Robotic Ultrasonic Testing Technology for Aero-Engine Blades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods and Configuration
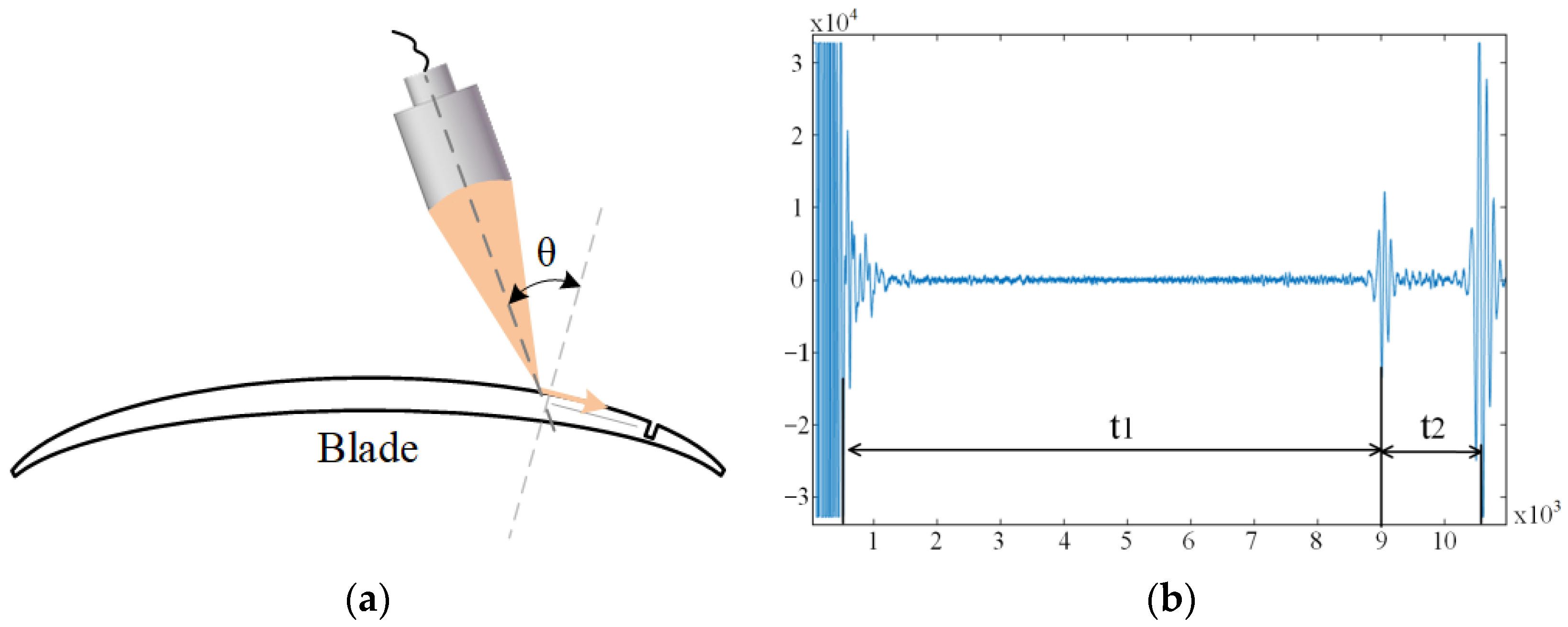
2.1. Thickness Measurement
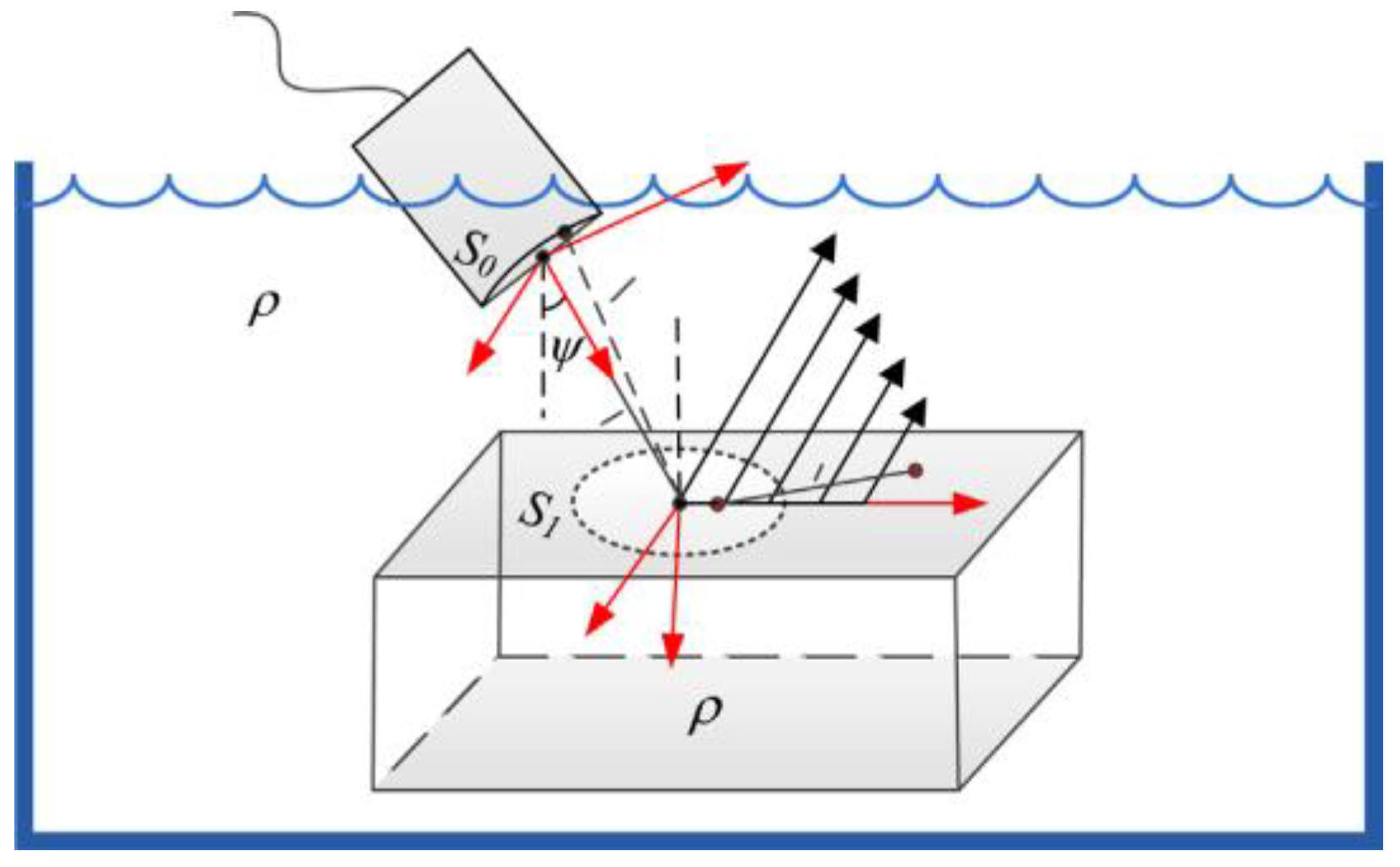
2.2. Inlet and Exhaust Side Defect Detection Method
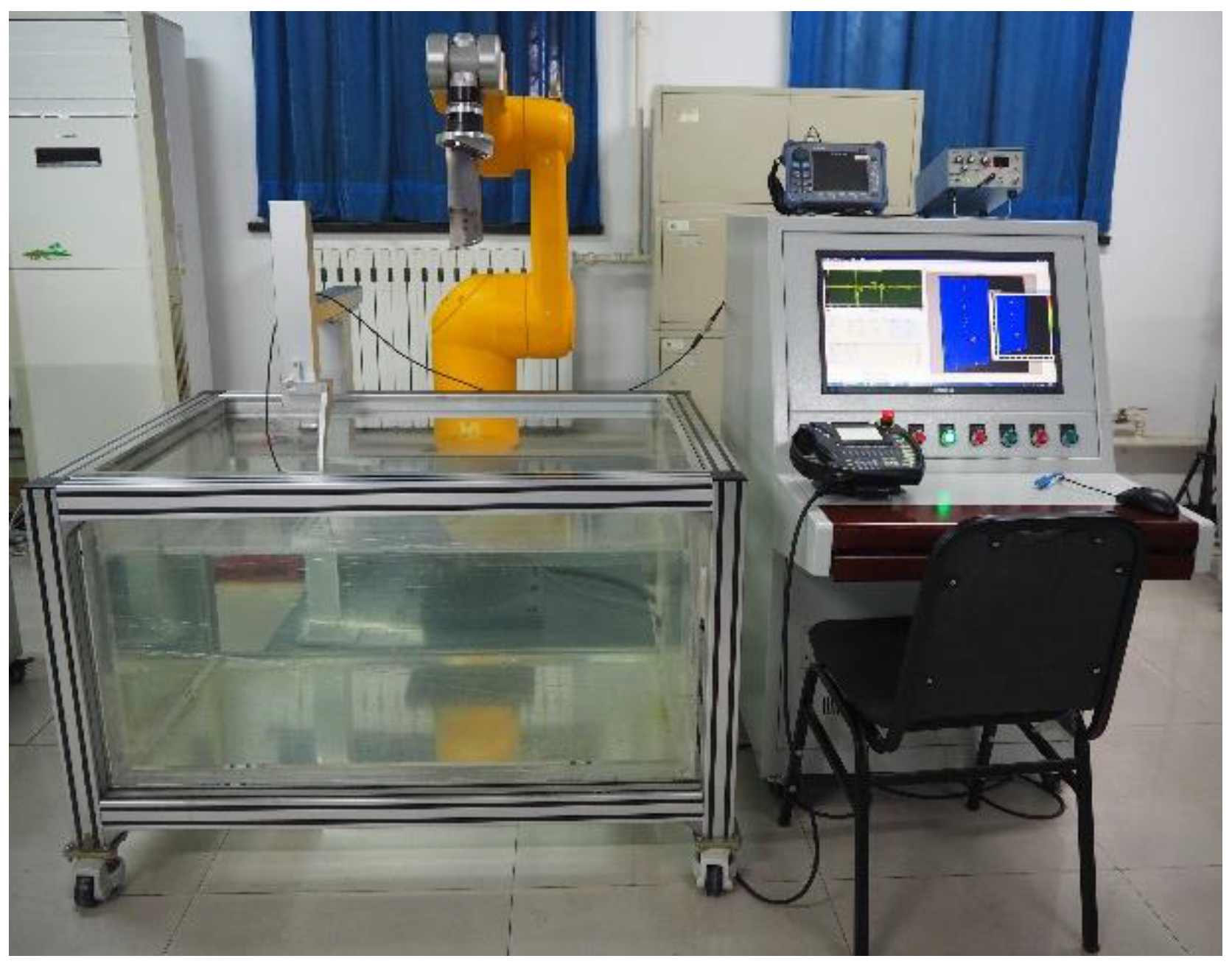
2.3. System Components
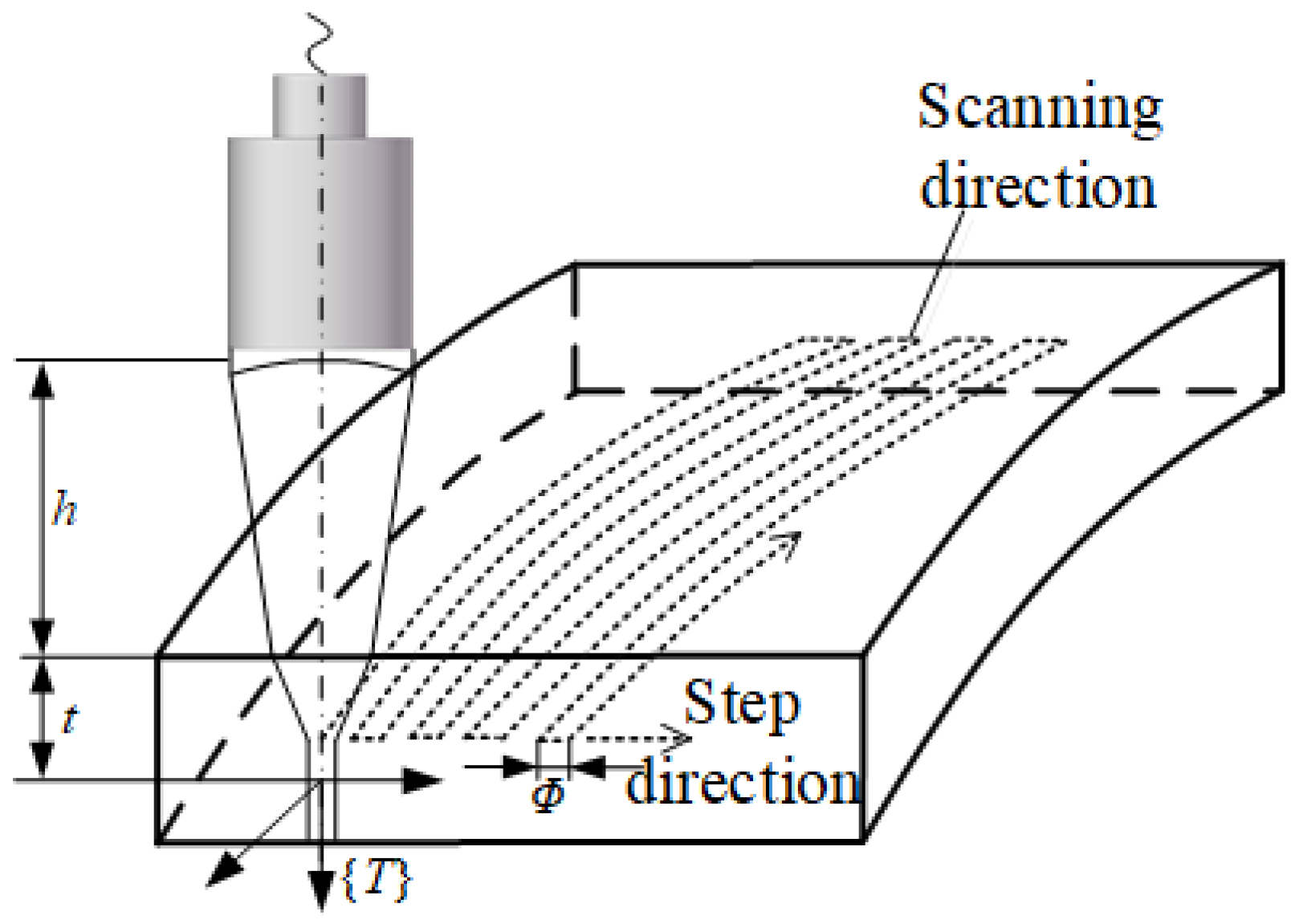
2.4. Robot Sweep Track Planning
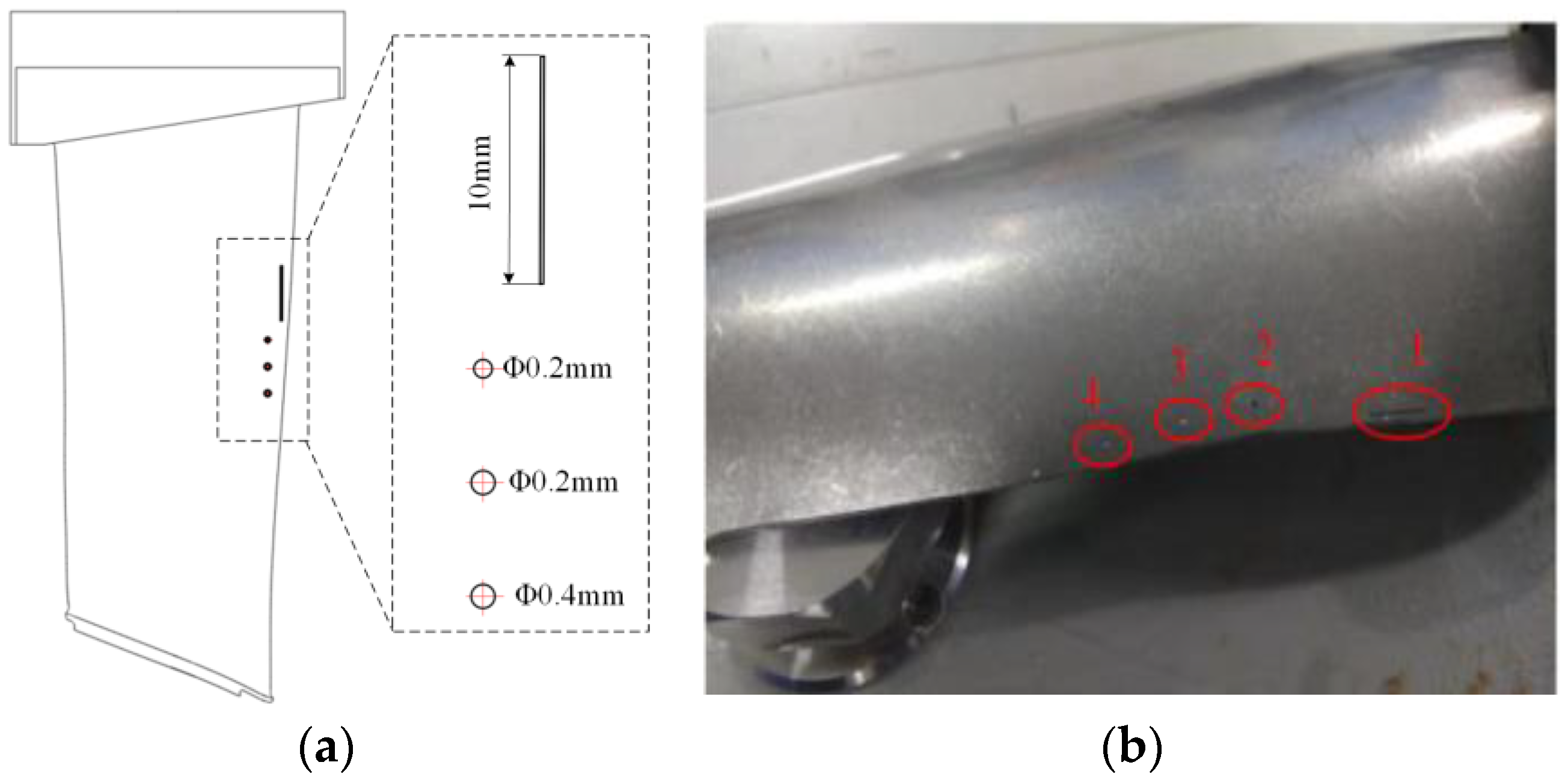
2.5. Samples Preparation
3. Experiment Results and Discussion
3.1. Thickness Measurement
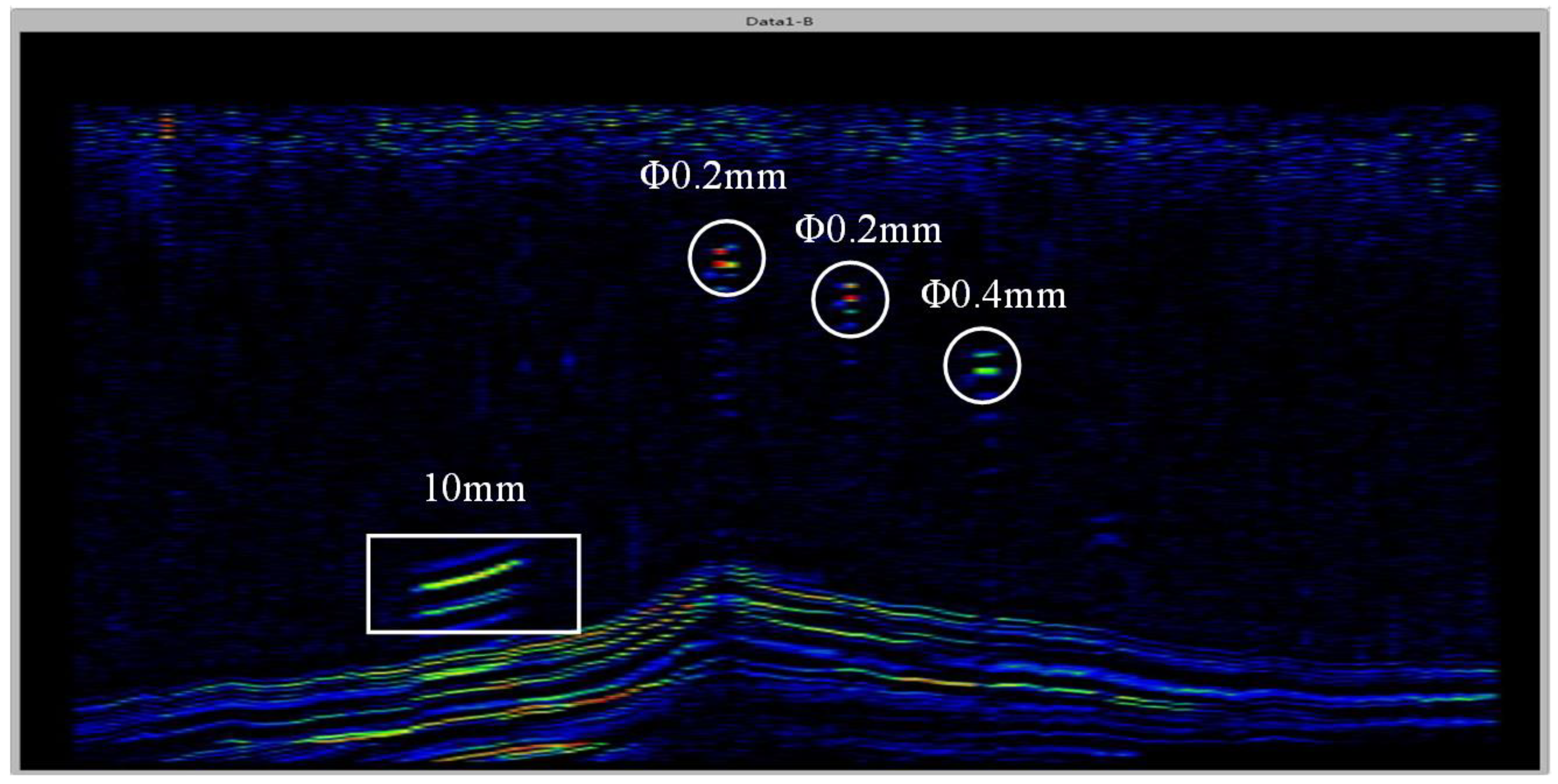
3.2. B-Scan Imaging of the Exhaust Gas Edge
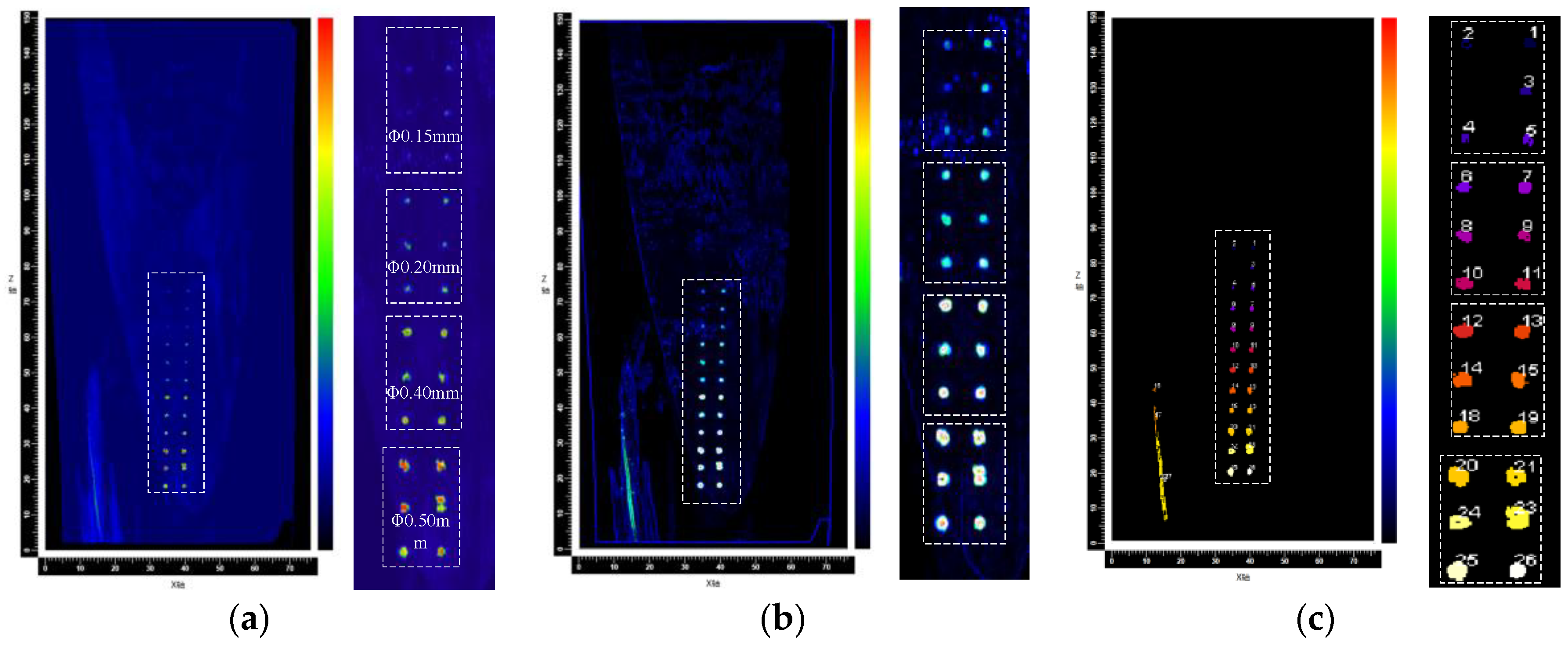
3.3. C-Scan Imaging of the Leaf body
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altenberger, I.; Nalla, R.K.; Sano, Y.; Wagner, L.; Ritchie, R.O. On the effect of deep rolling and laser peening on the stress-controlled low and high cycle fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V at elevated temperatures up to 550 °C. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 44, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.P. Physical Acoustics: Principles and Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Popovics, J.S.; Schubert, F. Leaky Rayleigh and Scholte waves at the fluid–solid interface subjected to transient point loading. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanyue, G.; Xiaokai, W.; Lin, H.; Li, L. Quantitative ultrasonic testing for near-surface defects of large ring forgings using feature extraction and GA-SVM. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107714. [Google Scholar]
- Wirdelius, H.; Persson, G. Simulation based validation of the detection capacity of an ultrasonic inspection procedure. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 41, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, A.; Wirdelius, H. Ultrasonic probe modeling and nondestructive crack detection. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; You, Y.; Xu, C.G.; Xiao, D.G. Profile tracking with ultrasonic alignment for automatic non-destructive testing of complex structures. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 49, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Secanellas, S.A.; León, I.G.; Parrilla, M. Methodology for the Generation of High-Quality Ultrasonic Images of Complex Geometry Pieces Using Industrial Robots. Sensors 2023, 23, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Xiao, D. Crack assessment of wheel hubs via an ultrasonic transducer and industrial robot. Sensors 2018, 18, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineo, C.; Pierce, S.G.; Wright, B.; Copper, I.; Nicholson, P.I. PAUT inspection of complex-shaped composite materials through six DOFs robotic manipulators. Insight Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2015, 57, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, C.; Pierce, S.G.; Nicholson, P.I.; Cooper, I. Robotic path planning for non-destructive testing—A custom MATLAB toolbox approach. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2016, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, M.; Mineo, C.; Pierce, S.G.; Nicholson, P.I.; Cooper, I. Computer-Aided Tool Path Generation for Robotic Non-Destructive Inspection. Conf. Br. Inst. Non-Destr. Test. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, M.; Pierce, S.G.; MacLeod, C.N.; Mineo, C.; Summan, R. Off-line Scan Path Planning for Robotic NDT. Measurement 2018, 122, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, C.; MacLeod, C.; Morozov, M.; Pierce, S.G.; Lardner, T.; Summan, R.; Powell, J.; McCubbin, P.; McCubbin, C.; Munro, G.; et al. Fast ultrasonic phased array inspection of complex geometries delivered through robotic manipulators and high speed data acquisition instrumentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Xu, C.; Hao, J.; Xiao, D.; Yang, W. Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing System of Semi-Enclosed Workpiece with Dual-Robot Testing System. Sensors 2019, 19, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Tian, T.T.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, J.B.; Liu, D.H. An ultrasonic testing method for wall thickness of turbine blades. Measurement 2022, 198, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jason, L.; Gilles, R.; Sylvain, C.; Lionel, L. Interactive Ultrasonic Field Simulation for Non Destructive Testing, Twelfth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision 2015, Le Creusot, France, 3–5 June 2015; Volume 9534. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Turner, J.A.; Schmerr, L.W.; Li, X. Non-paraxial multi-Gaussian beam model of Leaky Rayleigh waves generated by a focused immersion transducer. Ultrasonics 2019, 97, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Li, S. Study on PCA-SAFT imaging using leaky Rayleigh waves. Measurement 2021, 170, 108708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xu, C.; Xiao, D.; Liu, F.; Yin, M. An Optimized Robotic Scanning Scheme for Ultrasonic NDT of Complex Structures. Exp. Tech. 2017, 41, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Apparatus | Brand | Model | Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robot | Staubli | TX90L | Repeatability: 0.035 mm |
| Ultrasonic Pulser/Reciver | Olympus | 5077PR | Receiving bandwidth: 1 KHz–35 MHz |
| Ultrasonic probe | Olympus | V319 | 20 MHz |
| A/D Acquisition Card | Acquisition Logic | AL12200 | sample rate: 250 MHz |
| Container | Non-standard | Non-standard | Volume: 500 L |
| Standard Value | CMM Calibration | Measurement Results | Measurement Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.956 | 1.946 | −0.009 |
| 3.5 | 3.466 | 3.462 | −0.003 |
| 5 | 4.972 | 4.966 | −0.005 |
| 6.5 | 6.468 | 6.457 | −0.010 |
| 8 | 7.964 | 7.963 | −0.001 |
| 9.5 | 9.397 | 9.405 | 0.008 |
| 11 | 10.938 | 10.953 | 0.015 |
| 12 | 11.937 | 11.955 | 0.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, P.; Xu, C.; Xiao, D. Robotic Ultrasonic Testing Technology for Aero-Engine Blades. Sensors 2023, 23, 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073729
Ma P, Xu C, Xiao D. Robotic Ultrasonic Testing Technology for Aero-Engine Blades. Sensors. 2023; 23(7):3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073729
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Pengzhi, Chunguang Xu, and Dingguo Xiao. 2023. "Robotic Ultrasonic Testing Technology for Aero-Engine Blades" Sensors 23, no. 7: 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073729
APA StyleMa, P., Xu, C., & Xiao, D. (2023). Robotic Ultrasonic Testing Technology for Aero-Engine Blades. Sensors, 23(7), 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073729





