PET Foils Functionalized with Reactive Copolymers as Adaptable Microvolume ELISA Spot Array Platforms for Multiplex Serological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Polymer-Coated PET Foils
2.2. Protein Immobilization on PET
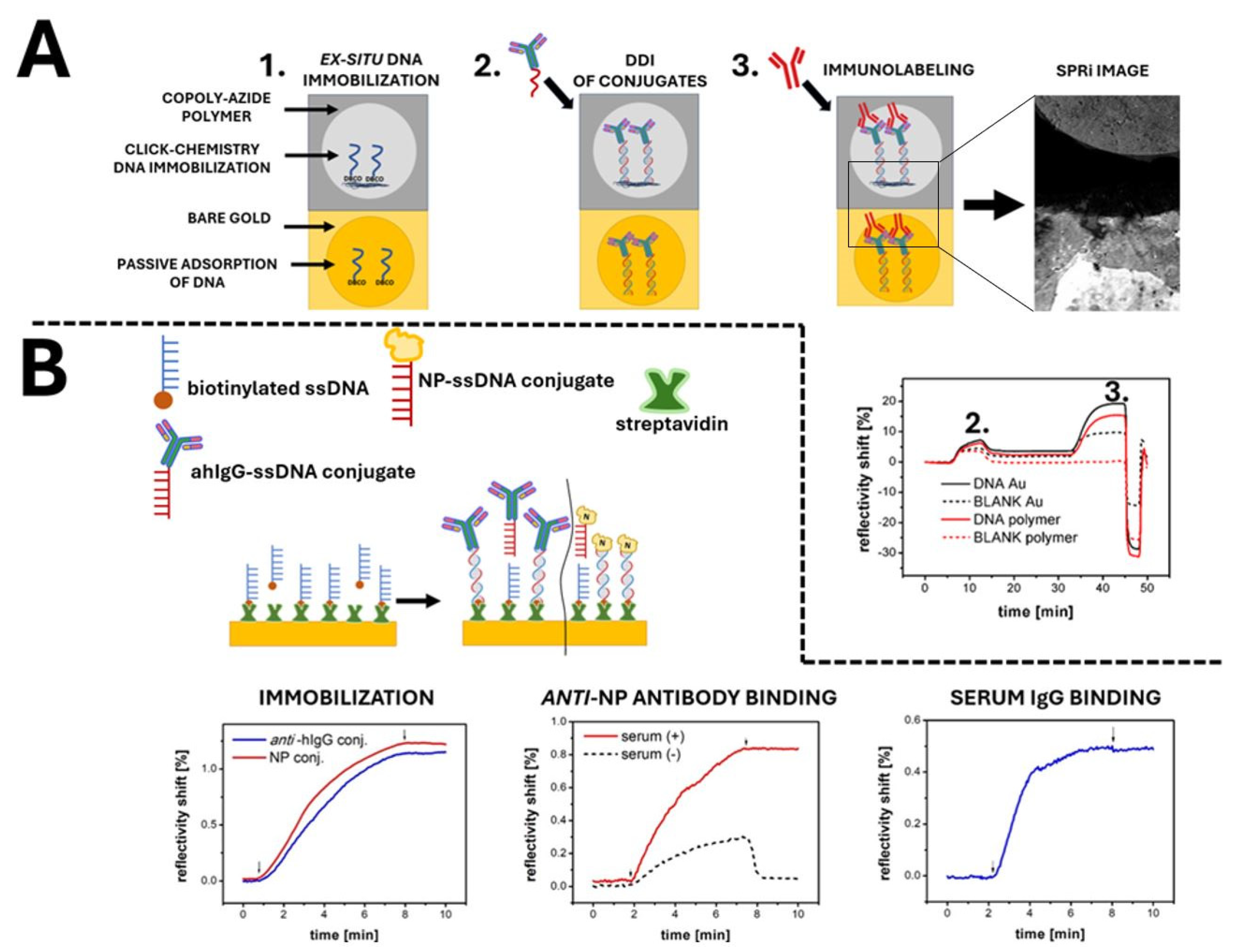
2.3. ELISA-like Assays on PET Foils
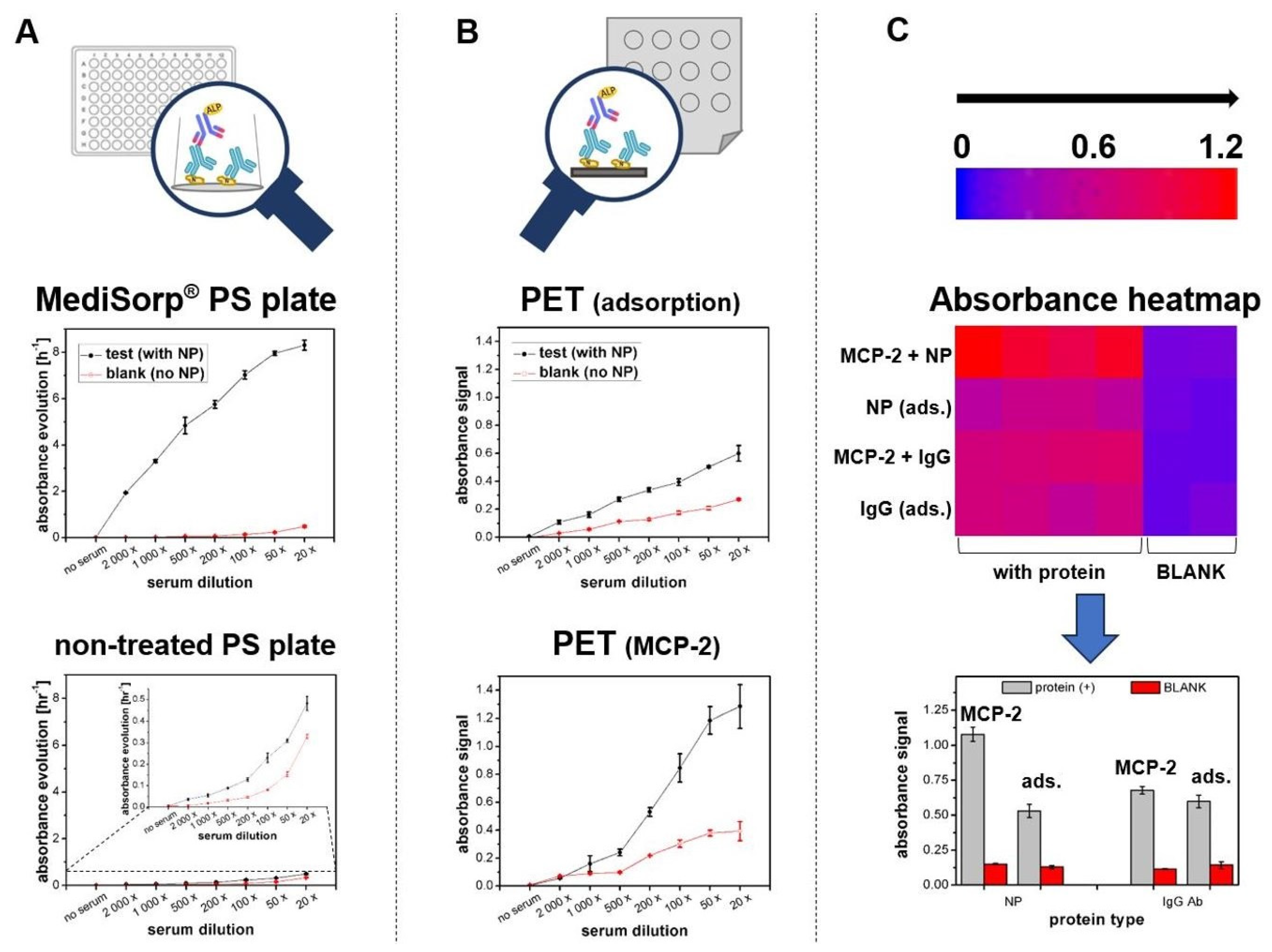
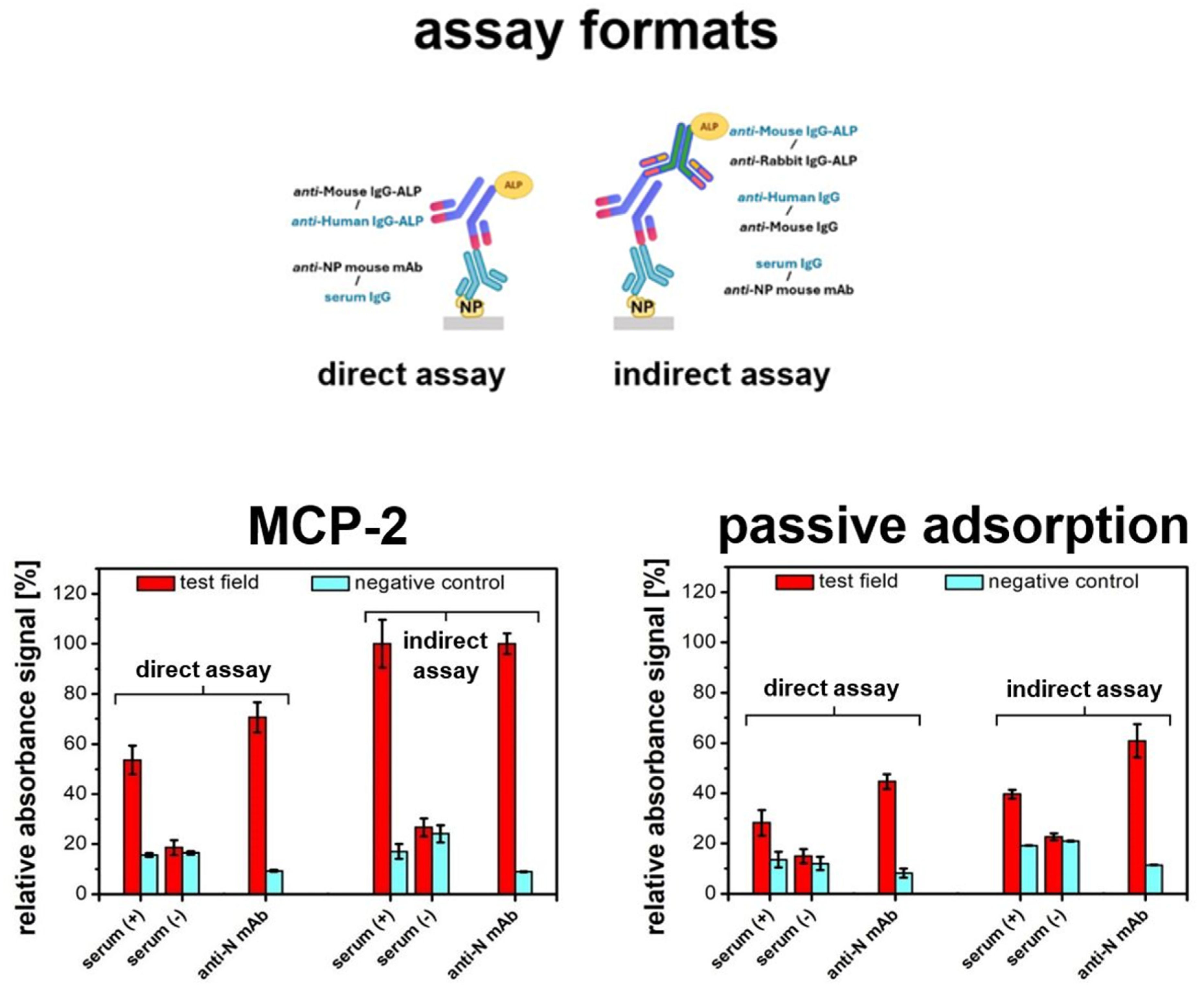
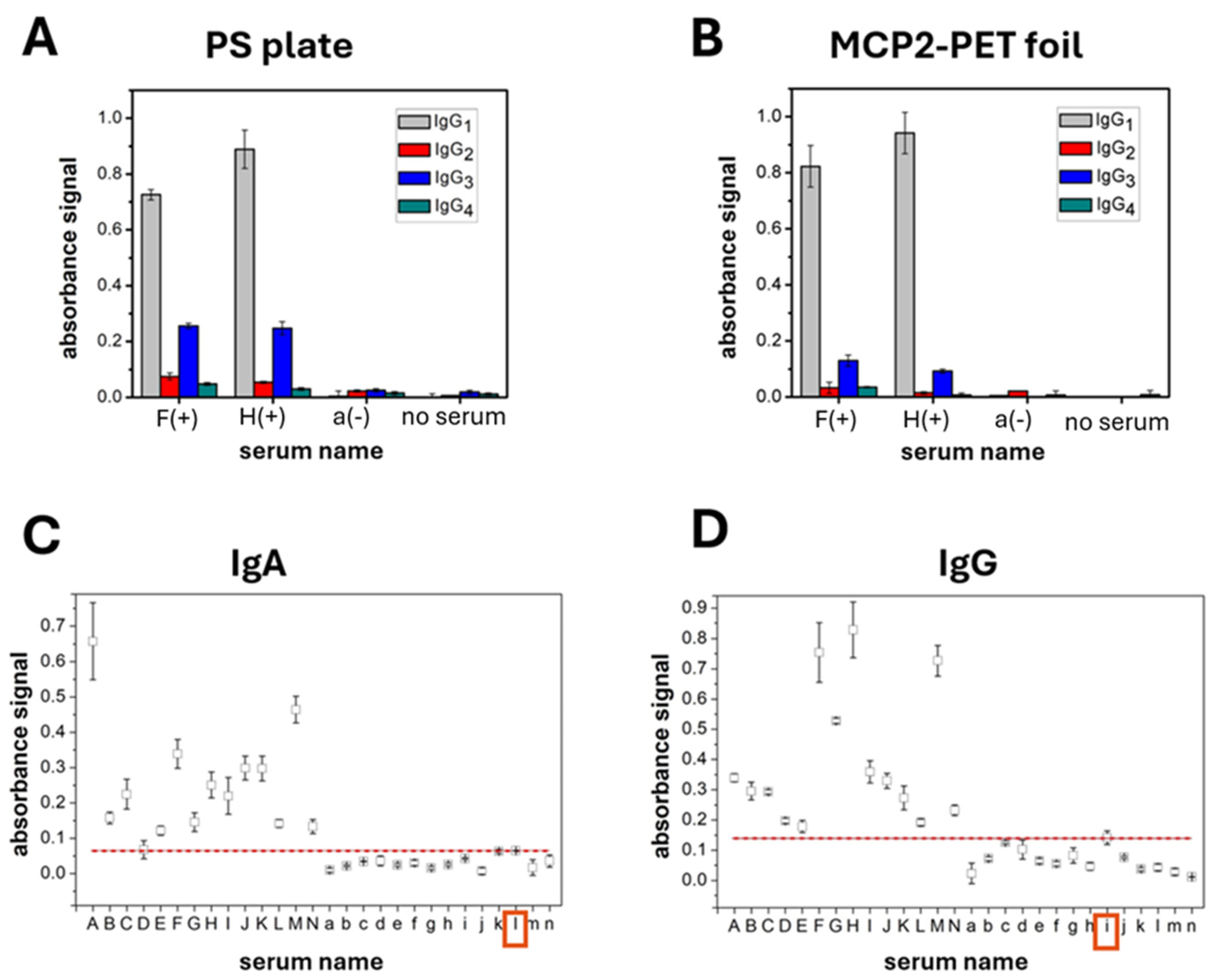
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rai, G.; Venkateswaran, K. Limitations and practical problems in enzyme linked immunosorbent assays. Def. Sci. J. 1992, 42, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Trends in miniaturized biosensors for point-of-care testing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ferris, B.; Li, H. Compartmentalized linker array: A scalable and transferrable microarray format for multiplexed immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9068–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Valdes, R.J.; Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L. Massive parallel analysis of single cells in an integrated microfluidic platform. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5210–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpetti, F.; Garcia-Cordero, J.; Maerkl, S.J. A microfluidic platform for high-throughput multiplexed protein quantitation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shen, M.; Xu, Y. A Portable microfluidic system for point-of-care detection of multiple protein biomarkers. Micromachines 2021, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Ojha, V.; Fricke, I.; Al-Sheboul, S.A.; Imarogbe, C.; Gravier, T.; Green, M.; Peterson, L.; Koutsaroff, I.P.; Demir, A.; et al. Innate and adaptive immunity during SARS-CoV-2 infection: Biomolecular cellular markers and mechanisms. Vaccines 2023, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Prévost, J.; Nayrac, M.; Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Benlarbi, M.; Gasser, R.; Brassard, N.; Laumaea, A.; Gong, S.Y.; Bourassa, C.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis of Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Spike in Convalescent Individuals up to 8 Months Post-Symptom Onset. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Li, T.-D.; Zheng, S.-F.; Su, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, F.; Ge, S.-X.; Zou, Q.-D.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Serology characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection since exposure and post-symptom onset. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woof, J.M.; Russell, M.W. Structure and function relationships in IgA. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndzouboukou, J.-L.B.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Fan, X.-L. Recent developments in SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing antibody detection methods. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, T.; Xia, X.; Su, B.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Bao, Z.; et al. Different profiles of antibodies and Cytokines were found between severe and moderate COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 723585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Xue, F.; Zuo, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Dai, J.; Ju, Y. A Universal Bacterial Catcher Au–PMBA-Nanocrab-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Pathogens Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Multiplexed detection of biomarkers in lateral-flow immunoassays. Analyst 2020, 145, 2828–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbáth, M.; Papp, K.; Balogh, A.; Matkó, J.; Prechl, J. Exploiting fluorescence for multiplex immunoassays on protein microarrays. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2014, 2, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Wu, P.; He, W.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Dai, J.; Ju, Y. A fluorescent and ratiometric colorimetric biosensor for detection of different hazard contaminants in dairy products. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Huertas, C.S.; Lechuga, L.M. Label-free plasmonic biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics: A review. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Krauss, T.F. Label-free affinity biosensor arrays: Novel technology for molecular diagnostics. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2017, 14, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiluk, T.; Sredzinska, M.; Rogowska, A.; Zebrowska, A.; Boczkowska-Radziwon, B.; Stasiak-Barmuta, A.; Radziwon, P. Analysis of the IgG subclass profile and IgG sum-total discrepancy in COVID-19 convalescent plasma donors: A single-centre prospective cohort study. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 62, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Zueva, E.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Liubimova, N.E.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Savin, T.V.; Stanevich, O.V.; et al. Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity. Viruses 2022, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Wen, F.; Liu, K.; Chen, Y. Detection methods and dynamic characteristics of specific antibodies in patients with COVID-19: A review of the early literature. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusmini, F.; Zhong, Z.; Feijen, J. Protein immobilization strategies for protein biochips. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Herr, A.E. Protein immobilization techniques for microfluidic assays. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 041501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Weinrich, D.; Waldmann, H. Protein biochips: Oriented surface immobilization of proteins. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, S.G.; Yagati, A.K.; Koyappayil, A.; Go, A.; Yeon, S.; Lee, M.-H. Recombinant histidine-tagged nano-protein-based highly sensitive electro-sensing device for salivary cortisol. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 144, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Klose, A.M.; Miller, B.L. label-free, multiplex glycan microarray biosensor for influenza virus detection. Bioconjug. Chem. 2021, 32, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd, M.; Ivanova, P.; Żukowski, K.; Tokarska, K.; Pietrzak, M.; Brzózka, Z.; Malinowska, E. Printer toner-assisted immobilization of antibodies on PET for genuinely-2D, flexible ELISA spot arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 403, 135173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhneva, E.; Farka, Z.; Skládal, P.; Zajíčková, L. Cyclopropylamine plasma polymer surfaces for label-free SPR and QCM immunosensing of Salmonella. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mei, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, C.M. Electrochemically enhanced antibody immobilization on polydopamine thin film for sensitive surface plasmon resonance immunoassay. Talanta 2018, 182, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, L.; Mallak, L.A.; Damin, F.; Mussida, A.; Brambilla, D.; Chiari, M. Optimization of functional group concentration of N, N-dimethylacrylamide-based polymeric coatings and probe immobilization for DNA and protein microarray applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, D.; Torti, A.; Damin, F.; Sola, L.; Rusnati, M.; Albisetti, E.; Bugatti, A.; Bertacco, R.; Chiari, M. Functionalization of gold surfaces with copoly(DMA-NAS-MAPS) by dip coating: Surface characterization and hybridization tests. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Byrne, H.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Antibodies and antibody-derived analytical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Guisán, J.M.; Rocha-Martin, J. Oriented immobilization of antibodies onto sensing platforms—A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1189, 338907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Does Thermo Fisher Scientific Have an Immunoassay Plate That Is Optimized for Research on SARS-CoV-2 Testing? Smart Notes n.d. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LPD/Application-Notes/elisa-smartnote.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Drozd, M.; Ivanova, P.; Tokarska, K.; Żukowski, K.; Kramarska, A.; Nowiński, A.; Kobylska, E.; Pietrzak, M.; Brzózka, Z.; Malinowska, E. Versatile and easily designable polyester-laser toner interfaces for site-oriented adsorption of antibodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, A.; Khan, S.; Didar, T.F. Conventional and emerging strategies for the fabrication and functionalization of PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3053–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, P.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Microspot-based ELISA in microfluidics: Chemiluminescence and colorimetry detection using integrated thin-film hydrogenated amorphous silicon photodiodes. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, C.; Qian, J.; Liu, S. Multianalyte immunoassay chip for detection of tumor markers by chemiluminescent and colorimetric methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3269–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. A high-throughput multiplexed microfluidic device for COVID-19 serology assays. Lab Chip 2020, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irena, G.; Jolanta, B.; Karolina, Z. Chemical modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and immobilization of the selected enzymes on the modified film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8293–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshaei, P.; Güven, O. Chemical modification of PET surface and subsequent graft copolymerization with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 118, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bùi, L.N.; Thompson, M.; McKeown, N.B.; Romaschin, A.D.; Kalman, P.G. Surface modification of the biomedical polymer poly(ethylene terephthalate). Analyst 1993, 118, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Long, F. Rapid and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody in serum using optofluidic point-of-care testing fluorescence biosensor. Talanta 2021, 235, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Nishizawa, T.; Yoshimizu, M. Non-specific adsorption of fish immunoglobulin M (IgM) to blocking reagents on ELISA plate wells. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 78, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajollahi, M.M.; Cook, D.B.; Hamzehlou, S.; Self, C.H. Reduction of non-specific binding in immunoassays requiring long incubations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wu, M.; Albo, J.; Rao, Q. Non-Specific Binding and Cross-Reaction of ELISA: A Case Study of Porcine Hemoglobin Detection. Foods 2021, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.M.; Nie, X.; Ai, S.S. Influence of Blocking Agents on Non-Specific Background of Polystyrene Microbeads in Serum Immunoassay. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 641–642, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, S.; Damin, F.; Ferraro, L.; Soriani, N.; Burgio, V.; Ronzoni, M.; Gianni, L.; Ferrari, M.; Chiari, M. Microarray Approach Combined with ddPCR: A Useful Pipeline for the Detection and Quantification of Circulating Tumour DNA Mutations. Cells 2019, 8, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, D.; Panico, F.; Zarini, L.; Mussida, A.; Ferretti, A.M.; Aslan, M.; Ünlü, M.S.; Chiari, M. Copolymer-Coated Gold Nanoparticles: Enhanced Stability and Customizable Functionalization for Biological Assays. Biosensors 2024, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, L.; Martinuzzi, D.; Hyseni, I.; Benincasa, L.; Molesti, E.; Casa, E.; Lapini, G.; Piu, P.; Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; et al. Comparative analyses of SARS-CoV-2 binding (IgG, IgM, IgA) and neutralizing antibodies from human serum samples. J. Immunol. Methods 2020, 489, 112937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Plavina, T.; Castro, A.; Berman, M.; Jaiswal, D.; Rivas, S.; Schlain, B.; Subramanyam, M. A second-generation ELISA (STRATIFY JCV™ DxSelect™) for detection of JC virus antibodies in human serum and plasma to support progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy risk stratification. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Jia, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; et al. The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 632814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Jin, T. Serum IgA, IgM, and IgG responses in COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinti, I.; Mortari, E.P.; Salinas, A.F.; Milito, C.; Carsetti, R. IgA antibodies and IgA deficiency in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 655896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluka, G.K.; Namubiru, P.; Kato, L.; Ankunda, V.; Gombe, B.; Cotten, M.; The COVID-19 Immunoprofiling Team; Musenero, M.; Kaleebu, P.; Fox, J.; et al. Optimisation and validation of a conventional ELISA and cut-offs for detecting and quantifying anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike, RBD, and Nucleoprotein IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies in Uganda. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastawicki, W.; Juszczyk, G.; Gierczyński, R.; Zasada, A.A. Comparison of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA antibody responses post complete vaccination, 7 months later and after 3rd dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine in healthy adults. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 152, 105193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boozer, C.; Ladd, J.; Chen, S.; Jiang, S. DNA-directed protein immobilization for simultaneous detection of multiple analytes by surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoń, S.; Drozd, M.; Malinowska, E. A careful insight into DDI-type receptor layers on the way to improvement of click-biology-based immunosensors. Biosensors 2024, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, B.; Löfås, S.; Lindquist, G.; Edström, Å.; Hillgren, R.M.; Hansson, A. Comparison of methods for immobilization to carboxymethyl dextran sensor surfaces by analysis of the specific activity of monoclonal antibodies. J. Mol. Recognit. 1995, 8, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E. Solid Supports in Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Other Solid-Phase Immunoassays. Methods 2000, 22, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Functional devices from DNA and proteins. Nano Today 2007, 2, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.F.; Ho, A.H.; Turner, A.P.; Mak, W.C. Integrated Printed Microfluidic Biosensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari, S.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. A Fully Integrated Microfluidic Device with Immobilized Dyes for Simultaneous Detection of Cell-Free DNA and Histones from Plasma Using Dehydrated Agarose Gates. Gels 2024, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Salahuddin, A.; Ahamed, M.J. Demonstration of a Transparent and Adhesive Sealing Top for Microfluidic Lab-Chip Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoń, S.; Porycka, K.; Lapitan, L.D.S., Jr.; Drozd, M.; Pietrzak, M.; Malinowska, E. A versatile approach to quality control of protein-based receptor layers by reversible, nonspecific staining for multiplex SPRi immunosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 421, 136512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 100.0% |
| Specificity | 92.9% |
| Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | 93.3% |
| Negative Predictive Value (NPV) | 100.0% |
| Accuracy | 96.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pniewska, S.; Drozd, M.; Mussida, A.; Brambilla, D.; Chiari, M.; Rastawicki, W.; Malinowska, E. PET Foils Functionalized with Reactive Copolymers as Adaptable Microvolume ELISA Spot Array Platforms for Multiplex Serological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Sensors 2024, 24, 7766. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237766
Pniewska S, Drozd M, Mussida A, Brambilla D, Chiari M, Rastawicki W, Malinowska E. PET Foils Functionalized with Reactive Copolymers as Adaptable Microvolume ELISA Spot Array Platforms for Multiplex Serological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Sensors. 2024; 24(23):7766. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237766
Chicago/Turabian StylePniewska, Sylwia, Marcin Drozd, Alessandro Mussida, Dario Brambilla, Marcella Chiari, Waldemar Rastawicki, and Elżbieta Malinowska. 2024. "PET Foils Functionalized with Reactive Copolymers as Adaptable Microvolume ELISA Spot Array Platforms for Multiplex Serological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infections" Sensors 24, no. 23: 7766. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237766
APA StylePniewska, S., Drozd, M., Mussida, A., Brambilla, D., Chiari, M., Rastawicki, W., & Malinowska, E. (2024). PET Foils Functionalized with Reactive Copolymers as Adaptable Microvolume ELISA Spot Array Platforms for Multiplex Serological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Sensors, 24(23), 7766. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237766







