Fine-YOLO: A Simplified X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Network Based on Feature Aggregation and Normalized Wasserstein Distance
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study proposes a high-density feature aggregation (HDFA) structure for the backbone feature network of YOLOv7, simplifying the network structure and enhancing its ability to capture global object information.
- A low-parameter feature aggregation (LPFA) structure is proposed for the YOLOv7-Tiny-SiLy neck feature fusion network, which improves the feature integration capability of the lightweight network, resulting in a finer and more comprehensive representation of target features.
- To avoid the loss of detailed information during feature transmission layer by layer, max-pooling operation is employed for the cross-layer connections. Moreover, the NWD loss function is utilized to enhance the detection of information from small objects given the size constraints of prohibited objects.
- Experiments conduct on the EDS dataset demonstrate a successful balance between the detection accuracy and speed. Furthermore, the results on the NEU-DET dataset illustrate the robustness of the model and its potential extension to various practical detection domains.
2. Related Works
2.1. Object Detection Algorithms
2.2. YOLO Series Object Setection Algorithm
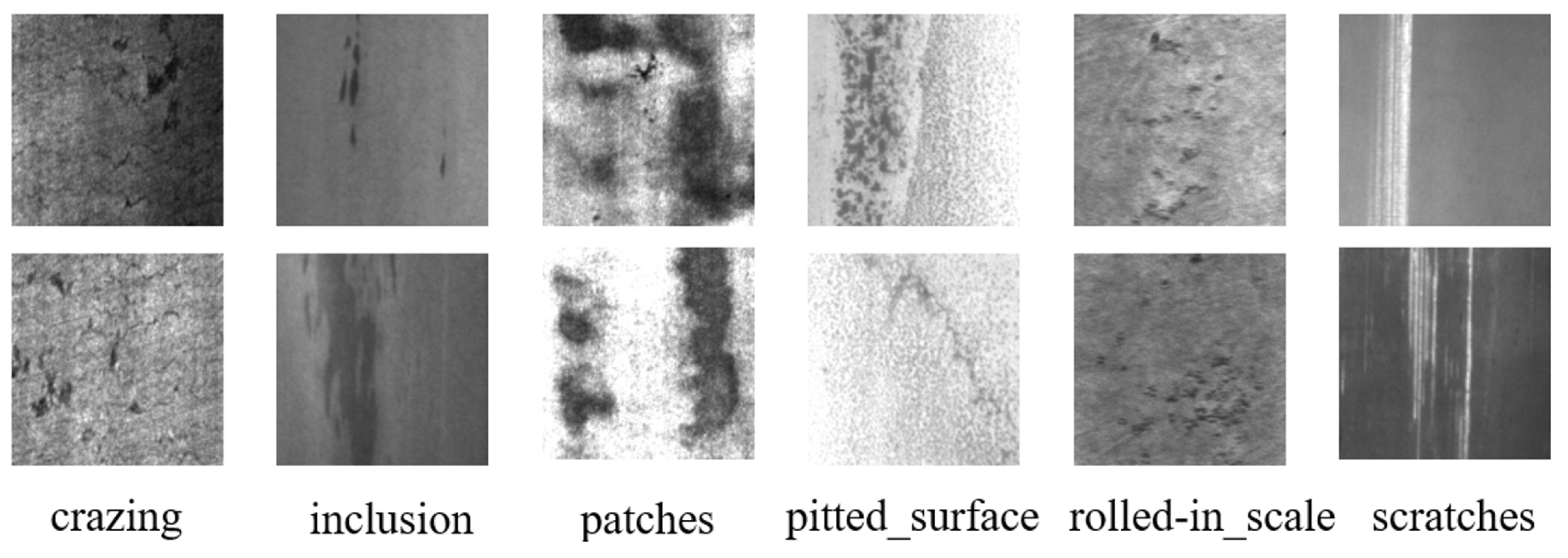
2.3. X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Datasets
3. Methods
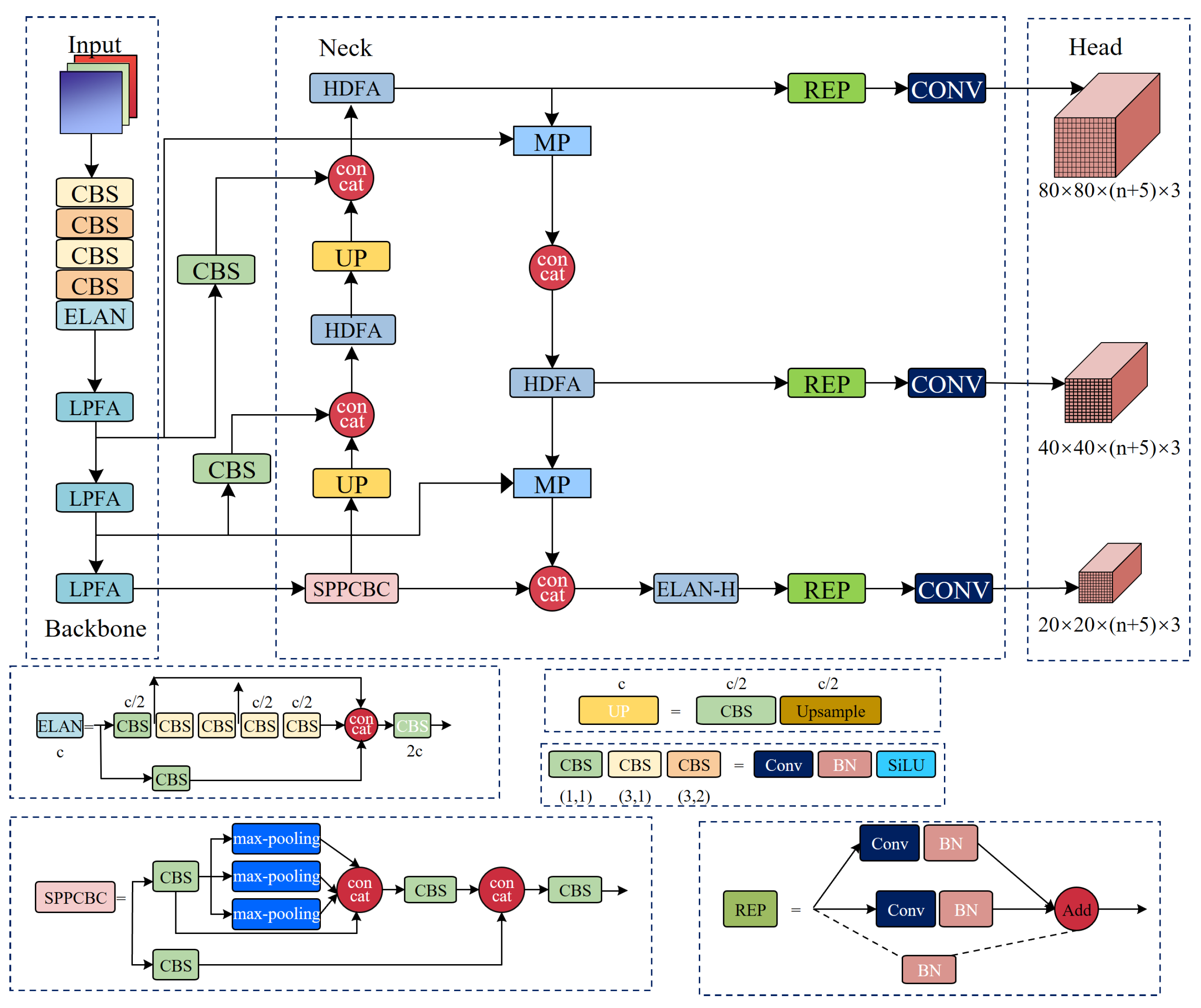
3.1. Overall Architecture
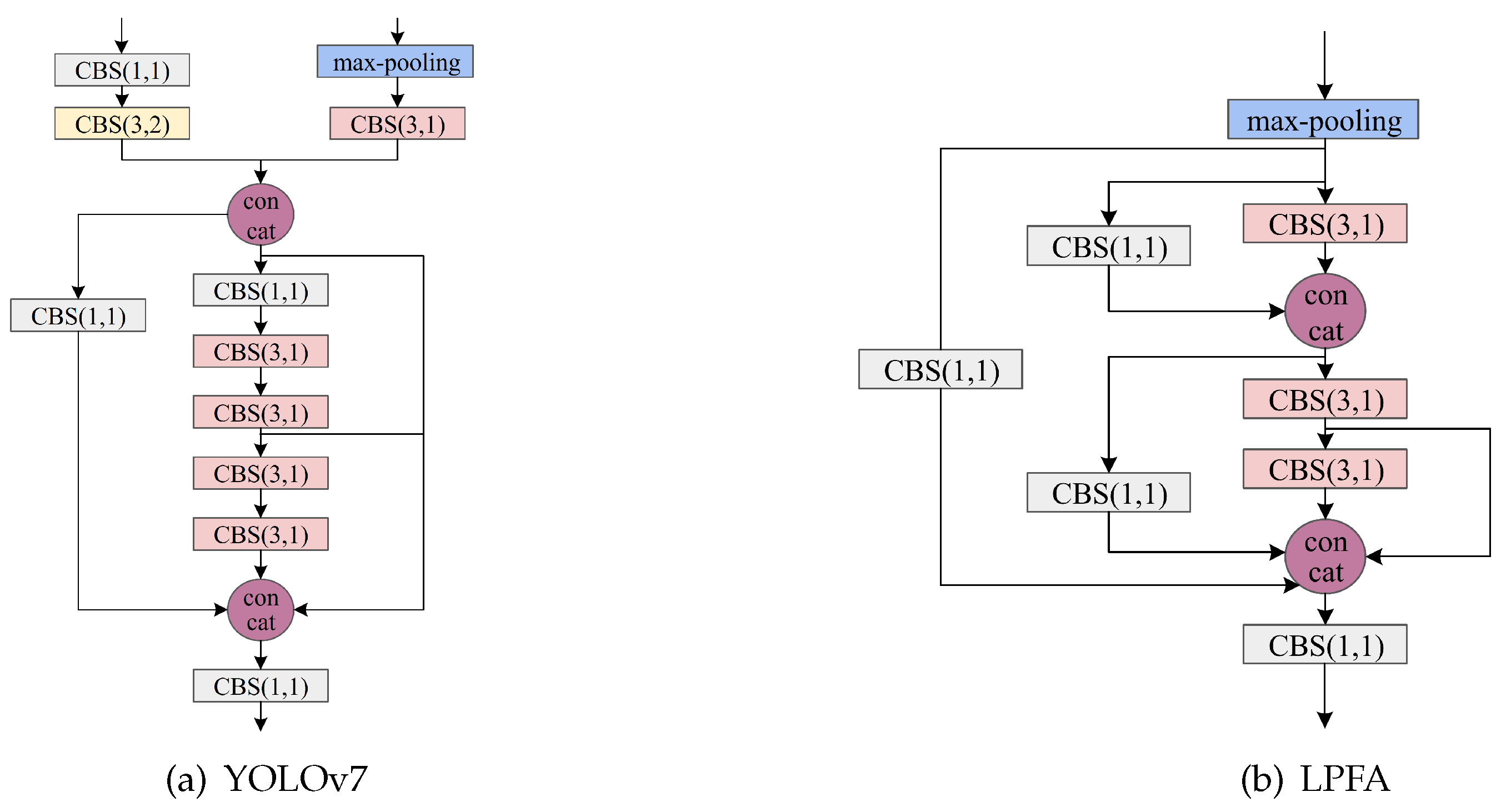
3.2. Low-Parameter Feature Aggregation
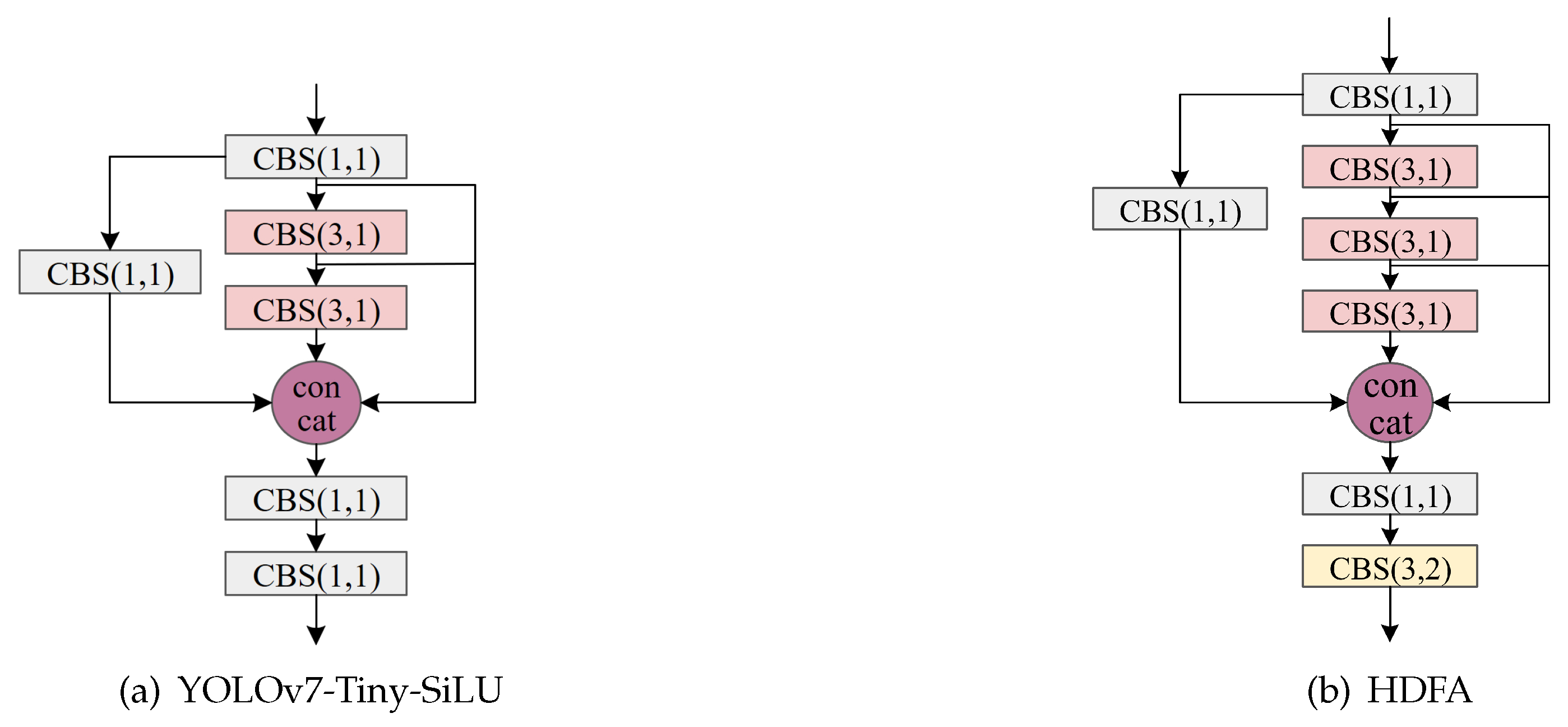
3.3. High-Density Feature Aggregation
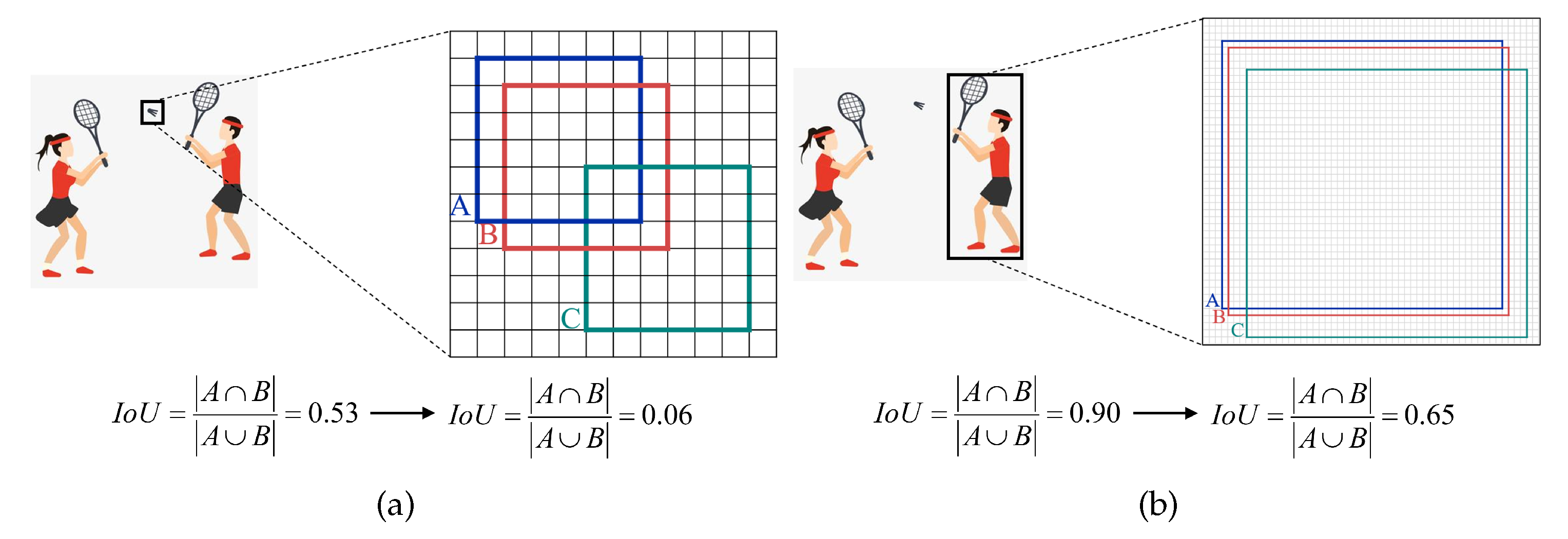
3.4. Normalized Wasserstein Distance
- (1)
- Bounding Box Two-Dimensional Gaussian Distribution Modeling
- (2)
- Normalized Gaussian Wasserstein Distance
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Performance of the Fine-YOLO Model
4.3.1. EDS Dataset
4.3.2. NEU-DET Dataset
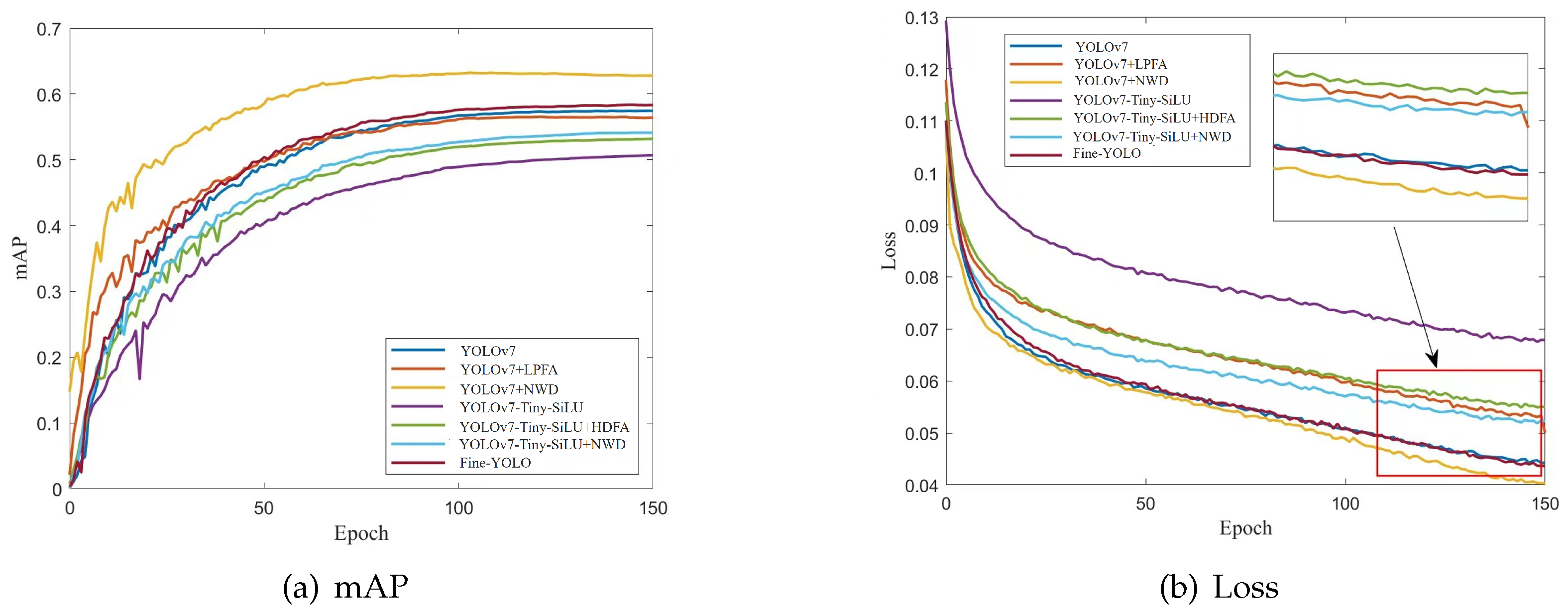
4.4. Ablation Study
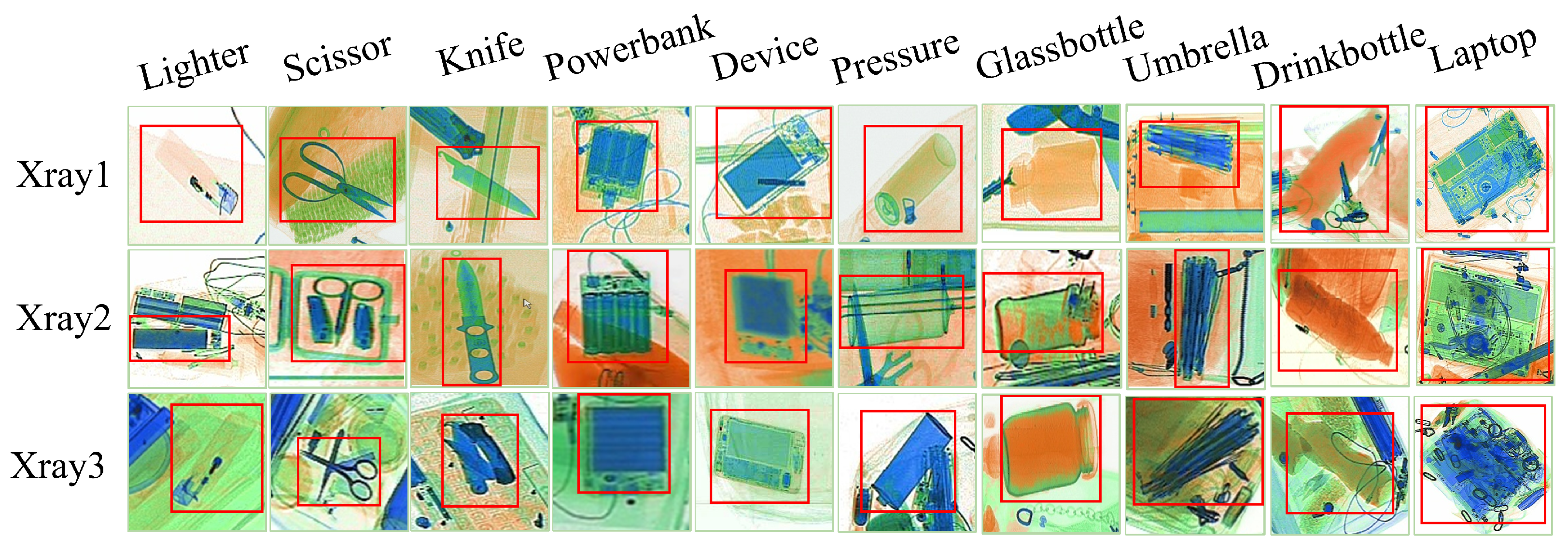
4.5. Visualization of the Detection Result
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| LPFA | low-parameter feature aggregation |
| HPFA | high-density feature aggregation |
| NWD | Normalized Wasserstein Distance |
| mAP | mean Average Precision |
| AP | Average Precision |
| Params. | parameters |
| FLOPs | Floating Point Operations |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
References
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Ye, J.; Ling, X. FDTNet: Enhancing frequency-aware representation for prohibited object detection from X-ray images via dual-stream transformers. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, T.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Li, J.; Ji, R. Local Relation Learning for Face Forgery Detection. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Ye, C.; Wang, H.; Huyan, J.; Yang, M.; Li, W. Foreign Bodies Detector Based on DETR for High-Resolution X-Ray Images of Textiles. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5007310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Cooperative distillation with X-ray images classifiers for prohibited items detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, L. Detecting prohibited objects with physical size constraint from cluttered X-ray baggage images. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 237, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Akcay, S.; Bennamoun, M.; Khan, S.; Werghi, N. A Novel Incremental Learning Driven Instance Segmentation Framework to Recognize Highly Cluttered Instances of the Contraband Items. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 6937–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, H. CFPA-Net: Cross-layer Feature Fusion Furthermore, Parallel Attention Network For Detection Furthermore, Classification of Prohibited Items in X-ray Baggage Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligent Systems (CCIS), Xi’an, China, 7–8 November 2021; pp. 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Zhuo, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. EAOD-Net: Effective anomaly object detection networks for X-ray images. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 2638–2651. Available online: https://ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1049/ipr2.12514 (accessed on 18 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Yu, G.; Peng, Y.; Sun, J. ThunderNet: Towards Real-Time Generic Object Detection on Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. CenterNet: Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: A Simple and Strong Anchor-Free Object Detector. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part III. Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Chaurasia, A.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Hajek, J.; Diaconu, L.; Kwon, Y.; Defretin, Y.; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v5. 0-YOLOv5-P6 1280 models, AWS, Supervise. ly and YouTube integrations. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M. YOLOv1 to v8: Unveiling Each Variant–A Comprehensive Review of YOLO. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 42816–42833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.J.; Heilmann, G.; Gregory, C.; Diallo, S.O.; Carlson, D.; Spell, G.P.; Sigman, J.B.; Roe, K.; Carin, L. Automatic threat recognition of prohibited items at aviation checkpoint with X-ray imaging: A deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the Anomaly Detection and Imaging with X-rays (ADIX) III; Ashok, A., Greenberg, J.A., Gehm, M.E., Neifeld, M.A., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: St. Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10632, p. 1063203. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, T.W.; Jaccard, N.; Morton, E.J.; Griffin, L.D. Automated X-ray image analysis for cargo security: Critical review and future promise. J. Ray Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The Pascal Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. Part IV. pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Mery, D.; Riffo, V.; Zscherpel, U.; Mondragón, G.; Lillo, I.; Zuccar, I.; Lobel, H.; Carrasco, M. GDXray: The Database of X-ray Images for Nondestructive Testing. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2015, 34, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Xie, L.; Wan, F.; Su, C.; Liu, H.; Jiao, J.; Ye, Q. SIXray: A Large-Scale Security Inspection X-Ray Benchmark for Prohibited Item Discovery in Overlapping Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Tao, R.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Occluded Prohibited Items Detection: An X-ray Security Inspection Benchmark and De-occlusion Attention Module. In Proceedings of the MM ’20: 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Towards Real-World X-Ray Security Inspection: A High-Quality Benchmark and Lateral Inhibition Module for Prohibited Items Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10923–10932. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Wei, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jin, B.; Zhi, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, A. Exploring Endogenous Shift for Cross-domain Detection: A Large-scale Benchmark and Perturbation Suppression Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21157–21167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, W.; Yu, L. A Normalized Gaussian Wasserstein Distance for Tiny Object Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.13389. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Ren, J.; Yang, J. LightRay: Lightweight network for prohibited items detection in X-ray images during security inspection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yuan, W.; Wang, A. X-ray Security Inspection Image Dangerous Goods Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv4. Electronics 2023, 12, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Duan, P.; Chen, L.; Du, Y. EM-YOLO: An X-ray Prohibited-Item-Detection Method Based on Edge and Material Information Fusion. Sensors 2023, 23, 8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Deng, H.; Zhang, G. A Contraband Detection Scheme in X-ray Security Images Based on Improved YOLOv8s Network Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Qi, H.; Jia, M.; Wang, W. Lightweight Detection Method for X-ray Security Inspection with Occlusion. Sensors 2024, 24, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Shu, X.; Yan, X.; Zuo, X.; Zhu, F. RDD-YOLO: A modified YOLO for detection of steel surface defects. Measurement 2023, 214, 112776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Du, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H. DCAM-Net: A Rapid Detection Network for Strip Steel Surface Defects Based on Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5005312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Fan, Y. An Infrared Image Defect Detection Method for Steel Based on Regularized YOLO. Sensors 2024, 24, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y. Steel Surface Defect Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOX. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 37643–37652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

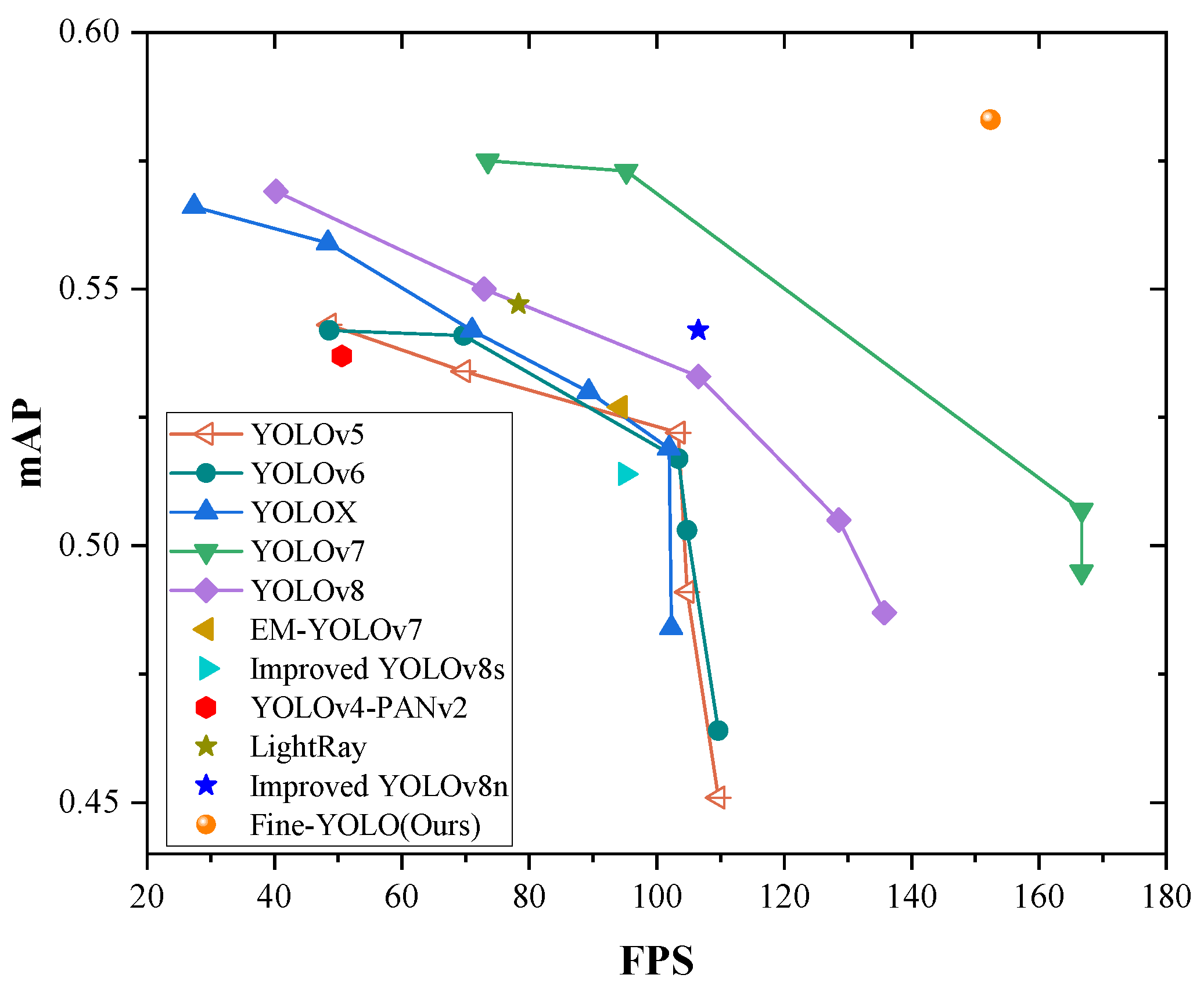

| Method | Precision | Recall | mAP | Params. | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN [10] | 0.603 | 0.451 | 0.491 | 136.9 M | 369.9 | 16.0 |
| SSD [13] | 0.621 | 0.432 | 0.405 | 24.8 M | 61.7 | 89.4 |
| RetinaNet [15] | 0.653 | 0.442 | 0.474 | 36.5 M | 148.2 | 46.3 |
| CenterNet [16] | 0.614 | 0.461 | 0.489 | 32.7 M | 70.2 | 19.4 |
| FCOS [17] | 0.675 | 0.542 | 0.559 | 32.1 M | 161.5 | 42.5 |
| YOLOv5-N [22] | 0.606 | 0.441 | 0.451 | 1.8 M | 2.6 | 156.3 |
| YOLOv5-S [22] | 0.624 | 0.477 | 0.491 | 7.1 M | 15.2 | 133.3 |
| YOLOv5-M [22] | 0.675 | 0.488 | 0.522 | 20.9 M | 26.8 | 111.1 |
| YOLOv5-L [22] | 0.704 | 0.498 | 0.534 | 46.2 M | 73.8 | 77.5 |
| YOLOv5-X [22] | 0.714 | 0.516 | 0.543 | 86.3 M | 155.7 | 47.2 |
| YOLOX-Nano [24] | 0.618 | 0.413 | 0.484 | 0.9 M | 2.8 | 102.3 |
| YOLOX-Tiny [24] | 0.646 | 0.448 | 0.519 | 5.0 M | 4.3 | 101.9 |
| YOLOX-S [24] | 0.651 | 0.454 | 0.530 | 8.9 M | 16.0 | 89.3 |
| YOLOX-M [24] | 0.663 | 0.480 | 0.542 | 25.3 M | 48.3 | 71.0 |
| YOLOX-L [24] | 0.672 | 0.496 | 0.559 | 54.1 M | 108.4 | 48.4 |
| YOLOX-X [24] | 0.675 | 0.504 | 0.566 | 99.0 M | 204.8 | 27.4 |
| YOLOv6-N [23] | 0.614 | 0.496 | 0.464 | 4.3 M | 11.1 | 109.7 |
| YOLOv6-T [23] | 0.649 | 0.511 | 0.503 | 9.7 M | 24.8 | 104.8 |
| YOLOv6-S [23] | 0.660 | 0.520 | 0.517 | 17.2 M | 44.1 | 103.4 |
| YOLOv6-M [23] | 0.673 | 0.534 | 0.541 | 34.2 M | 82.0 | 69.7 |
| YOLOv6-L [23] | 0.679 | 0.533 | 0.542 | 58.5 M | 143.8 | 48.6 |
| YOLOv7-Tiny [25] | 0.597 | 0.489 | 0.495 | 6.0 M | 13.3 | 166.7 |
| YOLOv7-Tiny-SiLU [25] | 0.643 | 0.481 | 0.507 | 6.0 M | 13.1 | 166.7 |
| YOLOv7 [25] | 0.721 | 0.532 | 0.573 | 37.2 M | 103.3 | 95.2 |
| YOLOv7-X [25] | 0.701 | 0.546 | 0.575 | 70.9 M | 189.1 | 73.5 |
| YOLOv8-N [26] | 0.562 | 0.502 | 0.487 | 3.0 M | 8.2 | 135.7 |
| YOLOv8-S [25] | 0.591 | 0.498 | 0.505 | 11.1 M | 28.7 | 128.6 |
| YOLOv8-M [25] | 0.637 | 0.516 | 0.533 | 25.9 M | 79.1 | 106.5 |
| YOLOv8-L [25] | 0.659 | 0.526 | 0.550 | 43.6 M | 165.4 | 72.9 |
| YOLOv8-X [25] | 0.667 | 0.544 | 0.569 | 68.2 M | 258.1 | 40.2 |
| Fine-YOLO (Ours) | 0.719 | 0.536 | 0.583 | 16.1 M | 56.9 | 152.4 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | mAP | Params. | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LightRay [37] | 0.667 | 0.519 | 0.547 | 19.0 M | 52.5 | 78.3 |
| YOLOv4-PANv2 [38] | 0.665 | 0.502 | 0.537 | 15.2 M | 38.5 | 50.6 |
| EM-YOLOv7 [39] | 0.640 | 0.512 | 0.527 | 37.2 M | 103.3 | 94.3 |
| Improved YOLOv8s [40] | 0.593 | 0.507 | 0.514 | 11.5 M | 30.6 | 95.0 |
| Improved YOLOv8n [41] | 0.633 | 0.491 | 0.542 | 25.8 M | 79.1 | 106.5 |
| Fine-YOLO (Ours) | 0.719 | 0.536 | 0.583 | 16.1 M | 56.9 | 152.4 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | mAP | Params. | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDD-YOLO [42] | 0.561 | 0.634 | 0.638 | 8.9 M | 13.9 | 130.4 |
| DCAM-Net [43] | 0.640 | 0.735 | 0.725 | 30.5 M | 73.0 | 100.2 |
| Regularized YOLO [44] | 0.638 | 0.675 | 0.703 | 3.0 M | 8.3 | 131.4 |
| Improved YOLOX [45] | 0.652 | 0.697 | 0.723 | 7.2 M | 20.7 | 100.0 |
| Fine-YOLO (Ours) | 0.698 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 16.1 M | 56.9 | 161.3 |
| Model | LPFA | HDFA | NWD | mAP | Params. | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7 | 0.573 | 37.2 M | 103.3 | 95.2 | |||
| √ | 0.564 | 12.0 M | 50.0 | 137.0 | |||
| √ | 0.627 | 37.2 M | 103.3 | 95.2 | |||
| √ | √ | 0.574 | 12.0 M | 50.0 | 137.0 | ||
| YOLOv7-Tiny-SiLU | 0.507 | 6.0 M | 13.1 | 166.7 | |||
| √ | 0.529 | 8.5 M | 17.3 | 161.3 | |||
| √ | 0.541 | 6.0 M | 13.1 | 166.7 | |||
| √ | √ | 0.552 | 8.5 M | 17.3 | 161.3 | ||
| Fine-YOLO | √ | √ | 0.567 | 16.1 M | 56.9 | 152.4 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.583 | 16.1 M | 56.9 | 152.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.-T.; Cao, K.-Y.; Li, D.; Piao, J.-C. Fine-YOLO: A Simplified X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Network Based on Feature Aggregation and Normalized Wasserstein Distance. Sensors 2024, 24, 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113588
Zhou Y-T, Cao K-Y, Li D, Piao J-C. Fine-YOLO: A Simplified X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Network Based on Feature Aggregation and Normalized Wasserstein Distance. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113588
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yu-Tong, Kai-Yang Cao, De Li, and Jin-Chun Piao. 2024. "Fine-YOLO: A Simplified X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Network Based on Feature Aggregation and Normalized Wasserstein Distance" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113588
APA StyleZhou, Y.-T., Cao, K.-Y., Li, D., & Piao, J.-C. (2024). Fine-YOLO: A Simplified X-ray Prohibited Object Detection Network Based on Feature Aggregation and Normalized Wasserstein Distance. Sensors, 24(11), 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113588






