Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods
Abstract
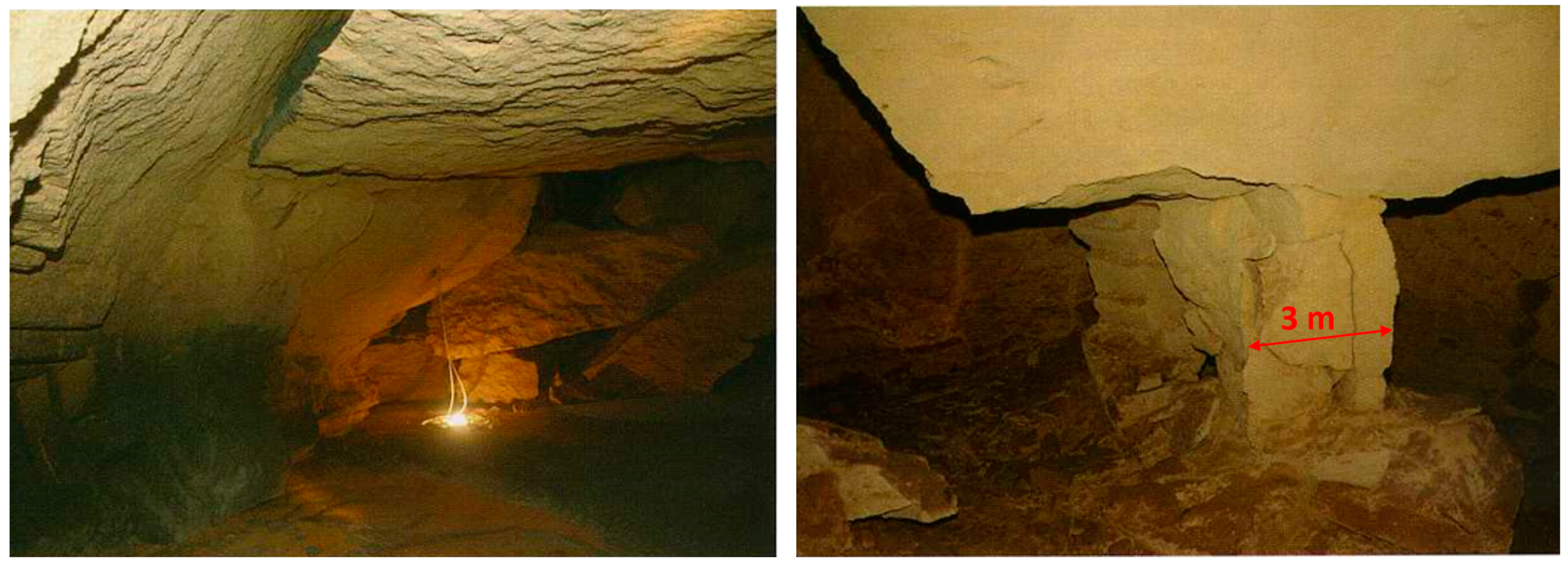
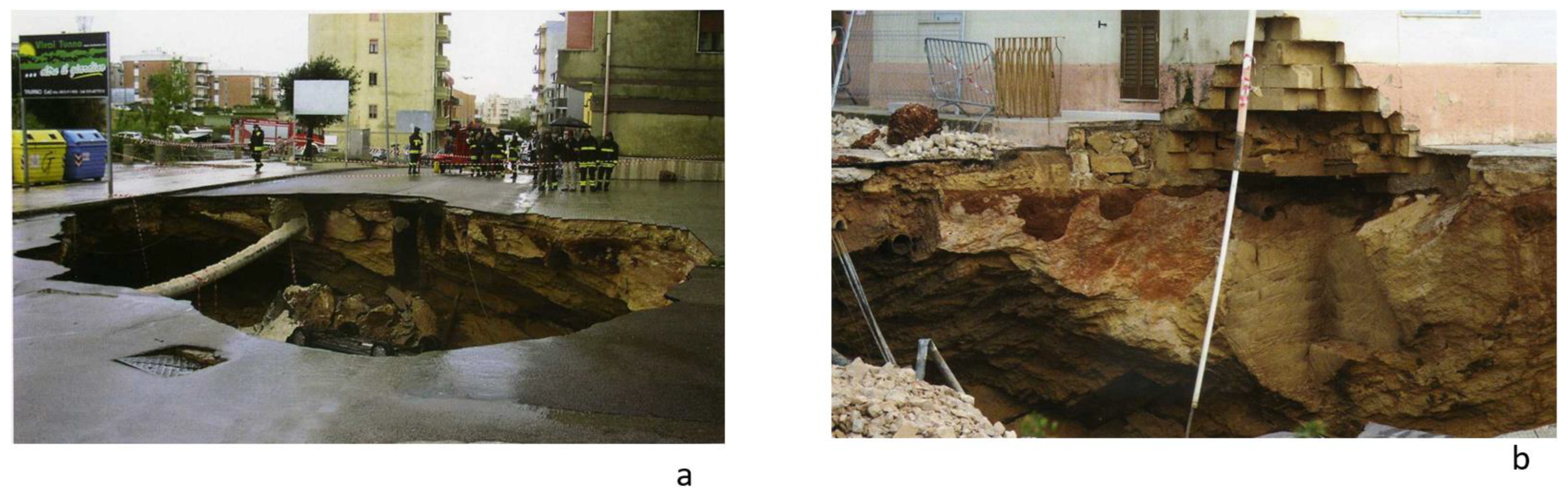
1. Introduction
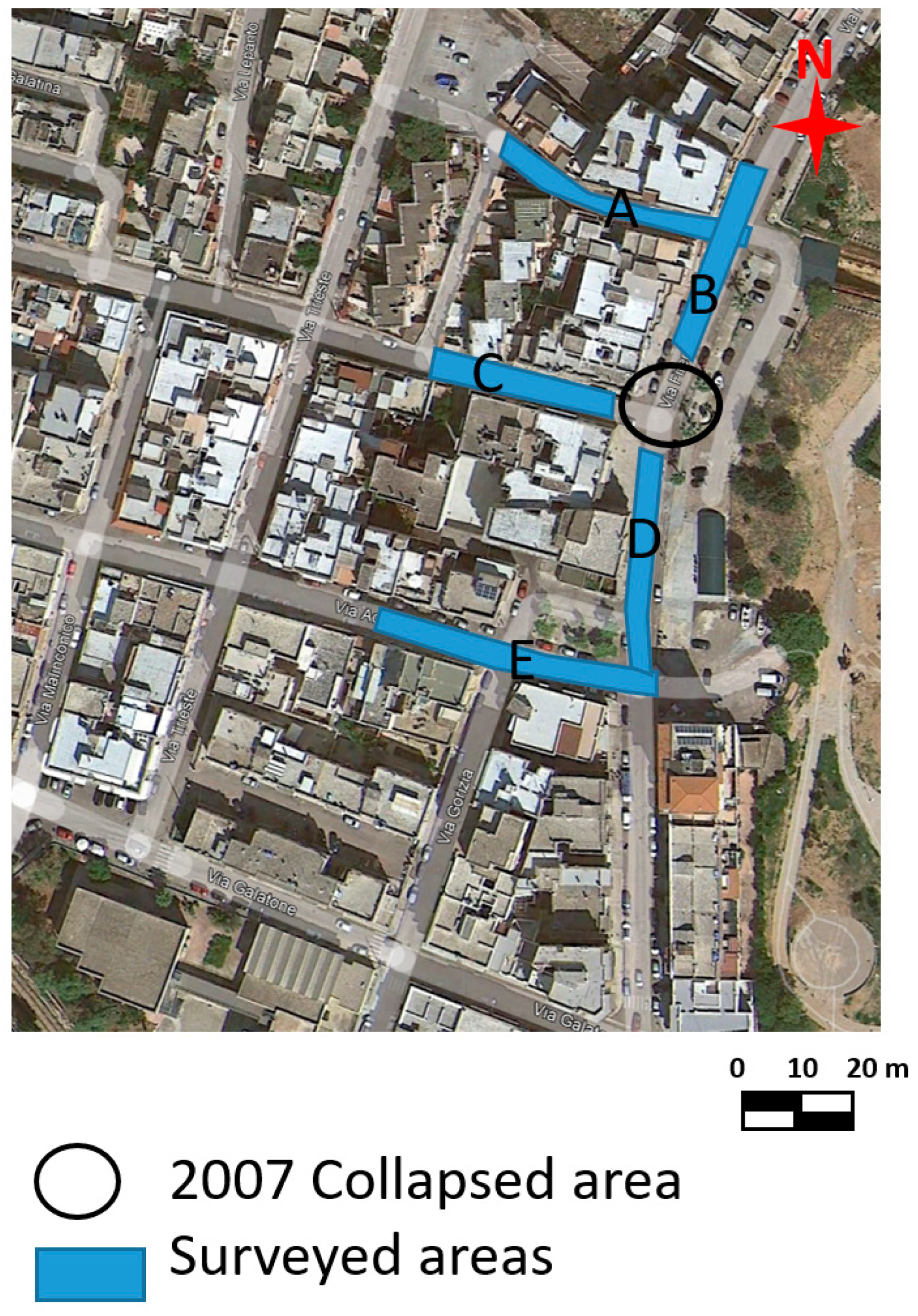
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
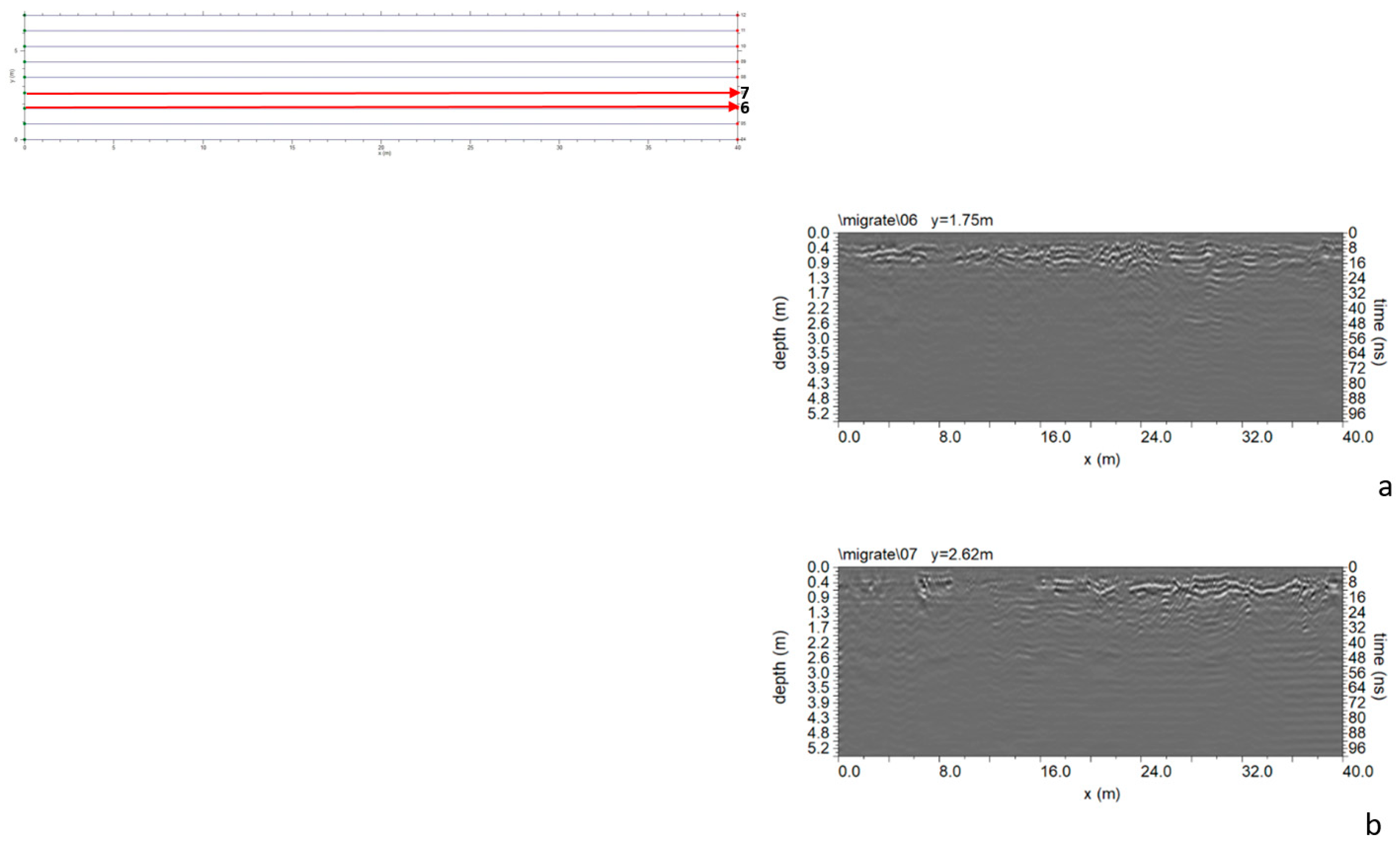
3.1. The 2007 GPR Data Analysis
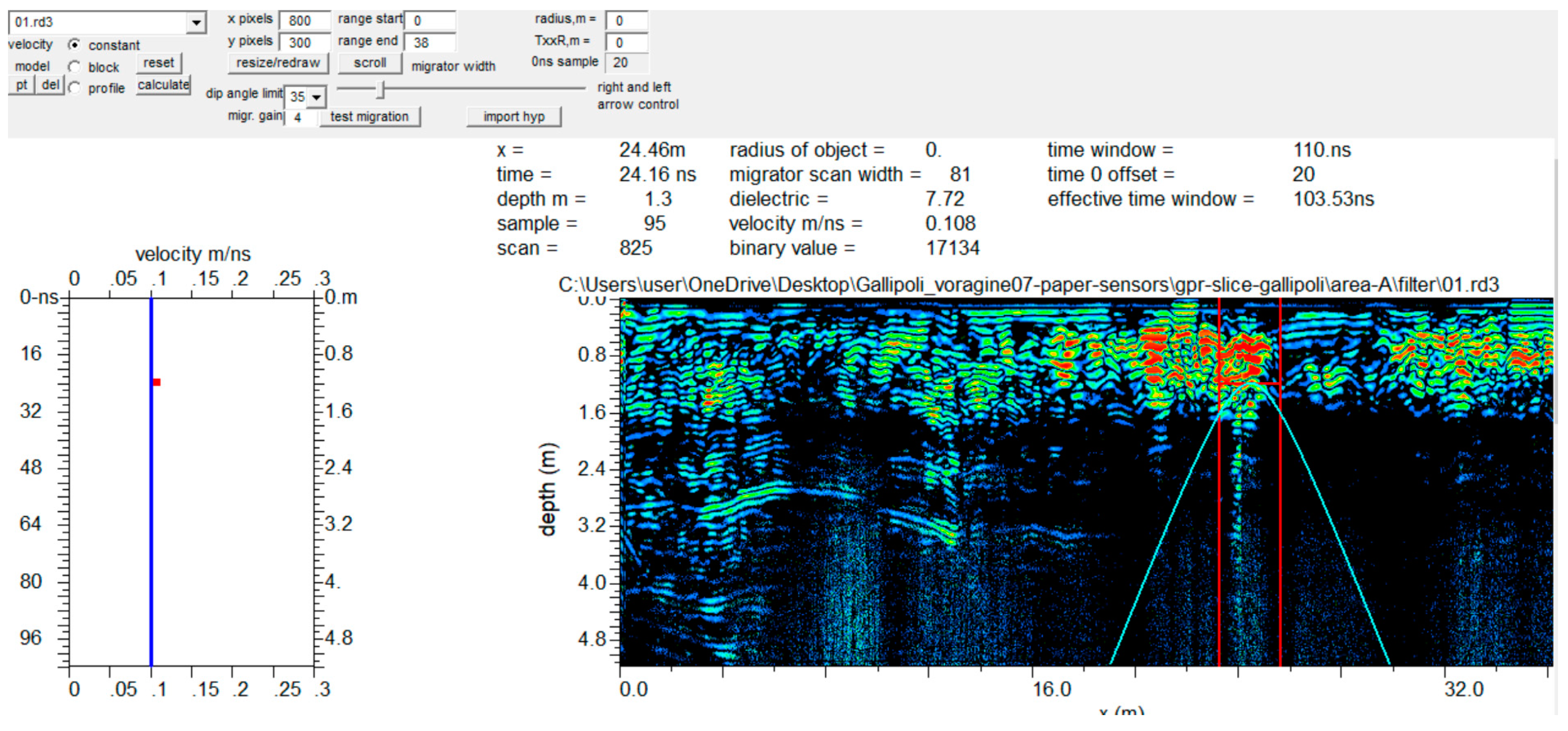
3.1.1. Area A
3.1.2. Area B
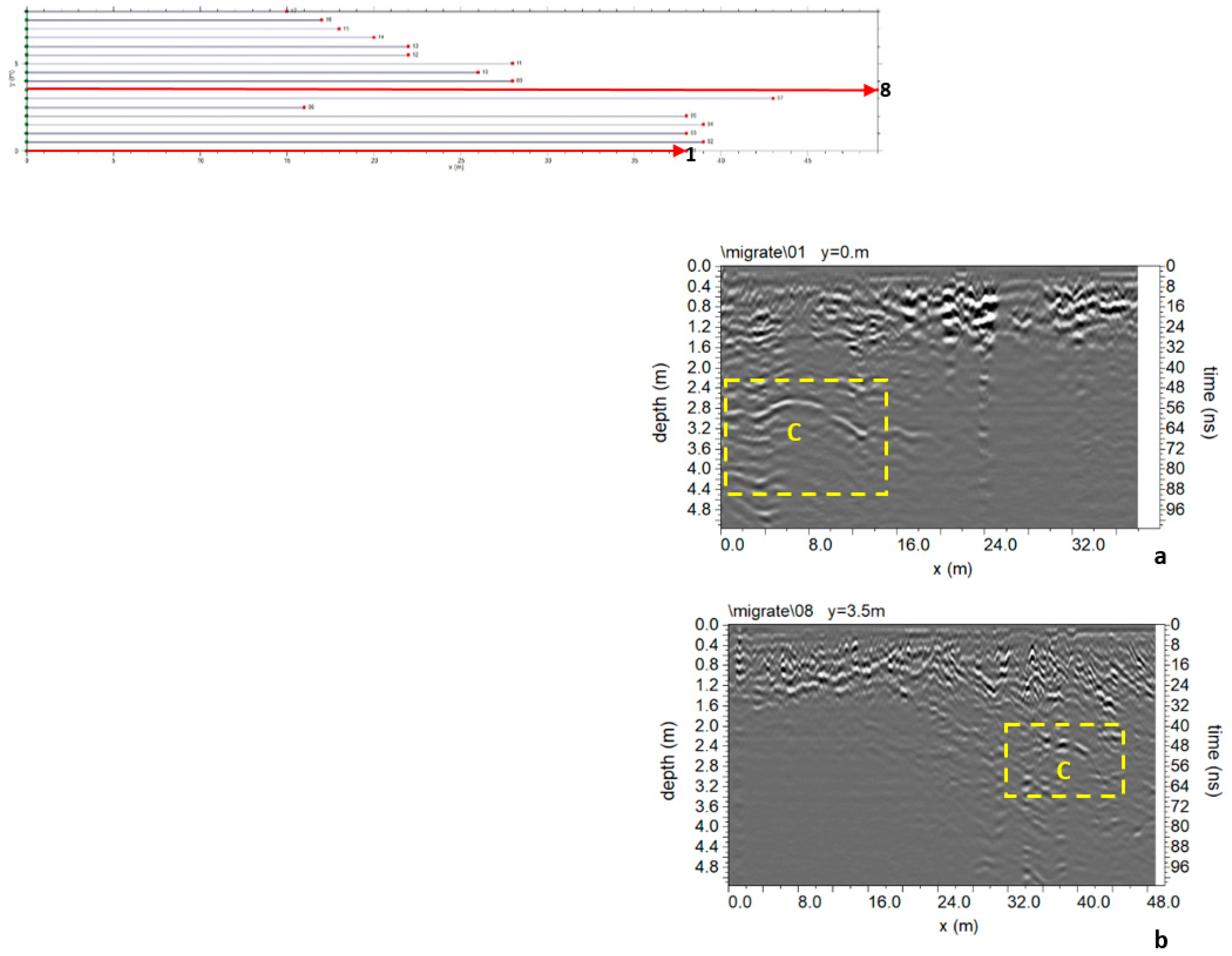
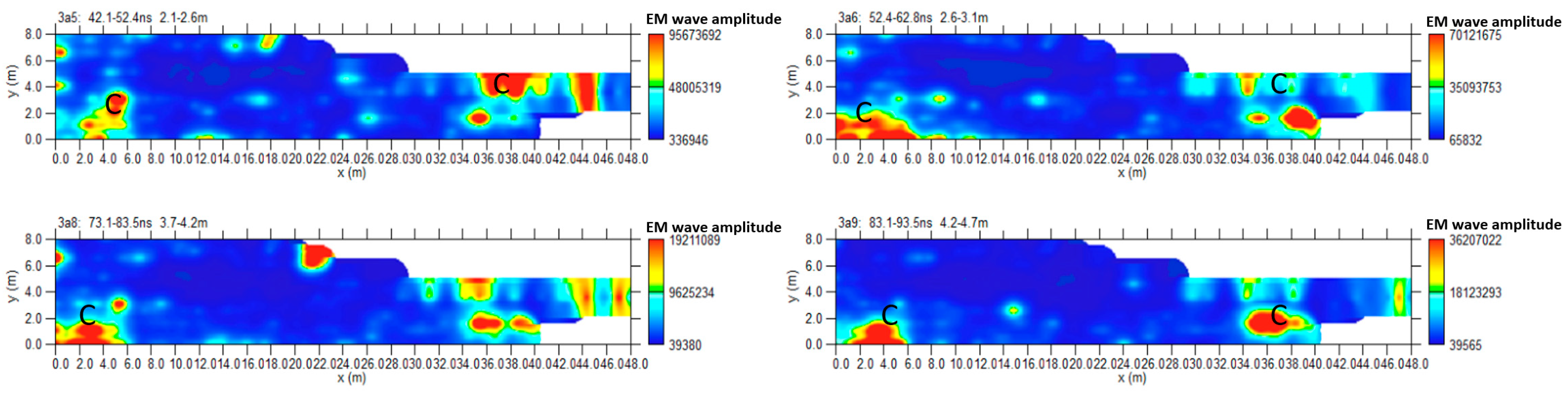
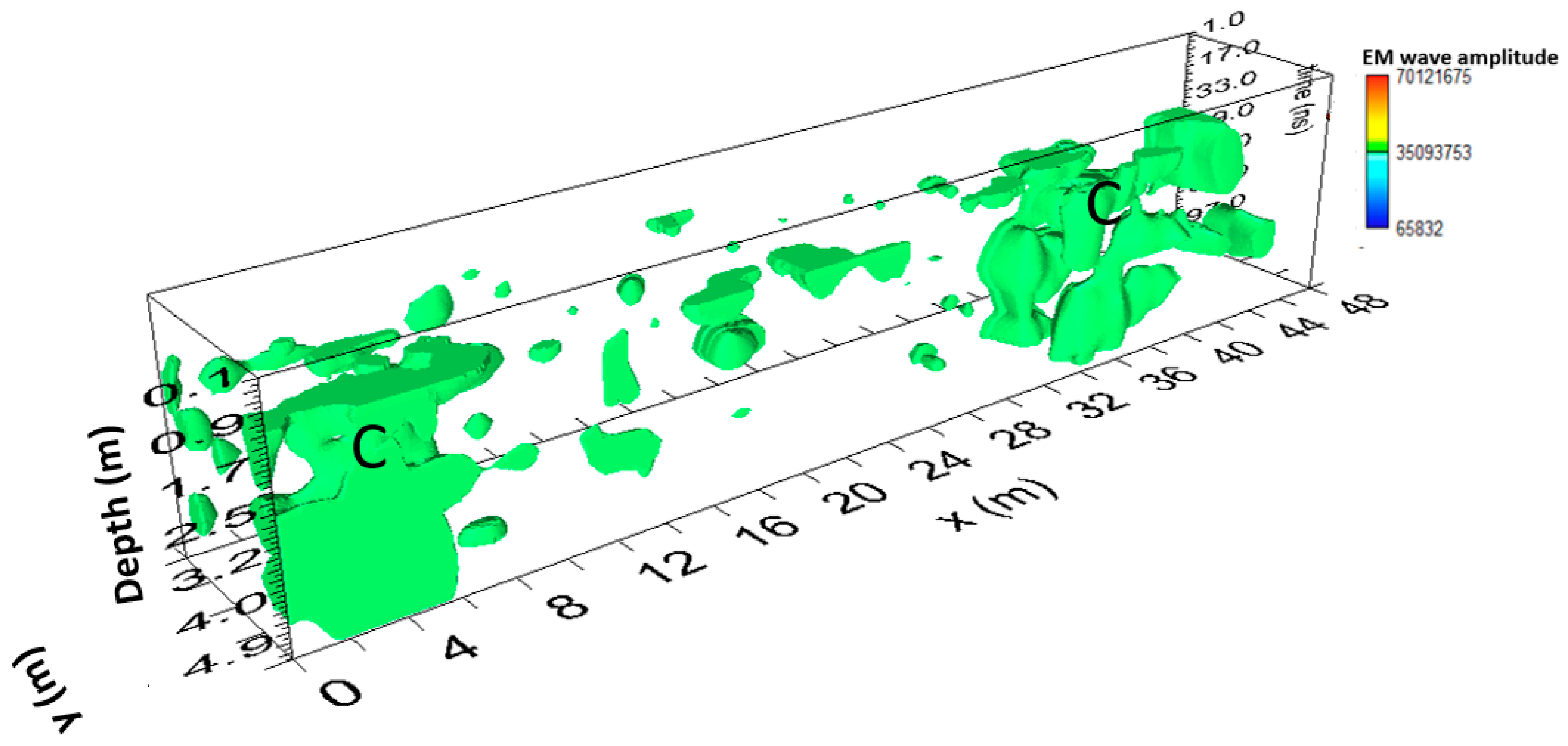
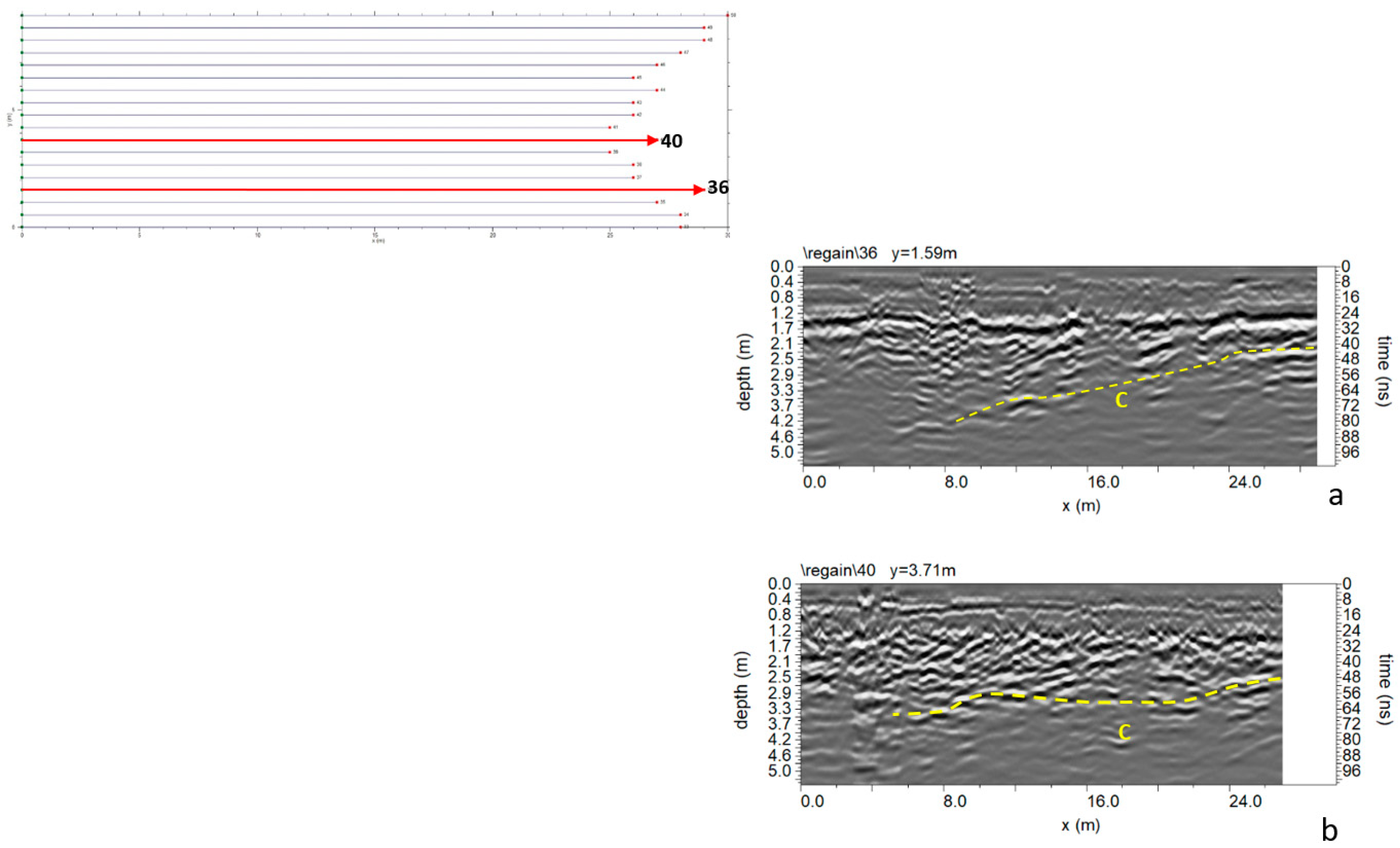
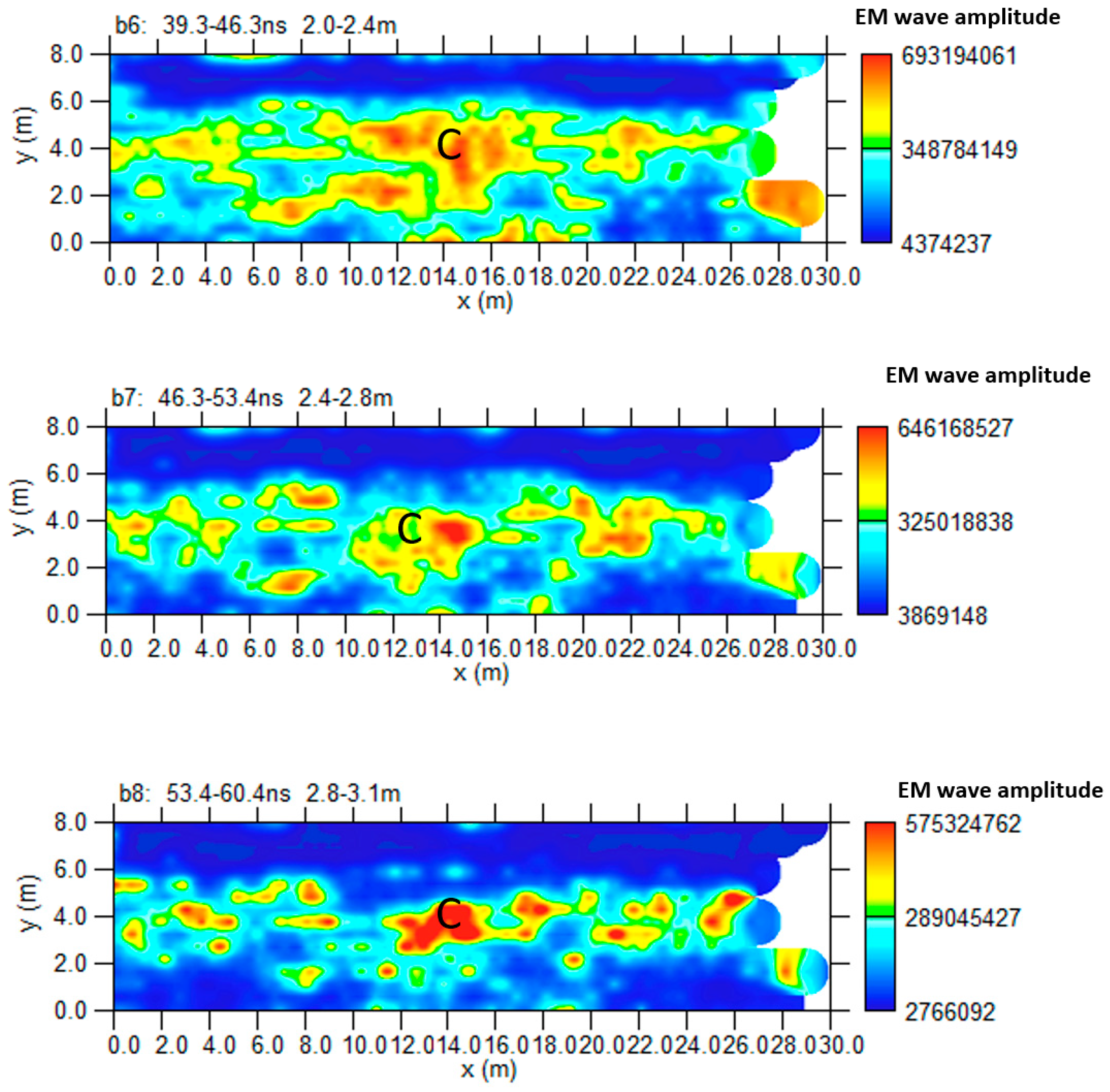
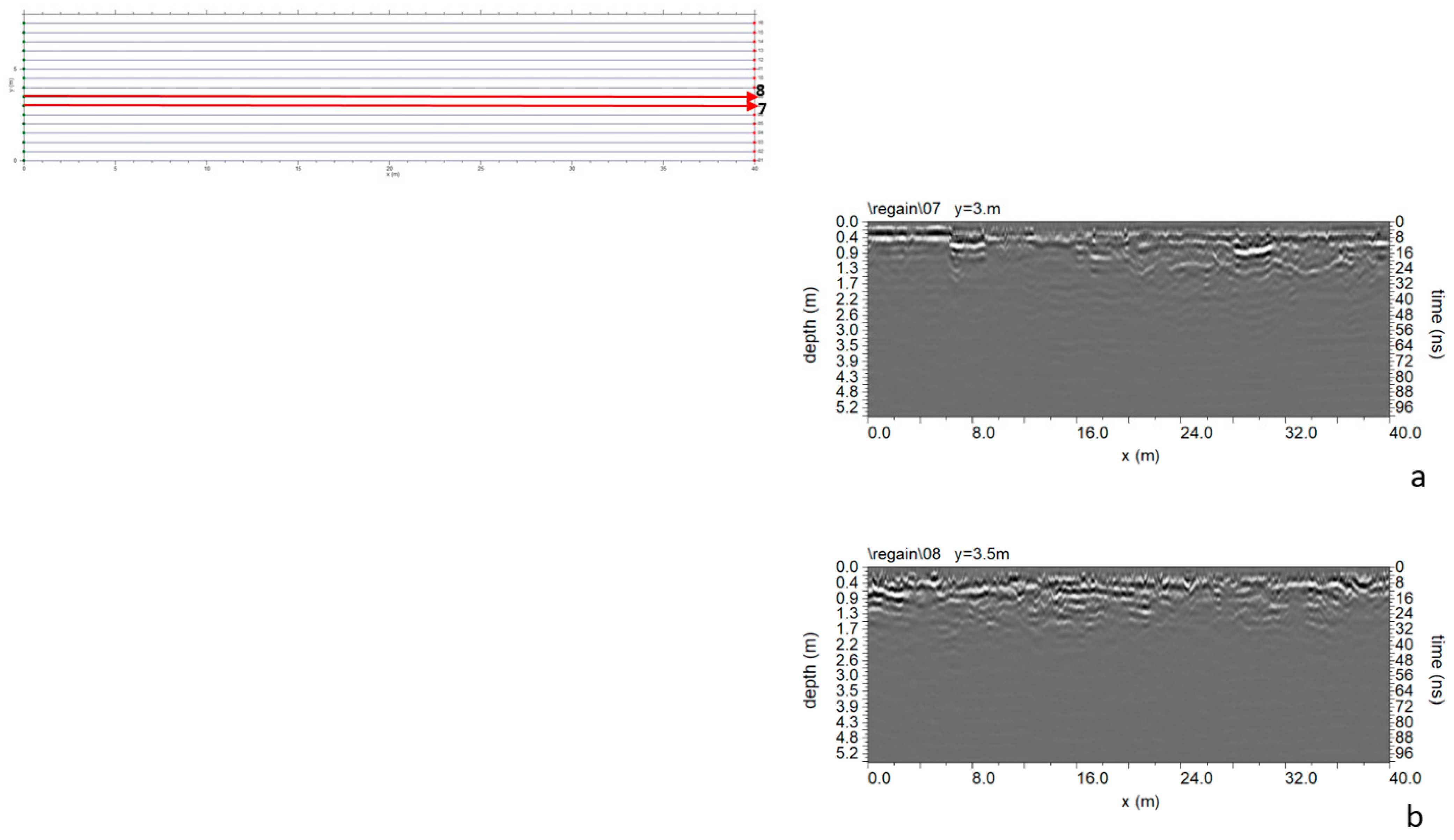
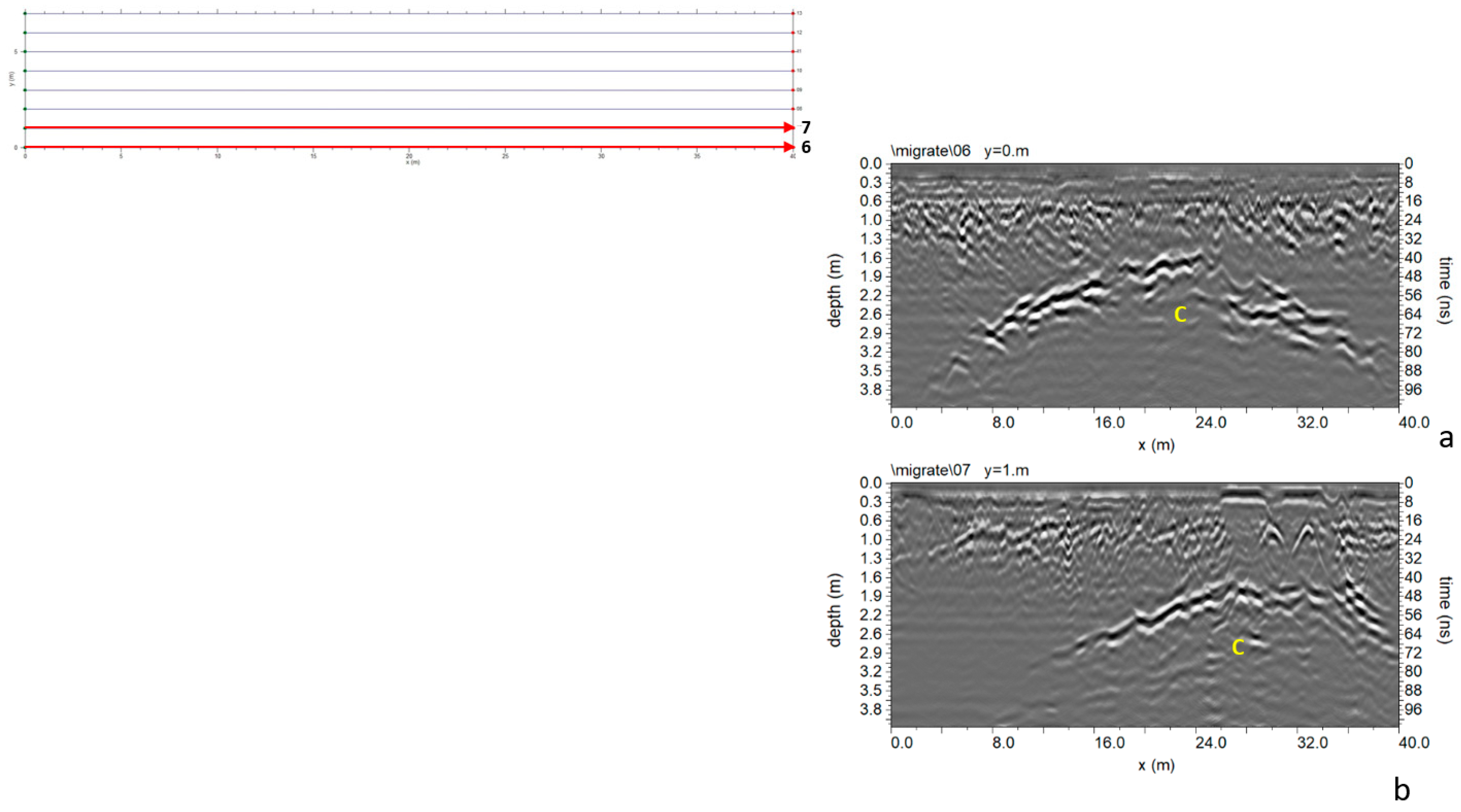
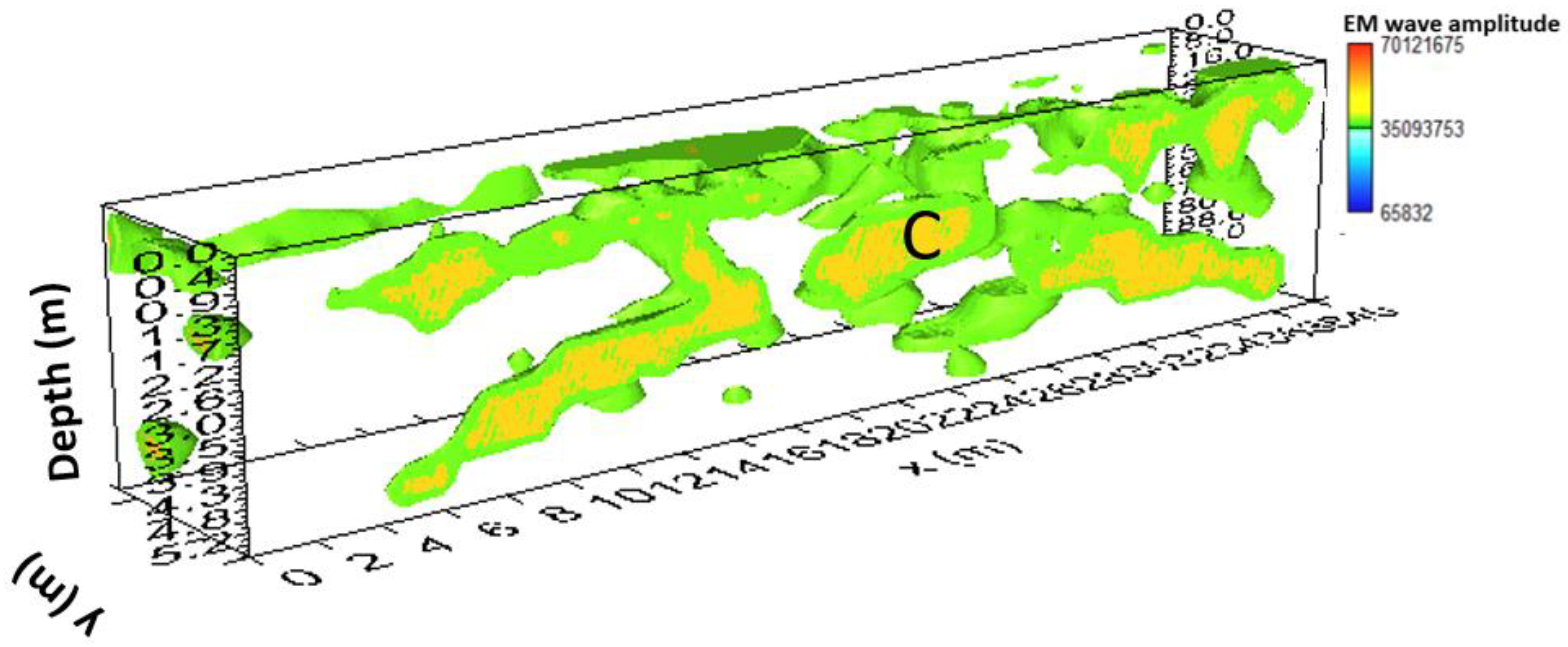
3.1.3. Area C
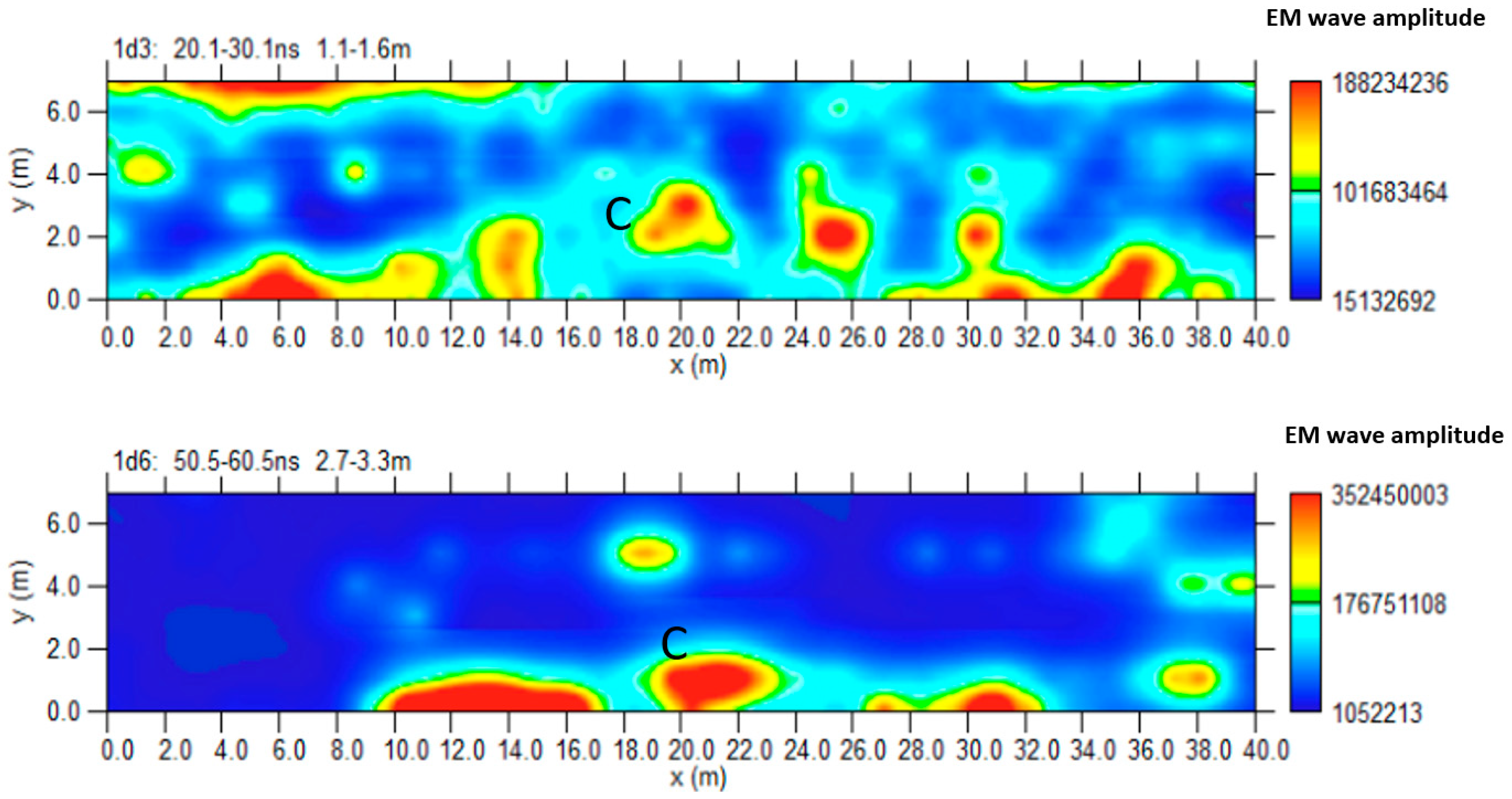
3.1.4. Area D
3.1.5. Area E
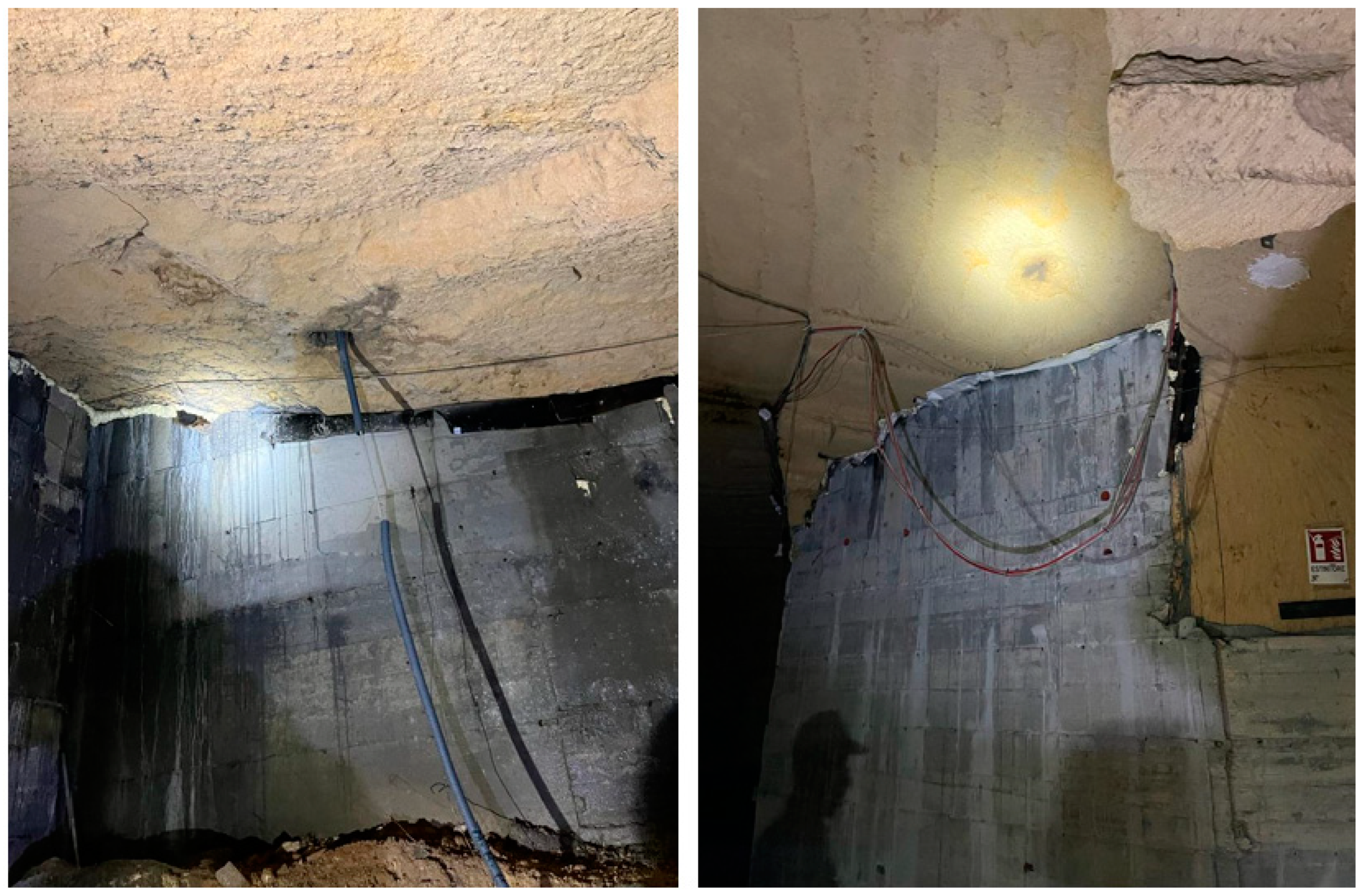
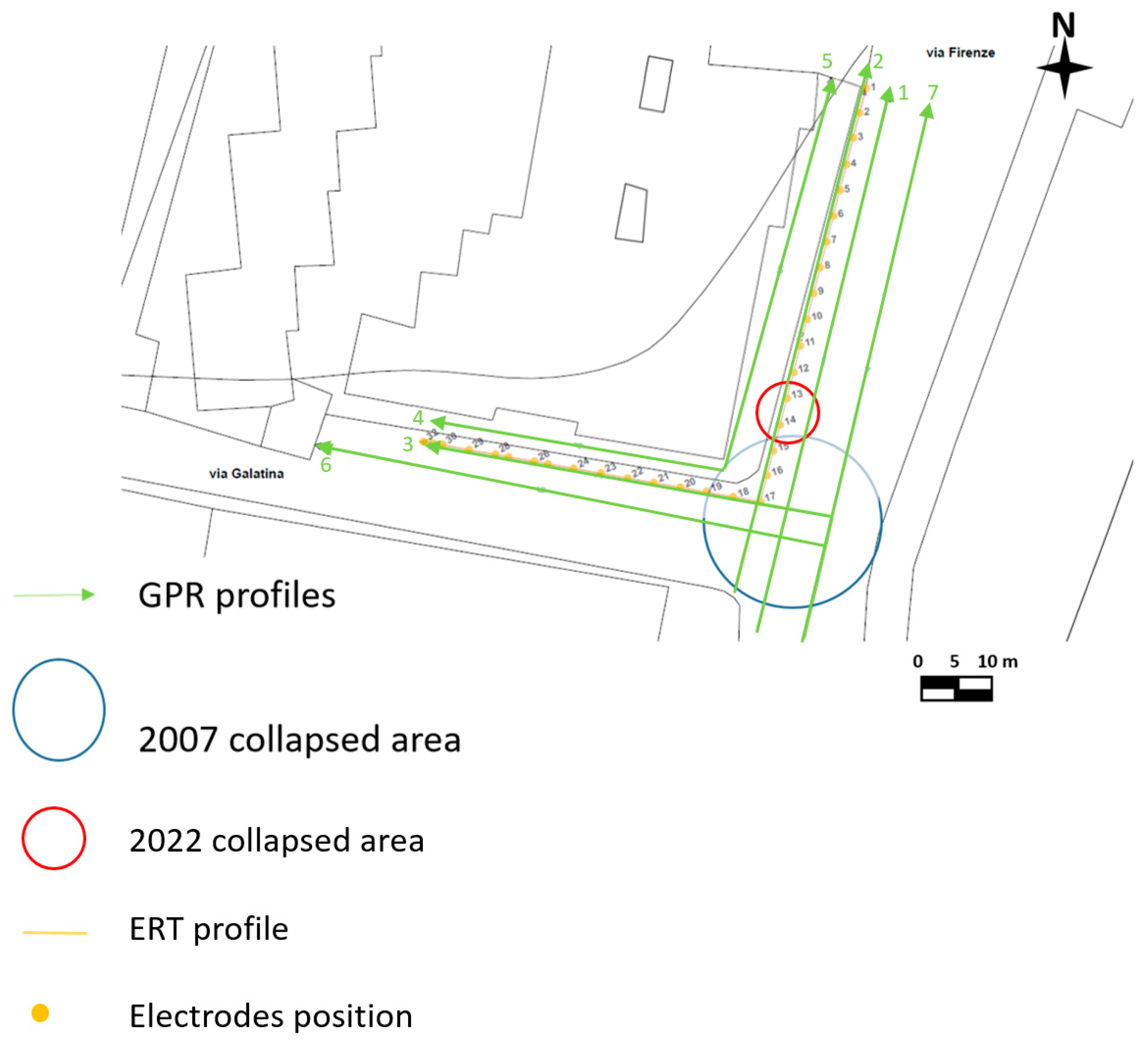
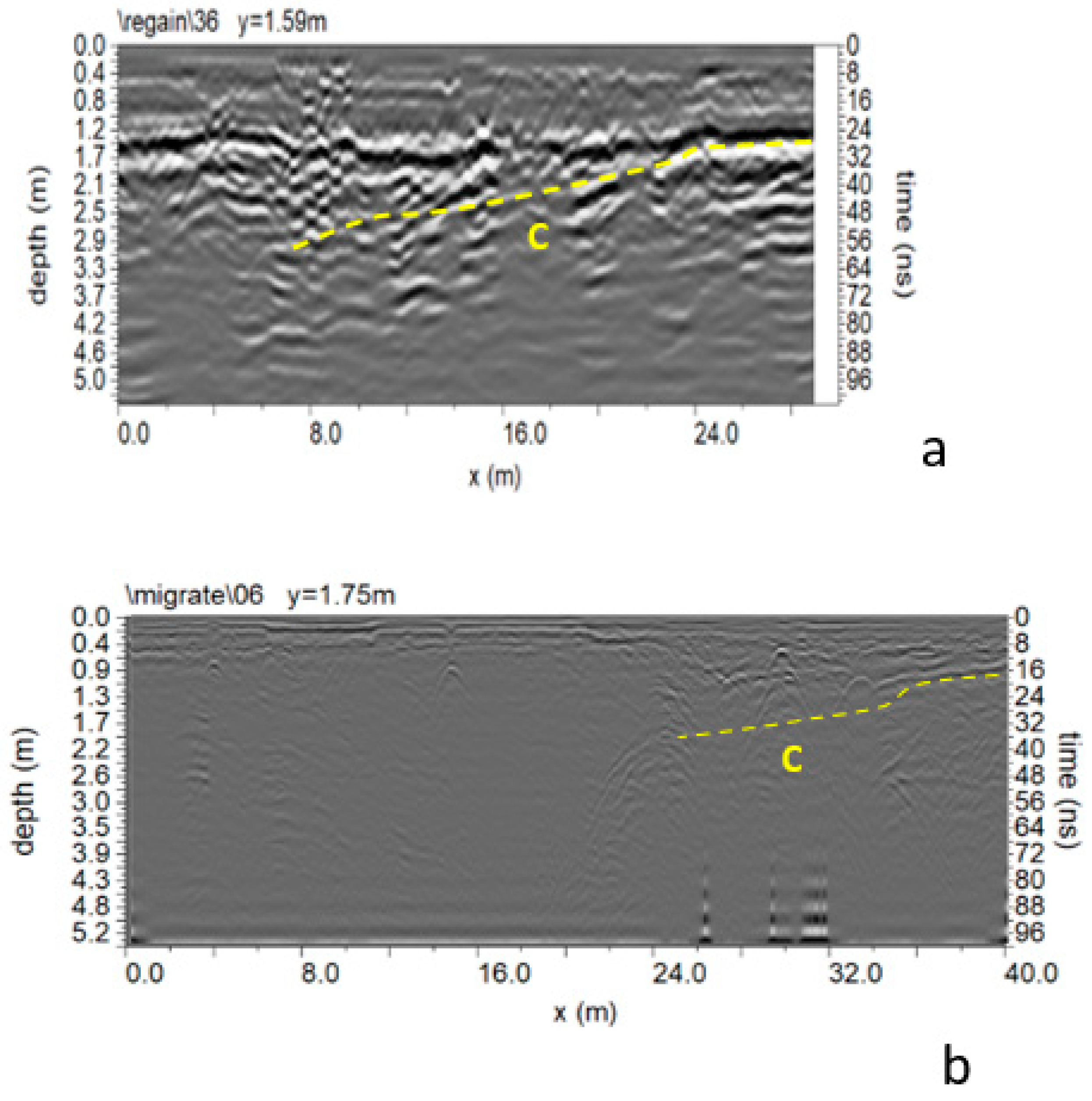
3.2. The 2022 GPR Data Analysis
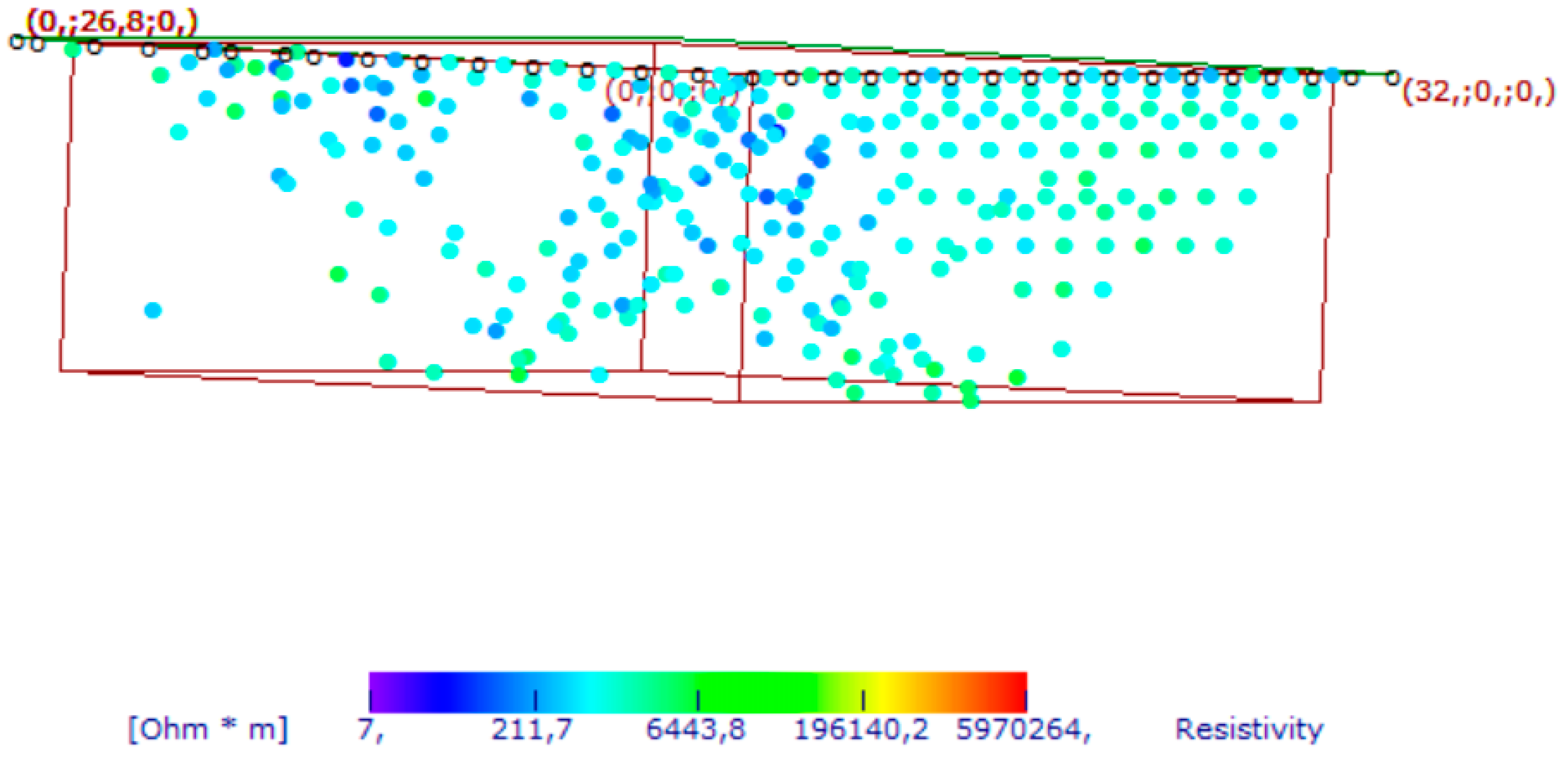
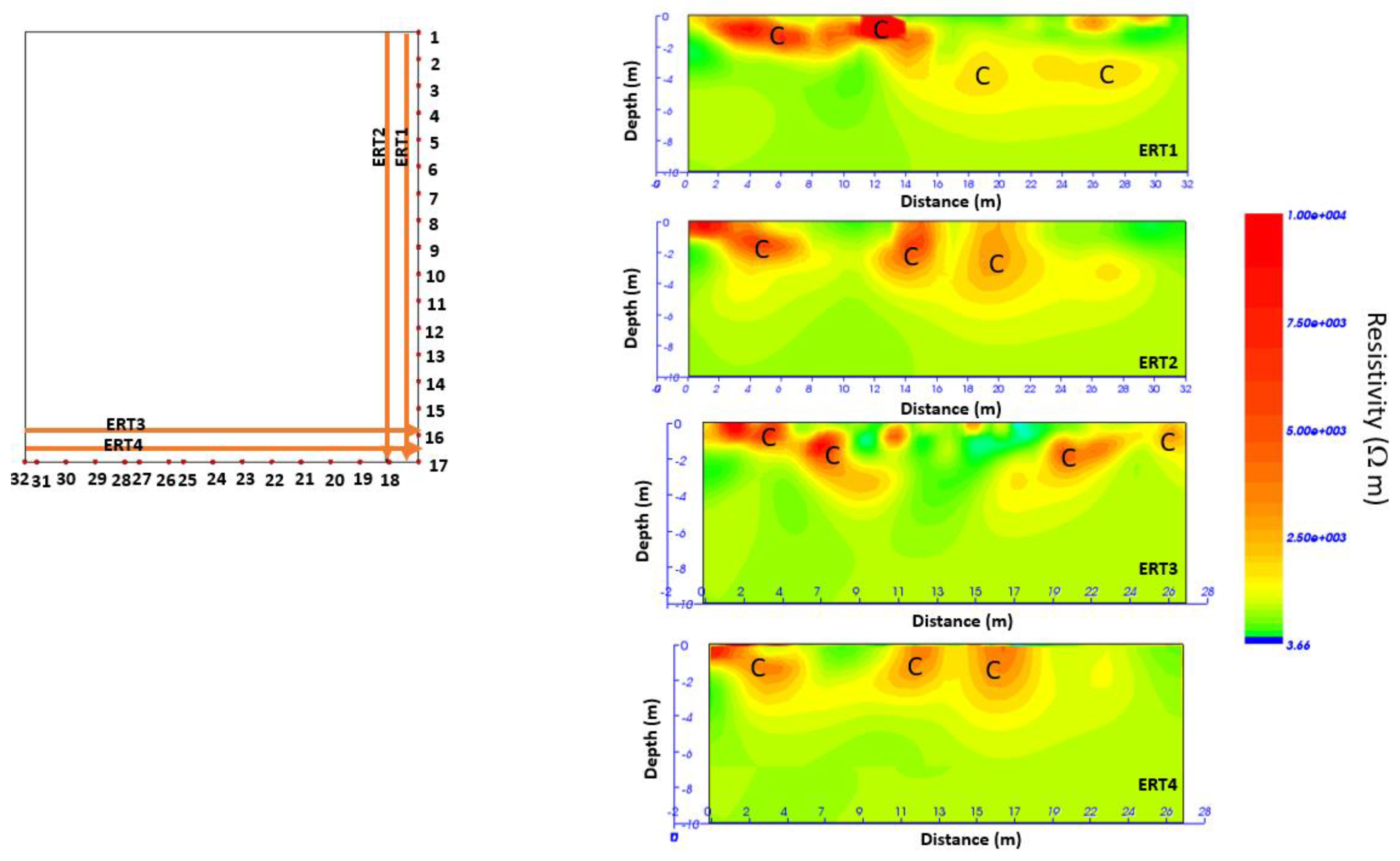
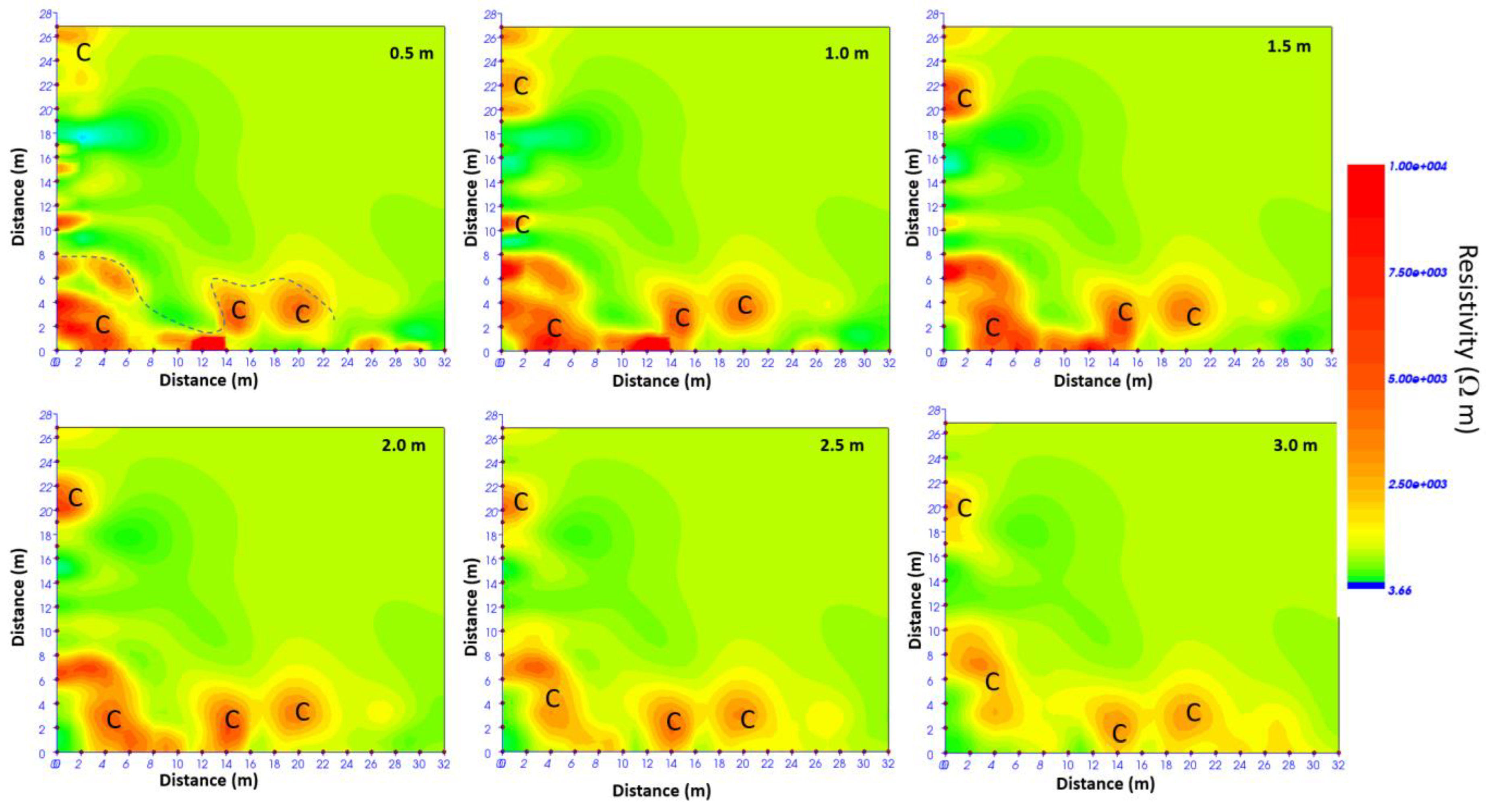
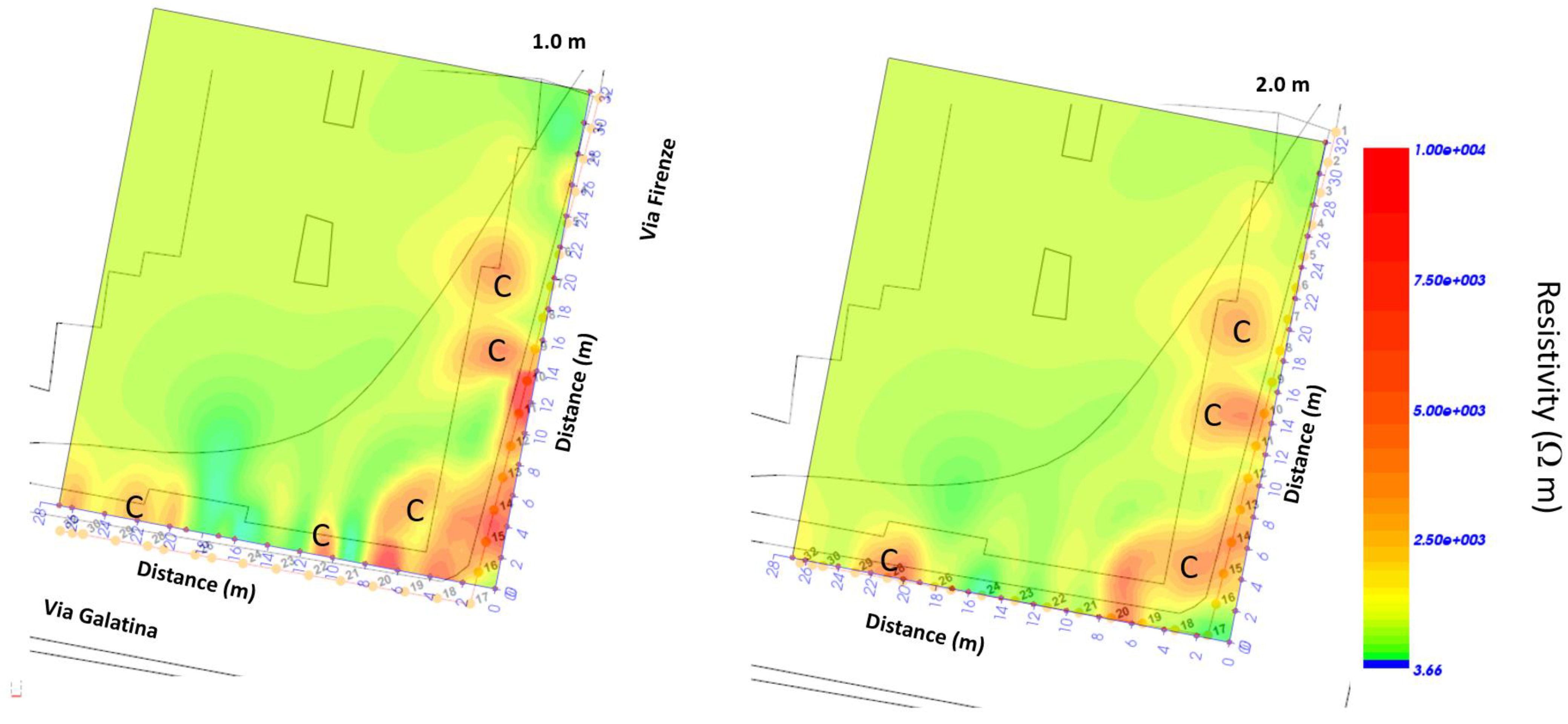
3.3. The 2022 ERT Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corazza, A. Censimento dei dissesti dovuti a cavità sotterranee in Italia. Atti del Convegno Stato Dell’arte Sullo Studio dei Fenomeni di Sinkholes e Ruolo Delle Amministrazioni Statali e Locali nel Governo del Territorio. 2004; pp. 307–318. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Delle Rose, M. Mediterranean Pliocene events in the salento geological records. Thalass. Salentina 2006, 29, 77–99. [Google Scholar]
- Delle Rose, M.; Federico, A. Karstik phenomena and environmental hazard in salento coastal plains. In Proceedings of the IX IAEG Congress Engineering Geology for Developing Countries, Durban, South Africa, 16–20 September 2002; pp. 1297–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Leucci, G.; De Giorgi, L. Microgravimetric and ground penetrating radar geophysical methods to map the shallow karstic cavities network in a coastal area (marina di capilungo, lecce—Italy). Explor. Geophys. 2010, 41, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, V.; Prada, A.; Garcia, F. A Multimodal Research Approach to Assessing the Karst Structural Conditions of the Ceiling of a Cave with Palaeolithic Cave Art Paintings: Polychrome Hall at Altamira Cave (Spain). Sensors 2023, 23, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schoor, M. Detection of sinkholes using 2D electrical resistivity imaging. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 50, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.L.; Chang, R.K.W.; Sham, J.F.C. A blind test of nondestructive underground void detection by ground penetrating radar (GPR). J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 194, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Q.; Binley, A. Evaluating the joint use of GPR and ERT on mapping shallow subsurface features of karst critical zone in southwest China. Vadose Zone J. 2021, 21, e20172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conyers, L.B. Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology; Altamira Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, L.B. Innovative ground-penetrating radar methods for archaeological mapping. Archaeol. Prospect. 2006, 13, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conyers, L.B. Interpreting Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, L.; Zhenshi, S.; Jianhui, L.; Choa, L.; Xu, M.; Yanliang, D.; Jie, C. Detection of road cavities in urban cities by 3D ground-penetrating radar. Geophysics 2021, 86, WA25–WA33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Uagoda, R.; Borges, W.; Nunes, J.; Hamza, O.; Condori, C.; Aslam, K.; Dou, J.; Cárdenas-Soto, M. The Potential Use of Geophysical Methods to Identify Cavities, Sinkholes and Pathways for Water Infiltration. Water 2020, 12, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argote-Espino, D.; Tejero-Andrade, A.; Cifuentes-Nava, G.; Iriarte, L.; Farıas, S.; Chavez, R.E.; Lopez, F. 3D electrical prospection in the archaeological site El Pahnu, Hidalgo State, Central Mexico. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, G.; Tejero, A.; Alcantara, M.A.; Chavez, R.E. The ‘L-Array’, a tool to characterize a fracture pattern in an urban zone: In expanded abstracts: Near surface 2011. Eur. Assoc. Geosci. Eng. 2011, 1, 114–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tejero-Andrade, A.; Cifuentes, G.; Chavez, R.E.; Lopez Gonzalez, A.; Delgado-Solorzano, C. ‘‘L’’ and ‘‘Corner’’ arrays for 3D electrical resistivity tomography: An alternative for urban zones. Near Surf. Geophys. 2015, 13, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisona, A.; Ishola, K.S.; Nawawi, M.N.M. Subsurface void mapping using geophysical and geotechnical techniques with uncertainties estimation: Case study of Kinta Valley, Perak, Malaysia. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidou, E.; Vargemezis, G.; Tsourlos, P. Combined application of seismic and electrical geophysical methods for karst cavities detection: A case study at the campus of the new University of Western Macedonia, Kozani, Greece. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 196, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, G. Nondestructive Testing for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: A Practical Guide and New Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; p. 217. ISBN 978-3-030-01898-6. [Google Scholar]
- Leucci, G. Advances in Geophysical Methods Applied to Forensic Investigations: New Developments in Acquisition and Data Analysis Methodologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; p. 200. ISBN 978-3-030-46241-3. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, D.; Piro, S. GPR Remote Sensing in Archaeology; Geotechnologies and the Environment Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 9, p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, D.; Steinberg, J.; Damiata, B.; Nishimure, Y.; Schneider, K.; Hiromichi, H.; Hisashi, N. GPR overlay analysis for archaeological prospection. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar, Columbus, OH, USA, 19–22 June 2006 [CD-ROM]. [Google Scholar]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Giorgi, L.; Barbolla, D.F.; Torre, C.; Settembrini, S.; Leucci, G. Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods. Sensors 2024, 24, 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123757
De Giorgi L, Barbolla DF, Torre C, Settembrini S, Leucci G. Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods. Sensors. 2024; 24(12):3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123757
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Giorgi, Lara, Dora Francesca Barbolla, Chiara Torre, Stefano Settembrini, and Giovanni Leucci. 2024. "Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods" Sensors 24, no. 12: 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123757
APA StyleDe Giorgi, L., Barbolla, D. F., Torre, C., Settembrini, S., & Leucci, G. (2024). Evaluation of a Ground Subsidence Zone in an Urban Area Using Geophysical Methods. Sensors, 24(12), 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123757








