Dense 3D Point Cloud Environmental Mapping Using Millimeter-Wave Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A method for constructing three-dimensional environmental maps using millimeter-wave radar aimed at scene reconstruction is proposed, generating high-density three-dimensional environmental point clouds comparable to those of multi-line LiDAR.
- A framework for semantic SLAM using millimeter-wave radar is proposed. On the one hand, it optimizes the point cloud density of SLAM environmental maps through semantic information learning. On the other hand, SLAM assists in enhancing the effectiveness of semantic deep learning training.
- Experiments across various scenarios were conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed methods in improving resolution, increasing point cloud density, and suppressing noise and interference.
2. Related Work
- In terms of algorithm practicality, existing methods are predominantly limited to reconstructing three-dimensional representations of specific targets and small indoor scenes, failing to meet the demands of larger outdoor environments.
- In terms of algorithm robustness, current methods struggle to adapt to the dynamic requirements of environmental mapping in real-time scenarios. Present deep learning networks typically operate with two types of inputs: one based on radar heatmaps, which suffer from sparsity and often fail to capture all details of a scene using a single heatmap, and the other based on sequences of radar heatmaps, which necessitate slow and consistent radar platform movement, thus precluding the accommodation of non-uniform platform motion.
- In terms of algorithm scalability, traditional signal processing methods and deep learning approaches have predominantly been pursued independently in most studies. Traditional methods rely on engineering expertise for design, whereas deep learning methods heavily rely on extensive datasets for performance enhancement. Each approach has its strengths, and combining the two could potentially yield superior performance and effectiveness.
3. Methodology
3.1. Method Pipeline
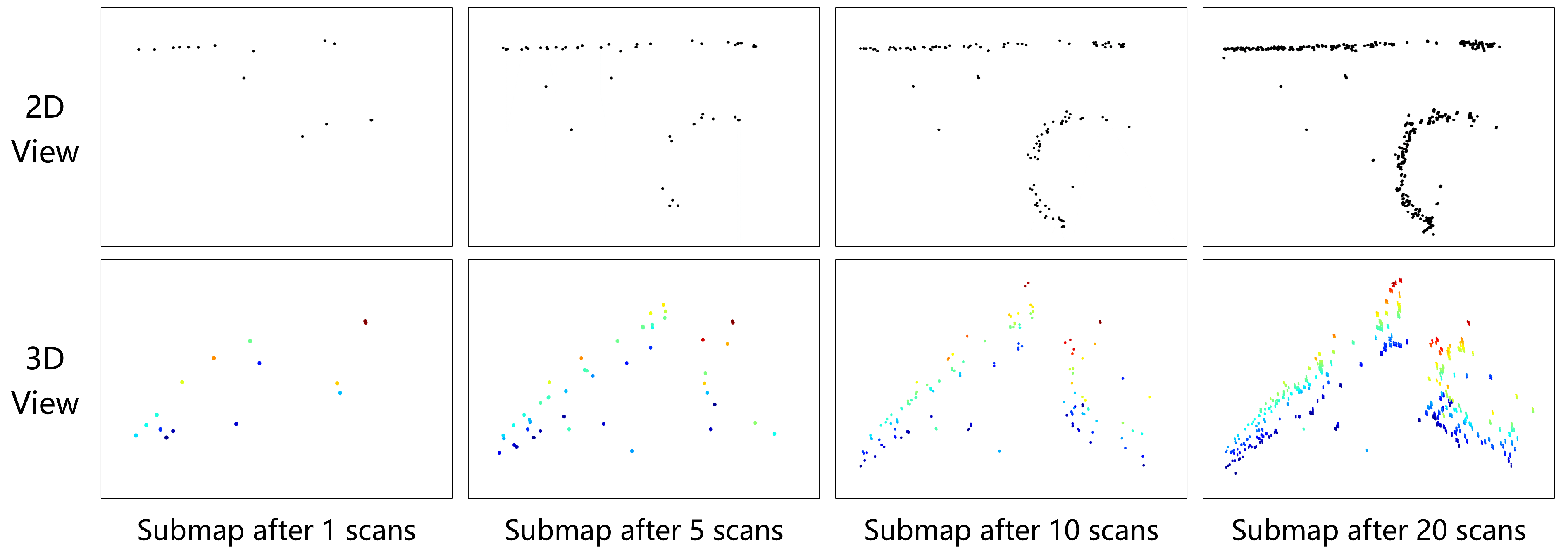
3.2. Radar Submap Generation
3.3. Depth Image Representation of Point Clouds
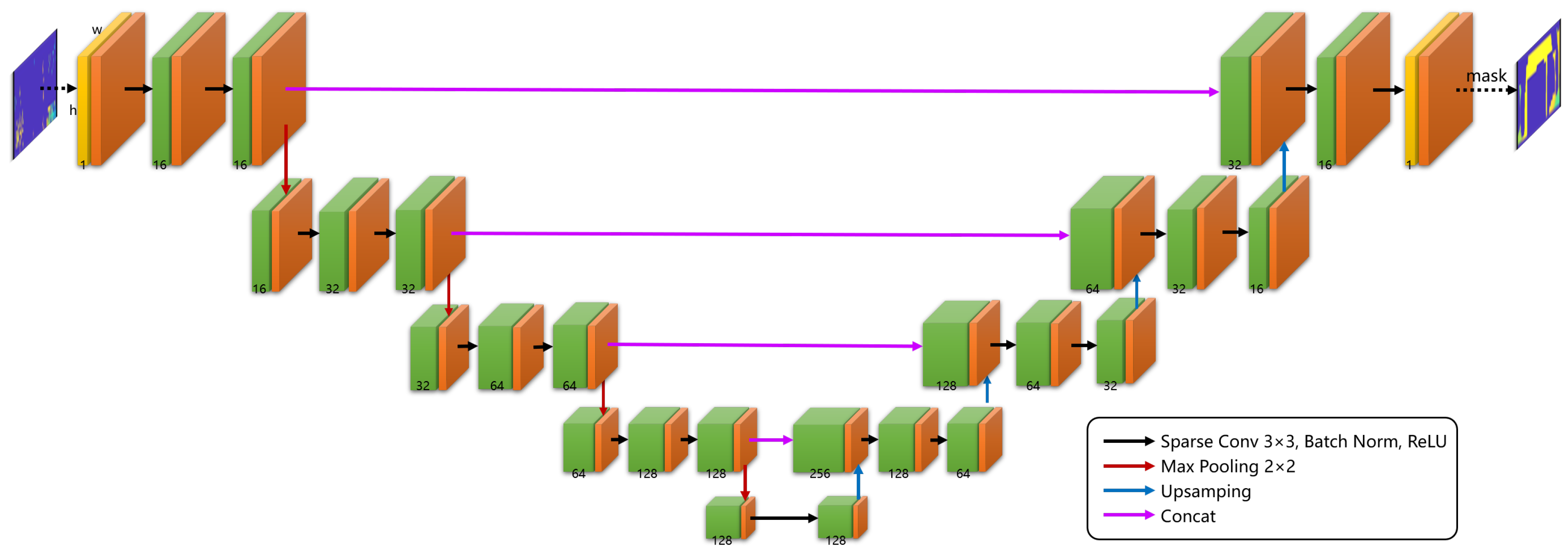
3.4. The 3D-RadarHR Network
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Performance Analysis
4.3.1. Performance Comparison in Variable-Speed Motion Applications
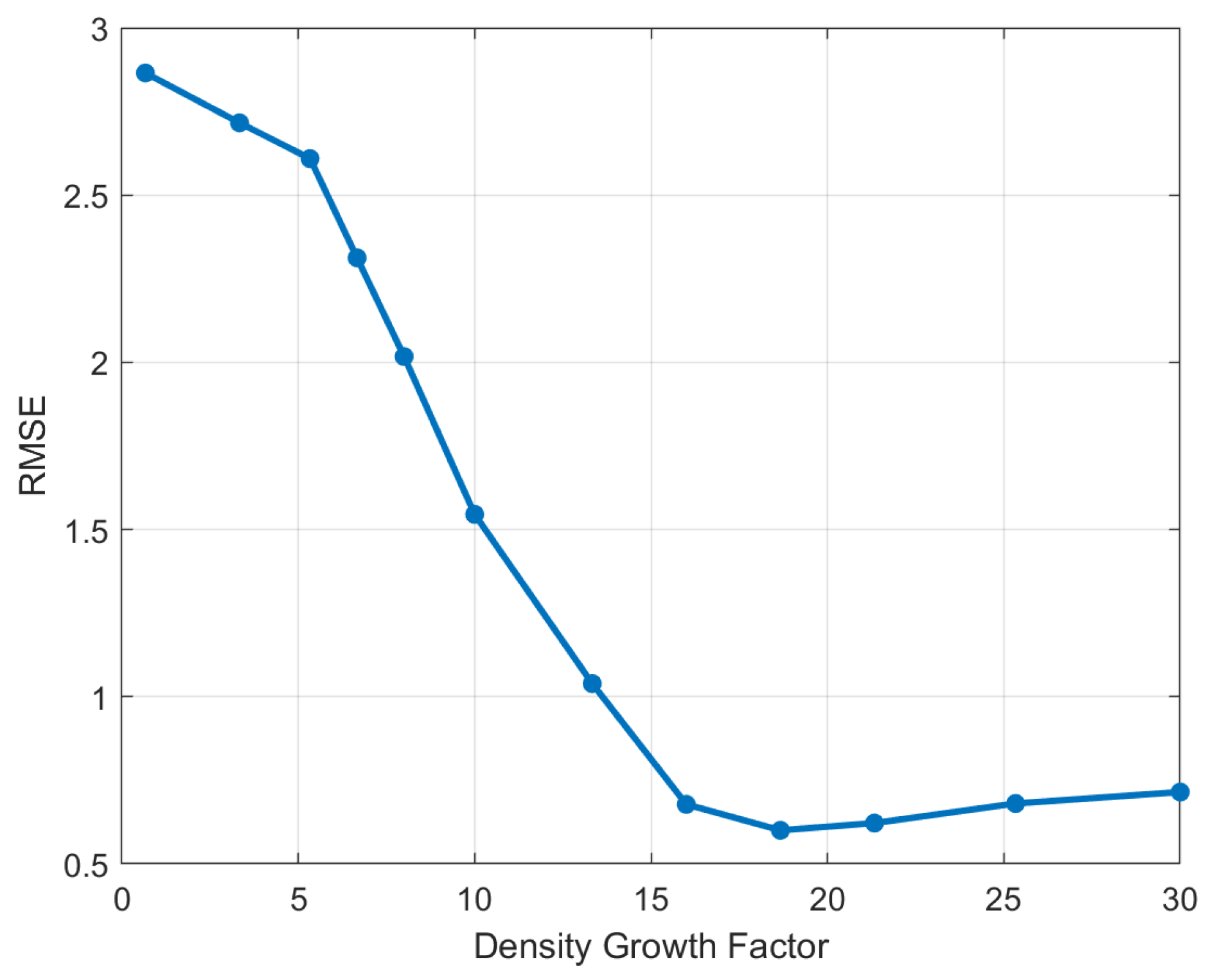
4.3.2. Impact of Radar Submap on 3D-RadarHR Network Reconstruction Errors
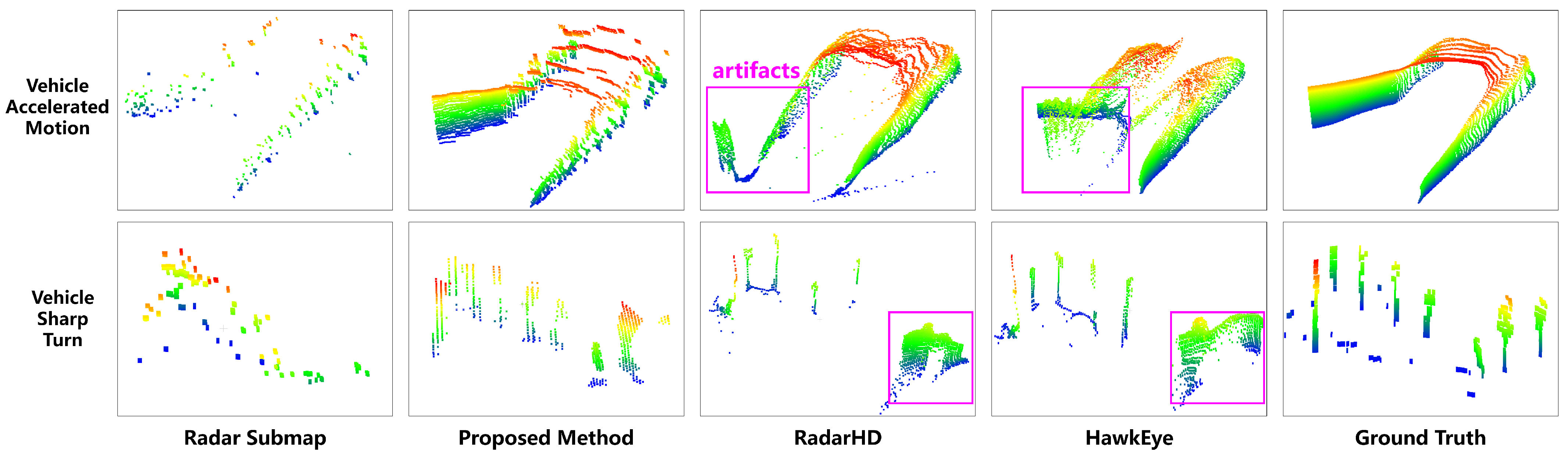
4.4. Mapping Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yurtsever, E.; Lambert, J.; Carballo, A.; Takeda, K. A survey of autonomous driving: Common practices and emerging technologies. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58443–58469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placitelli, A.P.; Gallo, L. Low-cost augmented reality systems via 3D point cloud sensors. In Proceedings of the 2011 Seventh International Conference Signal Image Technology Internet-Based System, Dijon, France, 28 November–1 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Patole, S.M.; Torlak, M.; Wang, D.; Ali, M. Automotive Radars: A review of signal processing techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34.2, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowok, S.; Kueppers, S.; Cetinkaya, H.; Schroeder, M.; Herschel, R. Millimeter wave radar for high resolution 3D near field imaging for robotics and security scans. In Proceedings of the International Radar Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 28–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, S.H.; Newman, P. Radar-only ego-motion estimation in difficult settings via graph matching. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ziyang, H.; Yvan, P.; Sen, W. RadarSLAM: Radar based Large-Scale SLAM in All Weathers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barjenbruch, M.; Kellner, D.; Klappstein, J.; Dickmann, J.; Dietmayer, K. Joint spatial- and Doppler-based ego-motion estimation for automotive radars. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 28 June–1 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hügler, P.; Grebner, T.; Knill, C.; Waldschmidt, C. UAV-borne 2-D and 3-D radar-based grid mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Dang, X.; Li, Y.; Bu, X.; Liang, X. Angular Super-Resolution Radar SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Almalioglu, Y.; Turan, M.; Lu, C.X.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Milli-RIO: Ego-motion estimation with low-cost millimetre-wave radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, B.; Huai, J.; Li, M. 4D iRIOM: 4D Imaging Radar Inertial Odometry and Mapping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 3246–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isele, S.T.; Fabian, H.F.; Marius, Z. SERALOC: SLAM on semantically annotated radar point-clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021.
- Sun, S.Q.; Athina, P.P.; Vincent, H.P. MIMO radar for advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous driving: Advantages and challenges. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37.4, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tan, B.; Li, S.; Long, K.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Wan, M.; et al. TJ4DRadSet: A 4D Radar Dataset for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Liang, X.D.; Dang, X.W.; Li, Y.L. Joint Velocity Ambiguity Resolution and Ego-Motion Estimation Method for mmWave Radar. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4753–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Timo, G.; Christian, W. Chirp-sequence-based imaging using a network of distributed single-channel radar sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Detroit, MI, USA, 15–16 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliaferri, D.; Rizzi, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Nicoli, M.; Russo, I.; Mazzucco, C.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.V.; Prati, C.M.; Spagnolini, U. Cooperative synthetic aperture radar in an urban connected car scenario. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications and Sensing (JCAS), Dresden, Germany, 23–24 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. 3D point cloud generation with millimeter-wave radar. ACM Interactive Mobile Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2020, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, D.; Rizzi, M.; Nicoli, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Russo, I.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.V.; Prati, C.M.; Spagnolini, U. Navigation-aided automotive sar for high-resolution imaging of driving environments. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 35599–35615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.F.; Madani, S.; Jog, S.; Gupta, S.; Hassanieh, H. Through fog high-resolution imaging using millimeter wave radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Xu, D. 3DRIMR: 3D reconstruction and imaging via mmWave radar based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Performance, Computing, and Communications Conference (IPCCC), Austin, TX, USA, 28–30 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, B. DeepPoint: A Deep Learning Model for 3D Reconstruction in Point Clouds via mmWave Radar. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.09188. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, B. R2p: A deep learning model from mmwave radar to point cloud. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN: International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Bristol, UK, 6–9 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.C.; Bastian, G.; Carsten, A. L2R GAN: LiDAR-to-radar translation. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.X.; Rosa, S.; Zhao, P.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Stankovic, J.A.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. See through smoke: Robust indoor mapping with low-cost mmwave radar. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakara, A.; Jin, T.; Das, A.; Bhatt, G.; Kumari, L.; Soltanaghai, E.; Bilmes, J.; Kumar, S.; Rowe, A. High Resolution Point Clouds from mmWave Radar. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.09273. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, P.P.; Sanjib, S. MilliPCD: Beyond Traditional Vision Indoor Point Cloud Generation via Handheld Millimeter-Wave Devices. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, Cancún, Mexico, 8–12 October 2023; Volume 6, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.Q.; Feger, R.; Wagner, T.; Stelzer, A. High Angular Resolution Method Based on Deep Learning for FMCW MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 5413–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.; Harakeh, A.; Waslander, S.L. In Defense of Classical Image Processing: Fast Depth Completion on the CPU. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), Toronto, ON, Canada, 8–10 May 2018; pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrig, J.; Schneider, N.; Schneider, L.; Franke, U.; Brox, T.; Geiger, A. Sparsity Invariant CNNs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Bao, C.; Ozay, M.; Fan, C.; Gao, Q.; Liu, H.; Lam, T.L. Deep Depth Completion From Extremely Sparse Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 8244–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Radar Frame | Radar Submap | Traditional ISP [29] | Sparsity Invariant CNN [30] | RadarHD [26] | HawkEye [20] | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Env. 1 | 1.5019 | 0.3935 | 0.2831 | 0.1494 | 0.1218 | 0.0968 | 0.1001 |
| Env. 2 | 2.2103 | 0.4033 | 0.2928 | 0.1392 | 0.1163 | 0.0908 | 0.1017 |
| Env. 3 | 1.0647 | 0.2636 | 0.1667 | 0.1340 | 0.0576 | 0.0388 | 0.0386 |
| Env. 4 | 2.2139 | 0.4029 | 0.2934 | 0.1901 | 0.0843 | 0.0476 | 0.0521 |
| Env. 5 | 1.8179 | 0.3299 | 0.2380 | 0.1548 | 0.0841 | 0.0576 | 0.0608 |
| Env. 6 | 2.2416 | 0.4410 | 0.3377 | 0.2501 | 0.0981 | 0.0754 | 0.0855 |
| Env. 7 | 1.9793 | 0.4719 | 0.3631 | 0.2155 | 0.1212 | 0.0489 | 0.0670 |
| Radar Frame | Radar Submap | Traditional ISP [29] | Sparsity Invariant CNN [30] | RadarHD [26] | HawkEye [20] | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Env. 1 | 2.2706 | 0.4641 | 0.3535 | 0.2133 | 0.1904 | 0.1827 | 0.1889 |
| Env. 2 | 2.2774 | 0.4725 | 0.3626 | 0.2141 | 0.1925 | 0.1713 | 0.1887 |
| Env. 3 | 1.8635 | 0.3617 | 0.2490 | 0.2235 | 0.1625 | 0.1489 | 0.1431 |
| Env. 4 | 2.4428 | 0.5329 | 0.4211 | 0.2805 | 0.1983 | 0.1467 | 0.1472 |
| Env. 5 | 2.3851 | 0.4982 | 0.3075 | 0.2273 | 0.1463 | 0.1330 | 0.1367 |
| Env. 6 | 2.6640 | 0.5612 | 0.4534 | 0.3308 | 0.2223 | 0.1915 | 0.2038 |
| Env. 7 | 2.6307 | 0.5255 | 0.4174 | 0.2825 | 0.2017 | 0.1249 | 0.1277 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Z.; Wen, J.; Luo, J.; Ding, G.; Geng, X. Dense 3D Point Cloud Environmental Mapping Using Millimeter-Wave Radar. Sensors 2024, 24, 6569. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206569
Zeng Z, Wen J, Luo J, Ding G, Geng X. Dense 3D Point Cloud Environmental Mapping Using Millimeter-Wave Radar. Sensors. 2024; 24(20):6569. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206569
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Zhiyuan, Jie Wen, Jianan Luo, Gege Ding, and Xiongfei Geng. 2024. "Dense 3D Point Cloud Environmental Mapping Using Millimeter-Wave Radar" Sensors 24, no. 20: 6569. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206569
APA StyleZeng, Z., Wen, J., Luo, J., Ding, G., & Geng, X. (2024). Dense 3D Point Cloud Environmental Mapping Using Millimeter-Wave Radar. Sensors, 24(20), 6569. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206569






