Performance Assessment of Two Low-Cost PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Networks in the Padana Plain (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. PurpleAir Low-Cost Sensors
2.2.2. AirQino Low-Cost Sensors
2.2.3. ARPA Reference Stations
2.3. Methods
3. Results
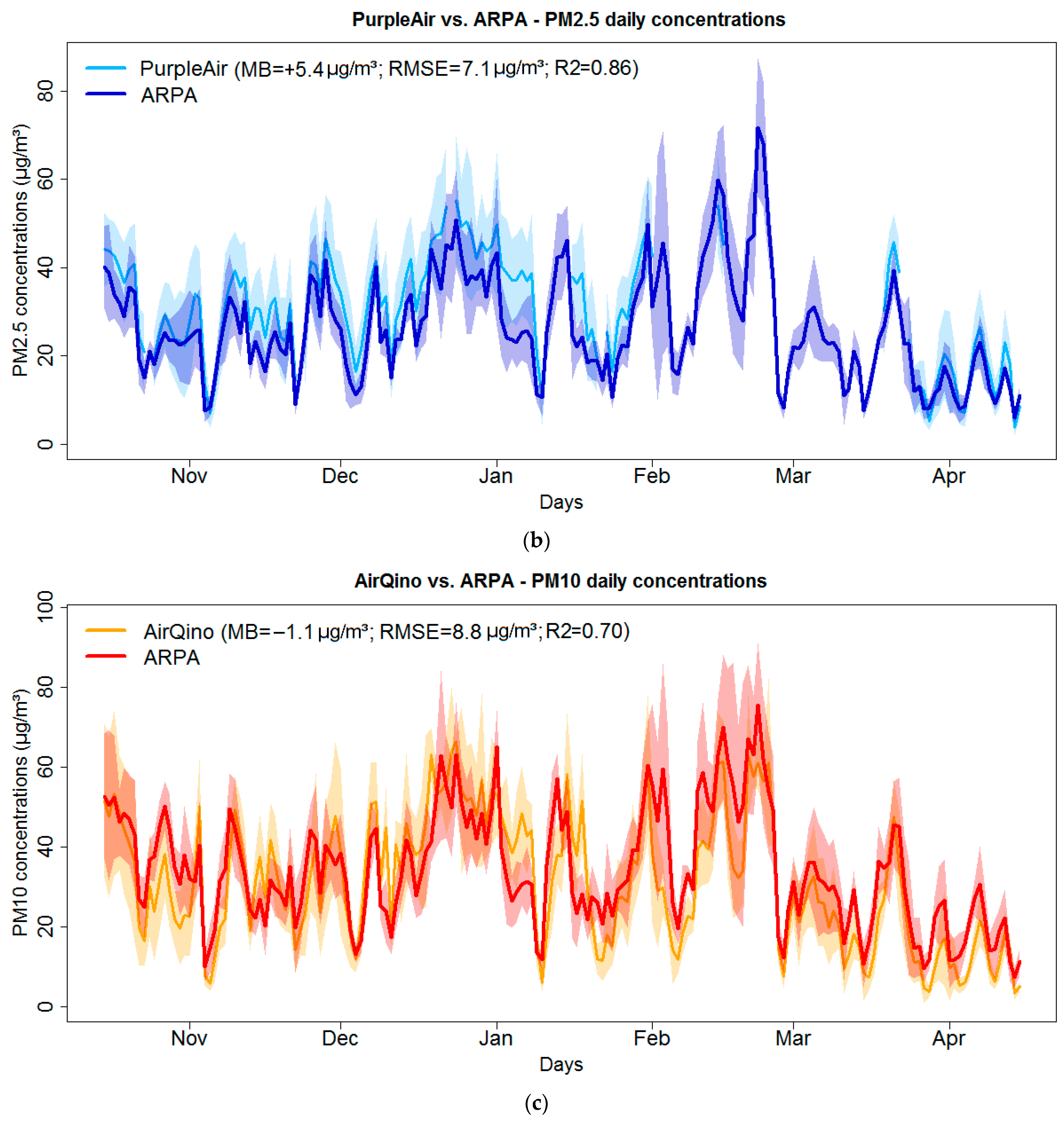
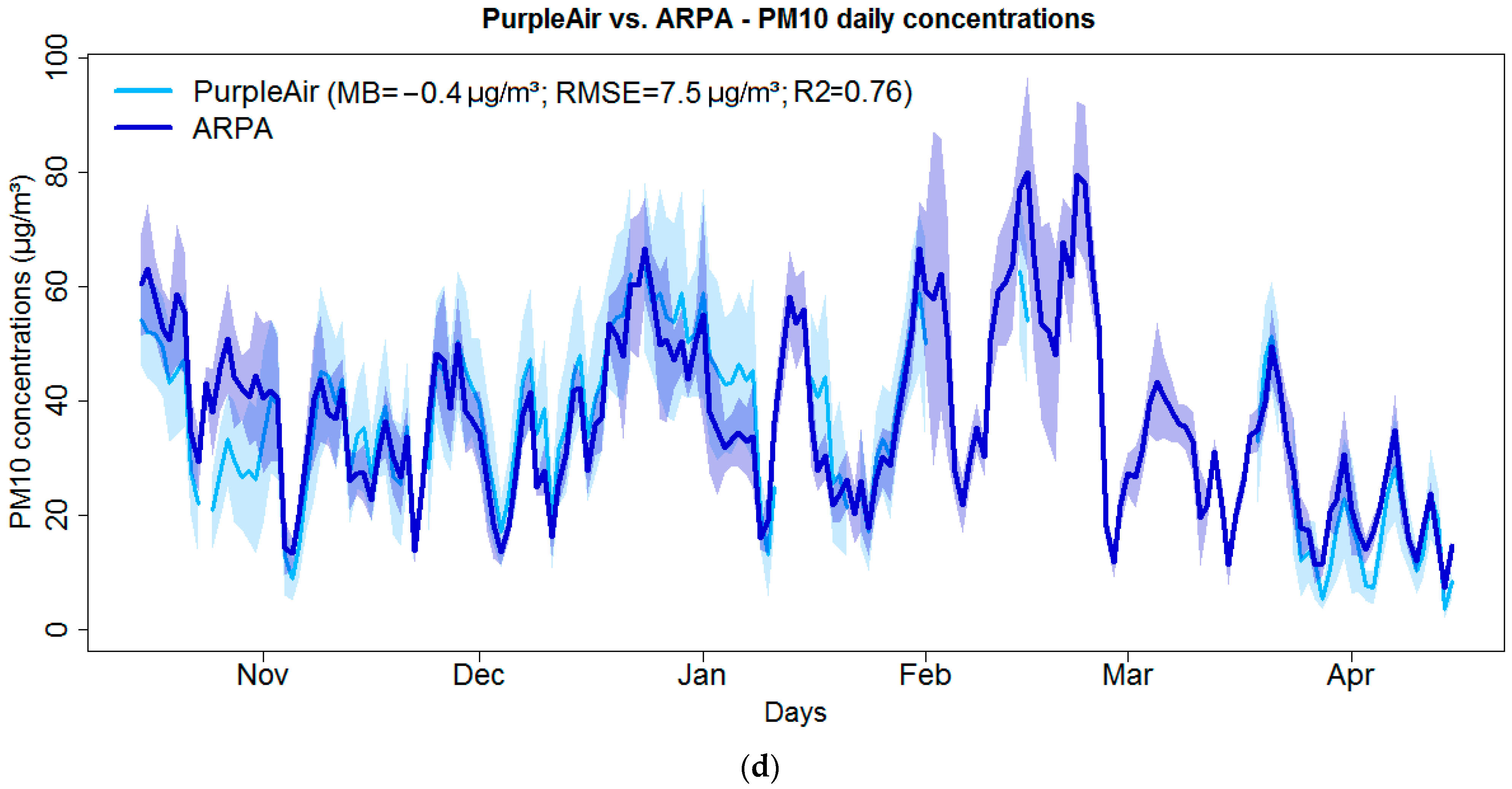
3.1. PM2.5 and PM10 Observed Concentrations
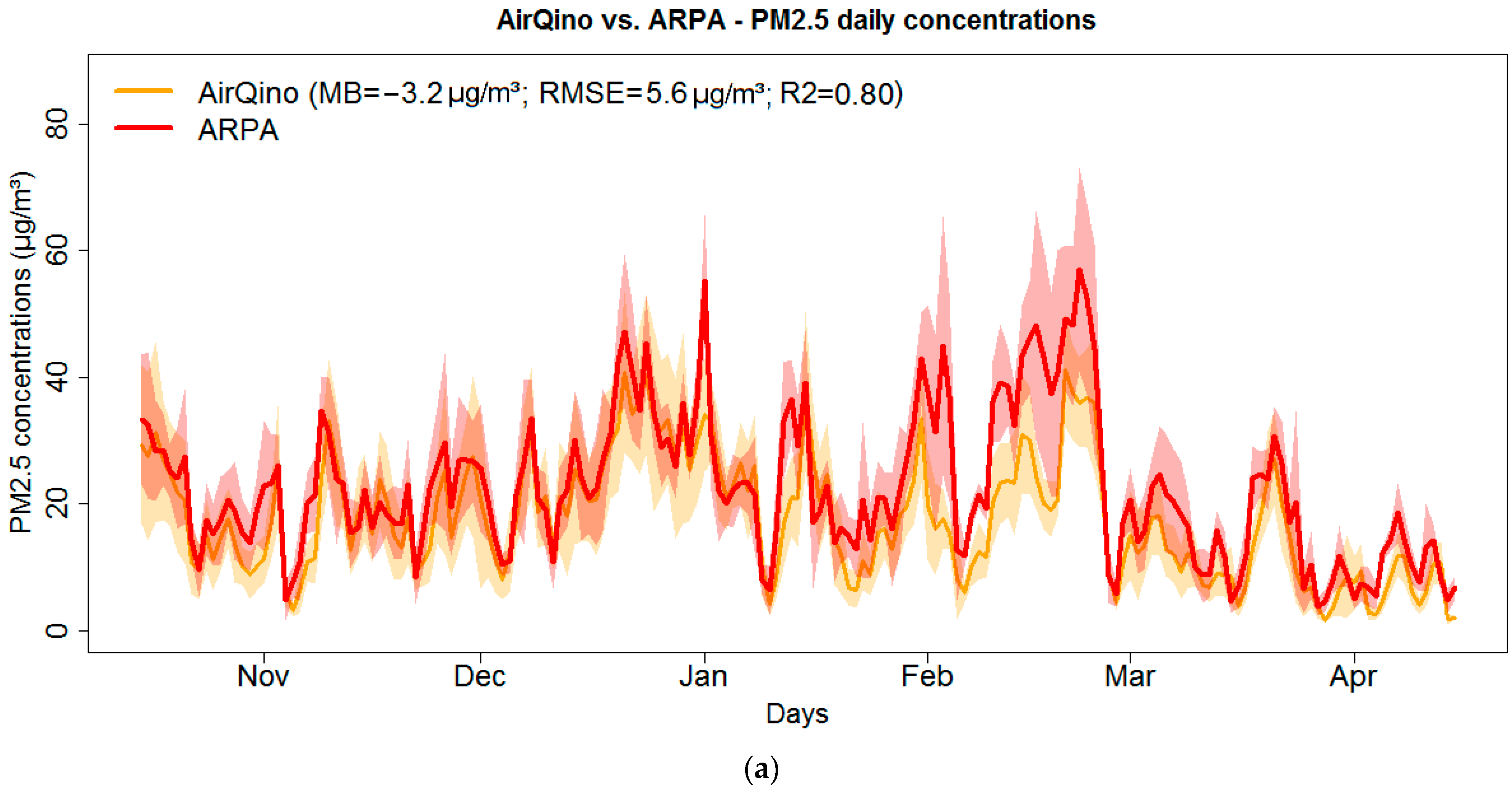
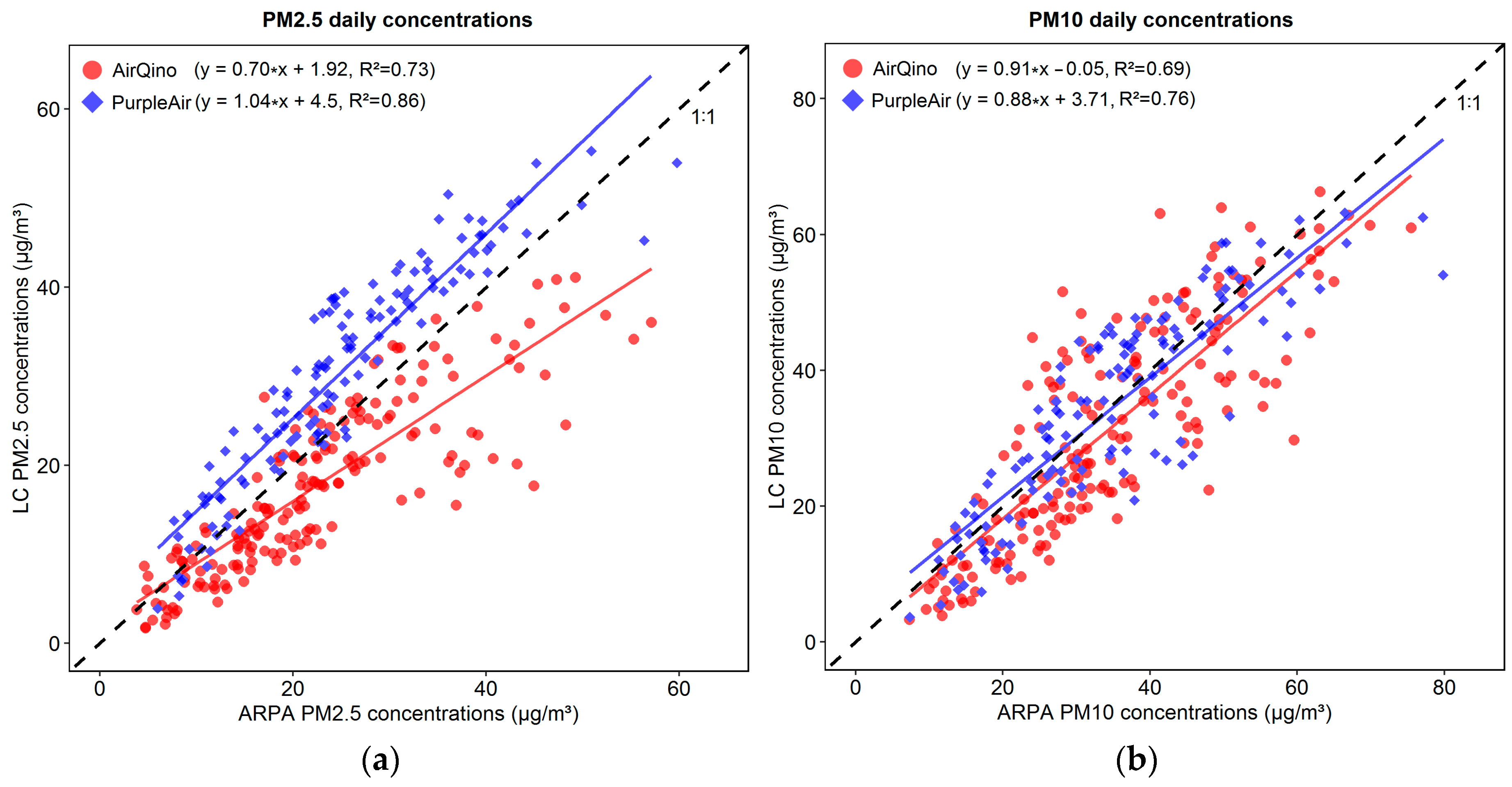
3.2. Scores by Station of Low-Cost Stations
3.3. Overall Scores by Monitoring Network of Low-Cost Stations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/air-pollution (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- EEAa. Europe’s Air Quality Status 2023. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/europes-air-quality-status-2023. (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Bigi, A.; Ghermandi, G. Trends and variability of atmospheric PM2.5 and PM10–2.5 concentration in the Po Valley, Italy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15777–15788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEAb. Air Quality Statistics. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/air-quality-statistics (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Gualtieri, G.; Brilli, L.; Carotenuto, F.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A.; Gioli, B. Long-Term COVID-19 Restrictions in Italy to Assess the Role of Seasonal Meteorological Conditions and Pollutant Emissions on Urban Air Quality. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, M.; E Williams, D.; Ainslie, B.; McKendry, I.; Salmond, J.; Grange, S.K.; Alavi-Shoshtari, M.; Steyn, D.; Henshaw, G.S. High density ozone monitoring using gas sensitive semi-conductor sensors in the Lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3970–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotenuto, F.; Bisignano, A.; Brilli, L.; Gualtieri, G.; Giovannini, L. Low-cost air quality monitoring networks for long-term field campaigns: A review. Meteorol. Appl. 2023, 30, e2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Thai, P.K.; Liu, X.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.; Ayoko, G.; Bartonova, A.; Bedini, A.; Chai, F.; Christensen, B.; Dunbabin, M.; et al. Applications of low-cost sensing technologies for air quality monitoring and exposure assessment: How far have they gone? Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryner, J.; L’Orange, C.; Mehaffy, J.; Miller-Lionberg, D.; Hofstetter, J.C.; Wilson, A.; Volckens, J. Laboratory evaluation of low-cost PurpleAir PM monitors and in-field correction using co-located portable filter samplers. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagulian, F.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Lagler, F.; Redon, N.; Crunaire, S.; Borowiak, A. Review of the performance of low-cost sensors for air quality monitoring. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N. Tutorial: Guidelines for implementing low-cost sensor networks for aerosol monitoring. J. Aerosol Sci. 2022, 159, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malings, C.; Tanzer, R.; Hauryliuk, A.; Saha, P.K.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A.; Subramanian, R. Fine particle mass monitoring with low-cost sensors: Corrections and long-term performance evaluation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Carmona, N.; Blanco, M.N.; Gassett, A.J.; Seto, E.; Szpiro, A.A.; Larson, T.V.; Sampson, P.D.; Kaufman, J.D.; Sheppard, L. Publicly available low-cost sensor measurements for PM2.5 exposure modeling: Guidance for monitor deployment and data selection. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raysoni, A.U.; Pinakana, S.D.; Mendez, E.; Wladyka, D.; Sepielak, K.; Temby, O. A Review of Literature on the Usage of Low-Cost Sensors to Measure Particulate Matter. Earth 2023, 4, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AQ-SPECa. PM Sensor Evaluations. Available online: http://www.aqmd.gov/aq-spec/evaluations/summary-pm (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Ardon-Dryer, K.; Dryer, Y.; Williams, J.N.; Moghimi, N. Measurements of PM2.5 with PurpleAir under atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5441–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISTAT. Gross Domestic Product Supply Side. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx?QueryId=11455&lang=en (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- ISTAT. Classification of Municipalities Based on Italian Ecoregions. 12 October 2023. Available online: https://www.istat.it/en/archivio/224797 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Gualtieri, G.; Carotenuto, F.; Finardi, S.; Tartaglia, M.; Toscano, P.; Gioli, B. Forecasting PM10 hourly concentrations in northern Italy: Insights on models performance and PM10 drivers through self-organizing maps. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Ghermandi, G.; Harrison, R.M. Analysis of the air pollution climate at a background site in the Po valley. J. Environ. Monitor. 2012, 14, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Wildani, A.; Chang, H.H.; Liu, Y. Incorporating low-cost sensor measurements into high-resolution PM2.5 modeling at a large spatial scale. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2152–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, Z.; Biswas, J.; Saha, J. Long-Term Assessment of PurpleAir Low-Cost Sensor for PM2.5 in California, USA. Pollutants 2023, 3, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, T.; Butterfield, A.; Kelly, K.E. Long-term field evaluation of the Plantower PMS low-cost particulate matter sensors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzer, R.; Malings, C.; Hauryliuk, A.; Subramanian, R.; Presto, A.A. Demonstration of a low-cost multi-pollutant network to quantify intra-urban spatial variations in air pollutant source impacts and to evaluate environmental justice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delp, W.W.; Singer, B.C. Wildfire smoke adjustment factors for low-cost and professional PM2.5 monitors with optical sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Han, P.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, N.; Liu, D.; Cai, Q.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Tang, X. Field evaluation of low-cost particulate matter sensors in Beijing. Sensors 2020, 20, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Michalopoulos, P.; Liakakou, E.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kalkavouras, P.; Fameli, K.M.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Field Evaluation of Low-Cost PM Sensors (Purple Air PA-II) Under Variable Urban Air Quality Conditions, in Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awokola, B.I.; Okello, G.; Mortimer, K.J.; Jewell, C.P.; Erhart, A.; Semple, S. Measuring air quality for advocacy in Africa (MA3): Feasibility and practicality of longitudinal ambient PM2.5 measurement using low-cost sensors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenkopf, C.A. Sharing lessons-learned on effective open data, open-source practices from OpenAQ, a global open air quality community. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2017, 2017, IN44A-08. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, G.; Camilli, F.; Cavaliere, A.; De Filippis, T.; Di Gennaro, F.; Di Lonardo, S.; Dini, F.; Gioli, B.; Matese, A.; Nunziati, W.; et al. An integrated low-cost road traffic and air pollution monitoring platform to assess vehicles’ air quality impact in urban areas. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 27, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnoli, C.; Martelli, F.; De Filippis, T.; Di Lonardo, S.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Matese, A.; Rocchi, L.; Toscano, P.; Zaldei, A. The SensorWebBike for air quality monitoring in a smart city. In Proceedings of the IET Conference on Future Intelligent Cities, London, UK, 4–5 December 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldei, A.; Vagnoli, C.; Di Lonardo, S.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Toscano, P.; Martelli, F.; Matese, A. AIRQino, a low-cost air quality mobile platform. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 12–17 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, G.; Ahbil, K.; Brilli, L.; Carotenuto, F.; Cavaliere, A.; Gioli, B.; Giordano, T.; Katiellou, G.L.; Mouhaimini, M.; Tarchiani, V.; et al. Potential of low-cost PM monitoring sensors to fill monitoring gaps in areas of Sub-Saharan Africa. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Martelli, F.; Matese, A.; Toscano, P.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A. Development of low-cost air quality stations for next generation monitoring networks: Calibration and validation of PM2.5 and PM10 sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilli, L.; Carotenuto, F.; Andreini, B.P.; Cavaliere, A.; Esposito, A.; Gioli, B.; Martelli, F.; Stefanelli, M.; Vagnoli, C.; Venturi, S.; et al. Low-Cost Air Quality Stations’ Capability to Integrate Reference Stations in Particulate Matter Dynamics Assessment. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, F.; Brilli, L.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Vagnoli, C.; Mazzola, M.; Viola, A.P.; Vitale, V.; Severi, M.; Traversi, R.; et al. Long-term performance assessment of low-cost atmospheric sensors in the arctic environment. Sensors 2020, 20, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikova, N.; Masiol, M.; Chalupa, D.C.; Rich, D.Q.; Ferro, A.R.; Hopke, P.K. Estimating hourly concentrations of PM2.5 across a metropolitan area using low-cost particle monitors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.; Clements, A.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Barkjohn, K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Fine Particulate Matter Air Sensors: Use in Ambient, Outdoor, Fixed Site, Non-Regulatory Supplemental and Informational Monitoring Applications; EPA/600/R-20/280, Technical Report; U.S. EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_Report.cfm?dirEntryId=350785&Lab=CEMM (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R Package “pastecs”: Package for Analysis of Space-Time Ecological Series (Version 1.4.2). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pastecs/index.html (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R Package “Metrics”: Evaluation Metrics for Machine Learning (Version 0.1.4). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Metrics/index.html (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R Stats Package. Version 4.5.0. Available online: https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/stats/html/00Index.html (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R Graphics Package. Version 4.5.0. Available online: https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/graphics/html/00Index.html (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- R package “ggplot2”: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics (Version 3.5.0). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/index.html (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geoph. Res. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badura, M.; Batog, P.; Drzeniecka-Osiadacz, A.; Modzel, P. Evaluation of low-cost sensors for ambient PM2.5 monitoring. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 5096540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Gantt, B.; Clements, A.L. Development and application of a United States-wide correction for PM2.5 data collected with the PurpleAir sensor. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 4617–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AQ-SPECb. Evaluation Summary of PurpleAir PA-II. Available online: http://www.aqmd.gov/docs/default-source/aq-spec/summary/purpleair-pa-ii---summary-report.pdf?sfvrsn=16 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Coker, E.S.; Amegah, A.K.; Mwebaze, E.; Ssematimba, J.; Bainomugisha, E. A land use regression model using machine learning and locally developed low cost particulate matter sensors in Uganda. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božilov, A.; Tasić, V.; Živković, N.; Lazović, I.; Blagojević, M.; Mišić, N.; Topalović, D. Performance assessment of NOVA SDS011 low-cost PM sensor in various microenvironments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
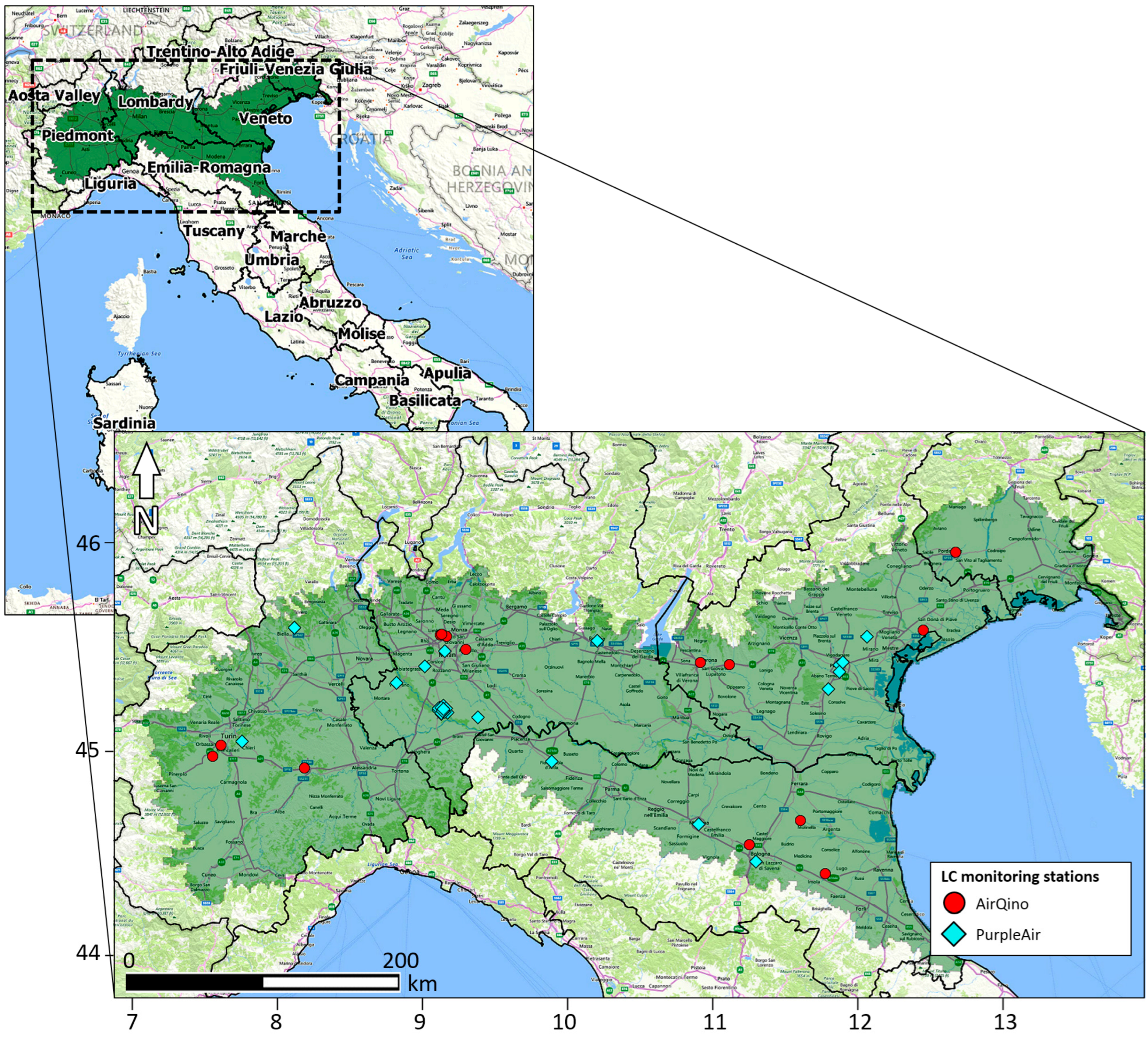
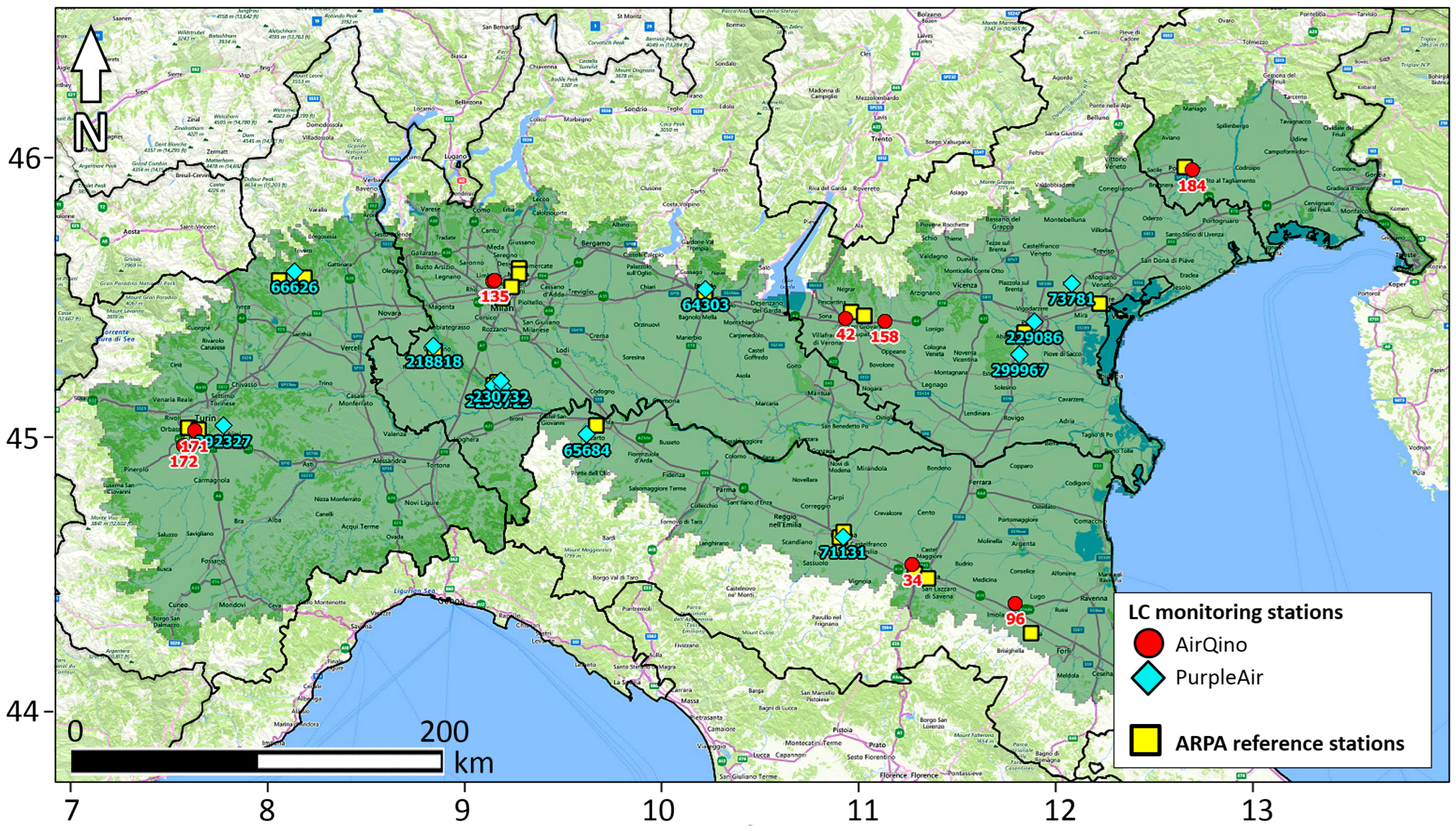
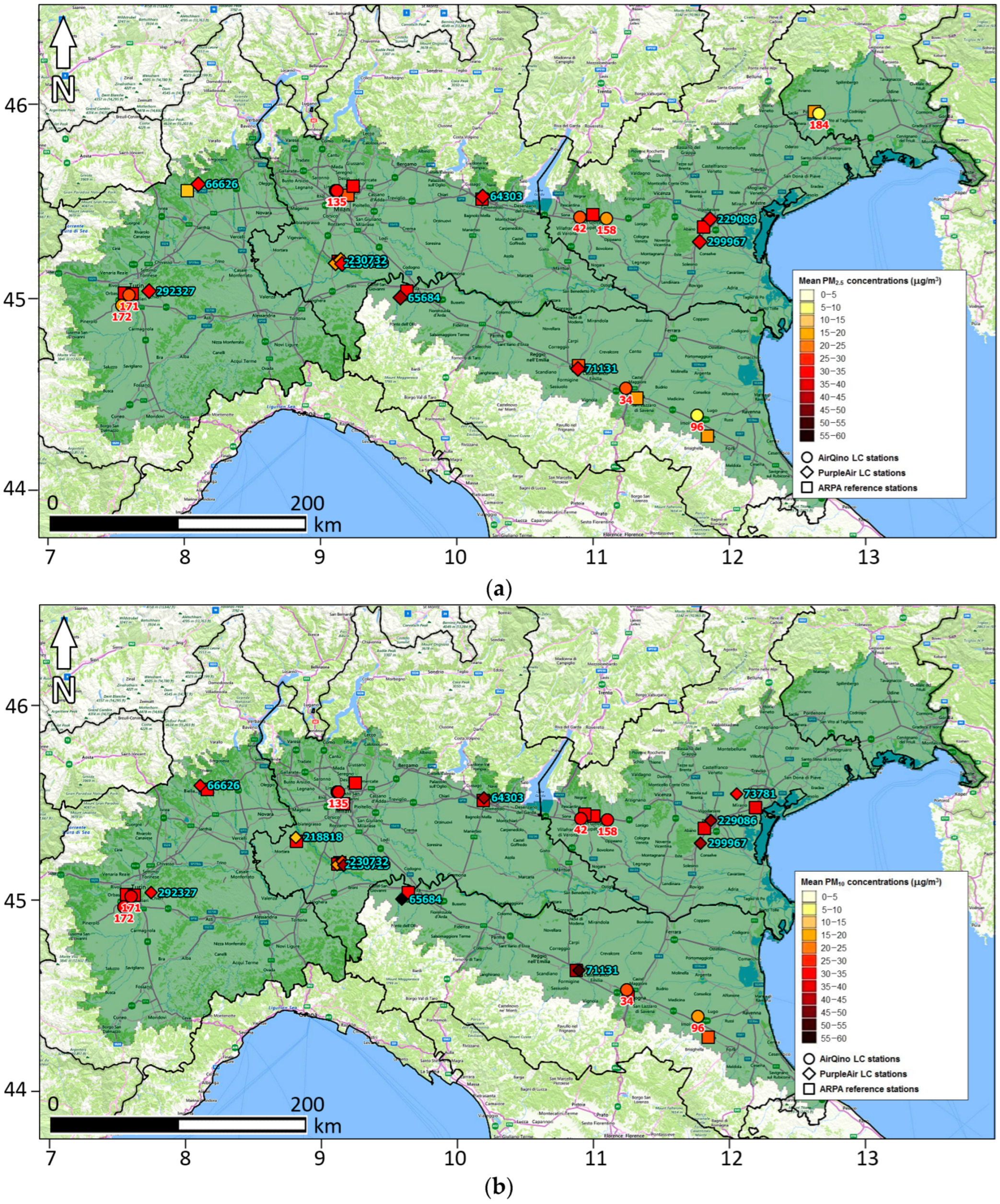


| Network | ID | Type 2 | Latitude (Deg N) | Longitude (Deg E) | Elevation (m a.s.l.) | Assessment vs. ARPA Stations 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM10 | ||||||
| AirQino | 34 | RB | 44.5336 | 11.2736 | 38 | x | x |
| 42 | SB | 45.4220 | 10.9343 | 75 | x | x | |
| 96 | RB | 44.3929 | 11.7959 | 19 | x | x | |
| 132 | SB | 45.5562 | 9.1422 | 158 | x | x | |
| 135 | RT | 45.5575 | 9.1520 | 159 | x | x | |
| 158 | RT | 45.4129 | 11.1315 | 42 | x | x | |
| 171 | UB | 45.0194 | 7.6285 | 246 | x | x | |
| 172 | RB | 44.9651 | 7.5732 | 245 | x | x | |
| 184 | SB | 45.9523 | 12.6914 | 23 | x | ||
| PurpleAir | 64303 | UB | 45.5271 | 10.2230 | 131 | x | x |
| 65684 | SB | 45.0039 | 9.6196 | 86 | x | x | |
| 66626 | RB | 45.5902 | 8.1347 | 383 | x | x | |
| 71131 | UT | 44.6351 | 10.9208 | 36 | x | x | |
| 73781 | SB | 45.5482 | 12.0797 | 14 | x | ||
| 218818 | SB | 45.3252 | 8.8417 | 112 | x | ||
| 229086 | UB | 45.4095 | 11.8895 | 12 | x | x | |
| 230713 | UT | 45.1827 | 9.1460 | 65 | x | x | |
| 230729 | RB | 45.1803 | 9.1913 | 73 | x | x | |
| 230732 | RB | 45.1994 | 9.1814 | 81 | x | x | |
| 292327 | SB | 45.0375 | 7.7728 | 455 | x | x | |
| 299967 | SB | 45.2945 | 11.8166 | 7 | x | x | |
| LC Stations | ARPA Stations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network | ID | Type 1 | Valid Data (%) 2 | PM2.5 Concentrations (µg/m3) | PM2.5 Concentrations (µg/m3) | ||
| Mean | St.dev. 4 | Mean | St.dev. | ||||
| AirQino | 34 | RB | 92.4 | 20.2 | 14.1 | 17.6 | 10.7 |
| 42 | SB | 75.4 | 21.2 | 13.7 | 20.8 | 15.0 | |
| 96 | RB | 60.7 | 9.1 | 5.5 | 15.2 | 9.9 | |
| 132 | SB | 91.8 | 18.7 | 11.3 | 26.8 | 13.0 | |
| 135 | RT | 92.9 | 25.6 | 16.3 | 22.8 | 11.1 | |
| 158 | RT | 78.7 | 16.3 | 11.5 | 25.1 | 18.5 | |
| 171 | UB | 91.3 | 20.1 | 9.0 | 25.5 | 12.1 | |
| 172 | RB | 89.6 | 15.0 | 7.2 | 25.2 | 11.5 | |
| 184 | SB | 65.6 | 6.0 | 3.2 | 16.4 | 9.0 | |
| Overall 3 | 17.8 | 9.5 | 22.5 | 11.5 | |||
| PurpleAir | 64303 | UB | 65.0 | 35.3 | 16.3 | 28.4 | 12.8 |
| 65684 | SB | 66.7 | 40.0 | 18.9 | 25.5 | 12.2 | |
| 66626 | RB | 65.0 | 27.8 | 14.1 | 13.8 | 7.0 | |
| 71131 | UT | 69.4 | 39.3 | 15.0 | 23.7 | 11.6 | |
| 229086 | UB | 66.7 | 33.7 | 16.4 | 29.2 | 17.2 | |
| 230713 | UT | 58.5 | 16.0 | 11.2 | 27.0 | 11.9 | |
| 230729 | RB | 61.2 | 34.5 | 14.9 | 26.2 | 12.3 | |
| 230732 | RB | 58.5 | 17.5 | 8.6 | 26.1 | 12.2 | |
| 292327 | SB | 66.1 | 27.6 | 12.0 | 26.6 | 13.0 | |
| 299967 | SB | 65.0 | 37.6 | 18.3 | 29.0 | 16.2 | |
| Overall 3 | 30.5 | 12.1 | 26.4 | 12.1 | |||
| LC Stations | ARPA Stations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network | ID | Type 1 | Valid Data (%) 2 | PM10 Concentrations (µg/m3) | PM10 Concentrations (µg/m3) | ||
| Mean | St.dev. | Mean | St.dev. | ||||
| AirQino | 34 | RB | 96.7 | 23.2 | 16.4 | 26.9 | 13.5 |
| 42 | SB | 79.2 | 31.0 | 18.1 | 34.5 | 17.8 | |
| 96 | RB | 63.4 | 17.5 | 9.5 | 24.3 | 12.0 | |
| 132 | SB | 85.8 | 31.3 | 19.5 | 32.8 | 17.0 | |
| 135 | RT | 97.3 | 38.2 | 23.1 | 38.8 | 17.3 | |
| 158 | RT | 92.4 | 28.1 | 19.5 | 36.2 | 17.0 | |
| 171 | UB | 90.7 | 36.8 | 19.8 | 33.7 | 16.1 | |
| 172 | RB | 92.4 | 31.5 | 16.2 | 33.3 | 14.7 | |
| Overall 3 | 31.2 | 15.9 | 34.3 | 14.5 | |||
| PurpleAir | 64303 | UB | 66.1 | 41.9 | 19.8 | 39.5 | 15.7 |
| 65684 | SB | 67.8 | 51.0 | 26.3 | 33.9 | 15.7 | |
| 66626 | RB | 68.9 | 32.7 | 17.5 | 25.3 | 10.5 | |
| 71131 | UT | 70.5 | 47.7 | 19.7 | 41.2 | 18.9 | |
| 73781 | SB | 71.0 | 33.8 | 19.0 | 38.0 | 25.2 | |
| 218818 | SB | 62.3 | 12.4 | 7.0 | 33.0 | 17.6 | |
| 229086 | UB | 68.9 | 41.4 | 22.1 | 36.5 | 20.1 | |
| 230713 | UT | 66.7 | 17.6 | 13.7 | 35.8 | 17.0 | |
| 230729 | RB | 67.8 | 41.3 | 18.6 | 33.8 | 15.4 | |
| 230732 | RB | 65.0 | 20.3 | 10.5 | 33.7 | 15.2 | |
| 292327 | SB | 65.6 | 32.7 | 15.6 | 35.8 | 16.4 | |
| 299967 | SB | 68.3 | 44.4 | 22.9 | 35.9 | 19.1 | |
| Overall 3 | 34.5 | 14.8 | 36.8 | 15.8 | |||
| Network | ID | Valid Data (%) | MB (µg/m3) | MAE (µg/m3) | Slope | Intercept (µg/m3) | RMSE (µg/m3) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AirQino | 34 | 92.4 | +2.6 | 6.6 | 1.06 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 0.65 |
| 42 | 75.4 | +0.4 | 8.5 | 0.64 | 7.9 | 11.2 | 0.49 | |
| 96 | 60.7 | −6.2 | 7.1 | 0.33 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 0.37 | |
| 132 | 91.8 | −8.1 | 8.6 | 0.73 | −0.8 | 10.8 | 0.70 | |
| 135 | 92.9 | +2.8 | 7.0 | 1.25 | −2.9 | 9.4 | 0.72 | |
| 158 | 78.7 | −8.8 | 11.0 | 0.50 | 3.8 | 14.6 | 0.64 | |
| 171 | 91.3 | −5.4 | 6.3 | 0.66 | 3.4 | 7.9 | 0.78 | |
| 172 | 89.6 | −10.1 | 10.3 | 0.49 | 2.7 | 12.5 | 0.61 | |
| 184 | 65.6 | −10.4 | 10.5 | 0.25 | 1.8 | 12.6 | 0.51 | |
| PurpleAir | 64303 | 65.0 | +7.0 | 8.4 | 1.15 | 2.8 | 10.1 | 0.81 |
| 65684 | 66.7 | +14.6 | 15.3 | 1.11 | 11.8 | 19.7 | 0.51 | |
| 66626 | 65.0 | +14.0 | 14.2 | 1.85 | 2.3 | 16.2 | 0.85 | |
| 71131 | 69.4 | +15.6 | 15.7 | 1.12 | 12.8 | 17.4 | 0.74 | |
| 229086 | 66.7 | +4.5 | 6.2 | 0.88 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 0.86 | |
| 230713 | 58.5 | −11.0 | 11.1 | 0.81 | −5.9 | 12.7 | 0.74 | |
| 230729 | 61.2 | +8.4 | 9.2 | 1.11 | 5.5 | 10.4 | 0.83 | |
| 230732 | 58.5 | −8.6 | 8.6 | 0.65 | 0.6 | 10.2 | 0.85 | |
| 292327 | 66.1 | +1.0 | 7.9 | 0.60 | 11.7 | 10.6 | 0.41 | |
| 299967 | 65.0 | +8.6 | 9.1 | 1.04 | 7.3 | 11.0 | 0.86 |
| Network | ID | Valid Data (%) | MB (µg/m3) | MAE (µg/m3) | Slope | Intercept (µg/m3) | RMSE (µg/m3) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AirQino | 34 | 96.7 | −3.8 | 9.2 | 0.92 | −1.7 | 11.3 | 0.58 |
| 42 | 79.2 | −3.4 | 10.3 | 0.78 | 4.3 | 12.8 | 0.58 | |
| 96 | 63.4 | −6.8 | 8.8 | 0.52 | 5.0 | 11.4 | 0.42 | |
| 132 | 85.8 | −1.5 | 10.8 | 0.84 | 3.7 | 13.5 | 0.54 | |
| 135 | 97.3 | −0.6 | 10.9 | 1.06 | −3.0 | 14.0 | 0.63 | |
| 158 | 92.4 | −8.1 | 12.5 | 0.89 | −4.1 | 14.8 | 0.61 | |
| 171 | 90.7 | +3.2 | 7.7 | 1.07 | 0.8 | 10.3 | 0.76 | |
| 172 | 92.4 | −1.9 | 8.7 | 0.83 | 3.8 | 11.1 | 0.57 | |
| PurpleAir | 64303 | 66.1 | +2.4 | 9.1 | 1.07 | −0.5 | 10.7 | 0.73 |
| 65684 | 67.8 | +17.1 | 20.4 | 1.02 | 16.4 | 26.9 | 0.37 | |
| 66626 | 68.9 | +7.4 | 9.7 | 1.47 | −4.4 | 12.2 | 0.77 | |
| 71131 | 70.5 | +6.6 | 11.7 | 0.84 | 13.1 | 13.7 | 0.65 | |
| 73781 | 71.0 | −4.2 | 8.1 | 0.69 | 7.6 | 11.8 | 0.83 | |
| 218818 | 62.3 | −20.6 | 20.6 | 0.35 | 0.8 | 23.7 | 0.79 | |
| 229086 | 68.9 | +5.0 | 7.6 | 1.03 | 4.0 | 9.4 | 0.87 | |
| 230713 | 66.7 | −18.1 | 18.2 | 0.58 | −3.1 | 21.7 | 0.51 | |
| 230729 | 67.8 | +7.5 | 11.0 | 1.00 | 7.3 | 12.7 | 0.69 | |
| 230732 | 65.0 | −13.4 | 13.4 | 0.57 | 1.2 | 16.1 | 0.67 | |
| 292327 | 65.6 | −3.1 | 10.0 | 0.60 | 11.2 | 14.0 | 0.40 | |
| 299967 | 68.3 | +8.5 | 10.0 | 1.11 | 4.6 | 12.3 | 0.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gualtieri, G.; Brilli, L.; Carotenuto, F.; Cavaliere, A.; Giordano, T.; Putzolu, S.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A.; Gioli, B. Performance Assessment of Two Low-Cost PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Networks in the Padana Plain (Italy). Sensors 2024, 24, 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123946
Gualtieri G, Brilli L, Carotenuto F, Cavaliere A, Giordano T, Putzolu S, Vagnoli C, Zaldei A, Gioli B. Performance Assessment of Two Low-Cost PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Networks in the Padana Plain (Italy). Sensors. 2024; 24(12):3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123946
Chicago/Turabian StyleGualtieri, Giovanni, Lorenzo Brilli, Federico Carotenuto, Alice Cavaliere, Tommaso Giordano, Simone Putzolu, Carolina Vagnoli, Alessandro Zaldei, and Beniamino Gioli. 2024. "Performance Assessment of Two Low-Cost PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Networks in the Padana Plain (Italy)" Sensors 24, no. 12: 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123946
APA StyleGualtieri, G., Brilli, L., Carotenuto, F., Cavaliere, A., Giordano, T., Putzolu, S., Vagnoli, C., Zaldei, A., & Gioli, B. (2024). Performance Assessment of Two Low-Cost PM2.5 and PM10 Monitoring Networks in the Padana Plain (Italy). Sensors, 24(12), 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123946











