Neural Signature and Decoding of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Operators in Emergency Scenarios Using Electroencephalography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Paradigm and Procedure
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Neural Signatures
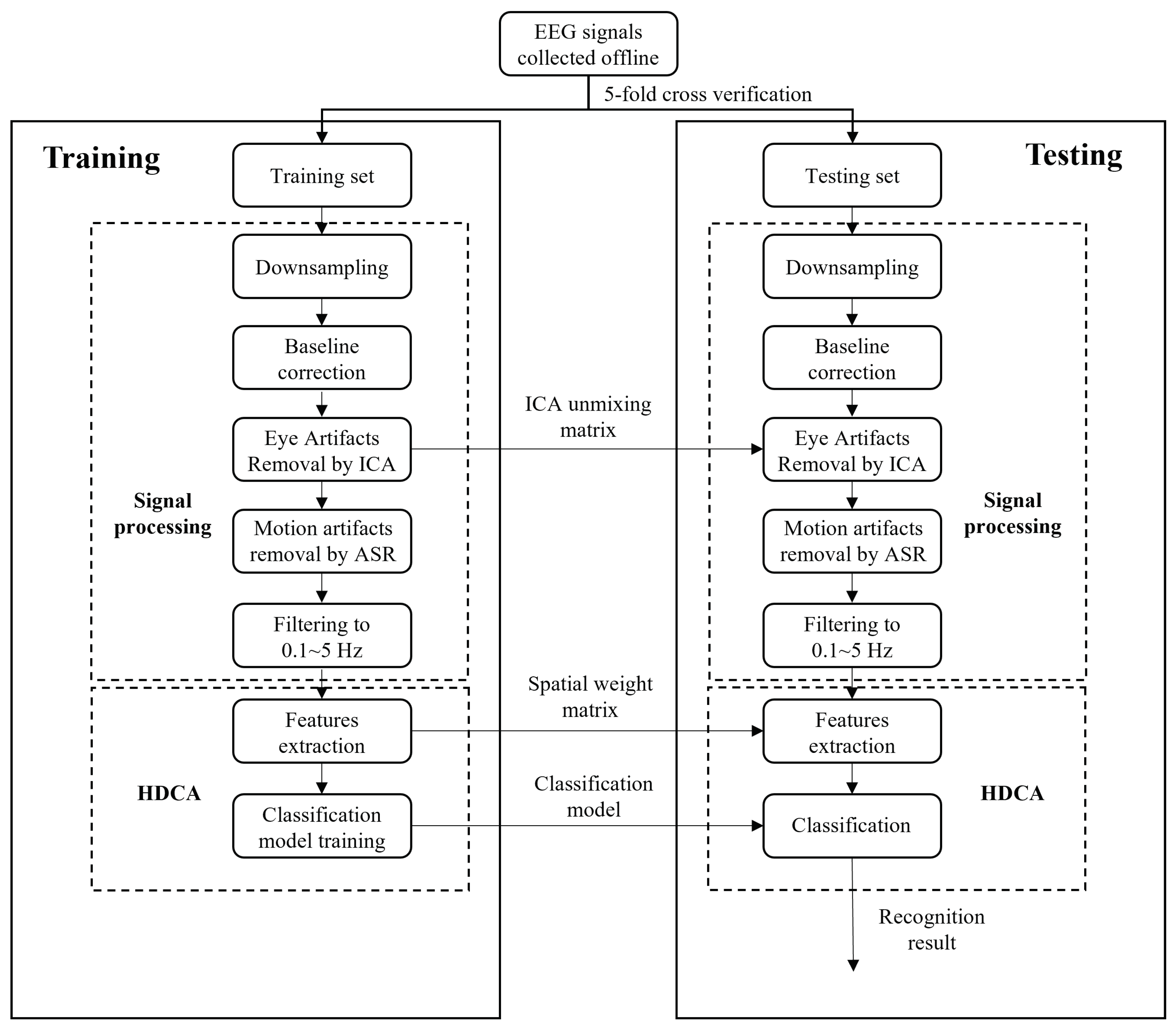
2.4. Decoding Models
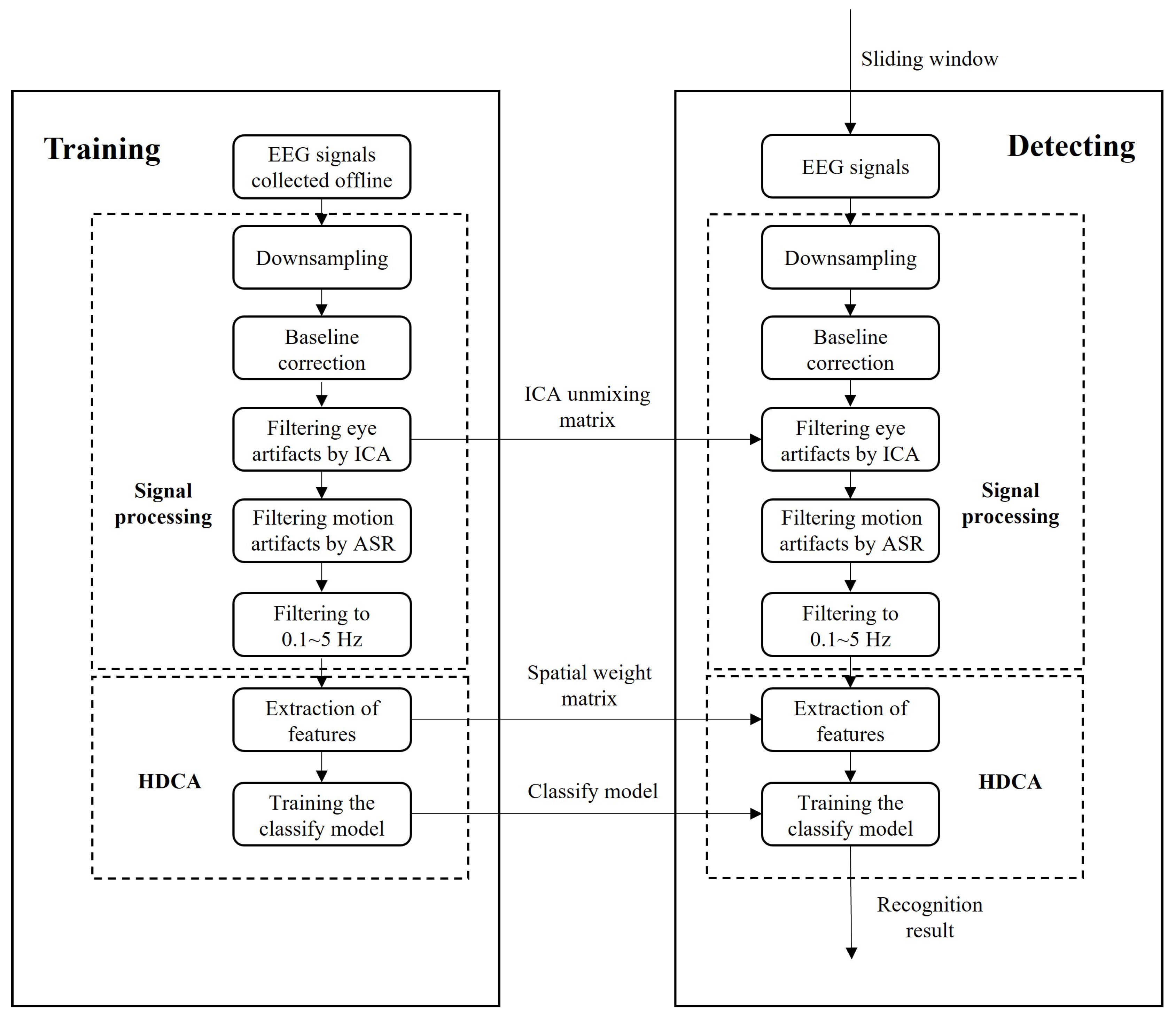
2.5. Online Detection System
| Algorithm 1 EEG Signal Processing and Experiment Execution |
|
3. Result and Discussion
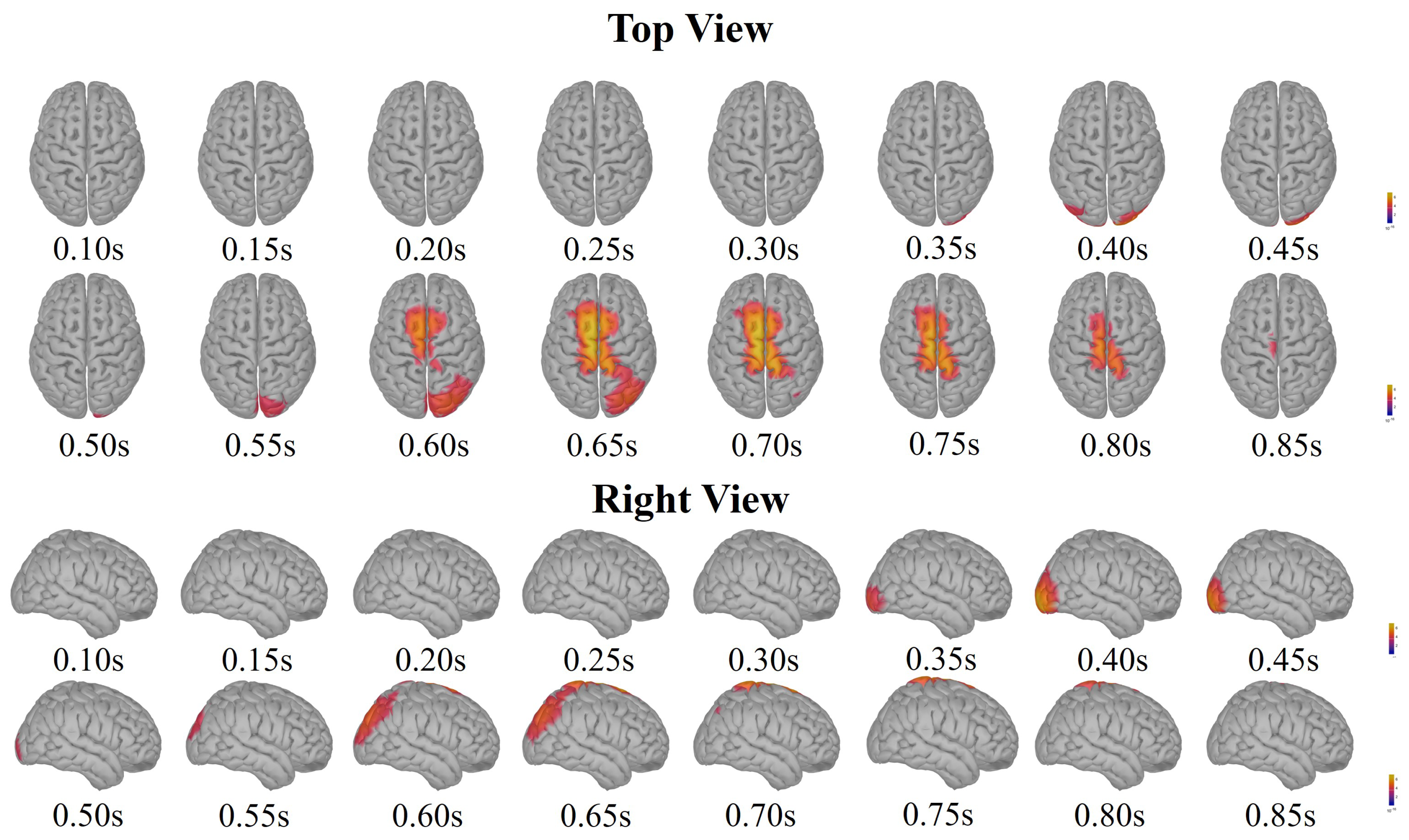
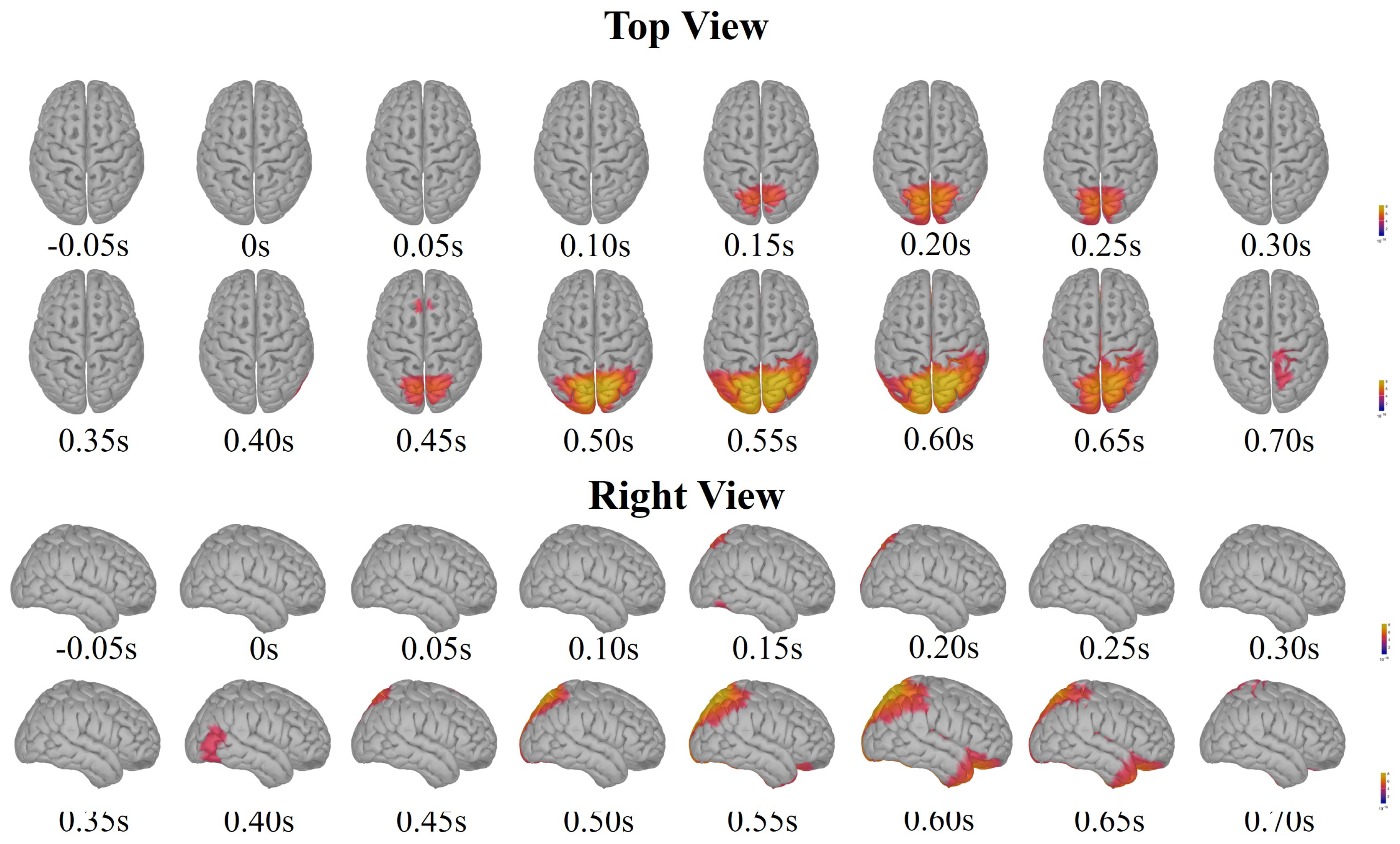
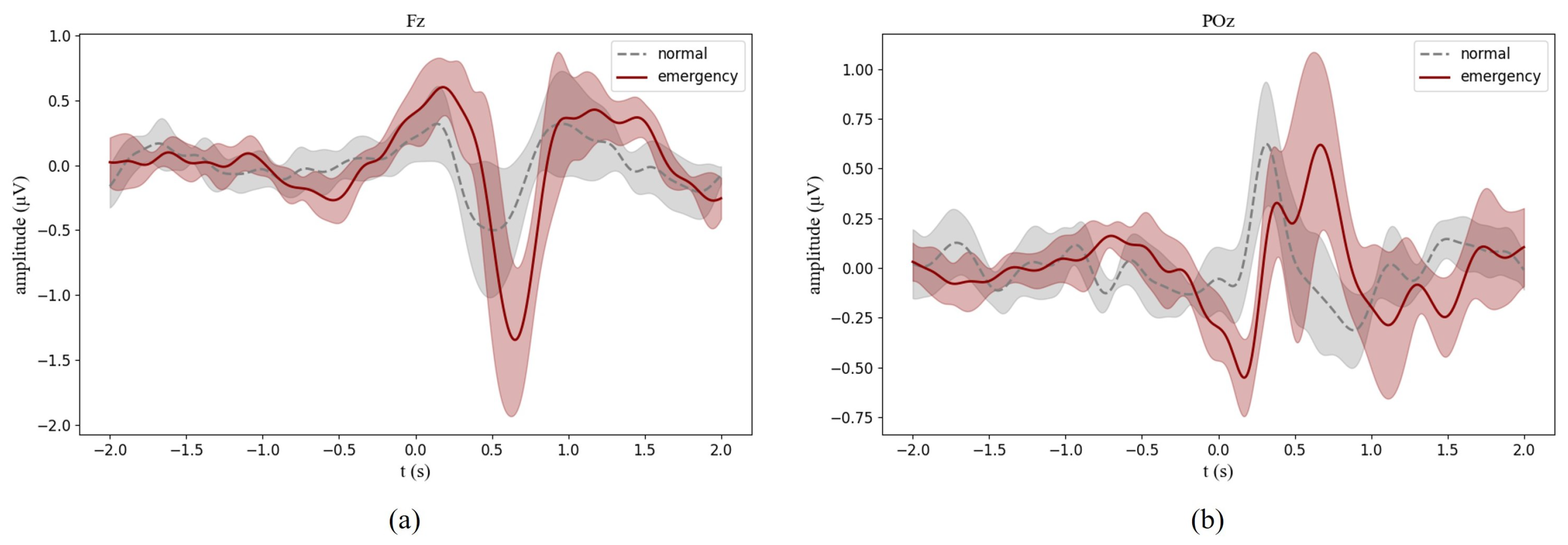
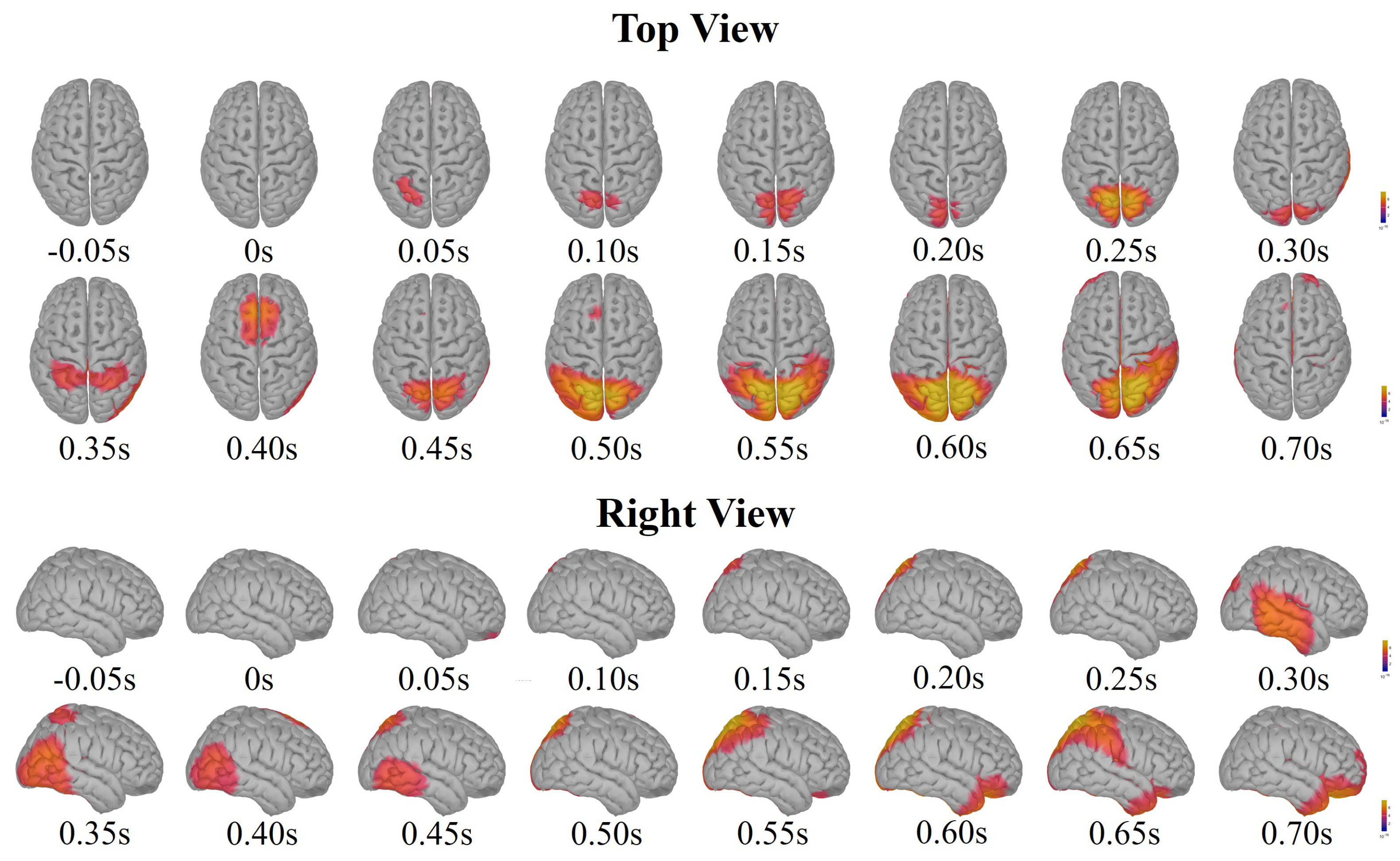
3.1. Neural Signatures
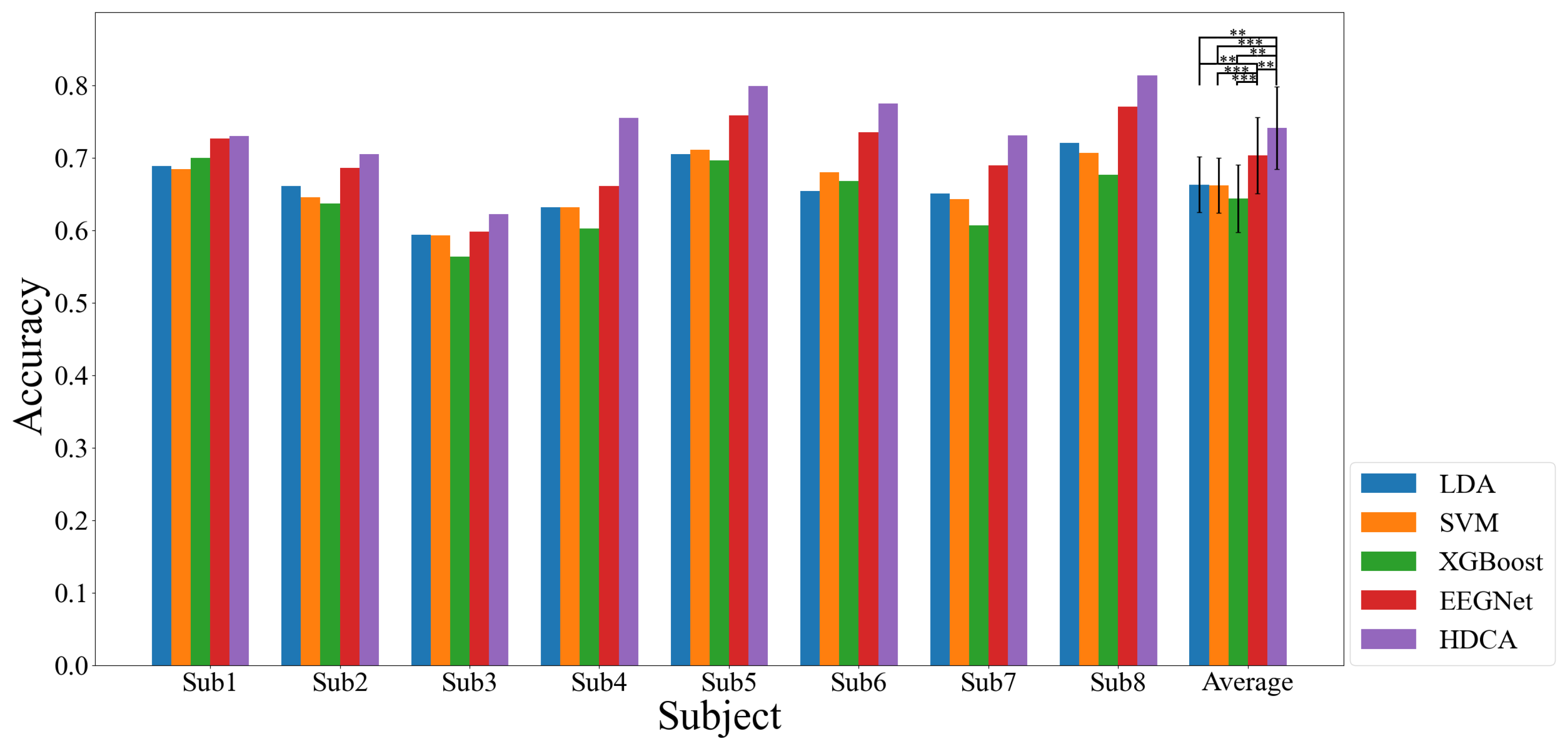
3.2. Classification Performance
3.3. Online System Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A





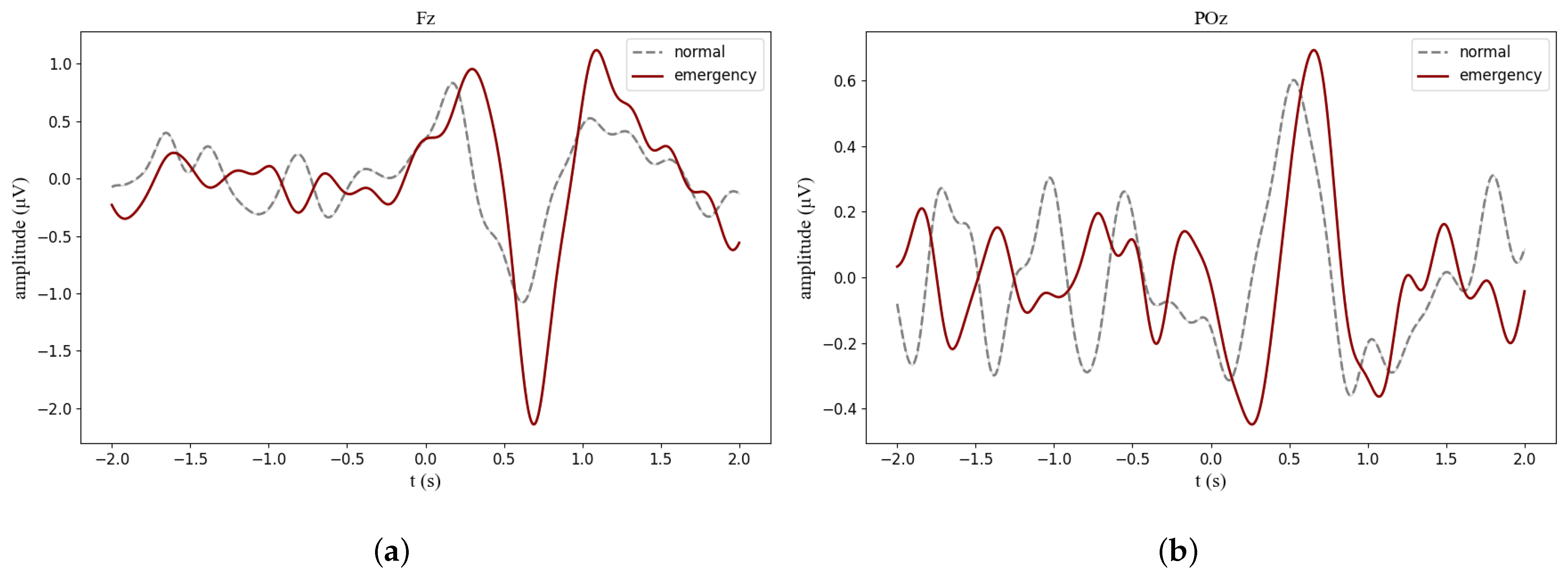
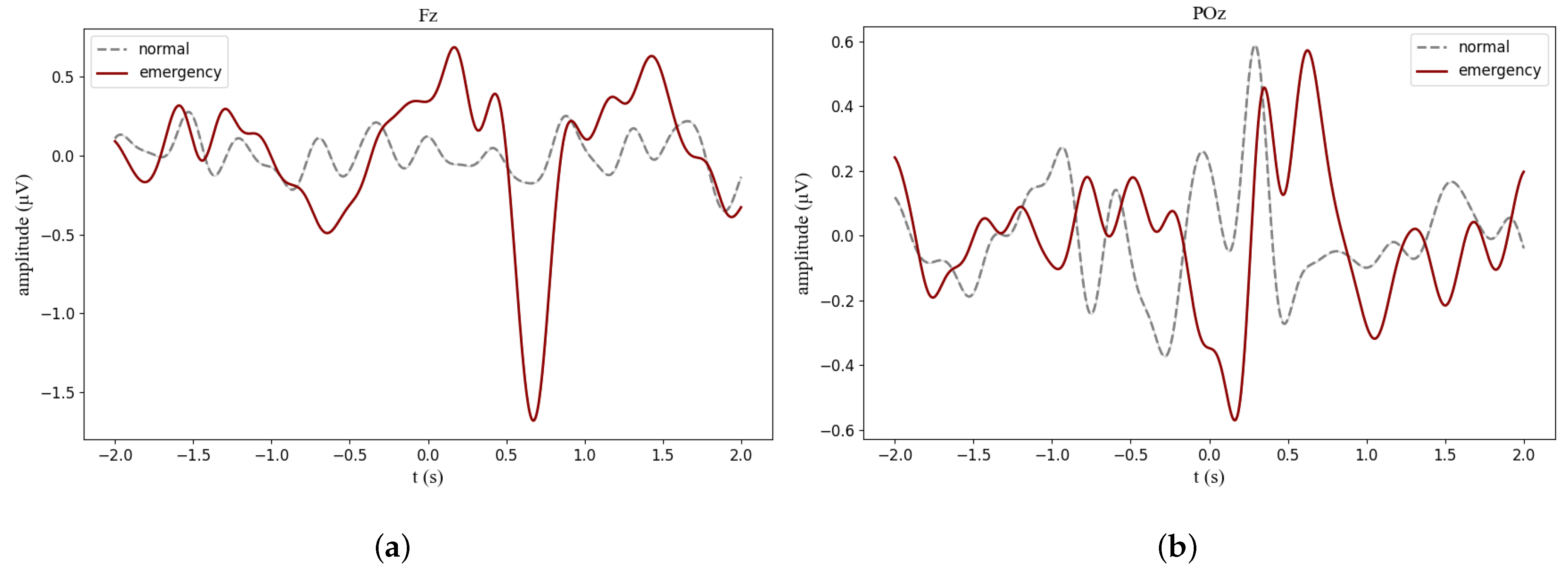

Appendix B
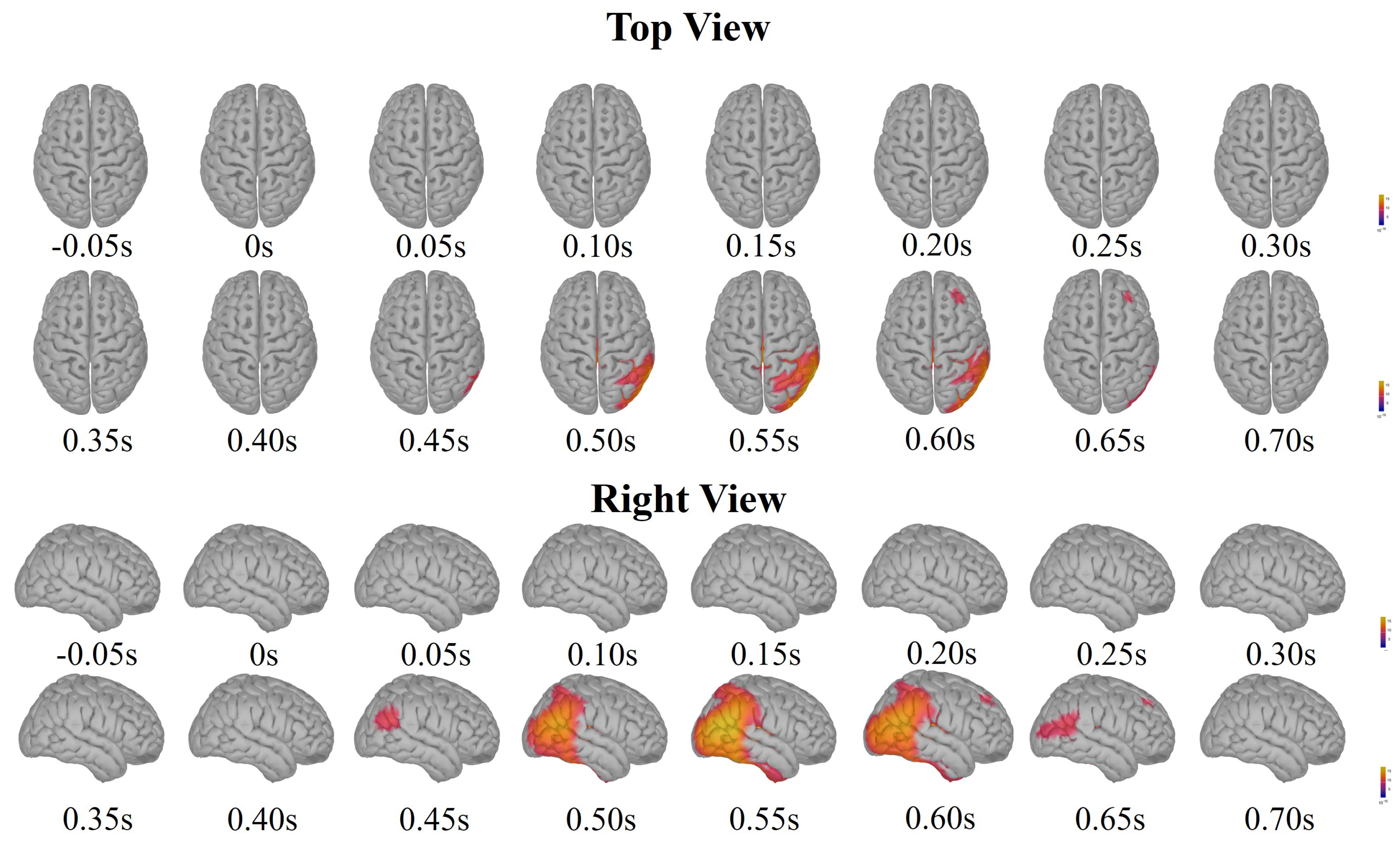
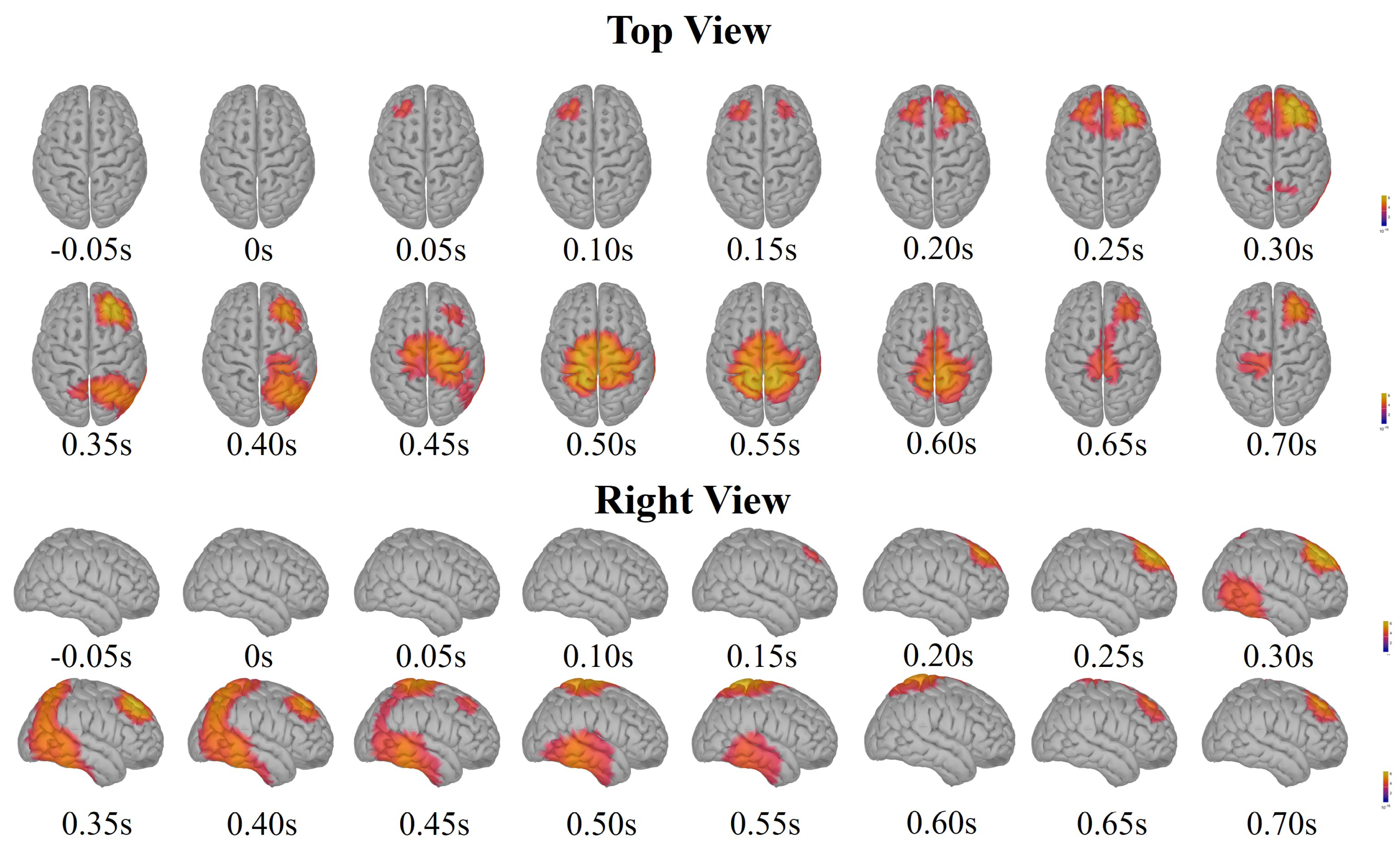



References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Fei, W. Multitask-oriented brain-controlled intelligent vehicle based on human–machine intelligence integration. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaumer, N.; Cohen, L.G. Brain–computer interfaces: Communication and restoration of movement in paralysis. J. Physiol. 2007, 579, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Bi, L.; Wang, Z.; Feleke, A.G.; Fei, W. Robust decoding of upper-limb movement direction under cognitive distraction with invariant patterns in embedding manifold. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Fei, W.; Guan, C. Decoding single-hand and both-hand movement directions from noninvasive neural signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Fei, W.; Xu, X.; Liu, A.; Mo, L.; Feleke, A.G. Neural Correlate and Movement Decoding of Simultaneous-and-Sequential Bimanual Movements Using EEG Signals. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Das, R.; Iversen, H.K.; Puthusserypady, S. Review on motor imagery based BCI systems for upper limb post-stroke neurorehabilitation: From designing to application. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.d.R.; Rupp, R.; Müller-Putz, G.R.; Murray-Smith, R.; Giugliemma, C.; Tangermann, M.; Vidaurre, C.; Cincotti, F.; Kübler, A.; Leeb, R.; et al. Combining brain–computer interfaces and assistive technologies: State-of-the-art and challenges. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Höller, M.K.; Pereira, J.; Ofner, P.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Decoding hand movements from human EEG to control a robotic arm in a simulation environment. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 036010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Halder Roy, A. EEG sensor driven assistive device for elbow and finger rehabilitation using deep learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, G.A.M.; De Miranda, L.C. Brain–computer interface games based on consumer-grade EEG Devices: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 36, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Tejada, L.A.; Puertas-González, A.; Yoshimura, N.; Koike, Y. Exploring EEG Characteristics to Identify Emotional Reactions under Videogame Scenarios. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, L.W.; Chang, Y.; Wu, P.L.; Tzou, H.A.; Chen, S.F.; Tang, S.C.; Yeh, C.L.; Chen, Y.J. Development of a smart helmet for strategical BCI applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandbagleh, A.; Sanei, S.; Azami, H. Implications of Aperiodic and Periodic EEG Components in Classification of Major Depressive Disorder from Source and Electrode Perspectives. Sensors 2024, 24, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar Neto, F.S.; Rosa, J.L.G. Depression biomarkers using non-invasive EEG: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 105, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, B. Review on portable EEG technology in educational research. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 81, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Kao, C.M. Mental effort detection using EEG data in E-learning contexts. Comput. Educ. 2018, 122, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W.; Doppelmayr, M.; Russegger, H.; Pachinger, T.; Schwaiger, J. Induced alpha band power changes in the human EEG and attention. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 244, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Song, D.; Hu, B.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Kumar, N.; Marttinen, P. EEG based emotion recognition: A tutorial and review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jap, B.T.; Lal, S.; Fischer, P.; Bekiaris, E. Using EEG spectral components to assess algorithms for detecting fatigue. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S.; Treder, M.S.; Gugler, M.F.; Sagebaum, M.; Curio, G.; Blankertz, B. EEG potentials predict upcoming emergency brakings during simulated driving. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 056001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Kim, J.W.; Haufe, S.; Lee, S.W. Detection of braking intention in diverse situations during simulated driving based on EEG feature combination. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 12, 016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Wang, H.; Teng, T.; Guan, C. A novel method of emergency situation detection for a brain-controlled vehicle by combining EEG signals with surrounding information. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiong, X.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y. A survey of indoor uav obstacle avoidance research. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 51861–51891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akce, A.; Johnson, M.; Dantsker, O.; Bretl, T. A brain–machine interface to navigate a mobile robot in a planar workspace: Enabling humans to fly simulated aircraft with EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 21, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothong, T.; Samawi, J.; Govalkar, A.; George, K. Brain-Computer Interface for Quadcopter Morphology Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 9–11 July 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, M.A.; Lin, C.W.; Chang, C.T. The human—Unmanned aerial vehicle system based on SSVEP—Brain computer interface. Electronics 2021, 10, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacem, A.N.; Lakas, A. A cooperative EEG-based BCI control system for robot–drone interaction. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Harbin, China, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Xu, X.; Bi, L.; Feleke, A.G.; Fei, W. Low-quality Video Target Detection Based on EEG Signal using Eye Movement Alignment. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 5, 0121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. Alpha-band oscillations, attention, and controlled access to stored information. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Ji, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S. Visual mismatch negativity reflects enhanced response to the deviant: Evidence from event-related potentials and electroencephalogram time-frequency analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 800855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanics, G.; Kremláček, J.; Czigler, I. Visual mismatch negativity: A predictive coding view. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecce, J.J. Contingent negative variation (CNV) and psychological processes in man. Psychol. Bull. 1972, 77, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, U.; Van Maanen, L.; Forstmann, B.; van Rijn, H. Trial-by-trial fluctuations in CNV amplitude reflect anticipatory adjustment of response caution. NeuroImage 2014, 96, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, A.R.; Ries, A.J.; McDowell, K. Sliding HDCA: Single-trial EEG classification to overcome and quantify temporal variability. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarski, K.; Latinus, M.; Charpentier, J.; Cléry, H.; Roux, S.; Houy-Durand, E.; Saby, A.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Batty, M.; Gomot, M. Facial expression related vMMN: Disentangling emotional from neutral change detection. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosburg, T.; Weigl, M.; Deuring, G. Enhanced processing of facial emotion for target stimuli. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 146, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kask, A.; Põldver, N.; Ausmees, L.; Kreegipuu, K. Subjectively different emotional schematic faces not automatically discriminated from the brain’s bioelectrical responses. Conscious. Cogn. 2021, 93, 103150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Subject | Accuracy | Recall | FAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73.42% | 70.33% | 23.50% |
| 2 | 72.05% | 69.75% | 25.65% |
| 3 | 60.84% | 60.22% | 38.52% |
| 4 | 75.11% | 76.00% | 25.77% |
| 5 | 80.74% | 82.11% | 20.63% |
| 6 | 78.35% | 75.21% | 18.51% |
| 7 | 73.12% | 74.84% | 28.60% |
| 8 | 80.67% | 78.28% | 16.93% |
| Mean ± | 74.29% | 73.34% | 24.76% |
| Std | 5.99% | 6.20% | 6.37% |
| Subject | Accuracy | Recall | FAR | Reponse Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 79.38% | 82.50% | 23.73% | 674.75 ms |
| 2 | 91.41% | 91.67% | 8.85% | 452.73 ms |
| 3 | 90.08% | 94.58% | 14.43% | 363.88 ms |
| 4 | 90.29% | 95.42% | 14.84% | 392.14 ms |
| 5 | 89.17% | 87.50% | 9.17% | 368.57 ms |
| 6 | 89.89% | 90.42% | 10.65% | 398.16 ms |
| 7 | 90.06% | 88.75% | 8.63% | 425.35 ms |
| 8 | 90.20% | 91.67% | 11.27% | 380.00 ms |
| Mean ± | 88.81% | 90.31% | 12.70% | 431.95 ms |
| Std | 3.61% | 3.86% | 4.73% | 95.85 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Feleke, A.G.; Fei, W.; Bi, L. Neural Signature and Decoding of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Operators in Emergency Scenarios Using Electroencephalography. Sensors 2024, 24, 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196304
Liu M, Liu Y, Feleke AG, Fei W, Bi L. Neural Signature and Decoding of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Operators in Emergency Scenarios Using Electroencephalography. Sensors. 2024; 24(19):6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Manyu, Ying Liu, Aberham Genetu Feleke, Weijie Fei, and Luzheng Bi. 2024. "Neural Signature and Decoding of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Operators in Emergency Scenarios Using Electroencephalography" Sensors 24, no. 19: 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196304
APA StyleLiu, M., Liu, Y., Feleke, A. G., Fei, W., & Bi, L. (2024). Neural Signature and Decoding of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Operators in Emergency Scenarios Using Electroencephalography. Sensors, 24(19), 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196304






