Weakly Supervised Pose Estimation of Surgical Instrument from a Single Endoscopic Image
Abstract
:1. Introduction
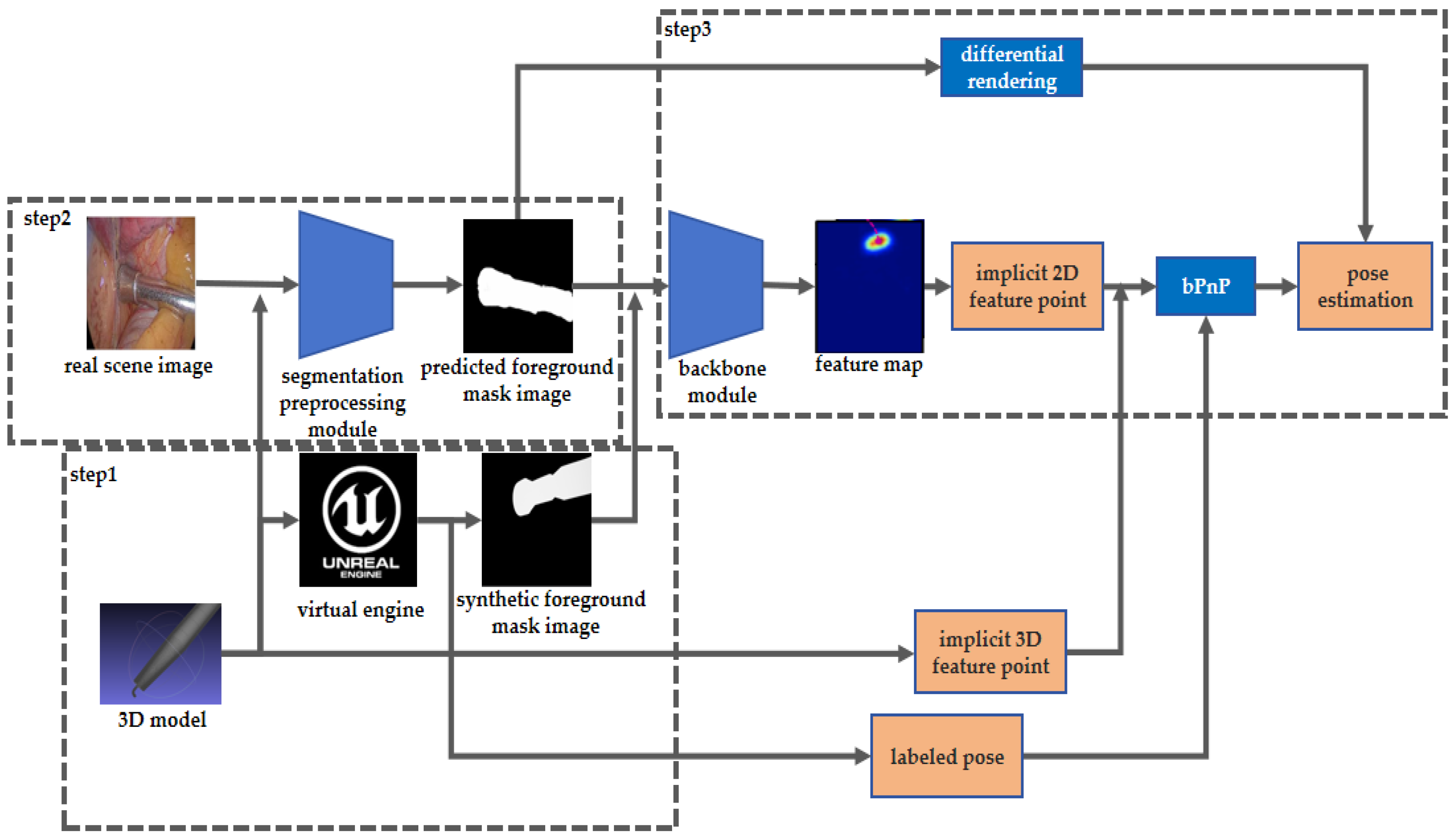
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Training Data Generation
2.2. Instrument Segmentation Preprocessing
2.3. Pose Estimation Module
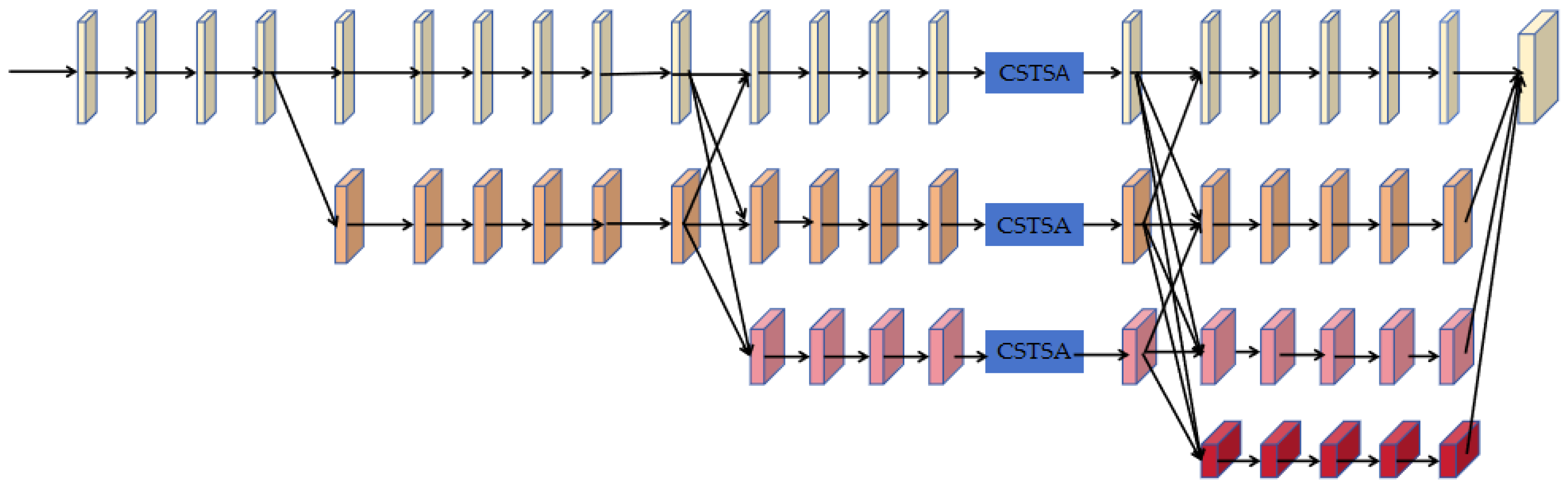
2.3.1. Multi-Scale Heatmap Feature Generation
2.3.2. Implicit Feature Point Projection Regression
2.3.3. Surgical Instrument Pose Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Metrics
3.2. Implementation Detail
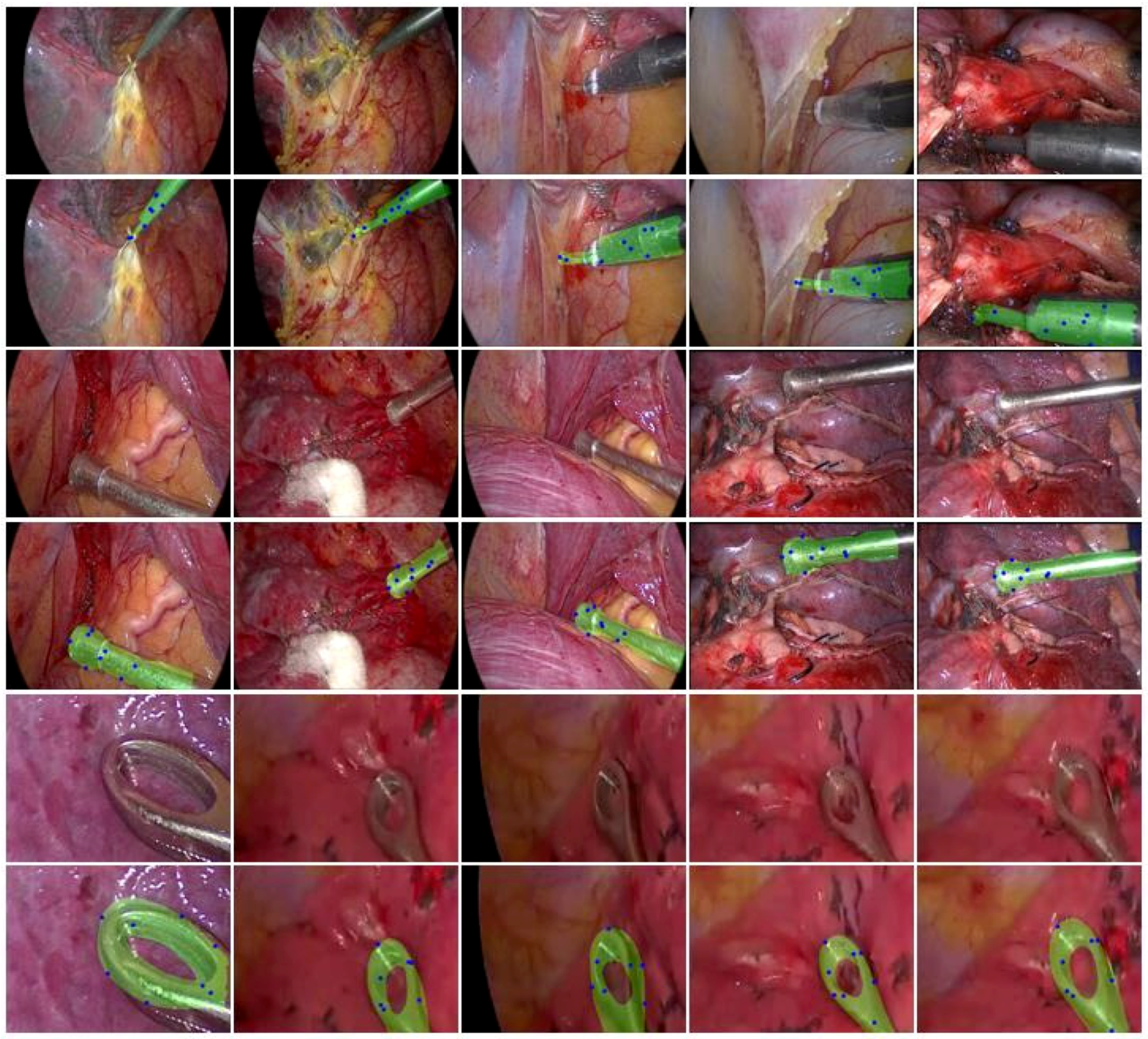
3.3. Comparisons of Pose Estimation Results
3.3.1. Real Surgery Scene Data Experiments
3.3.2. Synthetic Data Experiments
3.4. Ablation Study
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garrow, C.R.; Kowalewski, K.F.; Li, L.; Wagner, M.; Schmidt, M.W.; Engelhardt, S.; Hashimoto, D.A.; Kenngott, H.G.; Bodenstedt, S.; Speidel, S.; et al. Machine learning for surgical phase recognition: A systematic review. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawka, M.; Gall, T.M.H.; Fang, C.; Liu, R.; Jiao, L.R. Intraoperative video analysis and machine learning models will change the future of surgical training. Intell. Surg. 2022, 1, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaVinci Intuitive Surgical—Procedures. Available online: https://www.intuitive.com/en-us/products-andservices/da-vinci/education (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- D’Ettorre, C.; Mariani, A.; Stilli, A.; Baena, F.R.Y.; Valdastri, P.; Deguet, A.; Kazanzides, P.; Taylor, R.H.; Fischer, G.S.; DiMaio, S.P.; et al. Accelerating surgical robotics research: A review of 10 years with the da Vinci research kit. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2021, 28, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajkó, G.; Nagyne Elek, R.; Haidegger, T. Endoscopic image-based skill assessment in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Sensors 2021, 21, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanasio, A.; Alberti, C.; Scaglioni, B.; Marahrens, N.; Frangi, A.F.; Leonetti, M.; Biyani, C.S.; De Momi, E.; Valdastri, P. A comparative study of spatio-temporal U-nets for tissue segmentation in surgical robotics. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaguchi, D.; Takeshita, N.; Matsuzaki, H.; Takano, H.; Owada, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Oda, T.; Miura, H.; Yamanashi, T.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Real-time automatic surgical phase recognition in laparoscopic sigmoidectomy using the convolutional neural network-based deep learning approach. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 4924–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, X.A.; Ljuhar, D.; Pacilli, M.; Takano, H.; Owada, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Oda, T.; Miura, H.; Yamanashi, T.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Surgical skill levels: Classification and analysis using deep neural network model and motion signals. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 177, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Vedula, S.S.; Reiley, C.E.; Ahmidi, N.; Varadarajan, B.; Lin, H.C.; Tao, L.; Zappella, L.; Bejar, B.; Yuh, D.D.; et al. Jhu-isi gesture and skill assessment working set (jigsaws): A surgical activity dataset for human motion modeling. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Workshop: M2cai, Cambridge, MA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; Volume 3, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, K. An automated skill assessment framework based on visual motion signals and a deep neural network in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Sensors 2023, 23, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.M.; Trulls, E.; Lepetit, V.; Fua, P. Lift: Learned invariant feature transform. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part VI 14. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 467–483. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, P.; Apostolopoulos, S.; Mosinska, A.; Stucky, S.; Ciller, C.; Zanet, S.D. Glampoints: Greedily learned accurate match points. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 10732–10741. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, M.; Lepetit, V. BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3d poses of challenging objects without using depth. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 33828–33836. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, B.; Sinha, S.N.; Fua, P. Real-time seamless single shot 6d object pose prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, V.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Fua, P. EPnP: An accurate O (n) solution to the PnP problem. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 81, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Petersson, L.; Hartley, R. Cullnet: Calibrated and pose aware confidence scores for object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Peng, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, H.-S.; Li, C.; Lu, C. Estimating 6D pose from localizing designated surface keypoints. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.01387. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part VIII 14. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Hugonot, J.; Fua, P.; Salzmann, M. Segmentation-driven 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3385–3394. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Patten, T.; Vincze, M. Pix2Pose: Pixel-wise coordinate regression of objects for 6d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 7 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7668–7677. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, S.; Shugurov, I.; Ilic, S. DPOD: 6d pose object detector and refiner. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1941–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Ji, X. CDPN: Coordinates-based disentangled pose network for real-time rgb-based 6-dof object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7678–7687. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Doherty, K.; Severinsen, O.; Yang, E.; Leonard, J. SLAM-supported self-training for 6D object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 2833–2840. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, B.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Captra: Category-level pose tracking for rigid and articulated objects from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13209–13218. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Bao, H. PVNet: Pixel-wise voting network for 6dof pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4561–4570. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Song, J.; Huang, Q. HybridPose: 6d object pose estimation under hybrid representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Fan, H.; Sun, J. PVN3D: A deep point-wise 3d keypoints voting network for 6dof pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11632–11641. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.T.; Cai, M.; Pham, T.; Reid, I. Deep-6dpose: Recovering 6d object pose from a single rgb image. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.10367. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Fang, P.; Yao, Z.; Fan, R.; Pan, Z.; Sheng, W.; Yang, H. Recovering 6D object pose from RGB indoor image based on two-stage detection network with multi-task loss. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Marton, Z.C.; Durner, M.; Brucker, M. Implicit 3d orientation learning for 6d object detection from rgb images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 699–715. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fox, D. DeepIM: Deep iterative matching for 6d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 683–698. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; Van Der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. Flowet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Xiang, Y.; Mousavian, A.; Eppner, C.; Bretl, T.; Fox, D. Self-supervised 6d object pose estimation for robot manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May 2020; pp. 3665–3671. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Manhardt, F.; Shao, J.; Ji, X.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Self6D: Self-supervised monocular 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Parra, A.; Cao, J.; Li, N.; Chin, T.J. End-to-end learnable geometric vision by backpropagating pnp optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8100–8109. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, N.; Reizenstein, J.; Novotny, D.; Gordon, T.; Lo, W.Y.; Johnson, J.; Gkioxari, G. Accelerating 3d deep learning with pytorch3d. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.08501. [Google Scholar]
- Shvets, A.A.; Rakhlin, A.; Kalinin, A.A.; Iglovikov, V.I. Automatic instrument segmentation in robot-assisted surgery using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; pp. 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Fan, X.; Huang, D. Polarized self-attention: Towards high-quality pixel-wise regression. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.00782. [Google Scholar]
- Hinterstoisser, S.; Lepetit, V.; Ilic, S.; Holzer, S.; Bradski, G.; Konolige, K. Model based training, detection and pose estimation of texture-less 3d objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2012: 11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 5–9 November 2012; Revised Selected Papers, Part I 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 548–562. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Schmidt, T.; Narayanan, V.; Fox, D. PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6d object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00199. [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann, E.; Michel, F.; Krull, A.; Yang, M.Y.; Gumhold, S. Uncertainty-driven 6d pose estimation of objects and scenes from a single rgb image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3364–3372. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOV3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Quan, Z.; Nie, M.; Yang, W. Transpose: Keypoint localization via transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11802–11812. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, L. Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5386–5395. [Google Scholar]




| Model | IOU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | |
| Segmentation- driven-pose | 48.20 | 42.91 | 26.42 | 39.18 |
| Transpose + RansacPnP | 41.22 | 43.68 | 41.58 | 42.16 |
| Higherhrnet + RansacPnP | 64.65 | 42.06 | 51.84 | 52.85 |
| PVNet | 59.24 | 33.67 | 45.59 | 46.17 |
| Ours | 67.06 | 57.71 | 52.89 | 59.22 |
| Model | ADD(S)(0.1 d) | 2D Projection Error(5 px) | 2D Projection Error(3 px) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | |
| Segmentation- driven-pose | 98.48 | 63.63 | 98.48 | 86.86 | 28.79 | 42.42 | 10.61 | 27.27 | 7.58 | 16.67 | 4.55 | 9.60 |
| Transpose + RansacPnP | 48.48 | 48.48 | 75.76 | 57.57 | 6.06 | 53.03 | 43.94 | 34.34 | 1.52 | 13.64 | 12.12 | 9.09 |
| Higherhrnet + RansacPnP | 100 | 77.27 | 100 | 92.42 | 37.88 | 86.36 | 69.70 | 64.65 | 10.61 | 56.06 | 34.85 | 33.84 |
| PVNet | 98.48 | 33.33 | 100 | 77.27 | 37.88 | 28.79 | 80.30 | 48.99 | 12.12 | 10.61 | 42.42 | 21.72 |
| Ours | 100 | 86.36 | 100 | 95.45 | 46.97 | 89.39 | 84.85 | 73.74 | 19.70 | 68.18 | 43.94 | 43.94 |
| Synthetic Data | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | ADD(S)(0.1 d) | 2D Projection Error(5 px) | 2D Projection Error(3 px) | |||||||||
| Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | |
| MrC | 98.48 | 82.83 | 99.49 | 93.6 | 33.84 | 86.36 | 79.29 | 66.50 | 10.61 | 56.06 | 33.84 | 33.50 |
| MrC + CSTSA | 100 | 79.80 | 100 | 93.26 | 43.43 | 86.87 | 78.28 | 69.53 | 16.67 | 63.64 | 38.89 | 39.73 |
| MrC + CSTSA + BPnP | 99.49 | 86.36 | 100 | 95.28 | 44.44 | 86.36 | 81.82 | 70.87 | 17.68 | 65.15 | 44.44 | 42.42 |
| MrC + CSTSA + BPnP + DRPE | 100 | 86.36 | 100 | 95.45 | 46.97 | 89.39 | 84.85 | 73.74 | 19.70 | 68.18 | 43.94 | 43.94 |
| Model | IOU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucker | Hook | Clipper | Average | |
| MrC | 61.32 | 41.02 | 31.31 | 44.55 |
| MrC + CSTSA | 63.56 | 46.09 | 30.17 | 46.61 |
| MrC + CSTSA + BPnP | 64.78 | 44.99 | 33.94 | 47.90 |
| MrC + CSTSA + BPnP + DRPE | 67.06 | 57.71 | 52.89 | 59.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Feng, S.; Wang, B. Weakly Supervised Pose Estimation of Surgical Instrument from a Single Endoscopic Image. Sensors 2024, 24, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113355
Hu L, Feng S, Wang B. Weakly Supervised Pose Estimation of Surgical Instrument from a Single Endoscopic Image. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113355
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Lihua, Shida Feng, and Bo Wang. 2024. "Weakly Supervised Pose Estimation of Surgical Instrument from a Single Endoscopic Image" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113355
APA StyleHu, L., Feng, S., & Wang, B. (2024). Weakly Supervised Pose Estimation of Surgical Instrument from a Single Endoscopic Image. Sensors, 24(11), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113355





