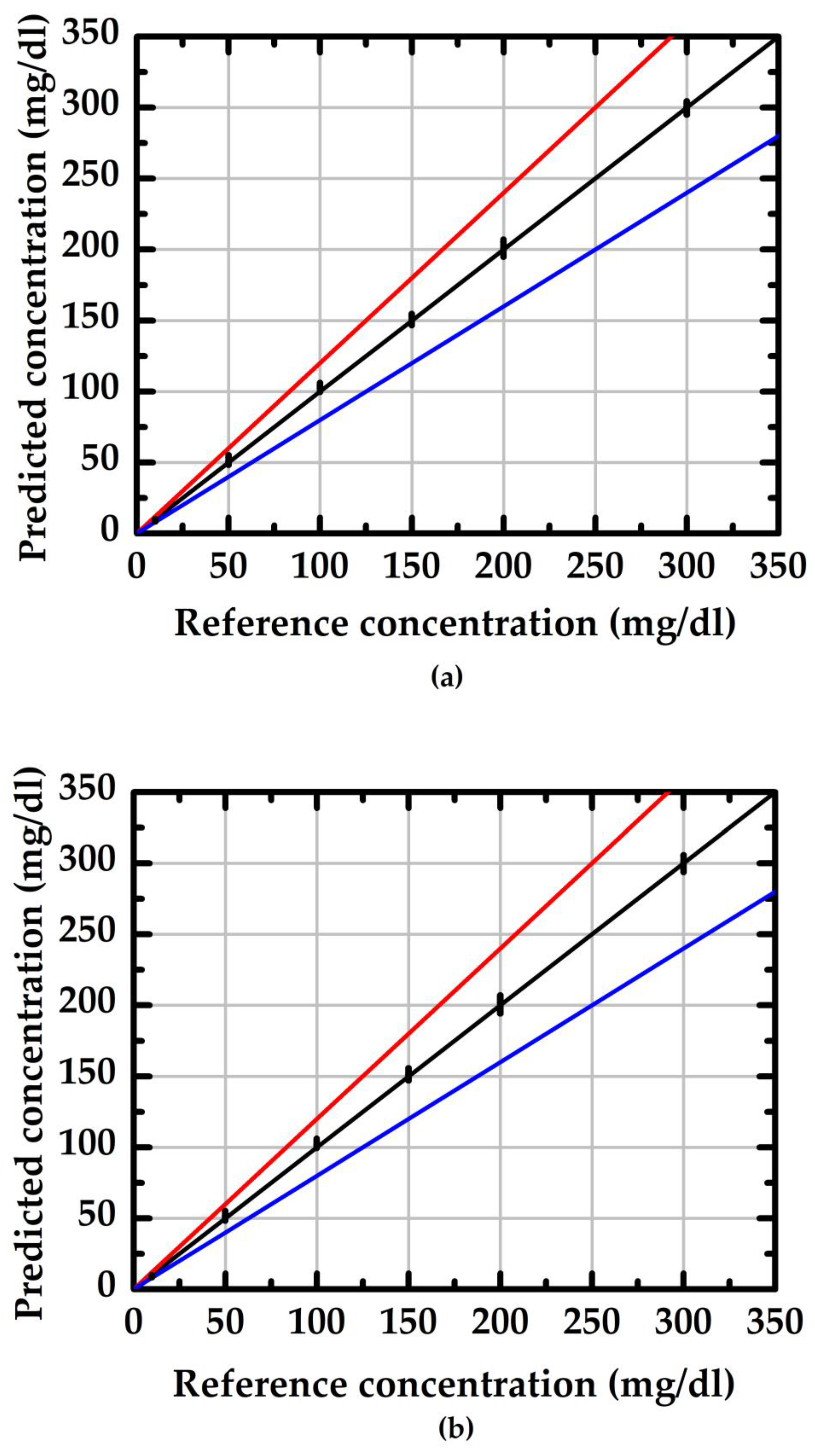
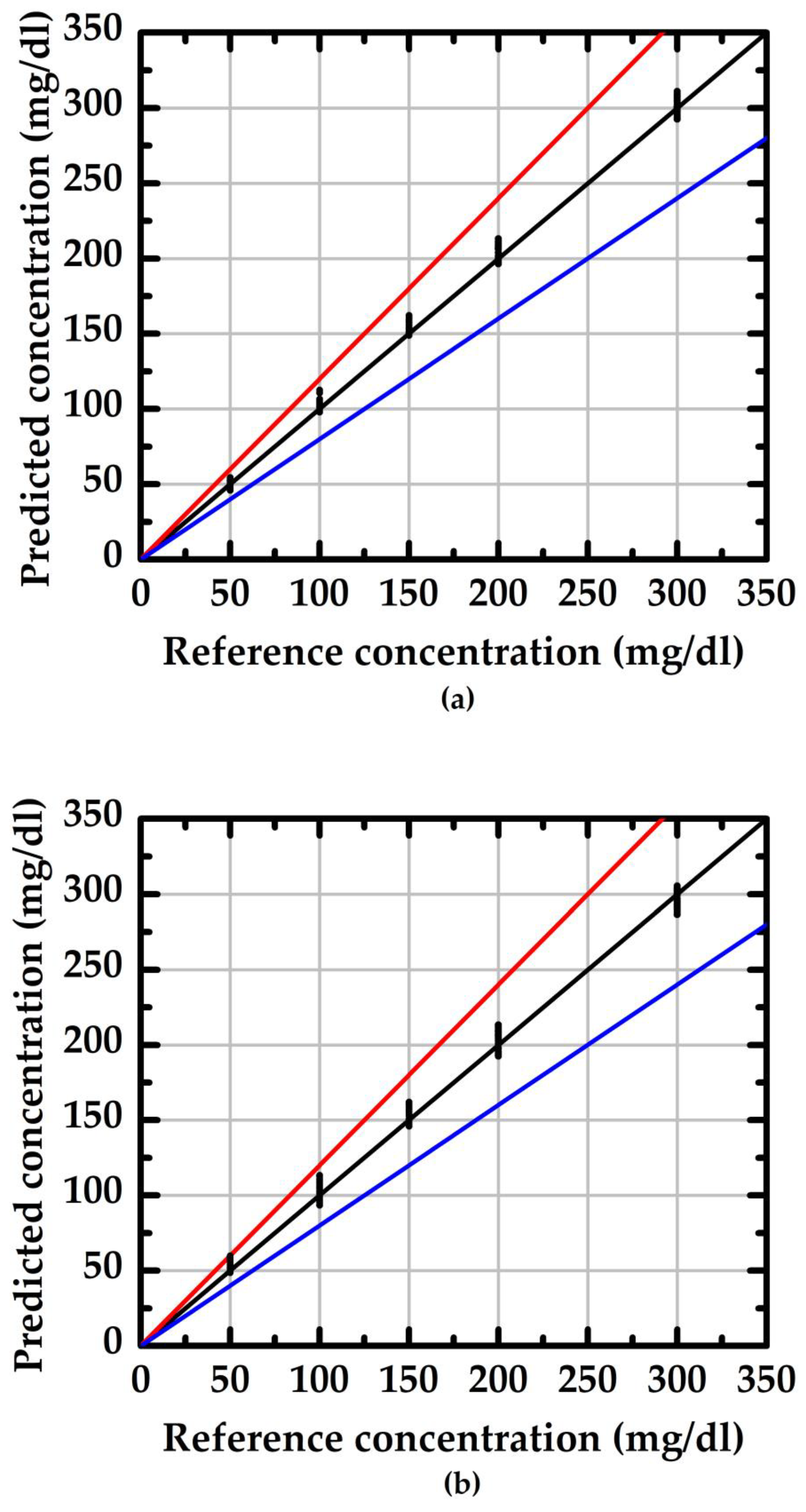


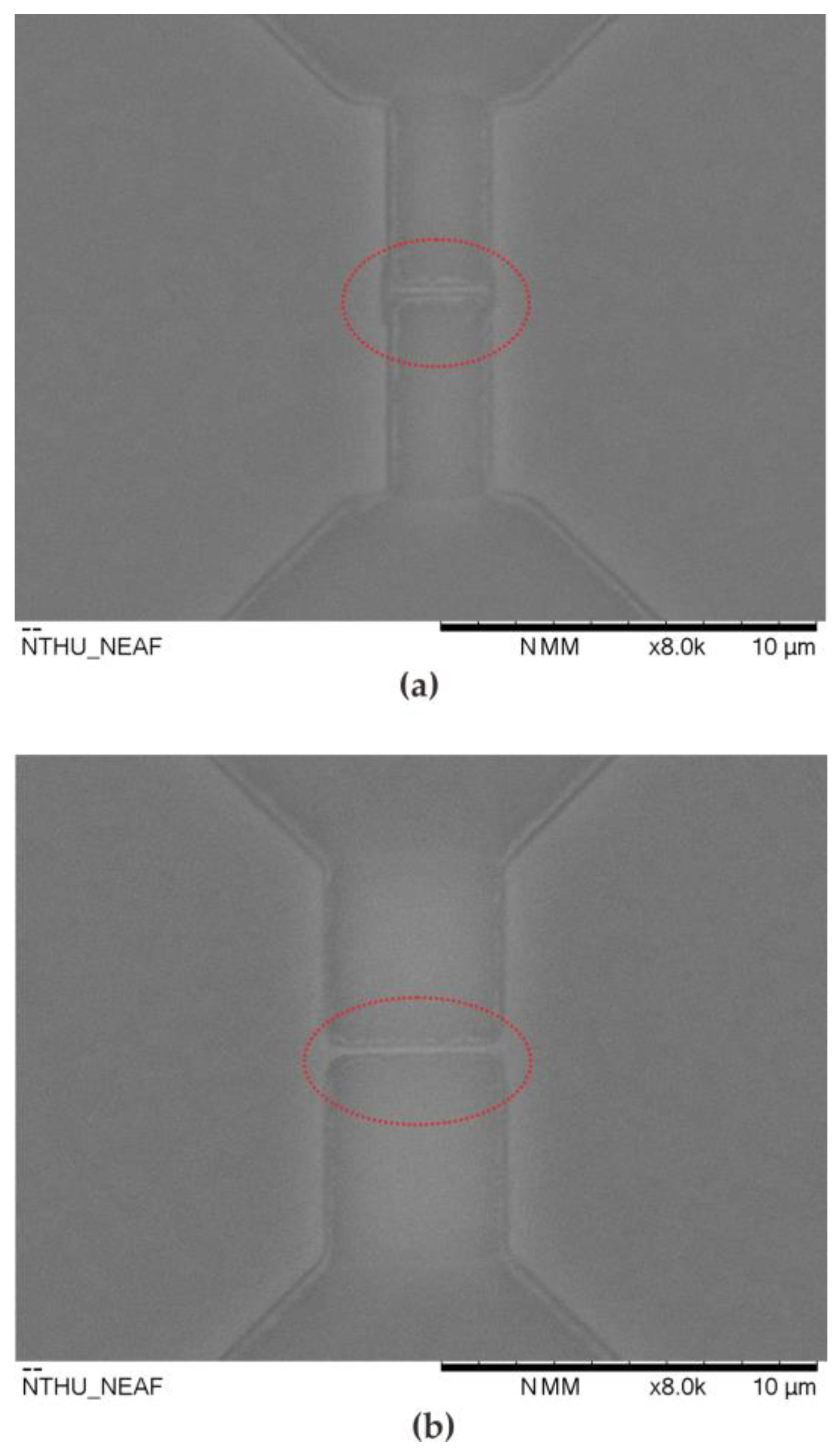
| Item | S (μA/(mg/dL)) | Theoretical | Practical | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔI (nA) | Cres (mg/dL) | ΔI (nA) | Cres (mg/dL) | ||
| A | 0.008 | 0.1 | 0.013 | 14 | 1.75 |
| B | 0.004 | 0.025 | 3.5 | ||
| C | 0.002 | 0.05 | 7 | ||
| D | 0.001 | 0.1 | 14 | ||
| Ref. | Detection Limit | Linear Range | Response Time | Reusability | Sample Type | Enzyme Adopted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15] | 0.16 mM | 0–10 mM | X | X | D-glucose | X |
| [16] | 0.1 μM | 3 μM–2 mM | X | X | D-glucose | X |
| [17] | 1.31 mM | 0–10 mM | >20 s | X | D-glucose/Rabbit blood serum | X |
| [18] | 1 mM | 0–8 mM | X | X | D-glucose | GOx |
| [19] | 3 μM | 10 μM–100 mM | X | X | D-glucose | GOx |
| [20] | 1.23 mg/dL | 10–300 mg/dL | <5 s | 10 times | D-glucose | GOx |
| This work | 1.75 mg/dL | 0–400 mg/dL | <5 s | 30 times | D-glucose | GOx |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-C.; Ho, W.-K.; Wu, C.-C.; Dai, C.-L. The Enzymatic Doped/Undoped Poly-Silicon Nanowire Sensor for Glucose Concentration Measurement. Sensors 2023, 23, 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063166
Hsu C-C, Ho W-K, Wu C-C, Dai C-L. The Enzymatic Doped/Undoped Poly-Silicon Nanowire Sensor for Glucose Concentration Measurement. Sensors. 2023; 23(6):3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063166
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Cheng-Chih, Wen-Kai Ho, Chyan-Chyi Wu, and Ching-Liang Dai. 2023. "The Enzymatic Doped/Undoped Poly-Silicon Nanowire Sensor for Glucose Concentration Measurement" Sensors 23, no. 6: 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063166
APA StyleHsu, C. -C., Ho, W. -K., Wu, C. -C., & Dai, C. -L. (2023). The Enzymatic Doped/Undoped Poly-Silicon Nanowire Sensor for Glucose Concentration Measurement. Sensors, 23(6), 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063166






