Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Can Detect Dynamic Imbalance in Subjects with Episodic Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
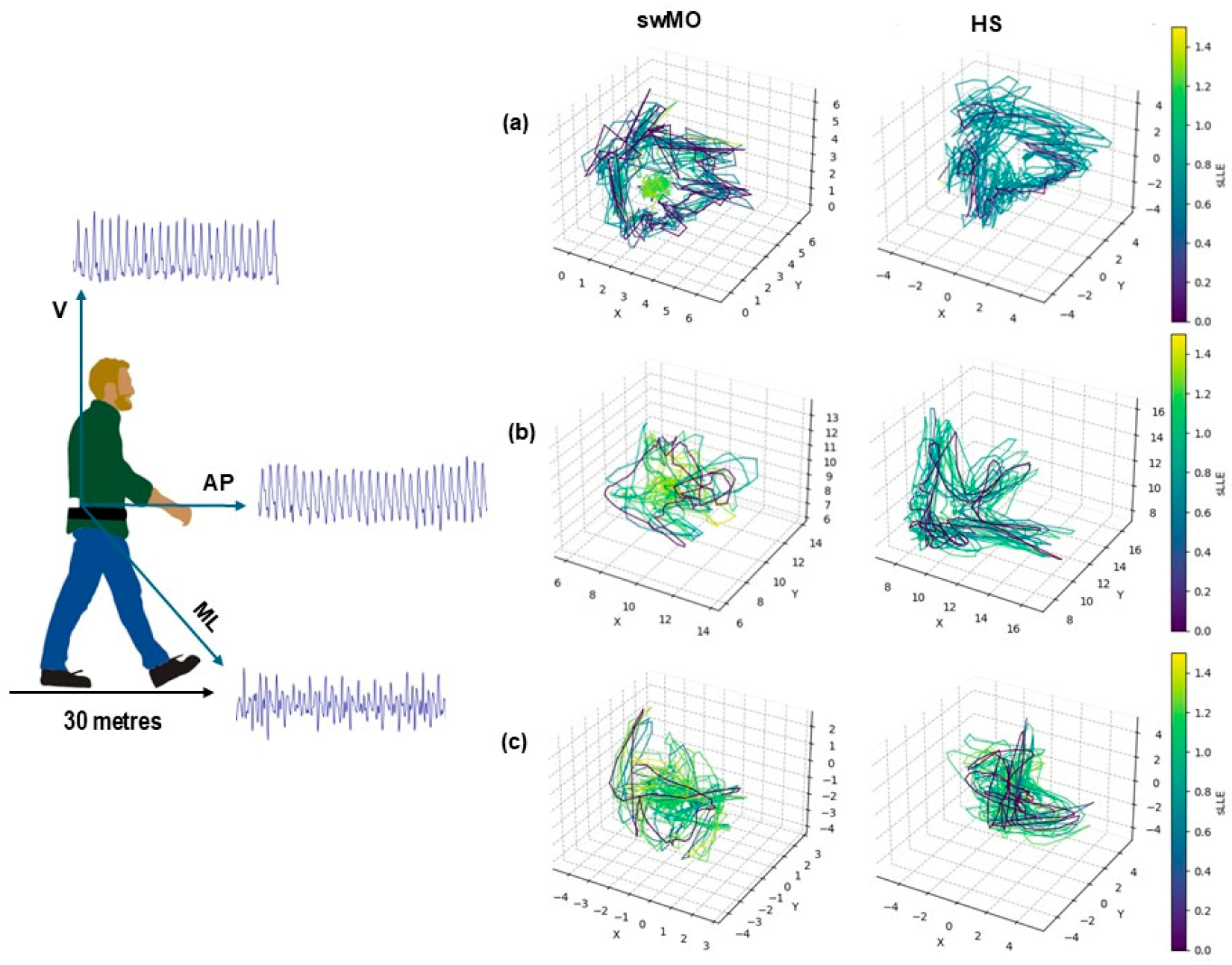
2.3. sLLE Calculations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
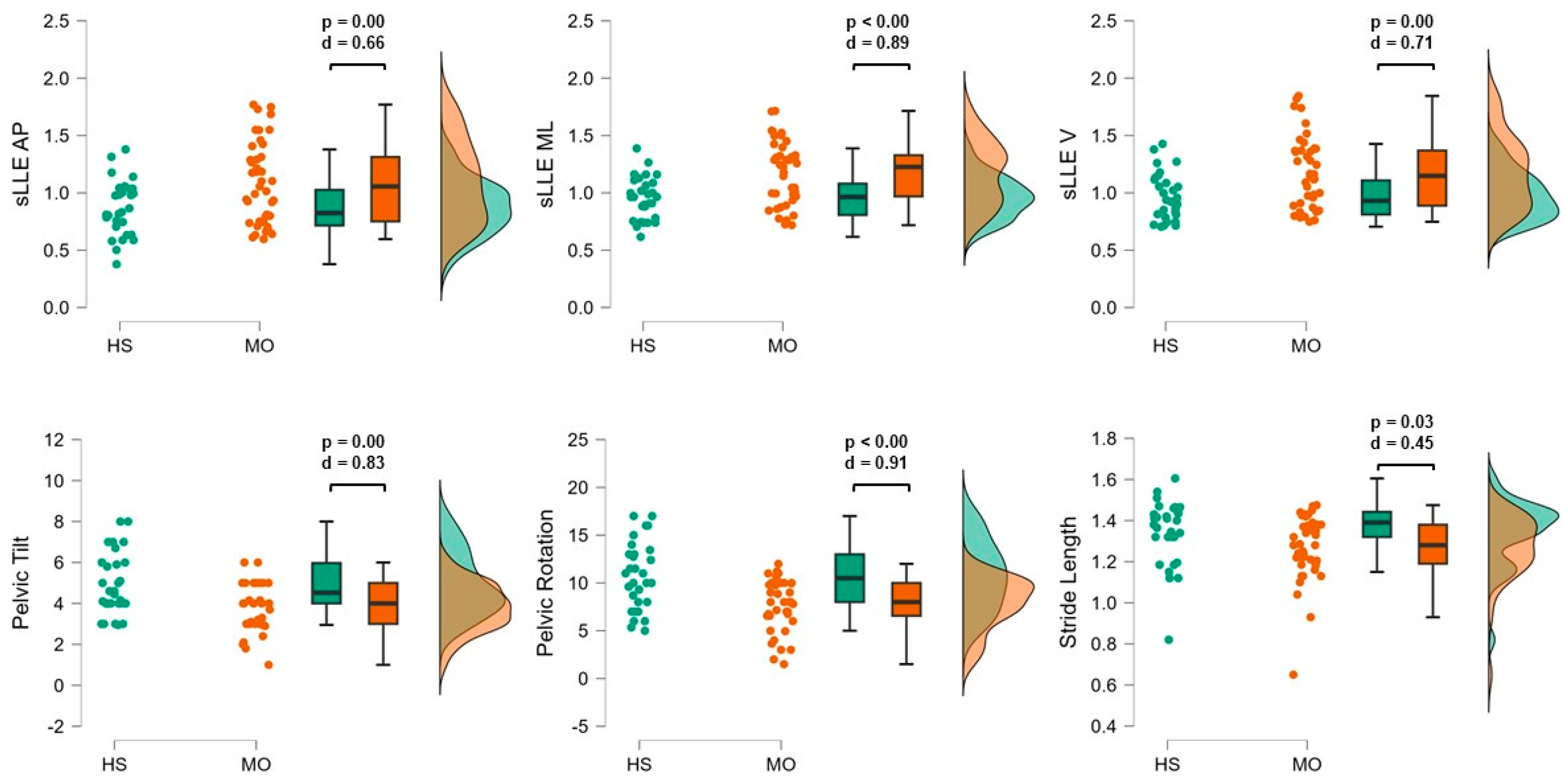
Trunk Acceleration-Derived Gait Indexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furman, J.M.; Marcus, D.A. Migraine and Motion Sensitivity. Continuum 2012, 18, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisdorff, A. Migraine and Dizziness. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014, 27, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastianelli, G.; Abagnale, C.; Casillo, F.; Cioffi, E.; Parisi, V.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Serrao, M.; Porcaro, C.; Schoenen, J.; Coppola, G. Bimodal Sensory Integration in Migraine: A Study of the Effect of Visual Stimulation on Somatosensory Evoked Cortical Responses. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puledda, F.; Viganò, A.; Sebastianelli, G.; Parisi, V.; Hsiao, F.J.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, W.T.; Massimini, M.; Coppola, G. Electrophysiological Findings in Migraine May Reflect Abnormal Synaptic Plasticity Mechanisms: A Narrative Review. Cephalalgia 2023, 43, 03331024231195780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, G.; Straumann, D. Moving in a Moving World: A Review on Vestibular Motion Sickness. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.K.; Park, C.H.; Lee, J.H. Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Migrainous Vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 144, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, J.; May, A. Functional and Structural Alterations in the Migraine Cerebellum. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdin, L.; Chamberlain, F.; Cheema, S.; Arshad, Q.; Gresty, M.A.; Golding, J.F.; Bronstein, A. Motion Sickness in Migraine and Vestibular Disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, T.; Arshad, Q.; Seemungal, B.M. Vestibular Deficits in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Balance, Dizziness, and Spatial Disorientation. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.F.; Becnel, A.R.; Miske, C.; Szikszay, T.M.; Adamczyk, W.M.; Luedtke, K. Postural Control Impairment in Patients with Headaches-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Headache 2022, 62, 241–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.F.; Bonato, P.; Florencio, L.L.; Pinheiro, C.F.; Dach, F.; Bigal, M.E.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Balance Impairments in Different Subgroups of Patients with Migraine. Headache 2017, 57, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.F.; Chaves, T.C.; Dach, F.; Pinheiro, C.F.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Florencio, L.L.; Ferreira, K.S.; Bigal, M.E.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Influence of Migraine and of Migraine Aura on Balance and Mobility—A Controlled Study. Headache 2013, 53, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumanlidag, S.; Milanlioglu, A. Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance Measurements among Chronic and Episodic Migraine Patients. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2021, 79, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.F.; Florencio, L.L.; Pinheiro, C.F.; Dach, F.; Bigal, M.E.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Functional Balance Deterioration on Daily Activities in Patients with Migraine: A Controlled Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdal, G.; Balci, B.D.; Angin, S.; Öztürk, V.; Halmagyi, G.M. A Longitudinal Study of Balance in Migraineurs. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manto, M.; Serrao, M.; Filippo Castiglia, S.; Timmann, D.; Tzvi-Minker, E.; Pan, M.K.; Kuo, S.H.; Ugawa, Y. Neurophysiology of Cerebellar Ataxias and Gait Disorders. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2023, 8, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, M.; Ranavolo, A.; Casali, C. Neurophysiology of Gait. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 154, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Horak, F.B. The Relevance of Clinical Balance Assessment Tools to Differentiate Balance Deficits. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 239. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglia, S.F.; Tatarelli, A.; Trabassi, D.; De Icco, R.; Grillo, V.; Ranavolo, A.; Varrecchia, T.; Magnifica, F.; Di Lenola, D.; Coppola, G.; et al. Ability of a Set of Trunk Inertial Indexes of Gait to Identify Gait Instability and Recurrent Fallers in Parkinson’s Disease. Sensors 2021, 21, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofré Lizama, L.E.; Strik, M.; Van der Walt, A.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Kolbe, S.C.; Galea, M.P. Gait Stability Reflects Motor Tracts Damage at Early Stages of Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronni, A.; Gervasoni, E.; Ferrarin, M.; Anastasi, D.; Brichetto, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Giovanni, R.; Di Prosperini, L.; Tacchino, A.; Solaro, C.; et al. Local Dynamic Stability of Gait in People with Early Multiple Sclerosis and No-to-Mild Neurological Impairment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chini, G.; Ranavolo, A.; Draicchio, F.; Casali, C.; Conte, C.; Martino, G.; Leonardi, L.; Padua, L.; Coppola, G.; Pierelli, F.; et al. Local Stability of the Trunk in Patients with Degenerative Cerebellar Ataxia During Walking. Cerebellum 2017, 16, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirpourabasi, A.; Lamb, S.E.; Chow, J.Y.; Williams, G.K.R. Nonlinear Dynamic Measures of Walking in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Scoping Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh, S. The Largest Lyapunov Exponent of Gait in Young and Elderly Individuals: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.; Bes, A.; Kunkel, R.; Lance, J.W.; Nappi, G.; Pfaffenrath, V.; Rose, F.C.; Schoenberg, B.S.; Soyka, D.; Tfelt-Hansen, P.; et al. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition (Beta Version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.F.; Lipton, R.B.; Dowson, A.J.; Sawyer, J. Development and Testing of the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) Questionnaire to Assess Headache-Related Disability. Neurology 2001, 56, S20–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Sung, H.K.; Kwon, N.Y.; Go, H.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Shin, S.M.; Lee, S. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Migraine Headache: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2021, 58, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E.; Ashina, S.; Burstein, R.; Silberstein, S.; Reed, M.L.; Serrano, D.; Stewart, W.F. Cutaneous Allodynia in the Migraine Population. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.I.; Wang, X.; Speicher, P.J.; Hwang, E.S.; Cheng, P.; Harpole, D.H.; Berry, M.F.; Schrag, D.; Pang, H.H. Reporting and Guidelines in Propensity Score Analysis: A Systematic Review of Cancer and Cancer Surgical Studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneberg, D.; Elshehabi, M.; Meyer, A.C.; Otte, K.; Doss, S.; Paul, F.; Nussbaum, S.; Berg, D.; Kühn, A.A.; Maetzler, W.; et al. Less Is More—Estimation of the Number of Strides Required to Assess Gait Variability in Spatially Confined Settings. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabassi, D.; Castiglia, S.F.; Bini, F.; Marinozzi, F.; Ajoudani, A.; Lorenzini, M.; Chini, G.; Varrecchia, T.; Ranavolo, A.; De Icco, R.; et al. Optimizing Rare Disease Gait Classification through Data Balancing and Generative AI: Insights from Hereditary Cerebellar Ataxia. Sensors 2024, 24, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, F.; Bisi, M.C.; Stagni, R. Gait Variability and Stability Measures: Minimum Number of Strides and within-Session Reliability. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 50, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekizos, A.; Santuz, A.; Schroll, A.; Arampatzis, A. The Maximum Lyapunov Exponent During Walking and Running: Reliability Assessment of Different Marker-Sets. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijn, S.M.; Meijer, O.G.; Beek, P.J.; Van Dieen, J.H. Assessing the Stability of Human Locomotion: A Review of Current Measures. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffalt, P.C.; Kent, J.A.; Wurdeman, S.R.; Stergiou, N. Selection Procedures for the Largest Lyapunov Exponent in Gait Biomechanics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallat, R. Pingouin: Statistics in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine: Epidemiology, Burden, and Comorbidity. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.F.; Luedtke, K.; Pinheiro, C.F.; Moraes, R.; Lemos, T.W.; Carneiro, C.G.; Bigal, M.E.; Dach, F.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Migraine and Balance Impairment: Influence of Subdiagnosis, Otoneurological Function, Falls, and Psychosocial Factors. Headache 2022, 62, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzin, L.; Carvalho, G.F.; Kreitewolf, J.; Teggi, R.; Pinheiro, C.F.; Moreira, J.R.; Dach, F.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Subdiagnosis, but Not Presence of Vestibular Symptoms, Predicts Balance Impairment in Migraine Patients—A Cross Sectional Study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, S.H. Postural Instability Induced by Visual Motion Stimuli in Patients with Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, L.P.; Silva, A.M.d.; Cusin, F.S.; Cesaroni, S.; Ganança, M.M.; Caovilla, H.H. Body Balance at Static Posturography in Vestibular Migraine. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 85, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, E.; Gerakoulis, S.; Voskou, P.; Kararizou, E. Postural Instability during Attacks of Migraine without Aura. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 319-e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Parisi, V.; Di Renzo, A.; Pierelli, F. Cortical Pain Processing in Migraine. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodato, M.; Granato, A.; Martini, M.; Buoite Stella, A.; Galmonte, A.; Murena, L.; Manganotti, P. Neurophysiological and Clinical Outcomes in Episodic Migraine Without Aura: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 41, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Guo, Y.; Yan, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, H. Altered Large-Scale Internetwork Functional Connectivity in Patients with Vestibular Migraine and Migraine without Aura. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 800, 137123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Kuang, C.; Huang, H.; Jiao, B.; Ma, L.; Lin, J. Altered Functional Brain Network Patterns in Patients with Migraine without Aura after Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abagnale, C.; Ranieri, F.; Di Renzo, A.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Lisicki, M.; Coppola, G.; Pierelli, F. Impaired Short-Term Visual Paired Associative Plasticity in Patients with Migraine between Attacks. Pain 2021, 162, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anarte-Lazo, E.; Carvalho, G.F.; Schwarz, A.; Luedtke, K.; Falla, D. Differentiating Migraine, Cervicogenic Headache and Asymptomatic Individuals Based on Physical Examination Findings: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglia, S.F.; Trabassi, D.; Conte, C.; Gioiosa, V.; Sebastianelli, G.; Abagnale, C.; Ranavolo, A.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Coppola, G.; Casali, C.; et al. Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Is Responsive to Rehabilitation in Subjects with Primary Degenerative Cerebellar Ataxia. Cerebellum 2024, 23, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MO (N = 47) | HS (N = 38) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age | 34.13 | 13.89 | 38.27 | 12.46 | |
| Sex | Females | 38 (81.25%) | 27 (71.79%) | ||
| Males | 9 (18.75%) | 11 (28.20%) | |||
| Disease duration (months) | 19.82 | 12.21 | |||
| N. migraine days/month | 5.64 | 4.63 | |||
| Duration of migraine attacks (hours) | 43.85 | 40.38 | |||
| Days since the last attack | 10.64 | 15.15 | |||
| N. acute medication doses/months | 6.78 | 6.30 | |||
| Medication types (%) | Triptans | 16.67% | |||
| Paracetamol | 8.33% | ||||
| NSAIDs | 75% | ||||
| MIDAS | 25.48 | 23.85 | |||
| HIT-6 | 62.15 | 7.23 | |||
| ASC 12 | 4.21 | 3.54 | |||
| Gait speed (m/s) | 1.16 | 0.17 | 1.21 | 0.15 | |
| Stance phase (% gait cycle) | 59.62 | 1.61 | 58.79 | 3.67 | |
| Swing phase (% gait cycle) | 40.80 | 2.94 | 40.62 | 1.45 | |
| Single support (% stance phase) | 40.48 | 1.54 | 40.33 | 1.55 | |
| Double support (% stance phase) | 9.62 | 1.60 | 9.39 | 1.44 | |
| Stride length (m) | 1.27 | 0.15 | 1.34 | 0.16 | |
| Cadence (steps/minute) | 108.86 | 5.97 | 111.27 | 8.64 | |
| Pelvic tilt (°) | 3.88 | 1.19 | 4.91 | 1.48 | |
| Pelvic obliquity (°) | 8.63 | 3.27 | 10.00 | 3.02 | |
| Pelvic rotation (°) | 7.60 | 2.45 | 10.54 | 3.60 | |
| sLLEAP | 1.08 | 0.35 | 0.88 | 0.23 | |
| sLLEML | 1.17 | 0.27 | 0.96 | 0.18 | |
| sLLEV | 1.16 | 0.31 | 0.98 | 0.19 | |
| AUC (95% CI) | OCP | LR+ | LR− | PTP + adj | PTP − adj | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sLLEAP | 0.68 (0.55; 0.78) | ≥1.10 | 3.36 | 0.61 | 31% | 8% |
| sLLEML | 0.73 (0.60; 0.82) | ≥1.18 | 20.32 | 0.47 | 73% | 6% |
| sLLEV | 0.65 (0.51; 0.76) | ≥1.09 | 2.12 | 0.59 | 22% | 7% |
| Pelvic tilt | 0.67 (0.52; 0.77) | ≤3.70 | 2.45 | 0.69 | 25% | 9% |
| Pelvic rotation | 0.71 (0.57; 0.82) | ≤11.50 | 17.07 | 0.63 | 70% | 8% |
| Stride length | 0.66 (0.50; 0.77) | ≤1.29 | 2.30 | 0.58 | 24% | 7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castiglia, S.F.; Sebastianelli, G.; Abagnale, C.; Casillo, F.; Trabassi, D.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Ziccardi, L.; Parisi, V.; Di Renzo, A.; De Icco, R.; et al. Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Can Detect Dynamic Imbalance in Subjects with Episodic Migraine. Sensors 2024, 24, 7627. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237627
Castiglia SF, Sebastianelli G, Abagnale C, Casillo F, Trabassi D, Di Lorenzo C, Ziccardi L, Parisi V, Di Renzo A, De Icco R, et al. Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Can Detect Dynamic Imbalance in Subjects with Episodic Migraine. Sensors. 2024; 24(23):7627. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237627
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastiglia, Stefano Filippo, Gabriele Sebastianelli, Chiara Abagnale, Francesco Casillo, Dante Trabassi, Cherubino Di Lorenzo, Lucia Ziccardi, Vincenzo Parisi, Antonio Di Renzo, Roberto De Icco, and et al. 2024. "Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Can Detect Dynamic Imbalance in Subjects with Episodic Migraine" Sensors 24, no. 23: 7627. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237627
APA StyleCastiglia, S. F., Sebastianelli, G., Abagnale, C., Casillo, F., Trabassi, D., Di Lorenzo, C., Ziccardi, L., Parisi, V., Di Renzo, A., De Icco, R., Tassorelli, C., Serrao, M., & Coppola, G. (2024). Local Dynamic Stability of Trunk During Gait Can Detect Dynamic Imbalance in Subjects with Episodic Migraine. Sensors, 24(23), 7627. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237627










