Multi-Boundary Empirical Path Loss Model for 433 MHz WSN in Agriculture Areas Using Fuzzy Linear Regression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A ML path loss model with RSSI fluctuation boundaries is proposed using MBFLR based on the measurements in different environments for short grass, tall grass, weeds, and blockage.
- (2)
- A breakpoint distance optimization is proposed for accurate prediction.
- (3)
- The measured RSSI data are captured using Lora LPWAN at 433 MHz for different environments.
2. Related Work
3. Multi-Boundary Fuzzy LR
4. Experimental Setup
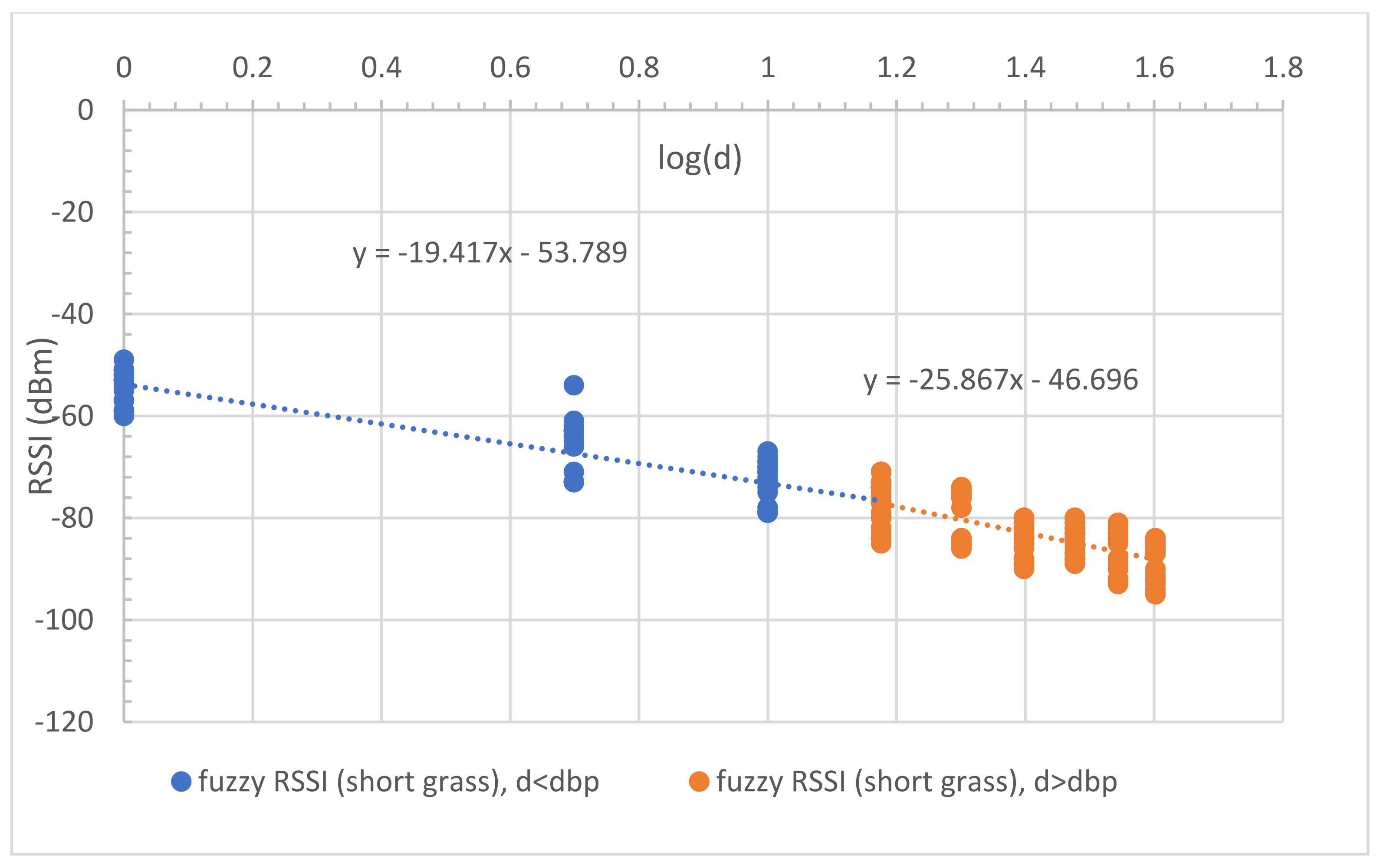
4.1. Short Grass
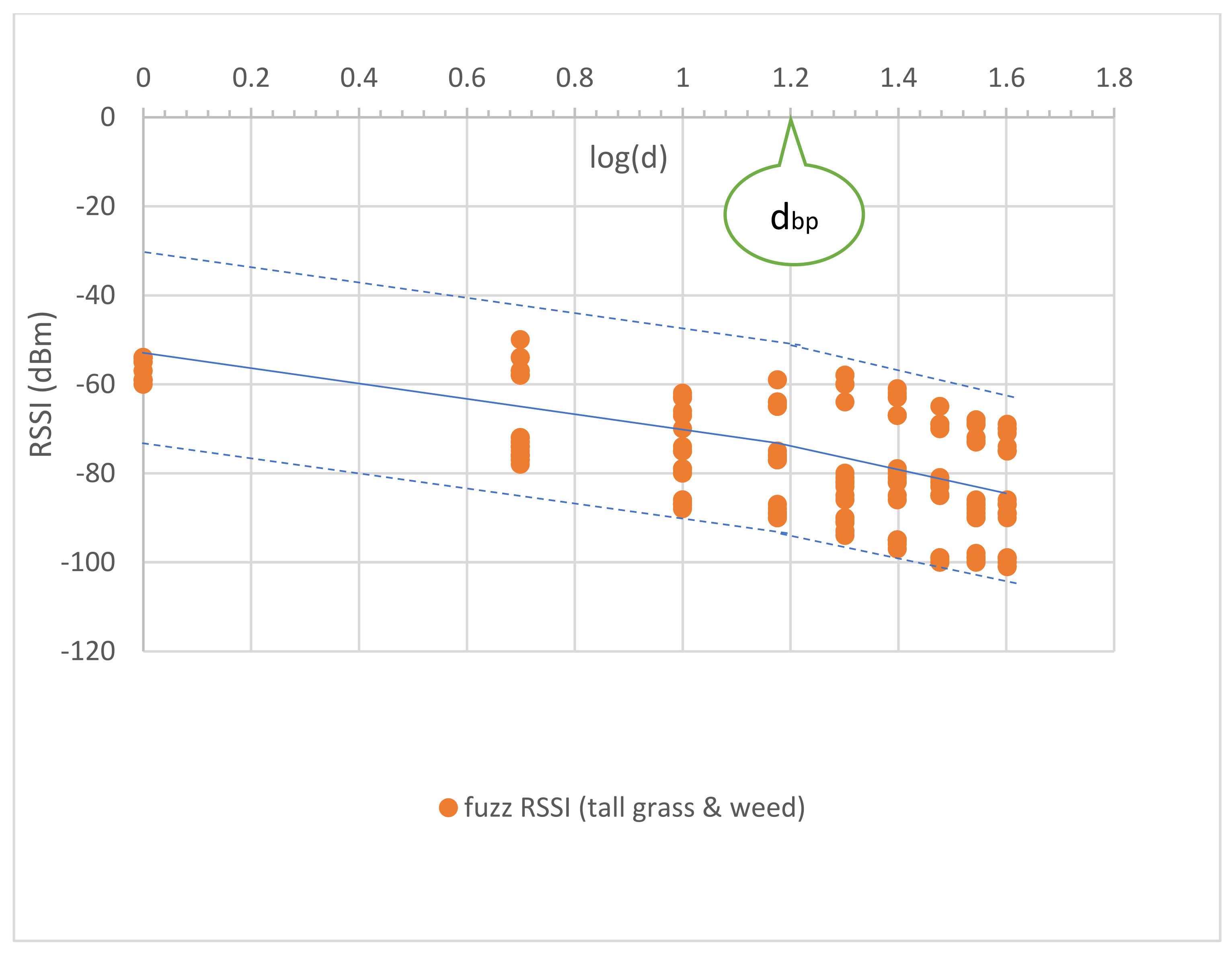
4.2. Tall Grass and Weeds
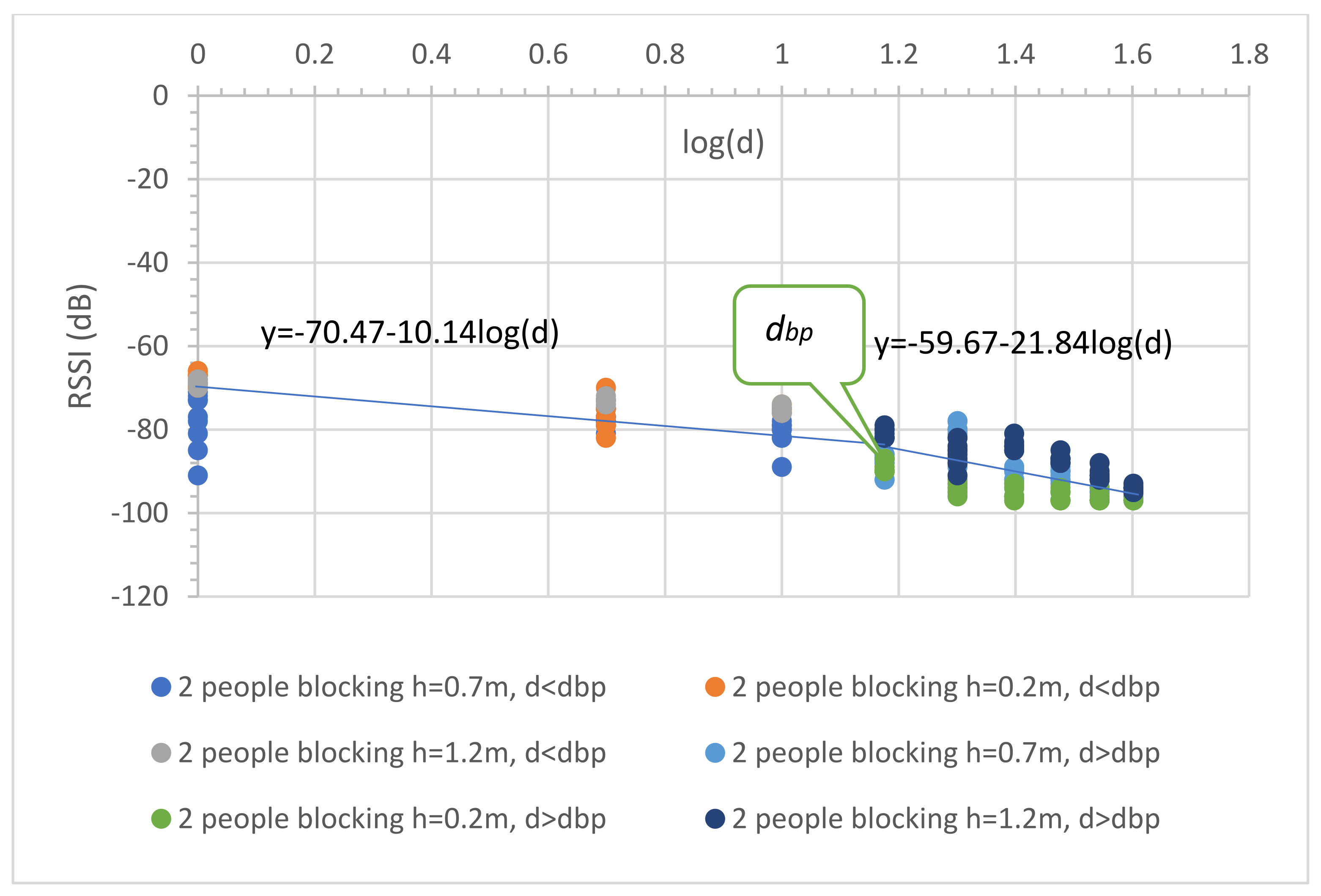
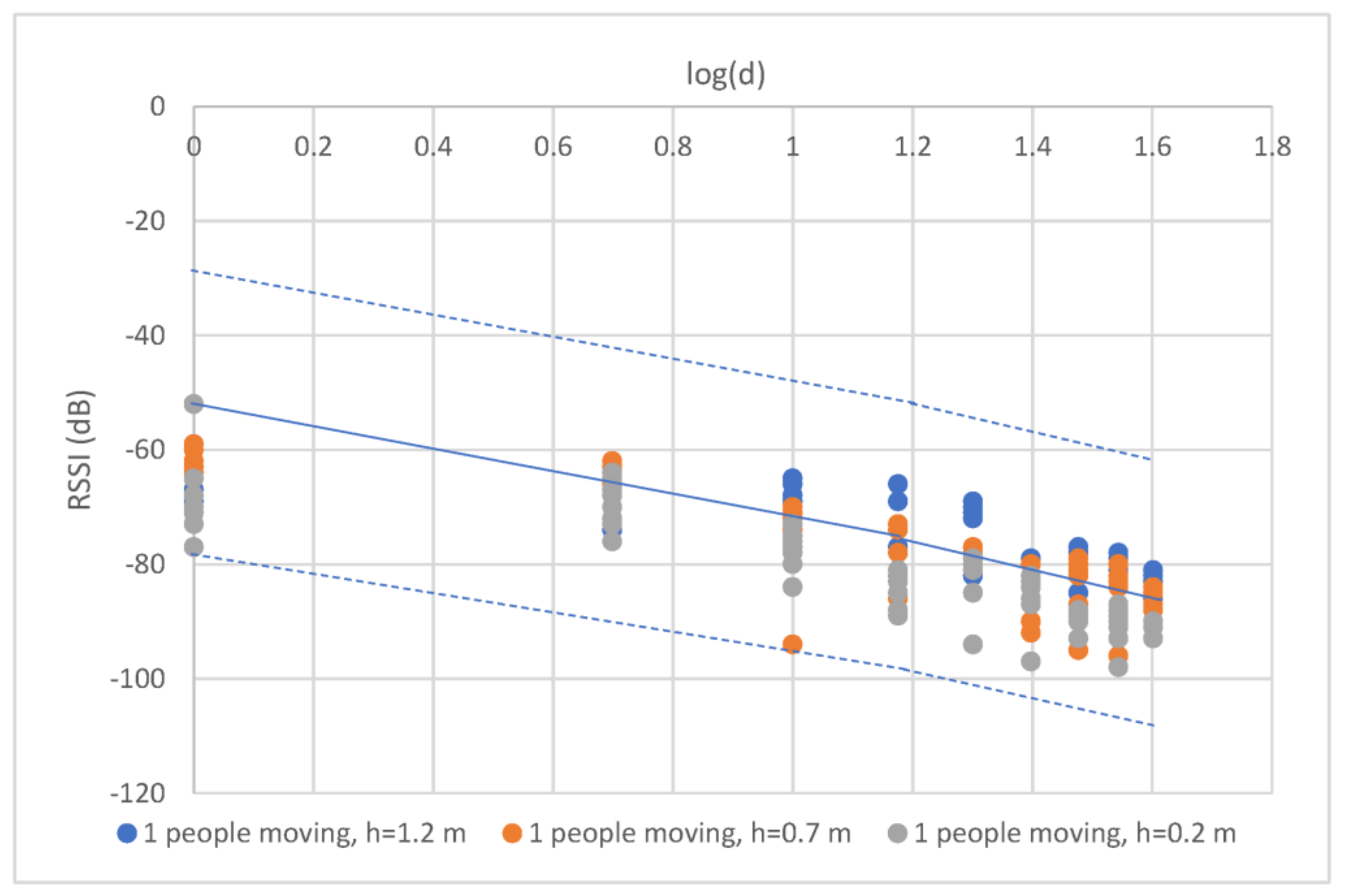
4.3. People Motion
5. Results
5.1. Proposed LR Models
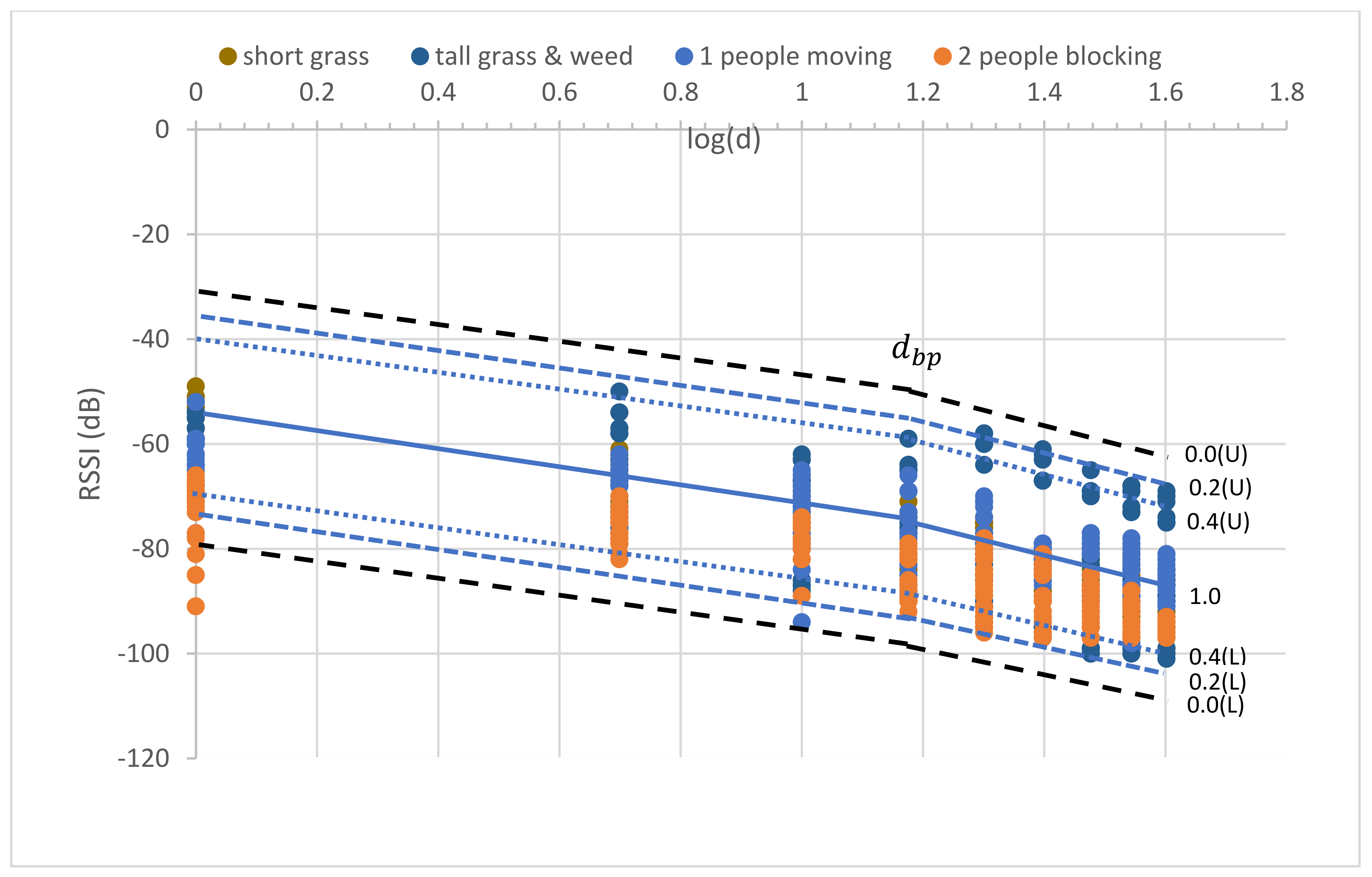
5.2. Proposed MBFLR Models
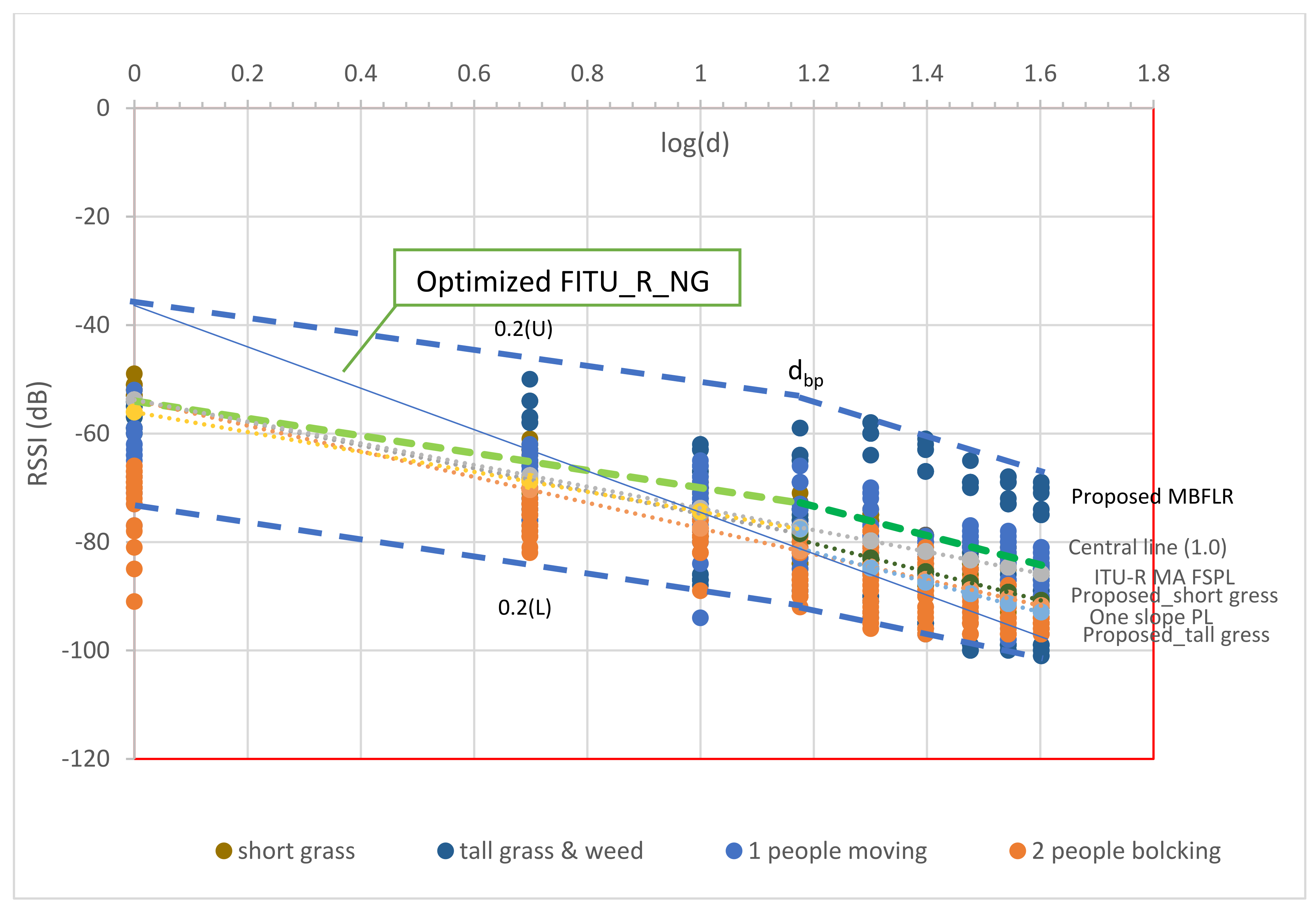
5.3. Model Comparison
- (1)
- One-slope Path Loss Prediction Model (433 MHz)
- (2)
- Optimized FITU-R Model for Near-ground Forest (Optimized FITU-R NGF)
- (3)
- ITU-R Maximum Attenuation and Free Space Path Loss (ITU-R MA FSPL)
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| Description | Abbreviation |
| Received signal strength indicator | RSSI |
| Fuzzy number of RSSI | RSSI’ |
| Distance between transmitting and receiving nodes | d |
| Central value | C |
| Left spread | L |
| Right spread | R |
| Breakpoint distance | |
| Coefficients of the relationship | A, B |
| Fuzzy coefficients of the relationship | |
| Multi-boundary fuzzy linear regression | MBFLR |
| Membership function | |
| Initial membership level |
References
- Citoni, B.; Fioranelli, F.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. Internet of Things and LoRaWAN-Enabled Future Smart Farming. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2019, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, B.; Bourennane, E.-B.; Boucherkha, S.; Chikhi, S. A study of LoRaWAN protocol performance for IoT applications in smart agriculture. Comput. Commun. 2020, 164, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzum, R.; Habaebi, M.H.; Islam, R.; Hakim, G.P.N. Modeling and Quantifying Palm Trees Foliage Loss using LoRa Radio Links for Smart Agriculture Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 7th International Conference on Smart Instrumentation, Measurement and Applications (ICSIMA), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–25 August 2021; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, P.; Sharma, R.P.; Tripathi, S.; Kumar, C.; Ramesh, D. 2.4 GHz RF Received Signal Strength Based Node Separation in WSN Monitoring Infrastructure for Millet and Rice Vegetation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18298–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzar, P.; Michelson, D.G.; Hamdi, M. RSSI-based distributed self-localization for wireless sensor networks used in precision agriculture. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2016, 15, 66386650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakim, G.P.N.; Alaydrus, M.; Bahaweres, R.B. Empirical Approach of Ad hoc Path Loss Propagation Model in Realistic Forest Environments. In Proceedings of the ICRAMET Conference, Jakarta, Indonesia, 3–5 October 2016; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Gzzar, W.T.; Nafea, H.B.; Zaki, F.W. Application of Wireless Sensor Networks Localization in Near Ground Radio Propagation Channel. In Proceedings of the 37th National Radio Science Conference (NRSC 2020), Cairo, Egypt, 8–10 September 2020; pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ostlin, E.; Zepernick, H.J.; Hajime Suzuki, H. Macro cell Path-Loss Prediction Using Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Tech. 2010, 59, 2735–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Du, J.; Chizhik, D.; Valenzuela, R.A.; Sellathurai, M. Machine Learning-Based Urban Canyon Path Loss Prediction Using 28 GHz Manhattan Measurements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 4096–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ma, S.; Lee, H. CNN-Based mmWave Path Loss Modeling for Fixed Wireless Access in Suburban Scenarios. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; He, D.; Ai, B.; Wang, J.; Qi, H.; Guan, K.; Zhong, Z. Artificial Neural Network Based Path Loss Prediction for Wireless Communication Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 199523–199538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, N.; Popoola, S.I.; Surajudeen-Bakinde, N.; Oloyede, A.; Abdulkarim, A.; Abiodun, O.; Ali, M.; Calafate, C.T.; Atayero, A.A. Path Loss Predictions in the VHF and UHF Bands within Urban Environments: Experimental Investigation of Empirical, Heuristics and Geospatial Models. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77293–77307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S.I.; Jefia, A.; Atayero, A.A.; Kinsley, O.; Faruk, N.; Oseni, O.F.; Abolade, R.O. Determination of Neural Network Parameters for Path Loss Prediction in Very High Frequency Wireless Channel. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150462–150483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Ulloa, A.; Ariza-Colpas, P.P.; Sánchez-Moreno, H.; Quintero-Linero, A.P.; Hoz-Franco, E.D. Modeling Radio Wave Propagation for Wireless Sensor Networks in Vegetated Environments: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olasupo, O.E.; Otero, C.E.; Olasupo, K.O.; Kostanic, I. Empirical Path Loss Models for Wireless Sensor Network Deployments in Short and Tall Natural Grass Environments. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayyari, A.; Aldosary, A. Path Loss Results for Wireless Sensor Network Deployment in a Long Grass Environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensors (ICWiSe), Langkawi, Malaysia, 21–22 November 2018; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. Empirical Near Ground Path Loss Modeling in a Forest at VHF and UHF Bands. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ma, X.; Wei, J.; Zhi, W. Measurement and analysis of near-ground propagation models under different terrains for wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anzum, R.; Habaebi, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Hakim, G.P.N.; Mayeen Uddin Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alamri, S.; AbdElrahim, E. A Multiwall Path-Loss Prediction Model Using 433 MHz LoRa-WAN Frequency to Charac-terize Foliage’s Influence in a Malaysian Palm Oil Plantation Environment. Sensors 2022, 22, 5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Parra, L.; Jimenez, J.M.; Parra, M. Deployment strategies of soil monitoring WSN for precision agriculture irrigation scheduling in rural areas. Sensors 2021, 21, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessales, D.; Poussard, A.-M.; Vauzelle, R.; Richard, N. Impact of People Motion on Radio Link Quality: Application to Building Monitoring WSN. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemavathi, N.; Meenalochani, M.; Sudha, S. Influence of Received Signal Strength on Prediction of Cluster Head and of Number Rounds. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, G.P.N.; Habaebi, M.H.; Toha, S.F.; Islam, M.R.; Yusoff, S.H.B.; Adesta, E.Y.T.; Anzum, R. Near Ground Path-loss Propagation Model Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System for Wireless Sensor Network Communication in Forest, Jungle and Open Dirt Road Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Infect. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Fuzzy Sets and Systems: Theory and Applications; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- D’Urso, P. Linear regression analysis for fuzzy/crisp input and fuzzy/crisp output data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2003, 42, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A. Fuzzy Regression Models; Penn State University: State College, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Xing, Y.; MacCartney, G.R.; Molisch, A.F.; Mellios, E.; Zhang, J. Overview of Millimeter Wave Communication for 5G Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6213–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, F. Cellular Mobile Systems Engineering; Artech House Publishers: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, T.S. Wireless Communication; Prentic Hall Publishers: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Al Salameh, M.S.H. Vegetation Attenuation Combined with Propagation Models versus Path Loss Measurements in Forest Areas. In World Symposium on Web Application and Networking-International Conference on Network Technologies and Communication Systems; Jordan University of Science and Technology: Irbid, Jordan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
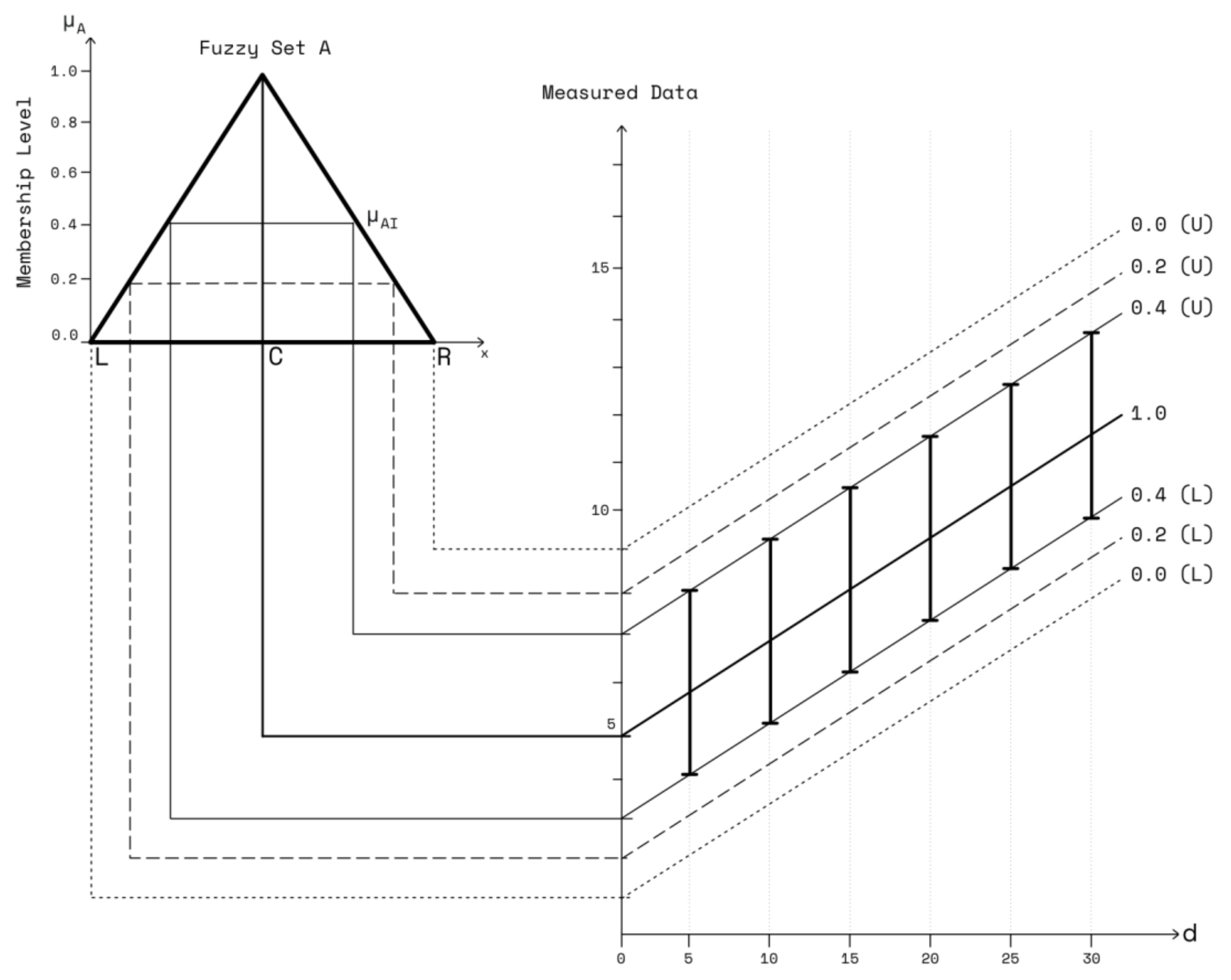



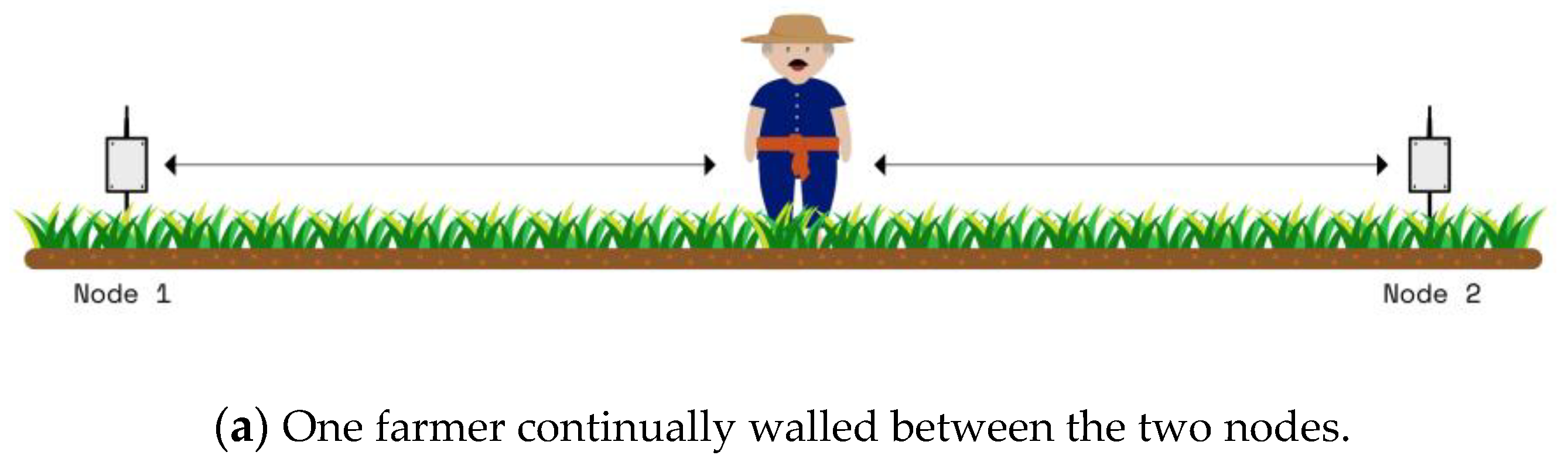




| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| (min, max) | ||
| Antenna gain (omni-directional) | 2.3 | dBi |
| Frequency | 433 | MHz |
| Bandwidth (BW) | 125 | kHz |
| Spreading Factor (SF) | SF7 | |
| Pr (d0 = 1 m) (average) | −57 | dBm |
| Output power | 10 | dBm |
| Coding Rate (CR) | 4/5 | |
| Antenna height (htx, hrx) | (0.2, 0.7, 1.2) | m |
| Short grass height | (0.0, 0.3) | m |
| Tall grass height | (0.3, 0.5) | m |
| Breakpoint distance | 15 | m |
| Small-scale distance (λ/4) | 0.4 | m |
| Large-scale distance (Tx-Rx) | (1, 40) | m |
| Name | Models | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short Grass | Tall Grass & Weed | People Blockage | ||
| Optimized FITU-R NG [17] | 25.2 | 27.7 | 24.7 | |
| FITU-R MA FSPL [31] | 4.3 | 10.9 | 8.1 | |
| One Slope PL LOS, 433 MHz [19] | (n = 2.37 for SF7 and BW 125 kHz) | 5.7 | 11.8 | 8.3 |
| Proposed dual-slope (Based on measurement) | - short grass: RSSI1(d) = −53.79 − 19.42log(d); d < dbp RSSI2(d) = −49.31 − 25.87log(d); d > dbp - tall grass: RSSI1(d) = −56.04 − 18.37log(d); d < dbp RSSI2(d) = −43.76 − 26.95log(d); d > dbp | 4.6 4.4 | 11.4 10.9 | 8.0 7.8 |
| Proposed (MBFLR) | RSSI(d) = [−55.4, −18.2] + [−16.2, 0.2]log(d), d < RSSI(d) = [−42.9, −22.5] + [−26.8, 4.9]log(d), d > - = 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phaiboon, S.; Phokharatkul, P. Multi-Boundary Empirical Path Loss Model for 433 MHz WSN in Agriculture Areas Using Fuzzy Linear Regression. Sensors 2023, 23, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073525
Phaiboon S, Phokharatkul P. Multi-Boundary Empirical Path Loss Model for 433 MHz WSN in Agriculture Areas Using Fuzzy Linear Regression. Sensors. 2023; 23(7):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073525
Chicago/Turabian StylePhaiboon, Supachai, and Pisit Phokharatkul. 2023. "Multi-Boundary Empirical Path Loss Model for 433 MHz WSN in Agriculture Areas Using Fuzzy Linear Regression" Sensors 23, no. 7: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073525
APA StylePhaiboon, S., & Phokharatkul, P. (2023). Multi-Boundary Empirical Path Loss Model for 433 MHz WSN in Agriculture Areas Using Fuzzy Linear Regression. Sensors, 23(7), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073525






