Remote Multi-Person Heart Rate Monitoring with Smart Speakers: Overcoming Separation Constraint
Abstract
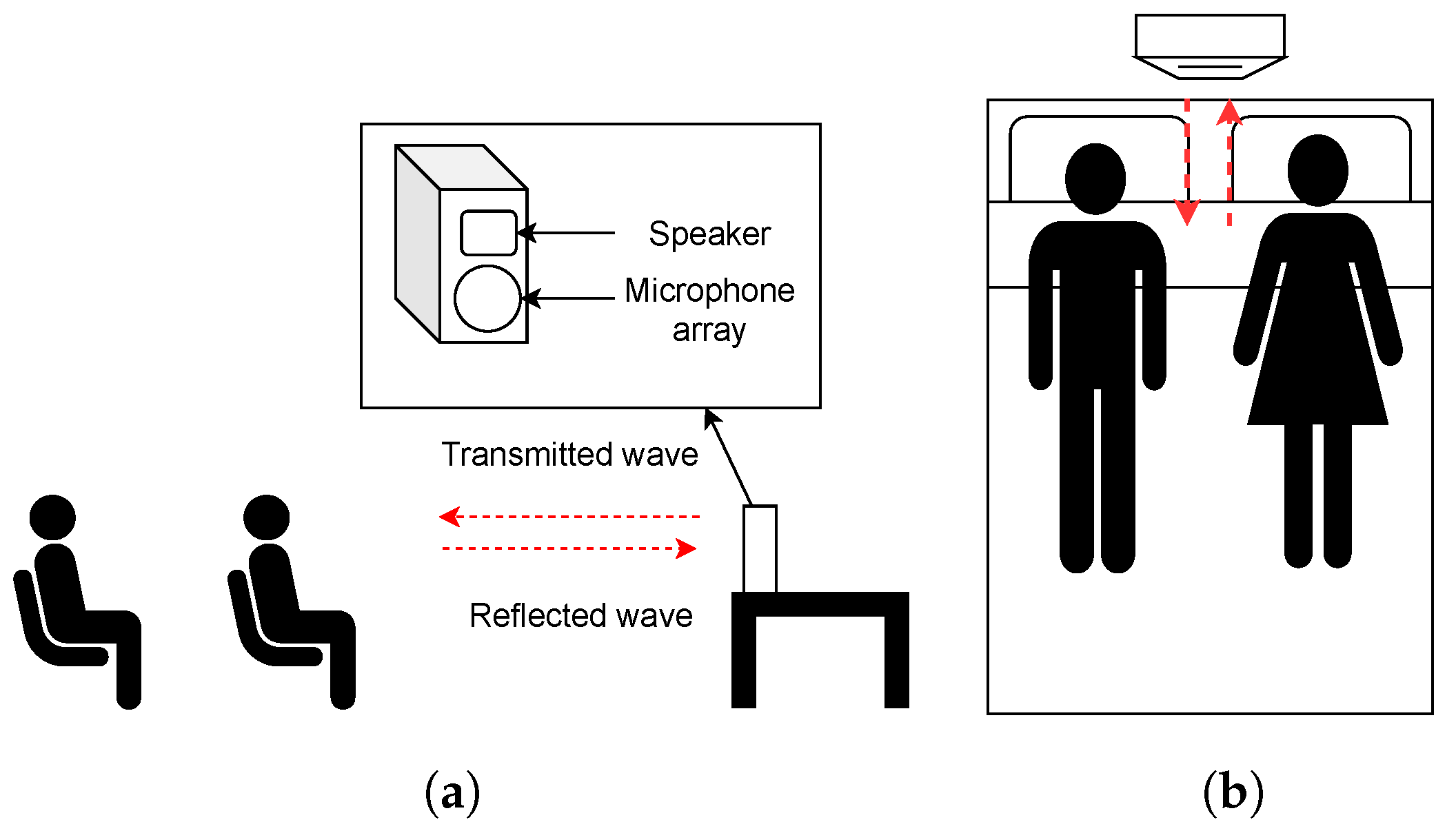
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Contact-Based Heart Rate Monitoring
2.2. RF-Based Heart Rate Monitoring
2.3. Acoustic-Based Heart Rate Monitoring
3. FMCW Background and Key Challenge
3.1. FMCW Background
3.2. Key Challenge: Signal Interference
4. System
4.1. System Overview
- Signal Processing: This module processes raw reflected signals received by the microphones, removes noise and frequencies outside the range of and , and performs a mix operation on each chirp to generate the heart rate–distance heatmap.
- Interference Removal: The generated heatmap produced in the previous step is prone to distance and frequency interference effects. This interference is canceled through a two-step algorithm in order to highlight the heart rate signals.
- Blob Detection: Next, users’ heart rates and distances are detected by applying a blob detection algorithm to the heatmap.
- Beamforming: Finally, beamforming is applied to detect each user’s azimuth angle based on their distance and heart rate.
4.2. Signal Processing
4.3. Interference Removal and Heart Rate Signal Amplification
| Algorithm 1: Remove interference and amplify heart rate signals |
Input: Heatmap S, with n rows and m columns Output: Interference-free and amplified heatmap S  |
4.4. Blob Detection
4.5. Beamforming
5. Results
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Overall Performance
5.3. Impact of Distance
5.4. Impact of Angle
5.5. Impact of Ambient Noise
5.6. Lying Down with Different Postures
5.7. Lying Down with Blanket
5.8. Impact of Movement
5.9. Impact of Number of Targets
5.10. Impact of Number of Microphones
5.11. Heart Rate Monitoring with Smartphone
6. Discussion
- Prone to Rhythmic Movement: Our approach can be susceptible to the impact of body movement, which is a known challenge for handling motion noise in acoustic-based methods. Because we assume that the user position falls within a frequency of 0.8 to 2.5 Hz (i.e., the normal heartbeat frequency range), any other modulation within this frequency range that does not originate from the human heart, although very unlikely, will confuse the system. As a result, although our system works well when the motion frequency is beyond the usual range of the heart rate (e.g., if the user shakes their head during measurement), it is suggested that users remain stationary during measurement to minimize possible noise that could fall within the heart rate frequency. In addition, we assumed that the device did not vibrate and that the background within the device’s working range contained no motion within the heartbeat frequency range. It is understood that voluntary or involuntary movement during signal acquisition typically reduces the fidelity of heart rate tracking [13,14].
- Lack of Evaluation of Standing Postures: While we conducted an extensive evaluation of our proposed system in various real-life scenarios, settings involving standing users were not included in our evaluation, as standing postures were not evaluated in any prior works in the literature. Therefore, we focused our evaluation on settings that were comparable with existing research. In fact, the standing setting is a challenge due to the difficulty of users maintaining stationary positions while in natural situations. For example, it is uncommon for an individual to remain completely still while standing for extended periods; a natural standing posture often involves walking or jogging. On the contrary, sitting or lying down naturally allows for more stationary positions. As a result, natural standing postures pose a great challenge in extracting subtle heartbeat signals, as we expect there to be significant motion noise. Consequently, we chose to leave the evaluation of different standing postures to future work.
- Performance of Heart Rate Detection: One assumption in our approach is that the normal heart rate falls within the range of 0.8 and 2.5 Hz, which is known as the normal heart rate range [37]. As such, any heart rate below 0.8 Hz may not be correctly detected, as the second harmonic of the respiration signal falls into this range and has significantly higher amplitude than the heartbeat.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acharya, U.R.; Joseph, K.P.; Kannathal, N.; Lim, C.M.; Suri, J.S. Heart rate variability: A review. Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taelman, J.; Vandeput, S.; Spaepen, A.; Van Huffel, S. Influence of mental stress on heart rate and heart rate variability. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, Antwerp, Belgium, 23–27 November 2008; pp. 1366–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Greenland, P.; Daviglus, M.L.; Dyer, A.R.; Liu, K.; Huang, C.F.; Goldberger, J.J.; Stamler, J. Resting heart rate is a risk factor for cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality: The Chicago Heart Association Detection Project in Industry. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, F.; Hobson, J.A.; Morrison, D.F.; Goldfrank, F. Changes in respiration, heart rate, and systolic blood pressure in human sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 1964, 19, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, Y.; Tarolli, C.G.; Crepeau, D.; Bukartyk, J.; Junna, M.R.; et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled detection and assessment of Parkinson’s disease using nocturnal breathing signals. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adib, F.; Mao, H.; Kabelac, Z.; Katabi, D.; Miller, R.C. Smart homes that monitor breathing and heart rate. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–23 April 2015; pp. 837–846. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; He, H.; Wang, H.; Rahul, H.; Katabi, D. Extracting multi-person respiration from entangled rf signals. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J. Tracking vital signs during sleep leveraging off-the-shelf wifi. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, Hangzhou, China, 22–25 June 2015; pp. 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Gu, T.; Xie, B. Human respiration detection with commodity wifi devices: Do user location and body orientation matter? In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, New York, NY, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Fu, S.; Yan, J.; Liang, H.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, S.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, N. Gait recognition for co-existing multiple people using millimeter wave sensing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Pathak, P.H.; Zeng, Y.; Liran, X.; Mohapatra, P. Monitoring vital signs using millimeter wave. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Symposium on Mobile ad hoc Networking and Computing, Paderborn, Germany, 5–8 July 2016; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gu, T.; Li, W.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D. DF-Sense: Multi-user Acoustic Sensing for Heartbeat Monitoring with Dualforming. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, Helsinki, Finland, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Nguyen, D.; Sridhar, A.R.; Gollakota, S. Using smart speakers to contactlessly monitor heart rhythms. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Jin, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, D. Your Smart Speaker Can “Hear” Your Heartbeat! Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2020, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Wu, C.; Xiao, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. Acousticcardiogram: Monitoring heartbeats using acoustic signals on smart devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2018—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 1574–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Sun, K.; Zhang, F.; Gu, T.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D. LoEar: Push the Range Limit of Acoustic Sensing for Vital Sign Monitoring. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UMA-8-SP USB mic Array. Available online: https://www.minidsp.com/products/usb-audio-interface/uma-8-sp-detail (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Amazon Echo Dot Smartspeaker. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/All-New-Amazon-Echo-Dot-Add-Alexa-To-Any-Room/dp/B01DFKC2SO (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Jin, B. Exploiting Passive Beamforming of Smart Speakers to Monitor Human Heartbeat in Real Time. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 7–11 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, S.A.; Irvine, J.M.; Cheng, A.; Wiederhold, M.D.; Wiederhold, B.K. ECG to identify individuals. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, C.; Tai, C. Detection of ECG characteristic points using wavelet transforms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M.; Vanello, N.; Galperti, G.; Greco, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Assessing the quality of heart rate variability estimated from wrist and finger ppg: A novel approach based on cross-mapping method. Sensors 2020, 20, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temko, A. Accurate heart rate monitoring during physical exercises using PPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.I.; Zhang, D.; Yan, T.; Fang, D. LungTrack: Towards contactless and zero dead-zone respiration monitoring with commodity RFIDs. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2019, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, S.; Elmer, T.W.; Cox, N.M.; Gopalsami, N.; Raptis, A.C.; Liao, S.; Mikhelson, I.; Sahakian, A.V. Compact millimeter-wave sensor for remote monitoring of vital signs. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 61, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.R.; Kuo, H.C.; Lin, F.L.; Huang, T.H.; Kuo, C.S.; Ou, Y.W. 60-GHz millimeter-wave life detection system (MLDS) for noncontact human vital-signal monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 12, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.Y.J.; Lin, J. Vital sign detection using 60-GHz Doppler radar system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Beijing, China, 14–18 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xie, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Bu, Y.; Lu, S. Rf-ecg: Heart rate variability assessment based on cots rfid tag array. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, R.; Gollakota, S.; Watson, N. Contactless sleep apnea detection on smartphones. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, T.; Zhou, X.; Dorizzi, B. C-FMCW based contactless respiration detection using acoustic signal. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 1, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, K. Beepbeep: A high accuracy acoustic ranging system using cots mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Sydney, Australia, 6–9 November 2007; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Gollakota, S. Millisonic: Pushing the limits of acoustic motion tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bachorowski, J.A.; Smoski, M.J.; Owren, M.J. The acoustic features of human laughter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.S.; Huertas, A.; Medioni, G. Fast convolution with Laplacian-of-Gaussian masks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-9, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.; Litva, J. MUSIC and maximum likelihood techniques on two-dimensional DOA estimation with uniform circular array. IEEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1995, 142, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polar H10 Heart Rate Sensor. Available online: https://www.polar.com/sg-en/sensors/h10-heart-rate-sensor/ (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Pulse Rate. Available online: https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/ask-the-experts/pulse-rate (accessed on 4 January 2024).




















| Study | Median Error (bpm) | Multiple Sensing | Separation | Distance (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15] | 0.6 | No | Not applicable | 0.3 |
| [14] | 0.75 | No | Not applicable | 0.2 |
| [19] | 0.6 | No | Not applicable | 0.6 |
| [13] | 1 | No | Not applicable | 0.4–0.6 |
| [16] | 0.8 | Yes | 40 cm and 10° | 3 |
| [12] | 1.18 | Yes | 50 cm | 3 |
| Our approach | 0.9 | Yes | Not required | 3 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Chirp frequency | 18 kHz to 23 kHz |
| Bandwidth | 5 kHz |
| Chirp length | 0.04 s |
| Maximum tracking distance | m |
| Sampling rate | 48 kHz |
| Sound pressure | 45 dB(A) at 0.3 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, T.; Ma, D.; Balan, R. Remote Multi-Person Heart Rate Monitoring with Smart Speakers: Overcoming Separation Constraint. Sensors 2024, 24, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020382
Tran T, Ma D, Balan R. Remote Multi-Person Heart Rate Monitoring with Smart Speakers: Overcoming Separation Constraint. Sensors. 2024; 24(2):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020382
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Thu, Dong Ma, and Rajesh Balan. 2024. "Remote Multi-Person Heart Rate Monitoring with Smart Speakers: Overcoming Separation Constraint" Sensors 24, no. 2: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020382
APA StyleTran, T., Ma, D., & Balan, R. (2024). Remote Multi-Person Heart Rate Monitoring with Smart Speakers: Overcoming Separation Constraint. Sensors, 24(2), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020382







