MXene-Based Flexible Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sample
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.2.1. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Method
2.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) Method
2.2.3. Mechanical Testing (Youngs Modulus)
2.2.4. ECG and EMG Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Composition Identification
3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Results
3.3. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) Results
3.4. Mechanical Testing Results
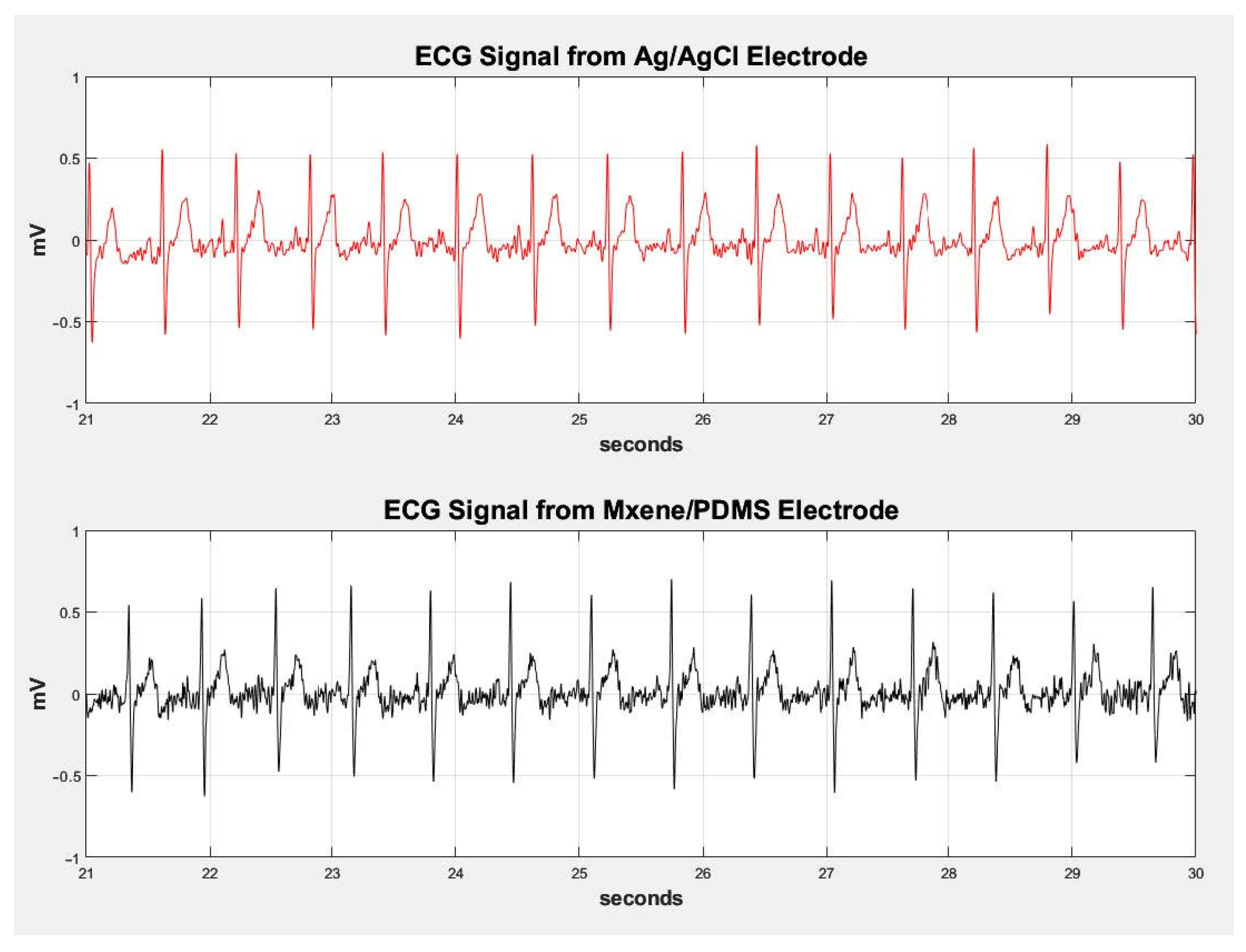
3.5. ECG and EMG Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratner, B.D.; Hoffman, A.S.; Schoen, F.J.; Lemons, J.E. Biomaterial Science, 3rd ed.; Elesevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Guo, A.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in Flexible Noninvasive Electrodes for Surface Electromyography Acquisition. npj Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, A.M.; Tayebi, L.; Abbasi, M.; Vaez, A.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Vafa, E. The Need for Smart Materials in an Expanding Smart World: MXene-Based Wearable Electronics and Their Advantageous Applications. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 3123–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.; Tran, J.; Liu, S.; Jang, H.; Jeong, H.; Mitbander, R.; Huh, H.; Qiu, Y.; Duong, J.; Wang, R.L.; et al. A Chest-Laminated Ultrathin and Stretchable E-Tattoo for the Measurement of Electrocardiogram, Seismocardiogram, and Cardiac Time Intervals. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ameri, S.K.; Jang, H.; Dai, Z.; Huang, Y.A.; Lu, N. Low-Cost, Μm-Thick, Tape-Free Electronic Tattoo Sensors with Minimized Motion and Sweat Artifacts. npj Flex. Electron. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yim, S.G.; Lee, G.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, D.Y.; An, B.S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, S.; Yang, S.Y. Self-Adherent Biodegradable Gelatin-Based Hydrogel Electrodes for Electrocardiography Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Park, J.; Sohn, J.; Cho, D.; Jeon, S. Bioinspired, Highly Stretchable, and Conductive Dry Adhesives Based on 1D-2D Hybrid Carbon Nanocomposites for All-in-One ECG Electrodes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4770–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhu, K.; Guo, W.; Wu, D.; Quan, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Adhesive and Hydrophobic Bilayer Hydrogel Enabled On-Skin Biosensors for High-Fidelity Classification of Human Emotion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Oh, J.Y.; Park, C.W.; Pi, J.E.; Yang, J.H.; Hwang, C.S. High Density Integration of Stretchable Inorganic Thin Film Transistors with Excellent Performance and Reliability. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.M.; Cha, D.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Yang, H.J.; Choi, K.S.; Choi, J.M.; Chang, S.P. Development of PDMS-Based Flexible Dry Type SEMG Electrodes by Micromachining Technologies. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2014, 116, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, K.; Takahashi, T.; Ho, J.C.; Ko, H.; Gillies, A.G.; Leu, P.W.; Fearing, R.S.; Javey, A. Nanowire Active-Matrix Circuitry for Low-Voltage Macroscale Artificial Skin. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Paul, A.; Xu, Y.; Hairston, W.D.; Cauwenberghs, G. Characterization of Ag/AgCl Dry Electrodes for Wearable Electrophysiological Sensing. Front. Electron. 2022, 2, 700363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, S.; Duan, Y.Y. Towards Conductive-Gel-Free Electrodes: Understanding the Wet Electrode, Semi-Dry Electrode and Dry Electrode-Skin Interface Impedance Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Fitting. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.C.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Y. Wearable Silver Nanowire Dry Electrodes for Electrophysiological Sensing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11627–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ji, S.; Chaturvedi, I.; Xia, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Pan, L.; Wan, C.; Qi, D.; Ong, Y.S.; et al. Adhesive Biocomposite Electrodes on Sweaty Skin for Long-Term Continuous Electrophysiological Monitoring. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Araújo, F.F. Study of PDMS Characterization and Its Applications in Biomedicine: A Review. J. Mech. Eng. Biomech. 2019, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatoom, A.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Nashash, H.; Al-Sayah, M. Development and Characterization of Novel Composite and Flexible Electrode Based on Titanium Dioxide. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 10, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Nashash, H. Flexible PDMS Composite Electrodes with Boronic Acid-Modified Carbon Dots for Surface Electrophysiological Signal Recording. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamhuri, A.; Lim, G.P.; Ma, N.L.; Tee, K.S.; Soon, C.F. MXene in the Lens of Biomedical Engineering: Synthesis, Applications and Future Outlook. Biomed. Eng. Online 2021, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, N.; Erickson, B.; Murphy, B.B.; Richardson, A.G.; Robbins, G.; Apollo, N.V.; Mentzelopoulos, G.; Mathis, T.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Bagga, P.; et al. MXene-Infused Bioelectronic Interfaces for Multiscale Electrophysiology and Stimulation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; He, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Z.; Meng, B. Recent Progress in MXene Hydrogel for Wearable Electronics. Biosensors 2023, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, N.; Richardson, A.G.; Maleski, K.; Anasori, B.; Adewole, O.; Lelyukh, P.; Escobedo, L.; Cullen, D.K.; Lucas, T.H.; Gogotsi, Y.; et al. Two-Dimensional Ti3C2 MXene for High-Resolution Neural Interfaces. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10419–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navitski, I.; Ramanaviciute, A.; Ramanavicius, S.; Pogorielov, M.; Ramanavicius, A. MXene-Based Chemo-Sensors and Other Sensing Devices. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. DNA-Templated Silver Nanoclusters as Dual-Mode Sensitive Probes for Self-Powered Biosensor Fueled by Glucose. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Wegener, A.J.; Vázquez-Guardado, A.; Efimov, A.I.; Lie, F.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Banks, A.; Li, Z.; et al. Preparation and Use of Wireless Reprogrammable Multilateral Optogenetic Devices for Behavioral Neuroscience. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 1073–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar Vattikuti, S.V.; Shim, J.; Rosaiah, P.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. Recent Advances and Strategies in MXene-Based Electrodes for Supercapacitors: Applications, Challenges and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, D.; Coen, C.T.; Hwaun, E.; Chen, G.; Wu, H.C.; Zhong, D.; Niu, S.; et al. Topological Supramolecular Network Enabled High-Conductivity, Stretchable Organic Bioelectronics. Science 2022, 375, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Wei, P.; Liu, N.; Wu, B.; Cheng, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, L. Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene)/Poly(Styrenesulfonate)-Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Interpenetrating Polymer Networks for Improving Optrode-Neural Tissue Interface in Optogenetics. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.; Zhu, Y.; Tawalbeh, M.; Tremblay, A.Y.; Ternan, M. Proton Conductivity and Morphology of New Composite Membranes Based on Zirconium Phosphates, Phosphotungstic Acid, and Silicic Acid for Direct Hydrocarbon Fuel Cells Applications. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Ness, J.P.; Brodnick, S.K.; Esquibel, C.; Novello, J.; Atry, F.; Baek, D.H.; Kim, H.; Bong, J.; Swanson, K.I.; et al. Electrical Neural Stimulation and Simultaneous in Vivo Monitoring with Transparent Graphene Electrode Arrays Implanted in GCaMP6f Mice. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, O.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Nashash, H.; Tawalbeh, M.; Almomani, F.; Rezakazemi, M. Fabrication of Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterial for Implantable Highly Flexible Composite Bioelectrode for Biosensing Applications. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, G.; Júnior, C.; Spinelli, B.; Damasceno, I.; Fiuza, F.; Morya, E. All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording. Biosensors 2022, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufleh, N.; Al-Othman, A.; Alani, Z.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Al-Nashash, H. Highly Flexible Polyaniline-Based Implantable Electrode Materials for Neural Sensing/Stimulation Applications. Electron. Mater. 2021, 2, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X. Flexible ECoG Electrode for Implantation and Neural Signal Recording Applications. Vacuum 2017, 140, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Lowe, A.; Al-Jumaily, A.M. Mechanical Behaviour of Skin: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 5, 1000254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Lou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Han, W.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. Biomimetic, Biocompatible and Robust Silk Fibroin-MXene Film with STable 3D Cross-Link Structure for Flexible Pressure Sensors. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, J.; Song, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, Z.; Song, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Self-Healing Ti3C2 MXene/PDMS Supramolecular Elastomers Based on Small Biomolecules Modification for Wearable Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45306–45314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
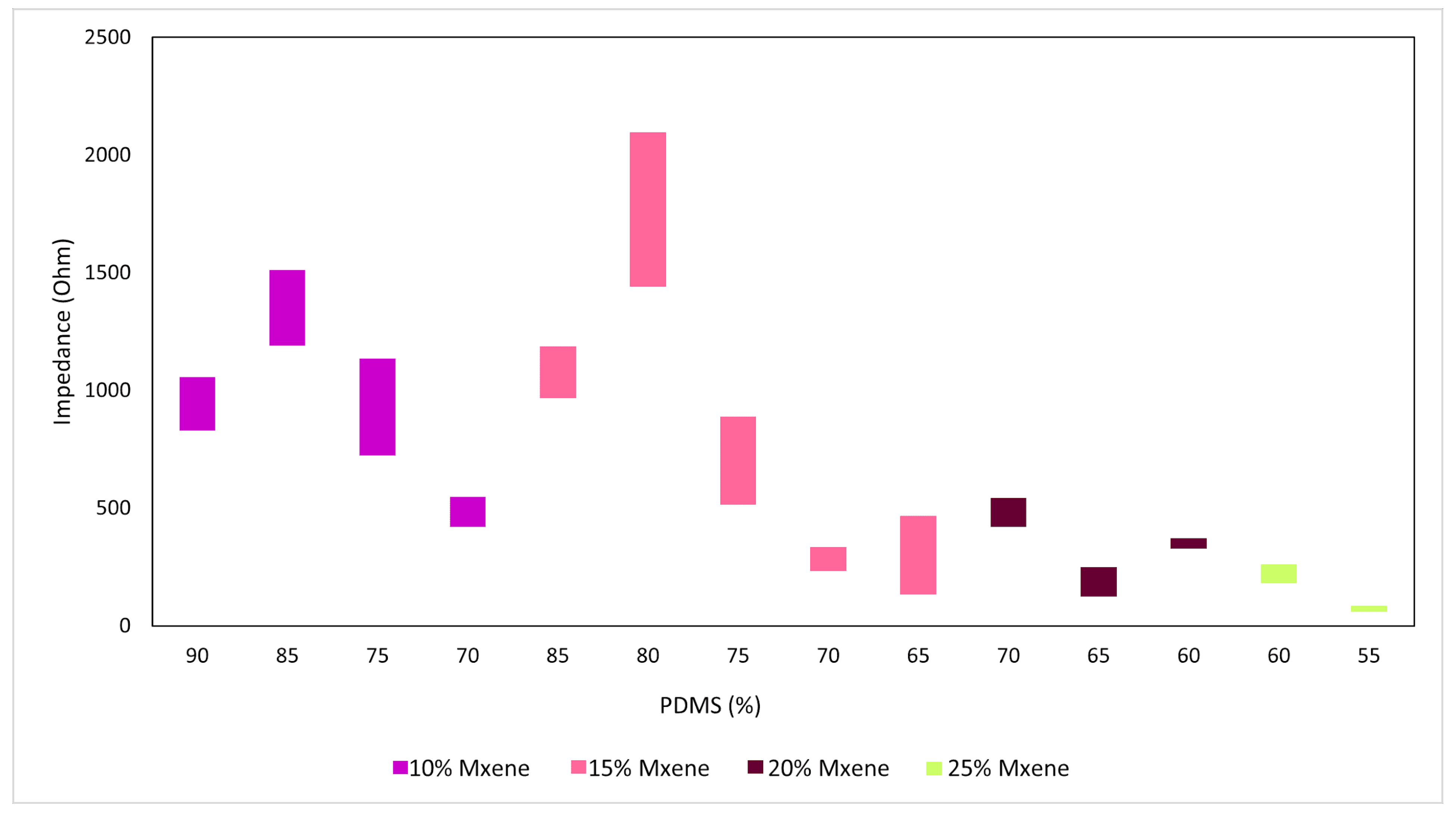


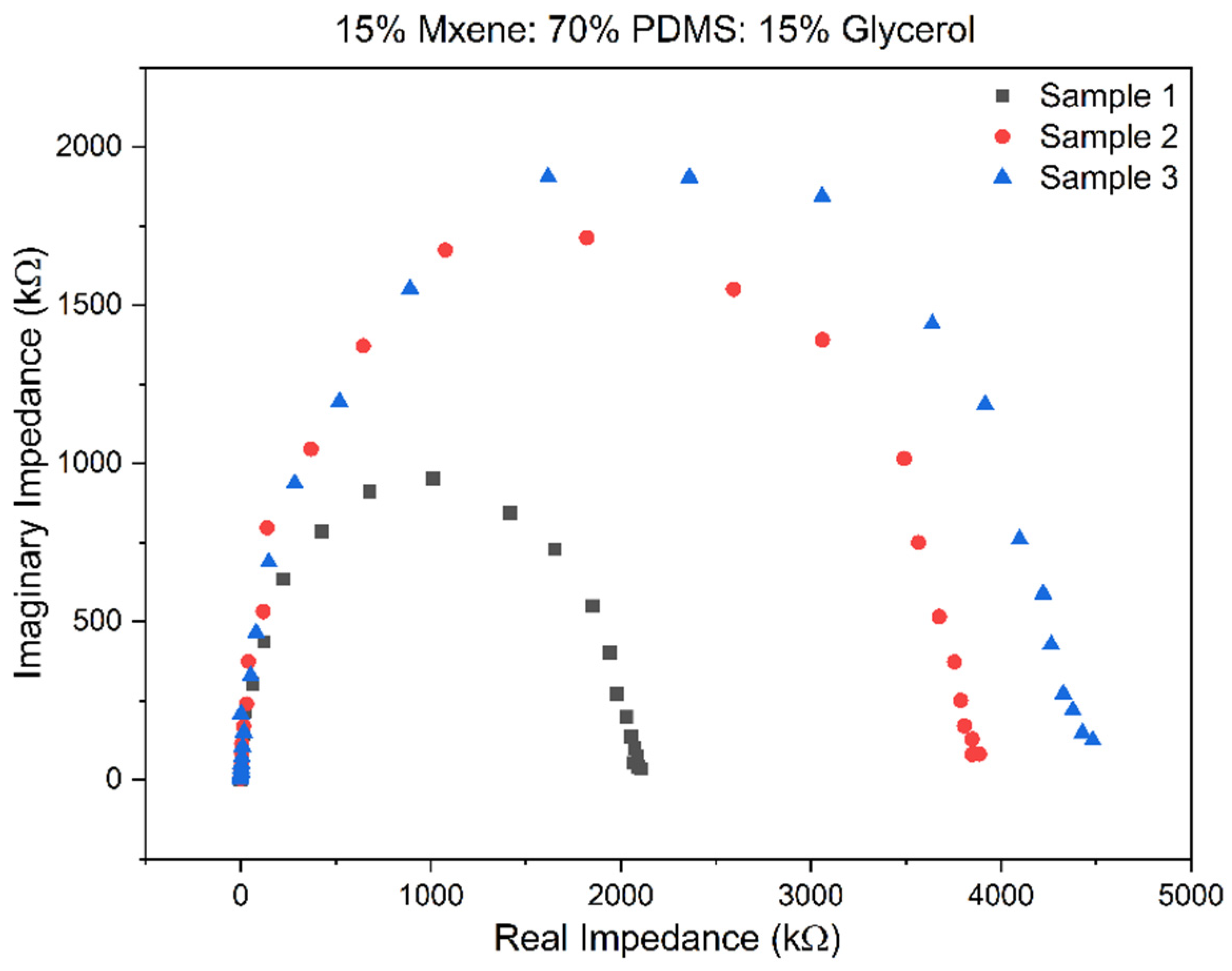
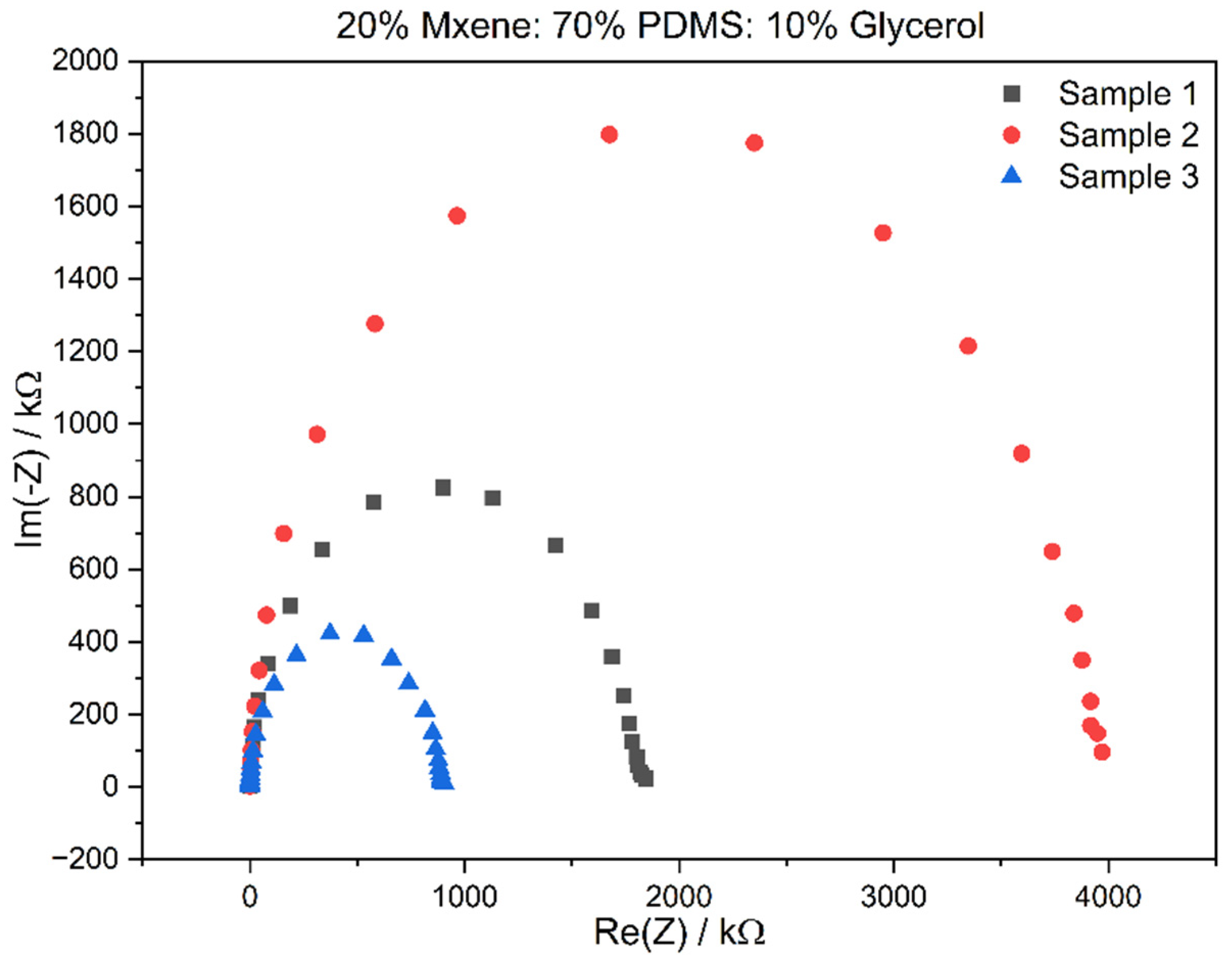

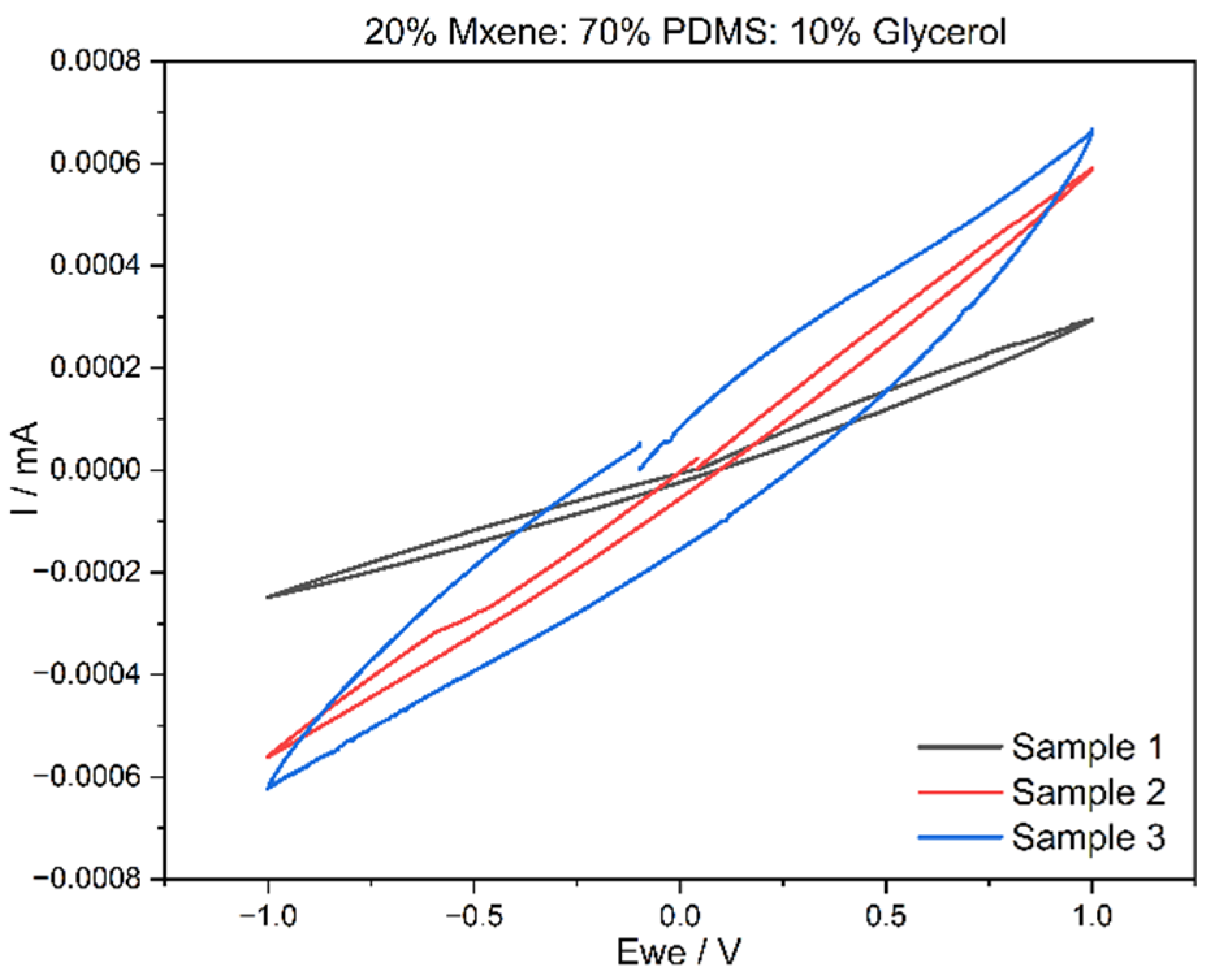



| MXene (%) | PDMS (Elastomer + Curing Agent 10:1 Ratio Mixed Separately) (%) | Glycerol (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 90 | 0 |
| 85 | 5 | |
| 80 | 10 | |
| 75 | 15 | |
| 70 | 20 | |
| 15 | 85 | 0 |
| 80 | 5 | |
| 75 | 10 | |
| 70 | 15 | |
| 65 | 20 | |
| 20 | 75 | 5 |
| 70 | 10 | |
| 65 | 15 | |
| 60 | 20 | |
| 25 | 60 | 15 |
| 55 | 20 |
| Material | Bulk Impedance in kilo Ohms | Impedance at 1 kilo Hertz | Conductivity in mS/cm | CSD in mC/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyamide/Cr-Ag-Cr [34] | 22.7 | 120 | - | - |
| PSS/PEDOT [32] | 2.23 | 2.54 | 0.012 | 4.86 ± 0.24 |
| PANI/PDMS [33] | 0.6–4 | 1.6–28 | 10−5–0.01 | - |
| TiO2/PDMS [17] | 0.790 | 24 | 0.722 | 27 ± 1.1 |
| TiO2/PMMA/Silicon [31] | 4.28 | 114.6 | 0.1 | 1.23 |
| PDMS/BA-CD/Glycerol [18] | 0.058 | 964 | 9.62 | 0.0214 |
| Composition 1 [this work] | 0.280 ± 0.04 | 3192 ± 1041 | 0.462 ± 0.07 | 0.665 ± 0.33 |
| Composition 2 [this work] | 0.111 ± 0.07 | 1986 ± 1566 | 1.533 ± 0.88 | 1.99 ± 1.25 |
| Material | Elongation | Young’s Modulus |
|---|---|---|
| PANI/PDMS based electrodes [33] | 308% | 75.312 MPa |
| TiO2/PDMS based implantable electrode [17] | 293% | 32.9 kPa |
| Silk fibroin/Ti3C2 film-based sensor for wearable pressure and electrical signal sensing [36] | — | 1.22 MPa |
| Self-healing MXene/PDMS wearable biosensor [37] | 181% | — |
| Composition 1 [this work] | 139 ± 11% | 2.61 ± 0.39 MPa |
| Composition 2 [this work] | 144 ± 13% | 2.18 ± 0.31 MPa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alex, M.; Khan, K.R.B.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Al Nashash, H. MXene-Based Flexible Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113260
Alex M, Khan KRB, Al-Othman A, Al-Sayah MH, Al Nashash H. MXene-Based Flexible Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113260
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlex, Meera, Kashif Rast Baz Khan, Amani Al-Othman, Mohammad H. Al-Sayah, and Hasan Al Nashash. 2024. "MXene-Based Flexible Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113260
APA StyleAlex, M., Khan, K. R. B., Al-Othman, A., Al-Sayah, M. H., & Al Nashash, H. (2024). MXene-Based Flexible Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring. Sensors, 24(11), 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113260








