Progressively Hybrid Transformer for Multi-Modal Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper proposes a multi-modal hybrid transformer, which applies the feature hybrid mechanism (FHM) to fuse multi-modal information at the feature level by the modal-specific controller and modal information embedding.
- This paper designs a random hybrid augmentation (RHA) to fuse multi-modal information at the image level, which upgrades the multi-modal hybrid transformer into a progressively hybrid transformer (PHT) that fuses multi-modal information at both image and feature levels.
- Experimental results on RGBNT100 and RGBN300 demonstrate that the proposed PHT outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
2. Related Works
2.1. Visible Re-Identification
2.2. Deep Architecture
2.3. Data Augmentation
3. Methodology
3.1. Random Hybrid Augmentation
- (1)
- Initializing a sized whose elements are equal to 1.
- (2)
- Random zero setting local regions of , that is,where and are y-coordinate and x-coordinate, respectively; is the j-th zero setting region that has a random aspect ratio and a random area. Please note that each zero setting region’s max height and width are and .
- (3)
- Cropping each modal image as follows.where ⊗ is element-wise multiplication operation; is the cropped part of the i-th modal image, and is the rest part that keeps unchanging.
3.2. Feature Hybrid Mechanism-Based Multi-Modal Hybrid Transformer
3.2.1. Modal-Specific Controller
3.2.2. Modal Information Embedding
3.3. Progressively Hybrid Transformer
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art
4.3. Analysis of Feature Hybrid Mechanism
4.3.1. Influence of Modal-Specific Controller
4.3.2. Role of Modal Information Embedding
4.3.3. Impact of Position Embedding
4.3.4. Effect of Feature Fusion
4.4. Analysis of Random Hybrid Augmentation
4.4.1. Comparison with the Preliminary Work
4.4.2. Role of Image Random Cropper
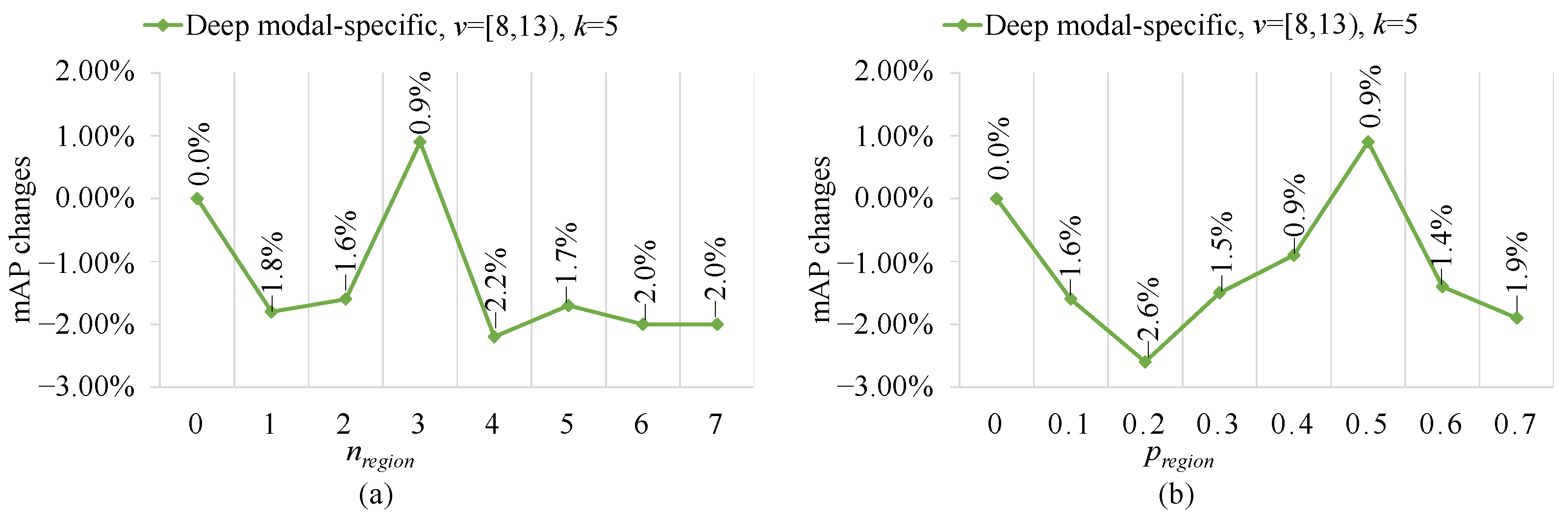
4.4.3. Impact of Local Region Hybrider
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ReID | Re-identification |
| PHT | Progressively hybrid transformer |
| RHA | Random hybrid augmentation |
| FHM | Feature hybrid mechanism |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| TIR | Thermal-infrared |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| IRC | Image random cropper |
| LRH | Local region hybrider |
| MC | Modal-specific controller |
| MIE | Modal information embedding |
| CMC | Cumulative matching characteristic |
| mAP | Mean average precision |
| R1 | Rank 1 identification rate |
| R5 | Rank 5 identification rate |
| R10 | Rank 10 identification rate |
| ViT | Vision transformer |
| SGD | Stochastic gradient descent |
References
- Avola, D.; Cinque, L.; Fagioli, A.; Foresti, G.L.; Pannone, D.; Piciarelli, C. Bodyprint—A meta-feature based LSTM hashing model for person re-identification. Sensors 2020, 20, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolanti, M.; Romeo, L.; Liciotti, D.; Pietrini, R.; Cenci, A.; Frontoni, E.; Zingaretti, P. Person re-identification with RGB-D camera in top-view configuration through multiple nearest neighbor classifiers and neighborhood component features selection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.K.; Bhuiyan, A.; Bappee, F.K.; Islam, M.M.; Hasan, M. Person Re-Identification with RGB–D and RGB–IR Sensors: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Hao, Y.; Khokhar, M.S.; Kumar, R.; Cai, J.; Kumar, J.; Aftab, M.U. Trends in vehicle re-identification past, present, and future: A comprehensive review. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Fu, P.; Ji, X. Voc-reid: Vehicle re-identification based on vehicle-orientation-camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 602–603. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Yao, Z.; Yi, S.; Shao, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Orientation invariant feature embedding and spatial temporal regularization for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Zha, Z.J.; Huang, Q. Fine-grained feature alignment with part perspective transformation for vehicle reid. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 619–627. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Shao, L. Aware attentive multi-view inference for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6489–6498. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Liao, S.; Lei, Z.; Cai, C.; Zheng, L. Vehicle re-identification using quadruple directional deep learning features. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.D.; Ullah, H. A survey of advances in vision-based vehicle re-identification. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 182, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, G.; Xiang, T.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C. Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 2872–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, P.; Fang, Z.; Lu, Q. Focus on the visible regions: Semantic-guided alignment model for occluded person re-identification. Sensors 2020, 20, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. A Binarized segmented ResNet based on edge computing for re-identification. Sensors 2020, 20, 6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, R.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Yang, S. Relation-based deep attention network with hybrid memory for one-shot person re-identification. Sensors 2021, 21, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Castrillón-Santana, M.; Hernández-Sosa, D. On the use of simple geometric descriptors provided by RGB-D sensors for re-identification. Sensors 2013, 13, 8222–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, A.; Luo, B. Multi-spectral vehicle re-identification: A challenge. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11345–11353. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Robust multi-modality person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3529–3537. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, A.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.; Tang, J.; Ma, J. Multi-spectral Vehicle Re-identification with Cross-directional Consistency Network and a High-quality Benchmark. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.00632. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zheng, A.; He, R.; Tang, J. Interact, embed, and enlarge: Boosting modality-specific representations for multi-modal person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virginia, VA, USA, 17–19 November 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2633–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Generative and Attentive Fusion for Multi-spectral Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 21–24 October 2022; pp. 1565–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenou, E.; Rincon, J.; Miller, P.; Devlin-Hill, P. Closing the Domain Gap for Cross-modal Visible-Infrared Vehicle Re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Montréal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 2728–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, X. H-ViT: Hybrid Vision Transformer for Multi-modal Vehicle Re-identification. In Proceedings of the CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 27–28 August 2022; pp. 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Qi, J.; Lu, H. Hat: Hierarchical aggregation transformers for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Khorramshahi, P.; Kumar, A.; Peri, N.; Rambhatla, S.S.; Chen, J.C.; Chellappa, R. A dual-path model with adaptive attention for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6132–6141. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, K.; Tang, M.; Wang, J. Two-level attention network with multi-grain ranking loss for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z. Exploiting Multi-view Part-wise Correlation via an Efficient Transformer for Vehicle Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 25, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chang, H.; Ma, B.; Bai, S.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Clothes-changing person re-identification with rgb modality only. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Deng, J.; Aftab, M.U.; Khokhar, M.S.; Kumar, R. Efficient and deep vehicle re-identification using multi-level feature extraction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chuang, Y.Y.; Satoh, S. Illumination-adaptive person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 3064–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Da Xu, R.Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Deng, C. Illumination adaptive person reid based on teacher-student model and adversarial training. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 2321–2325. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Nord, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-first AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, D.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Yu, N. Online multi-object tracking with unsupervised re-identification learning and occlusion estimation. Neurocomputing 2022, 483, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Only, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 6881–6890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gavves, E. Nformer: Robust person re-identification with neighbor transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–25 June 2022; pp. 7297–7307. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A survey on vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Cheng, M.M. P2T: Pyramid pooling transformer for scene understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ye, M.; Qi, M.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J.; Lin, C.W. Structure-aware positional transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Random erasing data augmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13001–13008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Learning generalisable omni-scale representations for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5056–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, F. Benchmarks for corruption invariant person re-identification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00880. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H. TumorGAN: A multi-modal data augmentation framework for brain tumor segmentation. Sensors 2020, 20, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojagh, S.; Cauteruccio, F.; Terracina, G.; Liang, S.H. Enhanced air quality prediction by edge-based spatiotemporal data preprocessing. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 96, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Qi, W.; Chan, S.C. A Color/Illuminance Aware Data Augmentation and Style Adaptation Approach to Person Re-Identification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 115826–115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5098–5107. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, D.; Brennan, S.; Tao, H. Evaluating appearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation for Tracking and Surveillance, Arusha, Tanzanian, 14 October 2007; Volume 3, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Exploring self-attention for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–18 June 2020; pp. 10076–10085. [Google Scholar]
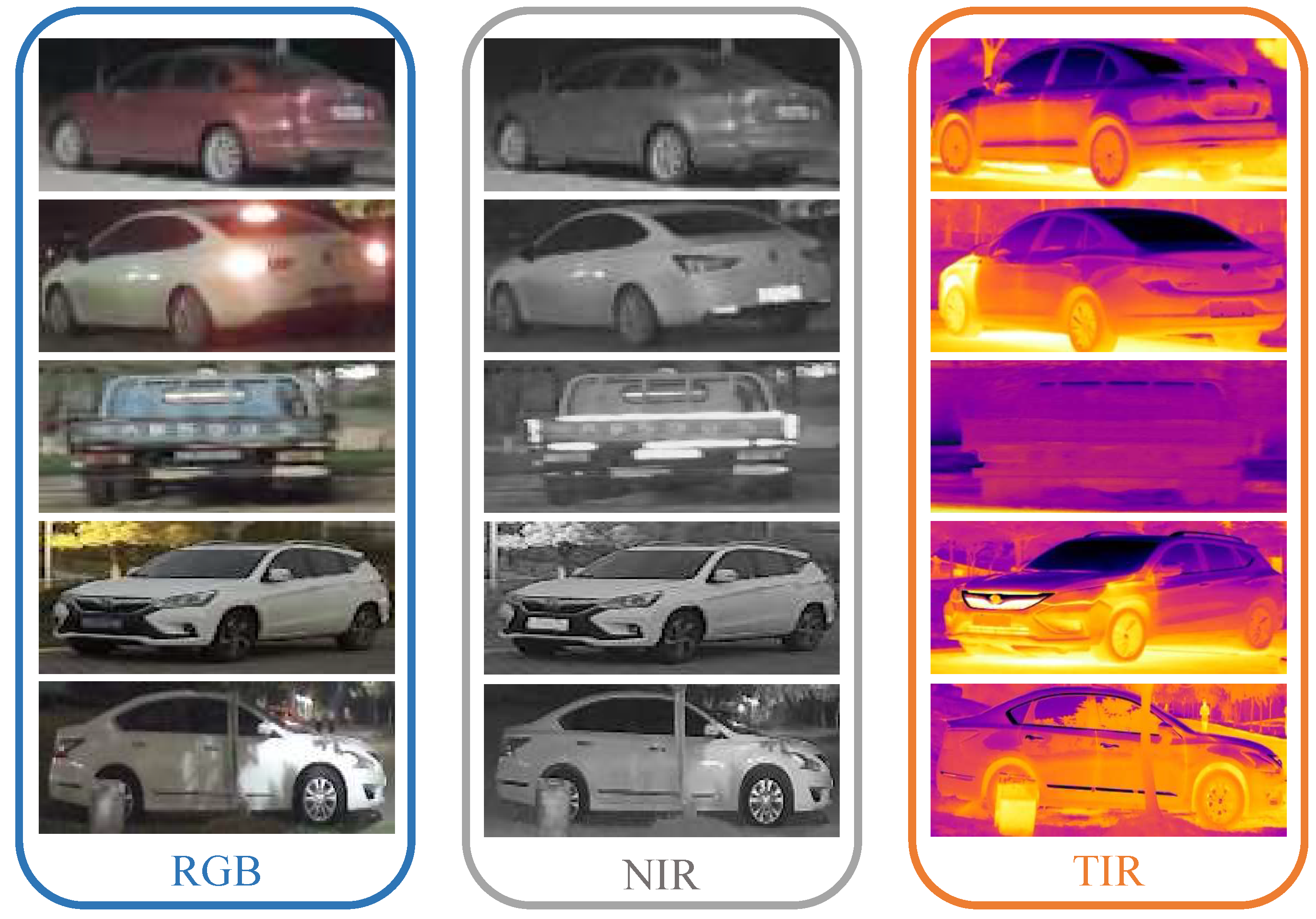





| RGBNT100 | RGBN300 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) | mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) |
| HAMNet [17] | 65.4 | 85.5 | 87.9 | 88.8 | 61.9 | 84.0 | 86.0 | 87.0 |
| TransReID [16] | 60.1 | 82.2 | 83.7 | 84.7 | 67.1 | 86.5 | 88.0 | 88.7 |
| GAFNet [21] | 74.4 | 93.4 | 94.5 | 95.0 | 72.7 | 91.9 | 93.6 | 94.2 |
| CCNet [19] | 77.2 | 96.3 | 97.2 | 97.7 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| DANet [22] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 71.0 | 89.9 | 90.9 | 91.5 |
| PHT (Proposed) | 79.9 | 92.7 | 93.2 | 93.7 | 79.3 | 93.7 | 94.8 | 95.3 |
| Type | v | k | Patch Embedding Layer | Transformer Encoder Layers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully modal common | 0 | 0 | 0 | Common | Common: all Layers |
| Fully modal specific | 0 | Specific | Specific: all Layers | ||
| Shallow modal specific | 0 | t | Specific | Specific: the first layers | |
| Medium modal specific | 1 | Common | Specific: the first k layers | ||
| Deep modal specific | 1 | Common | Specific: the last k layers | ||
| v | k | Type | RGBNT100 | RGBN300 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) | mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) | |||
| [0, 0) | 0 | Common | 76.5 | 91.5 | 93.1 | 93.6 | 77.2 | 91.2 | 92.5 | 93.1 |
| Specific | 76.1 | 91.5 | 92.9 | 93.4 | 77.8 | 92.8 | 93.6 | 93.8 | ||
| [0, 11) | 11 | Common | 78.1 | 91.9 | 92.7 | 93.2 | 78.8 | 93.5 | 94.5 | 95.2 |
| Specific | 77.7 | 92.1 | 92.9 | 93.7 | 79.0 | 93.7 | 94.7 | 95.1 | ||
| [1, 10) | 9 | Common | 78.2 | 93.4 | 94.2 | 94.8 | 78.4 | 93.4 | 94.4 | 94.8 |
| Specific | 76.7 | 91.7 | 93.1 | 93.9 | 78.4 | 93.2 | 94.2 | 94.8 | ||
| [8, 13) | 5 | Common | 79.0 | 93.4 | 94.4 | 95.3 | 78.5 | 92.3 | 93.1 | 93.7 |
| Specific | 77.6 | 90.6 | 91.6 | 92.1 | 78.4 | 92.8 | 93.7 | 94.2 | ||
| [0, 13) | 13 | Common | 76.2 | 92.7 | 93.6 | 94.3 | 77.5 | 92.4 | 93.3 | 94.0 |
| Specific | 76.9 | 92.8 | 94.2 | 94.6 | 77.2 | 92.5 | 93.2 | 93.7 | ||
| Fusion | RGBNT100 | RGBN300 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) | mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) | |
| Average | 79.0 | 93.4 | 94.4 | 95.3 | 78.5 | 92.3 | 93.1 | 93.7 |
| Hadamard Product | 45.2 | 63.0 | 65.9 | 67.6 | 72.0 | 89.1 | 90.5 | 91.2 |
| Concatenating | 74.9 | 92.4 | 93.5 | 94.1 | 75.6 | 91.2 | 92.3 | 92.9 |
| Local Region Hybrider | mAP (%) | R1 (%) | R5 (%) | R10 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 79.9 | 92.7 | 93.2 | 93.7 |
| Self-excluding Average | 78.7 | 91.8 | 92.6 | 93.1 |
| Hadamard Product | 78.8 | 91.7 | 92.9 | 93.6 |
| Self-excluding Hadamard Product | 76.8 | 91.1 | 92.1 | 92.5 |
| Randomly Swapping | 78.0 | 91.0 | 92.1 | 92.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, W.; Huang, L.; Liang, J.; Hong, L.; Zhu, J. Progressively Hybrid Transformer for Multi-Modal Vehicle Re-Identification. Sensors 2023, 23, 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094206
Pan W, Huang L, Liang J, Hong L, Zhu J. Progressively Hybrid Transformer for Multi-Modal Vehicle Re-Identification. Sensors. 2023; 23(9):4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094206
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Wenjie, Linhan Huang, Jianbao Liang, Lan Hong, and Jianqing Zhu. 2023. "Progressively Hybrid Transformer for Multi-Modal Vehicle Re-Identification" Sensors 23, no. 9: 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094206
APA StylePan, W., Huang, L., Liang, J., Hong, L., & Zhu, J. (2023). Progressively Hybrid Transformer for Multi-Modal Vehicle Re-Identification. Sensors, 23(9), 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094206






