Calibration of Low-Cost Moisture Sensors in a Biochar-Amended Sandy Loam Soil with Different Salinity Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
- Assessment of low-cost soil moisture sensors: this paper evaluates the accuracy and functionality of low-cost soil moisture sensors in sandy loam (SL) soil amended with biochar and fertilizers.
- Sensor calibration of soil biochar mixtures: a calibration for different biochar and fertilizer doses, applied across various soil moisture levels, is used to identify the reliability of soil moisture data under non-standard soil conditions.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soil Sampling and Amendment
3.2. Fertilizer Dosage Based on K and N
3.3. Preparation of Mixtures Incorporating Fertilizers and Biochar
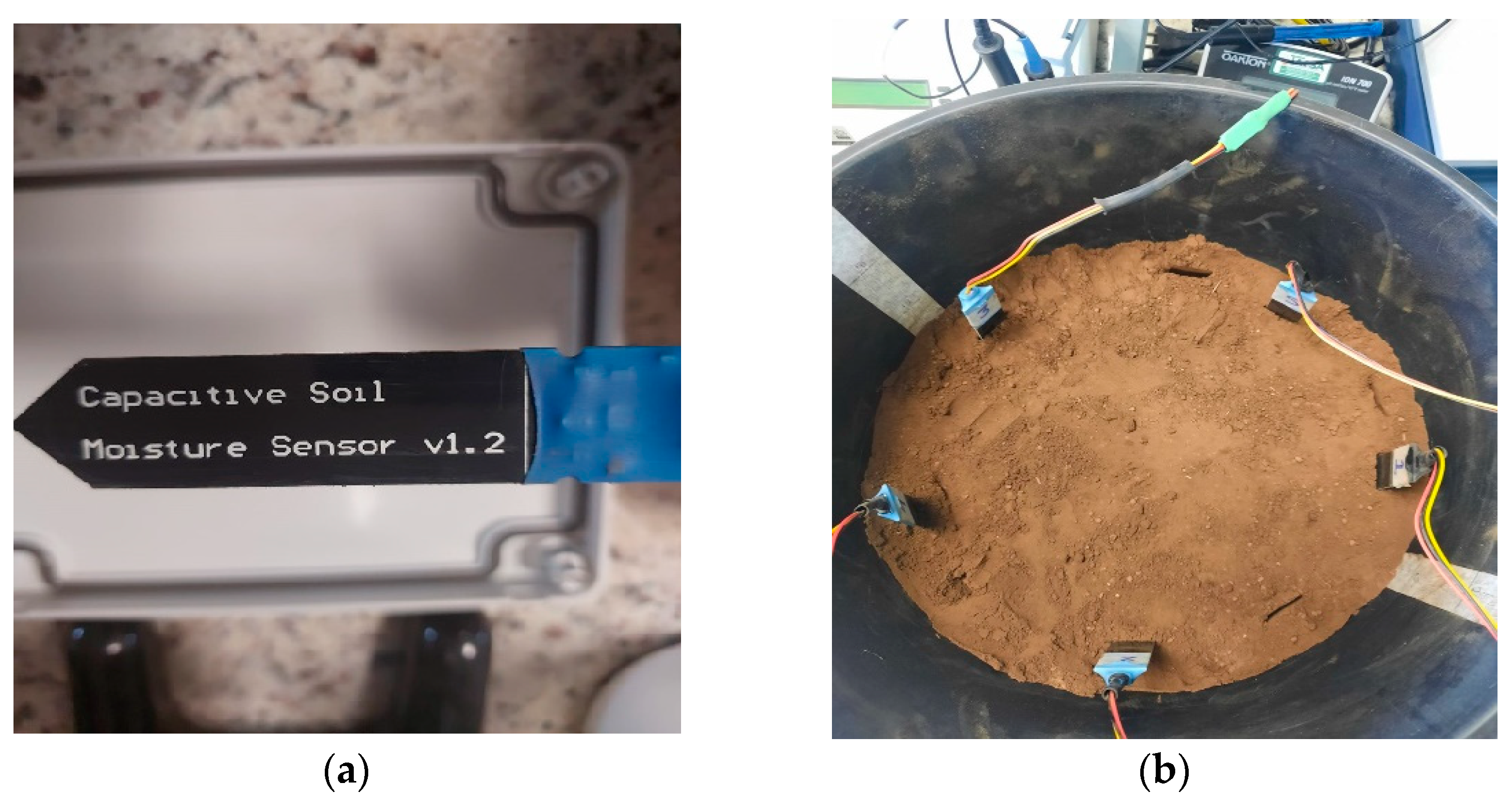
3.4. Sensor Description
3.5. Calibration Procedure
3.6. Statistical Analysis
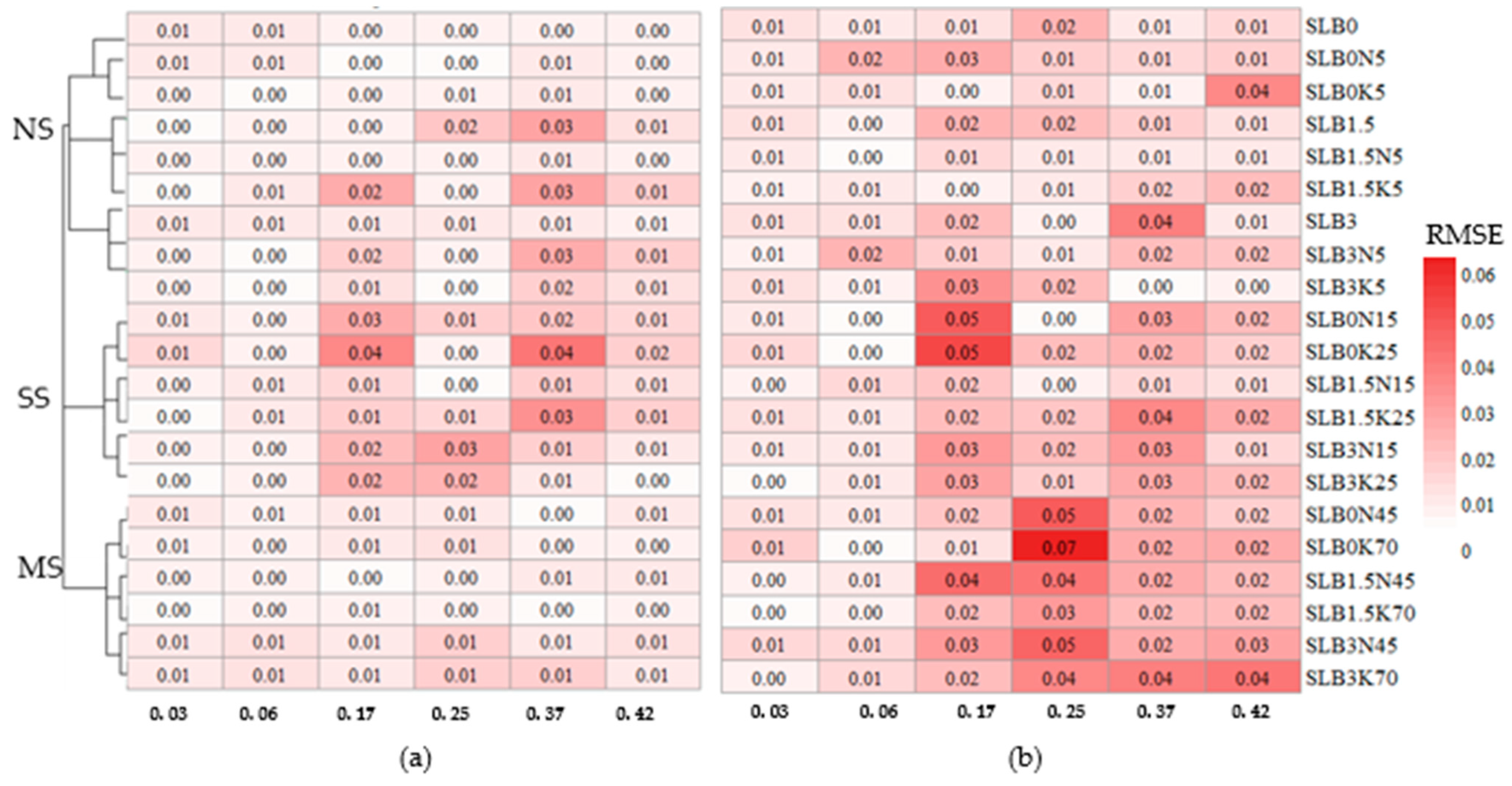
4. Results
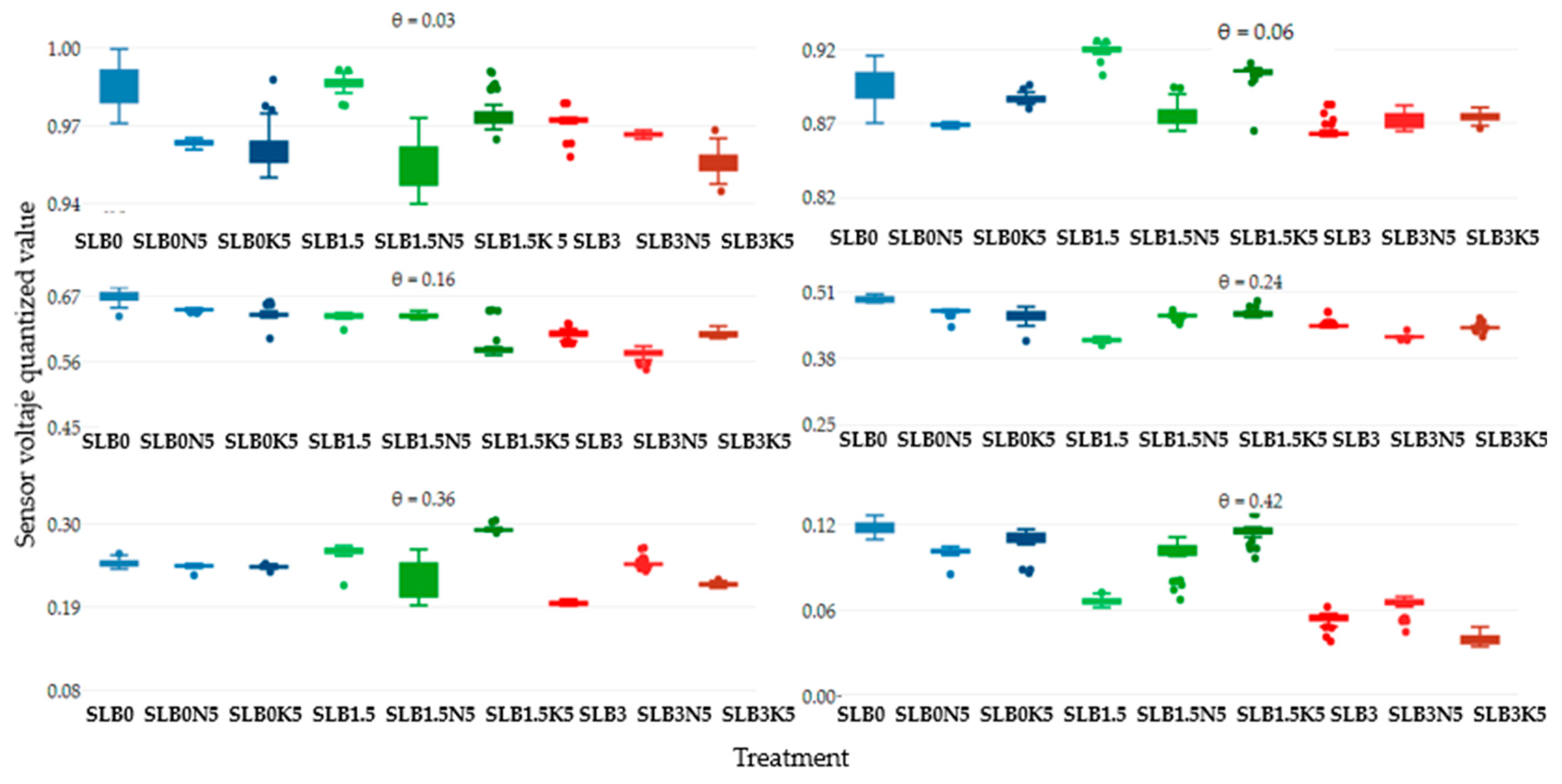
4.1. Sensor Variability
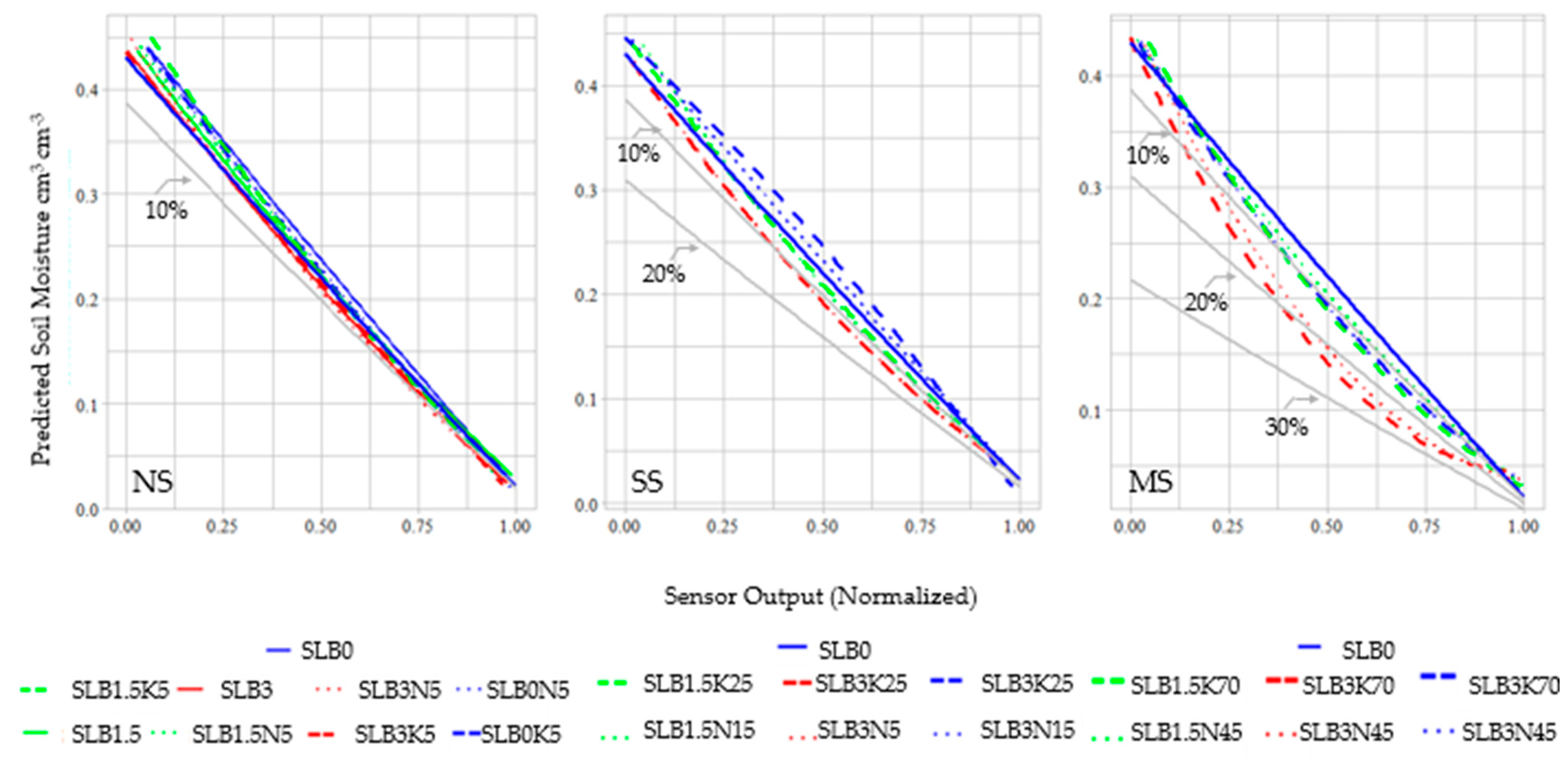
4.2. Sensor Performance
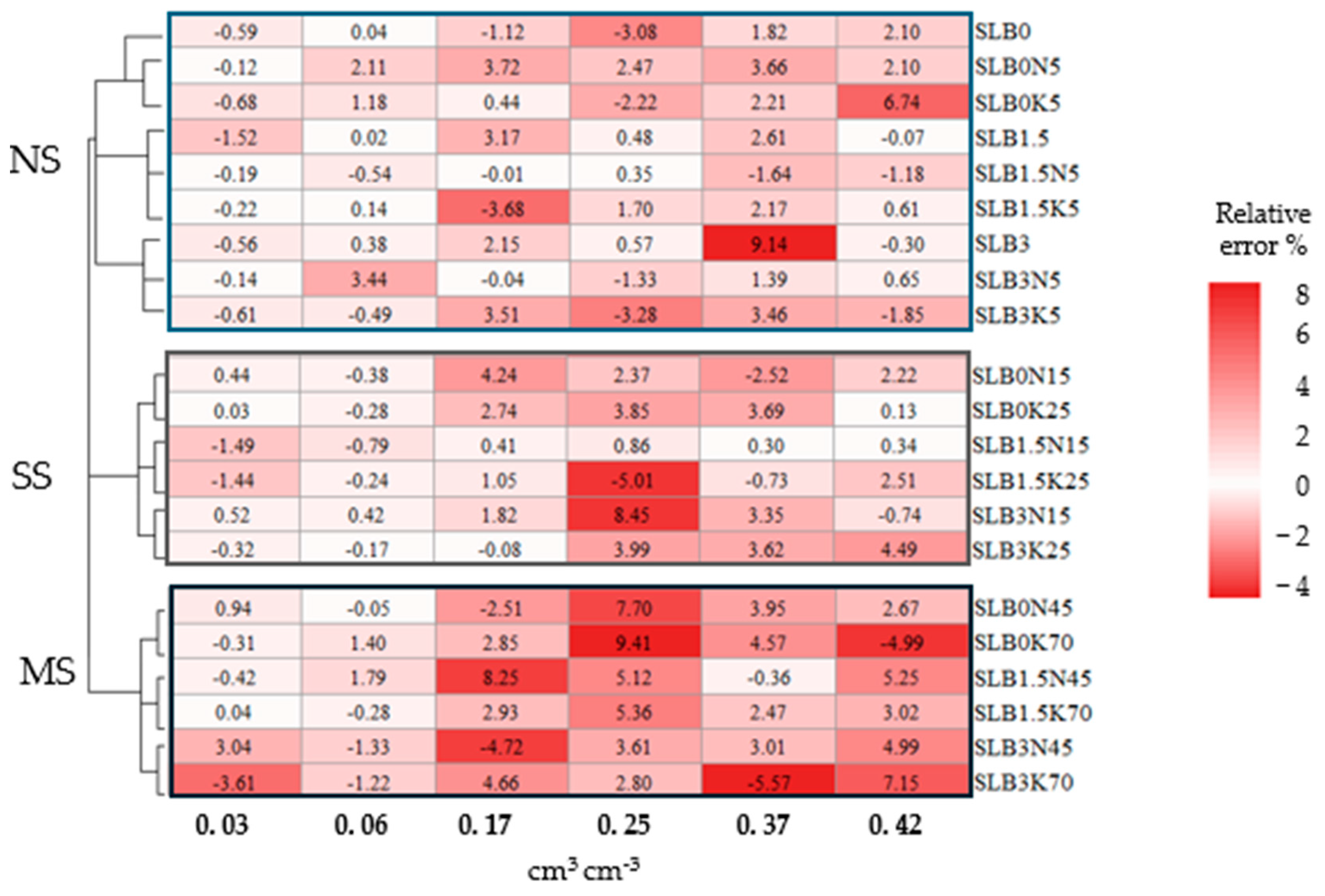
4.3. Sensor Stability
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations of the Study
5.2. Future Work and Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, H.; Cao, Y.; Marelli, B.; Zeng, X.; Mason, A.J.; Cao, C. Smart Agriculture Systems: Soil Sensors and Plant Wearables for Smart and Precision Agriculture. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Vashisht, B.B.; Jalota, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Sustainable Water Management Practices for Intensified Agriculture. In Soil-Water, Agriculture, and Climate Change; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 131–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M. (INVITED) Advances in fiber optic sensors for soil moisture monitoring: A review. Results Opt. 2022, 7, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, M.; Khanna, M.; Singh, M.; Singh, D.K.; Sudhishri, S.; Bhatia, A.; Ranjan, R. Automation of soil moisture sensor-based basin irrigation system. Smart Agric. Technol. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M. Review of Novel and Emerging Proximal Soil Moisture Sensors for Use in Agriculture. Sensors 2020, 20, 6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, S.; Casadesús, J.; Campillo, C.; Moñino, M.J.; Prieto, M.H. Using Soil Moisture Sensors for Automated Irrigation Scheduling in a Plum Crop. Water 2019, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gao, W.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Tao, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, G. Review of research progress on soil moisture sensor technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.; Das, N.; Singh, G.; Cosh, M.; Dong, Y. Advancements in dielectric soil moisture sensor Calibration: A comprehensive review of methods and techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Pahuja, R. Recalibration and performance comparison of soil moisture sensors using regression and neural network characteristic models. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4852–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.H.; Zhuang, X.; Rabczuk, T. Numerical model for the characterization of Maxwell-Wagner relaxation in piezoelectric and flexoelectric composite material. Comput. Struct. 2018, 208, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adla, S.; Rai, N.K.; Karumanchi, S.H.; Tripathi, S.; Disse, M.; Pande, S. Laboratory Calibration and Performance Evaluation of Low-Cost Capacitive and Very Low-Cost Resistive Soil Moisture Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi; Murtiningrum; Ngadisih; Muzdrikah, F.S.; Nuha, M.S.; Rizqi, F.A. Calibration of Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor (SKU:SEN0193). In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Science and Technology (ICST), IEEE, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 7–8 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddinti, S.R.; Hopmans, J.W.; Najm, M.A.; Kisekka, I. Assessing Effects of Salinity on the Performance of a Low-Cost Wireless Soil Water Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellini, J.; Farrugia, L.; Farhat, I.; Bonello, J.; Persico, R.; Sacco, A.; Spiteri, K.; Sammut, C.V. Broadband Measurements of Soil Complex Permittivity. Sensors 2023, 23, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargas, G.; Soulis, K.X. Performance evaluation of a recently developed soil water content, dielectric permittivity, and bulk electrical conductivity electromagnetic sensor. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta, J.H.; Hrisko, J. Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Theory, Calibration, and Testing. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342751186_Capacitive_Soil_Moisture_Sensor_Theory_Calibration_and_Testing (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Zemni, N.; Bouksila, F.; Persson, M.; Slama, F.; Berndtsson, R.; Bouhlila, R. Laboratory Calibration and Field Validation of Soil Water Content and Salinity Measurements Using the 5TE Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Teruel, J.D.; Jones, S.B.; Soto-Valles, F.; Torres-Sánchez, R.; Lebron, I.; Friedman, S.P.; Robinson, D.A. Dielectric Spectroscopy and Application of Mixing Models Describing Dielectric Dispersion in Clay Minerals and Clayey Soils. Sensors 2020, 20, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ramos, J.C.; Turini, T.; Wang, D.; Hale, L. Impacts of deficit irrigation and organic amendments on soil microbial populations and yield of processing tomatoes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Wong, J.T.F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Huang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Chang, S.X.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: A critical review. Biochar 2019, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolis, V.; Barouchas, P. Biochar as Soil Amendment: The Effect of Biochar on Soil Properties Using VIS-NIR Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy, Biochar Aging and Soil Microbiology—A Review. Land 2023, 12, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, J.; Kátai, L.; Szabó, I.; Korzenszky, P. An Electrical Conductivity Sensor for the Selective Determination of Soil Salinity. Sensors 2024, 24, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Villamil, M.B.; Davidson, P.C.; Akdeniz, N. A quantitative understanding of the role of co-composted biochar in plant growth using meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Mendoza, K.; Masís-Meléndez, F.; Quesada-Kimsey, J.; García-González, C.A.; Horn, R. Physicochemical Changes in Loam Soils Amended with Bamboo Biochar and Their Influence in Tomato Production Yield. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrisko, J. Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Calibration with Arduino. Mark et Portal. Available online: https://makersportal.com/blog/2020/5/26/capacitive-soil-moisture-calibration-with-arduino (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Schmugge, T.J.; Jackson, T.J.; McKim, H.L. Survey of methods for soil moisture determination. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Yang, G.; Fang, K.; Zhu, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y. Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeling, L.; Elmamooz, G.; Hoang, P.T.; Kozar, A.; Nicklas, D.; Sünkel, M.; Thurner, S.; Rauch, E. Training and Validating a Machine Learning Model for the Sensor-Based Monitoring of Lying Behavior in Dairy Cows on Pasture and in the Barn. Animals 2021, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, V.R. Optimal ratio for data splitting. Stat. Anal. Data Min. ASA Data Sci. J. 2022, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringo, M.Q.; Martinez, C.G.; Martinez, O.G.; Ella, V.B. Development of Low-cost Soil Moisture Monitoring System for Efficient Irrigation Water Management of Upland Crops. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1038, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, G.; Prasher, S.; Madani, A.; Rudra, R. Evaluating Three Hydrological Distributed Watershed Models: MIKE-SHE, APEX, SWAT. Hydrology 2014, 1, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of Automatic Calibration for Hydrologic Models: Comparison with Multilevel Expert Calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilski, B.M.; Granouillac, F.; Claverie, N.; Lemaire, B.; Brut, A.; Tallec, T. Calculation of soil water content using dielectric-permittivity-based sensors—Benefits of soil-specific calibration. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2023, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathbavan, M.; Kumar, G.J.; Udhayakumar, S.; Kamala Bharathi, K. Maxwell-Wagner Dielectric Relaxation Induced Superior Dielectric Properties and Phase Transitions in Na0.5bi0.5tio3 Nanorods. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulraheem, M.I.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Moshood, A.Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Taiwo, L.B.; Farooque, A.A.; Hu, J. Recent Advances in Dielectric Properties-Based Soil Water Content Measurements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.W.; Tang, J.; Sarwar, A.; Shah, S.; Saddique, N.; Khan, M.U.; Imran Khan, M.; Nawaz, S.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Aziz, M.; et al. Soil Moisture Measuring Techniques and Factors Affecting the Moisture Dynamics: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Mendoza, K.; Horn, R. Effect of biochar on the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of two amended soils. Int. Agrophys 2018, 32, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlor, J.; Ulaby, F. Dielectric Properties of Soils as a Function of Moisture Content. Lawrence, Kansas, 1974. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Dielectric-properties-of-soils-as-a-function-of-Cihlar-Ulaby/603de3b8e665b0e66ced05ea26f3d5d5811bb65c (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Santos, C.P.D.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Canafístula, F.J.F.; da Rocha Neto, O.C.; Daher, S.; Teixeira, A.D.S. Performance of the capacitive moisture sensor under different saline conditions. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2022, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, R.; Zand, M.M.; Majd, S.A. Designing wearable capacitive pressure sensors with arrangement of porous pyramidal microstructures. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocco, M.; Parrino, S.; Peruzzi, G.; Pozzebon, A. Estimating Volumetric Water Content in Soil for IoUT Contexts by Exploiting RSSI-Based Augmented Sensors via Machine Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.M.M.; Adla, S.; Jourdin, L.; Pande, S. Review of low-cost, off-grid, biodegradable in situ autonomous soil moisture sensing systems: Is there a perfect solution? Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payero, J.O. An Effective and Affordable Internet of Things (IoT) Scale System to Measure Crop Water Use. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafalla, M. Using 5TE Sensors for Monitoring Moisture Conditions in Green Parks. Sensors 2024, 24, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, J.; Huang, C. Basin Scale Soil Moisture Estimation with Grid SWAT and LESTKF Based on WSN. Sensors 2023, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Soil Physical Properties | Chemical Soil Properties | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil texture (%) | pH | cmol(+)/L | % | mg/L | dS/m | Ratio | |||||||
| Clay | Sand | Slit | H2O | Acidity | Ca | Mg | K | ECEC | AS | P | Mn | CE | C/N |
| 24.1 | 63.6 | 12.3 | 6.6 | 0.1 | 8.31 | 3.19 | 0.94 | 12.54 | 0.8 | 116 | 8 | 1.79 | 8.9 |
| Doses(g)/EC(dS/m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer | Non Saline (NS) | Slightly Saline (SS) | Moderately Saline (MS) |
| K | 0.76/1.8 | 0.23/3 | 6/4 |
| N | 0.70/1.8 | 0.38/3 | 10/4 |
| Treatment | Non-Saline NS (g) | Sightly Saline SS (g) | Moderately Saline MS (g) | Biochar (%) | No. of Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLB0 | - | - | - | 0 | 1 |
| SLB1.5 | - | - | - | 1.5 | 1 |
| SLB3 | - | - | - | 3 | 1 |
| SL0N | 5 | 15 | 45 | 0 | 3 |
| SLB1.5N | 5 | 15 | 45 | 1.5 | 3 |
| SLB3N | 5 | 15 | 45 | 3 | 3 |
| SL0K | 5 | 25 | 70 | 0 | 3 |
| SLB1.5K | 5 | 25 | 70 | 1.5 | 3 |
| SLB3K | 5 | 25 | 70 | 3 | 3 |
| Treatment | Polynomial Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2 | ||
| SLB0 | 0.216 | −2.248 | 0.031 |
| SLB0N5 | 0.216 | −2.248 | 0.035 |
| SLB0K5 | 0.216 | −2.247 | 0.079 |
| SLB1.5 | 0.216 | −2.237 | 0.096 |
| SLB1.5N5 | 0.216 | −2.247 | 0.049 |
| SLB1.5K5 | 0.216 | −2.228 | 0.164 |
| SLB3 | 0.216 | −2.245 | 0.089 |
| SLB3N5 | 0.216 | −2.234 | 0.149 |
| SLB3K5 | 0.216 | −2.245 | 0.037 |
| SLB0N15 | 0.216 | −2.237 | 0.026 |
| SLB0K25 | 0.216 | −2.218 | −0.069 |
| SLB1.5N15 | 0.216 | −2.238 | 0.183 |
| SLB1.5K25 | 0.216 | −2.230 | 0.144 |
| SLB3N15 | 0.216 | −2.229 | 0.211 |
| SLB3K25 | 0.216 | −2.228 | 0.204 |
| SLB0N45 | 0.216 | −2.234 | 0.251 |
| SLB0K70 | 0.216 | −2.241 | 0.177 |
| SLB1.5K70 | 0.216 | −2.231 | 0.284 |
| SLB1.5N45 | 0.216 | −2.242 | 0.172 |
| SLB3N45 | 0.216 | −2.200 | 0.449 |
| SLB3K70 | 0.216 | −2.199 | 0.450 |
| Treatment | Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | ||||
| SLB0 | 0.999 | 0.005 | 0.127 | 0.146 |
| SLB0N5 | 0.999 | 0.006 | 0.230 | 0.146 |
| SLB0K5 | 0.999 | 0.004 | −0.265 | 0.146 |
| SLB1.5 | 0.990 | 0.015 | −0.497 | 0.145 |
| SLB1.5N5 | 0.997 | 0.008 | −0.710 | 0.145 |
| SLB1.5K5 | 0.986 | 0.017 | −0.146 | 0.145 |
| SLB3 | 0.998 | 0.007 | 0.115 | 0.146 |
| SLB3N5 | 0.990 | 0.014 | −0.045 | 0.145 |
| SLB3K5 | 0.996 | 0.009 | −0.021 | 0.146 |
| SLB0N15 | 0.990 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.145 |
| SLB0K25 | 0.971 | 0.025 | 0.070 | 0.144 |
| SLB1.5N15 | 0.996 | 0.009 | −0.436 | 0.146 |
| SLB1.5K25 | 0.986 | 0.017 | −0.283 | 0.145 |
| SLB3N15 | 0.993 | 0.012 | −0.210 | 0.146 |
| SLB3K25 | 0.992 | 0.013 | 0.084 | 0.147 |
| SLB0N45 | 0.998 | 0.006 | −0.311 | 0.146 |
| SLB0K70 | 0.999 | 0.005 | −0.253 | 0.147 |
| SLB1.5K70 | 0.999 | 0.004 | 0.226 | 0.148 |
| SLB1.5N45 | 0.999 | 0.004 | −0.017 | 0.146 |
| SLB3N45 | 0.996 | 0.009 | −0.240 | 0.147 |
| SLB3K70 | 0.995 | 0.011 | −0.939 | 0.146 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Astorga, M.J.; Villagra-Mendoza, K.; Masís-Meléndez, F.; Ruíz-Barquero, A.; Rimolo-Donadio, R. Calibration of Low-Cost Moisture Sensors in a Biochar-Amended Sandy Loam Soil with Different Salinity Levels. Sensors 2024, 24, 5958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185958
Gómez-Astorga MJ, Villagra-Mendoza K, Masís-Meléndez F, Ruíz-Barquero A, Rimolo-Donadio R. Calibration of Low-Cost Moisture Sensors in a Biochar-Amended Sandy Loam Soil with Different Salinity Levels. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):5958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185958
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Astorga, María José, Karolina Villagra-Mendoza, Federico Masís-Meléndez, Aníbal Ruíz-Barquero, and Renato Rimolo-Donadio. 2024. "Calibration of Low-Cost Moisture Sensors in a Biochar-Amended Sandy Loam Soil with Different Salinity Levels" Sensors 24, no. 18: 5958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185958
APA StyleGómez-Astorga, M. J., Villagra-Mendoza, K., Masís-Meléndez, F., Ruíz-Barquero, A., & Rimolo-Donadio, R. (2024). Calibration of Low-Cost Moisture Sensors in a Biochar-Amended Sandy Loam Soil with Different Salinity Levels. Sensors, 24(18), 5958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185958






