Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods for the Front-End Readout Circuit of a Microelectromechanical Systems Gyroscope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analyses
2.1. Noise Analysis of the Readout Circuit
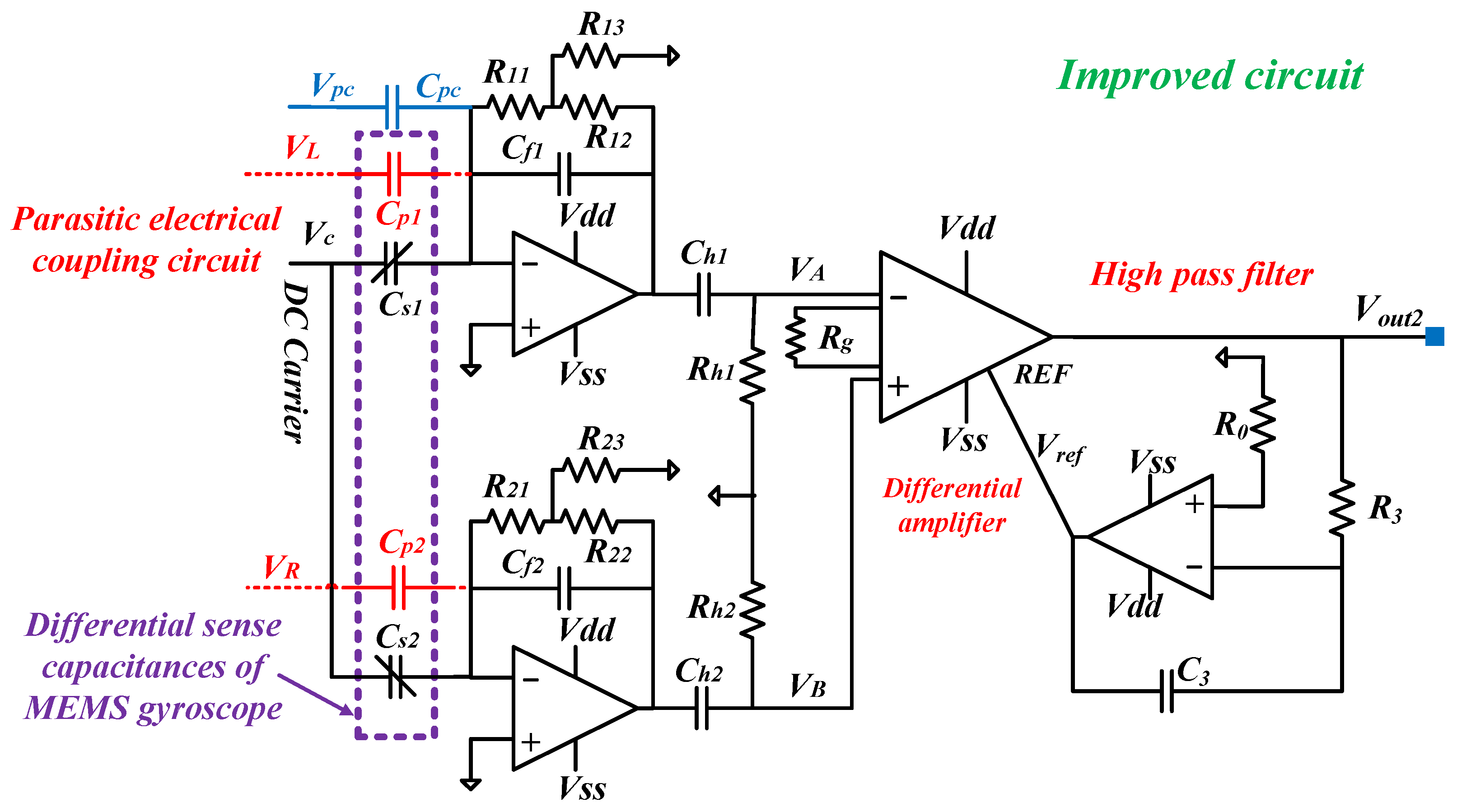
2.2. An Improved Readout Circuit Based on the T-Resistor Networks
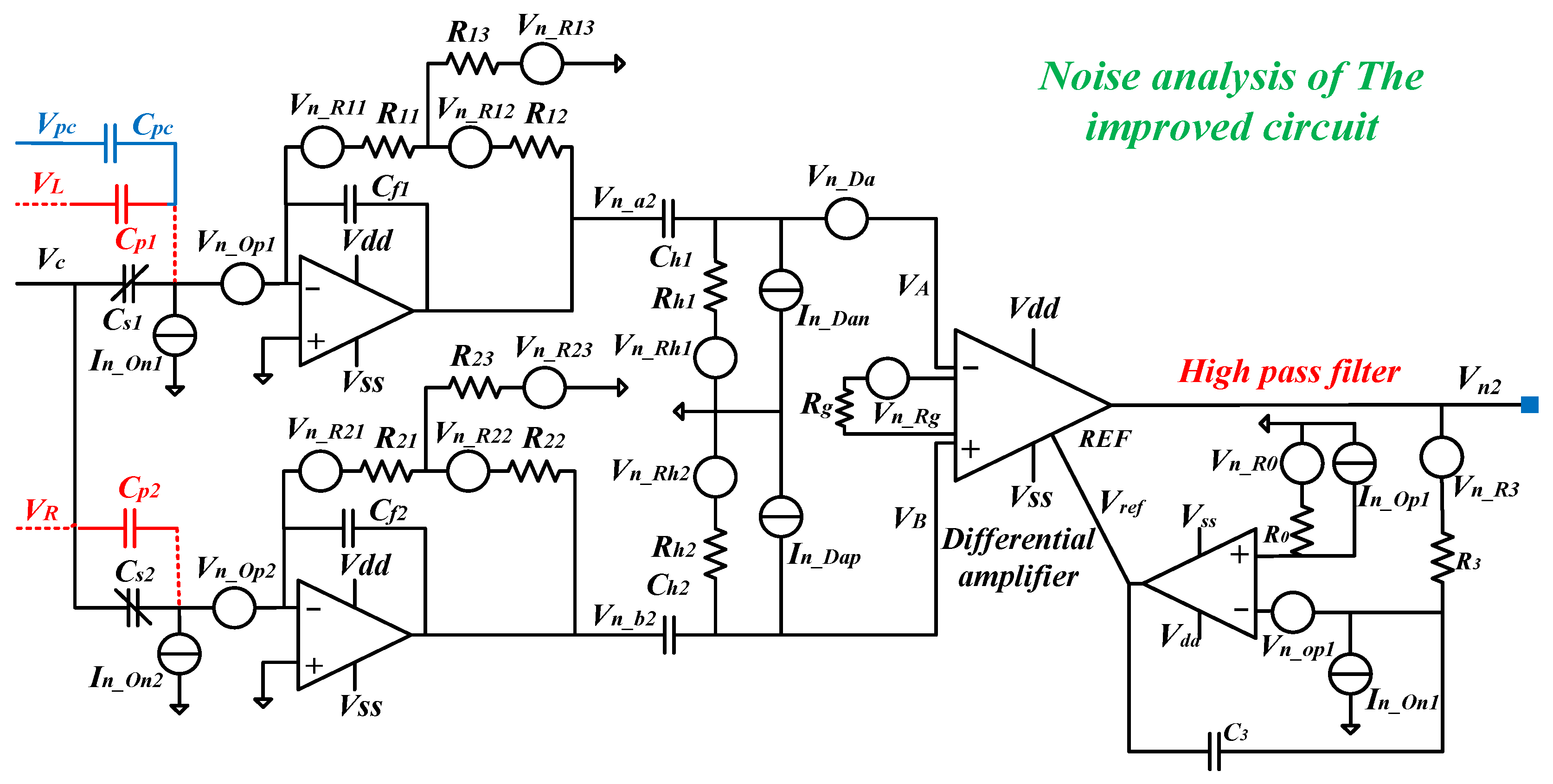
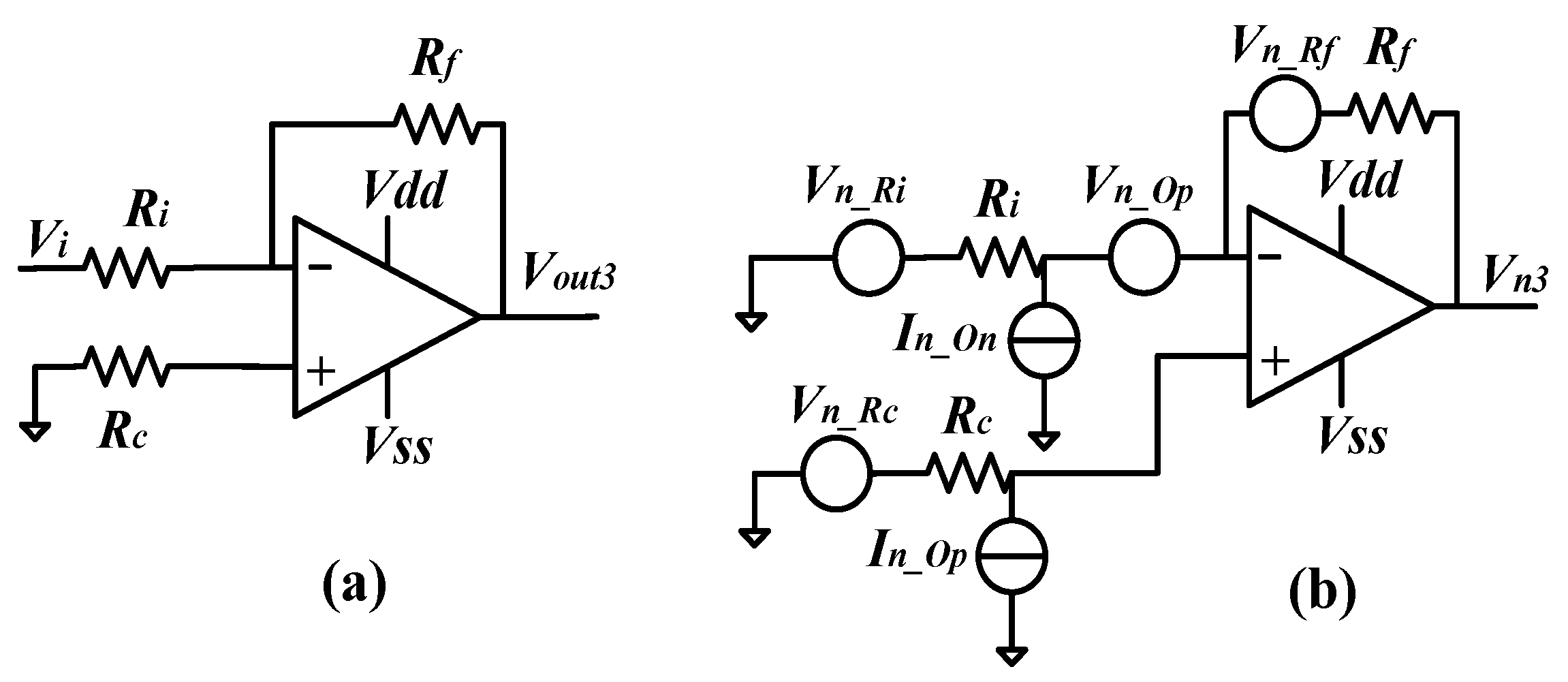
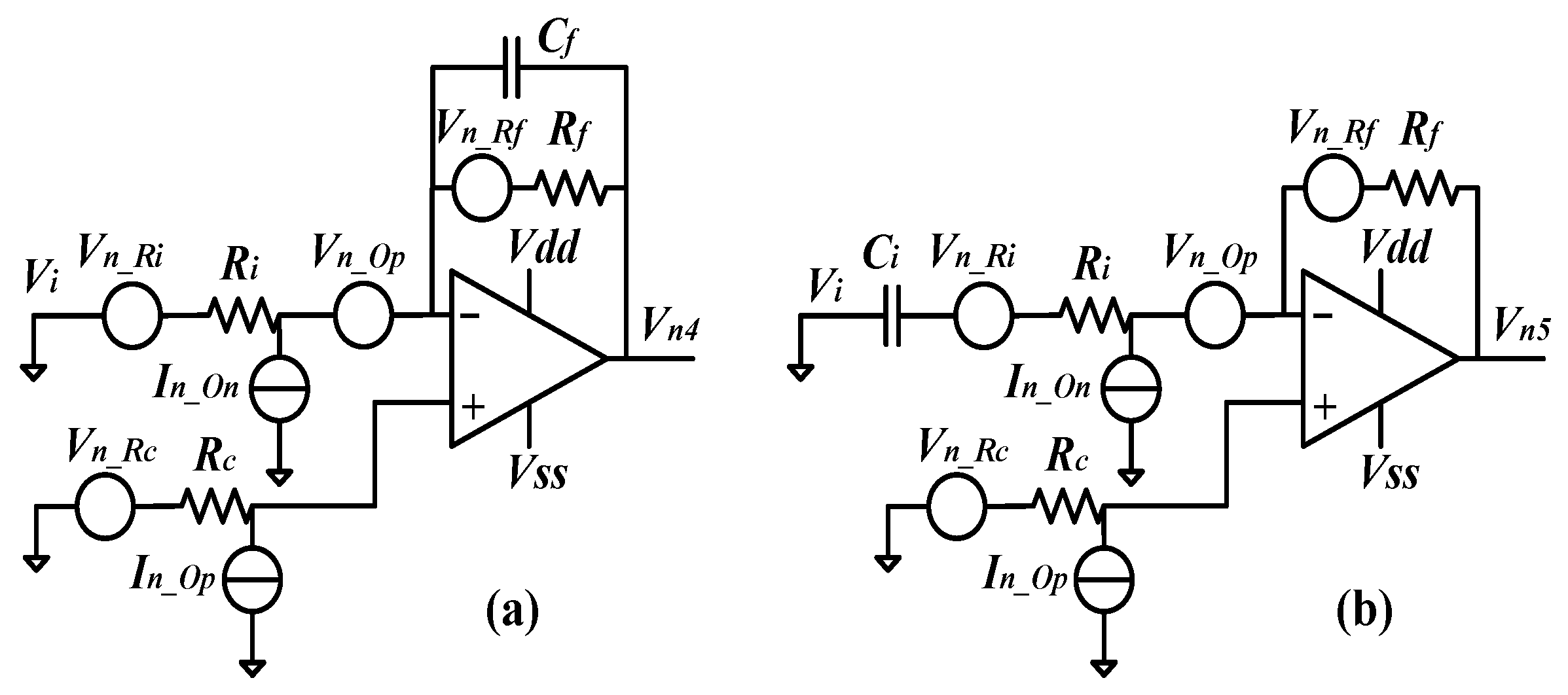
2.3. Noise Analysis of the Other Critical Circuits
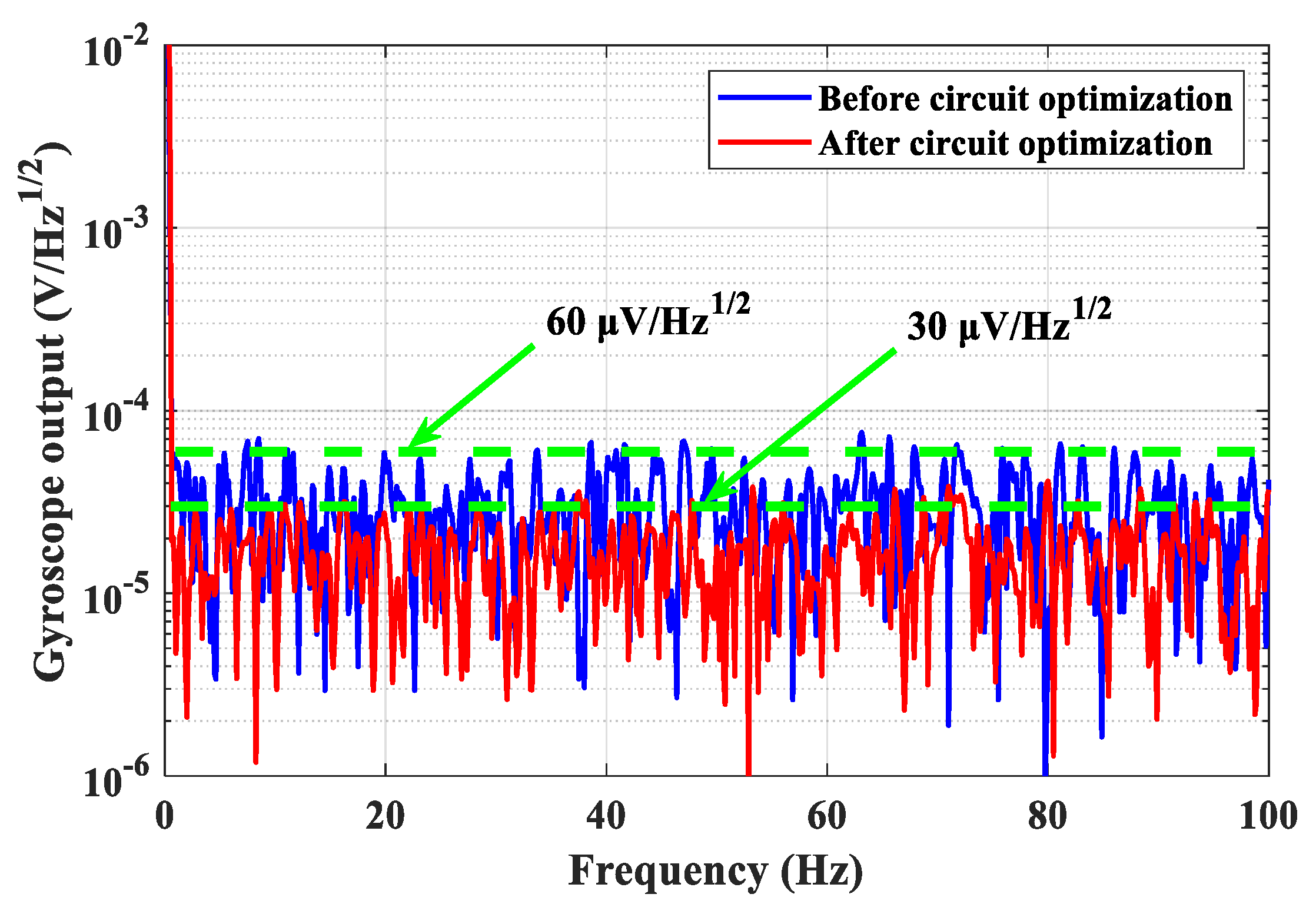
3. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samatas, G.G.; Pachidis, T.P. Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) in Mobile Robots over the Last Five Years: A Review. Designs 2022, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Cuignet, X.; Nessler, S.; De Dorigo, D.; Manoli, Y. An Automatic MEMS Gyroscope Mode Matching Circuit Based on Noise Observation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2019, 66, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudyk, A.V.; Semenov, A.O.; Kryvinska, N.; Semenova, O.O.; Kvasnikov, V.P.; Safonyk, A.P. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Systems for Positioning Mobile Robots—MEMS Gyroscopes Random Errors Analysis Using Allan Variance Method. Sensors 2020, 20, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffoli, A.; Gadola, M.; Sansa, M.; Langfelder, G. 0.02°/h, 0.004°/√h, 6.3-mA NEMS Gyroscope with Integrated Circuit. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2002108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Su, T.; Kong, J.; Zhang, B. Adaptive Filtering for MEMS Gyroscope with Dynamic Noise Model. ISA Transact. 2020, 101, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Kuang, J.; Hu, X.; Cai, X.; Shi, J. The Design of ΔΣ-ADC in MEMS Gyro Interface ASIC. Microelectron. J. 2023, 134, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Dubey, V.; Mishra, P.M.; Khan, I. MEMS Technology: A Review. J. Eng. Res. Rep 2019, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilli, M.; Paulasto-Kröckel, M.; Petzold, M.; Theuss, H.; Motooka, T.; Lindroos, V. Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 978-0-12-817787-7. [Google Scholar]
- Serri, M.; Saeedi, S. Ultra-Low-Noise TIA Topology for MEMS Gyroscope Readout. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 118, 153145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, D.; Hall, D.A. Current Sensing Front-Ends: A Review and Design Guidance. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22329–22346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindranath, A.; Arora, M. A Systematic Review of User—Conducted Calibration Methods for MEMS-Based IMUs. Measurement 2024, 225, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Shen, Y.; Xia, C.; Tong, W.; Jin, Z.; Ma, Z. Noise Analysis and Modeling for a Digital Control Architecture for Lissajous Frequency-Modulated MEMS Gyroscope with Amplitude-Modulated Readout. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2023, 33, 095008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Song, K. A Low-Noise Readout Interface for Silicon MEMS Vibratory Gyroscope. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 35, 2150069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wei, Q.; Ju, C.; Liao, H.; Gu, H.; Xing, B.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, R. A 0.82 μVrms Ultralow 1/f Noise Bandgap Reference for a MEMS Gyroscope. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Fu, Q. A Low-Noise Interface ASIC for MEMS Disk Resonator Gyroscope. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Meng, Z.; Omisore, O.; Akinyemi, T.; Yan, Y. Random Error Reduction Algorithms for MEMS Inertial Sensor Accuracy Improvement—A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y. A System Phase Noise Model for Frequency-Modulated MEMS Gyroscopes. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16124–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethander, K.A.; Taylor, C.N. Conservative Estimation of Inertial Sensor Errors Using Allan Variance Data. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2023, 70, navi.563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Fan, W.; Du, P.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, L.; Quan, W. Markov Noise in Atomic Spin Gyroscopes: Analysis and Suppression Based on Allan Deviation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 7002709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catelani, M.; Ciani, L.; Patrizi, G.; Singuaroli, R.; Carratù, M.; Sommella, P.; Pietrosanto, A. Analysis of Noise Contributions in Low-Cost IMUs through Allan’s Variance. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 10th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Milan, Italy, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Pham, L.; Tao, R.; Gutmann, A.; Guo, S.; Cywar, A.; Spirer, A.; Mansson, J.; Nguyen, K. A Low-Power, Wide-Bandwidth, Three-Axis MEMS Accelerometer ASIC Using Beyond-Resonant-Frequency Sensing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Z. A 63 Μg/√Hz Noise Floor and 14 pJ Power Efficiency Open-Loop MEMS Capacitive Accelerometer Using Closed-Loop Hybrid Dynamic Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Fan, B.; Xu, D.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H. Bandwidth and Noise Analysis of High-Q MEMS Gyroscope under Force Rebalance Closed-Loop Control. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Su, Y. A Phase Compensation Method for MEMS Quadruple Mass Gyroscope in Zero Bias Drift. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Wang, X.; Fan, B.; Guo, S.; Xu, D.; Xu, X.; Zhao, H. Noise Model Considering Electrical Feed-through under Force Rebalance Closed-Loop Detection of MEMS Gyroscope. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2020, 30, 055007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Huang, J.; Qiu, A. A Novel Frequency Readout Method and Circuit for Navigation-Grade Vibrating Beam Accelerometers. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 21363–21373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Z. Suppression of Self-Noise and Environmental Disturbances by Fusion in Fiber-Optic Gyroscopes for Precision Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 14084–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Yin, L.; Fu, Q. Analysis and Design of a Fourth-Order ΣΔ ADC for MEMS Digital Gyroscope Sensors. Microelectron. J. 2023, 141, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawase, R.; Futane, N.P. Angular Rate Error Compensation of MEMS Based Gyroscope Using Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Pervasive Computing (ICPC), Pune, India, 8–10 January 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, T. Modeling and Compensation of MEMS Gyroscope Output Data Based on Support Vector Machine. Measurement 2012, 45, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Su, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Qi, W. A Combined CKF-PSR Method for Random Noise Compensation of Vibratory Gyroscopes. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 25, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, J.; Hashemi, M.; Alasty, A. A Memory-Based Filter for Long-Term Error De-Noising of MEMS-Gyros. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 7503308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H. Temperature Influence on Silicon-Based MEMS Gyroscope and Suppression Method. In Dual-Mass Linear Vibration Silicon-Based MEMS Gyroscope; Cao, H., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 167–198. ISBN 978-981-19924-7-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, R.; Li, C.; Dean, R.N. Concepts, Roadmaps and Challenges of Ovenized MEMS Gyroscopes: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiancheng, F.; Jianli, L. Integrated Model and Compensation of Thermal Errors of Silicon Microelectromechanical Gyroscope. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Xia, G.; Qiu, A. Low-Noise Quality Factor Tuning in Nondegenerate MEMS Gyroscope Without Dedicated Tuning Electrode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 4230–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Yin, L.; Fu, Q. Design of MEMS Gyroscope Interface ASIC with On-Chip Temperature Compensation. Measurement 2023, 220, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, H.; Yaralioglu, G. Noise Analysis of Mode Matched Vibratory Gyroscopes. Microsyst Technol 2023, 29, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Guo, X.; Huang, X.; Yang, B. Microseismic Observation Enabled by High-Sensitivity Micromechanical Interferometers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 5349–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhou, X.; Yu, S.; Wu, X.; Xiao, D. Frequency-Modulated MEMS Gyroscopes: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 26426–26446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yan, G. An Electrical-Coupling-Suppressing MEMS Gyroscope with Feed-Forward Coupling Compensation and Scalable Fuzzy Control. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 042402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


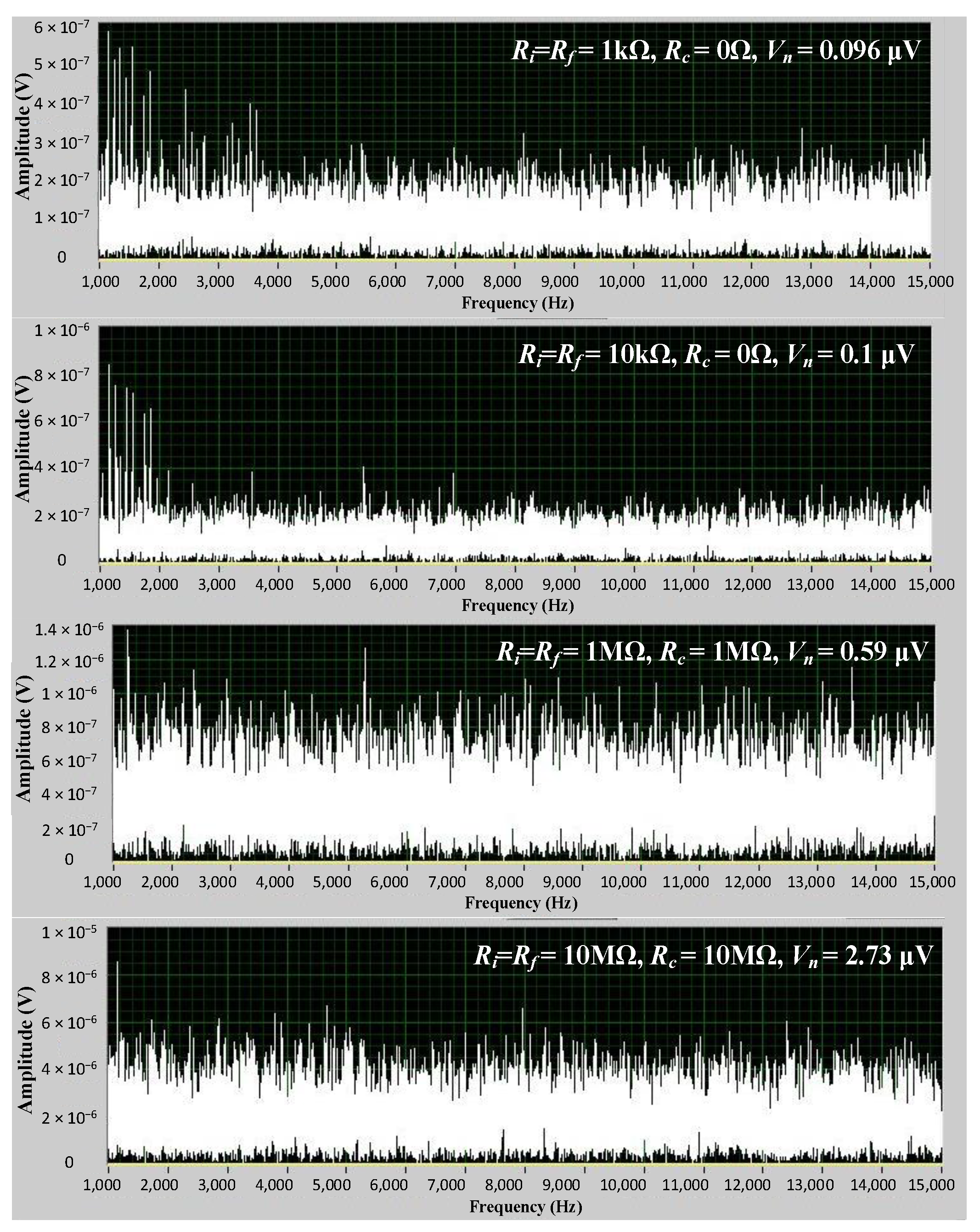


| Test | Ri (Ω) | Rf (Ω) | Rc (Ω) | Test Result Vn (μV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 k | 1 k | 0 | 0.096 |
| 2 | 1 k | 1 k | 10 M | 3 |
| 3 | 10 k | 10 k | 0 | 0.1 |
| 4 | 10 k | 10 k | 10 k | 0.11 |
| 5 | 100 k | 100 k | 0 | 0.13 |
| 6 | 100 k | 100 k | 100 k | 0.19 |
| 7 | 1 M | 1 M | 0 | 0.35 |
| 8 | 1 M | 1 M | 1 M | 0.59 |
| 9 | 10 M | 10 M | 0 | 1.98 |
| 10 | 10 M | 10 M | 10 M | 2.73 |
| Type | Before Circuit Optimization | After Circuit Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Chip selection | OP2177, AD8221 | AD8676, AD8421 |
| Transimpedance amplifier | Without T-resistor networks Rf = 1 MΩ, Cf = 1 pF | With T-resistor networks R11 = 100 kΩ, R12 = 1 kΩ, R13 = 110 Ω, Cf = 1 pF |
| Inverting amplifier | Rf = 100 kΩ, Ri = 100 kΩ, Rc = 100 kΩ | Rf = 1 kΩ, Ri = 1 kΩ, Rc = 0 Ω |
| LPF | Rf = 200 kΩ, Ri = 200 kΩ, Ci = 1 pF, Rc = 100 kΩ | Rf = 2 kΩ, Ri = 2 kΩ, Ci = 100 pF, Rc = 0 Ω |
| HPF | Rf = 200 kΩ, Ri = 200 kΩ, Ci = 0.01 μF, Rc = 100 kΩ | Rf = 2 kΩ, Ri = 2 kΩ, Ci = 1 μF, Rc = 0 Ω |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Cheng, L.; Yan, G.; Huang, Q. Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods for the Front-End Readout Circuit of a Microelectromechanical Systems Gyroscope. Sensors 2024, 24, 6283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196283
He C, Xu Y, Wang X, Wu H, Cheng L, Yan G, Huang Q. Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods for the Front-End Readout Circuit of a Microelectromechanical Systems Gyroscope. Sensors. 2024; 24(19):6283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196283
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chunhua, Yingyu Xu, Xiaoman Wang, Heng Wu, Lianglun Cheng, Guizhen Yan, and Qinwen Huang. 2024. "Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods for the Front-End Readout Circuit of a Microelectromechanical Systems Gyroscope" Sensors 24, no. 19: 6283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196283
APA StyleHe, C., Xu, Y., Wang, X., Wu, H., Cheng, L., Yan, G., & Huang, Q. (2024). Noise Analysis and Suppression Methods for the Front-End Readout Circuit of a Microelectromechanical Systems Gyroscope. Sensors, 24(19), 6283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196283






