Monoolein-Based Wireless Capacitive Sensor for Probing Skin Hydration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D)
2.3. Sensor Modification
2.4. Wireless Capacitive Measurements
2.5. Ex Vivo Wireless Measurements
2.6. Experimental Replications and Mathematical Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wireless Capacitance Measurements
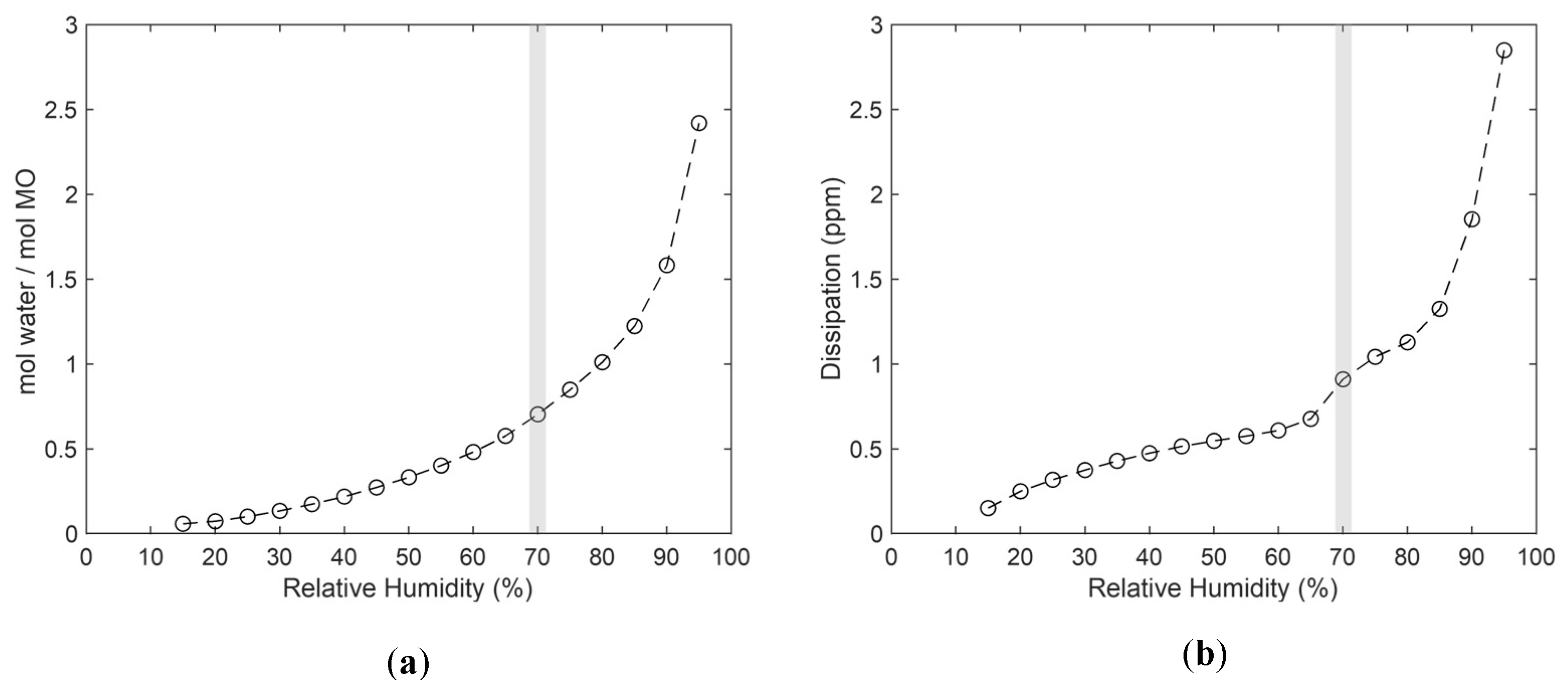
3.2. Water Uptake and Rheological Properties of MO
3.3. Variable Temperature–Capacitance Measurements
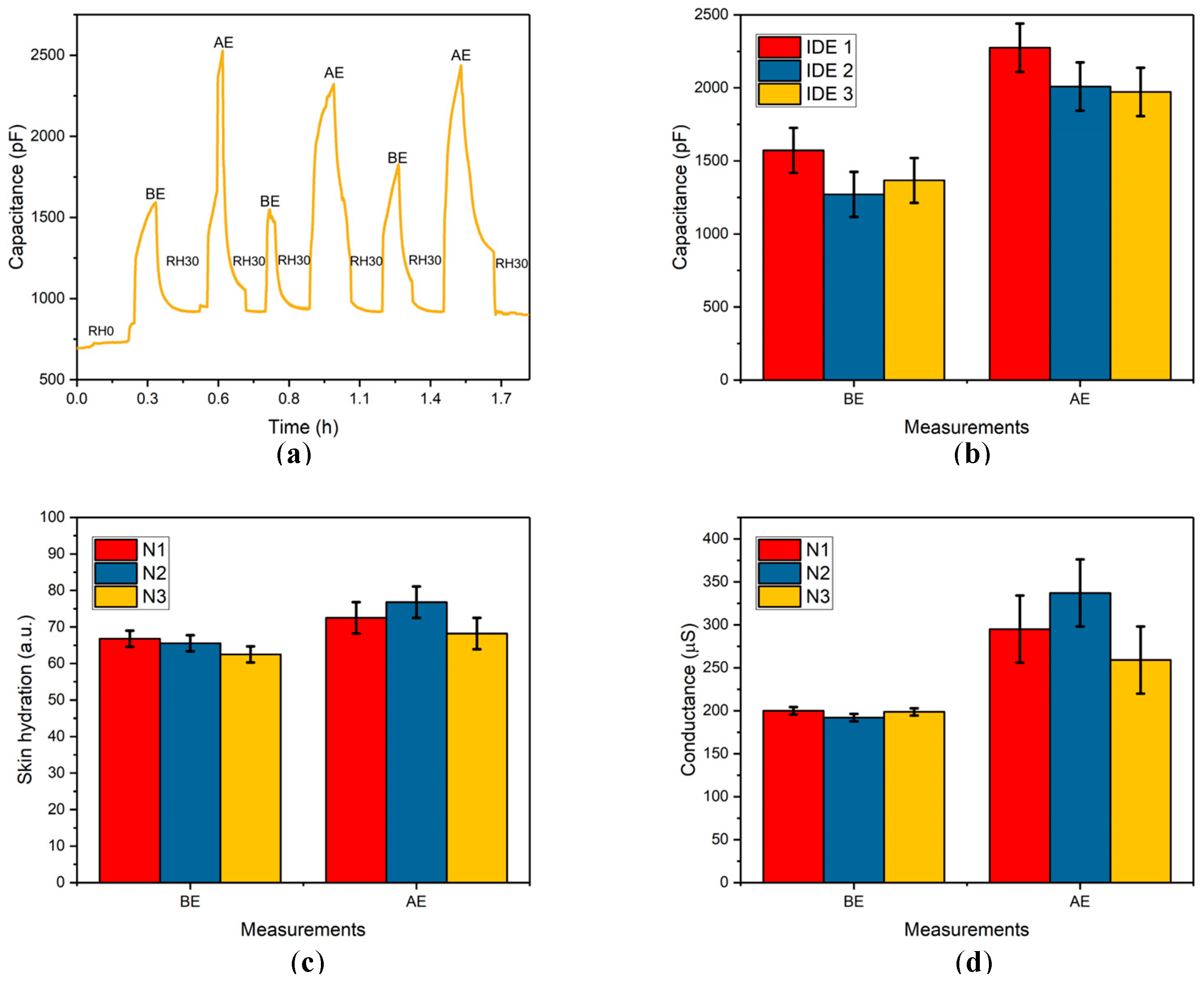
3.4. Wireless Capacitive Skin Hydration Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, D.-H.; Park, J.-W. Wireless sensor network-based greenhouse environment monitoring and automatic control system for dew condensation prevention. Sensors 2011, 11, 3640–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Fu, S.; Acevedo, M.F. Integration of wireless sensor networks in environmental monitoring cyber infrastructure. Wirel. Netw. 2010, 16, 1091–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corke, P.; Wark, T.; Jurdak, R.; Hu, W.; Valencia, P.; Moore, D. Environmental wireless sensor networks. Proc. IEEE Int. 2010, 98, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y. Development of an integrated wireless sensor network micro-environmental monitoring system. ISA Trans. 2008, 47, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Meng, Z.; Cui, S. A wireless sensor network prototype for environmental monitoring in greenhouses. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 21–25 September 2007; pp. 2344–2347. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, W.-Y.; Oh, S.-J. Remote monitoring system with wireless sensors module for room environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. Chem. 2006, 113, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell-Oliver, R.; Smettem, K.; Kranz, M.; Mayer, K. Field testing a wireless sensor network for reactive environmental monitoring [soil moisture measurement]. In Proceedings of the 2004 Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing Conference, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14–17 December 2004; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rittersma, Z. Recent achievements in miniaturised humidity sensors—A review of transduction techniques. Sens. Actuators A Phys. Phys. 2002, 96, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Matsuhisa, N.; Beker, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yun, Y.; Burnett, W. A wireless body area sensor network based on stretchable passive tags. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kim, J.; Won, S.M.; Ma, Y.; Kang, D.; Xie, Z.; Lee, K.-T.; Chung, H.U.; Banks, A.; Min, S. Battery-free, wireless sensors for full-body pressure and temperature mapping. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yick, J.; Mukherjee, B.; Ghosal, D. Wireless sensor network survey. Comput. Netw. 2008, 52, 2292–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Lu, C.; Srivastava, M.B.; Stankovic, J.A.; Terzis, A.; Welsh, M. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare. Proc. IEEE Int. 2010, 98, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Ashour, A.S.; Shi, F.; Fong, S.J.; Sherratt, R.S. Developing residential wireless sensor networks for ECG healthcare monitoring. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2017, 63, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangotra, D.K.; Singh, Y.; Selwal, A.; Kumar, N.; Singh, P.K.; Hong, W.-C. An intelligent opportunistic routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks and its application towards e-healthcare. Sensors 2020, 20, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanak, P.; Banerjee, I. Congestion free routing mechanism for IoT-enabled wireless sensor networks for smart healthcare applications. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2020, 66, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Sekine, T.; Takeda, Y.; Yokosawa, K.; Matsui, H.; Kumaki, D.; Shiba, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Tokito, S. Fully printed PEDOT: PSS-based temperature sensor with high humidity stability for wireless healthcare monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wu, R.; Patil, A.; Zhu, S.; Meng, Z.; Meng, H.; Hou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, R. Full-textile wireless flexible humidity sensor for human physiological monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkurti, L.; Bajrami, X.; Canhasi, E.; Limani, B.; Krrabaj, S.; Hulaj, A. Development of ambient environmental monitoring system through wireless sensor network (WSN) using NodeMCU and “WSN monitoring”. In Proceedings of the 2017 6th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Bar, Montenegro, 11–15 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdoush, S.; Li, X. Wireless sensor network system design using Raspberry Pi and Arduino for environmental monitoring applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, M.; Morito, T.; Morikawa, H.; Aoyama, T. Solar biscuit: A battery-less wireless sensor network system for environmental monitoring applications. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Networked Sensing Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–28 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dehennis, A.D.; Wise, K.D. A wireless microsystem for the remote sensing of pressure, temperature, and relative humidity. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yiu, C.; Song, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yao, K.; Wong, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Nejad, S.K. Electronic skin as wireless human-machine interfaces for robotic VR. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.R.; Su, C.J.; Xie, Z.; Patel, M.; Madhvapathy, S.R.; Xu, Y.; Freudman, J.; Ng, B.; Heo, S.Y.; Wang, H. Wireless, battery-free epidermal electronics for continuous, quantitative, multimodal thermal characterization of skin. Small 2018, 14, 1803192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Jajack, A.; Rogers, J.; Gutruf, P.; Tian, L.; Pan, T.; Li, R.; Khine, M.; Kim, J.; Wang, J. Wearable sensors: Modalities, challenges, and prospects. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pharr, M.; Salvatore, G.A. Lab-on-skin: A review of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable health monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9614–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, T.; Foster, R.; Hao, Y. Detecting vital signs with wearable wireless sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 10837–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Zheng, K.; Zheng, H. Throughput maximization of wireless-powered communication network with mobile access points. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 22, 4401–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Park, J.; Na, S.; Kim, M.P.; Ko, H. A fully biodegradable ferroelectric skin sensor from edible porcine skin gelatine. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2005010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.K.; Ha, I.; Kim, M.; Choi, J.; Won, P.; Jo, S.; Ko, S.H. A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Jayaraman, A.; Rogers, J.A. Skin sensors are the future of health care. Nature 2019, 571, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, D.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Yi, F. Recent progress in self-powered skin sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jackman, J.A.; Tan, E.-L.; Park, J.H.; Potroz, M.G.; Hwang, E.T.; Cho, N.-J. High-performance, flexible electronic skin sensor incorporating natural microcapsule actuators. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.; Park, H.W.; Park, D.H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, D.H. Highly sensitive and multimodal all-carbon skin sensors capable of simultaneously detecting tactile and biological stimuli. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4178–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhvapathy, S.R.; Wang, H.; Kong, J.; Zhang, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.B.; Jang, H.; Xie, Z.; Cao, J.; Avila, R. Reliable, low-cost, fully integrated hydration sensors for monitoring and diagnosis of inflammatory skin diseases in any environment. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, K.; Yin, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liang, X.; Lu, H.; Zhu, M. Physical sensors for skin-inspired electronics. InfoMat 2020, 2, 184–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Myers, A.; Malhotra, A.; Lin, F.; Bozkurt, A.; Muth, J.F.; Zhu, Y. A wearable hydration sensor with conformal nanowire electrodes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shin, W.J.; Fan, J.A.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.J.; Kong, G.W.; Chen, K.; Patnaik, D. Materials and designs for wireless epidermal sensors of hydration and strain. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirovano, P.; Dorrian, M.; Shinde, A.; Donohoe, A.; Brady, A.J.; Moyna, N.M.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D.; McCaul, M. A wearable sensor for the detection of sodium and potassium in human sweat during exercise. Talanta 2020, 219, 121145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshadri, D.R.; Li, R.T.; Voos, J.E.; Rowbottom, J.R.; Alfes, C.M.; Zorman, C.A.; Drummond, C.K. Wearable sensors for monitoring the physiological and biochemical profile of the athlete. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, M.C.; DeBrosse, M.; Grigsby, C.C.; Naik, R.R.; Hussain, S.M.; Heikenfeld, J.; Kim, S.S. Achievements and challenges for real-time sensing of analytes in sweat within wearable platforms. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariya, M.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Javey, A. Wearable sweat sensors. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ho, C.; Slappey, N.; Zhou, Z.; Snelgrove, S.; Brown, M.; Grabinski, A.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Miller, K. A wearable conductivity sensor for wireless real-time sweat monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schazmann, B.; Morris, D.; Slater, C.; Beirne, S.; Fay, C.; Reuveny, R.; Moyna, N.; Diamond, D. A wearable electrochemical sensor for the real-time measurement of sweat sodium concentration. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.U.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Xie, Z.; Ibler, E.M.; Lee, K.; Banks, A.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, J. Binodal, wireless epidermal electronic systems with in-sensor analytics for neonatal intensive care. Science 2019, 363, eaau0780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yeo, W.-H.; Liu, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Epidermal differential impedance sensor for conformal skin hydration monitoring. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, B.; Burnett, W.; Chung, J.W.; Bao, Z. Bring on the bodyNET. Nature 2017, 549, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Larsson, O.; Platt, D.; Nordlinder, S.; Engquist, I.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. An all-printed wireless humidity sensor label. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Min, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W. Wireless battery-free wearable sweat sensor powered by human motion. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.; An, T.; Yap, L.W.; Zhu, B.; Gong, S.; Cheng, W. Disruptive, soft, wearable sensors. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Salvatore, G.A.; Araki, H.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Xie, Z.; Banks, A.; Sheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Jang, K.-I. Battery-free, stretchable optoelectronic systems for wireless optical characterization of the skin. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Shin, W.J.; Lu, C.J.; Kong, G.W.; Patnaik, D.; Lee, S.H.; Cortes, J.F.; Rogers, J.A. Stretchable, wireless sensors and functional substrates for epidermal characterization of sweat. small 2014, 10, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Maurya, D.K.; Pandey, A.; Verma, A.; Tripathi, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, B. Design and development of flexible humidity sensor for baby diaper alarm: Experimental and theoretical study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Lu, Y.; Takei, K. Multifunctional skin-inspired flexible sensor systems for wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.R.; Kim, J.; Xie, Z.; Xue, Y.; Won, S.M.; Lee, G.; Jin, S.W.; Hong, S.Y.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y. A skin-attachable, stretchable integrated system based on liquid GaInSn for wireless human motion monitoring with multi-site sensing capabilities. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, E.; Deen, M.J.; Mondal, T. A wireless wearable ECG sensor for long-term applications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, C. Humidity sensors: A review of materials and mechanisms. Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, C.V.; Wachter, W.; Iglesias-Salto, G.; Engelskirchen, S.; Ahualli, S. Monoolein: A magic lipid? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3004–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donida, B.; Tauffner, B.; Raabe, M.; Immich, M.F.; de Farias, M.A.; de Sá Coutinho, D.; Machado, A.Z.; Kessler, R.G.; Portugal, R.V.; Bernardi, A. Monoolein-based nanoparticles for drug delivery to the central nervous system: A platform for lysosomal storage disorder treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Kocherbitov, V. Hydration-induced phase transitions in surfactant and lipid films. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Kocherbitov, V. Humidity scanning quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring setup for determination of sorption-desorption isotherms and rheological changes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Zeit. F. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.P.; Mulev, Y.; Goodwin, A.; Sengers, J.L. A database for the static dielectric constant of water and steam. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1995, 24, 33–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaturvedi, V.; Falk, M.; Björklund, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.F.; Shleev, S. Monoolein-Based Wireless Capacitive Sensor for Probing Skin Hydration. Sensors 2024, 24, 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144449
Chaturvedi V, Falk M, Björklund S, Gonzalez-Martinez JF, Shleev S. Monoolein-Based Wireless Capacitive Sensor for Probing Skin Hydration. Sensors. 2024; 24(14):4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144449
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaturvedi, Vivek, Magnus Falk, Sebastian Björklund, Juan F. Gonzalez-Martinez, and Sergey Shleev. 2024. "Monoolein-Based Wireless Capacitive Sensor for Probing Skin Hydration" Sensors 24, no. 14: 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144449
APA StyleChaturvedi, V., Falk, M., Björklund, S., Gonzalez-Martinez, J. F., & Shleev, S. (2024). Monoolein-Based Wireless Capacitive Sensor for Probing Skin Hydration. Sensors, 24(14), 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144449






